Utility of Enabling Technologies in Spinal Deformity Surgery: Optimizing Surgical Planning and Intraoperative Execution to Maximize Patient Outcomes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Modern Technology
2.1. Advances in Deformity Imaging
2.2. Robotic Assistance and Intraoperative Navigation
2.3. MIS Deformity
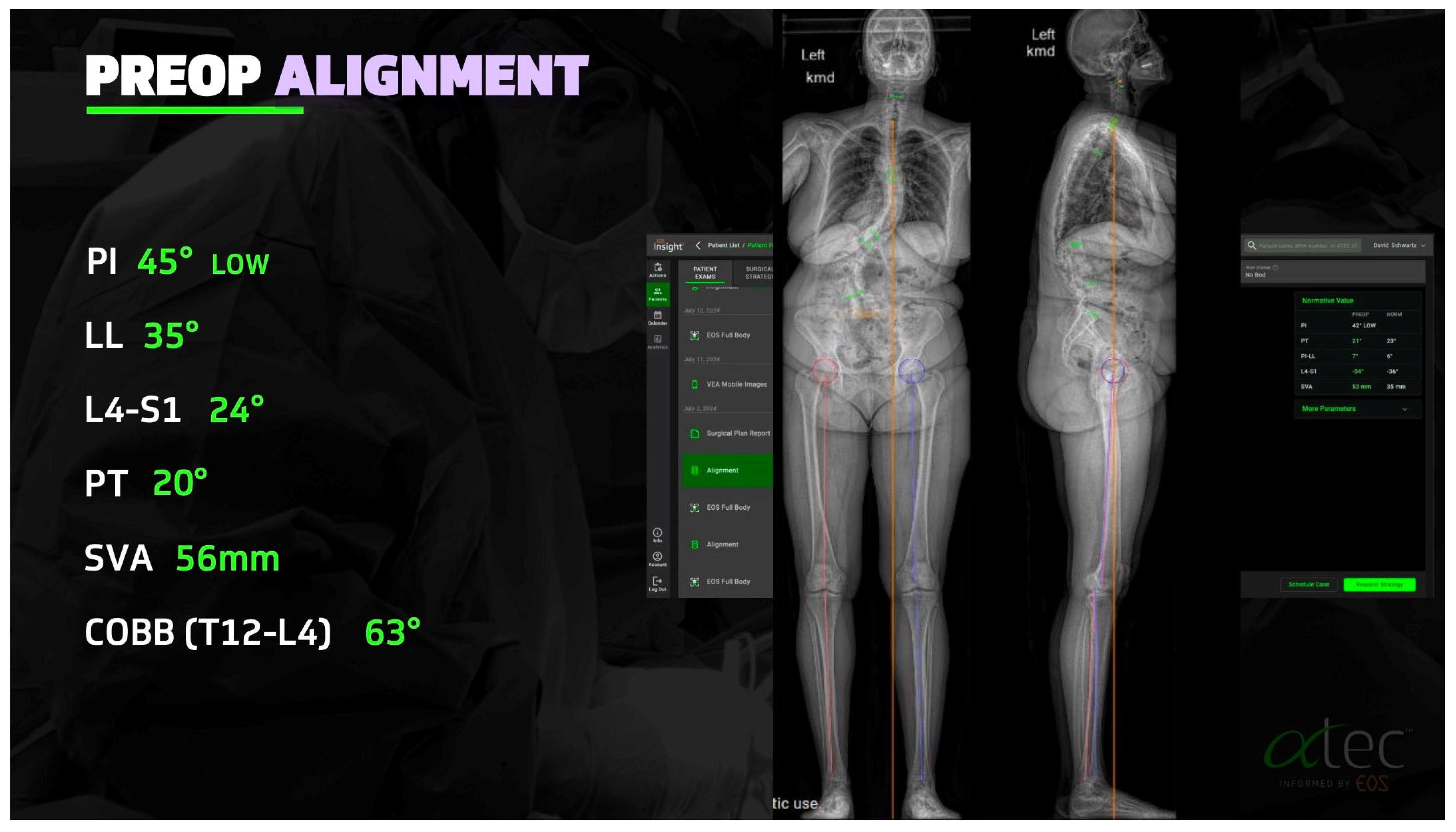
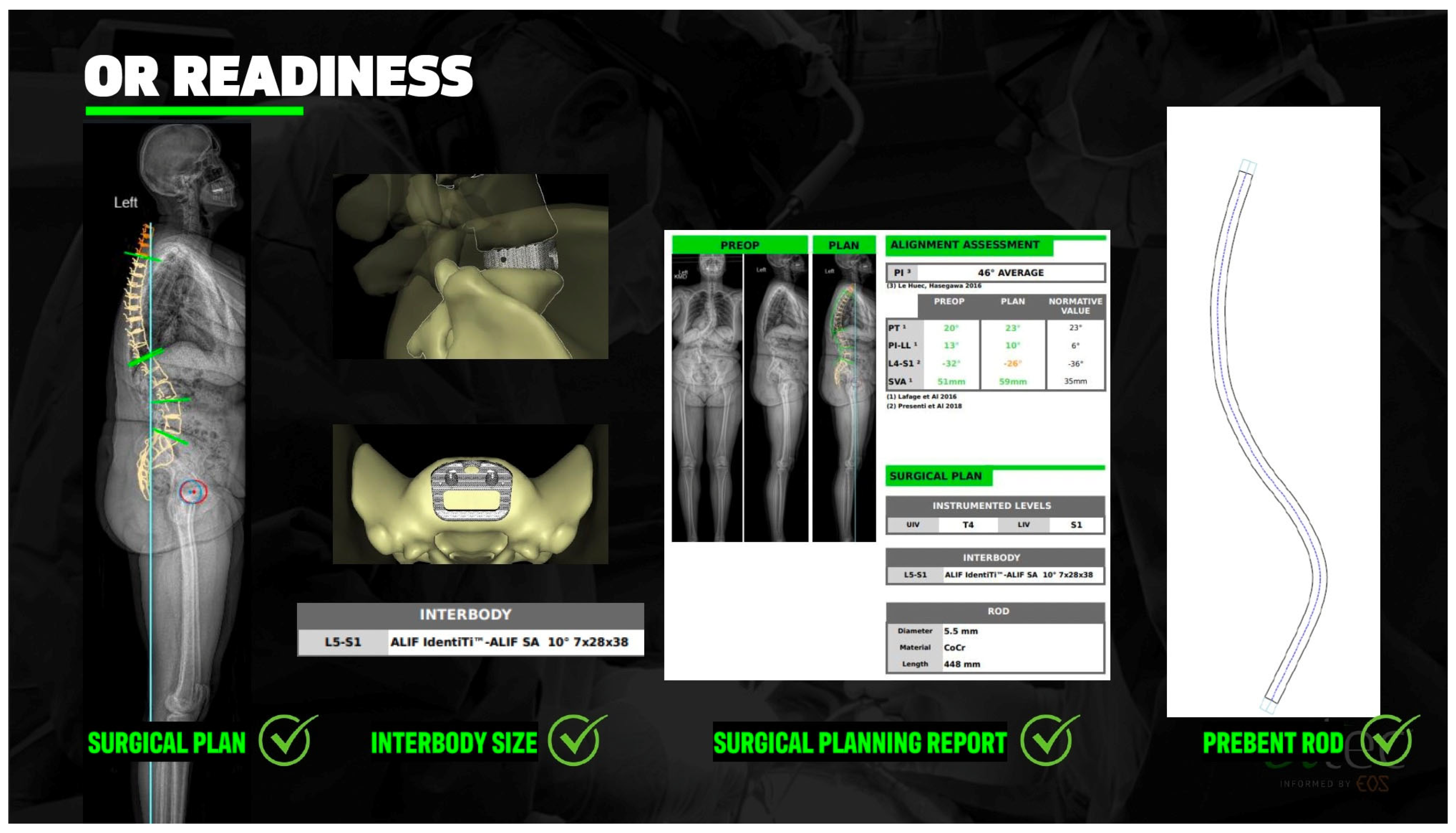
2.4. Preoperative Planning and Predictive Modeling
2.5. Machine Learning and Surgeon-Specific Predictive Modeling
2.6. Custom Patient-Specific Interbody Implants
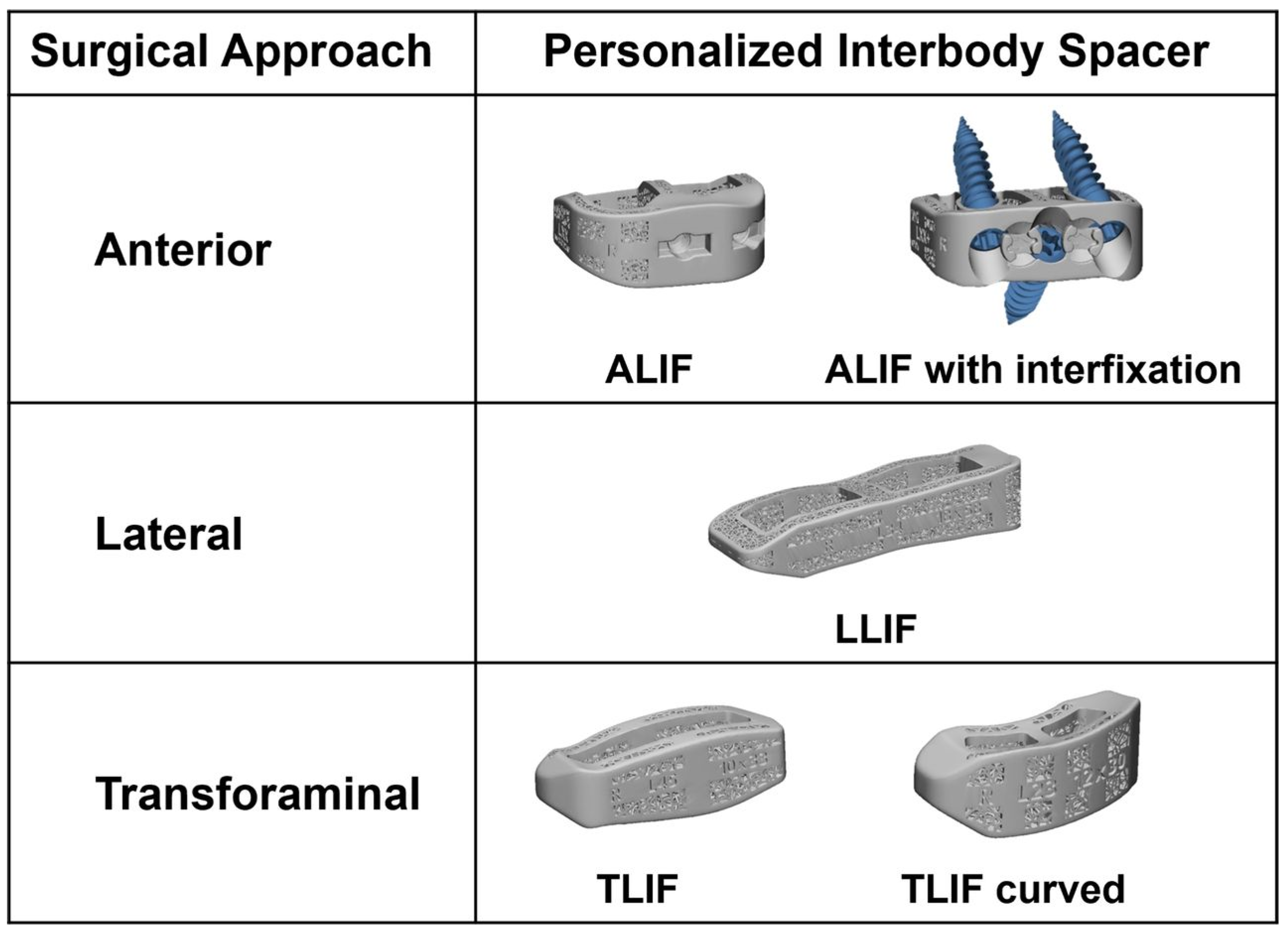
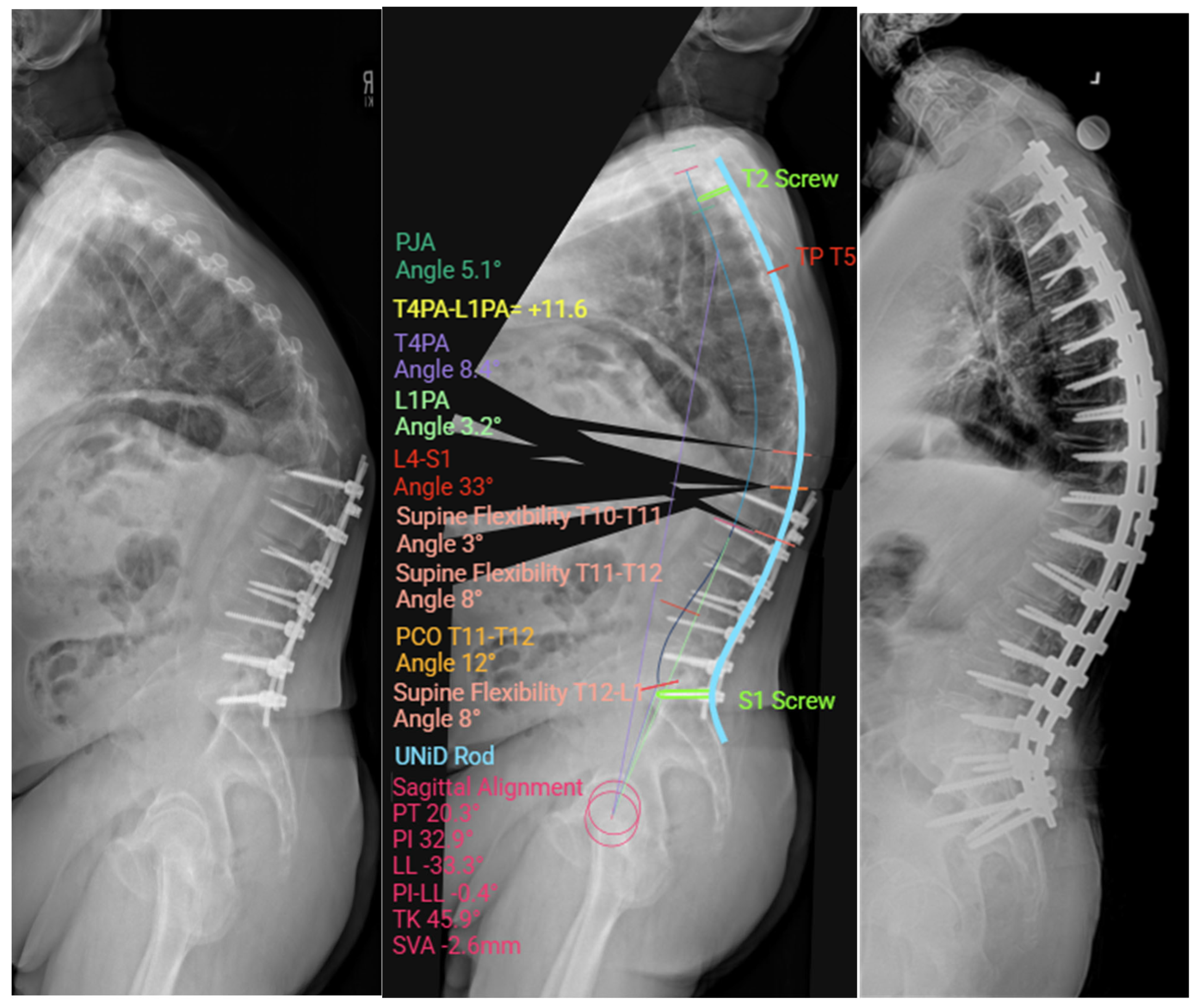
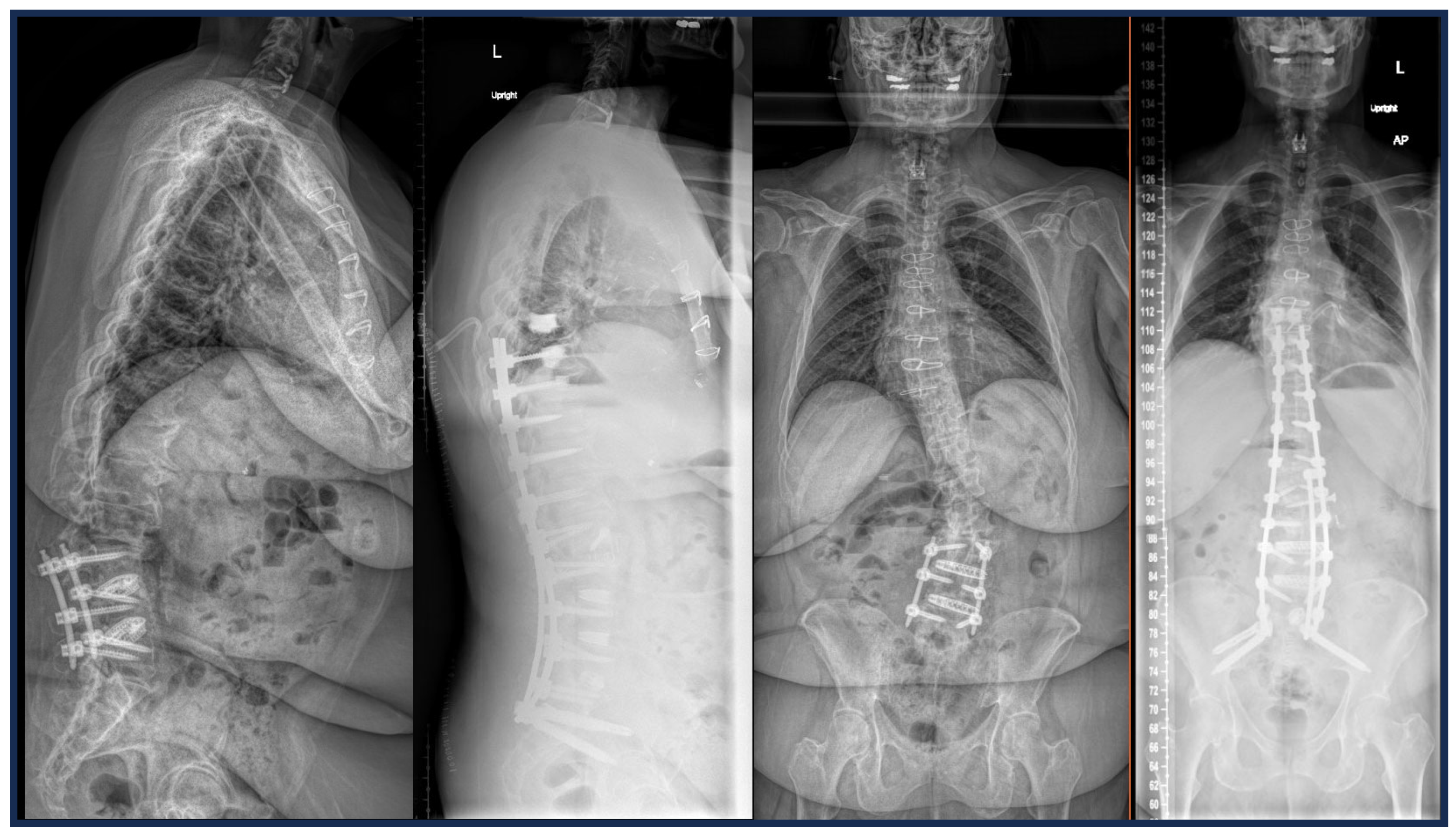
2.7. Custom Patient-Specific Rods
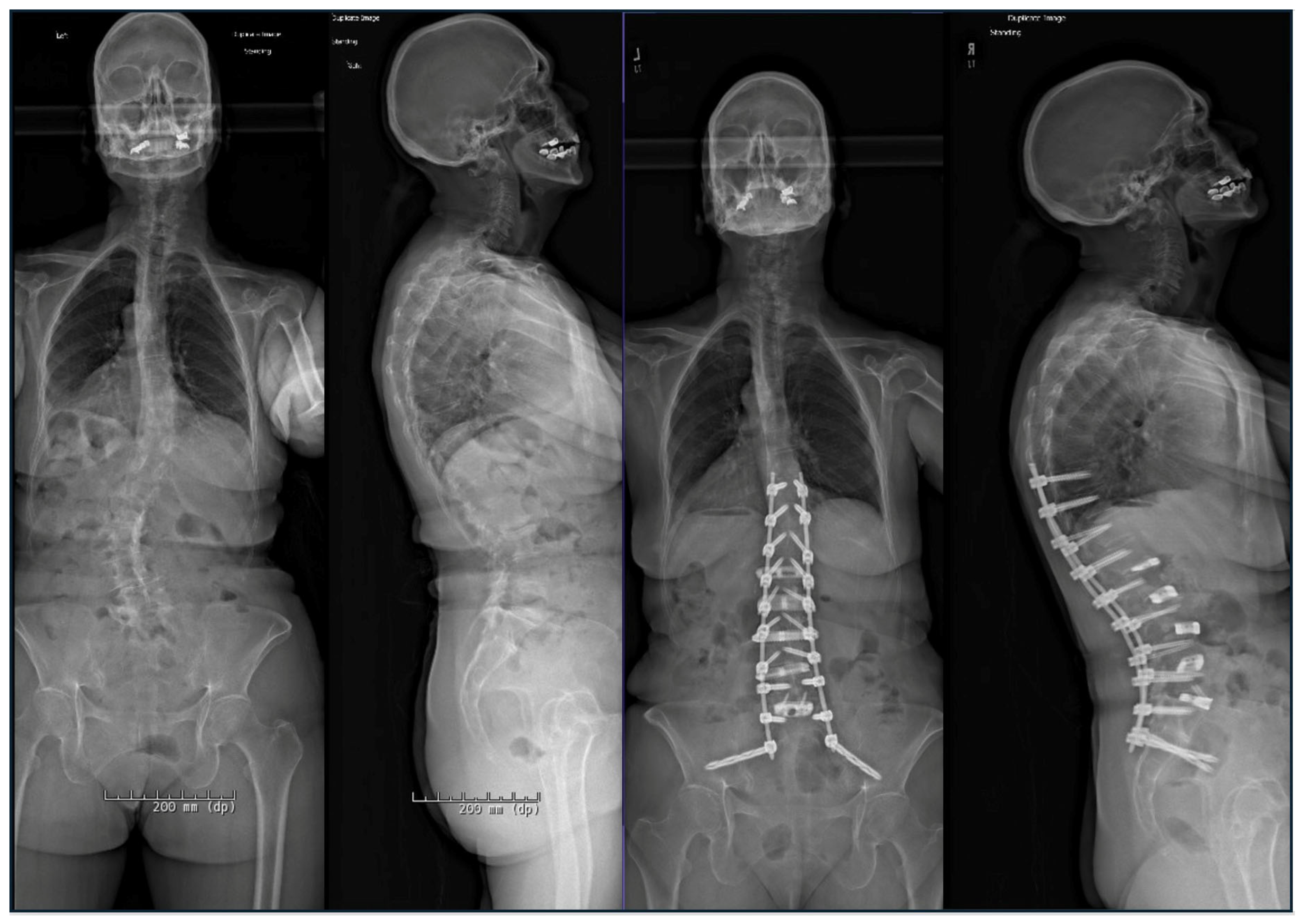
2.8. PJK Prevention: Tethers, Hooks, Kyphoplasty
2.8.1. Tethering Techniques
2.8.2. Proximal Anchor Modifications: Hooks vs. Screws
2.8.3. Vertebral Cement Augmentation (e.g., Kyphoplasty, Vertebroplasty)
3. Modern Medical Management
3.1. Bone Health Optimization
3.1.1. Preoperative Evaluation
3.1.2. Medical Intervention
3.1.3. Postoperative Management
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fayssoux, R.S.; Cho, R.H.; Herman, M.J. A History of Bracing for Idiopathic Scoliosis in North America. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2010, 468, 654–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, A.L.; Das, K. History of Surgery for the Correction of Spinal Deformity. Neurosurg. Focus 2003, 14, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luque, E.R. Segmental Spinal Instrumentation for Correction of Scoliosis. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1982, 163, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blount, W.P.; Schmidt, A.C. The Milwaukee brace. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1958, 40, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubousset, J. 3D analysis of scoliotic deformity development and 3D chain of balance in a scoliosis patient. Russ. J. Spine Surg. (Khirurgiya Pozvonochnika) 2016, 13, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, J.C.; Berthonnaud, E.; Deceuninck, J.; Journoud-Rozand, L.; Notin, G.; Chaleat-Valayer, E. Three-Dimensional Reconstructions of Lenke 1A Curves. Scoliosis Spinal Disord. 2018, 13, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabins, M.B.; Weinstein, J.N. The history of vertebral screw and pedicle screw fixation. Iowa Orthop. J 1991, 11, 127–136. [Google Scholar]
- Shakeri, M.; Mahdavi, S.M.; Rikhtehgar, M.; Soleimani, M.; Ghandhari, H.; Jafari, B.; Daneshmand, S. EOS® Is Reliable to Evaluate Spinopelvic Parameters: A Validation Study. BMC Med. Imaging 2024, 24, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapin, E.; Briot, K.; Kolta, S.; Gravel, P.; Skalli, W.; Roux, C.; Mitton, D. Bone Mineral Density Assessment Using the EOS Low-Dose X-Ray Device: A Feasibility Study. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H 2008, 222, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sielatycki, J.A.; Mitchell, K.; Leung, E.; Lehman, R.A. State of the Art Review of New Technologies in Spine Deformity Surgery-Robotics and Navigation. Spine Deform. 2022, 10, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, R.; McKenna, C.; Wade, R.; Yang, H.; Woolacott, N.; Sculpher, M. The EOS 2D/3D X-ray imaging system: A cost-effectiveness analysis quantifying the health benefits from reduced radiation exposure. Eur. J. Radiol. 2013, 82, e342–e349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, C.; Wade, R.; Faria, R.; Yang, H.; Stirk, L.; Gummerson, N.; Sculpher, M.; Woolacott, N. EOS 2D/3D X-ray imaging system: A systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol. Assess. 2012, 16, 1–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Cho, D.C.; Kim, K.T. Navigation-Guided/Robot-Assisted Spinal Surgery: A Review Article. Neurospine 2024, 21, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Tetreault, T.A.; Vaishnav, A.; York, P.J.; Staub, B.N. The Current State of Navigation in Robotic Spine Surgery. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laverdière, C.; Georgiopoulos, M.; Ames, C.P.; Corban, J.; Ahangar, P.; Awadhi, K.; Weber, M.H. Adult Spinal Deformity Surgery and Frailty: A Systematic Review. Glob. Spine J. 2022, 12, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naik, A.; Smith, A.D.; Shaffer, A.; Krist, D.T.; Moawad, C.M.; MacInnis, B.R.; Teal, K.; Hassaneen, W.; Arnold, P.M. Evaluating robotic pedicle screw placement against conventional modalities: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Neurosurg. Focus 2022, 52, E10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatima, N.; Massaad, E.; Hadzipasic, M.; Shankar, G.M.; Shin, J.H. Safety and accuracy of robot-assisted placement of pedicle screws compared to conventional free-hand technique: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Spine J. 2021, 21, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, P.K.; Poelstra, K.; Protopsaltis, T.S. Role of Robotics in Adult Spinal Deformity. Int. J. Spine Surg. 2021, 15, S56–S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochanski, R.B.; Lombardi, J.M.; Laratta, J.L.; Lehman, R.A.; O’Toole, J.E. Image-Guided Navigation and Robotics in Spine Surgery. Neurosurgery 2019, 84, 1179–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennington, Z.J.; Judy, B.F.; Zakaria, H.M.; Lakomkin, N.; Mikula, A.L.; Elder, B.D.; Theodore, N. Learning curves in robot-assisted spine surgery: A systematic review and proposal of application to residency curricula. Neurosurg. Focus 2022, 52, E3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamee, C.; Kelly, D.; McDonnell, J.M.; Sowa, A.M.; Pearl, A.M.; Darwish, S.; Butler, J.S. The learning curve of robotic-assisted pedicle screw placement: An individual patient data meta-analysis. Spine J. 2025, S1529-9430(25)00343-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturgill, D.; How, J.; Blajda, T.; Davis, Z.; Ali, M.; O’MAlley, G.; Patel, N.V.; Khan, M.F.; Goldstein, I. Are the clinical outcomes and cost-effectiveness of robot-assisted pedicle screw placement in lumbar fusion surgery superior to computed tomography navigation and free-hand fluoroscopy-guided techniques? World Neurosurg. 2024. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.S.; Klineberg, E.; Lafage, V.; Shaffrey, C.I.; Schwab, F.; Lafage, R.; Hostin, R.; Mundis, G.M.; Errico, T.J.; Kim, H.J.; et al. Prospective Multicenter Assessment of Perioperative and Minimum 2-Year Postoperative Complication Rates Associated with Adult Spinal Deformity Surgery. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2016, 25, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mummaneni, P.V.; Park, P.; Shaffrey, C.I.; Wang, M.Y.; Uribe, J.S.; Fessler, R.G.; Chou, D.; Kanter, A.S.; Okonkwo, D.O.; Mundis, G.M.; et al. The MISDEF2 Algorithm: An Updated Algorithm for Patient Selection in Minimally Invasive Deformity Surgery. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2019, 32, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, D.; Lafage, V.; Chan, A.Y.; Passias, P.; Mundis, G.M.; Eastlack, R.K.; Fu, K.M.; Fessler, R.G.; Gupta, M.C.; Than, K.D.; et al. Patient Outcomes after Circumferential Minimally Invasive Surgery Compared with Those of Open Correction for Adult Spinal Deformity: Initial Analysis of Prospectively Collected Data. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2021, 36, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, J.; Lee, S.H. Minimally Invasive Spinal Surgery for Adult Spinal Deformity. Neurospine 2018, 15, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Z.; Liang, H.; Li, S.; Ye, Z.; Wang, X. Comparison of open surgery versus minimally invasive surgery in nonsevere adult degenerative scoliosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2024, 49, E210–E220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lak, A.M.; Lamba, N.; Pompilus, F.; Yunusa, I.; King, A.; Sultan, I.; Amamoo, J.; Al-Otaibi, N.M.; Alasmari, M.; Zaghloul, I.; et al. Minimally invasive versus open surgery for the correction of adult degenerative scoliosis: A systematic review. Neurosurg. Rev. 2021, 44, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, R.M.; Mundis, G.M., Jr.; Ahmed, Y.; El Ahmadieh, T.Y.; Wang, M.Y.; Mummaneni, P.V.; Uribe, J.S.; Okonkwo, D.O.; Eastlack, R.K.; Anand, N.; et al. Comparison of radiographic results after minimally invasive, hybrid, and open surgery for adult spinal deformity: A multicenter study of 184 patients. Neurosurg. Focus 2014, 36, E13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe, J.S.; Beckman, J.M.; Mummaneni, P.V.; Okonkwo, D.; Nunley, P.; Wang, M.Y.; Mundis, G.M., Jr.; Park, P.; Eastlack, R.; Anand, N.; et al. Does MIS surgery allow for shorter constructs in the surgical treatment of adult spinal deformity? Neurosurgery 2017, 80, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, P.; Than, K.D.; Mummaneni, P.V.; Nunley, P.D.; Eastlack, R.K.; Uribe, J.S.; Wang, M.Y.; Le, V.; Fessler, R.G.; Okonkwo, D.O.; et al. Factors affecting approach selection for minimally invasive versus open surgery in the treatment of adult spinal deformity: Analysis of a prospective, nonrandomized multicenter study. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2020, 33, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harake, E.S.; Linzey, J.R.; Jiang, C.; Joshi, R.S.; Zaki, M.M.; Jones, J.C.; Khalsa, S.S.S.; Lee, J.H.; Wilseck, Z.; Joseph, J.R.; et al. Development and Validation of an Artificial Intelligence Model to Accurately Predict Spinopelvic Parameters. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2024, 41, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagi, M.; Hosogane, N.; Fujita, N.; Okada, E.; Tsuji, O.; Nagoshi, N.; Asazuma, T.; Tsuji, T.; Nakamura, M.; Matsumoto, M.; et al. Predictive Model for Major Complications 2 Years after Corrective Spine Surgery for Adult Spinal Deformity. Eur. Spine J. 2019, 28, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adida, S.; Legarreta, A.D.; Hudson, J.S.; McCarthy, D.; Andrews, E.; Shanahan, R.; Taori, S.; Lavadi, R.S.; Buell, T.J.; Hamilton, D.K.; et al. Machine Learning in Spine Surgery: A Narrative Review. Neurosurgery 2024, 94, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.A.; Houdane, A.; Hajja, A.; Nassar, J.E.; Alsoof, D.; Diebo, B.G.; Sardar, Z.M.; Abd-El-Barr, M.M.; Bourghli, A.; Konbaz, F. Assessing the Utility and Challenges of Machine Learning in Spinal Deformity Management: A Systematic Review. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Arvind, V.; Oermann, E.K.; Kaji, D.; Ranson, W.; Ukogu, C.; Hussain, A.K.; Caridi, J.; Cho, S.K. Predicting Surgical Complications in Patients Undergoing Elective Adult Spinal Deformity Procedures Using Machine Learning. Spine Deform. 2018, 6, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, Q.; Cui, P.; Wang, S.; Han, D.; Chen, X.; Lu, S. Machine-Learning Models for the Prediction of Ideal Surgical Outcomes in Patients with Adult Spinal Deformity. Bone Joint J. 2025, 107-B, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schonfeld, E.; Shah, A.; Johnstone, T.M.; Rodrigues, A.; Morris, G.K.; Stienen, M.N.; Veeravagu, A. Deep Learning Prediction of Cervical Spine Surgery Revision Outcomes Using Standard Laboratory and Operative Variables. World Neurosurg. 2024, 185, e691–e699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tragaris, T.; Benetos, I.S.; Vlamis, J.; Pneumaticos, S. Machine Learning Applications in Spine Surgery. Cureus 2023, 15, e48078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidat, B.; Kurapatti, M.; Gal, J.S.; Cho, S.K.; Kim, J.S. Explainable Machine Learning Approach to Prediction of Prolonged Intensive Care Unit Stay in Adult Spinal Deformity Patients: Machine Learning Outperforms Logistic Regression. Glob. Spine J. 2025, 15, 1992–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnard, J.L.; Parr, W.C.H.; Choy, W.J.; Walsh, W.R.; Mobbs, R.J. 3D-Printed Spine Surgery Implants: A Systematic Review of the Efficacy and Clinical Safety Profile of Patient-Specific and off-the-Shelf Devices. Eur. Spine J. 2020, 29, 1248–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laynes, R.A.; Kleck, C.J. Patient-Specific Implants and Spinal Alignment Outcomes. N. Am. Spine Soc. J. 2024, 20, 100559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, N.; Schaffer, N.E.; Aleem, I.S.; Patel, R. 3D-Printed Patient-Specific Spine Implants: A Systematic Review. Clin. Spine Surg. 2020, 33, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kent, R.S.; Ames, C.P.; Asghar, J.; Blaskiewicz, D.J.; Osorio, J.A.; Yen, C.-P.; Mullin, J.; Smith, J.S.; Small, J.M.; Temple-Wong, M.; et al. Radiographic Alignment in Deformity Patients Treated with Personalized Interbody Devices: Early Experience from the COMPASS Registry. Int. J. Spine Surg. 2024, 18, S6–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, R.J.R.; Gee, A.; Kanawati, A.J.; Siddiqi, F.; Rasoulinejad, P.; Zdero, R.; Bailey, C.S. Biomechanical Comparison of Subsidence Between Patient-Specific and Non-Patient-Specific Lumbar Interbody Fusion Cages. Glob. Spine J. 2024, 14, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, J.; Zafar, Z.; Skandalakis, G.; Kuruba, V.; Madan, S.; Kazim, S.F.; Bowers, C.A. Recent Advances of 3D-Printing in Spine Surgery. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2024, 15, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, V.K.; Kumar, P.; Kalra, P.; Sinha, R.K. Additive Manufacturing for Metallic Spinal Implants: A Systematic Review. Ann. 3D Print. Med. 2021, 3, 100021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picton, B.; Stone, L.E.; Liang, J.; Solomon, S.S.; Brown, N.J.; Luzzi, S.; Osorio, J.A.; Pham, M.H. Patient-Specific Rods in Adult Spinal Deformity: A Systematic Review. Spine Deform. 2024, 12, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista, A.G.; Reyes, J.L.; Lee, N.J.; Fields, M.W.; Sardar, Z.M.; Lenke, L.G.; Lombardi, J.M.; Lehman, R.A. Patient-Specific Rods in Adolescent and Adult Spinal Deformity Surgery: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Spine Surg. 2024, 18, S57–S63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prost, S.; Farah, K.; Pesenti, S.; Tropiano, P.; Fuentes, S.; Blondel, B. “Patient-Specific” Rods in the Management of Adult Spinal Deformity. One-Year Radiographic Results of a Prospective Study about 86 Patients. Neurochirurgie 2020, 66, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drexelius, K.; Kuris, E.O.; Sater, A.; Burger, E.L.; Ou-Yang, D.C.; Patel, V.V.; Kleck, C.J. The Impact of Patient-Specific Spine Rods on Spinopelvic Parameters after Short Segment Degenerative Lumbar Fusions. J. Spine Surg. 2025, 11, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulks, C.R.; Biddau, D.T.; Munday, N.R.; McKenzie, D.P.; Malham, G.M. Patient-Specific Spinal Rods in Adult Spinal Deformity Surgery Reduce Proximal Junctional Failure: A Review of Patient Outcomes and Surgical Technique in a Prospective Observational Cohort. J. Spine Surg. 2023, 9, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasto, L.A.; Paolicelli, C.; Sieczak, A.; Ulisse, P.; Cattolico, A.; Pola, E. Patient-Specific Rods vs Traditional Rods in Surgical Correction of Adult Spinal Deformities: A Case-Matched Study. Ann. Ital. Chir. 2025, 96, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solla, F.; Barrey, C.Y.; Burger, E.; Kleck, C.J.; Fière, V. Patient-Specific Rods for Surgical Correction of Sagittal Imbalance in Adults: Technical Aspects and Preliminary Results. Clin. Spine Surg. 2019, 32, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.J.; Bae, S.S.; Choi, H.Y.; Park, J.H.; Hyun, S.J.; Jo, D.J.; Cho, Y. Proximal Junctional Kyphosis or Failure After Adult Spinal Deformity Surgery—Review of Risk Factors and Its Prevention. Neurospine 2023, 20, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, T.; Takamizawa, Y.; Konishi, K.; Sano, H.; Takahashi, M.; Nakamichi, K.; Kono, H.; Hosogane, N. Evaluation of Intraoperative Coronal Alignment Using a Computer-Assisted Rod Bending System (CARBS) without Intraoperative Radiation Exposure in Adult Spinal Deformity Surgery: A Technical Note and Preliminary Results. Spine Deform. 2023, 11, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.S.; Shaffrey, E.; Klineberg, E.; Shaffrey, C.I.; Lafage, V.; Schwab, F.J.; Protopsaltis, T.; Scheer, J.K.; Mundis, G.M.; Fu, K.M.G.; et al. Prospective Multicenter Assessment of Risk Factors for Rod Fracture Following Surgery for Adult Spinal Deformity. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2014, 21, 994–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, J.M.; Poelstra, K.; Ammar, K.; McGirt, M.; Cormier, J.; Hart, R.; Bauman, J.; Cowart, P.; Sheth, I.; Singh, P.; et al. Characterization of Ion Release from a Novel Biomaterial, Molybdenum-47.5Rhenium, in Physiologic Environments. Spine J. 2023, 23, 900–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Park, J.S.; Kang, D.H.; Kang, M.; Jung, K.; Lee, C.S. Proximal Junctional Failure Development Despite Achieving Ideal Sagittal Correction According to Age-Adjusted Alignment Target in Patients with Adult Spinal Deformity: Risk Factor Analysis of 196 Cases Undergoing Low Thoracic to Pelvic Fusion. Neurospine 2024, 21, 1080–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buell, T.J.; Buchholz, A.L.; Quinn, J.C.; Bess, S.; Line, B.G.; Ames, C.P.; Schwab, F.J.; Lafage, V.; Shaffrey, C.I.; Smith, J.S. A Pilot Study on Posterior Polyethylene Tethers to Prevent Proximal Junctional Kyphosis After Multilevel Spinal Instrumentation for Adult Spinal Deformity. Oper. Neurosurg. 2019, 16, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buell, T.J.; Bess, S.; Xu, M.; Schwab, F.J.; Lafage, V.; Ames, C.P.; Shaffrey, C.I.; Smith, J.S. Optimal Tether Configurations and Preload Tensioning to Prevent Proximal Junctional Kyphosis: A Finite Element Analysis. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2019, 30, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bess, S.; Harris, J.E.; Turner, A.W.L.; LaFage, V.; Smith, J.S.; Shaffrey, C.I.; Schwab, F.J.; Haid, R.W. The Effect of Posterior Polyester Tethers on the Biomechanics of Proximal Junctional Kyphosis: A Finite Element Analysis. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2017, 26, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-J.; Park, J.-S.; Kang, D.-H.; Lee, C.-S.; Kim, H.-J. Risk Factors for Recurrent Proximal Junctional Failure Following Adult Spinal Deformity Surgery: Analysis of 60 Patients Undergoing Fusion Extension Surgery for Proximal Junctional Failure. Int. J. Spine Surg. 2024, 18, 8620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumura, A.; Namikawa, T.; Kato, M.; Oyama, S.; Hori, Y.; Yabu, A.; Hidaka, N.; Nakamura, H. Effect of Different Types of Upper Instrumented Vertebrae Instruments on Proximal Junctional Kyphosis Following Adult Spinal Deformity Surgery: Pedicle Screw versus Transverse Process Hook. Asian Spine J. 2018, 12, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theologis, A.A.; Burch, S. Prevention of Acute Proximal Junctional Fractures After Long Thoracolumbar Posterior Fusions for Adult Spinal Deformity Using 2-Level Cement Augmentation at the Upper Instrumented Vertebra and the Vertebra 1 Level Proximal to the Upper Instrumented Vertebra. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2015, 40, 1516–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raman, T.; Miller, E.; Martin, C.T.; Kebaish, K.M. The Effect of Prophylactic Vertebroplasty on the Incidence of Proximal Junctional Kyphosis and Proximal Junctional Failure Following Posterior Spinal Fusion in Adult Spinal Deformity: A 5-Year Follow-up Study. Spine J. 2017, 17, 1489–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, N.C.; Saag, K.G.; Dawson-Hughes, B.; Khosla, S.; Siris, E.S. The impact of the new National Bone Health Alliance (NBHA) diagnostic criteria on the prevalence of osteoporosis in the USA. Osteoporos. Int. 2017, 28, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimar, J.; Bisson, E.F.; Dhall, S.; Harrop, J.S.; Hoh, D.J.; Mohamed, B.; Wang, M.C.; Mummaneni, P.V. Congress of Neurological Surgeons Systematic Review and Evidence-based Guidelines for Perioperative Spine: Preoperative osteoporosis assessment. Neurosurgery 2021, 89 (Suppl. S1), S19–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.-C.; Chao, H.; Kao, K.-Y.; Chou, P.-H. CT Hounsfield unit is a reliable parameter for screw loosening or cage subsidence in minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schini, M.; Vilaca, T.; Gossiel, F.; Salam, S.; Eastell, R. Bone turnover markers: Basic biology to clinical applications. Endocr. Rev. 2023, 44, 417–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Preventive Services Task Force; Curry, S.J.; Krist, A.H.; Owens, D.K.; Barry, M.J.; Caughey, A.B.; Davidson, K.W.; Doubeni, C.A.; Epling, J.W., Jr.; Kemper, A.R.; et al. Screening for Osteoporosis to Prevent Fractures: Recommendation Statement. JAMA 2025, 333, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardar, Z.M.; Coury, J.R.; Cerpa, M.; DeWald, C.J.; Ames, C.P.; Shuhart, C.M.; Watkins, C.; Polly, D.W.; Dirschl, D.R.; Klineberg, E.O.; et al. Best practice guidelines for assessment and management of osteoporosis in adult patients undergoing elective spinal reconstruction. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2022, 47, 128–135, Erratum in Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2022, 47, E581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.-Z.; Jin, H.-J.; Suk, K.-S.; Lee, B.H.; Park, S.-Y.; Kim, H.-S.; Moon, S.-H.; Park, S.-R.; Kim, N.; Shin, J.W.; et al. Anti-osteoporosis medication in patients with posterior spine fusion: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Spine J. 2025, 45, S1529-9430(25)00204-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Najjar, Y.A.; Quraishi, D.A.; Kumar, N.; Hussain, I. Bone Health Optimization in Adult Spinal Deformity Patients: A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianferotti, L.; Cipriani, C.; Palermo, A.; Viapiana, O.; Zavatta, G.; Mazziotti, G. A practical approach for anabolic treatment of bone fragility with romosozumab. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2024, 47, 2649–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, P.A.; Binkley, N.C.; Bernatz, J.T. Bone Health Optimization (BHO) in Spine Surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2023, 48, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubelski, D.; Choma, T.J.; Steinmetz, M.P.; Harrop, J.S.; Mroz, T.E. Perioperative medical management of spine surgery patients with osteoporosis. Neurosurgery 2015, 77 (Suppl. S4), S92–S97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, N.C.; Johnson, E.; DeWald, C.; Lee, N.; Wang, T.Y. Utility of Enabling Technologies in Spinal Deformity Surgery: Optimizing Surgical Planning and Intraoperative Execution to Maximize Patient Outcomes. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5377. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155377
Kim NC, Johnson E, DeWald C, Lee N, Wang TY. Utility of Enabling Technologies in Spinal Deformity Surgery: Optimizing Surgical Planning and Intraoperative Execution to Maximize Patient Outcomes. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(15):5377. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155377
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Nora C., Eli Johnson, Christopher DeWald, Nathan Lee, and Timothy Y. Wang. 2025. "Utility of Enabling Technologies in Spinal Deformity Surgery: Optimizing Surgical Planning and Intraoperative Execution to Maximize Patient Outcomes" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 15: 5377. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155377
APA StyleKim, N. C., Johnson, E., DeWald, C., Lee, N., & Wang, T. Y. (2025). Utility of Enabling Technologies in Spinal Deformity Surgery: Optimizing Surgical Planning and Intraoperative Execution to Maximize Patient Outcomes. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(15), 5377. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155377





