Development and Validation of Transformer- and Convolutional Neural Network-Based Deep Learning Models to Predict Curve Progression in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
2.2. Patient Enrollment
2.3. Conservative Treatment
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Prediction Task and Ground Truth Definition
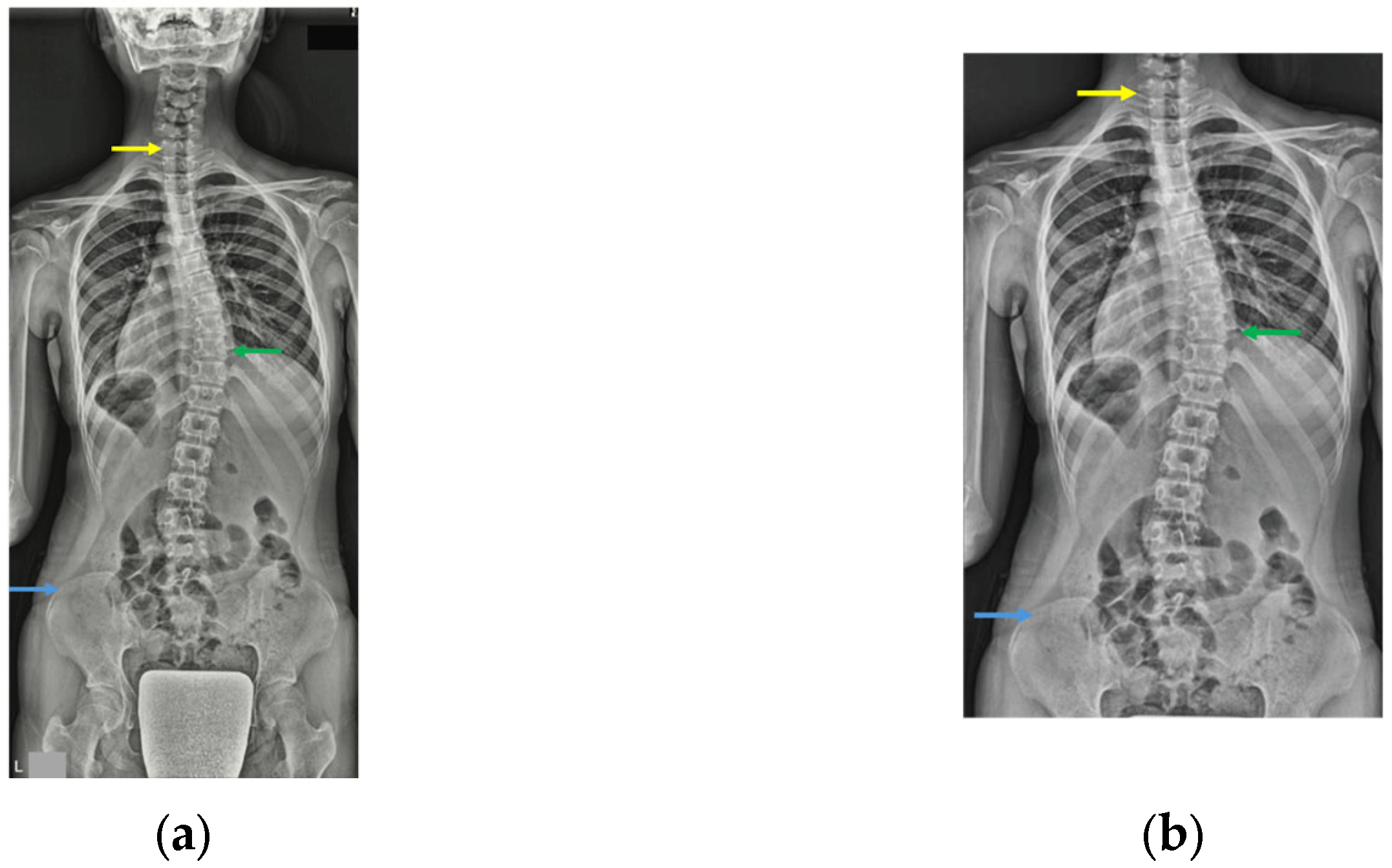
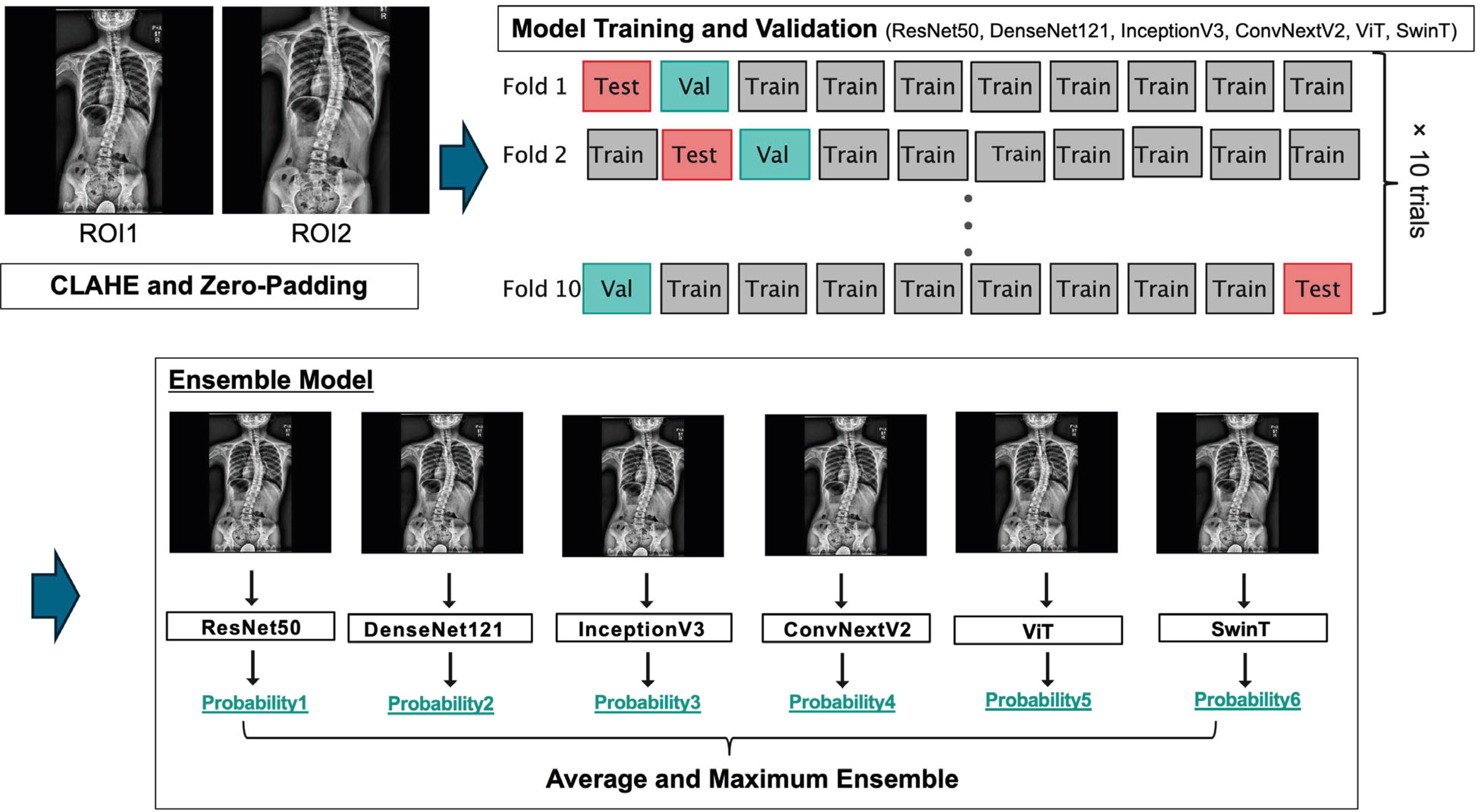
2.6. Imaging Preparation and Preprocessing
2.7. Deep Learning Model Architectures
2.8. Model Training and Validation
2.9. Model Interpretability
2.10. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Model Performance with ROI 1 (Full Image)
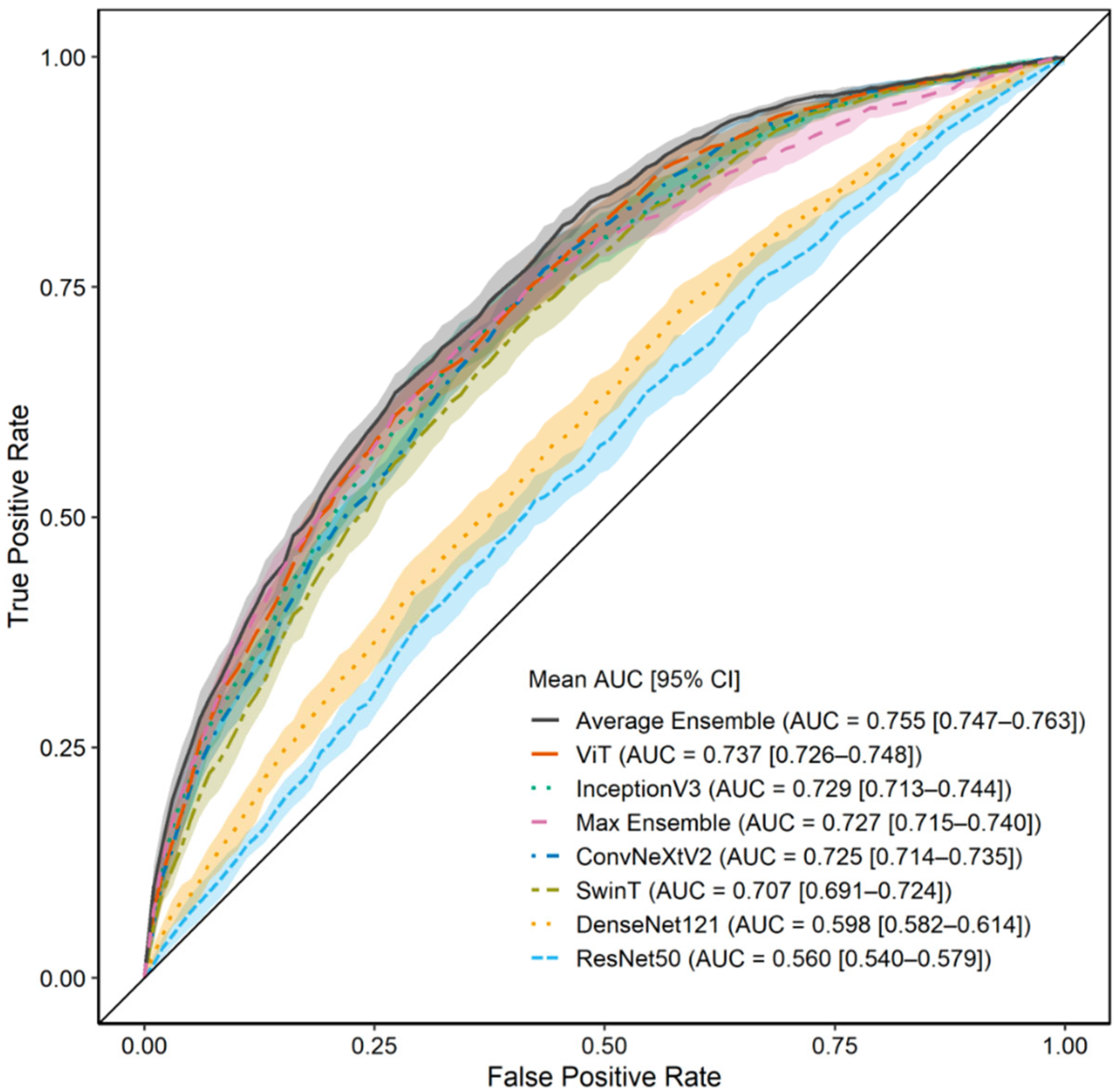
3.3. Model Performance with ROI 2 (C7 to Iliac Crest)
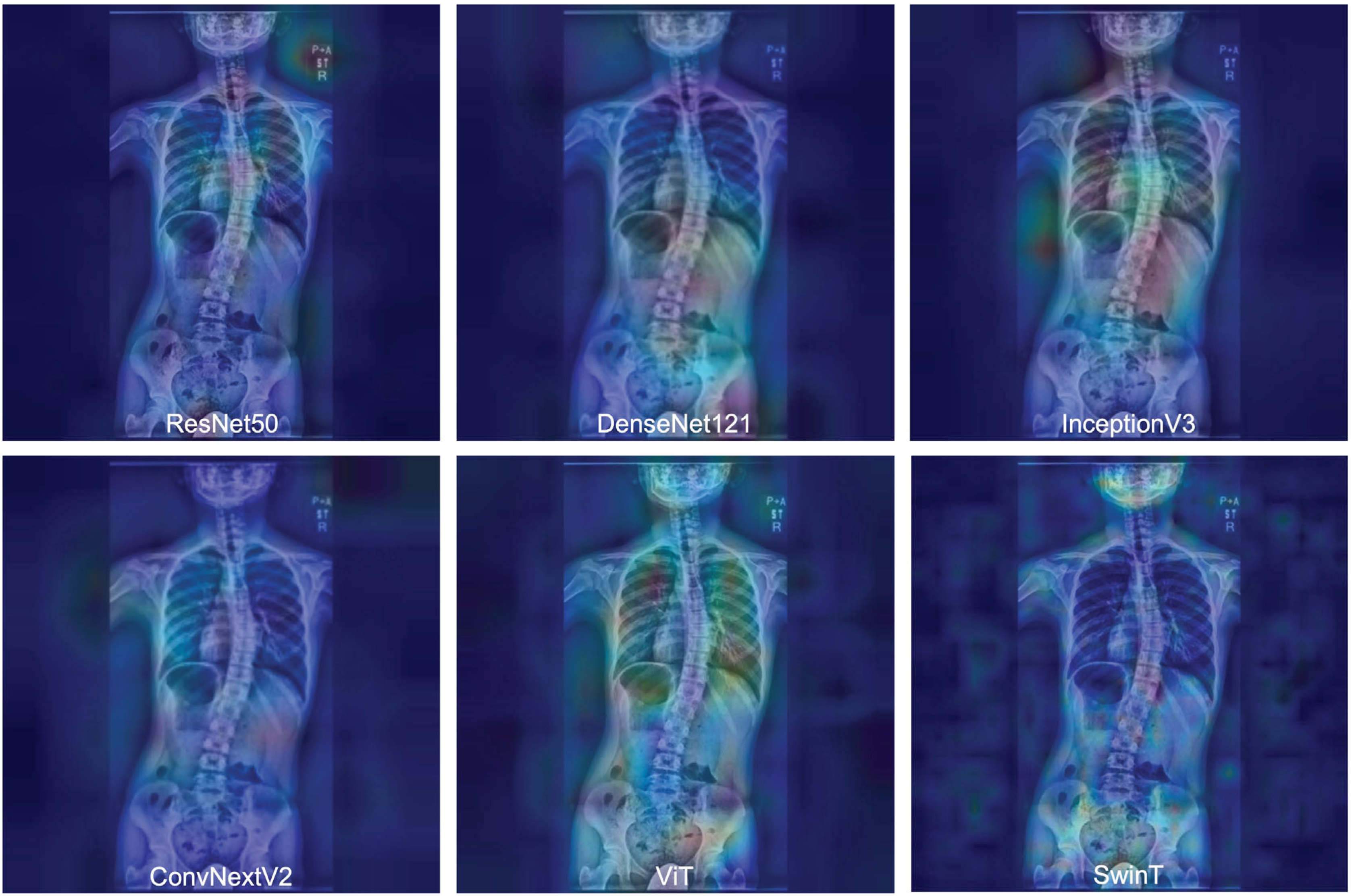
3.4. Gradient-Weighted Class Activation Mapping Attention Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kikanloo, S.R.; Tarpada, S.P.; Cho, W. Etiology of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Literature Review. Asian Spine J. 2019, 13, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, M.; Oikonomidis, S.; Harland, A.; Fürnstahl, P.; Farshad, M.; Bredow, J.; Eysel, P.; Scheyerer, M.J. Scoliosis and Prognosis-a Systematic Review Regarding Patient-Specific and Radiological Predictive Factors for Curve Progression. Eur. Spine J. 2021, 30, 1813–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noshchenko, A.; Hoffecker, L.; Lindley, E.M.; Burger, E.L.; Cain, C.M.J.; Patel, V.V.; Bradford, A.P. Predictors of Spine Deformity Progression in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. World J. Orthop. 2015, 6, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitoula, P.; Verma, K.; Holmes, L.; Gabos, P.G.; Sanders, J.O.; Yorgova, P.; Neiss, G.; Rogers, K.; Shah, S.A. Prediction of Curve Progression in Idiopathic Scoliosis: Validation of the Sanders Skeletal Maturity Staging System. Spine 2015, 40, 1006–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busscher, I.; Wapstra, F.H.; Veldhuizen, A.G. Predicting Growth and Curve Progression in the Individual Patient with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: Design of a Prospective Longitudinal Cohort Study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2010, 11, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahara, Y.; Tamura, M.; Seki, S.; Kondo, Y.; Makino, H.; Watanabe, K.; Kamei, K.; Futakawa, H.; Kawaguchi, Y. A Deep Convolutional Neural Network to Predict the Curve Progression of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Pilot Study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Zhai, X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Yang, M.; Yang, C.; Bai, Y.; Li, M. Deep Learning Based Decision-Making and Outcome Prediction for Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Patients with Posterior Surgery. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzubaidi, L.; Zhang, J.; Humaidi, A.J.; Al-Dujaili, A.; Duan, Y.; Al-Shamma, O.; Santamaría, J.; Fadhel, M.A.; Al-Amidie, M.; Farhan, L. Review of Deep Learning: Concepts, CNN Architectures, Challenges, Applications, Future Directions. J. Big Data 2021, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornung, A.L.; Hornung, C.M.; Mallow, G.M.; Barajas, J.N.; Rush, A.; Sayari, A.J.; Galbusera, F.; Wilke, H.-J.; Colman, M.; Phillips, F.M.; et al. Artificial Intelligence in Spine Care: Current Applications and Future Utility. Eur. Spine J. 2022, 31, 2057–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabu, A.; Hoshino, M.; Tabuchi, H.; Takahashi, S.; Masumoto, H.; Akada, M.; Morita, S.; Maeno, T.; Iwamae, M.; Inose, H.; et al. Using Artificial Intelligence to Diagnose Fresh Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures on Magnetic Resonance Images. Spine J. 2021, 21, 1652–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijowski, R.; Liu, F.; Caliva, F.; Pedoia, V. Deep Learning for Lesion Detection, Progression, and Prediction of Musculoskeletal Disease. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 52, 1607–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moldovan, F.; Moldovan, L. A Modeling Study for Hip Fracture Rates in Romania. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Region-Based Convolutional Networks for Accurate Object Detection and Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 38, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, X.; Kolesnikov, A.; Houlsby, N.; Beyer, L. Scaling Vision Transformers. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 1204–1213. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, S.; Qureshi, A.N.; Li, J.; Mahmood, T. On the Analyses of Medical Images Using Traditional Machine Learning Techniques and Convolutional Neural Networks. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2023, 30, 3173–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasha, S. 3D Spinal and Rib Cage Predictors of Brace Effectiveness in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2019, 20, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivas, T.B.; Vasiliadis, E.; Soultanis, K.; Lykissas, M.; Katzouraki, G.; Sekouris, N.; Lykouris, D.; Mazioti, C.; Mamzeri, A.; Papagianni, D.; et al. Idiopathic Scoliosis Progression: Presenting Rib and Segmental Rib Index as Predictors-A Literature Review. Med. Sci. 2025, 13, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhojanapalli, S.; Chakrabarti, A.; Glasner, D.; Li, D.; Unterthiner, T.; Veit, A. Understanding Robustness of Transformers for Image Classification. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 10211–10221. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer Using Shifted Windows. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 9992–10002. [Google Scholar]
- Shea, K.G.; Stevens, P.M.; Nelson, M.; Smith, J.T.; Masters, K.S.; Yandow, S. A Comparison of Manual versus Computer-Assisted Radiographic Measurement. Intraobserver Measurement Variability for Cobb Angles. Spine 1998, 23, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, A.P. The Use of the Area under the ROC Curve in the Evaluation of Machine Learning Algorithms. Pattern Recognit. 1997, 30, 1145–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicco, D.; Jurman, G. The Advantages of the Matthews Correlation Coefficient (MCC) over F1 Score and Accuracy in Binary Classification Evaluation. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolova, M.; Lapalme, G. A Systematic Analysis of Performance Measures for Classification Tasks. Inf. Process. Manag. 2009, 45, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faldini, C.; Manzetti, M.; Neri, S.; Barile, F.; Viroli, G.; Geraci, G.; Ursini, F.; Ruffilli, A. Epigenetic and Genetic Factors Related to Curve Progression in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Systematic Scoping Review of the Current Literature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.-J.; Moe, M.M.; Vaithinathan, R.; Wong, H.-K. Curve Progression in Idiopathic Scoliosis: Follow-up Study to Skeletal Maturity. Spine 2009, 34, 697–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, K.A.; Sucato, D.J.; Lee, M.C.; Jo, C.H. Skeletally Immature Patients With Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Curves 15°–24° Are at High Risk for Progression. Spine Deform. 2019, 7, 870–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonstein, J.E.; Carlson, J.M. The Prediction of Curve Progression in Untreated Idiopathic Scoliosis during Growth. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1984, 66, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, L.P.K.; Cheung, P.W.H.; Cheung, J.P.Y. Curve Type, Flexibility, Correction, and Rotation Are Predictors of Curve Progression in Patients with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Undergoing Conservative Treatment: A Systematic Review. Bone Jt. J. 2022, 104-B, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, B.H.K.; Yu, F.W.P.; Wang, Z.; Hung, V.W.Y.; Lam, T.P.; Ng, B.K.W.; Zhu, F.; Cheng, J.C.Y. Prognostic Value of Bone Mineral Density on Curve Progression: A Longitudinal Cohort Study of 513 Girls with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, S.N.; Hui, A.T.; Choi, S.; Mbamalu, E.K.; Tirabady, P.; Eleswarapu, A.S.; Gomez, J.A.; Alvandi, L.M.; Fornari, E.D. Applications of Artificial Intelligence for Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: Mapping the Evidence. Spine Deform. 2024, 12, 1545–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.; Kim, M.; Bae, S.J.; Lee, S.H.; Koh, J.-M.; Kim, N. Opportunistic Osteoporosis Screening Using Chest Radiographs With Deep Learning: Development and External Validation With a Cohort Dataset. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2022, 37, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Zhu, Y.; Luo, X.; Yang, S.; Xin, E.; Zeng, Y.; Fu, J.; Ruan, Z.; Wang, R.; Yang, L.; et al. A Novel Hybrid Deep Learning Framework Based on Biplanar X-Ray Radiography Images for Bone Density Prediction and Classification. Osteoporos. Int. 2025, 36, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, C.; Shi, L.; Ng, S.Y.-L.; Yan, H.-C.; Yeung, K.C.-M.; Wong, J.S.-H.; Cheung, K.M.-C.; Shea, G.K.-H. An Intelligent Composite Model Incorporating Global/Regional X-Rays and Clinical Parameters to Predict Progressive Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Curvatures and Facilitate Population Screening. EBioMedicine 2023, 95, 104768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, K.; Kuang, X.; Cheung, P.W.H.; Li, S.; Zhang, T.; Cheung, J.P.Y. Predicting Progression in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis at the First Visit by Integrating 2D Imaging and 1D Clinical Information. Glob. Spine J. 2025, 15, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wong, M.S. The Application of Machine Learning Methods for Predicting the Progression of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Systematic Review. Biomed. Eng. Online 2024, 23, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamichhane, D. Advanced Detection of AI-Generated Images Through Vision Transformers. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 3644–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, K.; Ogilvie, J.; Argyle, V.; Nelson, L.; Meade, M.; Braun, J.; Chettier, R. Polygenic Inheritance of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Study of Extended Families in Utah. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2010, 152A, 1178–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Non-Progression N = 196 | Progression N = 294 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (yrs) | 12.9 (1.9) | 12.6 (1.8) | 0.091 |
| Sex (female) | 181 (92.3%) | 266 (90.5%) | 0.369 |
| Height (cm) | 153.9 (7.5) | 153.5 (9.2) | 0.565 |
| Weight (kg) | 45.9 (8.1) | 44.8 (9.2) | 0.293 |
| Menarche | 0.269 | ||
| Not yet | 66 (33.7%) | 113 (38.4%) | |
| 2 yrs | 99 (50.5%) | 148 (50.3%) | |
| >2 yrs | 31 (15.8%) | 33 (11.2%) | |
| Brace (>12 h/day) | 24 (12.2%) | 19 (6.7%) | 0.040 |
| Risser sign | 0.012 | ||
| Grade 0 | 48 (24.5%) | 119 (40.5%) | |
| Grade 1 | 30 (15.3%) | 30 (10.2%) | |
| Grade 2 | 42 (21.4%) | 55 (18.7%) | |
| Grade 3 | 19 (9.7%) | 27 (9.2%) | |
| Grade 4 | 56 (28.6%) | 62 (21.1%) | |
| Grade 5 | 1 (0.5%) | 1 (0.3%) | |
| Cobb angle (°) | 23.8 (8.2) | 30.9 (10.6) | <0.001 |
| 10–25° | 114 (58.2%) | 89 (30.2%) | <0.001 |
| >25° | 82 (41.8%) | 205 (69.8%) |
| Model | AUC | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | Accuracy | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Ensemble | 0.769 ± 0.014 | 0.714 ± 0.079 | 0.689 ± 0.078 | 0.778 ± 0.027 | 0.622 ± 0.043 | 0.704 ± 0.020 | 0.741 ± 0.033 |
| ViT | 0.755 ± 0.021 | 0.738 ± 0.079 | 0.652 ± 0.090 | 0.764 ± 0.033 | 0.631 ± 0.046 | 0.704 ± 0.019 | 0.748 ± 0.031 |
| Max Ensemble | 0.751 ± 0.017 | 0.668 ± 0.074 | 0.732 ± 0.065 | 0.792 ± 0.026 | 0.599 ± 0.035 | 0.694 ± 0.022 | 0.722 ± 0.037 |
| SwinT | 0.748 ± 0.026 | 0.687 ± 0.079 | 0.695 ± 0.065 | 0.774 ± 0.023 | 0.601 ± 0.036 | 0.690 ± 0.030 | 0.725 ± 0.045 |
| ConvNeXtV2 | 0.748 ± 0.014 | 0.745 ± 0.096 | 0.637 ± 0.088 | 0.758 ± 0.028 | 0.636 ± 0.058 | 0.702 ± 0.026 | 0.747 ± 0.043 |
| InceptionV3 | 0.705 ± 0.027 | 0.650 ± 0.106 | 0.670 ± 0.116 | 0.753 ± 0.039 | 0.568 ± 0.041 | 0.658 ± 0.029 | 0.691 ± 0.051 |
| DenseNet121 | 0.657 ± 0.039 | 0.649 ± 0.125 | 0.603 ± 0.135 | 0.717 ± 0.040 | 0.545 ± 0.056 | 0.631 ± 0.033 | 0.673 ± 0.058 |
| ResNet50 | 0.620 ± 0.028 | 0.655 ± 0.180 | 0.553 ± 0.150 | 0.690 ± 0.022 | 0.543 ± 0.080 | 0.614 ± 0.052 | 0.659 ± 0.092 |
| Model | AUC | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | Accuracy | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Ensemble | 0.755 ± 0.013 | 0.714 ± 0.107 | 0.679 ± 0.109 | 0.775 ± 0.035 | 0.625 ± 0.060 | 0.700 ± 0.025 | 0.737 ± 0.044 |
| ViT | 0.737 ± 0.018 | 0.726 ± 0.128 | 0.644 ± 0.142 | 0.762 ± 0.044 | 0.628 ± 0.063 | 0.693 ± 0.025 | 0.735 ± 0.051 |
| InceptionV3 | 0.729 ± 0.025 | 0.673 ± 0.065 | 0.680 ± 0.059 | 0.761 ± 0.023 | 0.584 ± 0.035 | 0.676 ± 0.026 | 0.712 ± 0.035 |
| Max Ensemble | 0.727 ± 0.020 | 0.667 ± 0.083 | 0.701 ± 0.073 | 0.772 ± 0.025 | 0.589 ± 0.038 | 0.680 ± 0.026 | 0.712 ± 0.043 |
| ConvNeXtV2 | 0.725 ± 0.017 | 0.772 ± 0.093 | 0.574 ± 0.062 | 0.732 ± 0.010 | 0.641 ± 0.071 | 0.693 ± 0.034 | 0.749 ± 0.045 |
| SwinT | 0.707 ± 0.027 | 0.715 ± 0.108 | 0.605 ± 0.095 | 0.733 ± 0.026 | 0.598 ± 0.062 | 0.671 ± 0.035 | 0.719 ± 0.051 |
| DenseNet121 | 0.598 ± 0.026 | 0.650 ± 0.148 | 0.526 ± 0.153 | 0.678 ± 0.030 | 0.510 ± 0.042 | 0.600 ± 0.035 | 0.652 ± 0.079 |
| ResNet50 | 0.560 ± 0.031 | 0.623 ± 0.191 | 0.485 ± 0.177 | 0.647 ± 0.037 | 0.479 ± 0.056 | 0.568 ± 0.057 | 0.620 ± 0.105 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takahashi, S.; Ichikawa, S.; Watanabe, K.; Ueda, H.; Arima, H.; Yamato, Y.; Takeuchi, T.; Hosogane, N.; Okamoto, M.; Umezu, M.; et al. Development and Validation of Transformer- and Convolutional Neural Network-Based Deep Learning Models to Predict Curve Progression in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7216. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207216
Takahashi S, Ichikawa S, Watanabe K, Ueda H, Arima H, Yamato Y, Takeuchi T, Hosogane N, Okamoto M, Umezu M, et al. Development and Validation of Transformer- and Convolutional Neural Network-Based Deep Learning Models to Predict Curve Progression in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(20):7216. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207216
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakahashi, Shinji, Shota Ichikawa, Kei Watanabe, Haruki Ueda, Hideyuki Arima, Yu Yamato, Takumi Takeuchi, Naobumi Hosogane, Masashi Okamoto, Manami Umezu, and et al. 2025. "Development and Validation of Transformer- and Convolutional Neural Network-Based Deep Learning Models to Predict Curve Progression in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 20: 7216. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207216
APA StyleTakahashi, S., Ichikawa, S., Watanabe, K., Ueda, H., Arima, H., Yamato, Y., Takeuchi, T., Hosogane, N., Okamoto, M., Umezu, M., Oba, H., Kondo, Y., & Seki, S. (2025). Development and Validation of Transformer- and Convolutional Neural Network-Based Deep Learning Models to Predict Curve Progression in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(20), 7216. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207216






