Enhancing Image Quality in Dental-Maxillofacial CBCT: The Impact of Iterative Reconstruction and AI on Noise Reduction—A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Article Selection and Data Extraction Process Overview
2.2. Article Search
(“CBCT” OR “cone-beam computed tomography”) AND (“denoising” OR “denoise” OR “noise reduction”) AND (“oral cavity” OR “maxillofacial” OR “dental”)
2.3. Eligibility Criteria
2.4. Data Extraction
2.5. Risk of Bias
3. Results
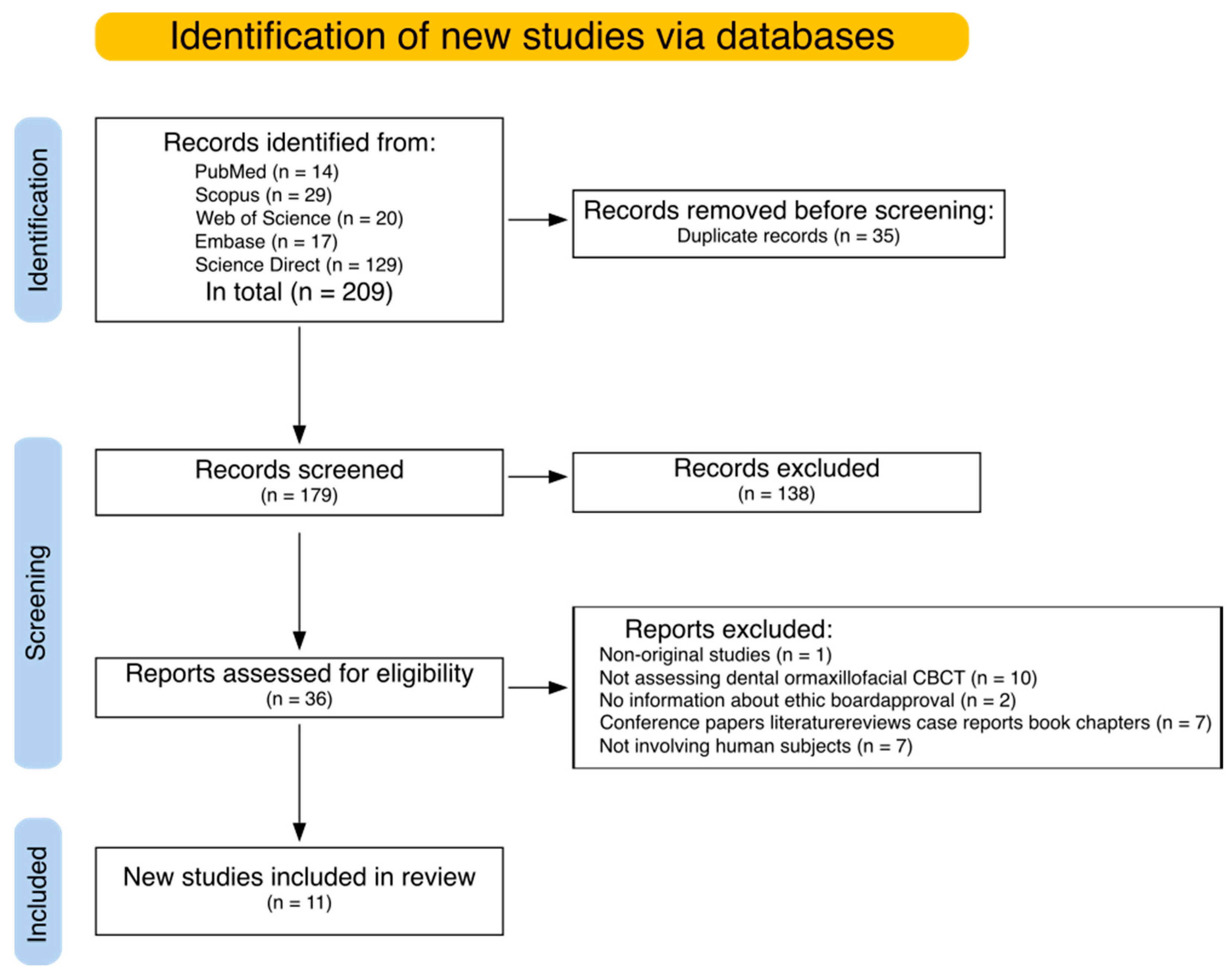
3.1. Search Results
3.2. Risk of Bias
3.3. Study Objectives
3.4. Metrics and Evaluation
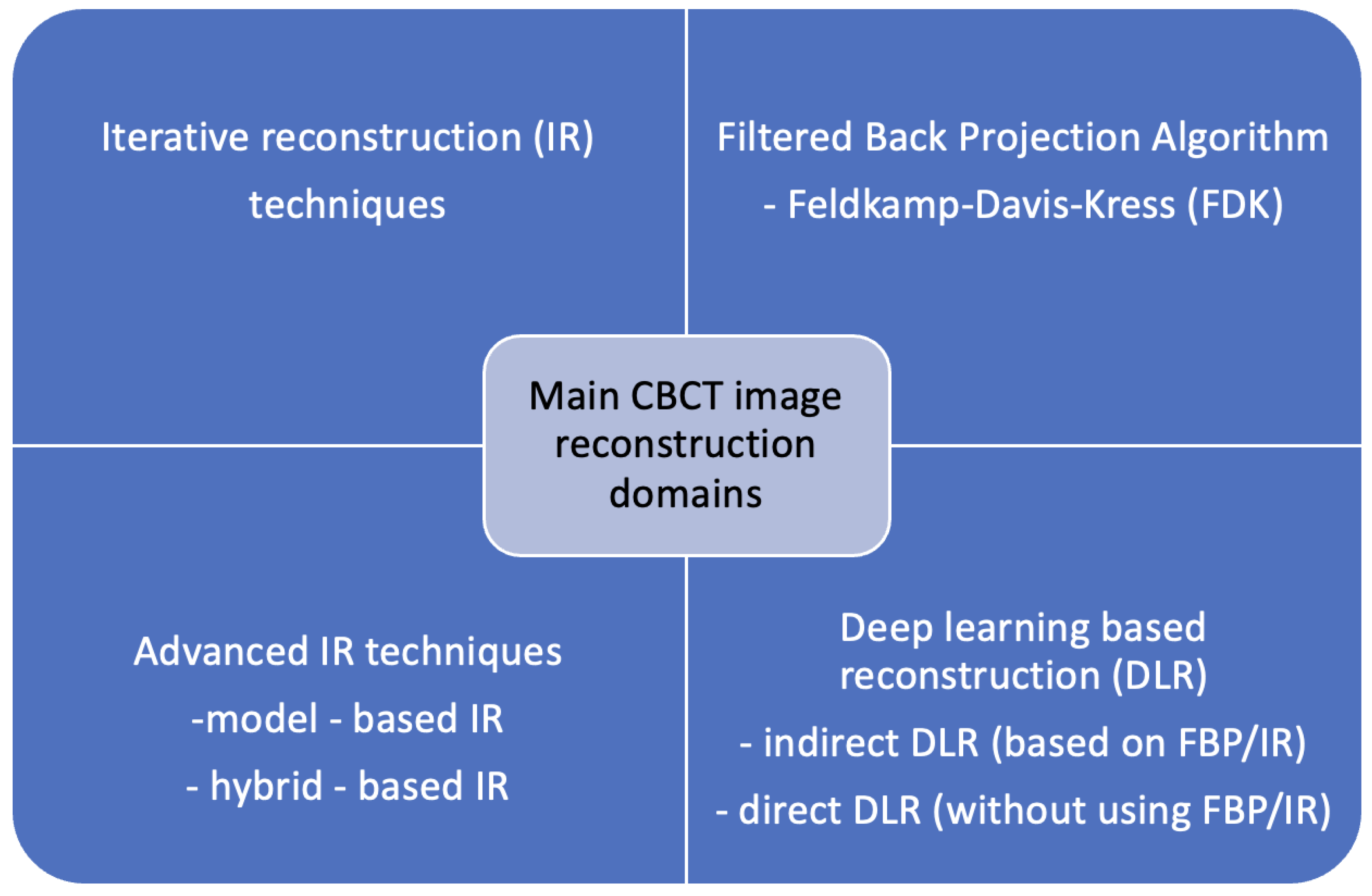
3.5. Classical Methods in Image Denoising
3.6. Evaluation of AI-Based Denoising Models
3.7. Transforming Images Between Techniques
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison of Traditional and AI-Based Tools
4.2. Limitations
4.3. Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Gaêta-Araujo, H.; Leite, A.F.; Vasconcelos, K.d.F.; Jacobs, R. Two Decades of Research on CBCT Imaging in DMFR—An Appraisal of Scientific Evidence. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2021, 50, 20200367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawood, A.; Patel, S.; Brown, J. Cone Beam CT in Dental Practice. Br. Dent. J. 2009, 207, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puleio, F.; Lizio, A.S.; Coppini, V.; Lo Giudice, R.; Lo Giudice, G. CBCT-based assessment of vapor lock effects on endodontic disinfection. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauwels, R.; Araki, K.; Siewerdsen, J.H.; Thongvigitmanee, S.S. Technical Aspects of Dental CBCT: State of the Art. Dentomaxillofacial Radiol. 2015, 44, 20140224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, R.; Heil, U.; Groβ, D.; Bruellmann, D.D.; Dranischnikow, E.; Schwanecke, U.; Schoemer, E. Artefacts in CBCT: A Review. Dentomaxillofacial Radiol. 2011, 40, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, M.; Tsunoo, T.; Nakamori, N.; Yoshida, K. Effect of Scatter Radiation on Image Noise in Cone Beam CT. Med. Phys. 2001, 28, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, R.; Bender, R.; Herman, G.T. Algebraic Reconstruction Techniques (ART) for Three-Dimensional Electron Microscopy and X-Ray Photography. J. Theor. Biol. 1970, 29, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Park, J.; Choi, Y.; Park, K.R.; Min, B.J.; Lee, I.J. Low-Dose CBCT Reconstruction via Joint Non-Local Total Variation Denoising and Cubic B-Spline Interpolation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldkamp, L.A.; Davis, L.C.; Kress, J.W. Practical Cone-Beam Algorithm. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1984, 1, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchers, R.E. On the ALARP Approach to Risk Management. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2001, 71, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willemink, M.J.; de Jong, P.A.; Leiner, T.; de Heer, L.M.; Nievelstein, R.A.J.; Budde, R.P.J.; Schilham, A.M.R. Iterative Reconstruction Techniques for Computed Tomography Part 1: Technical Principles. Eur. Radiol. 2013, 23, 1623–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noël, P.B.; Fingerle, A.A.; Renger, B.; Münzel, D.; Rummeny, E.J.; Dobritz, M. Initial Performance Characterization of a Clinical Noise–Suppressing Reconstruction Algorithm for MDCT. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011, 197, 1404–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheffel, H.; Stolzmann, P.; Schlett, C.L.; Engel, L.-C.; Major, G.P.; Károlyi, M.; Do, S.; Maurovich-Horvat, P.; Hoffmann, U. Coronary Artery Plaques: Cardiac CT with Model-Based and Adaptive-Statistical Iterative Reconstruction Technique. Eur. J. Radiol. 2012, 81, e363–e369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Kalra, M.K.; Gilman, M.D.; Hsieh, J.; Pien, H.H.; Digumarthy, S.R.; Shepard, J.-A.O. Adaptive Statistical Iterative Reconstruction Technique for Radiation Dose Reduction in Chest CT: A Pilot Study. Radiology 2011, 259, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ylisiurua, S.; Sipola, A.; Nieminen, M.T.; Brix, M.A.K. Deep Learning Enables Time-Efficient Soft Tissue Enhancement in CBCT: Proof-of-Concept Study for Dentomaxillofacial Applications. Phys. Medica 2024, 117, 103184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Gang, G.J.; Siewerdsen, J.H. Noise, Sampling, and the Number of Projections in Cone-Beam CT with a Flat-Panel Detector. Med. Phys. 2014, 41, 061909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaasalainen, T.; Ekholm, M.; Siiskonen, T.; Kortesniemi, M. Dental Cone Beam CT: An Updated Review. Phys. Medica Eur. J. Med. Phys. 2021, 88, 193–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolterink, J.M.; Leiner, T.; Viergever, M.A.; Išgum, I. Generative Adversarial Networks for Noise Reduction in Low-Dose CT. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 36, 2536–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Kalra, M.K.; Lin, F.; Chen, Y.; Liao, P.; Zhou, J.; Wang, G. Low-Dose CT With a Residual Encoder-Decoder Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 36, 2524–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, F.K.; Catalano, M.; Pfeiffer, D.; Rummeny, E.J.; Noël, P.B. Evaluation of a Machine Learning Based Model Observer for X-Ray CT. In Proceedings of the Proc. SPIE, Houston, TX, USA, 7 March 2018; Volume 10577, p. 105770S. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Kim, K.; El Fakhri, G.; Li, Q. Iterative Low-Dose CT Reconstruction With Priors Trained by Artificial Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 36, 2479–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Chandler, J.; Welch, V.A.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Thomas, J. Updated Guidance for Trusted Systematic Reviews: A New Edition of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 10, ED000142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McHugh, M. Interrater Reliability: The Kappa Statistic. Biochem. Medica Časopis Hrvat. Društva Med. Biokem./HDMB 2012, 22, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir-Behghadami, M.; Janati, A. Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcomes and Study (PICOS) Design as a Framework to Formulate Eligibility Criteria in Systematic Reviews. Emerg. Med. J. 2020, 37, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiting, P.F.; Rutjes, A.W.S.; Westwood, M.E.; Mallett, S.; Deeks, J.J.; Reitsma, J.B.; Leeflang, M.M.G.; Sterne, J.A.C.; Bossuyt, P.M.M. QUADAS-2: A Revised Tool for the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 155, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costarelli, D.; Pozzilli, P.; Seracini, M.; Vinti, G. Enhancement of Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Dental-Maxillofacial Images by Sampling Kantorovich Algorithm. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierczak, W.; Kędziora, K.; Janiszewska-Olszowska, J.; Kazimierczak, N.; Serafin, Z. Noise-Optimized CBCT Imaging of Temporomandibular Joints—The Impact of AI on Image Quality. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierczak, W.; Wajer, R.; Komisarek, O.; Dyszkiewicz-Konwińska, M.; Wajer, A.; Kazimierczak, N.; Janiszewska-Olszowska, J.; Serafin, Z. Evaluation of a Vendor-Agnostic Deep Learning Model for Noise Reduction and Image Quality Improvement in Dental CBCT. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, K.; Lee, C.; Han, Y.; Pang, S.; Kim, Y.H.; Choi, C.; Jang, I.; Han, S.S. Multi-Planar 2.5D U-Net for Image Quality Enhancement of Dental Cone-Beam CT. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0285608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, Y.J.; Lee, J.S. Generating Synthetic CT Images from Unpaired Head and Neck CBCT Images and Validating the Importance of Detailed Nasal Cavity Acquisition through Simulations. Comput. Biol. Med. 2025, 185, 109568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestergaard, C.D.; Elstrøm, U.V.; Muren, L.P.; Ren, J.; Nørrevang, O.; Jensen, K.; Taasti, V.T. Proton Dose Calculation on Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Using Unsupervised 3D Deep Learning Networks. Phys. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 32, 100658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wajer, R.; Wajer, A.; Kazimierczak, N.; Wilamowska, J.; Serafin, Z. The Impact of AI on Metal Artifacts in CBCT Oral Cavity Imaging. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Ding, S.G.; Gong, X.C.; Yuan, X.X.; Lin, J.F.; Chen, Q.; Li, J.G. Generating Synthesized Computed Tomography from CBCT Using a Conditional Generative Adversarial Network for Head and Neck Cancer Patients. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2022, 21, 15330338221085358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yang, W.; Pallikonda Rajasekaran, M. Iterative Noise Reduction Algorithm-Based Cone Beam Computed Tomography Image Analysis for Dental Pulp Disease in Root Canal Therapies. Sci. Program. 2022, 2022, 7322332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Du, Y.; Peng, Y. VVBPNet: Deep Learning Model in View-by-View Backprojection (VVBP) Domain for Sparse-View CBCT Reconstruction. Biomed. Signal Process Control 2025, 102, 107195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.H.; Park, E.-A.; Lee, W.; Ahn, C.; Kim, J.-H. Incremental Image Noise Reduction in Coronary CT Angiography Using a Deep Learning-Based Technique with Iterative Reconstruction. Korean J. Radiol. 2020, 21, 1165–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadia, R.T.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J. CT Image Denoising Methods for Image Quality Improvement and Radiation Dose Reduction. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2024, 25, e14270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorenstein, L.; Onn, A.; Green, M.; Mayer, A.; Segev, S.; Marom, E.M. A Novel Artificial Intelligence Based Denoising Method for Ultra-Low Dose CT Used for Lung Cancer Screening. Acad. Radiol. 2023, 30, 2588–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brendlin, A.S.; Schmid, U.; Plajer, D.; Chaika, M.; Mader, M.; Wrazidlo, R.; Männlin, S.; Spogis, J.; Estler, A.; Esser, M.; et al. AI Denoising Improves Image Quality and Radiological Workflows in Pediatric Ultra-Low-Dose Thorax Computed Tomography Scans. Tomography 2022, 8, 1678–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramage, A.; Lopez Gutierrez, B.; Fischer, K.; Sekula, M.; Santaella, G.M.; Scarfe, W.; Brasil, D.M.; de Oliveira-Santos, C. Filtered Back Projection vs. Iterative Reconstruction for CBCT: Effects on Image Noise and Processing Time. Dentomaxillofacial Radiol. 2023, 52, 20230109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, T.; Xing, L. Iterative Image Reconstruction for CBCT Using Edge-Preserving Prior. Med. Phys. 2009, 36, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.; Sun, N.; Wang, J.; Tan, S. Iterative CBCT Reconstruction Using Hessian Penalty. Phys. Med. Biol. 2015, 60, 1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Kalra, M.; Do, S.; Thibault, J.-B.; Pien, H.; O’Connor, O.; Blake, M. Comparison of Hybrid and Pure Iterative Reconstruction Techniques With Conventional Filtered Back Projection: Dose Reduction Potential in the Abdomen. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2012, 36, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morsbach, F.; Desbiolles, L.; Raupach, R.; Leschka, S.; Schmidt, B.; Alkadhi, H. Noise Texture Deviation: A Measure for Quantifying Artifacts in Computed Tomography Images With Iterative Reconstructions. Investig. Radiol. 2017, 52, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L. Model-Based Iterative Reconstruction: A Promising Algorithm for Today’s Computed Tomography Imaging. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Sci. 2014, 45, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mileto, A.; Zamora, D.; Alessio, A.; Pereira, C.; Liu, J.; Bhargava, P.; Carnell, J.; Cowan, S.; Dighe, M.; Gunn, M.; et al. CT Detectability of Small Low-Contrast Hypoattenuating Focal Lesions: Iterative Reconstructions versus Filtered Back Projection. Radiology 2018, 289, 180137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, Q.; Zhou, L.; Li, F. Deep Learning-Based Algorithms for Low-Dose CT Imaging: A Review. Eur. J. Radiol. 2024, 172, 111355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Digumarthy, S.R.; Muse, V.V.; Kambadakone, A.R.; Blake, M.A.; Tabari, A.; Hoi, Y.; Akino, N.; Angel, E.; Madan, R.; et al. Image Quality and Lesion Detection on Deep Learning Reconstruction and Iterative Reconstruction of Submillisievert Chest and Abdominal CT. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 214, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamabuchi, N.; Ohno, Y.; Kimata, H.; Ito, Y.; Fujii, K.; Akino, N.; Takenaka, D.; Yoshikawa, T.; Oshima, Y.; Matsuyama, T.; et al. Effectiveness of Deep Learning Reconstruction on Standard to Ultra-Low-Dose High-Definition Chest CT Images. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2023, 41, 1373–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Cheng, M.; Wei, H.; Liang, Z. A Joint Learning Framework for Multisite CBCT-to-CT Translation Using a Hybrid CNN-Transformer Synthesizer and a Registration Network. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1440944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadra, S.; Kelkar, V.A.; Brooks, F.J.; Anastasio, M.A. On Hallucinations in Tomographic Image Reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2021, 40, 3249–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruetters, M.; Sen, S.; Gehrig, H.; Bruckner, T.; Kim, T.-S.; Lux, C.J.; Schlemmer, H.-P.; Heinze, S.; Maier, J.; Kachelrieß, M.; et al. Dental Imaging Using an Ultra-High Resolution Photon-Counting CT System. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanon, C.; Pepe, A.; Cademartiri, F.; Bini, C.; Maffei, E.; Quaia, E.; Stellini, E.; Di Fiore, A. Potential Benefits of Photon-Counting CT in Dental Imaging: A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawall, S.; Maier, J.; Sen, S.; Gehrig, H.; Kim, T.-S.; Schlemmer, H.-P.; Schönberg, S.O.; Kachelrieß, M.; Rütters, M. Dental Imaging in Clinical Photon-Counting CT at a Quarter of DVT Dose. J. Dent. 2024, 142, 104859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Zhou, H.; He, J.; Xie, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, W.; Zhang, X.; et al. Texture-Preserving Diffusion Model for CBCT-to-CT Synthesis. Med. Image Anal. 2025, 99, 103362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Haddad, A.A.; Al-Haddad, L.A.; Al-Haddad, S.A.; Jaber, A.A.; Khan, Z.H.; Rehman, H.Z.U. Towards Dental Diagnostic Systems: Synergizing Wavelet Transform with Generative Adversarial Networks for Enhanced Image Data Fusion. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 182, 109241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueno, M.R.; Estrela, C.; Azevedo, B.C.; Diogenes, A. Development of a New Cone—Beam Computed Tomography Software for Endodontic Diagnosis. Braz. Dent. J. 2018, 29, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, M.R.; Estrela, C.; Azevedo, B.C.; Cintra Junqueira, J.L. Root Canal Shape of Human Permanent Teeth Determined by New Cone-Beam Computed Tomographic Software. J. Endod. 2020, 46, 1662–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao-Ngoc, L.; Du, Y.-C. Generative Noise Reduction in Dental Cone-Beam CT by a Selective Anatomy Analytic Iteration Reconstruction Algorithm. Electronics 2019, 8, 1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budaraju, D.; Narayanappa, C.K.; Hiremath, B.; Ravi, P.; Lakshminarayana, M.; Neelapu, B.; Jayaraman, S. Enhancement of Three-Dimensional Medical Images. In Computer-Aided Diagnosis (CAD) Tools and Applications for 3D Medical Imaging; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; Volume 136, ISBN 9780323988575. [Google Scholar]
- Friot--Giroux, L.; Peyrin, F.; Maxim, V. Iterative Tomographic Reconstruction with TV Prior for Low-Dose CBCT Dental Imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 2022, 67, 205010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GAN, J.; Yu, N.; Qian, G.; He, N. Concrete Learning Method for Segmentation and Denoising Using CBCT Image. In Proceedings of the 2023 4th International Conference on Control, Robotics and Intelligent System, Association for Computing Machinery, Guangzhou, China, 25–27 August 2023; pp. 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Hegazy, M.; Cho, M.; Lee, S. Half-Scan Artifact Correction Using Generative Adversarial Network for Dental CT. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 132, 104313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, K.; Hu, D.; Gao, X. StarAN: A Star Attention Network Utilizing Inter-View and Intra-View Correlations for Sparse-View Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Reconstruction. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2024, 258, 125099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Lim, C.; Shin, J.; Chung, M.; Jung, Y.G. Enhanced Artificial Intelligence-Based Diagnosis Using CBCT with Internal Denoising: Clinical Validation for Discrimination of Fungal Ball, Sinusitis, and Normal Cases in the Maxillary Sinus. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2023, 240, 107708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroon, D.-J.; Slump, C.; Maal, T. Optimized Anisotropic Rotational Invariant Diffusion Scheme on Cone-Beam CT. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2010: 13th International Conference, Beijing, China, 20–24 September 2010; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 13, ISBN 978-3-642-15710-3. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, C.; Mengfei, X.; Wang, S.; Liang, Y.; Yi, R.; Wen, Y.-H.; Liu, Y.-J. Automatic Tooth Arrangement with Joint Features of Point and Mesh Representations via Diffusion Probabilistic Models. Comput. Aided Geom. Des. 2024, 111, 102293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.; Park, S.; Jeon, D.; Kim, W.; Lee, S.; Cho, H. Eliminating Metal Artifacts in Dental Computed Tomography Using an Elaborate Sinogram Normalization Interpolation Method with CNR-Based Metal Segmentation. J. Instrum. 2024, 19, C11003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, S.; Tohidypour, H.R.; Nasiopoulos, P.; Mirabbasi, S. An Efficient Quality Enhancement Method for Low-Dose CBCT Imaging. WSEAS Trans. Biol. Biomed. 2024, 22, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.; Schaub, S.; Dagassan-Berndt, D.; Bieder, F.; Cattin, P.; Bornstein, M. Development and Evaluation of a Deep Learning Model to Reduce Exomass-Related Metal Artefacts in Cone-Beam Computed Tomography of the Jaws. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2024, 54, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Jeon, K.; Lee, S.-H.; Seo, J. Unpaired-Paired Learning for Shading Correction in Cone-Beam Computed Tomography. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 26140–26148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagawa, M.; Miyoseta, Y.; Hayakawa, Y.; Honda, A. Comparison of Two—And Three-Dimensional Filtering Methods to Improve Image Quality in Multiplanar Reconstruction of Cone-Beam Computed Tomography. Oral Radiol. 2009, 25, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Jin, Z.; Chen, X. CDRMamba: A Framework for Automated Craniomaxillofacial Defect Reconstruction Using Mamba-Based Modeling. Biomed. Signal Process Control 2025, 103, 107376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, A.; Haiter-Neto, F.; Frydenberg, M.; Kirkevang, L.-L. Variable-Resolution Cone-Beam Computerized Tomography with Enhancement Filtration Compared with Intraoral Photostimulable Phosphor Radiography in Detection of Transverse Root Fractures in an in Vitro Model. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 2009, 108, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widmann, G.; Al-Ekrish, A.A. Ultralow Dose MSCT Imaging in Dental Implantology. Open Dent. J. 2018, 12, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, F.; Zhang, R.; Dai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Luan, Q.-X. Clinical Application of Mixed Reality Holographic Imaging Technology in Scaling and Root Planing of Severe Periodontitis: A Proof of Concept. J. Dent. 2024, 149, 105284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.; Jeong, U.; Kwon, T.; Choi, D.; Lee, T.; Ye, S.-J.; Cho, G.; Cho, S. Penalty-Driven Enhanced Self-Supervised Learning (Noise2Void) for CBCT Denoising. In Proceedings of the Proc. SPIE., San Diego, CA, USA, 7 April 2023; Volume 12463, p. 1246327. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, A.; Jia, X.; Wu, S.; Qi, H.; Zhou, L.; Xu, Y. Scatter Correction Based on Adaptive Photon Path-Based Monte Carlo Simulation Method in Multi-GPU Platform. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 194, 105487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study | Year | Country | Study Type/ No. of Patients | Reference Standard—Quantitative Evaluation | Reference Standard—Qualitative Evaluation | Anatomical Region | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Costarelli et al. [27] | 2021 | Italy | Patients/2 | MSE, PSNR | NA | dental-maxillofacial region |
| 2. | Kazimierczak et al. [28] | 2024 | Poland | Patients/50 | CNR | A radiologist and orthodontist | temporomandibular joints |
| 3. | Kazimierczak et al. [29] | 2024 | Poland | Patients/93 | CNR | A radiologist and two dentists | dental-maxillofacial region |
| 4. | Ryu K. et al. [30] | 2023 | South Korea, USA | Patients/30 Phantom/6 | MAE, NRMSE, SSIM | Two radiologists | head and neck |
| 5. | Ryu S. et al. [31] | 2025 | South Korea, USA | Patients/33 | MAE, PSNR, SSIM | Unspecified researchers | head and neck |
| 6. | Vestergaard et al. [32] | 2024 | Denmark | Patients/102 | PSNR, SSIM, MAE, ME | NA | head and neck |
| 7. | Wajer et al. [33] | 2024 | Poland | Patients/61 | CNR, ΔVV, AIx | A radiologist and a dentist | dental-maxillofacial region |
| 8. | Ylisiurua et al. [15] | 2024 | Finland | Patients/32 | SSIM, PSNR | One dentomaxillofacial radiologist | dental-maxillofacial region |
| 9. | Zhang Y. et al. [34] | 2022 | China | Patients/120 | MAE, RMSE, SSIM, PSNR | NA | head and neck |
| 10. | Zhang K. et al. [35] | 2022 | China | Patients/88 | PSNR, CORR | NA | affected teeth |
| 11. | Zhao et al. [36] | 2025 | China | Patients/223 | RMSE, PSNR, SSIM, FSIM | NA | head |
| Study | Year | Anatomical Region | Model Used |
|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1—Denoising by classical methods (iterative reconstructions, filtering algorithms) | |||
| Costarelli et al. [27] | 2021 | dental-maxillofacial region | Sampling Kantorovich (SK) |
| Zhang K. et al. [35] | 2022 | affected teeth | INR algorithm-based CBCT |
| Group 2—Evaluation of AI-based denoising model | |||
| Kazimierczak et al. [28] | 2024 | temporomandibular joints | ClariCT.AI (commercial) |
| Kazimierczak et al. [29] | 2024 | dental-maxillofacial region | ClariCT.AI (commercial) |
| Wajer et al. [33] | 2024 | dental-maxillofacial region | ClariCT.AI (commercial) |
| Group 3—Transforming images between techniques | |||
| Ryu S. et al. [31] | 2025 | head and neck | CycleGAN |
| Vestergaard et al. [32] | 2024 | head and neck | CycleGAN/CUT |
| Zhang Y. et al. [34] | 2022 | head and neck | GAN |
| Ylisiurua et al. [15] | 2024 | dental-maxillofacial region | UNIT and U-Net |
| Ryu K. et al. [30] | 2023 | head and neck | UNet |
| Zhao et al. [36] | 2025 | head | VVBPNet |
| Study | Risk of Bias | Applicability Concerns | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient Selection | Index Test | Reference Standard | Flow and Timing | Patient Selection | Index Test | Reference Standard | |
| Costarelli et al., 2021 [27] | High | Unclear | Low | High | High | Low | Low |
| Kazimierczak et al., 2024 [28] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Kazimierczak et al., 2024 [29] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Ryu K. et al., 2023 [30] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Ryu S. et al., 2025 [31] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Vestergaard et al., 2024, [32] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Wajer et al., 2024 [33] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Ylisiurua et al., 2024 [15] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Zhang Y. et al., 2022 [34] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Zhang K. et al., 2022 [35] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Zhao et al., 2025 [36] | Unclear | Unclear | Low | Low | Unclear | Low | Low |
| Study | Algorithm Name | Comparison with Ground Truth | Comparison with Classical Method | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ground Truth Images | Metric | Mean Metric Value | Rel. Metric Enhancement | Reference Method | Rel. Metric Enhancement | ||
| Classical image denoising | |||||||
| Costarelli et al. [27] | Sampling Kantorovich (SK) | Original CBCT images | PSNR | 58.1 dB | --- | Bilinear B-spline | 15.5% |
| Bicubic B-spline | 13.8% | ||||||
| Zhang K. et al. [35] | Iterative Noise Reduction (INR) | Original CBCT images | PSNR (shifted) | 191 dB | --- | PWLS | 2.1% |
| PSNR—90 dB * | 101 dB | --- | 4.1% | ||||
| CORR | 0.993 | --- | 0.3% | ||||
| Evaluation of AI-based denoising | |||||||
| Kazimierczak et al. [28] | ClariCT.AI | Original CBCT images | CNR | 11.03 | 44.8% | --- | --- |
| Kazimierczak et al. [29] | ClariCT.AI | Original CBCT images | CNR | 9.92 | 35.6% | --- | --- |
| Wajer et al. [33] | ClariCT.AI | Original CBCT images | CNR ** | 0.93 | 17.2% | --- | --- |
| AIx | 350.92 | −5.0% | |||||
| ΔVV | 341.04 | −0.2% | |||||
| Transforming images between techniques | |||||||
| Ylisiurua et al. [15] | UNet | CBCT scans after PLS-TV regularization | PSNR | 77.4 dB | --- | FDK denoised images | 52.9% |
| SSIM | 1.0 | --- | 7.5% | ||||
| UNIT | PSNR | 74.6 dB | --- | 47.4% | |||
| SSIM | 1.0 | --- | 7.5% | ||||
| Ryu K. et al. [30] | COMPUNet | MDCT images | NRMSE | 0.14 | --- | Comparison with original CBCT | 35.7% |
| SSIM | 0.84 | --- | 10.5% | ||||
| Ryu S. et al. [31] | CycleGAN with MAEVGG loss | Ground truth CT scans | PSNR | 28.65 dB | --- | Comparison with original CBCT | 28.3% |
| SSIM | 0.87 | --- | 40.2 | ||||
| Vestergaard et al. [32] | CycleGAN | Ground truth CT scans | PSNR | 31.8 dB | --- | Comparison with original CBCT | 24.2% |
| SSIM | 0.97 | --- | 2.1% | ||||
| CUT | PSNR | 31.8 dB | --- | 24.2% | |||
| SSIM | 0.97 | --- | 2.1% | ||||
| CycleCUT | PSNR | 31.8 dB | --- | 24.2% | |||
| SSIM | 0.97 | --- | 2.1% | ||||
| Zhang Y. et al. [34] | cGAN | Reference CT images | PSNR | 30.58 dB | --- | Comparison with original CBCT | 20.7% |
| SSIM | 0.90 | --- | 8.4% | ||||
| CycleGAN | PSNR | 29.29 dB | --- | 15.6% | |||
| SSIM | 0.92 | --- | 10.8% | ||||
| UNet | PSNR | 30.48 dB | --- | 20.3% | |||
| SSIM | 0.90 | --- | 8.4% | ||||
| Zhao et al. [36] | VVBPNet | Reconstructed from full view projections | PSNR | 37.3 dB | --- | FDK denoised images | 21.9% |
| SSIM | 0.90 | --- | 26.4% | ||||
| FSIM | 0.99 | --- | 0.1% | ||||
| Study | Task | Model Architectures | Dataset Size (Train/Valid/Test) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ryu K. et al. [30] | CBCT -> MDCT | UNet | 30 (30/0/0) |
| Ryu S. et al. [31] | CBCT -> CT | CycleGAN | 33 (22/0/11)—cross validation |
| Vestergaard et al. [32] | CBCT -> CT | CycleGAN, CUT, CycleCut | 102 (77/5/20) |
| Zhang et al. [34] | CBCT -> CT | GAN | 120 (80/10/30) |
| Ylisiurua et al. [15] | Simulated CBCT -> CBCT | UNet, UNIT | 22 (22/0/0) |
| Zhao et al. [36] | Sparse CBCT -> CBCT | UNet | 223 (163/30/30) |
| Category | Classic Method | Deep Learning Model |
|---|---|---|
| Quantitative analysis | New algorithms (SK, INR) perform much better than older ones. | Models performing resonably good in denoising images. |
| Subjective anaysis | The images cleaner, however, the sample of methods is small. | Mixed feelings—in most cases the images are smoother, clearner, brighter, yet in some cases the experts prefered the output of classic methods. |
| Time of analysis | Rather slow. | Speed up 1–2 orders of magnitude. |
| Usage | Denoising, further downstream tasks. | Obtaining synthetic images from different techniques, more precise radiation dose calculation, lowering dose using sparse view. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wajer, R.; Dabrowski-Tumanski, P.; Wajer, A.; Kazimierczak, N.; Serafin, Z.; Kazimierczak, W. Enhancing Image Quality in Dental-Maxillofacial CBCT: The Impact of Iterative Reconstruction and AI on Noise Reduction—A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4214. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124214
Wajer R, Dabrowski-Tumanski P, Wajer A, Kazimierczak N, Serafin Z, Kazimierczak W. Enhancing Image Quality in Dental-Maxillofacial CBCT: The Impact of Iterative Reconstruction and AI on Noise Reduction—A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(12):4214. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124214
Chicago/Turabian StyleWajer, Róża, Pawel Dabrowski-Tumanski, Adrian Wajer, Natalia Kazimierczak, Zbigniew Serafin, and Wojciech Kazimierczak. 2025. "Enhancing Image Quality in Dental-Maxillofacial CBCT: The Impact of Iterative Reconstruction and AI on Noise Reduction—A Systematic Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 12: 4214. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124214
APA StyleWajer, R., Dabrowski-Tumanski, P., Wajer, A., Kazimierczak, N., Serafin, Z., & Kazimierczak, W. (2025). Enhancing Image Quality in Dental-Maxillofacial CBCT: The Impact of Iterative Reconstruction and AI on Noise Reduction—A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(12), 4214. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124214









