Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Diabetes—A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
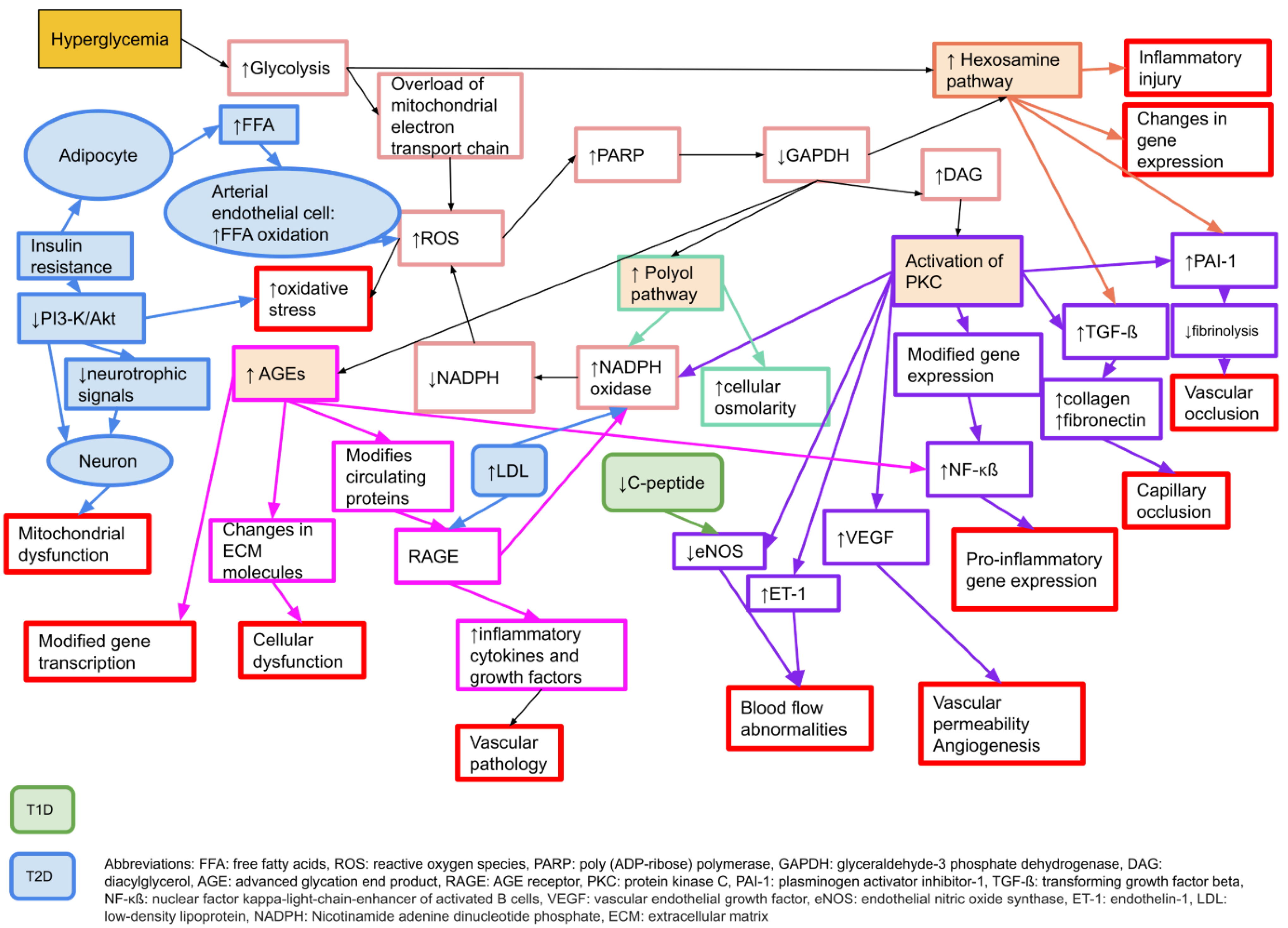
2. Neuropathy in Diabetes
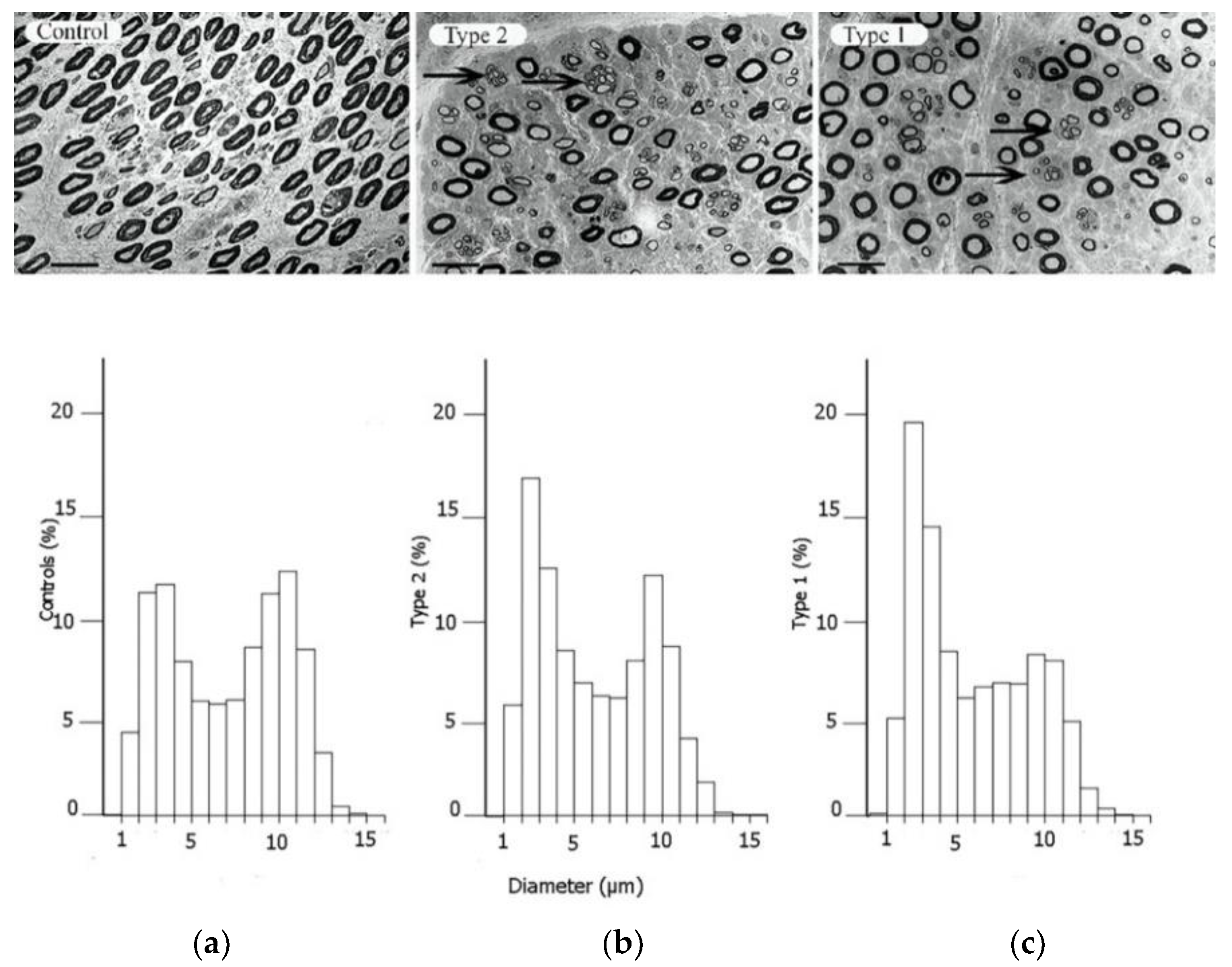
3. The Increased Susceptibility to Nerve Compression in Diabetes
4. Symptoms and Clinical Signs of CTS
5. CTS and Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
6. Sex Differences in CTS and Diabetes
7. Value of Electrophysiology in CTS and Diabetes
8. Treatment Options
9. Outcome of Surgery
| Author, Year | Study Design | N of Individuals (Hands) | Diabetes | Type of Diabetes | Neuropathy | Outcome Measure | Follow-Up Time | Results, Diabetes vs. No Diabetes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Haupt 1993 [78] | Prospective | 60 (86) | 10/60 (17%) | Not reported | Not reported | Motor function, sensory deficit, trophic changes, neurography and electro-myography | 5.5 years | Marginally less pain relief in individuals with diabetes |
| al-Qattan 1994 [97] | Retrospective | 15 (20) | 15/15 (100%) | Not reported | 15/15 | Grading: excellent/good/poor | 18 months | 5 hands had poor improvement—all of these had normal/mild neurography pre-op |
| Choi 1998 [98] | Retrospective | 154 (294) | 19/154 (12%) | Not reported | 3 (1.9%) | Symptom resolution (poor-excellent) | 12 months | No difference |
| Ozkul 2002 [79] | Prospective | 47 (60) | 22/47 (47%) | T2D | Excluded | PROM: global symptom score, neurography | 12 months | Better PROMs and neurography recovery in individuals without diabetes |
| Mondelli 2004 [99] | Prospective case series | 96 (96) | 24/96 (25%) | T1D: 19 T2D: 5 | 6/24 (25%) | BCTQ | 6 months | No difference |
| Thomsen 2009 [81] | Prospective | 66 (66) | 35/66 (53%) | T1D: 15 T2D: 20 | 14/35 (40%) | Monofilament, 2PD, APB strength, grip strength, key pinch, lateral pinch, pillar pain, postoperative questionnaire (VAS questions) | 52 weeks | Individuals with diabetes had the same beneficial outcome after carpal tunnel release as non-diabetes individuals |
| Thomsen 2010 [59] | Prospective | 66 (66) | 35/66 (53%) | T1D: 15 T2D: 20 | 14/35 (40%) | Electrophysiology testing | 12 months | Electrophysiology improved as much in individuals with as without diabetes |
| Jenkins 2012 [83] | Prospective | 1564 (1564) | 176/1564 (11.3%) | Not reported | Not reported | QuickDASH | 12 months | Poorer functional scores after 12 months in individuals with diabetes, but doubtful whether of clinical significance |
| Isik 2013 [84] | Retrospective case-control | 74 (99) | 36/74 (49%) | T2D | none | PROM questions on symptoms | 12 months | Worse post-op symptoms in individuals with diabetes |
| Zyluk 2013 [85] | Retrospective | 386 (386) | 41/386 (11%) | T1D: 11 T2D: 30 | None | BCTQ | 6 months | Clinical benefit: no difference. DM individuals had weaker grip strength and poorer perception of touch |
| Ebrahimzadeh 2013 [100] | Retrospective | 74 (74) | 35/74 (47%) | T1D: 14 T2D: 21 | Not reported | WHOQOL-BREEF; MHQ | 3 months | Worse results in individuals with diabetes, MHQ-scores better in T2D than T1D |
| Cagle 2014 [86] | Prospective | 826 (950) | 90/950 (10%) | Not reported | 20/950 (2%) | BCTQ | 12 weeks | Individuals with diabetes improved but took longer |
| Gulabi 2014 [87] | Prospective | 69 (69) | 27/69 (39%) | T1D: 18 T2D: 9 | Not reported | BCTQ | 10 years | Individuals with diabetes worse at the 10 years follow-up. No difference at 6 m. |
| Thomsen 2014 [82] | Prospective | 66 (66) | 35/66 (53%) | T1D: 15 T2D: 20 | 14/35 (40%) | BCTQ, monofilament, 2PD, APB strength, grip strength, key pinch, lateral pinch, pillar pain, VAS questions | 5 years | Excellent long-term improvement in individuals with diabetes |
| Yucel 2015 [101] | Retrospective | 83 (101) | 35/83 (42%) | Not reported | Not reported | VAS-questions, BCTQ, monofilament, grip and pinch strength | Not specified | Individuals with diabetes had more symptoms in BCTQ |
| Zimmerman 2016 [89] | Retrospective | 493 (531) | 76/531 (14%) | T1D: 18 T2D: 58 | 18/76 | QuickDASH | 12 months | Same improvement, but more persistent symptoms in individuals with diabetes and polyneuropathy |
| Thomsen 2017 [60] | Prospective | 57 (57) | 27/57 (47%) | T1D: 13 T2D: 14 | 10/27 (37%) | Electrophysiology parameters | 5 years | Long-term electrophysio-logy improvement was seen in both diabetes and non-diabetes individuals |
| Watchmaker 2017 [88] | Prospective | 1031 (1037) | 133/1031 (13%) | Not reported | Not reported | Symptom survey | 6 months | Individuals with diabetes had the same symptom resolution |
| Zhang 2018 [102] | Retrospective | 904 (1144) | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Secondary surgery | 60 months | DM associated with greater risk of secondary surgery |
| Zimmerman 2019 [90] | Retrospective | 9049 (10,770) | 1508/9049 (17%) | T1D: 335 T2D: 1150 | Not reported | QuickDASH | 12 months | Individuals with diabetes benefitted from surgery, but not to same extent as patients without diabetes |
10. Controversies in Nerve Compression and Diabetes
11. Future Perspectives—The Diabetic Nerve
12. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Latinovic, R.; Gulliford, M.C.; Hughes, R.A. Incidence of common compressive neuropathies in primary care. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2006, 77, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, M.; Hall, E.; Carlsson, K.S.; Nyman, E.; Dahlin, L.B. Socioeconomic factors predicting outcome in surgically treated carpal tunnel syndrome: A national registry-based study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, M.; Nyman, E.; Steen Carlsson, K.; Dahlin, L.B. Socioeconomic Factors in Patients with Ulnar Nerve Compression at the Elbow: A National Registry-Based Study. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 5928649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atroshi, I.; Gummesson, C.; Johnsson, R.; Ornstein, E.; Ranstam, J.; Rosen, I. Prevalence of carpal tunnel syndrome in a general population. JAMA 1999, 282, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atroshi, I. Incidence of physician-diagnosed carpal tunnel syndrome in the general population. Arch. Intern. Med. 2011, 171, 943–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadjerbashi, K.; Åkesson, A.; Atroshi, I. Incidence of referred carpal tunnel syndrome and carpal tunnel release surgery in the general population: Increase over time and regional variations. J. Orthop. Surg. 2019, 27, 2309499019825572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordstrom, D.L.; DeStefano, F.; Vierkant, R.A.; Layde, P.M. Incidence of diagnosed carpal tunnel syndrome in a general population. Epidemiology 1998, 9, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, J.D.; Rudolfer, S.M. Clinical surveillance of carpal tunnel syndrome in two areas of the United Kingdom, 1991–2001. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2003, 74, 1674–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiberg, A.; Ng, M.; Schmid, A.B.; Smillie, R.W.; Baskozos, G.; Holmes, M.V.; Künnapuu, K.; Mägi, R.; Bennett, D.L.; Furniss, D. A genome-wide association analysis identifies 16 novel susceptibility loci for carpal tunnel syndrome. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, E.; Jacques, D.; Chammas, M.; Poirier, J.L.; Bonifacj, C.; Jaffiol, C.; Simon, L.; Allieu, Y. Increased prevalence of soft tissue hand lesions in type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus: Various entities and associated significance. Diabete Metab. 1994, 20, 513–521. [Google Scholar]
- Papanas, N.; Maltezos, E. The diabetic hand: A forgotten complication? J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2010, 24, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rydberg, M.; Zimmerman, M.; Gottsäter, A.; Svensson, A.; Eeg-Olofsson, K.; Dahlin, L.B. The Diabetic Hand-prevalence and incidence of diabetic hand problems using data from 1.1 million inhabitants in southern Sweden. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2022, 10, e002614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rota, E.; Morelli, N. Entrapment neuropathies in diabetes mellitus. World J. Diabetes 2016, 7, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rydberg, M.; Zimmerman, M.; Gottsäter, A.; Nilsson, P.M.; Melander, O.; Dahlin, L.B. Diabetes mellitus as a risk factor for compression neuropathy: A longitudinal cohort study from southern Sweden. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2020, 8, e001298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upton, A.R.; McComas, A.J. The double crush in nerve entrapment syndromes. Lancet 1973, 2, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, N.O.; Mojaddidi, M.; Malik, R.A.; Dahlin, L.B. Reduced myelinated nerve fibre and endoneurial capillary densities in the forearm of diabetic and non-diabetic patients with carpal tunnel syndrome. Acta Neuropathol. 2009, 118, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlin, L.; Sanden, H.; Dahlin, E.; Zimmerman, M.; Thomsen, N.; Bjorkman, A. Low myelinated nerve-fibre density may lead to symptoms associated with nerve entrapment in vibration-induced neuropathy. J. Occup. Med. Toxicol. 2014, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop-Busui, R.; Boulton, A.J.; Feldman, E.L.; Bril, V.; Freeman, R.; Malik, R.A.; Sosenko, J.M.; Ziegler, D. Diabetic Neuropathy: A Position Statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Factors in development of diabetic neuropathy. Baseline analysis of neuropathy in feasibility phase of Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT). The DCCT Research Group. Diabetes 1988, 37, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvotelli, L.; Stoico, V.; Perrone, F.; Cacciatori, V.; Negri, C.; Brangani, C.; Pichiri, I.; Targher, G.; Bonora, E.; Zoppini, G. Prevalence of neuropathy in type 2 diabetic patients and its association with other diabetes complications: The Verona Diabetic Foot Screening Program. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2015, 29, 1066–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, E.L.; Callaghan, B.C.; Pop-Busui, R.; Zochodne, D.W.; Wright, D.E.; Bennett, D.L.; Bril, V.; Russell, J.W.; Viswanathan, V. Diabetic neuropathy. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partanen, J.; Niskanen, L.; Lehtinen, J.; Mervaala, E.; Siitonen, O.; Uusitupa, M. Natural history of peripheral neuropathy in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 333, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aaberg, M.L.; Burch, D.M.; Hud, Z.R.; Zacharias, M.P. Gender differences in the onset of diabetic neuropathy. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2008, 22, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brownlee, M. The pathobiology of diabetic complications: A unifying mechanism. Diabetes 2005, 54, 1615–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albers, J.W.; Pop-Busui, R. Diabetic Neuropathy: Mechanisms, Emerging Treatments, and Subtypes. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2014, 14, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, M. The Diabetic Nerve. Studies on Outcome after Open Carpal Tunnel Release and the Development of Autonomic Neuropathy. Ph.D. Dissertation, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Baptista, F.I.; Pinheiro, H.; Gomes, C.A.; Ambrósio, A.F. Impairment of Axonal Transport in Diabetes: Focus on the Putative Mechanisms Underlying Peripheral and Central Neuropathies. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 2202–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medori, R.; Autilio-Gambetti, L.; Jenich, H.; Gambetti, P. Changes in axon size and slow axonal transport are related in experimental diabetic neuropathy. Neurology 1988, 38, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohseni, S.; Badii, M.; Kylhammar, A.; Thomsen, N.O.B.; Eriksson, K.F.; Malik, R.A.; Rosen, I.; Dahlin, L.B. Longitudinal study of neuropathy, microangiopathy, and autophagy in sural nerve: Implications for diabetic neuropathy. Brain Behav. 2017, 7, e00763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaghan, B.C.; Cheng, H.; Stables, C.L.; Smith, A.L.; Feldman, E.L. Diabetic neuropathy: Clinical manifestations and current treatments. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sima, A.A.F.; Zhang, W.; Grunberger, G. Type 1 Diabetic Neuropathy and C-peptide. Exp. Diabesity Res. 2004, 5, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, D.M. The diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications study at 30 years: Overview. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callaghan, B.C.; Little, A.A.; Feldman, E.L.; Hughes, R.A. Enhanced glucose control for preventing and treating diabetic neuropathy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 6, Cd007543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callaghan, B.; Feldman, E. The metabolic syndrome and neuropathy: Therapeutic challenges and opportunities. Ann. Neurol. 2013, 74, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callaghan, B.C.; Gallagher, G.; Fridman, V.; Feldman, E.L. Diabetic neuropathy: What does the future hold? Diabetologia 2020, 63, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eid, S.; Sas, K.M.; Abcouwer, S.F.; Feldman, E.L.; Gardner, T.W.; Pennathur, S.; Fort, P.E. New insights into the mechanisms of diabetic complications: Role of lipids and lipid metabolism. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 1539–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohkubo, Y.; Kishikawa, H.; Araki, E.; Miyata, T.; Isami, S.; Motoyoshi, S.; Kojima, Y.; Furuyoshi, N.; Shichiri, M. Intensive insulin therapy prevents the progression of diabetic microvascular complications in Japanese patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: A randomized prospective 6-year study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 1995, 28, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Lancet 1998, 352, 837–853. [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.A.; Dahlin, L.B.; Thomsen, N.O.; Mohseni, S. Autophagy in the posterior interosseous nerve of patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus: An ultrastructural study. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sunderland, S. Nerves and Nerve Injuries, 2nd ed.; Edinburgh; Churchill Livingstone: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Boron, W.F.B.; Emile, L. Medical Physiology, 2nd ed.; Saunders; Elsevier: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- King, R. Peripheral Nerve Disorders; Vallat, J.-M., Weis, J., Eds.; International Society of Neuropathology Series; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlin, L.B.; Shyu, B.C.; Danielsen, N.; Andersson, S.A. Effects of nerve compression or ischaemia on conduction properties of myelinated and non-myelinated nerve fibres. An experimental study in the rabbit common peroneal nerve. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1989, 136, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleigh, J.N.; Rossor, A.M.; Fellows, A.D.; Tosolini, A.P.; Schiavo, G. Axonal transport and neurological disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlin, L.B.; Meiri, K.F.; McLean, W.G.; Rydevik, B.; Sjostrand, J. Effects of nerve compression on fast axonal transport in streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus. An experimental study in the sciatic nerve of rats. Diabetologia 1986, 29, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snedeker, J.G.; Gautieri, A. The role of collagen crosslinks in ageing and diabetes-the good, the bad, and the ugly. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2014, 4, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samii, A.; Unger, J.; Lange, W. Vascular endothelial growth factor expression in peripheral nerves and dorsal root ganglia in diabetic neuropathy in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 1999, 262, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundborg, G.; Myers, R.; Powell, H. Nerve compression injury and increased endoneurial fluid pressure: A “miniature compartment syndrome”. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1983, 46, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshminarayanan, K.; Shah, R. Median nerve and carpal arch morphology changes in women with type 2 diabetes: A case–control study. J. Ultrasound 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mojaddidi, M.A.; Ahmed, M.S.; Ali, R.; Jeziorska, M.; Al-Sunni, A.; Thomsen, N.O.; Dahlin, L.B.; Malik, R.A. Molecular and pathological studies in the posterior interosseous nerve of diabetic and non-diabetic patients with carpal tunnel syndrome. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 1711–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strömberg, T.; Dahlin, L.B.; Brun, A.; Lundborg, G. Structural nerve changes at wrist level in workers exposed to vibration. Occup. Environ. Med. 1997, 54, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinik, A.; Mehrabyan, A.; Colen, L.; Boulton, A. Focal entrapment neuropathies in diabetes. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 1783–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackinnon, S.E. Pathophysiology of nerve compression. Hand Clin. 2002, 18, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlin, L.B. Aspects on pathophysiology of nerve entrapments and nerve compression injuries. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 1991, 2, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Rowshan, K.; Chao, T.; Mozaffar, T.; Steward, O. Chronic nerve compression induces local demyelination and remyelination in a rat model of carpal tunnel syndrome. Exp. Neurol. 2004, 187, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboonq, M.S. Pathophysiology of carpal tunnel syndrome. Neurosciences 2015, 20, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lundborg, G.; Dahlin, L.B. Anatomy, function, and pathophysiology of peripheral nerves and nerve compression. Hand Clin. 1996, 12, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapadia, M.; Mozaffar, T.; Gupta, R. Compressive Neuropathies of the Upper Extremity: Pathophysiology, Classification, Electrodiagnostic Findings. J. Hand Surg. 2010, 35, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, N.O.B.; Rosén, I.; Dahlin, L.B. Neurophysiologic recovery after carpal tunnel release in diabetic patients. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2010, 121, 1569–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, N.O.B.; Andersson, G.S.; Bjork, J.; Dahlin, L.B. Neurophysiological recovery 5 years after carpal tunnel release in patients with diabetes. Muscle Nerve 2017, 56, E59–E64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Collins, J.; Blazar, P.; Earp, B.E. Factors Associated With Advanced Presentation for Carpal Tunnel Release. J. Hand Surg. Am. 2020, 45, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackinnon, S.E.; Dellon, A.L.; Hudson, A.R.; Hunter, D.A. Chronic human nerve compression—A histological assessment. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 1986, 12, 547–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiberg, A.; Smillie, R.W.; Dupré, S.; Schmid, A.B.; Bennett, D.L.; Furniss, D. Replication of epidemiological associations of carpal tunnel syndrome in a UK population-based cohort of over 400,000 people. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2021; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourmemari, M.H.; Shiri, R. Diabetes as a risk factor for carpal tunnel syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabet. Med. 2016, 33, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padua, L.; Padua, R.; Aprile; Tonali, P. Italian multicentre study of carpal tunnel syndrome. Differences in the clinical and neurophysiological features between male and female patients. J. Hand Surg. Br. 1999, 24, 579–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caliandro, P.; Torre, L.G.; Padua, R.; Giannini, F.; Padua, L. Treatment for ulnar neuropathy at the elbow. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 11, CD006839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ennis, S.L.; Galea, M.P.; O’Neal, D.N.; Dodson, M.J. Peripheral neuropathy in the hands of people with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2016, 119, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, N.O.; Englund, E.; Thrainsdottir, S.; Rosen, I.; Dahlin, L.B. Intraepidermal nerve fibre density at wrist level in diabetic and non-diabetic patients. Diabet. Med. 2009, 26, 1120–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagci, I.; Gunduz, O.H.; Sancak, S.; Agirman, M.; Mesci, E.; Akyuz, G. Comparative electrophysiological techniques in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome in patients with diabetic polyneuropathy. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2010, 88, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlin, E.; Zimmerman, M.; Bjorkman, A.; Thomsen, N.O.; Andersson, G.S.; Dahlin, L.B. Impact of smoking and preoperative electrophysiology on outcome after open carpal tunnel release. J. Plast. Surg. Hand Surg. 2016, 51, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osiak, K.; Mazurek, A.; Pękala, P.; Koziej, M.; Walocha, J.A.; Pasternak, A. Electrodiagnostic Studies in the Surgical Treatment of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome-A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, B.A.; Olaleye, D.; Bril, V. Carpal tunnel syndrome in patients with diabetic polyneuropathy. Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyck, P.J.; Kratz, K.M.; Karnes, J.L.; Litchy, W.J.; Klein, R.; Pach, J.M.; Wilson, D.M.; O’Brien, P.C.; Melton, L.J., 3rd; Service, F.J. The prevalence by staged severity of various types of diabetic neuropathy, retinopathy, and nephropathy in a population-based cohort: The Rochester Diabetic Neuropathy Study. Neurology 1993, 43, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerritsen, A.A.; de Vet, H.C.; Scholten, R.J.; Bertelsmann, F.W.; de Krom, M.C.; Bouter, L.M. Splinting vs surgery in the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2002, 288, 1245–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, A.C.; Wong, S.; Leung, C.H.; Tong, P.; Mok, V.; Poon, D.; Li-Tsang, C.W.; Wong, L.K.; Boet, R. A randomized controlled trial of surgery vs steroid injection for carpal tunnel syndrome. Neurology 2005, 64, 2074–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarvik, J.G.; Comstock, B.A.; Kliot, M.; Turner, J.A.; Chan, L.; Heagerty, P.J.; Hollingworth, W.; Kerrigan, C.L.; Deyo, R.A. Surgery versus non-surgical therapy for carpal tunnel syndrome: A randomised parallel-group trial. Lancet 2009, 374, 1074–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulkkonen, S.; Lampainen, K.; Auvinen, J.; Miettunen, J.; Karppinen, J.; Ryhänen, J. Incidence and operations of median, ulnar and radial entrapment neuropathies in Finland: A nationwide register study. J. Hand Surg. Eur. Vol. 2020, 45, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haupt, W.F.; Wintzer, G.; Schop, A.; Lottgen, J.; Pawlik, G. Long-term results of carpal tunnel decompression. Assessment of 60 cases. J. Hand Surg. Br. 1993, 18, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkul, Y.; Sabuncu, T.; Kocabey, Y.; Nazligul, Y. Outcomes of carpal tunnel release in diabetic and non-diabetic patients. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2002, 106, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Kim, Y.W.; Lee, S.C.; Yang, S.N.; Chang, J.S.; Yoon, S.Y. Effects of diabetes mellitus on the rate of carpal tunnel release in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, N.O.B.; Cederlund, R.; Rosén, I.; Björk, J.; Dahlin, L.B. Clinical Outcomes of Surgical Release Among Diabetic Patients With Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Prospective Follow-Up With Matched Controls. J. Hand Surg. 2009, 34, 1177–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, N.O.; Cederlund, R.I.; Andersson, G.S.; Rosen, I.; Bjork, J.; Dahlin, L.B. Carpal tunnel release in patients with diabetes: A 5-year follow-up with matched controls. J. Hand Surg. Am. 2014, 39, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, P.J.; Duckworth, A.D.; Watts, A.C.; McEachan, J.E. The outcome of carpal tunnel decompression in patients with diabetes mellitus. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. Vol. 2012, 94-B, 811–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isik, C.; Uslu, M.; Inanmaz, M.E.; Karabekmez, F.E.; Kose, K.C. The effects of diabetes on symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome treated with mini-open surgery. Acta Orthop. Belg. 2013, 79, 381–385. [Google Scholar]
- Zyluk, A.; Puchalski, P. A comparison of outcomes of carpal tunnel release in diabetic and non-diabetic patients. J. Hand Surg. Eur. Vol. 2013, 38, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cagle, P.J., Jr.; Reams, M.; Agel, J.; Bohn, D. An outcomes protocol for carpal tunnel release: A comparison of outcomes in patients with and without medical comorbidities. J. Hand Surg. Am. 2014, 39, 2175–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulabi, D.; Cecen, G.; Guclu, B.; Cecen, A. Carpal tunnel release in patients with diabetes result in poorer outcome in long-term study. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. Orthop. Traumatol. 2014, 24, 1181–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watchmaker, J.D.; Watchmaker, G.P. Independent Variables Affecting Outcome of Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery. Hand 2017, 13, 1558944717703739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, M.; Dahlin, E.; Thomsen, N.O.; Andersson, G.S.; Bjorkman, A.; Dahlin, L.B. Outcome after carpal tunnel release: Impact of factors related to metabolic syndrome. J. Plast. Surg. Hand Surg. 2016, 51, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, M.; Eeg-Olofsson, K.; Svensson, A.; Astrom, M.; Arner, M.; Dahlin, L. Open carpal tunnel release and diabetes: A retrospective study using PROMs and national quality registries. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e030179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, A.; Sadr, A.; Ebrahimzadeh, M.H.; Hassankhani, G.G.; Mehrad-Majd, H. Does diabetes mellitus change the carpal tunnel release outcomes? Evidence from a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hand Ther. 2020, 33, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rijk, M.C.; Vermeij, F.H.; Suntjens, M.; van Doorn, P.A. Does a carpal tunnel syndrome predict an underlying disease? J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2007, 78, 635–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, B.C.; Teran, V.A.; Deal, D.N. Patient-Related Risk Factors for Infection Following Open Carpal Tunnel Release: An Analysis of Over 450,000 Medicare Patients. J. Hand Surg. Am. 2018, 43, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harness, N.G.; Inacio, M.C.; Pfeil, F.F.; Paxton, L.W. Rate of Infection After Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery and Effect of Antibiotic Prophylaxis. J. Hand Surg. 2010, 35, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, B.C.; Teran, V.A.; Cancienne, J.; Deal, D.N. The Association of Perioperative Glycemic Control With Postoperative Surgical Site Infection Following Open Carpal Tunnel Release in Patients With Diabetes. Hand 2019, 14, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, P.S.; Apel, P.J.; Truong, A.Y.; Zarei, M.; Lozano, A.J.; Capito, A.E. The Utility of Preoperative HbA1c as a Standardized Protocol in Elective Carpal Tunnel Release: A Retrospective Review of Clinical Outcomes. Hand 2022, 17, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Qattan, M.M.; Manktelow, R.T.; Bowen, C.V. Outcome of carpal tunnel release in diabetic patients. J. Hand Surg. Br. 1994, 19, 626–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.J.; Ahn, D.S. Correlation of clinical history and electrodiagnostic abnormalities with outcome after surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1998, 102, 2374–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondelli, M.; Padua, L.; Reale, F.; Signorini, A.M.; Romano, C. Outcome of surgical release among diabetics with carpal tunnel syndrome. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2004, 85, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimzadeh, M.H.; Mashhadinejad, H.; Moradi, A.; Kachooei, A.R. Carpal tunnel release in diabetic and non-diabetic patients. Arch. Bone Jt. Surg. 2013, 1, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Yucel, H. Factors affecting symptoms and functionality of patients with carpal tunnel syndrome: A retrospective study. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2015, 27, 1097–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Blazar, P.; Earp, B.E. Rates of Complications and Secondary Surgeries of Mini-Open Carpal Tunnel Release. Hand 2018, 14, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellon, A.L. Susceptibility of nerve in diabetes to compression: Implications for pain treatment. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2014, 134, 142s–150s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmiento, S.; Pierre, J.A., Jr.; Dellon, A.L.; Frick, K.D. Tibial nerve decompression for the prevention of the diabetic foot: A cost-utility analysis using Markov model simulations. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e024816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellon, A.L.; Muse, V.L.; Nickerson, D.S.; Akre, T.; Anderson, S.R.; Barrett, S.L.; Biddinger, K.R.; Bregman, P.J.; Bullard, B.P.; Dauphinee, D.M.; et al. Prevention of ulceration, amputation, and reduction of hospitalization: Outcomes of a prospective multicenter trial of tibial neurolysis in patients with diabetic neuropathy. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2012, 28, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornblath, D.R.; Vinik, A.; Feldman, E.; Freeman, R.; Boulton, A.J. Surgical decompression for diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 421–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickerson, D.S. Nerve decompression and neuropathy complications in diabetes: Are attitudes discordant with evidence? Diabet. Foot Ankle 2017, 8, 1367209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhry, V.; Stevens, J.C.; Kincaid, J.; So, Y.T. Practice Advisory: Utility of surgical decompression for treatment of diabetic neuropathy: Report of the Therapeutics and Technology Assessment Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2006, 66, 1805–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinkel, W.D.; Fakkel, T.M.; Castro Cabezas, M.; Birnie, E.; Coert, J.H. (Cost-)effectiveness of lower extremity nerve decompression surgery in subjects with diabetes: The DeCompression (DECO) trial-study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e035644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlin, L.B.; Rix, K.R.; Dahl, V.A.; Dahl, A.B.; Jensen, J.N.; Cloetens, P.; Pacureanu, A.; Mohseni, S.; Thomsen, N.O.B.; Bech, M. Three-dimensional architecture of human diabetic peripheral nerves revealed by X-ray phase contrast holographic nanotomography. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ising, E.; Åhrman, E.; Thomsen, N.O.B.; Eriksson, K.F.; Malmström, J.; Dahlin, L.B. Quantitative proteomic analysis of human peripheral nerves from subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2021, 38, e14658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| OR (95% CI) | Men with Diabetes | Women with Diabetes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.99 (1.81–2.19) | 2.63 (2.42–2.86) | |||
| T1D | T2D | T1D | T2D | |
| Prevalence | 6.8% | 5.0% | 13.5% | 10.1% |
| Incidence rate/ 10,000 person-years | 58.1 | 31.6 | 95.5 | 52.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zimmerman, M.; Gottsäter, A.; Dahlin, L.B. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Diabetes—A Comprehensive Review. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11061674
Zimmerman M, Gottsäter A, Dahlin LB. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Diabetes—A Comprehensive Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(6):1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11061674
Chicago/Turabian StyleZimmerman, Malin, Anders Gottsäter, and Lars B. Dahlin. 2022. "Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Diabetes—A Comprehensive Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 6: 1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11061674
APA StyleZimmerman, M., Gottsäter, A., & Dahlin, L. B. (2022). Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Diabetes—A Comprehensive Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(6), 1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11061674







