From Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) to Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD)—New Terminology in Pediatric Patients as a Step in Good Scientific Direction?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Definition of Metabolic Syndrome in Children and Adolescents
3. Pathogenetic Mechanisms Linking NAFLD and MetS in Obese Children, Adolescents, and Adults
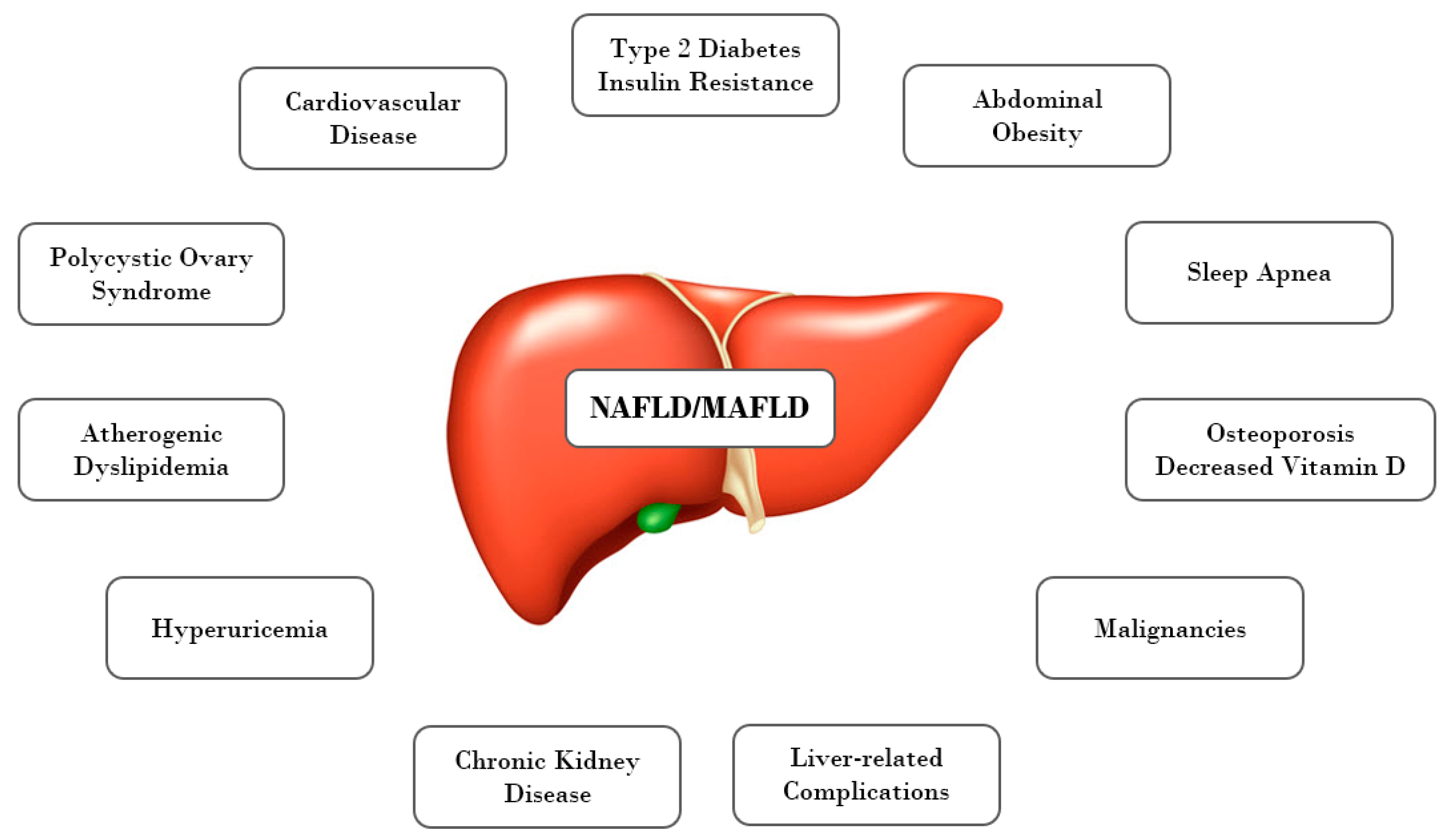
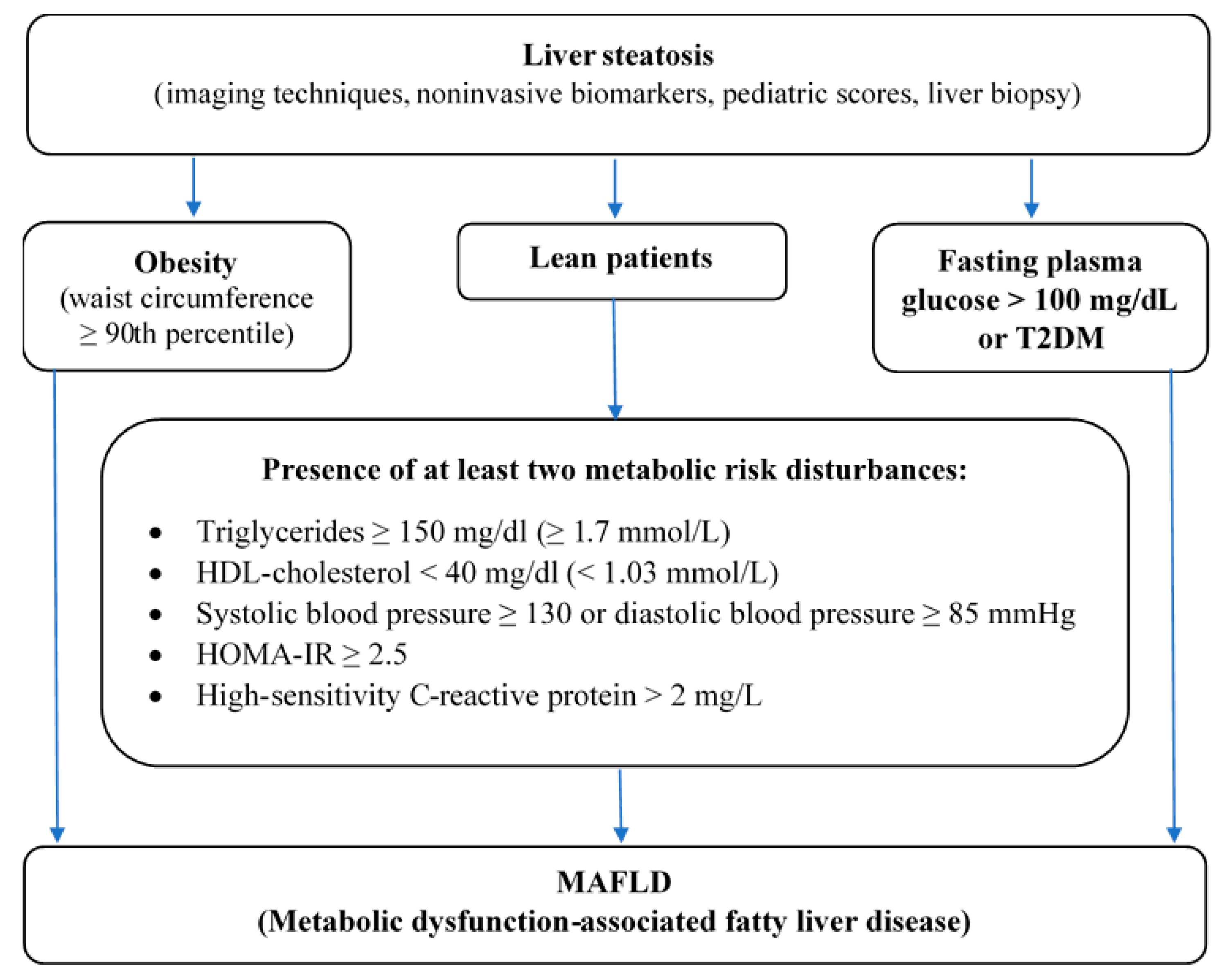
4. From NAFLD to MAFLD
- Abdominal obesity assessed by WC ≥ 90th percentile adjusted for age and gender,
- High fasting plasma glucose > 100 mg/dl or known T2DM or
- Presence of at least two metabolic risk disturbances in lean patients—elevated triglycerides, low HDL-C, high blood pressure, HOMA-IR ≥ 2,5, increased hs-CRP (Figure 2).
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bertot, L.C.; Adams, L.A. The Natural Course of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratziu, V.; Bellentani, S.; Cortez-Pinto, H.; Day, C.; Marchesini, G. A position statement on NAFLD/NASH based on the EASL 2009 special conference. J. Hepatol. 2010, 53, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumpail, B.J.; Khan, M.A.; Yoo, E.R.; Cholankeril, G.; Kim, D.; Ahmed, A. Clinical epidemiology and disease burden of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 8263–8276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, E.L.; Howe, L.D.; Jones, H.E.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Lawlor, D.A.; Fraser, A. The Prevalence of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, J.P.; Valenti, L.; Scorletti, E.; Byrne, C.D.; Nobili, V. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children. Semin. Liver Dis. 2018, 38, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajro, P.; Lenta, S.; Socha, P.; Dhawan, A.; McKiernan, P.; Baumann, U.; Durmaz, O.; Lacaille, F.; McLin, V.A.; Nobili, V. Diagnosis of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children and Adolescents. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2012, 54, 700–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.-L.; Chen, H.; Wang, C.-L.; Liang, L. Pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescence: From “two hit theory” to “multiple hit model”. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 2974–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nier, A.; Brandt, A.; Conzelmann, I.B.; Özel, Y.; Bergheim, I. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Overweight Children: Role of Fructose Intake and Dietary Pattern. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safari, Z.; Gérard, P. The links between the gut microbiome and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 1541–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Ji, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.Z. New insight into inter-organ crosstalk contributing to the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Protein Cell 2018, 9, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weihe, P.; Weihrauch-Blüher, S. Metabolic Syndrome in Children and Adolescents: Diagnostic Criteria, Therapeutic Options and Perspectives. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2019, 8, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Kountouras, J.; Mantzoros, C.S. Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: From pathophysiology to therapeutics. Metabolism 2019, 92, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Chung, G.E.; Kwak, M.-S.; Bin Seo, H.; Kang, J.H.; Kim, W.; Kim, Y.J.; Yoon, J.-H.; Lee, H.-S.; Kim, C.Y. Body Fat Distribution and Risk of Incident and Regressed Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 14, 132–138.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, M.J.; Miotto, P.M.; De Nardo, W.; Montgomery, M.K. The Liver as an Endocrine Organ—Linking NAFLD and Insulin Resistance. Endocr. Rev. 2019, 40, 1367–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gastaldelli, A. Insulin resistance and reduced metabolic flexibility: Cause or consequence of NAFLD? Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 2701–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballestri, S.; Zona, S.; Targher, G.; Romagnoli, D.; Baldelli, E.; Nascimbeni, F.; Roverato, A.; Guaraldi, G.; Lonardo, A. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with an almost twofold increased risk of incident type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome. Evidence from a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 31, 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsiki, N.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Mantzoros, C.S. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and dyslipidemia: An update. Metabology 2016, 65, 1109–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaggini, M.; Morelli, M.; Buzzigoli, E.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Bugianesi, E.; Gastaldelli, A. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Its Connection with Insulin Resistance, Dyslipidemia, Atherosclerosis and Coronary Heart Disease. Nutrients 2013, 5, 1544–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, T.; Sun, X.; Yuan, G.; Zhou, X.; Lu, H.; Lin, X.; Yu, X. Lipid phenotypes in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Metabology 2016, 65, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-C.; Zhao, G.-J.; Chen, Z.; She, Z.-G.; Cai, J.; Li, H. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hypertension AHA 2020, 75, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobrus-Chociej, A.; Wasilewska, N.; Flisiak-Jackiewicz, M.; Lebensztejn, D. Cardiovascular Risk in Children with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). Curr. Pediatr. Rev. 2021, 16, 294–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotronen, A.; Yki-Järvinen, H. Fatty Liver. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tune, J.D.; Goodwill, A.G.; Sassoon, D.J.; Mather, K.J. Cardiovascular consequences of metabolic syndrome. Transl. Res. 2017, 183, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mottillo, S.; Filion, K.B.; Genest, J.; Joseph, L.; Pilote, L.; Poirier, P.; Rinfret, S.; Schiffrin, E.L.; Eisenberg, M.J. The Metabolic Syndrome and Cardiovascular Risk. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 56, 1113–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluvic, Z.; Zaric, B.; Resanovic, I.; Obradovic, M.; Mitrovic, A.; Radak, D.; Isenovic, E. Link between Metabolic Syndrome and Insulin Resistance. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2016, 15, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobato, A.O.; Vasques, A.C.J.; Zambon, M.P.; Filho, A.D.A.B.; Hessel, G. Metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance in obese adolescents. Rev. Paul. de Pediatr. 2014, 32, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, K.; Wong, M.; Khalechelvam, P.; Tam, W. Waist-to-height ratio, body mass index and waist circumference for screening paediatric cardio-metabolic risk factors: A meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2016, 17, 1258–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özhan, B.; Ersoy, B.; Özkol, M.; Kiremitci, S.; Ergin, A. Waist to height ratio: A simple screening tool for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in obese children. Turk. J. Pediatr. 2016, 58, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manco, M.; Bedogni, G.; Marcellini, M.; DeVito, R.; Ciampalini, P.; Sartorelli, M.R.; Comparcola, D.; Piemonte, F.; Nobili, V. Waist circumference correlates with liver fibrosis in children with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Gut 2008, 57, 1283–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blüher, S.; Molz, E.; Wiegand, S.; Otto, K.-P.; Sergeyev, E.; Tuschy, S.; L’Allemand-Jander, D.; Kiess, W.; Holl, R.W.; Adiposity Patients Registry Initiative and the German Competence Net Obesity. Body Mass Index, Waist Circumference, and Waist-to-Height Ratio as Predictors of Cardiometabolic Risk in Childhood Obesity Depending on Pubertal Development. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 3384–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, D.S.; Mei, Z.; Srinivasan, S.R.; Berenson, G.S.; Dietz, W.H. Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Excess Adiposity Among Overweight Children and Adolescents: The Bogalusa Heart Study. J. Pediatr. 2007, 150, 12–17.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokha, J.S.; Srinivasan, S.R.; DasMahapatra, P.; Fernandez, C.; Chen, W.; Xu, J.; Berenson, G.S. Utility of waist-to-height ratio in assessing the status of central obesity and related cardiometabolic risk profile among normal weight and overweight/obese children: The Bogalusa Heart Study. BMC Pediatr. 2010, 10, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinehr, T.; De Sousa, G.; Toschke, A.M.; Andler, W. Comparison of metabolic syndrome prevalence using eight different definitions: A critical approach. Arch. Dis. Child. 2007, 92, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, G.J.P. Metabolic syndrome in children and teenagers: Worth assessing it, but how? Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 61, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti, K.G.M.M.; Zimmet, P.; Shaw, J. The metabolic syndrome—a new worldwide definition. Lancet 2005, 366, 1059–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmet, P.; Alberti, K.G.M.; Kaufman, F.; Tajima, N.; Silink, M.; Arslanian, S.; Wong, G.; Bennett, P.; Shaw, J.; Caprio, S.; et al. The metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents? an IDF consensus report. Pediatr. Diabetes 2007, 8, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.; Lent-Schochet, D.; Ramakrishnan, N.; McLaughlin, M.; Jialal, I. Metabolic syndrome is an inflammatory disorder: A conspiracy between adipose tissue and phagocytes. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 496, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansyur, M.A.; Bakri, S.; Patellongi, I.J.; Rahman, I.A. The association between metabolic syndrome components, low-grade systemic inflammation and insulin resistance in non-diabetic Indonesian adolescent male. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2020, 35, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, K.; Ryu, S.; Lee, J.; Park, J.-D. Higher and increased concentration of hs-CRP within normal range can predict the incidence of metabolic syndrome in healthy men. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2018, 12, 977–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirhafez, S.R.; Ebrahimi, M.; Karimian, M.S.; Avan, A.; Tayefi, M.; Heidari-Bakavoli, A.; Parizadeh, M.R.; Moohebati, M.; Azarpazhooh, M.R.; Esmaily, H.; et al. Serum high-sensitivity C-reactive protein as a biomarker in patients with metabolic syndrome: Evidence-based study with 7284 subjects. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 70, 1298–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Adamo, E.; Marcovecchio, M.L.; Giannini, C.; Capanna, R.; Impicciatore, M.; Chiarelli, F.; Mohn, A. The possible role of liver steatosis in defining metabolic syndrome in prepubertal children. Metabology 2010, 59, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, M.S.; Tiwari, A.; Mandal, A.; Shrestha, B.; Kafle, P.; Chaulagai, B.; Kc, S. Metabolic Syndrome in Patients with Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Community Based Cross-sectional study. Cureus 2019, 11, 4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bussler, S.; Penke, M.; Flemming, G.; Elhassan, Y.S.; Kratzsch, J.; Sergeyev, E.; Lipek, T.; Vogel, M.; Spielau, U.; Körner, A.; et al. Novel Insights in the Metabolic Syndrome in Childhood and Adolescence. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2017, 88, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Karaksy, H.M.; Helmy, H.M.; Anwar, G.M.; El-Hennawy, A.M.; El-Koofy, N.M.; El-Raziky, M.S.; El-Mougy, F.M.; Hassanin, F.M. The association of metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in overweight/obese children. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, Y.-W.; Wong, S.-W.; Zaini, A.A.; Mohamed, R.; Jalaludin, M.Y. Metabolic Syndrome Is Associated With Advanced Liver Fibrosis Among Pediatric Patients With Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flisiak-Jackiewicz, M.; Bobrus-Chociej, A.; Wasilewska, N.; Tarasow, E.; Wojtkowska, M.; Lebensztejn, D.M. Can hepatokines be regarded as novel non-invasive serum biomarkers of intrahepatic lipid content in obese children? Adv. Med Sci. 2019, 64, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotman, Y.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A. Liver fat accumulation as a barometer of insulin responsiveness again points to adipose tissue as the culprit. Hepatology 2017, 65, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papandreou, D.; Karavetian, M.; Karabouta, Z.; Andreou, E. Obese Children with Metabolic Syndrome Have 3 Times Higher Risk to Have Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Compared with Those without Metabolic Syndrome. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 2017, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokopowicz, Z.; Malecka-Tendera, E.; Matusik, P. Predictive Value of Adiposity Level, Metabolic Syndrome, and Insulin Resistance for the Risk of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Diagnosis in Obese Children. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 2018, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashaj, B.; Luciano, R.; Contoli, B.; Morino, G.S.; Spreghini, M.R.; Rustico, C.; Sforza, R.W.; Dallapiccola, B.; Manco, M. Reference ranges of HOMA-IR in normal-weight and obese young Caucasians. Acta Diabetol. 2015, 53, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patton, H.M.; Yates, K.; Unalp-Arida, A.; Behling, C.A.; Huang, T.T.-K.; Rosenthal, P.; Sanyal, A.J.; Schwimmer, J.B.; LaVine, J.E. Association Between Metabolic Syndrome and Liver Histology Among Children With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 2093–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, K.P.; Hou, J.; Crimmins, N.A.; LaVine, J.E.; Barlow, S.E.; Xanthakos, S.A.; Africa, J.; Behling, C.; Donithan, M.; Clark, J.M.; et al. Prevalence of Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes in Children With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. JAMA Pediatr. 2016, 170, e161971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazzo, E.; Jimenez, L.S.; Gallo, F.D.F.; Pareja, J.C.; Chaim, E.A. Influence of type 2 diabetes mellitus on liver histology among morbidly obese individuals. A cross-sectional study. Sao Paulo Med J. 2016, 134, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newfield, R.S.; Graves, C.L.; Newbury, R.O.; Schwimmer, J.B.; Proudfoot, J.A.; Say, D.S.; Feldstein, A.E. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in pediatric type 2 diabetes: Metabolic and histologic characteristics in 38 subjects. Pediatr. Diabetes 2018, 20, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutny, F.; Weghuber, D.; Bollow, E.; Greber-Platzer, S.; Hartmann, K.; Körner, A.; Reinehr, T.; Roebl, M.; Simic-Schleicher, G.; Wabitsch, M.; et al. Prevalence of prediabetes and type 2 diabetes in children with obesity and increased transaminases in European German-speaking countries. Analysis of the APV initiative. Pediatr. Obes. 2019, 15, e12601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loomba, R.; Abraham, M.; Unalp, A.; Wilson, L.; LaVine, J.; Doo, E.; Bass, N.M.; the Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Clinical Research Network. Association between diabetes, family history of diabetes, and risk of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and fibrosis. Hepatology 2012, 56, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Adamo, E.; Castorani, V.; Nobili, V. The Liver in Children With Metabolic Syndrome. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobili, V.; Bedogni, G.; Canani, R.B.; Brambilla, P.; Cianfarani, S.; Pietrobelli, A.; Agostoni, C. The potential role of fatty liver in paediatric metabolic syndrome: A distinct phenotype with high metabolic risk? Pediatr. Obes. 2012, 7, e75–e80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gepstein, V.; Weiss, R. Obesity as the Main Risk Factor for Metabolic Syndrome in Children. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, V.T.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanisms for Insulin Resistance: Common Threads and Missing Links. Cell 2012, 148, 852–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutari, C.; Perakakis, N.; Mantzoros, C.S. Association of Adipokines with Development and Progression of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 33, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kłusek-Oksiuta, M.; Bialokoz-Kalinowska, I.; Tarasów, E.; Wojtkowska, M.; Werpachowska, I.; Lebensztejn, D.M. Chemerin as a novel non-invasive serum marker of intrahepatic lipid content in obese children. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2014, 40, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.A. Circulating adipokines in children with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Possible noninvasive diagnostic markers. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2017, 30, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebensztejn, D.; Wojtkowska, M.; Skiba, E.; Werpachowska, I.; Tobolczyk, J.; Kaczmarski, M. Serum concentration of adiponectin, leptin and resistin in obese children with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Adv. Med Sci. 2009, 54, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kahn, C.R.; Wang, G.; Lee, K.Y. Altered adipose tissue and adipocyte function in the pathogenesis of metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 3990–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, J.P.; Raponi, M.; Nobili, V. Clinical implications of understanding the association between oxidative stress and pediatric NAFLD. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 11, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonardo, A.; Ballestri, S.; Marchesini, G.; Angulo, P.; Loria, P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A precursor of the metabolic syndrome. Dig. Liver Dis. 2015, 47, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yki-Järvinen, H. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease as a cause and a consequence of metabolic syndrome. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonardo, A.; Nascimbeni, F.; Mantovani, A.; Targher, G. Hypertension, diabetes, atherosclerosis and NASH: Cause or consequence? J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Africa, J.A.; Newton, K.P.; Schwimmer, J.B. Lifestyle Interventions Including Nutrition, Exercise, and Supplements for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2016, 61, 1375–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslam, M.; Newsome, P.N.; Sarin, S.K.; Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Dufour, J.-F.; Schattenberg, J.M.; et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdanowicz, K.; Białokoz-Kalinowska, I.; Lebensztejn, D.M. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in non-obese children. Hong Kong Med J. 2020, 26, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Esmaili, S.; Rogers, G.B.; Bugianesi, E.; Petta, S.; Marchesini, G.; Bayoumi, A.; Metwally, M.; Azardaryany, M.K.; Coulter, S.; et al. Lean NAFLD: A Distinct Entity Shaped by Differential Metabolic Adaptation. Hepatology 2020, 71, 1213–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvakumar, P.K.C.; Kabbany, M.N.; Lopez, R.; Rayas, M.S.; Lynch, J.L.; Alkhouri, N. Prevalence of Suspected Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Lean Adolescents in the United States. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2018, 67, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampuero, J.; Aller, R.; Gallego-Durán, R.; Banales, J.M.; Crespo, J.; García-Monzón, C.; Pareja, M.J.; Vilar-Gómez, E.; Caballería, J.; Escudero-García, D.; et al. The effects of metabolic status on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease-related outcomes, beyond the presence of obesity. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 48, 1260–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adinolfi, L.E.; Rinaldi, L.; Guerrera, B.; Restivo, L.; Marrone, A.; Giordano, M.; Zampino, R. NAFLD and NASH in HCV Infection: Prevalence and Significance in Hepatic and Extrahepatic Manifestations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, G.; Macdonald, S.; Cronberg, A.; Rosselli, M.; Khera-Butler, T.; Sumpter, C.; Al-Khatib, S.; Jain, A.; Maurice, J.; Charalambous, C.; et al. Short-term abstinence from alcohol and changes in cardiovascular risk factors, liver function tests and cancer-related growth factors: A prospective observational study. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e020673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, Y.; Sivri, H.S. Inborn errors of metabolism in the differential diagnosis of fatty liver disease. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 31, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.R.; Cassiman, D.; Blau, N. Clinical and biochemical footprints of inherited metabolic diseases. II. Metabolic liver diseases. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2019, 127, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, M.; Lacaille, F.; Berthiller, J.; Joly, P.; Dumortier, J.; Aumar, M.; Bridoux-Henno, L.; Jacquemin, E.; Lamireau, T.; Broué, P.; et al. Liver disease related to alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency in French children: The DEFI-ALPHA cohort. Liver Int. 2018, 39, 1136–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flisiak-Jackiewicz, M.; Lebensztejn, D.M. Update on pathogenesis, diagnostics and therapy of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2019, 5, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Flisiak-Jackiewicz, M.; Bobrus-Chociej, A.; Wasilewska, N.; Lebensztejn, D.M. From Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) to Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD)—New Terminology in Pediatric Patients as a Step in Good Scientific Direction? J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10050924
Flisiak-Jackiewicz M, Bobrus-Chociej A, Wasilewska N, Lebensztejn DM. From Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) to Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD)—New Terminology in Pediatric Patients as a Step in Good Scientific Direction? Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(5):924. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10050924
Chicago/Turabian StyleFlisiak-Jackiewicz, Marta, Anna Bobrus-Chociej, Natalia Wasilewska, and Dariusz Marek Lebensztejn. 2021. "From Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) to Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD)—New Terminology in Pediatric Patients as a Step in Good Scientific Direction?" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 5: 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10050924
APA StyleFlisiak-Jackiewicz, M., Bobrus-Chociej, A., Wasilewska, N., & Lebensztejn, D. M. (2021). From Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) to Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD)—New Terminology in Pediatric Patients as a Step in Good Scientific Direction? Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(5), 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10050924




