Association between Initial Severity of Facial Weakness and Outcomes of Bell’s Palsy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population and Design
2.2. Assessment of Outcome and Clinical Factors
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Strengths and Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- May, M.; Hughes, G.B. Facial nerve disorders: Update 1987. Otol. Neurotol. 1987, 8, 167–180. [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan, F.M.; Swan, I.R.; Donnan, P.T.; Morrison, J.M.; Smith, B.H.; McKinstry, B.; Davenport, R.J.; Vale, L.D.; Clarkson, J.E.; Hammersley, V.; et al. Early treatment with prednisolone or acyclovir in Bell’s palsy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 1598–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoo, M.C.; Soh, Y.; Chon, J.; Lee, J.H.; Jung, J.; Kim, S.S.; You, M.-W.; Byun, J.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Yeo, S.G. Evaluation of Factors Associated with Favorable Outcomes in Adults with Bell Palsy. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2020, 146, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somasundara, D.; Sullivan, F. Management of Bell’s palsy. Aust. Prescr. 2017, 40, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilden, D.H. Bell’s palsy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1323–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baugh, R.F.; Basura, G.J.; Ishii, L.E.; Schwartz, S.R.; Drumheller, C.M.; Burkholder, R.; Deckard, N.A.; Dawson, C.; Driscoll, C.; Gillespie, M.B.; et al. Clinical practice guideline: Bell’s palsy. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2013, 149, S1–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Veen, E.L.; Rovers, M.M.; de Ru, J.A.; van der Heijden, G.J. A small effect of adding antiviral agents in treating patients with severe Bell palsy. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2012, 146, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hato, N.; Yamada, H.; Kohno, H.; Matsumoto, S.; Honda, N.; Gyo, K.; Fukuda, S.; Furuta, Y.; Ohtani, F.; Aizawa, H.; et al. Valacyclovir and prednisolone treatment for Bell’s palsy: A multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Otol. Neurotol. 2007, 28, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Jung, S.; Byun, J.; Park, M.; Yeo, S. Steroid plus antiviral treatment for Bell’s palsy. J. Intern. Med. 2015, 277, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.Y.; Byun, J.Y.; Park, M.S.; Yeo, S.G. Steroid-antiviral treatment improves the recovery rate in patients with severe Bell’s palsy. Am. J. Med. 2013, 126, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagyor, I.; Madhok, V.B.; Daly, F.; Sullivan, F. Antiviral treatment for Bell’s palsy (idiopathic facial paralysis). Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 9, Cd001869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- House, W.E. Facial nerve grading system. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1985, 93, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, I.; Maynard, C.; Mountain, R.; Barr-Hamilton, R.; Armstrong, M.; Murray, J.A.M. The prognostic value of facial electroneurography in Bell’s palsy. Clin. Otolaryngol. Allied Sci. 1994, 19, 201–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, T.; Marsk, E.; Engström, M.; Hultcrantz, M.; Hadziosmanovic, N.; Jonsson, L. The effect of study design and analysis methods on recovery rates in Bell’s palsy. Laryngoscope 2009, 119, 2046–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, S.-W.; Lee, D.-H.; Jun, B.-C.; Chang, K.-H.; Park, Y.-S. Analysis of prognostic factors in Bell’s palsy and Ramsay Hunt syndrome. Auris Nasus Larynx 2007, 34, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantsopoulos, K.; Psillas, G.; Psychogios, G.; Brase, C.; Iro, H.; Constantinidis, J. Predicting the long-term outcome after idiopathic facial nerve paralysis. Otol. Neurotol. 2011, 32, 848–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavares-Brito, J.; van Veen, M.M.; Dusseldorp, J.R.; Bahmad, F., Jr.; Hadlock, T.A. Facial palsy-specific quality of life in 920 patients: Correlation with clinician-graded severity and predicting factors. Laryngoscope 2019, 129, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moxon, W. Apoplexy into canal of Fallopius in a case of Bright’s disease, causing facial paralysis. Trans. Pathol. Soc. Lond. 1869, 20, 420–422. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Patterson, M.J.; Pulec, J.L.; Yanagihara, N. Facial nerve biopsy for etiologic clarification of Bell’s palsy. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1988, 97, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.Y.; Byun, J.Y.; Park, M.S.; Yeo, S.G. Effect of aging on the prognosis of Bell’s palsy. Otol. Neurotol. 2013, 34, 766–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monier-Vinard, P.P.; Puech, P. Nephrite chronique et paralysie faciale. Bull. Mem. Soc. Med. Hop. Paris 1930, 20, 977–980. [Google Scholar]
- Voorhees, R.; Zeitzer, L.; Eoss, M. Hypertension and associated peripheral facial paralysis. Laryngoscope 1972, 82, 899–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliçora, S.Ş.; Erdem, D. Does Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Affect the Healing of Bell’s Palsy in Adults? Can. J. Diabetes 2018, 42, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, W.B. The Acute Facial Palsies—Investigation on the Localization and Pathogenesis of Meato-Labyrinthine Facial Palsies; Neurology Series, No. 18; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 1977; p. 164. [Google Scholar]
- Fisch, U. Maximal nerve excitability testing vs. electroneuronography. Arch. Otolaryngol. 1980, 106, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisch, U. Surgery for Bell’s palsy. Arch. Otolaryngol. 1981, 107, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, M.; Klein, S.R.; Taylor, F.H. Idiopathic (Bell’s) facial palsy: Natural history defies steroid or surgical treatment. Laryngoscope 1985, 95, 406–409. [Google Scholar]
- Tojima, H.; Aoyagi, M.; Inamura, H.; Koike, Y. Clinical advantages of electroneurography in patients with Bell’s palsy within two weeks after onset. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 1994, 114, 147–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilden, D. Treatment of Bell’s palsy—The pendulum has swung back to steroids alone. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 976–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engström, M.; Berg, T.; Stjernquist-Desatnik, A.; Axelsson, S.; Pitkäranta, A.; Hultcrantz, M.; Kanerva, M.; Hanner, P.; Jonsson, L. Prednisolone and valaciclovir in Bell’s palsy: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 993–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, K.; Inamura, H.; Abe, Y.; Koshu, H.; Takashita, E.; Muraki, Y.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Nishimura, H.; Ishikawa, H.; Fukao, A.; et al. Reactivation of herpes simplex virus type 1 and varicella-zoster virus and therapeutic effects of combination therapy with prednisolone and valacyclovir in patients with Bell’s palsy. Laryngoscope 2007, 117, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variable | n | H-B Grades 3–4 (n = 1019) | H-B Grades 5–6 (n = 296) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | |||||
| Male | 616 | 477 (46.8) | 139 (47.0) | 0.96 | |
| Female | 699 | 542 (53.2) | 157 (53.0) | ||
| Age group (years) | |||||
| First tertile (19–40) | 361 | 273 (26.8) | 88 (29.7) | 0.39 | |
| Second tertile (41–65) | 765 | 603 (59.2) | 162 (54.7) | ||
| Third tertile (≥66) | 189 | 143 (14.0) | 46 (15.6) | ||
| Electrophysiologic test (result) | |||||
| ENoG (Good) * | 1240 | 961 (94.3) | 279 (94.3) | 0.97 | |
| ENoG (Poor) | 75 | 58 (5.7) | 20 (5.7) | ||
| EMG (Good) ** | 898 | 697 (68.4) | 201 (67.9) | 0.87 | |
| EMG (Poor) | 417 | 322 (31.6) | 95 (32.1) | ||
| Underlying disease | |||||
| Controlled hypertension | |||||
| Yes | 823 | 643 (63.1) | 180 (60.8) | 0.47 | |
| No | 492 | 376 (36.9) | 116 (39.2) | ||
| Diabetes | |||||
| No | 1132 | 881 (86.5) | 251 (84.8) | 0.47 | |
| Yes | 183 | 138 (13.5) | 45 (15.2) | ||
| Treatment method | |||||
| Oral steroids only | 623 | 474 (46.5) | 149 (50.3) | 0.25 | |
| Combination antiviral therapy | 692 | 545 (53.5) | 147 (49.7) | ||
| Outcome | |||||
| Favorable *** | 1047 | 845 (82.9) | 202 (68.2) | <0.001 | |
| Unfavorable | 268 | 174 (17.1) | 94 (31.8) | ||
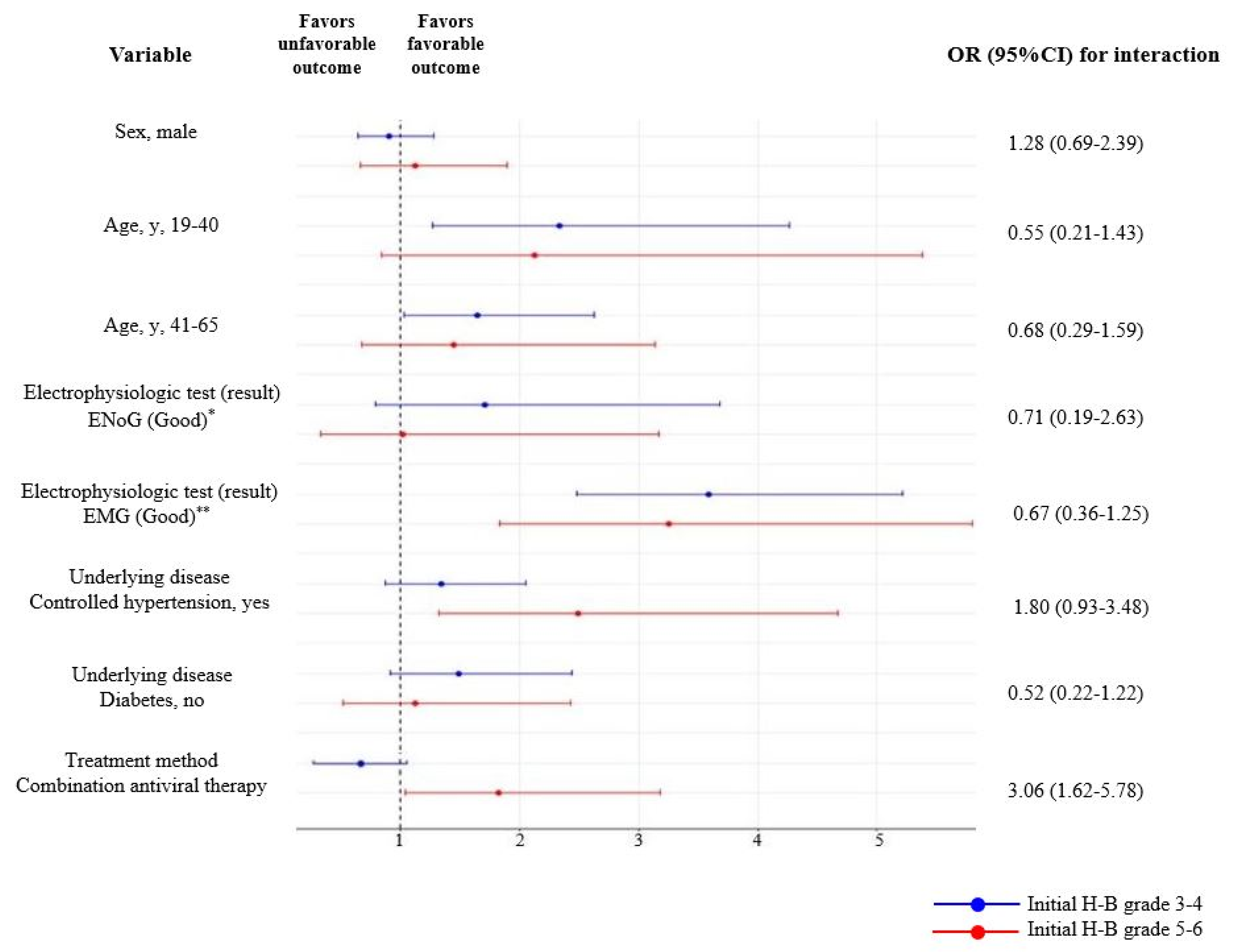
| Variable | Initial H-B Grades 3–4 | Initial H-B Grades 5–6 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Odds Ratio (95% CI) | Odds Ratio (95% CI) | ||
| Sex | |||
| Male | 0.90 (0.64–1.28) | 1.12 (0.66–1.89) | |
| Female | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) | |
| Age group (years) | |||
| First tertile (19–40) | 2.33 (1.27–4.26) | 2.12 (0.84–5.38) | |
| Second tertile (41–65) | 1.64 (1.03–2.62) | 1.45 (0.67–3.14) | |
| Third tertile (≥66) | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) | |
| Electrophysiologic test (result) | |||
| ENoG (Good) * | 1.71 (0.79–3.68) | 1.02 (0.33–3.17) | |
| ENoG (Poor) | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) | |
| EMG (Good) ** | 3.59 (2.48–5.21) | 3.25 (1.83–5.80) | |
| EMG (Poor) | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) | |
| Underlying disease | |||
| Controlled hypertension | |||
| Yes | 1.34 (0.87–2.05) | 2.49 (1.32–4.67) | |
| No | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) | |
| DM | |||
| Absent | 1.49 (0.91–2.44) | 1.12 (0.52–2.43) | |
| Present | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) | |
| Treatment method | |||
| Oral steroids only | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) | |
| Combination antiviral therapy | 0.73 (0.45–1.09) | 1.82 (1.04–3.18) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoo, M.C.; Park, D.C.; Yeo, S.G. Association between Initial Severity of Facial Weakness and Outcomes of Bell’s Palsy. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3914. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10173914
Yoo MC, Park DC, Yeo SG. Association between Initial Severity of Facial Weakness and Outcomes of Bell’s Palsy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(17):3914. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10173914
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoo, Myung Chul, Dong Choon Park, and Seung Geun Yeo. 2021. "Association between Initial Severity of Facial Weakness and Outcomes of Bell’s Palsy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 17: 3914. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10173914
APA StyleYoo, M. C., Park, D. C., & Yeo, S. G. (2021). Association between Initial Severity of Facial Weakness and Outcomes of Bell’s Palsy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(17), 3914. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10173914






