Abstract
Reduced-dose nonvitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants (NOACs) are commonly prescribed to Asian patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation (NVAF). We aimed to compare the risk of stroke/systemic embolism (S/SE) and major bleeding (MB) between patients treated with reduced-dose NOACs and those treated with warfarin, using the claims database in Korea. Patients with NVAF newly initiated on oral anticoagulants (OACs; apixaban, dabigatran, rivaroxaban, and warfarin) between 1 July 2015 and 30 November 2016 were included. Among all patients with NVAF treated with OACs, 5249, 6033, 7602, and 8648 patients were treated with reduced-dose apixaban, dabigatran, rivaroxaban, and warfarin, respectively. Patients treated with reduced-dose NOACs were older and had higher CHA2DS2-VASc and HAS-BLED scores than those treated with warfarin. Compared to warfarin, all reduced-dose NOACs showed significantly lower risk of S/SE (hazard ratios (95% confidence interval), 0.63 (0.52–0.75) for apixaban; 0.51 (0.42–0.61) for dabigatran; and 0.67 (0.57–0.79) for rivaroxaban) and MB (0.54 (0.45–0.65) for apixaban; 0.58 (0.49–0.69) for dabigatran; 0.73 (0.63–0.85) for rivaroxaban). In the real-world practice among Asians with NVAF, all reduced-dose NOACs were associated with a significantly lower risk of S/SE and MB compared to those of warfarin.
1. Introduction
Oral anticoagulants (OACs) have taken a crucial role in the treatment strategy of atrial fibrillation (AF) to prevent stroke [1,2,3]. Although warfarin is known as an effective agent for reducing the risk of stroke in AF, there have been challenges in using warfarin in Asian patients, including the possibility of difference in the optimal target of international normalized ratio (INR) [4,5,6]. Several studies investigating acceptable outcomes with lower INR levels in Asian populations have considered not only bleeding or ischemic events but also its pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic characteristics [7,8,9,10]. Moreover, due to the higher incidence rate of hemorrhagic stroke in Asians undergoing Vitamin K Antagonist (VKA) therapy, careful assessment of bleeding complications of OACs among Asians in general is crucial [6,11].
Nonvitamin K OACs (NOACs), now recommended as the choice of treatment, are widely used based on evidence from recent large randomized controlled trials (RCTs), which have demonstrated their noninferiority and superior efficacy/tolerability compared with those of warfarin [12,13,14,15]. All these studies have shown fewer bleeding events with a standard dose of NOACs compared to warfarin. Nevertheless, it has been reported that physicians tend to prescribe reduced-dose NOACs to Asian patients with AF in real practice, owing to a major concern of bleeding complications [16,17]. The real-world evaluations assessing the effectiveness of reduced-dose NOACs in Asian are limited, and only a few studies reported about the conflicting results in the view of the stroke event risk [18,19].
Therefore, this study aimed to compare the risk of stroke/systemic embolism (S/SE) and major bleeding (MB) in Korean patients treated with reduced-dose NOACs versus warfarin under real clinical practice.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
The Korean Health Insurance Review and Assessment (HIRA) Service claims data from 1 January 2007 to 30 November 2016 were used in this study. The HIRA database includes data covering the entire population under the universal health insurance system in Korea [20]. These data included information on demographics, diagnoses, health services, and prescriptions and were provided after being anonymized [20]. Diagnosis codes in these data were based on the International Classification of Diseases 10th Revision (ICD-10) [20]. The Pusan National University Institutional Review Board determined that this study did not require ethical review (PNU IRB/2016_137_HR).
2.2. Study Population
The study included OAC-naïve patients who had one or more prescriptions for apixaban, dabigatran, or rivaroxaban during the intake period of 1 July 2015–30 November 2016. We defined the index date as the first OAC prescription date. The inclusion criteria were patients above 18 years of age on the index date and a minimum of two outpatient visits or one hospitalization with AF diagnosis (i.e., ICD-10 code I48) before or on the index date. The latter inclusion criterion performed well in a previous validation study with a positive predictive value of 94.1% [21]. As the Korean health insurance policy allows reimbursement for anticoagulant prescription in AF patients with CHA2DS2-VASc score of 2 or higher, all included patients are considered indicated for anticoagulation therapy.
Patients with the following conditions were excluded: hip or knee replacement surgery within six weeks prior to or on the index date; valvular AF, prosthetic heart valves, venous thromboembolism, thyrotoxicosis, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, end-stage chronic kidney disease, kidney transplant, dialysis, pericarditis, elective defibrillation, radiofrequency ablation, or left atrial appendage occlusion during the 12-month baseline period; NOAC or warfarin use within 1 year prior to the index date; more than one OAC prescription on the index date; both standard and reduced dose on the index date; both standard and other dose on the index date; or both reduced and other dose on the index date.
Standard dose was defined as the general recommended dose for patients with AF as specified in the package insert (i.e., 10, 300, and 20 mg as a daily dose for apixaban, dabigatran, and rivaroxaban, respectively). Reduced dose was defined as the recommended dose for patients who have renal dysfunction and/or low body weight or are elderly as specified in the package insert (i.e., 5, 220, and 15 mg as a daily dose for apixaban, dabigatran, and rivaroxaban, respectively). Other dose was defined as a dose lower than the reduced dose on label or higher than the standard dose (Table 1).

Table 1.
Definition of dose groups at the index date.
The follow-up period was from the index date to the date of switching from index OAC treatment to another OAC, treatment discontinuation, death, or 30 November 2016, whichever came first. Discontinuation was defined as the absence of prescription for any OACs within 30 days after the last day of supply of the last filled prescription. Medication switch was defined as the presence of a prescription filled for nonindex OAC treatment within 30 days after the last day of supply of the last filled prescription.
2.3. Study Endpoints
S/SE was the effectiveness outcome and included ischemic stroke, hemorrhagic stroke, and systemic embolism. Diagnosis codes with hospitalization and brain computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) records were used to identify stroke [22,23], whereas diagnosis codes with hospitalization and any CT or MRI records were used to identify SE. MB was the safety outcome and included intracranial hemorrhage (ICH), gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding, and other bleeding. ICH was defined using diagnosis codes with hospitalization and brain CT or MRI records. The remaining safety outcomes (i.e., GI and other bleeding) were defined using diagnosis codes with hospitalization. Primary and all secondary diagnosis codes were used to define each outcome. Additional details regarding the effectiveness and safety outcomes are provided in Supplementary Materials Table S1.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Propensity score matching (PSM) using propensity scores was conducted to balance baseline demographics and clinical characteristics. Propensity score is the probability of receiving treatment, which is based on the observed characteristics [24]. We used PSM rather than inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) because the proportion of patients who received treatment contrary to prediction was substantial, which can cause unstable results. If there is instability in the estimated propensity score, PSM may be preferable to IPTW [24]. Propensity scores were estimated using logistic regression and included information on baseline demographics and clinical characteristics, including age, sex, insurance type, baseline medication use, baseline comorbidities, Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI), CHA2DS2-VASc score, HAS-BLED score, and individual risk factors of CHA2DS2-VASc and HAS-BLED scores. The details on CHA2DS2-VASc and HAS-BLED scores, baseline medication use, and CCI are provided in Supplementary Materials Tables S2–S5. For the matching to make comparable groups, we used a caliper of 0.01. The balance for each variable between the treatment groups was evaluated using standardized differences in the matched sample [24], and a standardized difference below 10% was considered acceptable [24]. In the presence of an imbalance, the variable was included in the Cox proportional hazards model. The Cox proportional hazards model was used to compare outcomes between the treatment groups. Proportional hazard assumption was evaluated using several methods, such as log–log plots, Schoenfeld’s residuals, and time-dependent covariates [25]. If the proportional hazard assumption was not met, hazard ratio (HR) with 95% confidence interval (CI) at 1 year was estimated using the extended Cox model which contains the product term of the variable with a log of time [25].
For analysis, the following three comparisons were performed: (1) reduced-dose apixaban versus warfarin, (2) reduced-dose dabigatran versus warfarin, and (3) reduced-dose rivaroxaban versus warfarin. All statistical analyses were performed using SAS 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
A total of 48,389 OAC-naïve patients who newly initiated OACs were identified: 10,548 apixaban, 11,414 dabigatran, 17,779 rivaroxaban, and 8648 warfarin. Among these patients, 5249, 6033, and 7602 patients received reduced-dose apixaban, dabigatran, and rivaroxaban, respectively (Figure 1). Before matching, patients treated with reduced-dose NOACs were older and had higher CHA2DS2-VASc and HAS-BLED scores compared to those of patients treated with warfarin (Supplementary Materials Table S6). After matching, all differences in baseline characteristics were balanced (p > 0.05; absolute standardized difference <0.1; Table 2).
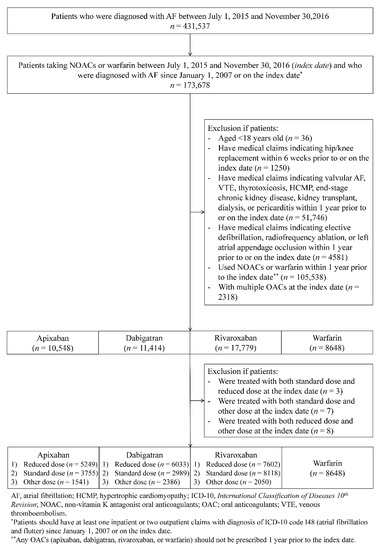
Figure 1.
Cohort creation flow of oral anticoagulant users.

Table 2.
Baseline characteristics of patients receiving reduced-dose nonvitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants and warfarin after propensity score matching.
3.2. Effectiveness Outcomes
The effectiveness outcomes based on the comparisons of reduced-dose NOACs with warfarin are summarized in Figure 2. Reduced-dose apixaban, dabigatran, and rivaroxaban were associated with a lower risk of S/SE compared to that of warfarin (HR (95% CI), 0.63 (0.52–0.75) for reduced-dose apixaban versus warfarin; HR (95% CI), 0.51 (0.42–0.61) for reduced-dose dabigatran versus warfarin; HR (95% CI), 0.67 (0.57–0.79) for reduced-dose rivaroxaban versus warfarin) (Figure 2). Among the comparisons of reduced-dose NOACs with warfarin, dabigatran showed the lowest crude event rate of S/SE (5.88 per 100 person-years) (Table 3).
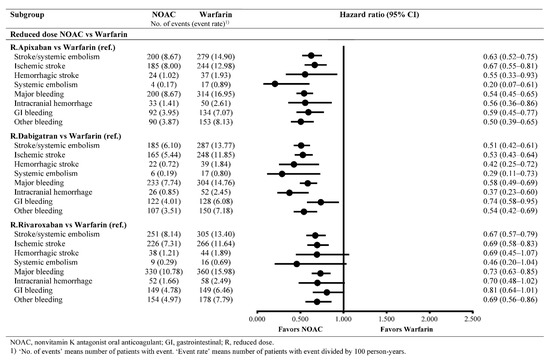
Figure 2.
Event rates and hazard ratios in propensity score-matched cohorts for the comparison of reduced-dose NOACs with warfarin.

Table 3.
The summary of crude event rates in patients taking reduced-dose NOACs and warfarin.
3.3. Safety Outcomes
The safety outcomes based on the comparisons of reduced-dose NOACs with warfarin are summarized in Figure 2. Reduced-dose apixaban, dabigatran, and rivaroxaban were associated with a lower risk of MB compared with that of warfarin (HR (95% CI), 0.54 (0.45–0.65) for reduced-dose apixaban versus warfarin; HR (95% CI), 0.58 (0.49–0.69) for reduced-dose dabigatran versus warfarin; and HR (95% CI), 0.73 (0.63–0.85) for reduced-dose rivaroxaban versus warfarin) (Figure 2). Among the comparisons of reduced-dose NOACs with warfarin, dabigatran showed the lowest crude event rate of MB (7.60 per 100 person-years) (Table 3).
4. Discussion
In this study, we measured the risk of thromboembolic and bleeding events in patients with AF who were newly initiated on reduced-dose NOACs or warfarin for stroke prevention. This large real-world cohort of Korean patients taking daily doses of 5 mg apixaban, 15 mg rivaroxaban, or 220 mg dabigatran was compared with those taking warfarin. We found that the risk of S/SE was lower in patients treated with 5 mg apixaban, 15 mg rivaroxaban, or 220 mg dabigatran daily than in those treated with warfarin. Furthermore, significantly lower bleeding risk was observed in all reduced-dose NOAC treatment groups compared with the warfarin group.
We observed differences in the baseline characteristics between the reduced-dose NOAC and warfarin cohorts. There were more females in the NOAC cohorts; furthermore, the patients were older and had higher CHA2DS2-VASc scores with more comorbidities in general. Among the NOAC cohorts, the patients treated with dabigatran generally had a lower number of comorbid diseases, were younger, and had lower CHA2DS2-VASc and HAS-BLED scores than those treated with the other NOACs. On the other hand, the CHA2DS2-VASc score and proportion of patients with comorbidities, such as renal disease, history of bleeding, and prior ischemic stroke, were the highest among those treated with apixaban within the NOAC cohort. Similar patient characteristic patterns have also been observed in the Western population, wherein those with apixaban had more comorbid diseases and were generally older [18].
Dose reduction in NOACs is primarily recommended according to the dose-reduction criteria established by pivotal RCTs. In the 2019 AHA/ACC/HRS guidelines, dose adjustment of NOACs is based on the Food and Drug Administration dosing guidelines [26]. In patients for whom combination therapy with a P2Y12 inhibitor and NOAC is considered, reduced-dose rivaroxaban (15 mg once daily) is recommended [26]. The 2018 ACCP guidelines recommend label-adjusted NOAC dosing, which reflects the dose-reduction criteria of the pivotal RCTs [27]. This consensus on the use of NOACs is also followed by the 2021 EHRA practical guidelines [28]. However, in Japan, the standard rivaroxaban dose is 15 mg once daily, and 10 mg rivaroxaban once daily is prescribed for patients with renal impairment based on the pharmacokinetic data available for elderly Japanese patients with AF. In Korea, the dose recommendation for all NOACs follows US or EU therapeutic labels.
Each NOAC has specific criteria for dose reduction, which might be considered complex by physicians. Due to the concerns regarding excessive bleeding among Asian patients on warfarin therapy [4,29], maintenance of a lower INR range has become a usual treatment approach [7,9], which may deliver on the perception that lower doses of NOACs would be sufficient. Subsequently, choosing the right dose for each patient has become a challenge in clinical settings, and the assumption that a certain proportion of patients treated with NOACs did not receive appropriate doses cannot be ruled out in this study.
In a US prospective registry for patients with AF receiving NOACs (n = 5738), 87% of patients were prescribed on-label NOAC doses; the rates of underdosing and overdosing were 9.4% and 3.4%, respectively [30]. These rates were markedly higher in the Asian population [31]. As mentioned in the Comparison Study of Drugs for Symptom Control and Complication Prevention of AF (CODE-AF) Registry with Korean patients with AF, substantial proportion of Korean patients with AF received off-label reduced-dose NOAC: 53.9% of rivaroxaban users, 55% of apixaban users, and 23.5% of edoxaban users [31]. The off-label reduced dose was administered to older patients and females, and the patients had lower body weight, renal dysfunction, history of stroke and bleeding, hypertension, and concomitant medication use.
There are several potential reasons for frequent use of reduced-dose NOACs in Asian patients with AF. Asians tended to have lower body weight and smaller body size than non-Asians who were mainly included in the pivotal NOAC RCTs. Moreover, Asians showed a higher risk of ICH when compared to non-Asians in the warfarin era [4]. The clinical factors such as previous bleeding history and fluctuation of renal function or body weight could influence the physicians’ choice of dosing in real-world practice. Thus, clinicians may prescribe OAC therapy in Asian AF patients in a conservative manner due to the possibility of adverse bleeding events.
Several subanalyses have revealed that outcomes after using the on-label reduced dose of NOACs versus warfarin are overall consistent with standard dose versus warfarin. In a meta-analysis of three pivotal RCTs, reduced-dose NOACs in patients who were eligible for dose reduction were associated with similar risk of ischemic stroke and lower risk of hemorrhagic stroke, ICH, and fatal bleeding compared to those of warfarin [32]. Favorable result of the reduced-dose NOACs in comparison to warfarin was also documented in a meta-analysis of 18 real-world data studies, especially in Asians [33]. Other studies have demonstrated that clinical benefits were reduced with NOAC underdosing; however, off-label reduced doses continue to be prescribed [31]. Large randomized or observational studies are warranted to determine the efficacy and safety of reduced-dose NOACs in real-world settings.
Although this study could not differentiate between the appropriate and inappropriate use of reduced-dose NOACs, the study findings revealed the clinically significant data on reduced-dose NOACs that may provide benefits in real-world practice compared to warfarin therapy. However, caution is warranted in its interpretation and use of reduced-dose NOACs should be strictly based on prescribing labels. This finding suggests that NOACs, regardless of dosage, may provide better clinical outcomes in patients with AF for whom warfarin is indicated. Poor INR control and low treatment satisfaction of VKA users among Korean patients with AF might be one of the potential underlying reasons for the observed differences in outcomes between warfarin and reduced-dose NOACs in this study [34]. In another study evaluating the effectiveness and safety of NOACs versus warfarin among the Korean population with AF, NOACs had an overall favorable clinical benefit compared to that of warfarin, although 50–75% of the cohort included patients on reduced-dose NOAC treatment [17]. Similar results were obtained from our previous study in which the risk of S/SE and MB were compared between NOACs (including all dosages) and warfarin in the OAC taking AF patients [35]. Considering that reduced dosing is recommended for patient groups associated with a higher risk of not only bleeding (HAS-BLED) but also for stroke (CHA2DS2-VASc), this study’s results provide additional information on the benefit of NOACs over warfarin in Asian patients requiring anticoagulation for stroke prevention.
Limitations
This study has some inherent limitations associated with the retrospective analysis of claims data. First, the HIRA database does not include data on some patient characteristics such as body weight or laboratory data, including INR and those related to renal and liver function. Therefore, assessing whether patients were managed with appropriate doses of anticoagulants was challenging. In addition, the adequacy of anticoagulation in patients in the warfarin group could not be determined due to lack of information on INR, which may affect the clinical interpretation of the study results, as Asian AF patients tend to be kept at a lower INR range compared to that of non-Asians. Second, the claims database that we utilized in this study cannot discern the specific type of AF (i.e., paroxysmal, persistent). Third, despite the careful adjustment of confounders by PSM, thereby allowing a close balance between the groups, the presence of unmeasured confounding factors cannot be ruled out. Finally, the study follow-up period was relatively short as reimbursement of NOACs as first-line therapy was initiated on 1 July 2015. Therefore, further studies are necessary to explore the long-term effectiveness and safety of NOACs. However, the Cox proportional hazards model revealed significant differences in all comparisons; therefore, the relatively short follow-up period might not have had a significant impact on the main findings of this study.
5. Conclusions
In a large observational study of reduced-dose NOACs, NOACs were associated with lower thromboembolic and bleeding risk compared to those of warfarin. Nevertheless, the use of NOACs should adhere to dose-reduction criteria indicated in the therapeutic label. This study provides further evidence for the use of NOACs in Asian patients with NVAF.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jcm10173918/s1, Table S1: International Classification of Disease, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) codes for the study outcomes, Table S2: Scoring and International Classification of Disease, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) codes for the factors included in the CHA2DS2-VASc score, Table S3: Scoring and International Classification of Disease, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) codes for the factors include in the HAS-BLED score, Table S4: Types of baseline medications, Table S5: Scoring and International Classification of Disease, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) codes for the factors included in the Charlson Comorbidity Index, Table S6: Baseline characteristics of patients receiving reduced-dose nonvitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants and warfarin before propensity score matching.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: S.H. (Sola Han), Y.K.O., Y.-J.P. and H.S.S.; methodology: S.H. (Sola Han) and H.S.S.; formal analysis: S.H. (Sola Han) and H.S.S.; investigation: S.H. (Sola Han), Y.-H.K., M.-Y.L., O.Y.B., S.-W.J., S.H. (Seongwook Han), Y.K.O. and H.S.S.; data curation: S.H. (Sola Han) and H.S.S.; writing—original draft: S.H. (Sola Han), Y.-J.P., Y.K.O. and H.S.S.; writing—review and editing: S.H. (Sola Han), Y.-H.K., M.-Y.L., O.Y.B., S.-W.J., S.H. (Seongwook Han), Y.-J.P., S.K., Y.K.O. and H.S.S.; supervision: Y.-H.K., Y.-J.P., S.K., Y.K.O. and H.S.S.; project administration: Y.-J.P. and S.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was sponsored by Pfizer and Bristol Myers Squibb.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The Pusan National University Institutional Review Board determined that this study did not require ethical review (PNU IRB/2016_137_HR).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The study data were extracted and analyzed from the Korea Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service (HIRA) claims database, and additional data may be obtained from a third party (with appropriate authorization approval) but are not publicly available.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Enago (www.enago.co.kr (accessed on 29 August 2021)) for the editorial support with regards to manuscript formatting, which was funded by Pfizer and Bristol Myers Squibb.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Y.-J.P. and S.K are full-time employees and stockholders of Pfizer Inc. Authors S.H. (Sola Han), Y-H.K., M.-Y.L., O.Y.B., S.-W.J., S.H. (Seongwook Han), Y.K.O. and H.S.S. are paid consultants for Pfizer Korea Ltd.
References
- Mozaffarian, D.; Benjamin, E.J.; Go, A.S.; Arnett, D.K.; Blaha, M.J.; Cushman, M.; de Ferranti, S.; Després, J.P.; Fullerton, H.J.; Howard, V.J.; et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2015 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2015, 131, e29–e322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Savelieva, I.; Bajpai, A.; Camm, A.J. Stroke in atrial fibrillation: Update on pathophysiology, new antithrombotic therapies, and evolution of procedures and devices. Ann. Med. 2007, 39, 371–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- January, C.T.; Wann, L.S.; Alpert, J.S.; Calkins, H.; Cigarroa, J.E.; Cleveland, J.C.; Conti, J.B.; Ellinor, P.T.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Field, M.E.; et al. 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines and the heart rhythm society. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 64, e1–e76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, A.Y.-J.; Yao, J.F.; Brar, S.S.; Jorgensen, M.B.; Chen, W. Racial/Ethnic Differences in the Risk of Intracranial Hemorrhage Among Patients With Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 50, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Asch, C.J.; Luitse, M.J.; Rinkel, G.J.; van der Tweel, I.; Algra, A.; Klijn, C.J. Incidence, case fatality, and functional outcome of intracerebral haemorrhage over time, according to age, sex, and ethnic origin: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.-E.; Wang, K.-L.; Lip, G.Y.H. Stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation: An Asian perspective. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 111, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inoue, H.; Okumura, K.; Atarashi, H.; Yamashita, T.; Origasa, H.; Kumagai, N.; Sakurai, M.; Kawamura, Y.; Kubota, I.; Matsumoto, K.; et al. Target international normalized ratio values for preventing thromboembolic and hemorrhagic events in Japanese patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation: Results of the J-RHYTHM Registry. Circ. J. 2013, 77, 2264–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheung, C.-M.; Tsoi, T.-H.; Huang, C.-Y. The Lowest Effective Intensity of Prophylactic Anticoagulation for Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2005, 20, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Hui, J.; Hou, Y.-Y.; Zou, Y.; Jiang, W.-P.; Yang, X.-J.; Wang, X.-H. Meta-Analysis of Efficacy and Safety of Low-Intensity Warfarin Therapy for East Asian Patients with Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2017, 120, 1562–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.-H.; Lee, K.-T.; Kao, Y.-W.; Huang, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-L.; Hang, S.C.-L.; Chu, P.-H. The comparison of non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants versus well-managed warfarin with a lower INR target of 1.5 to 2.5 in Asians patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chiang, C.-E.; Okumura, K.; Zhang, S.; Chao, T.-F.; Siu, C.-W.; Lim, T.W.; Saxena, A.; Takahashi, Y.; Siong Teo, W. 2017 consensus of the Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society on stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation. J. Arrhythmia 2017, 33, 345–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, S.J.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Yusuf, S.; Eikelboom, J.; Oldgren, J.; Parekh, A.; Pogue, J.; Reilly, P.A.; Themeles, E.; Varrone, J.; et al. Dabigatran versus Warfarin in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giugliano, R.P.; Ruff, C.T.; Braunwald, E.; Murphy, S.A.; Wiviott, S.D.; Halperin, J.L.; Waldo, A.L.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Weitz, J.I.; Špinar, J.; et al. Edoxaban versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 2093–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Granger, C.B.; Alexander, J.H.; McMurray, J.J.; Lopes, R.D.; Hylek, E.M.; Hanna, M.; Al-Khalidi, H.R.; Ansell, J.; Atar, D.; Avezum, A.; et al. Apixaban versus Warfarin in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 981–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.R.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Garg, J.; Pan, G.; Singer, D.E.; Hacke, W.; Breithardt, G.; Halperin, J.L.; Hankey, G.J.; Piccini, J.P.; et al. Riva-roxaban versus warfarin in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steinberg, B.A.; Shrader, P.; Pieper, K.; Thomas, L.; Allen, L.A.; Ansell, J.; Chan, P.S.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Fonarow, G.C.; Freeman, J.V.; et al. Frequency and Outcomes of Reduced Dose Non-Vitamin K Antagonist Anticoagulants: Results From ORBIT-AF II (The Outcomes Registry for Better Informed Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation II). J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e007633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, M.S.; Yun, J.E.; Park, J.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.; Park, D.-W.; Nam, G.-B. Outcomes after Use of Standard- and Low-Dose Non–Vitamin K Oral Anticoagulants in Asian Patients With Atrial Fibrillation. Stroke 2019, 50, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, P.B.; Skjøth, F.; Søgaard, M.; Kjældgaard, J.N.; Lip, G.Y.; Larsen, T.B. Effectiveness and safety of reduced dose non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants and warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation: Propensity weighted nationwide cohort study. BMJ 2017, 356, j510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, X.; Shah, N.D.; Sangaralingham, L.R.; Gersh, B.J.; Noseworthy, P.A. Non–Vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulant Dosing in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation and Renal Dysfunction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 2779–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-A.; Yoon, S.; Kim, L.-Y.; Kim, D.-S. Towards Actualizing the Value Potential of Korea Health Insurance Review and Assessment (HIRA) Data as a Resource for Health Research: Strengths, Limitations, Applications, and Strategies for Optimal Use of HIRA Data. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2017, 32, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Yang, P.S.; Uhm, J.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Pak, H.N.; Lee, M.H.; Joung, B.; Lip, G.Y.H. CHA2DS2-VASc score (congestive heart failure, hypertension, age ≥75 [doubled], diabetes mellitus, prior stroke or transient ischemic attack [doubled], vascular disease, age 65–74, female) for stroke in Asian patients with atrial fibrillation: A Korean nationwide sample cohort study. Stroke 2017, 48, 1524–1530. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, T.H.; Choi, J.C. Validation of Stroke and Thrombolytic Therapy in Korean National Health Insurance Claim Data. J. Clin. Neurol. 2016, 12, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cha, M.J.; Choi, E.K.; Han, K.D.; Lee, S.R.; Lim, W.H.; Oh, S.; Lip, G.Y.H. Effectiveness and safety of non-vitamin k antagonist oral anticoagulants in Asian patients with atrial fibrillation. Stroke 2017, 48, 3040–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, P.C. The use of propensity score methods with survival or time-to-event outcomes: Reporting measures of effect similar to those used in randomized experiments. Stat. Med. 2014, 33, 1242–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kleinbaum, D.G.; Klein, M. Survival Analysis: A Self-Learning Text, 2nd ed.; Springer Science+Business Media, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- January, C.T.; Wann, L.S.; Calkins, H.; Chen, L.Y.; Cigarroa, J.E.; Cleveland, J.C., Jr.; Ellinor, P.T.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Field, M.E.; Furie, K.L.; et al. 2019 AHA/ACC/HRS focused update of the 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on clinical practice guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 104–132. [Google Scholar]
- Lip, G.Y.H.; Banerjee, A.; Boriani, G.; Chiang, C.E.; Fargo, R.; Freedman, B.; Lane, D.A.; Ruff, C.T.; Turakhia, M.; Werring, D.; et al. Antithrombotic therapy for atrial fibrillation: CHEST guideline and expert panel report. Chest 2018, 154, 1121–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steffel, J.; Collins, R.; Antz, M.; Cornu, P.; Desteghe, L.; Haeusler, K.G.; Oldgren, J.; Reinecke, H.; Roldan-Schilling, V.; Rowell, N.; et al. 2021 European Heart Rhythm Association practical guide on the use of non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants in patients with atrial fibrillation. Europace 2021, euab157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyer, T.P.; O’Kane, D.J.; Baudhuin, L.M.; Wiley, C.L.; Fortini, A.; Fisher, P.K.; Dupras, D.M.; Chaudhry, R.; Thapa, P.; Zinsmeister, A.R.; et al. Warfarin Sensitivity Genotyping: A Review of the Literature and Summary of Patient Experience. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2009, 84, 1079–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steinberg, B.A.; Shrader, P.; Thomas, L.; Ansell, J.; Fonarow, G.C.; Gersh, B.J.; Kowey, P.R.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Naccarelli, G.; Reiffel, J.; et al. Off-label dosing of non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants and adverse outcomes: The ORBIT-AF II registry. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 2597–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-R.; Lee, Y.S.; Park, J.-S.; Cha, M.-J.; Kim, T.-H.; Park, J.; Park, J.-K.; Lee, J.-M.; Kang, K.-W.; Shim, J.; et al. Label Adherence for Non-Vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulants in a Prospective Cohort of Asian Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Yonsei Med. J. 2019, 60, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.L.; Lopes, R.D.; Patel, M.R.; Büller, H.R.; Tan, D.S.; Chiang, C.E.; Giugliano, R.P. Efficacy and safety of reduced-dose non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants in patients with atrial fibrillation: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 1492–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fang, L.; Liu, B.; Zheng, Y.; Zeng, J. Real-world comparisons of reduced-dose non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants versus warfarin in atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart Fail. Rev. 2020, 25, 973–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Kim, J.-S.; Oh, Y.-S.; Shin, D.-G.; Pak, H.-N.; Hwang, G.-S.; Choi, K.-J.; Kim, J.-B.; Lee, M.-Y.; Park, H.-W.; et al. Quality of Anticoagulation and Treatment Satisfaction in Patients with Non-Valvular Atrial Fibrillation Treated with Vitamin K Antagonist: Result from the KORean Atrial Fibrillation Investigation II. J. Korean Med Sci. 2018, 33, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, O.Y.; On, Y.K.; Lee, M.Y.; Jang, S.W.; Han, S.; Han, S.; Won, M.M.; Park, Y.J.; Lee, J.M.; Choi, H.Y.; et al. The risk of stroke/systemic embolism and major bleeding in Asian patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation treated with non-vitamin K oral anticoagulants compared to warfarin: Results form a real-world data analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).