Forward Osmosis Application in Manufacturing Industries: A Short Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Demand for Innovative, Energy-Efficient Water and Wastewater Treatment
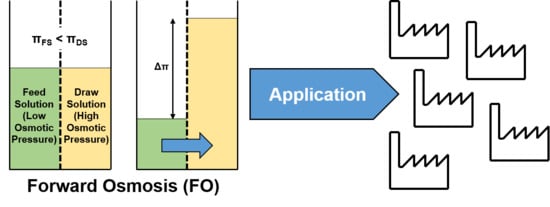
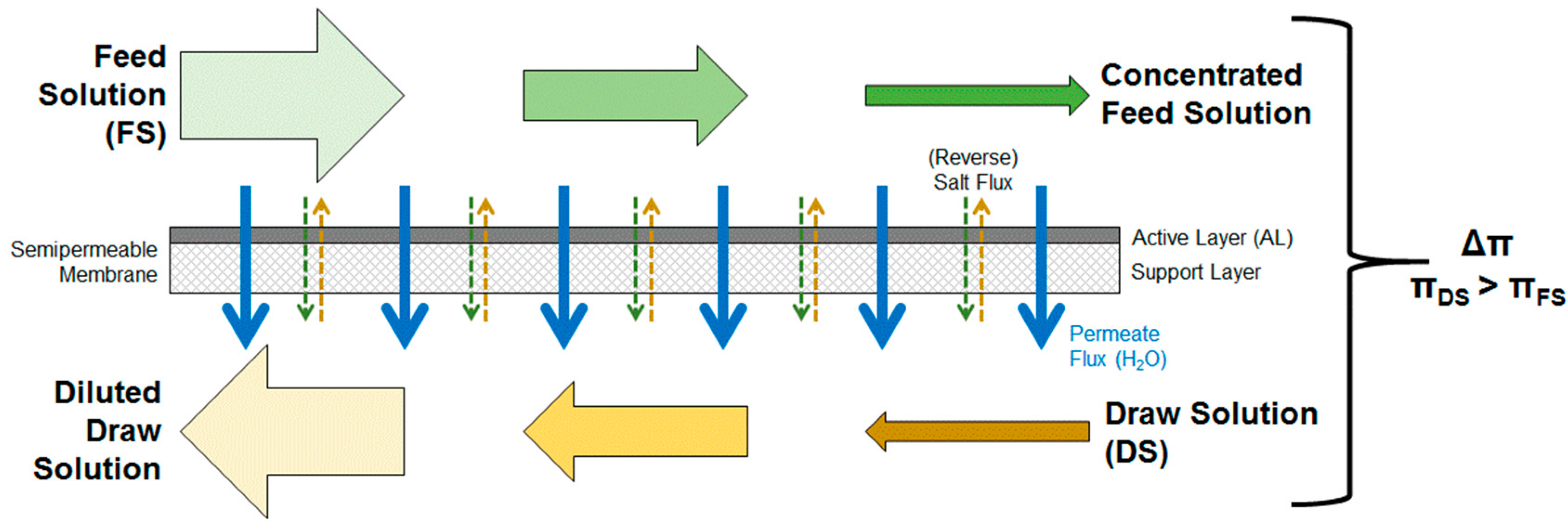
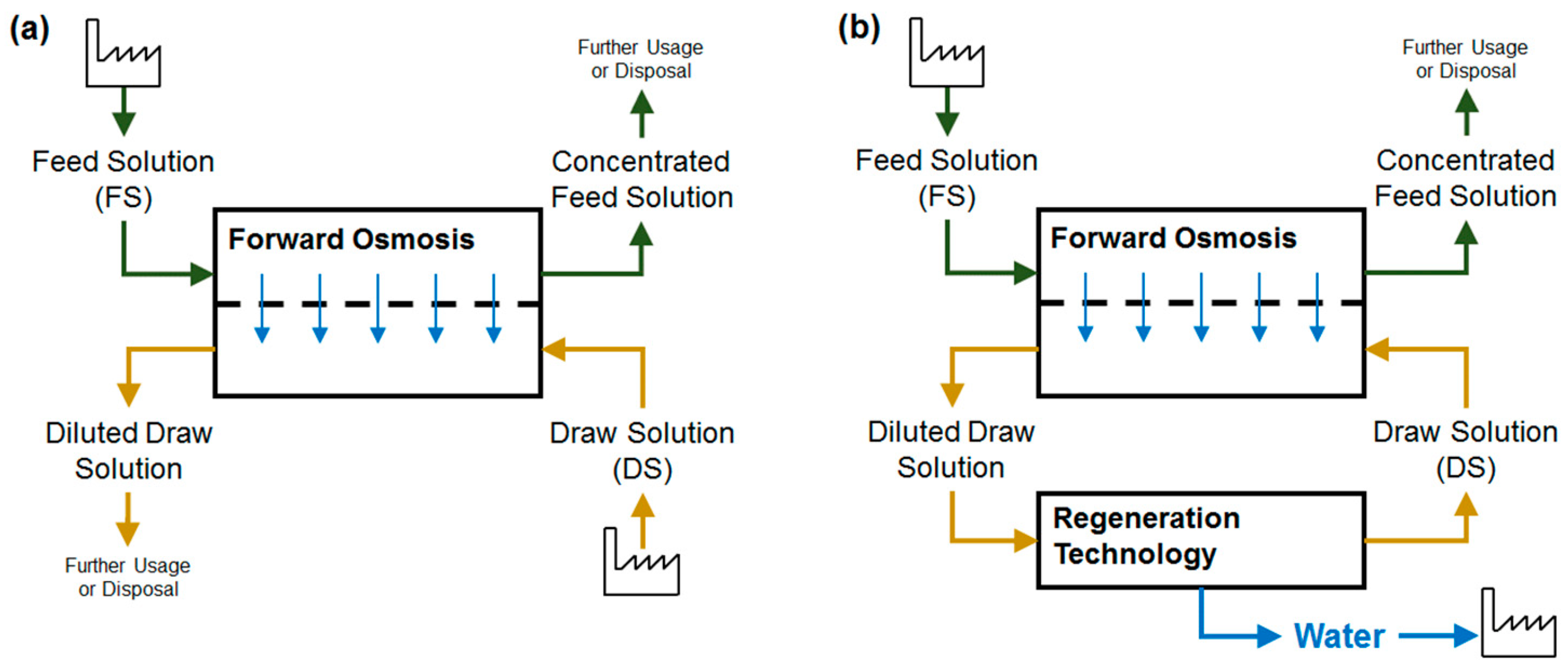
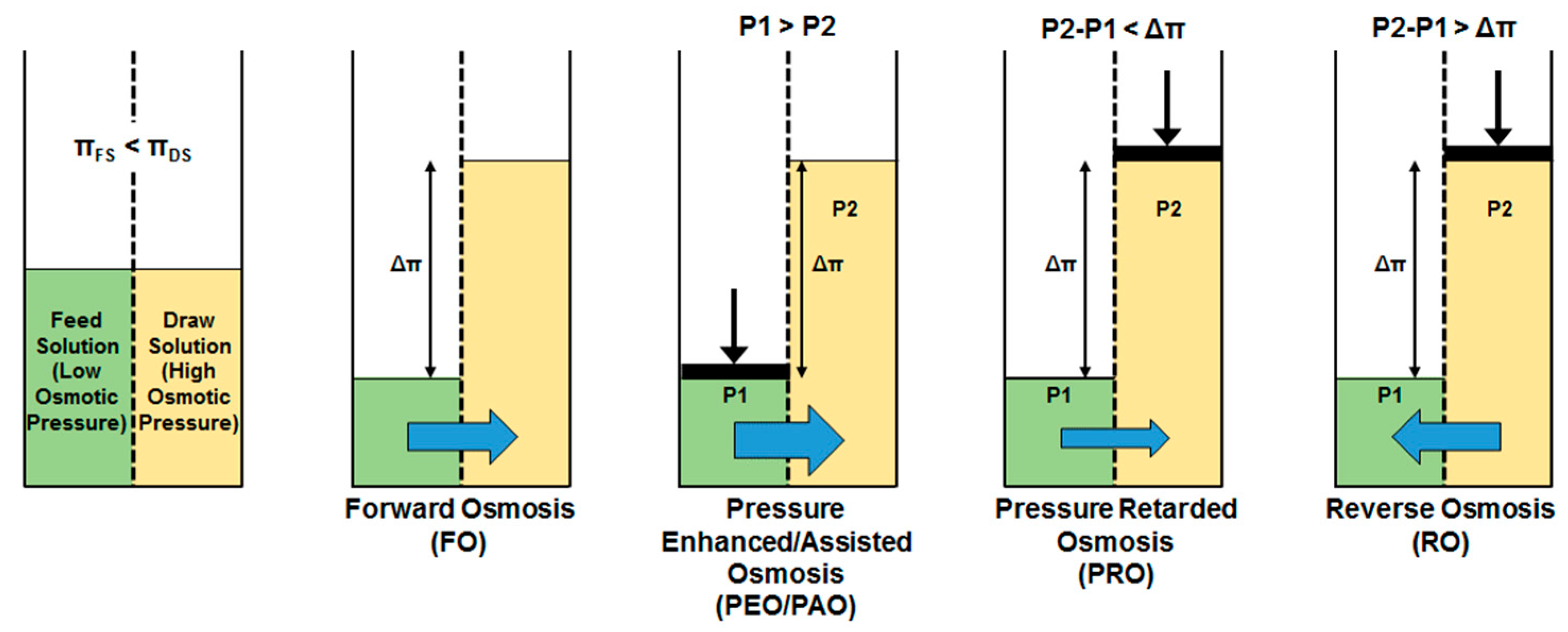
1.2. Forward Osmosis Technology
- low energy consumption,
- simultaneous treatment of two streams in one treatment step,
- easy removability of fouling layers due to absence of compression,
- treatment of liquids that are not suitable for other membrane processes.
- gases and volatile compounds,
- inorganic draw solutes (e.g., salts),
- organic draw solutes (e.g., sugar, organic ionic liquids, switchable polarity solvents (SPS), organic ionic salts, polyelectrolytes, polymers, hydrogels),
- functionalized nanoparticles.
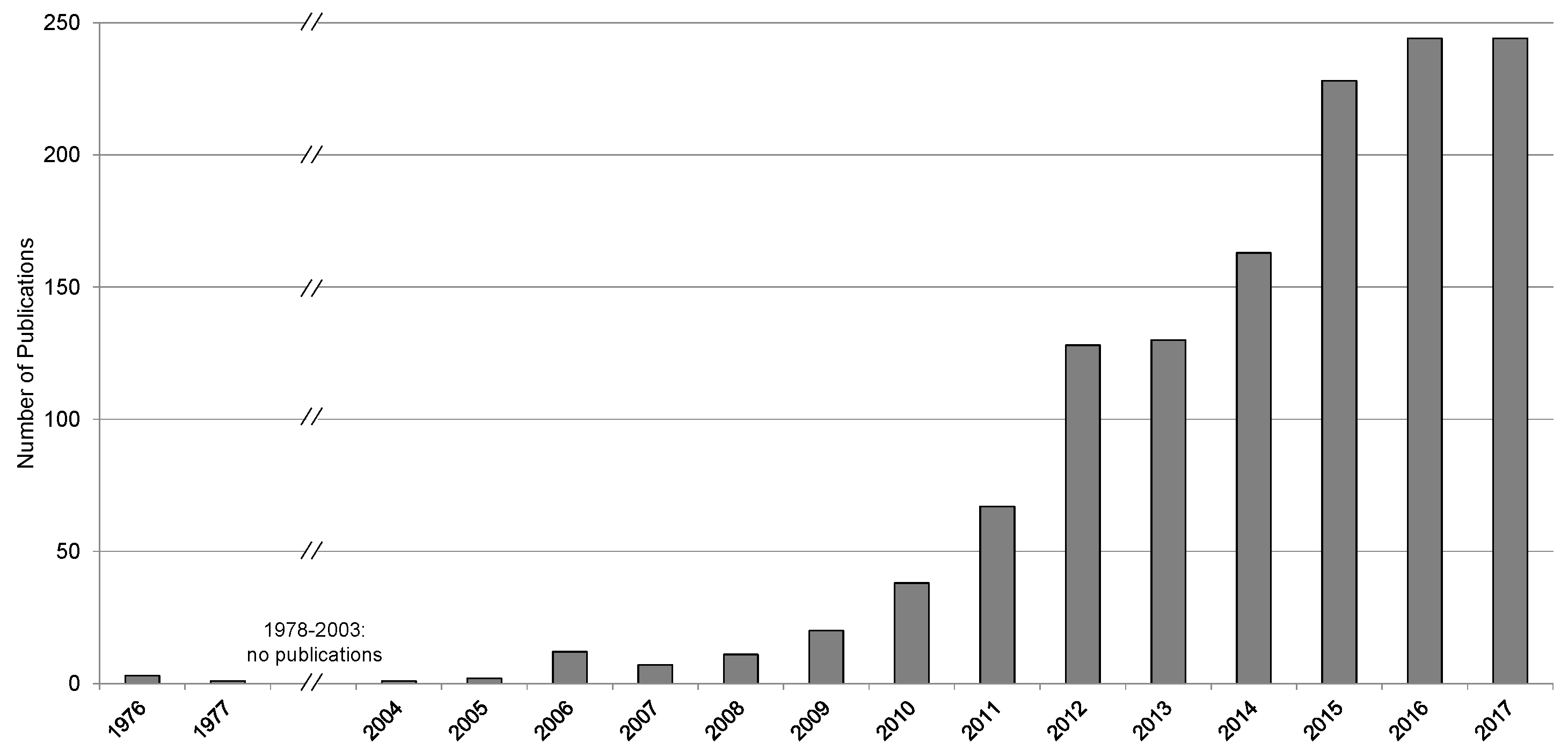
2. Forward Osmosis Application—State of Implementation
2.1. Bench- and Lab-Scale
2.2. Pilot-Scale
2.3. Industrial Scale
- De.mem Ltd. (Singapore) [73],
- Fluid Technology Solutions, Inc. (FTS, Albany, OR, USA) [74],
- Hydration Technology Innovations, LLC (HTI, Albany, OR, USA)—meanwhile out of business [52],
- Porifera, Inc. (Hayward, CA, USA) [55],
- Toray Chemical Korea, Inc. (Seoul, Korea) [52],
- Trevi Systems, Inc. (Petaluma, CA, USA) [77],
- W.O.G. Technologies Pte Ltd. (Singapore) [69].
2.4. Fields of Forward Osmosis Application
- emergency water supply with so-called hydration bags [78],
3. Application of Forward Osmosis Technology in Manufacturing Industries
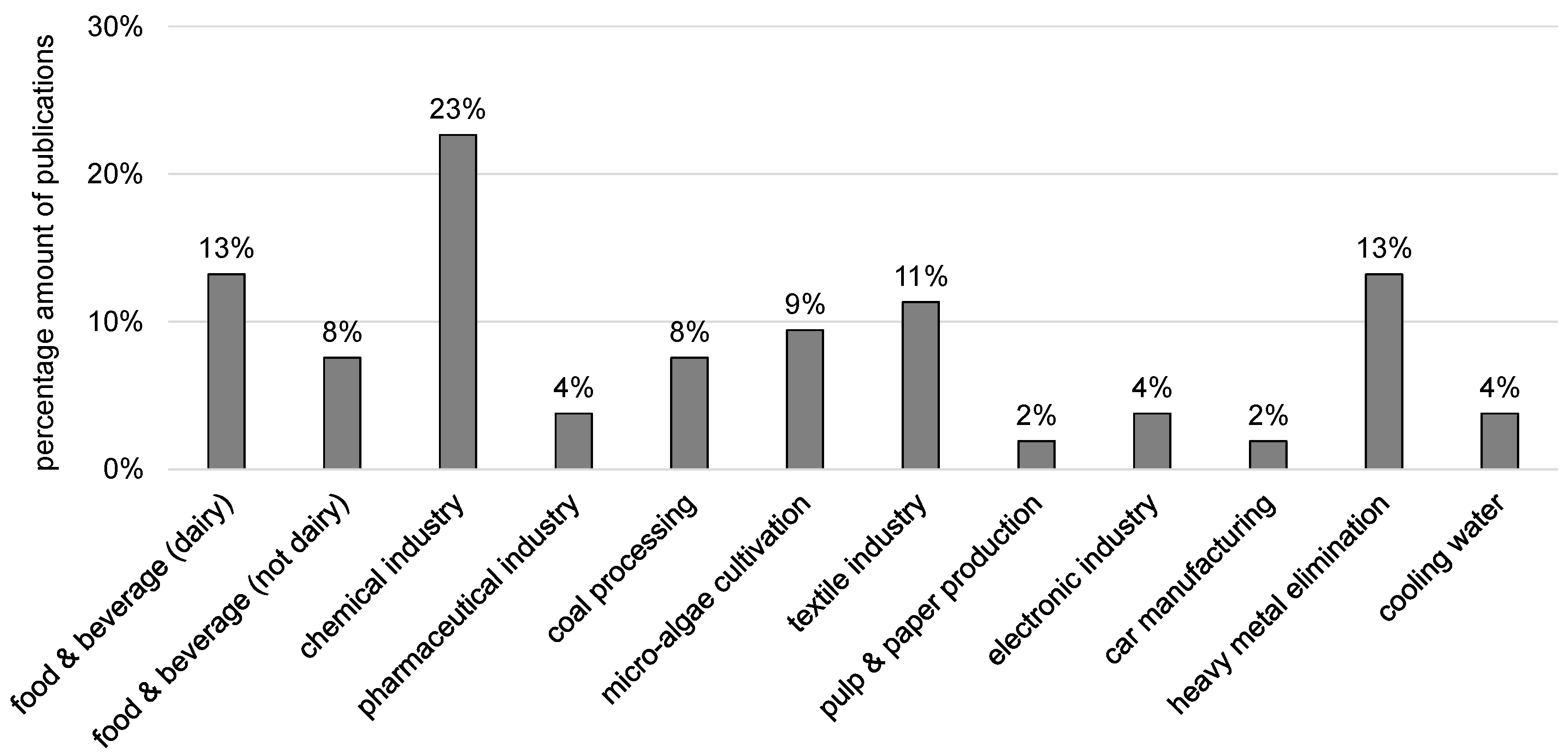
3.1. Overview
- food and beverage industry,
- chemical industry,
- pharmaceutical industry,
- coal processing industry,
- micro-algae cultivation,
- textile industry,
- pulp and paper industry,
- electronic industry,
- car manufacturing industry,
- industries with heavy metal usage.
3.2. Food & Beverage Industry
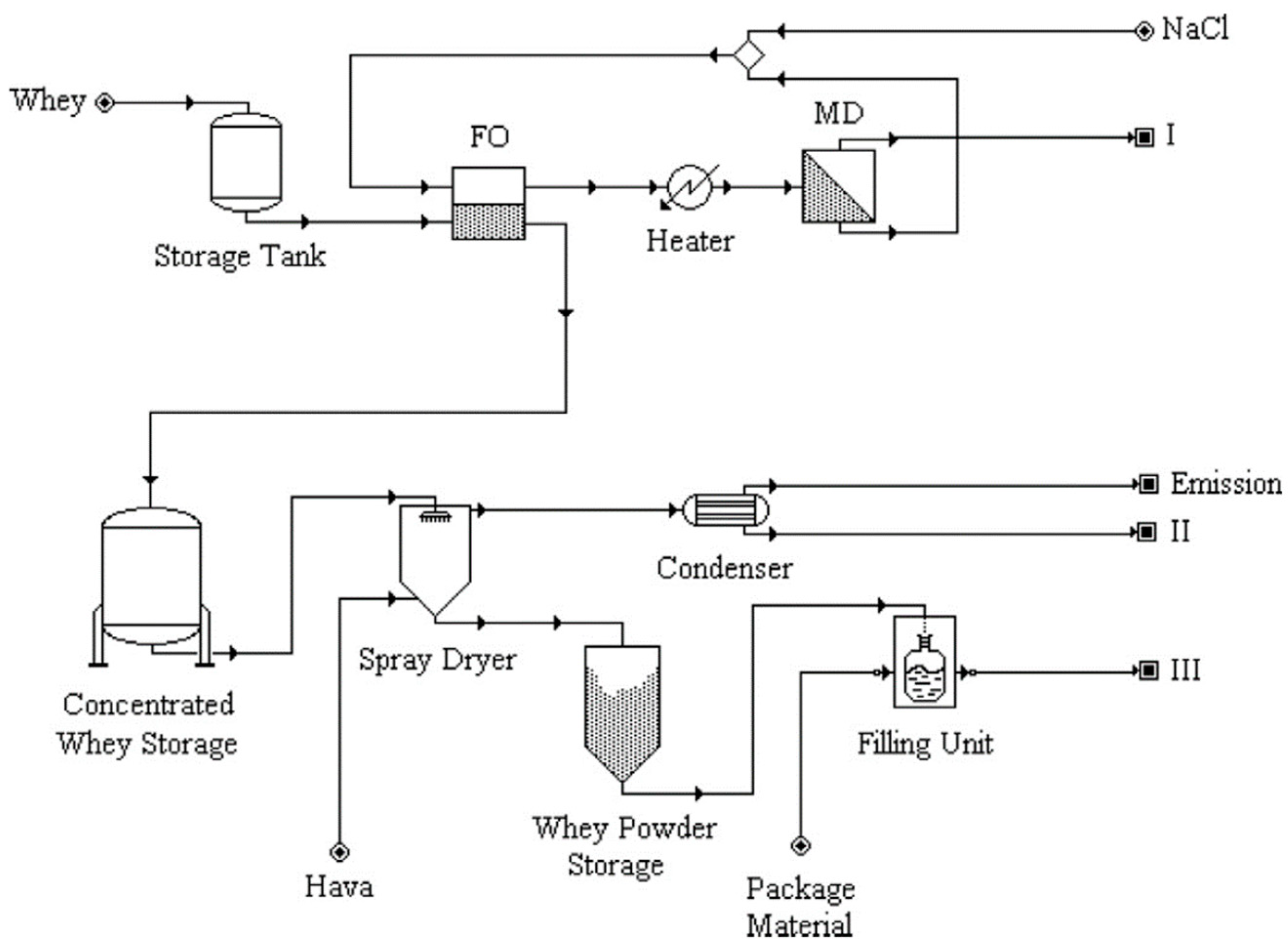
3.2.1. Dairy Industry
- forward osmosis with reverse osmosis (FO-RO, 2 M NH4HCO3 as DS with thermal enhanced DS regeneration) [106],
3.2.2. Juice Processing
3.2.3. Other Food & Beverage Application
3.3. Chemical Industry
3.4. Pharmaceutical Industry
3.5. Coal Processing
3.6. Micro Algae Cultivation
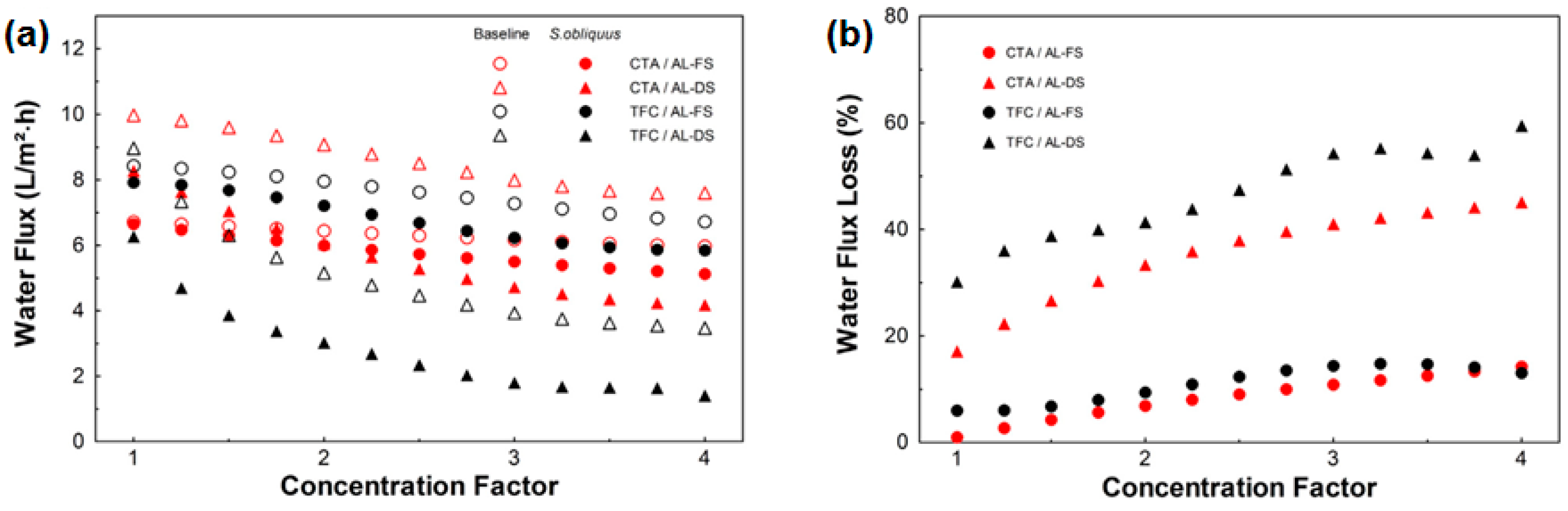
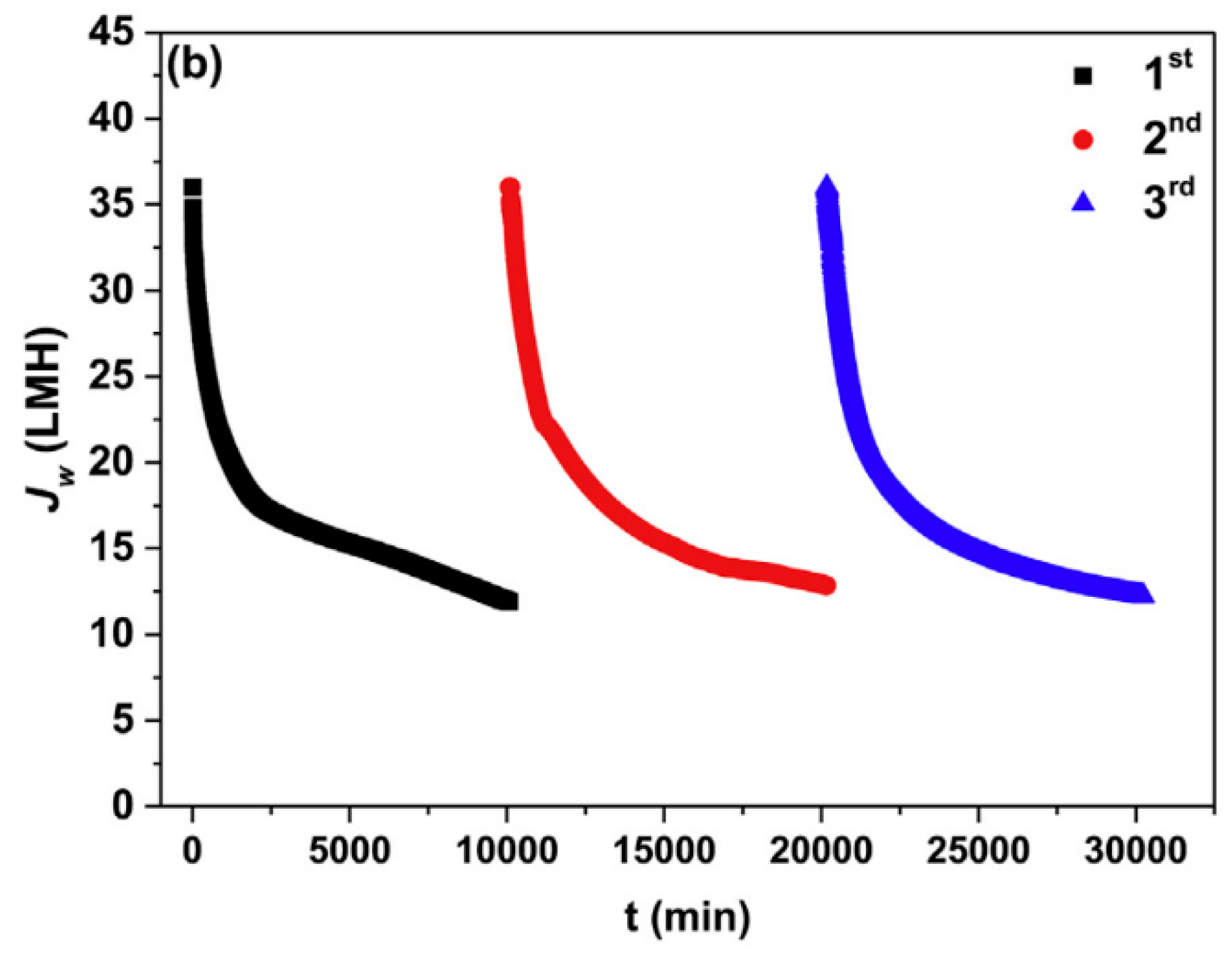
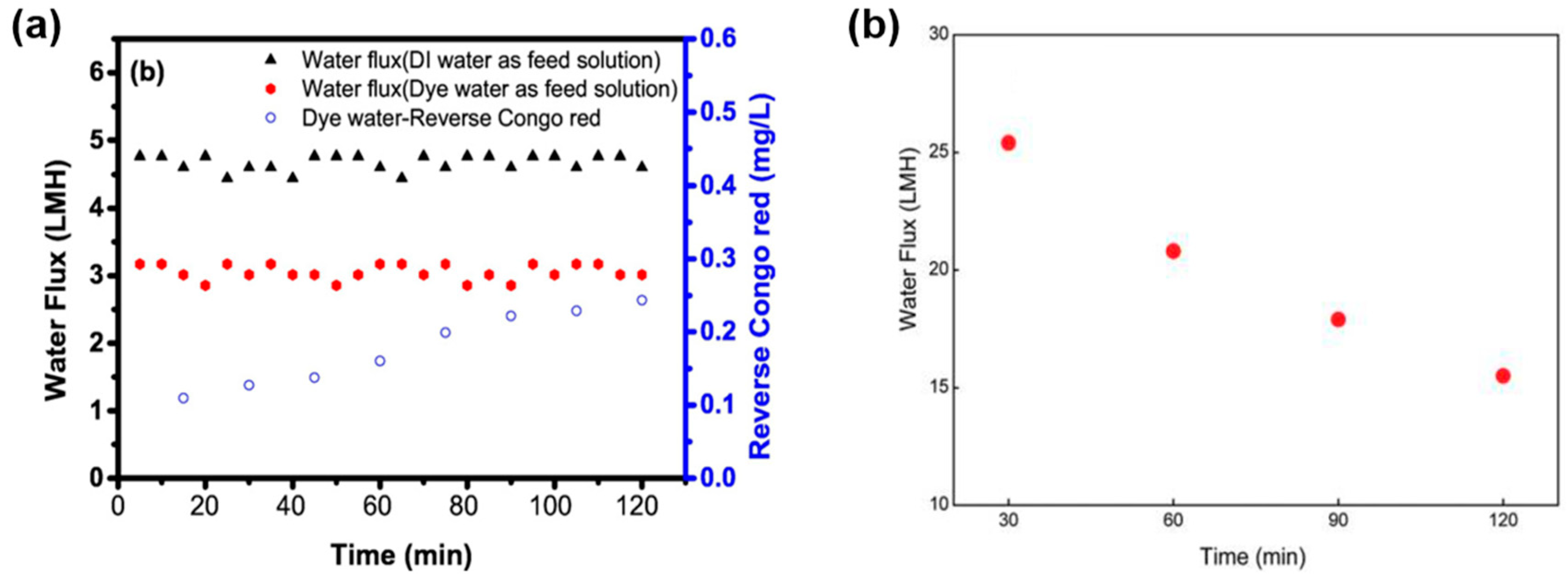
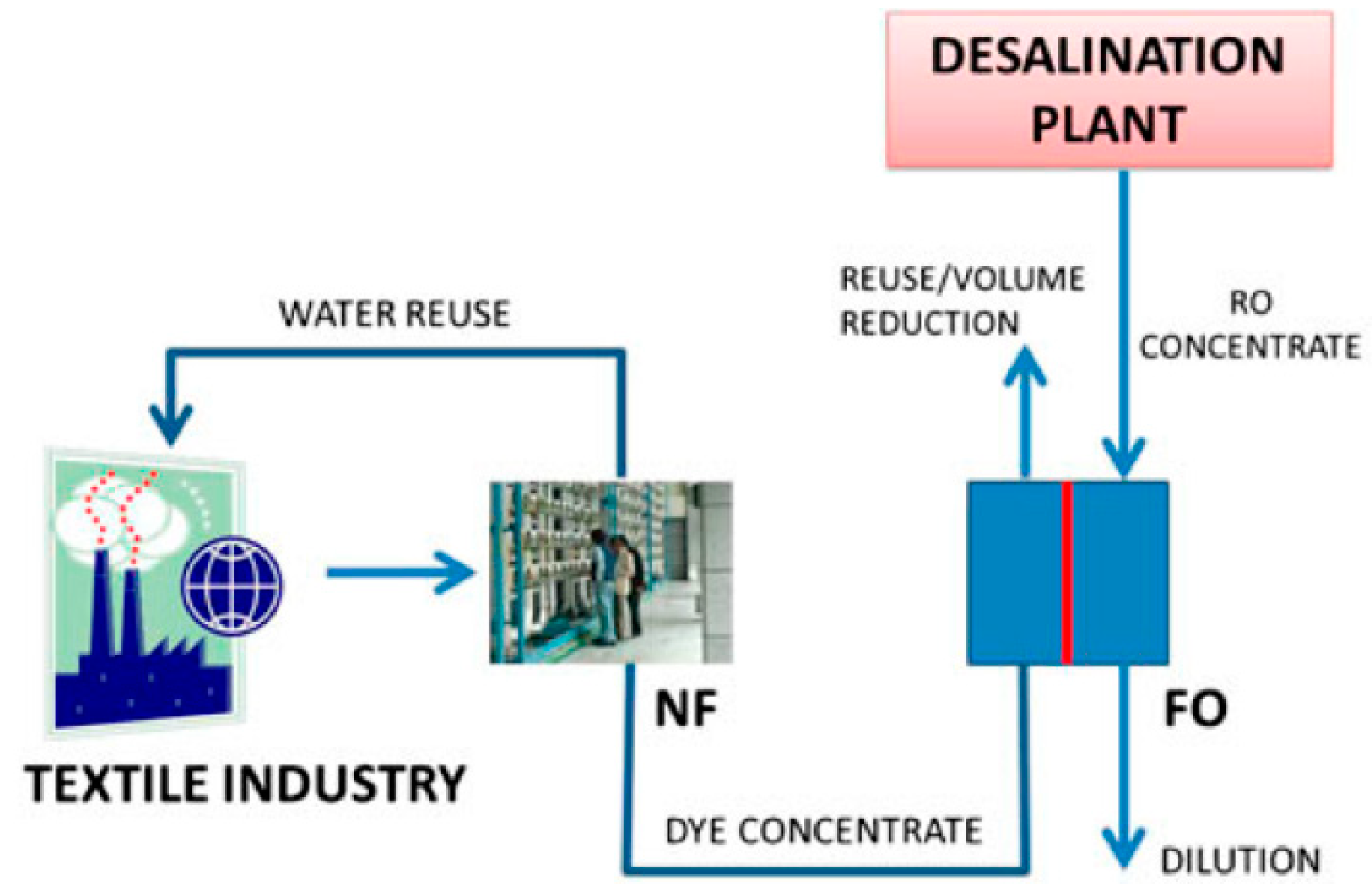
3.7. Textile Industry
3.8. Pulp and Paper Production
3.9. Electronic Industry
3.10. Car Manufacturing Wastewater
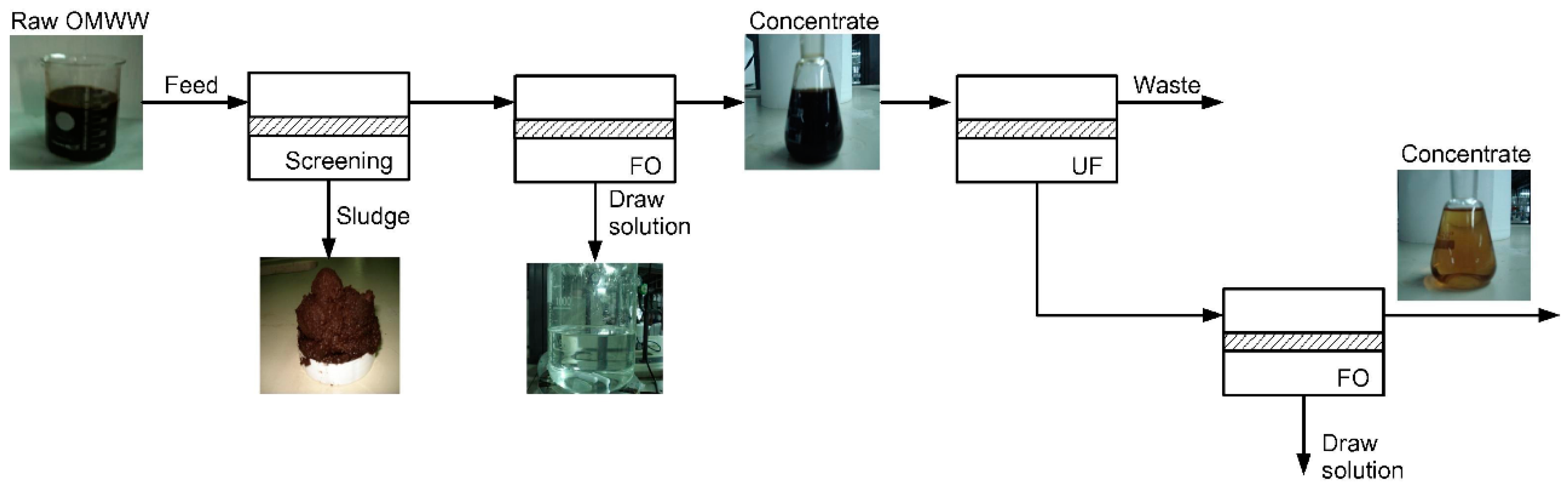
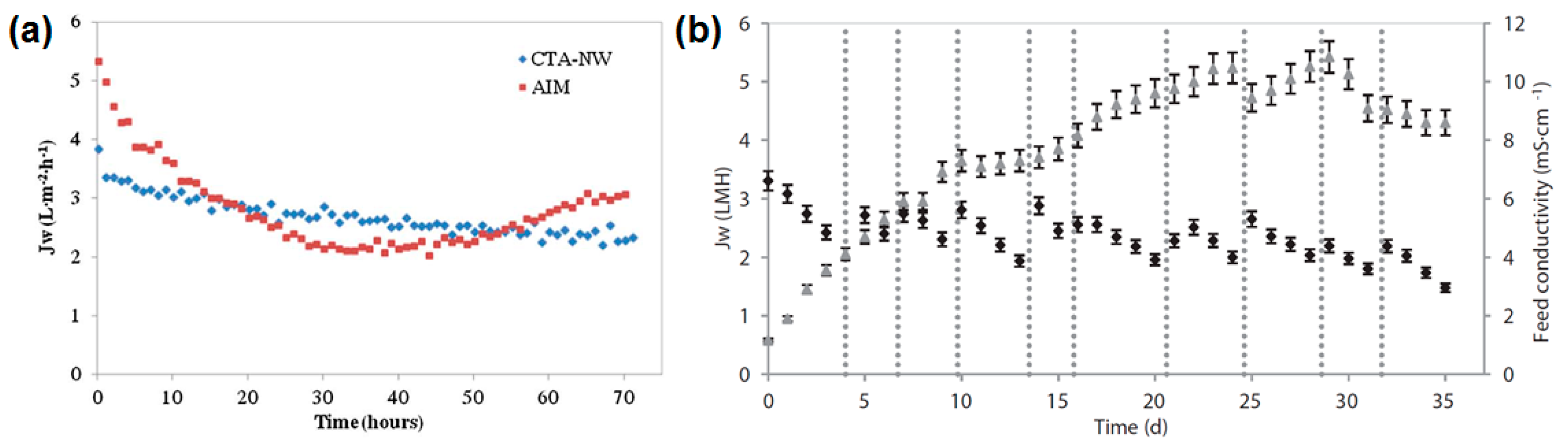
3.11. General Industrial Application
4. Concluding Remarks
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development (A/RES/70/1); United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ait-Kadi, M. Water for Development and Development for Water: Realizing the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Vision. Aquat. Procedia 2016, 6, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WWAP. The United Nations World Water Development Report 2017: Wastewater, The Untapped Resource; WWAP (United Nations World Water Assessment Programme); UNESCO: Paris, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cath, T.Y.; Childress, A.E.; Elimelech, M. Forward osmosis: Principles, applications, and recent developments. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 281, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazlan, N.M.; Peshev, D.; Livingston, A.G. Energy consumption for desalination—A comparison of forward osmosis with reverse osmosis, and the potential for perfect membranes. Desalination 2016, 377, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zou, S.; Zhang, B.; Wang, L.; He, Z. Forward osmosis promoted in-situ formation of struvite with simultaneous water recovery from digested swine wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 342, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodi, T.; Didaskalou, C.; Kupai, J.; Balogh, G.T.; Huszthy, P.; Szekely, G. Nanofiltration-Enabled In Situ Solvent and Reagent Recycle for Sustainable Continuous-Flow Synthesis. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 3435–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaepertoens, M.; Didaskalou, C.; Kim, J.F.; Livingston, A.G.; Szekely, G. Solvent recycle with imperfect membranes: A semi-continuous workaround for diafiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 514, 646–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chávez-Castilla, L.R.; Aguilar, O. An integrated process for the in situ recovery of prodigiosin using micellar ATPS from a culture of Serratia marcescens. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2016, 91, 2896–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zou, L.; Tang, C.Y.; Mulcahy, D. Recent developments in forward osmosis: Opportunities and challenges. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 396, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreedhar, I.; Khaitan, S.; Gupta, R.; Reddy, B.M.; Venugopal, A. An odyssey of process and engineering trends in forward osmosis. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2018, 4, 129–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCutcheon, J.R. Forward osmosis: A technology platform here to stay. Desalination 2017, 421, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, T.-S.; Luo, L.; Wan, C.F.; Cui, Y.; Amy, G. What is next for forward osmosis (FO) and pressure retarded osmosis (PRO). Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 156, 856–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, P.; Sewilam, H. Forward osmosis: An alternative sustainable technology and potential applications in water industry. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2015, 17, 2079–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, D.L.; Werber, J.R.; Jaramillo, H.; Lin, S.; Elimelech, M. Forward osmosis: Where are we now? Desalination 2015, 356, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, T.-S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, K.Y.; Su, J.; Ling, M.M. Forward osmosis processes: Yesterday, today and tomorrow. Desalination 2012, 287, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, L.A.; Phillip, W.A.; Tiraferri, A.; Yip, N.Y.; Elimelech, M. Forward with Osmosis: Emerging Applications for Greater Sustainability. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9824–9830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, Y.; Mulcahy, D.; Zou, L.; Kim, I.S. A Short Review of Membrane Fouling in Forward Osmosis Processes. Membranes 2017, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Liu, X.; Li, H. A review of forward osmosis membrane fouling: Types, research methods and future prospects. Environ. Technol. Rev. 2017, 6, 26–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Q.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G.; Tang, C.Y. Membrane fouling in osmotically driven membrane processes: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 499, 201–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Gwak, G.; Hong, S. Review on methodology for determining forward osmosis (FO) membrane characteristics: Water permeability (A), solute permeability (B), and structural parameter (S). Desalination 2017, 422, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.J.; Suwaileh, W.A.; Mohammed, A.W.; Hilal, N. Osmotic’s potential: An overview of draw solutes for forward osmosis. Desalination 2018, 434, 100–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Hu, X. ‘Matthew’ A critical review on draw solutes development for forward osmosis. Desalination 2016, 391, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, T.C.; Tao, T.; Zhou, A.; Chen, L.; Bie, X. A review on the recovery methods of draw solutes in forward osmosis. J. Water Process Eng. 2014, 4, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandin, G.; Verliefde, A.R.D.; Comas, J.; Rodriguez-Roda, I.; Le-Clech, P. Efficiently Combining Water Reuse and Desalination through Forward Osmosis—Reverse Osmosis (FO-RO) Hybrids: A Critical Review. Membranes 2016, 6, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chekli, L.; Phuntsho, S.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, J.; Choi, J.Y.; Choi, J.-S.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.H.; Hong, S.; Sohn, J.; et al. A comprehensive review of hybrid forward osmosis systems: Performance, applications and future prospects. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 497, 430–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou El-Nour, F.H. Water Desalination Studies Using Forward Osmosis Technology, a Review. Arab J. Nucl. Sci. Appl. 2016, 49, 167–176. [Google Scholar]
- Qasim, M.; Darwish, N.A.; Sarp, S.; Hilal, N. Water desalination by forward (direct) osmosis phenomenon: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2015, 374, 47–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akther, N.; Sodiq, A.; Giwa, A.; Daer, S.; Arafat, H.A.; Hasan, S.W. Recent advancements in forward osmosis desalination: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 281, 502–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valladares Linares, R.; Li, Z.; Sarp, S.; Bucs, S.S.; Amy, G.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S. Forward osmosis niches in seawater desalination and wastewater reuse. Water Res. 2014, 66, 122–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.-J.; Lay, W.C.L.; Kekre, K.A. Recent developments and future challenges of forward osmosis for desalination: A review. Desalination Water Treat. 2012, 39, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutchmiah, K.; Verliefde, A.R.D.; Roest, K.; Rietveld, L.C.; Cornelissen, E.R. Forward osmosis for application in wastewater treatment: A review. Water Res. 2014, 58, 179–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munirasu, S.; Haija, M.A.; Banat, F. Use of membrane technology for oil field and refinery produced water treatment—A review. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2016, 100, 183–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coday, B.D.; Xu, P.; Beaudry, E.G.; Herron, J.; Lampi, K.; Hancock, N.T.; Cath, T.Y. The sweet spot of forward osmosis: Treatment of produced water, drilling wastewater, and other complex and difficult liquid streams. Desalination 2014, 333, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, N.K. Opportunities and Challenges in Application of Forward Osmosis in Food Processing. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 266–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, A.J.; Hai, F.I.; Price, W.E.; Drewes, J.E.; Nghiem, L.D. Forward osmosis as a platform for resource recovery from municipal wastewater—A critical assessment of the literature. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 529, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chang, V.W.C.; Tang, C.Y. Osmotic membrane bioreactor (OMBR) technology for wastewater treatment and reclamation: Advances, challenges, and prospects for the future. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 504, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCutcheon, J.R.; Elimelech, M. Influence of concentrative and dilutive internal concentration polarization on flux behavior in forward osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 284, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yangali-Quintanilla, V.; Li, Z.; Valladares, R.; Li, Q.; Amy, G. Indirect desalination of Red Sea water with forward osmosis and low pressure reverse osmosis for water reuse. Desalination 2011, 280, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGinnis, R.L.; Elimelech, M. Energy requirements of ammonia–carbon dioxide forward osmosis desalination. Desalination 2007, 207, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoll, P.G. Forward Osmosis a Brief Introduction. In Proceedings IDA World Congress on Desalination and Water Reuse; IDA (International Desalination Association): Tianjin, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Votta, F.; Barnett, S.M.; Anderson, D.K. Concentration of industrial waste by direct osmosis. In Completion Report; University of Rhode Island: Kingston, RI, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, D.K. Concentration of Dilute Industrial Wastes by Direct Osmosis. Master’s Thesis, University of Rhode Island, Kingston, RI, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.P.; Arnot, T.C.; Mattia, D. A review of reverse osmosis membrane materials for desalination—Development to date and future potential. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 370, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Yan, Y.; Wang, H. Recent advances in polymer and polymer composite membranes for reverse and forward osmosis processes. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 61, 104–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Chen, Q.; Ge, Q. Recent advances in forward osmosis (FO) membrane: Chemical modifications on membranes for FO processes. Desalination 2017, 419, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razali, M.; Kim, J.F.; Attfield, M.; Budd, P.M.; Drioli, E.; Lee, Y.M.; Szekely, G. Sustainable wastewater treatment and recycling in membrane manufacturing. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 5196–5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Yasukawa, M.; Matsuyama, H. Highly condensed polyvinyl chloride latex production by forward osmosis: Performance and characteristics. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 514, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lei, X.; Wang, L.; Jia, J.; Liang, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, H. Investigation on the removal performances of heavy metal ions with the layer-by-layer assembled forward osmosis membranes. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 327, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.-X.; Low, Z.-X.; Feng, Y.; Wei, J.; Wang, H. Investigating forward osmosis process for simultaneous preparation of brown coal slurry and wastewater reclamation. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 131, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuntsho, S.; Kim, J.E.; Johir, M.A.H.; Hong, S.; Li, Z.; Ghaffour, N.; Leiknes, T.; Shon, H.K. Fertiliser drawn forward osmosis process: Pilot-scale desalination of mine impaired water for fertigation. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 508, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Blandin, G.; Phuntsho, S.; Verliefde, A.; Le-Clech, P.; Shon, H. Practical considerations for operability of an 8″ spiral wound forward osmosis module: Hydrodynamics, fouling behaviour and cleaning strategy. Desalination 2017, 404, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Phuntsho, S.; Lotfi, F.; Shon, H.K. Investigation of pilot-scale 8040 FO membrane module under different operating conditions for brackish water desalination. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 53, 2782–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Im, S.-J.; Jeong, S.; Jang, A. Evaluation of an element-scale plate-type forward osmosis: Effect of structural parameters and operational conditions. Desalination 2018, 430, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, Y.C. Performance analysis of plate-and-frame forward osmosis membrane elements and implications for scale-up design. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 550, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazner, C.; Wünsch, R.; Remmen, K.; Wintgens, T. Membranbasierte Behandlungsverfahren für hoch-belastete Abwässer in der Chemieindustrie mit dem Ziel Zero-Liquid-Discharge. In Proceedings of the 89. Darmstädter Seminar Abwassertechnik, Darmstadt, Germany, 18 January 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wünsch, R.; Remmen, K.; Pătruț, C.; Dijk, L.; Moerland, M.; Palacin, J.; Kochan, J.; Kazner, C. Water Recovery by Forward Osmosis from Challenging Industrial Effluents towards Zero Liquid Discharge: Selection of a Suitable Draw Solution. In Proceedings of the 12. Aachener Tagung Wassertechnologie, Aachen, Germany, 24–25 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- INSPIREWATER—Innovative Solutions in the Process Industry for Next Generation Resource Efficient Water Management|SPIRE. Available online: https://www.spire2030.eu/inspirewater (accessed on 8 June 2018).
- Aquaporin|Singapore Is Increasing Its Waste Water Reuse. Available online: https://aquaporin.dk/2017/07/10/singapore-is-increasing-its-waste-water-reuse/ (accessed on 8 June 2018).
- Milk Concentration with Porifera. Available online: https://www.porifera.com/food-and-beverage/ (accessed on 8 June 2018).
- Aquaporin|Arla Featuring Aquaporin InsideTM in the Dairy Industry. Available online: https://aquaporin.dk/2017/09/20/arla-featuring-aquaporin-inside-in-the-dairy-industry/ (accessed on 8 June 2018).
- Modern Water Modern Water secures sale of FO system to China’s Hangzhou Water. Membr. Technol. 2017, 2017, 5–6. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0958211817301118 (accessed on 22 July 2018). [CrossRef]
- Modern Water makes first forward osmosis technology sale in China. Pump Ind. Anal. 2017, 2017, 2. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S135961281730126X (accessed on 22 July 2018). [CrossRef]
- Modern Water makes first FO technology sale in China. Filtr. Sep. 2017, 54, 4. [CrossRef]
- Oasys Water—Case Study: Wastewater: Changxing. Available online: http://oasyswater.com/case-study-post/changxing/ (accessed on 8 June 2018).
- Aquaporin launches commercial forward osmosis element. Membr. Technol. 2017, 2017, 2. [CrossRef]
- Aquaporin sets up first full-scale production plant at its headquarters. Membr. Technol. 2017, 2017, 5. [CrossRef]
- Aquaporin Asia receives first prototypes of spiral-wound FO elements. Membr. Technol. 2017, 2017, 1. [CrossRef]
- Aquaporin and WOG study FO as a pre-concentration step for ZLD. Membr. Technol. 2016, 2016, 2–3. [CrossRef]
- Remmen, K.; Wünsch, R.; Heisele, A.; Dijk, L.; Schwantes, R.; Wintgens, T.; Kazner, C. Optimization of Forward Osmosis in challenging environmental applications. In Proceedings of the 11th IWA International Conference on Water Reclamation and Reuse, Long Beach, CA, USA, 23–27 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Aquaporin and Darco pilot low-energy ZLD systems based on FO technology. Membr. Technol. 2016, 2016, 16. [CrossRef]
- Darco collaborates with Aquaporin on FO project. Pump Ind. Anal. 2016, 2016, 4. [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, S. De. mem adds membrane technology with large market potential to its proprietary technology portfolio. Membr. Technol. 2018, 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Nghiem, L.D.; Song, J.; Bao, R.; Li, X.; He, T. Phenol rejection by cellulose triacetate and thin film composite forward osmosis membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 186, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Growth of activity in China expands commercialisation of Oasys’ FO-based ZLD technology. Membr. Technol. 2016, 2016, 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Oasys enhances its ClearFlo technology platform. Membr. Technol. 2017, 2017, 2–3. [CrossRef]
- Trevi Systems reports “lowest energy use” from forward osmosis desalination trial in Abu Dhabi. Water Wastewater International WWi, 7 March 2017.
- Loo, S.-L.; Fane, A.G.; Krantz, W.B.; Lim, T.-T. Emergency water supply: A review of potential technologies and selection criteria. Water Res. 2012, 46, 3125–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coday, B.D.; Hoppe-Jones, C.; Wandera, D.; Shethji, J.; Herron, J.; Lampi, K.; Snyder, S.A.; Cath, T.Y. Evaluation of the transport parameters and physiochemical properties of forward osmosis membranes after treatment of produced water. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 499, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiruvenkatachari, R.; Francis, M.; Cunnington, M.; Su, S. Application of integrated forward and reverse osmosis for coal mine wastewater desalination. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 163, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Minier-Matar, J.; Chou, S.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G.; Adham, S. Gas field produced/process water treatment using forward osmosis hollow fiber membrane: Membrane fouling and chemical cleaning. Desalination 2017, 402, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, P.; Fu, X.; Chung, T.-S. Sustainable water recovery from oily wastewater via forward osmosis-membrane distillation (FO-MD). Water Res. 2014, 52, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chekli, L.; Kim, Y.; Phuntsho, S.; Li, S.; Ghaffour, N.; Leiknes, T.; Shon, H.K. Evaluation of fertilizer-drawn forward osmosis for sustainable agriculture and water reuse in arid regions. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 187, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chekli, L.; Kim, J.E.; El Saliby, I.; Kim, Y.; Phuntsho, S.; Li, S.; Ghaffour, N.; Leiknes, T.; Kyong Shon, H. Fertilizer drawn forward osmosis process for sustainable water reuse to grow hydroponic lettuce using commercial nutrient solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 181, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Phuntsho, S.; Chekli, L.; Hong, S.; Ghaffour, N.; Leiknes, T.; Choi, J.Y.; Shon, H.K. Environmental and economic impacts of fertilizer drawn forward osmosis and nanofiltration hybrid system. Desalination 2017, 416, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, Y. Performance evaluation of a microfiltration-osmotic membrane bioreactor (MF-OMBR) during removing silver nanoparticles from simulated wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luján-Facundo, M.J.; Soler-Cabezas, J.L.; Mendoza-Roca, J.A.; Vincent-Vela, M.C.; Bes-Piá, A.; Doñate-Hernández, S. A study of the osmotic membrane bioreactor process using a sodium chloride solution and an industrial effluent as draw solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 322, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandin, G.; Gautier, C.; Sauchelli Toran, M.; Monclús, H.; Rodriguez-Roda, I.; Comas, J. Retrofitting membrane bioreactor (MBR) into osmotic membrane bioreactor (OMBR): A pilot scale study. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 339, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelissen, E.R.; Harmsen, D.; de Korte, K.F.; Ruiken, C.J.; Qin, J.-J.; Oo, H.; Wessels, L.P. Membrane fouling and process performance of forward osmosis membranes on activated sludge. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 319, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Nghiem, L.D.; Price, W.E.; Elimelech, M. Toward Resource Recovery from Wastewater: Extraction of Phosphorus from Digested Sludge Using a Hybrid Forward Osmosis–Membrane Distillation Process. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2014, 1, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway, R.W.; Childress, A.E.; Dennett, K.E.; Cath, T.Y. Forward osmosis for concentration of anaerobic digester centrate. Water Res. 2007, 41, 4005–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Zou, S.; Yang, Y.; Qian, G.; He, Z. Enhancing the performance of an osmotic microbial fuel cell through self-buffering with reverse-fluxed sodium bicarbonate. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 349, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M.; Hynes, E.A.; Abu-Reesh, I.M.; He, Z. Ammonium removal from synthetic wastewater promoted by current generation and water flux in an osmotic microbial fuel cell. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 149, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Qin, M.; Yang, X.; He, Z. Sustainable operation of osmotic microbial fuel cells through effective reproduction of polyelectrolyte draw solutes facilitated by cathodic pH increase. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 168, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, E.; Chae, K.-J.; Alayande, A.B.; Kim, K.-Y.; Kim, I.S. Concurrent performance improvement and biofouling mitigation in osmotic microbial fuel cells using a silver nanoparticle-polydopamine coated forward osmosis membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 513, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mamun, A.; Baawain, M.S.; Dhar, B.R.; Kim, I.S. Improved recovery of bioenergy and osmotic water in an osmotic microbial fuel cell using micro-diffuser assisted marine aerobic biofilm on cathode. Biochem. Eng. J. 2017, 128, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, Y. Integrating microbial fuel cells with anaerobic acidification and forward osmosis membrane for enhancing bio-electricity and water recovery from low-strength wastewater. Water Res. 2017, 110, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Brastad, K.S.; He, Z. Integrating Forward Osmosis into Microbial Fuel Cells for Wastewater Treatment, Water Extraction and Bioelectricity Generation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 6690–6696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, M.; Luo, W.; Guo, H.; Nghiem, L.D.; Tang, C.Y.; Gray, S.R. Trace organic contaminant rejection by aquaporin forward osmosis membrane: Transport mechanisms and membrane stability. Water Res. 2018, 132, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alturki, A.A.; McDonald, J.A.; Khan, S.J.; Price, W.E.; Nghiem, L.D.; Elimelech, M. Removal of trace organic contaminants by the forward osmosis process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 103, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Price, W.E.; Nghiem, L.D.; Elimelech, M. Effects of feed and draw solution temperature and transmembrane temperature difference on the rejection of trace organic contaminants by forward osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 438, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Nghiem, L.D.; Price, W.E.; Elimelech, M. Comparison of the removal of hydrophobic trace organic contaminants by forward osmosis and reverse osmosis. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2683–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, N.T.; Xu, P.; Heil, D.M.; Bellona, C.; Cath, T.Y. Comprehensive Bench- and Pilot-Scale Investigation of Trace Organic Compounds Rejection by Forward Osmosis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 8483–8490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valladares Linares, R.; Yangali-Quintanilla, V.; Li, Z.; Amy, G. Rejection of micropollutants by clean and fouled forward osmosis membrane. Water Res. 2011, 45, 6737–6744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, F.; Prazeres, A.R.; Rivas, J. Cheese whey wastewater: Characterization and treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 445, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydiner, C.; Sen, U.; Koseoglu-Imer, D.Y.; Can Dogan, E. Hierarchical prioritization of innovative treatment systems for sustainable dairy wastewater management. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 4605–4617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydiner, C.; Sen, U.; Topcu, S.; Ekinci, D.; Altinay, A.D.; Koseoglu-Imer, D.Y.; Keskinler, B. Techno-economic viability of innovative membrane systems in water and mass recovery from dairy wastewater. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 458, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydiner, C.; Sen, U.; Topcu, S.; Sesli, D.; Ekinci, D.; Altınay, A.D.; Ozbey, B.; Koseoglu-Imer, D.Y.; Keskinler, B. Techno-economic investigation of water recovery and whey powder production from whey using UF/RO and FO/RO integrated membrane systems. Desalin. Water Treat. 2014, 52, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydiner, C.; Topcu, S.; Tortop, C.; Kuvvet, F.; Ekinci, D.; Dizge, N.; Keskinler, B. A novel implementation of water recovery from whey: “Forward–reverse osmosis” integrated membrane system. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 51, 786–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seker, M.; Buyuksari, E.; Topcu, S.; Babaoglu, D.S.; Celebi, D.; Keskinler, B.; Aydiner, C. Effect of pretreatment and membrane orientation on fluxes for concentration of whey with high foulants by using NH3/CO2 in forward osmosis. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 243, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seker, M.; Buyuksari, E.; Topcu, S.; Sesli, D.; Celebi, D.; Keskinler, B.; Aydiner, C. Effect of process parameters on flux for whey concentration with NH3/CO2 in forward osmosis. Food Bioprod. Process. 2017, 105, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-N.; Wang, R.; Li, W.; Tang, C.Y. Whey recovery using forward osmosis—Evaluating the factors limiting the flux performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 533, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, P.; Nayak, J. Development and analysis of a sustainable technology in manufacturing acetic acid and whey protein from waste cheese whey. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Xie, F.; Chen, W.; Liu, J. FO/MD hybrid system for real dairy wastewater recycling. Environ. Technol. 2017, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haupt, A.; Lerch, A. Forward osmosis treatment of effluents from dairy and automobile industry—Results from short-term experiments to show general applicability. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Marques, M.P.; Alves, V.D.; Coelhoso, I.M. Concentration of Tea Extracts by Osmotic Evaporation: Optimisation of Process Parameters and Effect on Antioxidant Activity. Membranes 2016, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebreyohannes, A.Y.; Curcio, E.; Poerio, T.; Mazzei, R.; Di, P.; Drioli, E.; Giorno, L. Treatment of Olive Mill Wastewater by Forward Osmosis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 147, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Petrinic, I.; Hélix-Nielsen, C.; Basu, S.; Balakrishnan, M. Concentrating molasses distillery wastewater using biomimetic forward osmosis (FO) membranes. Water Res. 2018, 130, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salih, H.H.; Dastgheib, S.A. Treatment of a hypersaline brine, extracted from a potential CO2 sequestration site, and an industrial wastewater by membrane distillation and forward osmosis. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 325, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Lv, Z.; Yun, Y.; Li, J.; Li, C.; Zhu, S. Preparation of cellulose triacetate forward osmosis membranes for treating esterification wastewater. Desalin. Water Treat. 2017, 61, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler-Cabezas, J.L.; Mendoza-Roca, J.A.; Vincent-Vela, M.C.; Luján-Facundo, M.J.; Pastor-Alcañiz, L. Simultaneous concentration of nutrients from anaerobically digested sludge centrate and pre-treatment of industrial effluents by forward osmosis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 193, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, J.Y.; Mohammad, A.W. Osmotic concentration of succinic acid by forward osmosis: Influence of feed solution pH and evaluation of seawater as draw solution. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 26, 976–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.N.; Choi, J.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, J.W.; Park, S.; Kim, W.; Kim, T.-W.; Jung, K.; Park, G.; Kong, W.; et al. Method of Concentrating Low Titer Fermentation Broths Using Forward Osmosis. U.S. Patent 20120118827A1, 17 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, Y.H.; Lee, H.D.; Park, H.B. Integrated Membrane Processes for Separation and Purification of Organic Acid from a Biomass Fermentation Process. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 10207–10219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihalainen, H. Concentration of Lactic Acid by Forward Osmosis. Master’s Thesis, Lappeenranta University of Technology, Lappeenranta, Finland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kalafatakis, S.; Braekevelt, S.; Carlsen, V.; Lange, L.; Skiadas, I.V.; Gavala, H.N. On a novel strategy for water recovery and recirculation in biorefineries through application of forward osmosis membranes. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 311, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, M.; Yasukawa, M.; Sasaki, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Kondo, A.; Matsuyama, H. Up-concentration of sugars in pretreated-rice straw by an osmotic pressure-driven method. Biochem. Eng. J. 2017, 121, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, M.; Sasaki, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Yasukawa, M.; Takahashi, T.; Kondo, A.; Matsuyama, H. Development of combined nanofiltration and forward osmosis process for production of ethanol from pretreated rice straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 235, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruprakobkit, T.; Ruprakobkit, L.; Ratanatamskul, C. Carboxylic acid concentration by forward osmosis processes: Dynamic modeling, experimental validation and simulation. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 306, 538–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Chung, T.-S. Pharmaceutical concentration using organic solvent forward osmosis for solvent recovery. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.Y.; Teoh, M.M.; Nugroho, A.; Chung, T.-S. Integrated forward osmosis–membrane distillation (FO–MD) hybrid system for the concentration of protein solutions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 2421–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Pal, P. A novel forward osmosis-nano filtration integrated system for coke-oven wastewater reclamation. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2015, 100, 542–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, P.; Kumar, R. Treatment of Coke Wastewater: A Critical Review for Developing Sustainable Management Strategies. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2014, 43, 89–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, C.; Hou, D. Effects of feed solution pH and draw solution concentration on the performance of phenolic compounds removal in forward osmosis process. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2508–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, G.B.; Abdelaziz, A.E.M.; Hallenbeck, P.C. Algal biofuels: Challenges and opportunities. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 145, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markou, G.; Nerantzis, E. Microalgae for high-value compounds and biofuels production: A review with focus on cultivation under stress conditions. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 1532–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razzak, S.A.; Hossain, M.M.; Lucky, R.A.; Bassi, A.S.; de Lasa, H. Integrated CO2 capture, wastewater treatment and biofuel production by microalgae culturing—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 27, 622–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, W.; Soh, L.; Werber, J.R.; Elimelech, M.; Zimmerman, J.B. Application of membrane dewatering for algal biofuel. Algal Res. 2015, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilad, M.R.; Arafat, H.A.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Membrane technology in microalgae cultivation and harvesting: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 1283–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larronde-Larretche, M.; Jin, X. Microalgal biomass dewatering using forward osmosis membrane: Influence of microalgae species and carbohydrates composition. Algal Res. 2017, 23, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larronde-Larretche, M.; Jin, X. Microalgae (Scenedesmus obliquus) dewatering using forward osmosis membrane: Influence of draw solution chemistry. Algal Res. 2016, 15, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Wang, Y.-N.; Wicaksana, F.; Aung, T.; Wong, P.C.Y.; Fane, A.G.; Tang, C.Y. Direct microscopic observation of forward osmosis membrane fouling by microalgae: Critical flux and the role of operational conditions. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 436, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Gu, Y.; Xiao, D.; Tang, C.Y. The role of physical and chemical parameters on forward osmosis membrane fouling during algae separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 366, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckwalter, P.; Embaye, T.; Gormly, S.; Trent, J.D. Dewatering microalgae by forward osmosis. Desalination 2013, 312, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcucci, M.; Nosenzo, G.; Capannelli, G.; Ciabatti, I.; Corrieri, D.; Ciardelli, G. Treatment and reuse of textile effluents based on new ultrafiltration and other membrane technologies. Desalination 2001, 138, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holkar, C.R.; Jadhav, A.J.; Pinjari, D.V.; Mahamuni, N.M.; Pandit, A.B. A critical review on textile wastewater treatments: Possible approaches. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 182, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammar, A.; Dofan, I.; Jegatheesan, V.; Muthukumaran, S.; Shu, L. Comparison between nanofiltration and forward osmosis in the treatment of dye solutions. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 54, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Liang, C.-Z.; Chung, T.-S.; Weber, M.; Staudt, C.; Maletzko, C. Combination of forward osmosis (FO) process with coagulation/flocculation (CF) for potential treatment of textile wastewater. Water Res. 2016, 91, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Long, Q.; Xiong, S.; Shen, L.; Wang, Y. Application of poly (4-styrenesulfonic acid-co-maleic acid) sodium salt as novel draw solute in forward osmosis for dye-containing wastewater treatment. Desalination 2017, 421, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.; Wang, P.; Wan, C.; Chung, T.-S. Polyelectrolyte-Promoted Forward Osmosis–Membrane Distillation (FO–MD) Hybrid Process for Dye Wastewater Treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6236–6243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Gao, B.; Xu, S.; Kong, J.; Ma, D.; Shon, H.K.; Yue, Q.; Liu, P. Polyelectrolyte-promoted forward osmosis process for dye wastewater treatment—Exploring the feasibility of using polyacrylamide as draw solute. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 264, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
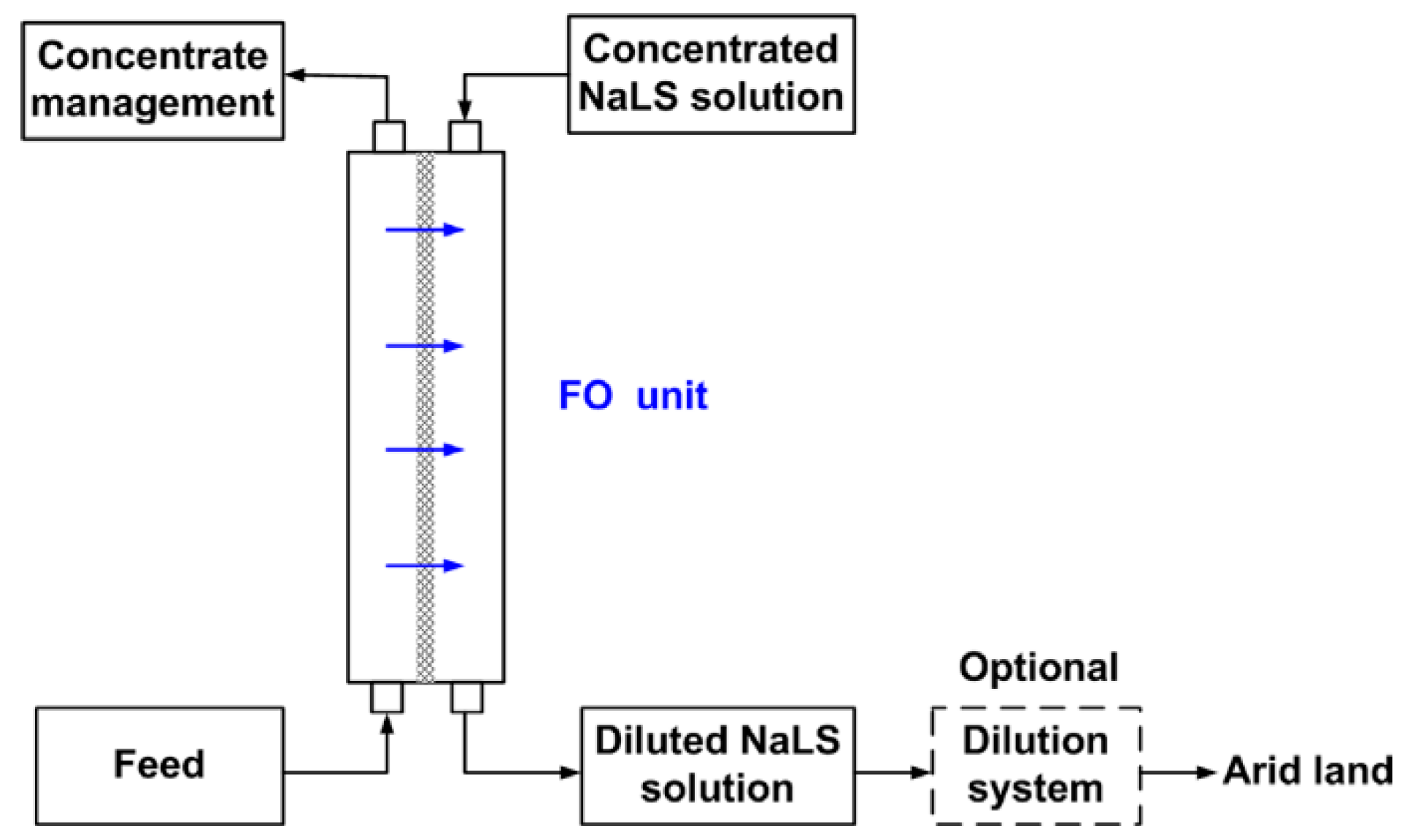
- Duan, J.; Litwiller, E.; Choi, S.-H.; Pinnau, I. Evaluation of sodium lignin sulfonate as draw solute in forward osmosis for desert restoration. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 453, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
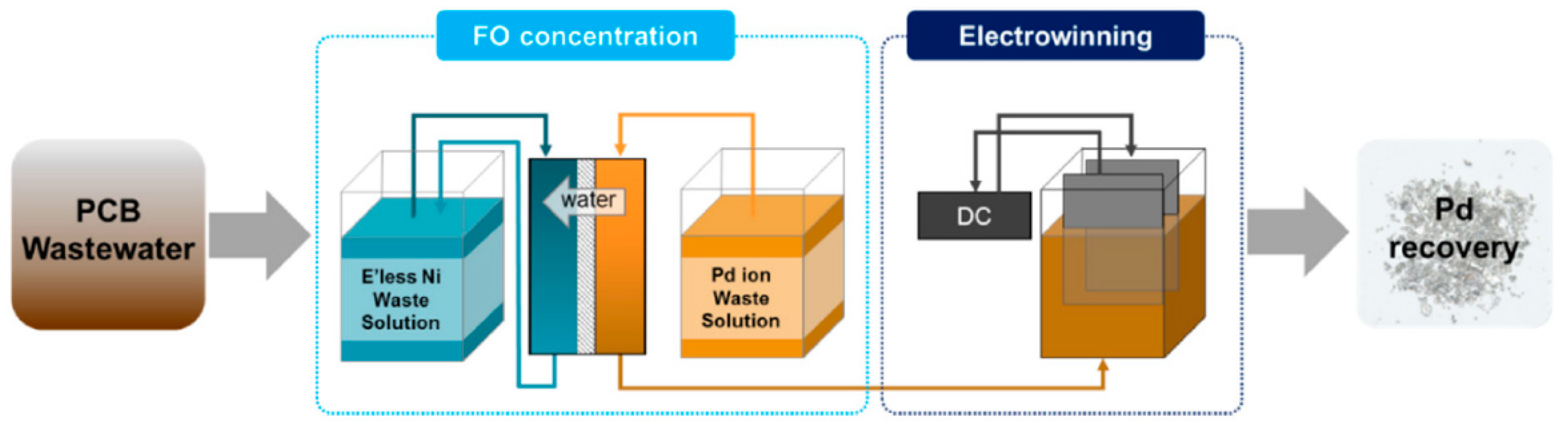
- Gwak, G.; Kim, D.I.; Hong, S. New industrial application of forward osmosis (FO): Precious metal recovery from printed circuit board (PCB) plant wastewater. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 552, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwak, G.; Kim, D.I.; Lim, J.A.; Hong, S. New Industrial Application of Forward Osmosis: Precious Metal Recovery. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 552, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.C.; Chen, S.-S.; Weng, Y.-T.; Thi Nguyen, H.; Ray, S.S.; Li, C.-W.; Yan, B.; Wang, J. Iodide recovery from thin film transistor liquid crystal display plants by using potassium hydroxide—Driven forward osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 520, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, C. Efficient removal of heavy metal ions based on the optimized dissolution-diffusion-flow forward osmosis process. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 1128–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Ge, Q.; Liu, X.-Y.; Chung, T.-S. Novel forward osmosis process to effectively remove heavy metal ions. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 467, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.; Lu, J.; Tang, C.Y.; Wang, X. Rejection of heavy metals in acidic wastewater by a novel thin-film inorganic forward osmosis membrane. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 320, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Gao, B.; Yue, Q.; Liu, S.; Shon, H.K. The performance of forward osmosis in treating high-salinity wastewater containing heavy metal Ni2+. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 288, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-Y.; Mouri, H.; Chen, S.-S.; Zhang, D.-Z.; Koga, M.; Kobayashi, J. Removal of trace-amount mercury from wastewater by forward osmosis. J. Water Process Eng. 2016, 14, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Esparra-Alvarado, M.; Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Xie, Y. Effects of pH and temperature on forward osmosis membrane flux using rainwater as the makeup for cooling water dilution. Desalination 2014, 351, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
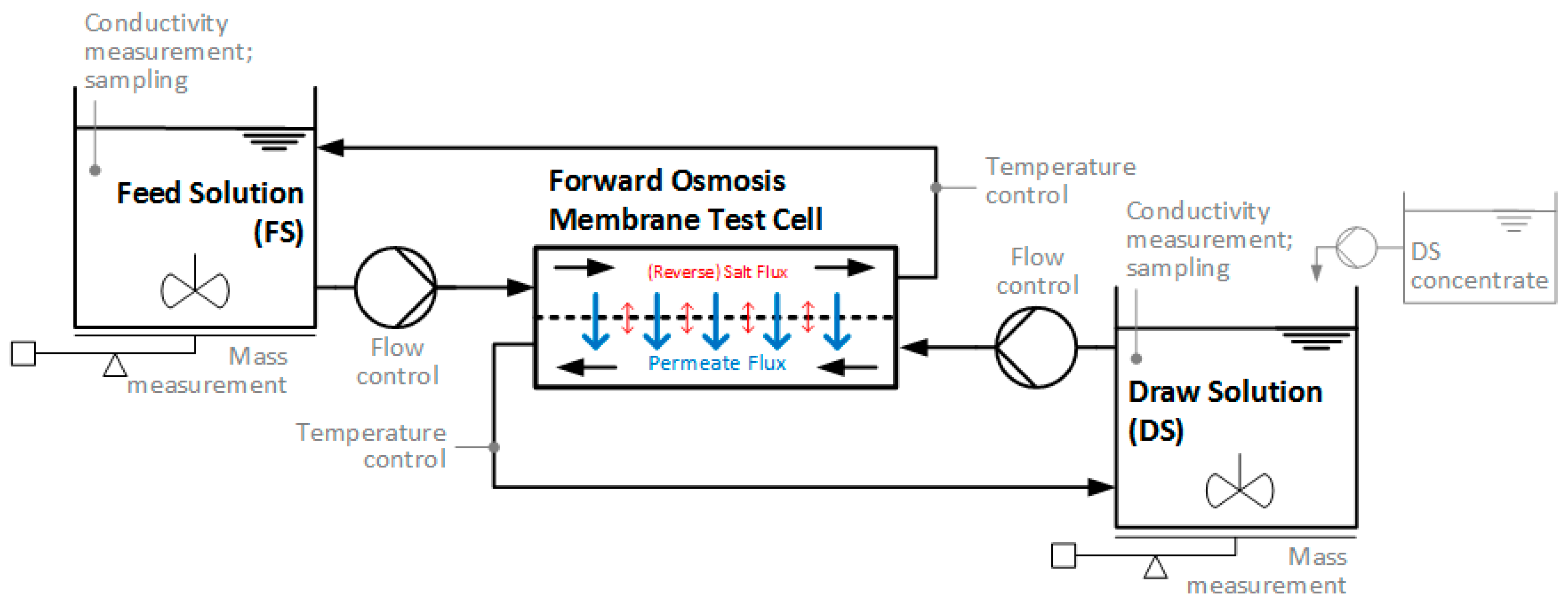


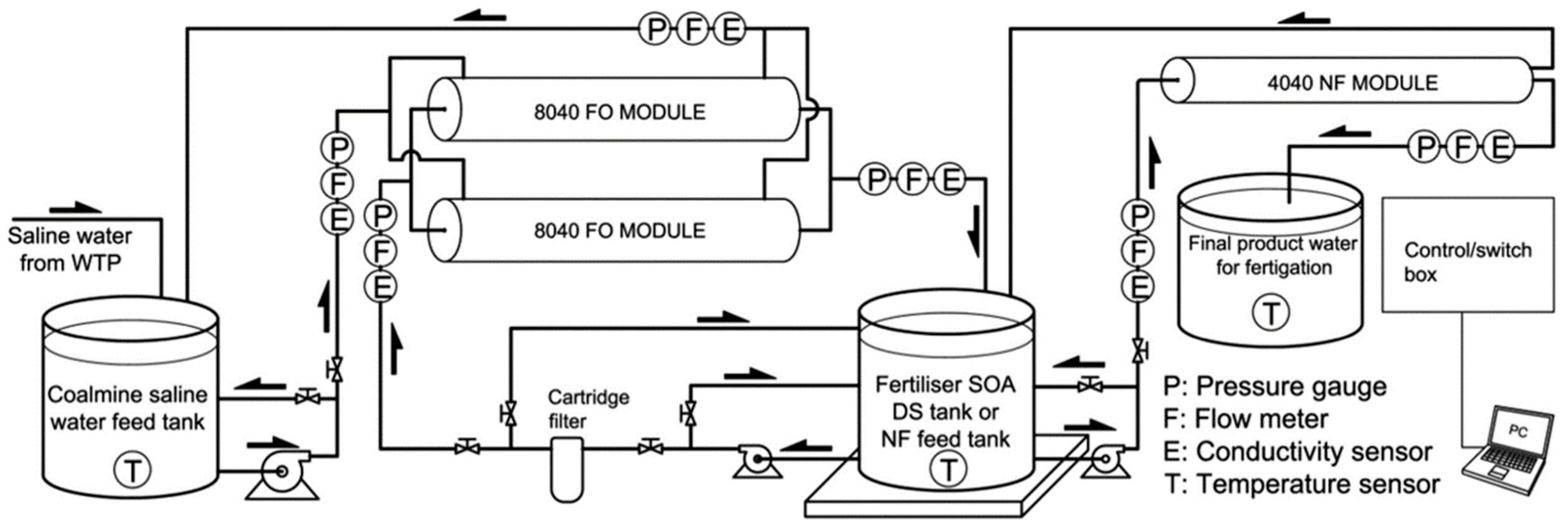
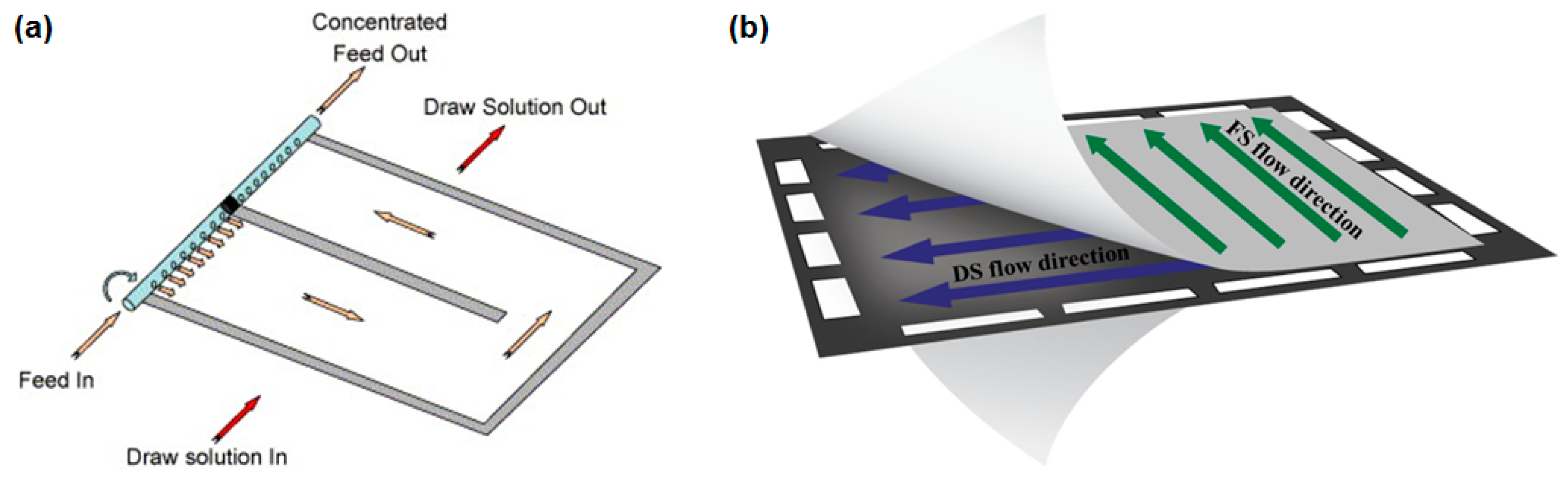

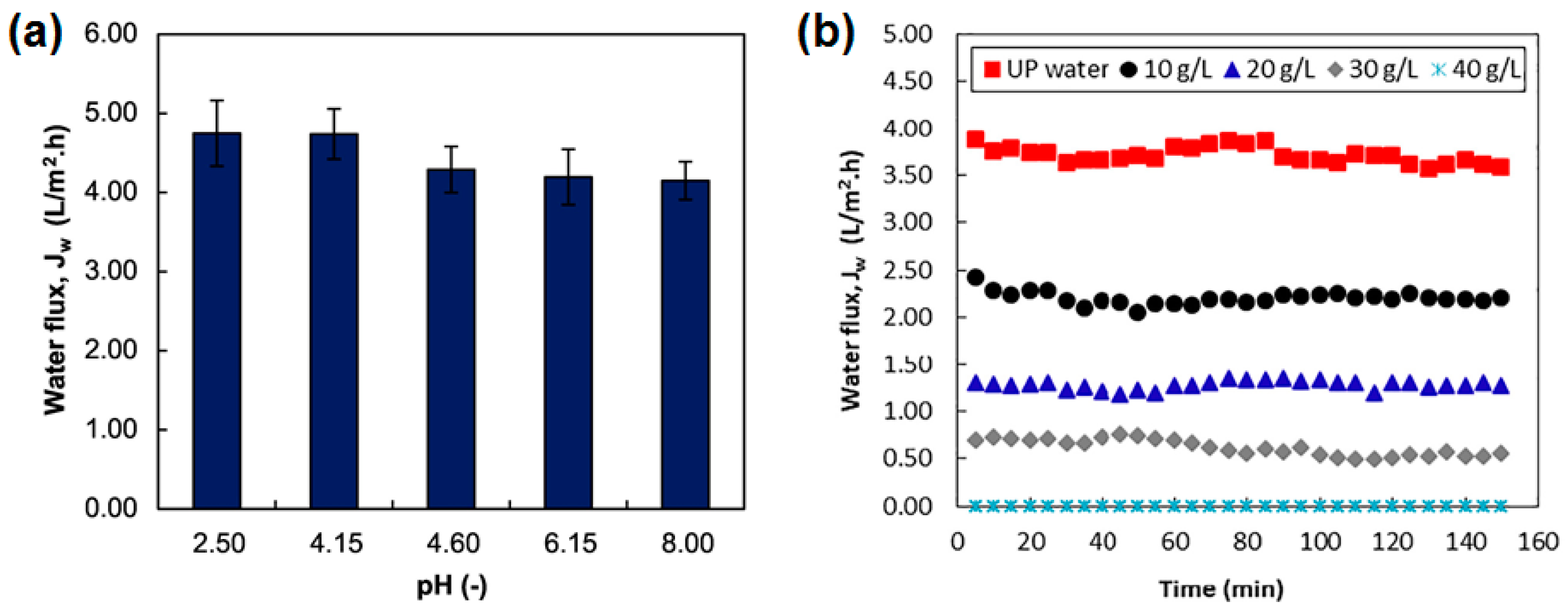
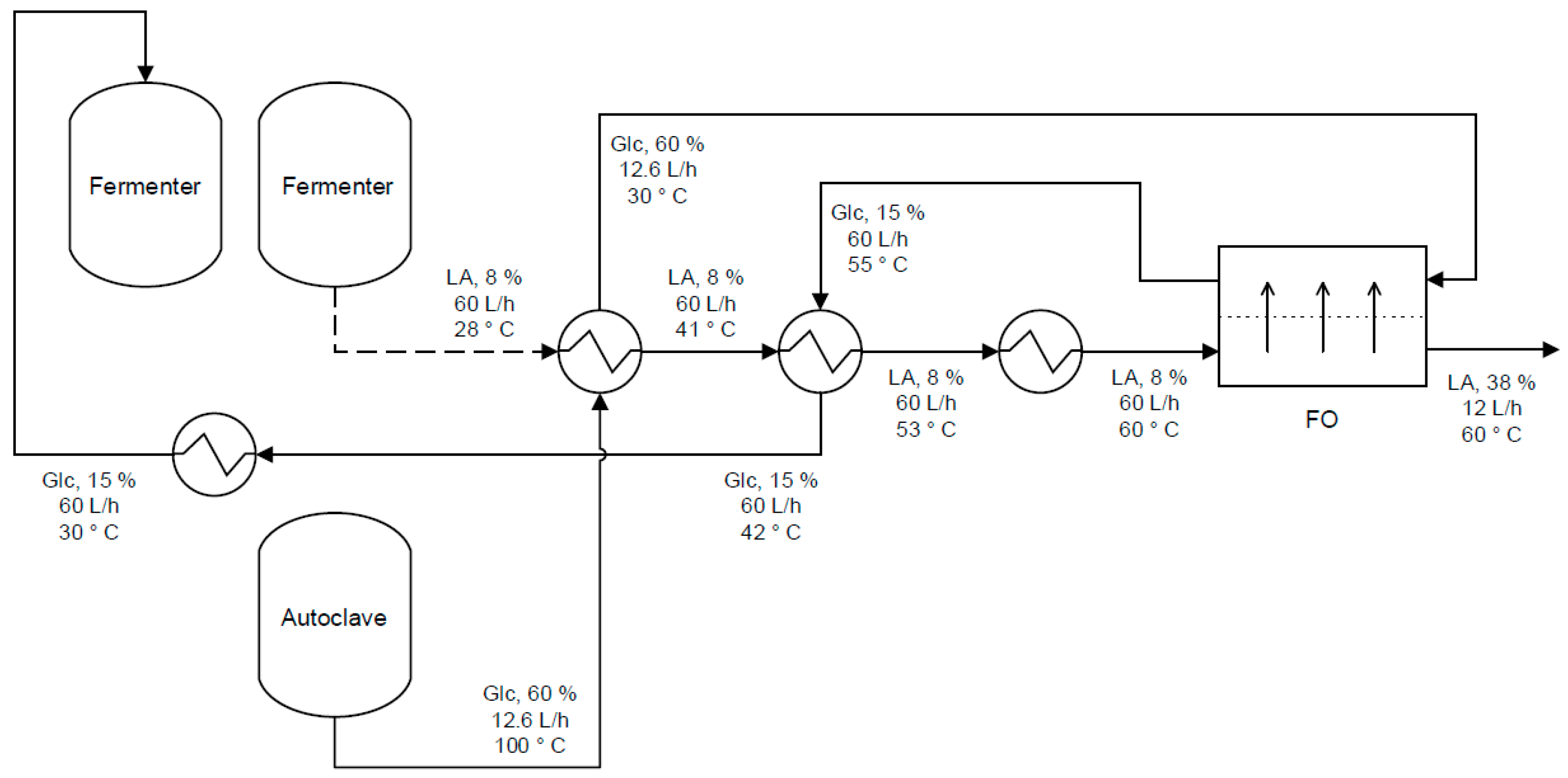
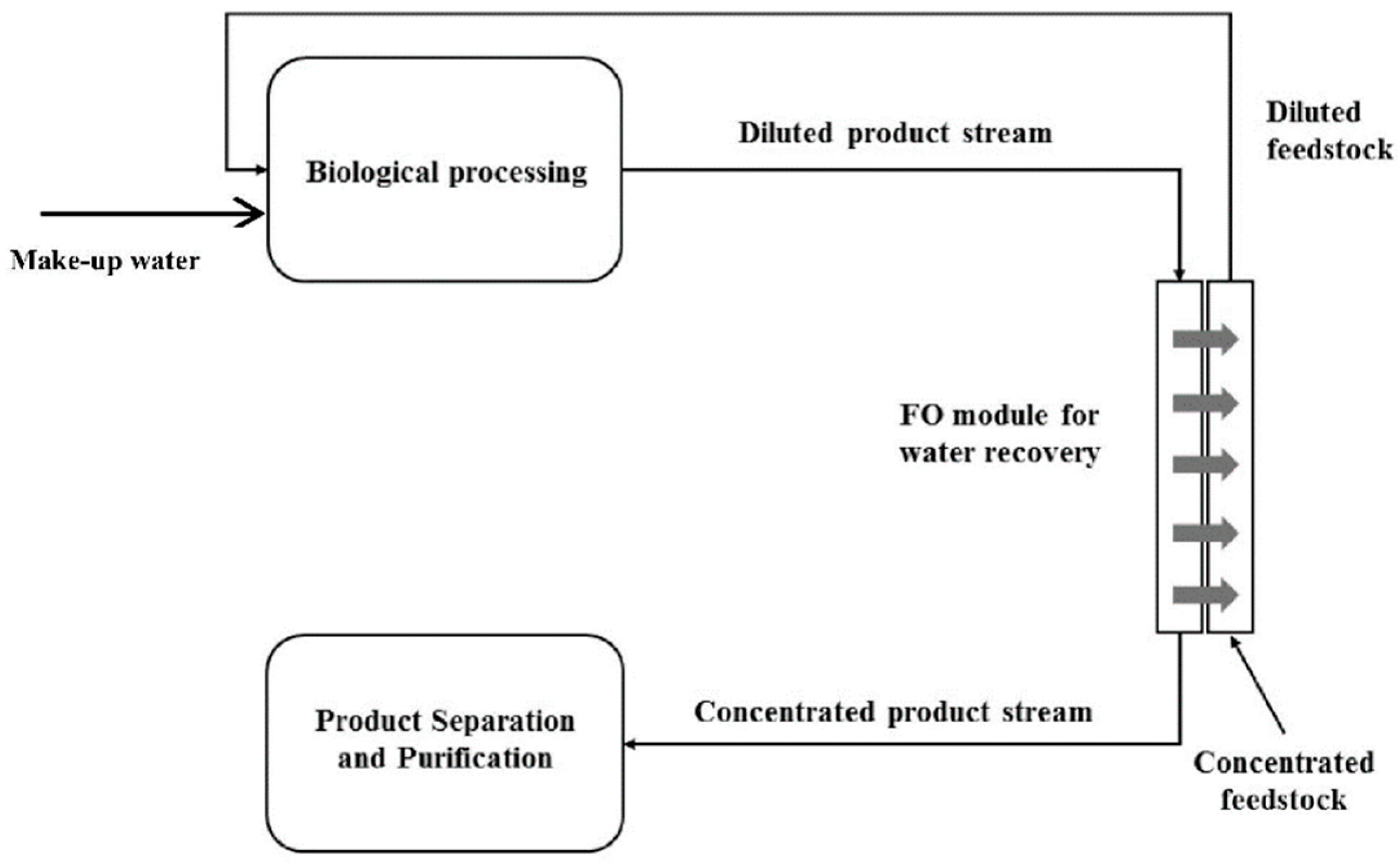
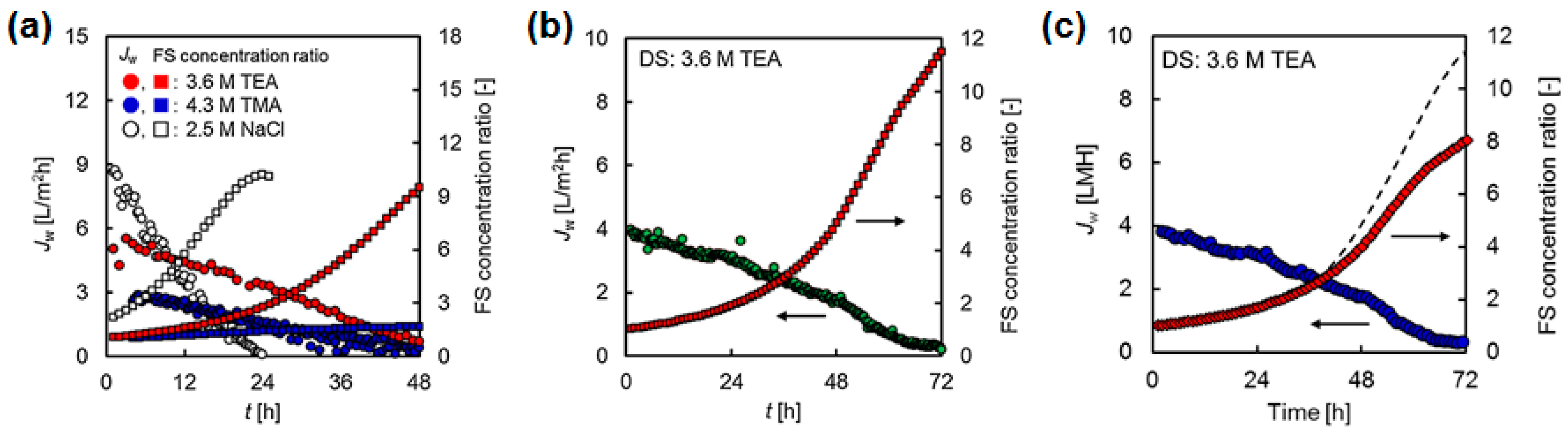
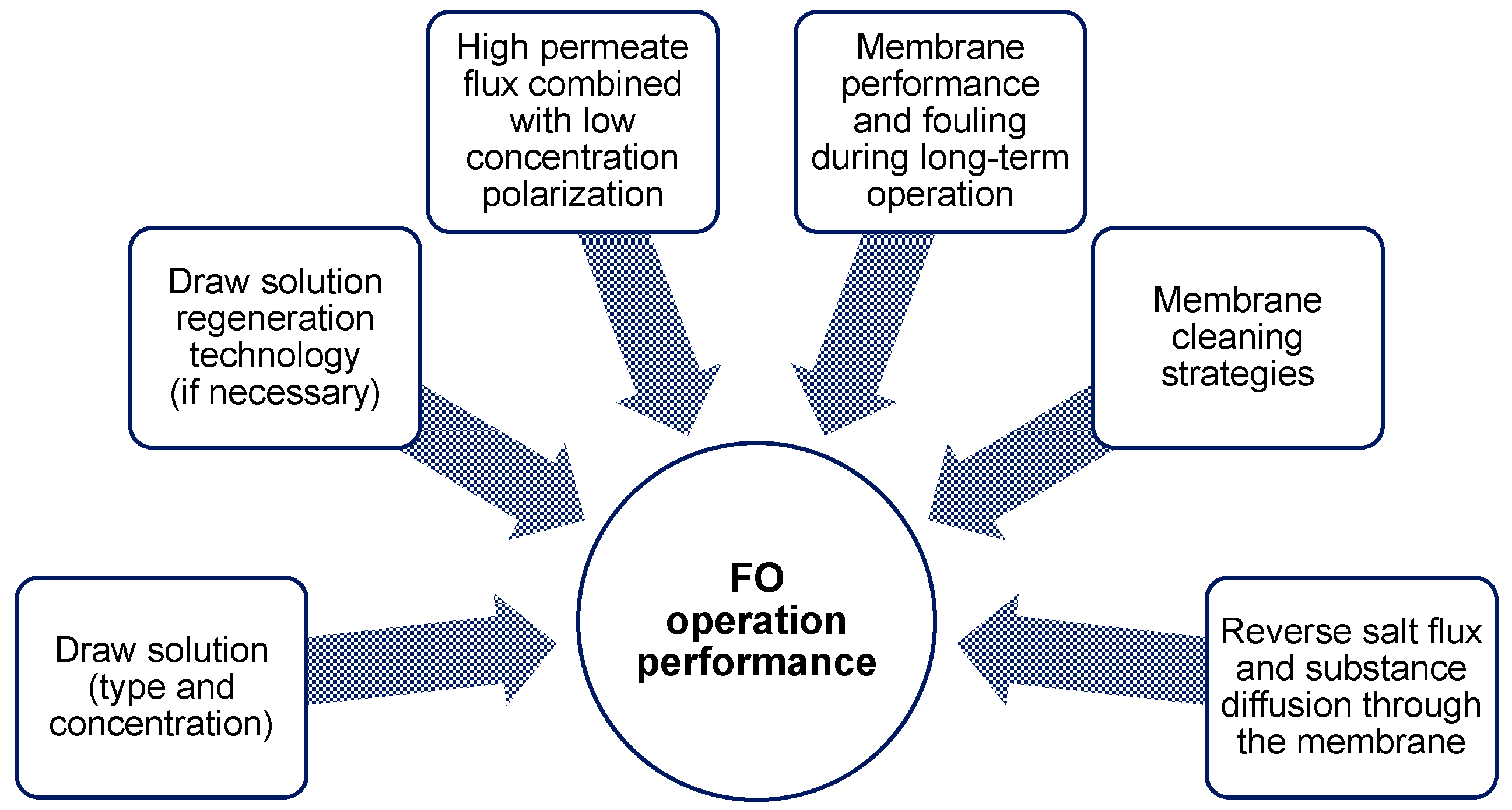
| Feed Solution | Draw Solution | Membrane | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haupt, A.; Lerch, A. Forward Osmosis Application in Manufacturing Industries: A Short Review. Membranes 2018, 8, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8030047
Haupt A, Lerch A. Forward Osmosis Application in Manufacturing Industries: A Short Review. Membranes. 2018; 8(3):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8030047
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaupt, Anita, and André Lerch. 2018. "Forward Osmosis Application in Manufacturing Industries: A Short Review" Membranes 8, no. 3: 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8030047
APA StyleHaupt, A., & Lerch, A. (2018). Forward Osmosis Application in Manufacturing Industries: A Short Review. Membranes, 8(3), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8030047