Auxiliary Subunits: Shepherding AMPA Receptors to the Plasma Membrane
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. The Discovery of TARPs and Their Functional Properties
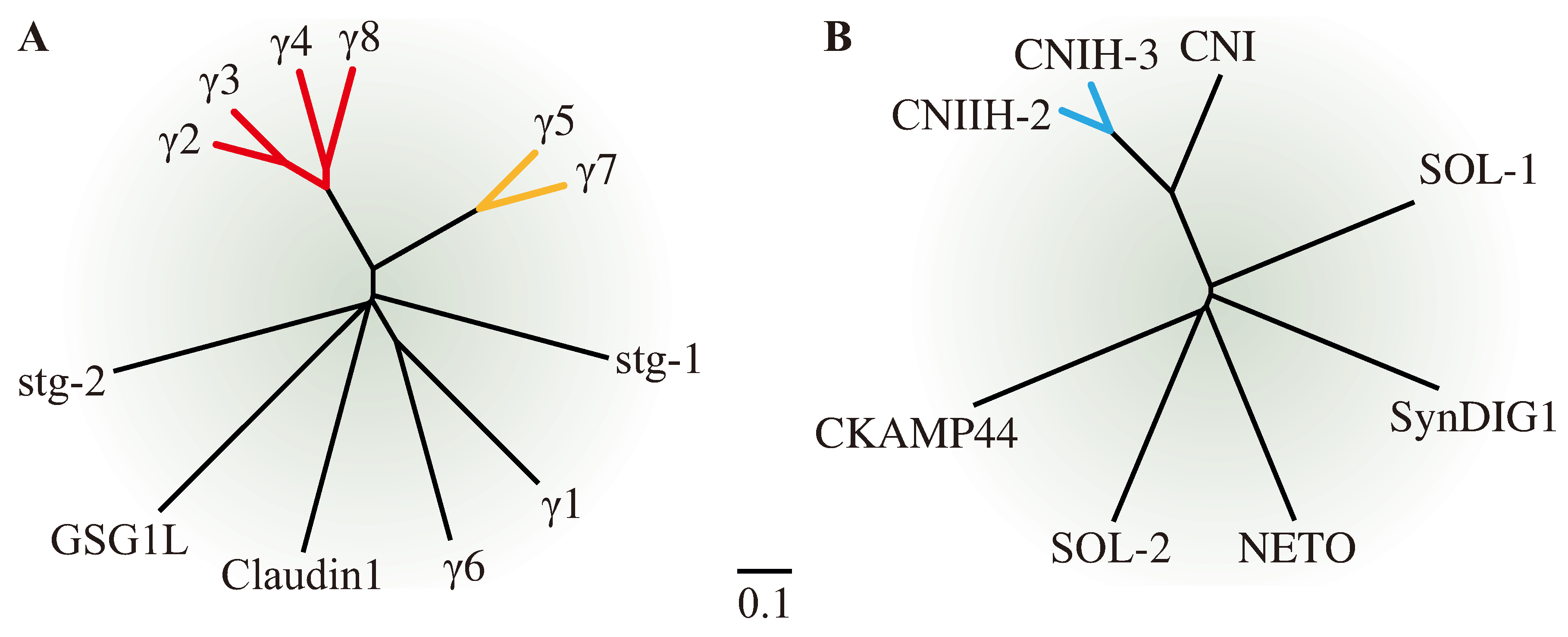
1.2. More Recently Discovered AMPAR Auxiliary Subunits
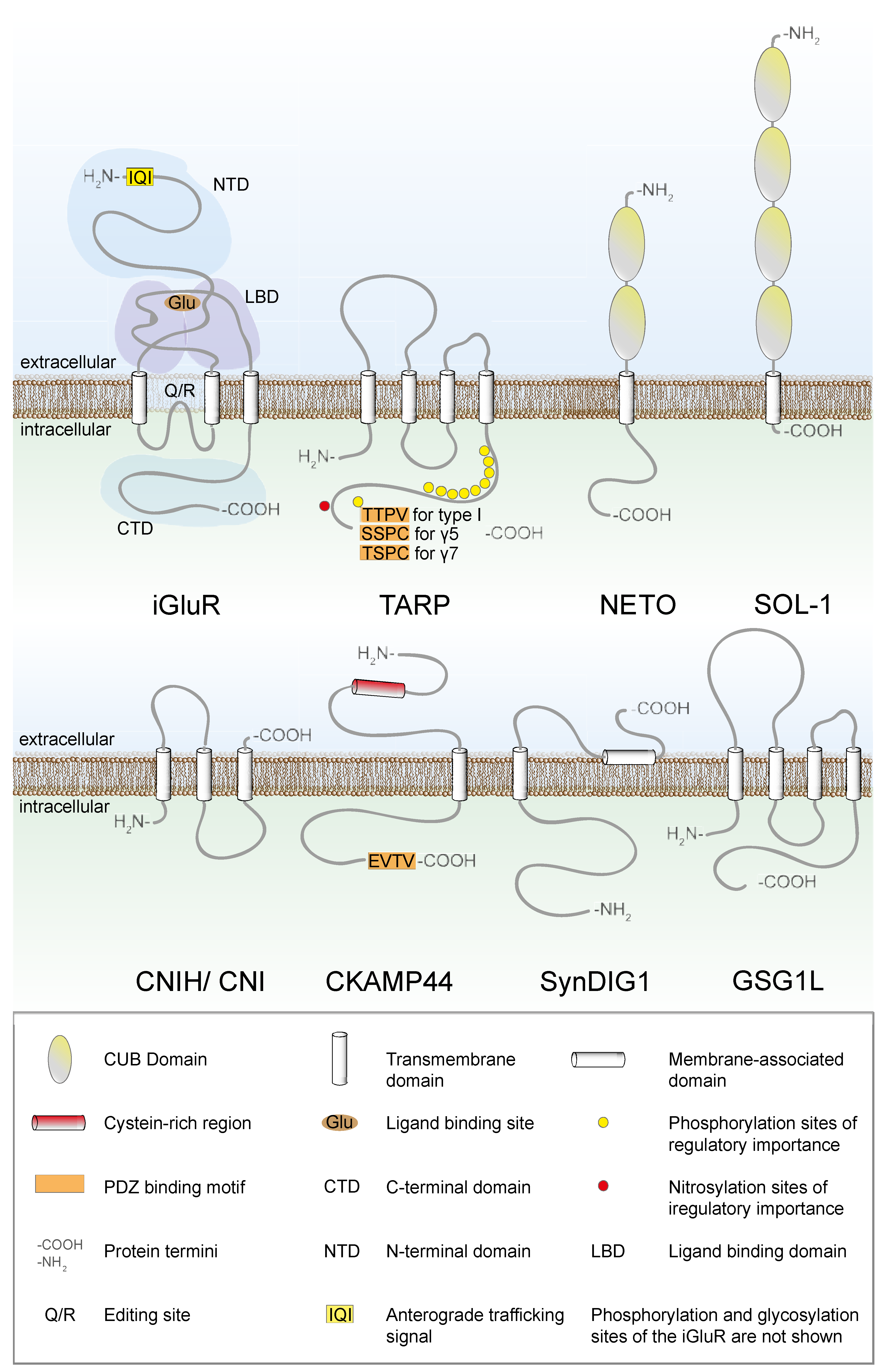
2. Trafficking of AMPARs between the ER and the Golgi Apparatus
2.1. TARPs and AMPAR Trafficking between the ER and the Golgi Apparatus
2.2. Other Auxiliary Subunits Impacting Trafficking between the ER and the Golgi Apparatus
3. Trafficking of AMPARs to the Plasma Membrane
3.1. The Role of TARPs in Trafficking to the Plasma Membrane
3.2. Impact of Other Auxiliary Subunits on Trafficking to the Plasma Membrane
4. Synaptic Targeting and Anchoring of AMPARs
4.1. TARPs and Synaptic Targeting and Anchoring
| Level of Influence | Interaction with AMPARs | Agonist Efficacy | Amplitude | Desensitization/Activation | ER/Golgi Export/Traffick | Maturation | Plasma Membrane Expression | Synaptic Targeting/Anchoring | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| γ1 | N/A | 0 A | 0 B | N/A | N/A | N/A | 0 C | N/A | ||
| γ2 | + D | + E | + F | − G | + H | + I | + J | + K | ||
| γ3 | + L | + M | + N | − O | (+) N/A P | + Q | + R | (+) N/A S | ||
| γ4 | + T | + U | + V | − W | (+) N/A X | (+) N/A Y | + Z | (+) N/A AA | ||
| γ5 | + AB | − AC | + AD | + AE | N/A | N/A | ~ AF | ~ AG | ||
| γ6 | N/A | N/A | 0 AH | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | ||
| γ7 | + AI | + AJ | + AK | − AL | N/A | N/A | + AM | + AN | ||
| γ8 | + AO | + AP | + AQ | − AR | (+) N/A AS | (+) N/A AT | + AU | + AV | ||
| A: [21] | Q: [54] | AG: [13,67,69,99] | ||||||||
| B: [13,21] | R: [50,51,54] | AH: [68,69] | ||||||||
| C: [21,50] | S: [9,71,75,88,94,104] | AI: [18,34,68,69,99] | ||||||||
| D: [9,10,13,55,75,88] | T: [13] | AJ: [62,68] | ||||||||
| E: [10,17,19,20,21,22,51,62,67,68,101] | U: [10,17,21,22,51,67,101,102] | AK: [34,62,69] | ||||||||
| F: [10,13,18,19,20,21,22,34,51,62,69,92,101,102,103] | V: [10,13,20,21,22,34,51,101,102,103] | AL: [14,68] | ||||||||
| G: [6,10,18,19,21,51,55,67,68,101,102] | W: [10,21,51,101,102] | AM: [14,51,68,71] | ||||||||
| H: [13,16,50,55] | X: [13,16,50,55] | AN: [14,51,68,71] | ||||||||
| I: [13,16,45,50,54] | Y: [13,16,45,50,54] | AO: [13] | ||||||||
| J: [9,19,21,23,50,54,55,67,71,88,104,105] | Z: [51] | AP: [10,17,20,21,22,34,62,67,102] | ||||||||
| K: [9,71,75,88,94,104] | AA: [9,71,75,88,94,104] | AQ: [10,13,21,22,34,51,62,65,102,103] | ||||||||
| L: [7,13] | AB: [13,18,34,68,69,99] | AR: [10,34,51,62,102] | ||||||||
| M: [10,17,21,22,51,67,102] | AC: [7,67,69] | AS: [13,16,50,55] | ||||||||
| N: [10,13,20,21,22,34,51,102,103] | AD: [13,34,68,69,99] | AT: [13,16,45,50,54] | ||||||||
| O: [10,21,51,102] | AE: [68,69,99] | AU: [34,65,71,106] | ||||||||
| P: [13,16,50,55] | AF: [13,67,69,99] | AV: [34,65,71,106] | ||||||||
| Level of Influence | Interaction with AMPARs | Agonist Efficacy | Amplitude | Desensitization/Activation | ER/Golgi Export/Traffick. | Maturation | Plasma Membrane Expression | Synaptic Targeting/Anchoring | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stg-1 | + A | N/A | + B | − C | N/A | N/A | 0D | N/A | |||
| SOL-1 | + E | N/A | + F | − G | N/A | N/A | 0H | N/A | |||
| SOL-2 | + I | + J | + K | + L | N/A | N/A | 0M | N/A | |||
| CNIH-2 | + N | ~ ° | + P | ~ Q | + R | + S | 0 T | ~ U | |||
| CNIH-3 | + V | 0 W | + X | − Y | + Z | + AA | 0 AB | ~ AC | |||
| CKAMP44 | + AD | + AE | N/A | + des. AF − deac. | N/A | N/A | 0 AG | (+) N/A AH | |||
| SynDIG–1 | + AI | 0 AJ | 0 AK | 0 AL | N/A | N/A | N/A | + AM | |||
| GSG1L | + AN | N/A | + AO | − AP | N/A | N/A | + AQ | N/A | |||
| A: [24] | L: [28] | W: [35] | AH: [42,44] | ||||||||
| B: [24,25] | M: [28] | X: [29,35] | AI: [40,108] | ||||||||
| C: [25] | N: [29,32,34,107] | Y: [6,29,35] | AJ: [41] | ||||||||
| D: [24,25] | O: [31,34,35,62,102] | Z: [30,58,60,61,62] | AK: [41] | ||||||||
| E: [25,26,27,28] | P: [29,31,34,35,61,62,102] | AA: [32] | AL: [41] | ||||||||
| F: [25,26,27,28] | Q: [6,31,34,35,62,102] | AB: [29] | AM: [39,40,108] | ||||||||
| G: [25] | R: [30,58,60,61,62] | AC: [29,31,34] | AN: [6,45] | ||||||||
| H: [24,25,26,27] | S: [32] | AD: [42] | AO: [6] | ||||||||
| I: [28] | T: [29,31,34,61] | AE: [42] | AP: [6,45] | ||||||||
| J: [28] | U: [6,29,31] | AF: [42,43] | AQ: [45] | ||||||||
| K: [28] | V: [29] | AG: [42,43] | |||||||||
4.2. The Impact of Other Auxiliary Subunits on Synaptic Targeting and Anchoring
5. Conclusions and Outlook
Definitions
| AMPA | α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid |
| AMPAR | AMPA receptor |
| AP-4 | adaptor protein-4 |
| CAMKII | Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II |
| CKAMP | cysteine-knot AMPAR modulating protein |
| CNI | cornichon |
| CNIH | cornichon homologue |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| ER | endoplasmic reticulum |
| γ2-ΔC | γ2 lacking the C-terminal domain |
| GLR | glutamate receptor-like protein |
| GSG1L | germ cell-specific gene 1-like |
| HEK | human embryonic kidney |
| iGluR | ionotropic glutamate receptor |
| LC2 | light chain protein 2 |
| LTD | long-term depression |
| LTP | long-term potentiation |
| MAGI-2 | membrane-associated guanylate kinase inverted-2 |
| MAGUK | membrane-associated guanylate kinase |
| MAP1A | microtubule-associated protein 1A |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| mEPSP | miniature excitatory postsynaptic potential |
| Neto | neuropilin and tolloid-like |
| NMDA | N-methyl-d-aspartate |
| NMDAR | NMDA receptor |
| nPIST | neuronal isoform of protein interacting specifically with TC10 |
| PKC | protein kinase C |
| PDZ | PSD-95/discs large/zonula occludens-1 |
| PP | protein phosphatase |
| PSD | postsynaptic density |
| SAP | synapse-associated protein |
| SOL | suppressor of lurcher |
| SynDIG | synapse differentiation-induced gene I |
| TARP | transmembrane AMPA receptor regulatory protein |
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Opazo, P.; Choquet, D. A three-step model for the synaptic recruitment of AMPA receptors. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2011, 46, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anggono, V.; Huganir, R.L. Regulation of AMPA receptor trafficking and synaptic plasticity. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2012, 22, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letts, V.A.; Felix, R.; Biddlecome, G.H.; Arikkath, J.; Mahaffey, C.L.; Valenzuela, A.; Bartlett, F.S., II; Mori, Y.; Campbell, K.P.; Frankel, W.N. The mouse stargazer gene encodes a neuronal Ca2+-channel gamma subunit. Nat. Genet. 1998, 19, 340–347. [Google Scholar]
- Fukata, Y.; Tzingounis, A.V.; Trinidad, J.C.; Fukata, M.; Burlingame, A.L.; Nicoll, R.A.; Bredt, D.S. Molecular constituents of neuronal AMPA receptors. J. Cell Biol. 2005, 169, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, T.; Cheng, Y.; Ramm, E.; Sheng, M.; Walz, T. Structure and different conformational states of native AMPA receptor complexes. Nature 2005, 433, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwenk, J.; Harmel, N.; Brechet, A.; Zolles, G.; Berkefeld, H.; Muller, C.S.; Bildl, W.; Baehrens, D.; Huber, B.; Kulik, A.; et al. High-resolution proteomics unravel architecture and molecular diversity of native AMPA receptor complexes. Neuron 2012, 74, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, S.; Fukata, M.; Nicoll, R.A.; Bredt, D.S. Dynamic interaction of stargazin-like TARPs with cycling AMPA receptors at synapses. Science 2004, 303, 1508–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenberghe, W.; Nicoll, R.A.; Bredt, D.S. Stargazin is an AMPA receptor auxiliary subunit. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bats, C.; Groc, L.; Choquet, D. The interaction between Stargazin and PSD-95 regulates AMPA receptor surface trafficking. Neuron 2007, 53, 719–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, C.H.; St-Gelais, F.; Zhang, W.; Tomita, S.; Howe, J.R. Two families of TARP isoforms that have distinct effects on the kinetic properties of AMPA receptors and synaptic currents. Neuron 2007, 55, 890–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukaya, M.; Yamazaki, M.; Sakimura, K.; Watanabe, M. Spatial diversity in gene expression for VDCCgamma subunit family in developing and adult mouse brains. Neurosci. Res. 2005, 53, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menuz, K.; Kerchner, G.A.; O’Brien, J.L.; Nicoll, R.A. Critical role for TARPs in early development despite broad functional redundancy. Neuropharmacology 2009, 56, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, S.; Chen, L.; Kawasaki, Y.; Petralia, R.S.; Wenthold, R.J.; Nicoll, R.A.; Bredt, D.S. Functional studies and distribution define a family of transmembrane AMPA receptor regulatory proteins. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 161, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Studniarczyk, D.; Coombs, I.; Cull-Candy, S.G.; Farrant, M. TARP gamma-7 selectively enhances synaptic expression of calcium-permeable AMPARs. Nat. Neurosci. 2013, 16, 1266–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, S.; Nicoll, R.A.; Bredt, D.S. PDZ protein interactions regulating glutamate receptor function and plasticity. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 153, F19–F24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoll, R.A.; Tomita, S.; Bredt, D.S. Auxiliary subunits assist AMPA-type glutamate receptors. Science 2006, 311, 1253–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menuz, K.; Stroud, R.M.; Nicoll, R.A.; Hays, F.A. TARP auxiliary subunits switch AMPA receptor antagonists into partial agonists. Science 2007, 318, 815–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priel, A.; Kolleker, A.; Ayalon, G.; Gillor, M.; Osten, P.; Stern-Bach, Y. Stargazin reduces desensitization and slows deactivation of the AMPA-type glutamate receptors. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 2682–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turetsky, D.; Garringer, E.; Patneau, D.K. Stargazin modulates native AMPA receptor functional properties by two distinct mechanisms. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 7438–7448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, M.; Ohno-Shosaku, T.; Fukaya, M.; Kano, M.; Watanabe, M.; Sakimura, K. A novel action of stargazin as an enhancer of AMPA receptor activity. Neurosci. Res. 2004, 50, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sager, C.; Terhag, J.; Kott, S.; Hollmann, M. C-terminal domains of transmembrane α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionate (AMPA) receptor regulatory proteins not only facilitate trafficking but are major modulators of AMPA receptor function. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 32413–32424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kott, S.; Sager, C.; Tapken, D.; Werner, M.; Hollmann, M. Comparative analysis of the pharmacology of GluR1 in complex with transmembrane AMPA receptor regulatory proteins γ2, γ3, γ4, and γ8. Neuroscience 2009, 158, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; El-Husseini, A.; Tomita, S.; Bredt, D.S.; Nicoll, R.A. Stargazin differentially controls the trafficking of alpha-amino-3-hydroxyl-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionate and kainate receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2003, 64, 703–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, C.S.; Brockie, P.J.; Madsen, D.M.; Francis, M.M.; Zheng, Y.; Koduri, S.; Mellem, J.E.; Strutz-Seebohm, N.; Maricq, A.V. Reconstitution of invertebrate glutamate receptor function depends on stargazin-like proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10781–10786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, C.S.; Francis, M.M.; Brockie, P.J.; Madsen, D.M.; Zheng, Y.; Maricq, A.V. Conserved SOL-1 proteins regulate ionotropic glutamate receptor desensitization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10787–10792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Brockie, P.J.; Mellem, J.E.; Madsen, D.M.; Walker, C.S.; Francis, M.M.; Maricq, A.V. SOL-1 is an auxiliary subunit that modulates the gating of GLR-1 glutamate receptors in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 1100–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Mellem, J.E.; Brockie, P.J.; Madsen, D.M.; Maricq, A.V. SOL-1 is a CUB-domain protein required for GLR-1 glutamate receptor function in C. elegans. Nature 2004, 427, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Mellem, J.E.; Jensen, M.; Brockie, P.J.; Walker, C.S.; Hoerndli, F.J.; Hauth, L.; Madsen, D.M.; Maricq, A.V. The SOL-2/Neto auxiliary protein modulates the function of AMPA-subtype ionotropic glutamate receptors. Neuron 2012, 75, 838–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwenk, J.; Harmel, N.; Zolles, G.; Bildl, W.; Kulik, A.; Heimrich, B.; Chisaka, O.; Jonas, P.; Schulte, U.; Fakler, B.; et al. Functional proteomics identify cornichon proteins as auxiliary subunits of AMPA receptors. Science 2009, 323, 1313–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brockie, P.J.; Jensen, M.; Mellem, J.E.; Jensen, E.; Yamasaki, T.; Wang, R.; Maxfield, D.; Thacker, C.; Hoerndli, F.; Dunn, P.J.; et al. Cornichons control ER export of AMPA receptors to regulate synaptic excitability. Neuron 2013, 80, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Suh, Y.H.; Milstein, A.D.; Isozaki, K.; Schmid, S.M.; Roche, K.W.; Nicoll, R.A. Functional comparison of the effects of TARPs and cornichons on AMPA receptor trafficking and gating. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 16315–16319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herring, B.E.; Shi, Y.; Suh, Y.H.; Zheng, C.Y.; Blankenship, S.M.; Roche, K.W.; Nicoll, R.A. Cornichon proteins determine the subunit composition of synaptic AMPA receptors. Neuron 2013, 77, 1083–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brockie, P.J.; Maricq, A.V. In a pickle: Is cornichon just relish or part of the main dish? Neuron 2010, 68, 1017–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, A.S.; Gill, M.B.; Ho, M.T.; Yu, H.; Tu, Y.; Siuda, E.R.; Wang, H.; Qian, Y.W.; Nisenbaum, E.S.; Tomita, S.; et al. Hippocampal AMPA receptor gating controlled by both TARP and cornichon proteins. Neuron 2010, 68, 1082–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coombs, I.D.; Soto, D.; Zonouzi, M.; Renzi, M.; Shelley, C.; Farrant, M.; Cull-Candy, S.G. Cornichons modify channel properties of recombinant and glial AMPA receptors. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 9796–9804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tigaret, C.; Choquet, D. Neuroscience. More AMPAR garnish. Science 2009, 323, 1295–1296. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, A.C.; Nicoll, R.A. Neuroscience: AMPA receptors get ‘pickled’. Nature 2009, 458, 585–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, E.; Ge, Y.; Yang, Y.H.; Loh, K.C.; Serafini, T.A.; Okazaki, Y.; Hayashizaki, Y.; Speed, T.P.; Ngai, J.; Scheiffele, P. Molecular analysis of gene expression in the developing pontocerebellar projection system. Neuron 2002, 36, 417–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, E. SynDIG1 regulation of synaptic AMPA receptor targeting. Commun. Integr. Biol. 2010, 3, 347–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalashnikova, E.; Lorca, R.A.; Kaur, I.; Barisone, G.A.; Li, B.; Ishimaru, T.; Trimmer, J.S.; Mohapatra, D.P.; Diaz, E. SynDIG1: An activity-regulated, AMPA-receptor-interacting transmembrane protein that regulates excitatory synapse development. Neuron 2010, 65, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovero, K.L.; Blankenship, S.M.; Shi, Y.; Nicoll, R.A. SynDIG1 promotes excitatory synaptogenesis independent of AMPA receptor trafficking and biophysical regulation. PLoS One 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Engelhardt, J.; Mack, V.; Sprengel, R.; Kavenstock, N.; Li, K.W.; Stern-Bach, Y.; Smit, A.B.; Seeburg, P.H.; Monyer, H. CKAMP44: A brain-specific protein attenuating short-term synaptic plasticity in the dentate gyrus. Science 2010, 327, 1518–1522. [Google Scholar]
- Farrant, M.; Cull-Candy, S.G. Neuroscience. AMPA receptors—Another twist? Science 2010, 327, 1463–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karataeva, A.R.; Klaassen, R.V.; Stroder, J.; Ruiperez-Alonso, M.; Hjorth, J.J.; van Nierop, P.; Spijker, S.; Mansvelder, H.D.; Smit, A.B. C-terminal interactors of the AMPA receptor auxiliary subunit shisa9. PLoS One 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanks, N.F.; Savas, J.N.; Maruo, T.; Cais, O.; Hirao, A.; Oe, S.; Ghosh, A.; Noda, Y.; Greger, I.H.; Yates, J.R., 3rd; et al. Differences in AMPA and kainate receptor interactomes facilitate identification of AMPA receptor auxiliary subunit GSG1L. Cell Rep. 2012, 1, 590–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, D.; Pitcher, G.M.; Szilard, R.K.; Sertie, A.; Kanisek, M.; Clapcote, S.J.; Lipina, T.; Kalia, L.V.; Joo, D.; McKerlie, C.; et al. Neto1 is a novel CUB-domain NMDA receptor-interacting protein required for synaptic plasticity and learning. PLoS Biol. 2009, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; St-Gelais, F.; Grabner, C.P.; Trinidad, J.C.; Sumioka, A.; Morimoto-Tomita, M.; Kim, K.S.; Straub, C.; Burlingame, A.L.; Howe, J.R.; et al. A transmembrane accessory subunit that modulates kainate-type glutamate receptors. Neuron 2009, 61, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Bao, H.; Bonanno, L.; Zhang, B.; Serpe, M. Drosophila Neto is essential for clustering glutamate receptors at the neuromuscular junction. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 974–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayalon, G.; Stern-Bach, Y. Functional assembly of AMPA and kainate receptors is mediated by several discrete protein-protein interactions. Neuron 2001, 31, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenberghe, W.; Nicoll, R.A.; Bredt, D.S. Interaction with the unfolded protein response reveals a role for stargazin in biosynthetic AMPA receptor transport. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milstein, A.D.; Zhou, W.; Karimzadegan, S.; Bredt, D.S.; Nicoll, R.A. TARP subtypes differentially and dose-dependently control synaptic AMPA receptor gating. Neuron 2007, 55, 905–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, R.A.; Hansen, A.; Andersen, P.H.; Soderling, T.R. Surface expression of the AMPA receptor subunits GluR1, GluR2, and GluR4 in stably transfected baby hamster kidney cells. J. Neurochem. 1997, 68, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessels, H.W.; Kopec, C.D.; Klein, M.E.; Malinow, R. Roles of stargazin and phosphorylation in the control of AMPA receptor subcellular distribution. Nat. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menuz, K.; O’Brien, J.L.; Karmizadegan, S.; Bredt, D.S.; Nicoll, R.A. TARP redundancy is critical for maintaining AMPA receptor function. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 8740–8746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedoukian, M.A.; Weeks, A.M.; Partin, K.M. Different domains of the AMPA receptor direct stargazin-mediated trafficking and stargazin-mediated modulation of kinetics. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 23908–23921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedoukian, M.A.; Whitesell, J.D.; Peterson, E.J.; Clay, C.M.; Partin, K.M. The stargazin C terminus encodes an intrinsic and transferable membrane sorting signal. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 1597–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, H.; von Zastrow, M.; Malenka, R.C. A novel anterograde trafficking signal present in the N-terminal extracellular domain of ionotropic glutamate receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 47765–47769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bokel, C.; Dass, S.; Wilsch-Brauninger, M.; Roth, S. Drosophila Cornichon acts as cargo receptor for ER export of the TGFalpha-like growth factor Gurken. Development 2006, 133, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, S.; Neuman-Silberberg, F.S.; Barcelo, G.; Schupbach, T. Cornichon and the EGF receptor signaling process are necessary for both anterior-posterior and dorsal-ventral pattern formation in Drosophila. Cell 1995, 81, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillon, G.A.; Watanabe, R.; Taylor, M.; Schwabe, T.M.; Riezman, H. Concentration of GPI-anchored proteins upon ER exit in yeast. Traffic 2009, 10, 186–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmel, N.; Cokic, B.; Zolles, G.; Berkefeld, H.; Mauric, V.; Fakler, B.; Stein, V.; Klocker, N. AMPA receptors commandeer an ancient cargo exporter for use as an auxiliary subunit for signaling. PLoS One 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, M.B.; Kato, A.S.; Roberts, M.F.; Yu, H.; Wang, H.; Tomita, S.; Bredt, D.S. Cornichon-2 modulates AMPA receptor-transmembrane AMPA receptor regulatory protein assembly to dictate gating and pharmacology. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 6928–6938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ives, J.H.; Fung, S.; Tiwari, P.; Payne, H.L.; Thompson, C.L. Microtubule-associated protein light chain 2 is a stargazin-AMPA receptor complex-interacting protein in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 31002–31009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, S.; Miura, E.; Matsuda, K.; Kakegawa, W.; Kohda, K.; Watanabe, M.; Yuzaki, M. Accumulation of AMPA receptors in autophagosomes in neuronal axons lacking adaptor protein AP-4. Neuron 2008, 57, 730–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouach, N.; Byrd, K.; Petralia, R.S.; Elias, G.M.; Adesnik, H.; Tomita, S.; Karimzadegan, S.; Kealey, C.; Bredt, D.S.; Nicoll, R.A. TARP gamma-8 controls hippocampal AMPA receptor number, distribution and synaptic plasticity. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 1525–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnell, E.; Sizemore, M.; Karimzadegan, S.; Chen, L.; Bredt, D.S.; Nicoll, R.A. Direct interactions between PSD-95 and stargazin control synaptic AMPA receptor number. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 13902–13907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, S.; Adesnik, H.; Sekiguchi, M.; Zhang, W.; Wada, K.; Howe, J.R.; Nicoll, R.A.; Bredt, D.S. Stargazin modulates AMPA receptor gating and trafficking by distinct domains. Nature 2005, 435, 1052–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, A.S.; Zhou, W.; Milstein, A.D.; Knierman, M.D.; Siuda, E.R.; Dotzlaf, J.E.; Yu, H.; Hale, J.E.; Nisenbaum, E.S.; Nicoll, R.A.; et al. New transmembrane AMPA receptor regulatory protein isoform, gamma-7, differentially regulates AMPA receptors. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 4969–4977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, A.S.; Siuda, E.R.; Nisenbaum, E.S.; Bredt, D.S. AMPA receptor subunit-specific regulation by a distinct family of type II TARPs. Neuron 2008, 59, 986–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bats, C.; Soto, D.; Studniarczyk, D.; Farrant, M.; Cull-Candy, S.G. Channel properties reveal differential expression of TARPed and TARPless AMPARs in stargazer neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, M.; Fukaya, M.; Hashimoto, K.; Yamasaki, M.; Tsujita, M.; Itakura, M.; Abe, M.; Natsume, R.; Takahashi, M.; Kano, M.; et al. TARPs gamma-2 and gamma-7 are essential for AMPA receptor expression in the cerebellum. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2010, 31, 2204–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zonouzi, M.; Renzi, M.; Farrant, M.; Cull-Candy, S.G. Bidirectional plasticity of calcium-permeable AMPA receptors in oligodendrocyte lineage cells. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 1430–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanley, J.G. Subunit-specific trafficking mechanisms regulating the synaptic expression of Ca-permeable AMPA receptors. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2013, 2013, 14–22. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, H.; Grooms, S.Y.; Bennett, M.V.; Zukin, R.S. The AMPAR subunit GluR2: Still front and center-stage. Brain Res. 2000, 886, 190–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Chetkovich, D.M.; Petralia, R.S.; Sweeney, N.T.; Kawasaki, Y.; Wenthold, R.J.; Bredt, D.S.; Nicoll, R.A. Stargazin regulates synaptic targeting of AMPA receptors by two distinct mechanisms. Nature 2000, 408, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Bao, S.; Qiao, X.; Thompson, R.F. Impaired cerebellar synapse maturation in waggler, a mutant mouse with a disrupted neuronal calcium channel gamma subunit. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 12132–12137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, K.; Fukaya, M.; Qiao, X.; Sakimura, K.; Watanabe, M.; Kano, M. Impairment of AMPA receptor function in cerebellar granule cells of ataxic mutant mouse stargazer. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 6027–6036. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Sheng, M. PDZ domain proteins of synapses. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2004, 5, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beique, J.C.; Andrade, R. PSD-95 regulates synaptic transmission and plasticity in rat cerebral cortex. J. Physiol. 2003, 546, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrlich, I.; Malinow, R. Postsynaptic density 95 controls AMPA receptor incorporation during long-term potentiation and experience-driven synaptic plasticity. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 916–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Husseini, A.E.; Schnell, E.; Chetkovich, D.M.; Nicoll, R.A.; Bredt, D.S. PSD-95 involvement in maturation of excitatory synapses. Science 2000, 290, 1364–1368. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, V.; House, D.R.; Bredt, D.S.; Nicoll, R.A. Postsynaptic density-95 mimics and occludes hippocampal long-term potentiation and enhances long-term depression. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 5503–5506. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Elias, G.M.; Funke, L.; Stein, V.; Grant, S.G.; Bredt, D.S.; Nicoll, R.A. Synapse-specific and developmentally regulated targeting of AMPA receptors by a family of MAGUK scaffolding proteins. Neuron 2006, 52, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beique, J.C.; Lin, D.T.; Kang, M.G.; Aizawa, H.; Takamiya, K.; Huganir, R.L. Synapse-specific regulation of AMPA receptor function by PSD-95. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 19535–19540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dakoji, S.; Tomita, S.; Karimzadegan, S.; Nicoll, R.A.; Bredt, D.S. Interaction of transmembrane AMPA receptor regulatory proteins with multiple membrane associated guanylate kinases. Neuropharmacology 2003, 45, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inamura, M.; Itakura, M.; Okamoto, H.; Hoka, S.; Mizoguchi, A.; Fukazawa, Y.; Shigemoto, R.; Yamamori, S.; Takahashi, M. Differential localization and regulation of stargazin-like protein, gamma-8 and stargazin in the plasma membrane of hippocampal and cortical neurons. Neurosci. Res. 2006, 55, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, F.; Price, M.G.; Davis, C.F.; Mori, M.; Burgess, D.L. Stargazin and other transmembrane AMPA receptor regulating proteins interact with synaptic scaffolding protein MAGI-2 in brain. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 7875–7884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chetkovich, D.M.; Chen, L.; Stocker, T.J.; Nicoll, R.A.; Bredt, D.S. Phosphorylation of the postsynaptic density-95 (PSD-95)/discs large/zona occludens-1 binding site of stargazin regulates binding to PSD-95 and synaptic targeting of AMPA receptors. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 5791–5796. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Ko, J.; Park, E.; Lee, J.R.; Yoon, J.; Lim, S.; Kim, E. Phosphorylation of stargazin by protein kinase A regulates its interaction with PSD-95. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 12359–12363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumioka, A.; Yan, D.; Tomita, S. TARP phosphorylation regulates synaptic AMPA receptors through lipid bilayers. Neuron 2010, 66, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, M.F.; Taylor, D.W.; Unger, V.M. Two modes of interaction between the membrane-embedded TARP stargazin’s C-terminal domain and the bilayer visualized by electron crystallography. J. Struct. Biol. 2011, 174, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, S.; Stein, V.; Stocker, T.J.; Nicoll, R.A.; Bredt, D.S. Bidirectional synaptic plasticity regulated by phosphorylation of stargazin-like TARPs. Neuron 2005, 45, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsui, J.; Malenka, R.C. Substrate localization creates specificity in calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II signaling at synapses. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 13794–13804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, T.; Kakegawa, W.; Matsuda, S.; Kohda, K.; Nishiyama, J.; Takahashi, T.; Yuzaki, M. Cerebellar long-term depression requires dephosphorylation of TARP in Purkinje cells. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2012, 35, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, R.C.; Nicoll, R.A.; Malenka, R.C. Effects of PKA and PKC on miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents in CA1 pyramidal cells. J. Neurophysiol. 1998, 80, 2797–2800. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Opazo, P.; Labrecque, S.; Tigaret, C.M.; Frouin, A.; Wiseman, P.W.; de Koninck, P.; Choquet, D. CaMKII triggers the diffusional trapping of surface AMPARs through phosphorylation of stargazin. Neuron 2010, 67, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merrill, M.A.; Chen, Y.; Strack, S.; Hell, J.W. Activity-driven postsynaptic translocation of CaMKII. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2005, 26, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, E.L.; Chetkovich, D.M. Regulation of stargazin synaptic trafficking by C-terminal PDZ ligand phosphorylation in bidirectional synaptic plasticity. J. Neurochem. 2010, 113, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto, D.; Coombs, I.D.; Renzi, M.; Zonouzi, M.; Farrant, M.; Cull-Candy, S.G. Selective regulation of long-form calcium-permeable AMPA receptors by an atypical TARP, gamma-5. Nat. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuadra, A.E.; Kuo, S.H.; Kawasaki, Y.; Bredt, D.S.; Chetkovich, D.M. AMPA receptor synaptic targeting regulated by stargazin interactions with the Golgi-resident PDZ protein nPIST. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 7491–7502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Körber, C.; Werner, M.; Kott, S.; Ma, Z.-L.; Hollmann, M. The transmembrane AMPA receptor regulatory protein γ4 is a more effective modulator of AMPA receptor function than stargazin (γ2). J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 8442–8447. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, M.B.; Kato, A.S.; Wang, H.; Bredt, D.S. AMPA receptor modulation by cornichon-2 dictated by transmembrane AMPA receptor regulatory protein isoform. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2012, 35, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kott, S.; Werner, M.; Körber, C.; Hollmann, M. Electrophysiological properties of AMPA receptors are differentially modulated depending on the associated member of the TARP family. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 3780–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, A.C.; Nicoll, R.A. Stargazin (TARP gamma-2) is required for compartment-specific AMPA receptor trafficking and synaptic plasticity in cerebellar stellate cells. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 3939–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, S.; Shenoy, A.; Fukata, Y.; Nicoll, R.A.; Bredt, D.S. Stargazin interacts functionally with the AMPA receptor glutamate-binding module. Neuropharmacology 2007, 52, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukaya, M.; Tsujita, M.; Yamazaki, M.; Kushiya, E.; Abe, M.; Akashi, K.; Natsume, R.; Kano, M.; Kamiya, H.; Watanabe, M.; et al. Abundant distribution of TARP gamma-8 in synaptic and extrasynaptic surface of hippocampal neurons and its major role in AMPA receptor expression on spines and dendrites. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006, 24, 2177–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauric, V.; Molders, A.; Harmel, N.; Heimrich, B.; Sergeeva, O.A.; Klocker, N. Ontogeny repeats the phylogenetic recruitment of the cargo exporter cornichon into AMPA receptor signaling complexes. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2013, 56, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, E. SynDIG1 regulation of excitatory synapse maturation. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumioka, A.; Brown, T.E.; Kato, A.S.; Bredt, D.S.; Kauer, J.A.; Tomita, S. PDZ binding of TARPgamma-8 controls synaptic transmission but not synaptic plasticity. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 1410–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Rostamiani, K.; Hsu, Y.T.; Wang, Y.; Bi, X.; Baudry, M. Calpain-mediated regulation of stargazin in adult rat brain. Neuroscience 2011, 178, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvakumar, B.; Huganir, R.L.; Snyder, S.H. S-nitrosylation of stargazin regulates surface expression of AMPA-glutamate neurotransmitter receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 16440–16445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Husseini Ael, D.; Schnell, E.; Dakoji, S.; Sweeney, N.; Zhou, Q.; Prange, O.; Gauthier-Campbell, C.; Aguilera-Moreno, A.; Nicoll, R.A.; Bredt, D.S. Synaptic strength regulated by palmitate cycling on PSD-95. Cell 2002, 108, 849–863. [Google Scholar]
- Kösters, S.C.; Hollmann, M. 612.26 Identification of Certain Claudins as Possible Type III TARPs. In Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Society for Neuroscience, San Diego, CA, USA, 12 November 2013.
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Haering, S.C.; Tapken, D.; Pahl, S.; Hollmann, M. Auxiliary Subunits: Shepherding AMPA Receptors to the Plasma Membrane. Membranes 2014, 4, 469-490. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes4030469
Haering SC, Tapken D, Pahl S, Hollmann M. Auxiliary Subunits: Shepherding AMPA Receptors to the Plasma Membrane. Membranes. 2014; 4(3):469-490. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes4030469
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaering, Simon C., Daniel Tapken, Steffen Pahl, and Michael Hollmann. 2014. "Auxiliary Subunits: Shepherding AMPA Receptors to the Plasma Membrane" Membranes 4, no. 3: 469-490. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes4030469
APA StyleHaering, S. C., Tapken, D., Pahl, S., & Hollmann, M. (2014). Auxiliary Subunits: Shepherding AMPA Receptors to the Plasma Membrane. Membranes, 4(3), 469-490. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes4030469




