The Mysterious Ways of ErbB2/HER2 Trafficking
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. ErbB2 Molecular Conformation and Interaction with Hsp90
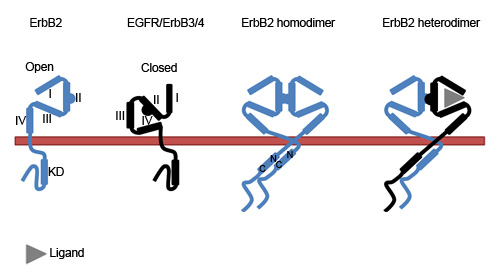
2.1. The Molecular Conformation of ErbB2
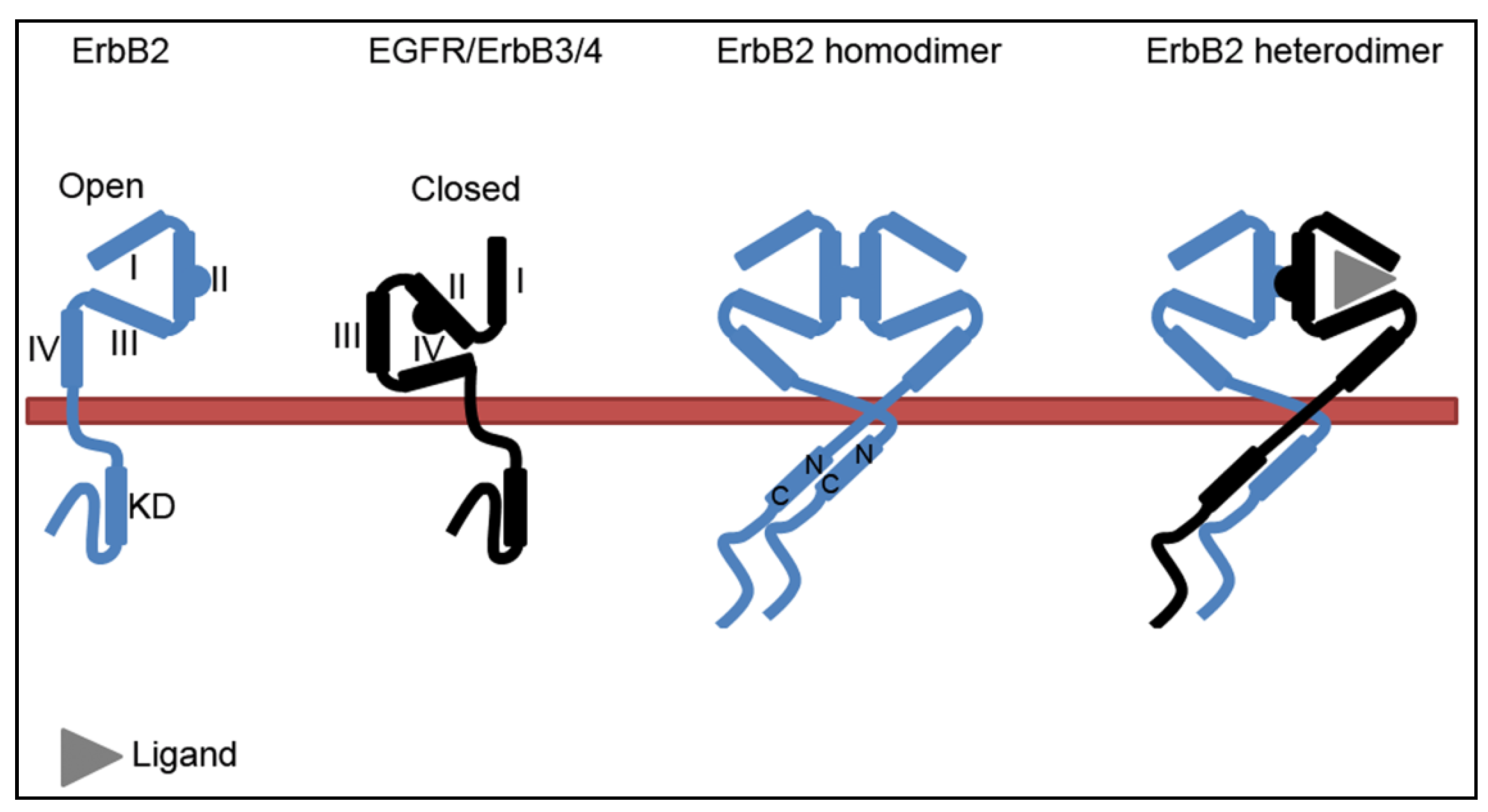
2.2. The ErbB2-Hsp90 Complex
3. Why is ErbB2 Resistant to down-Regulation?
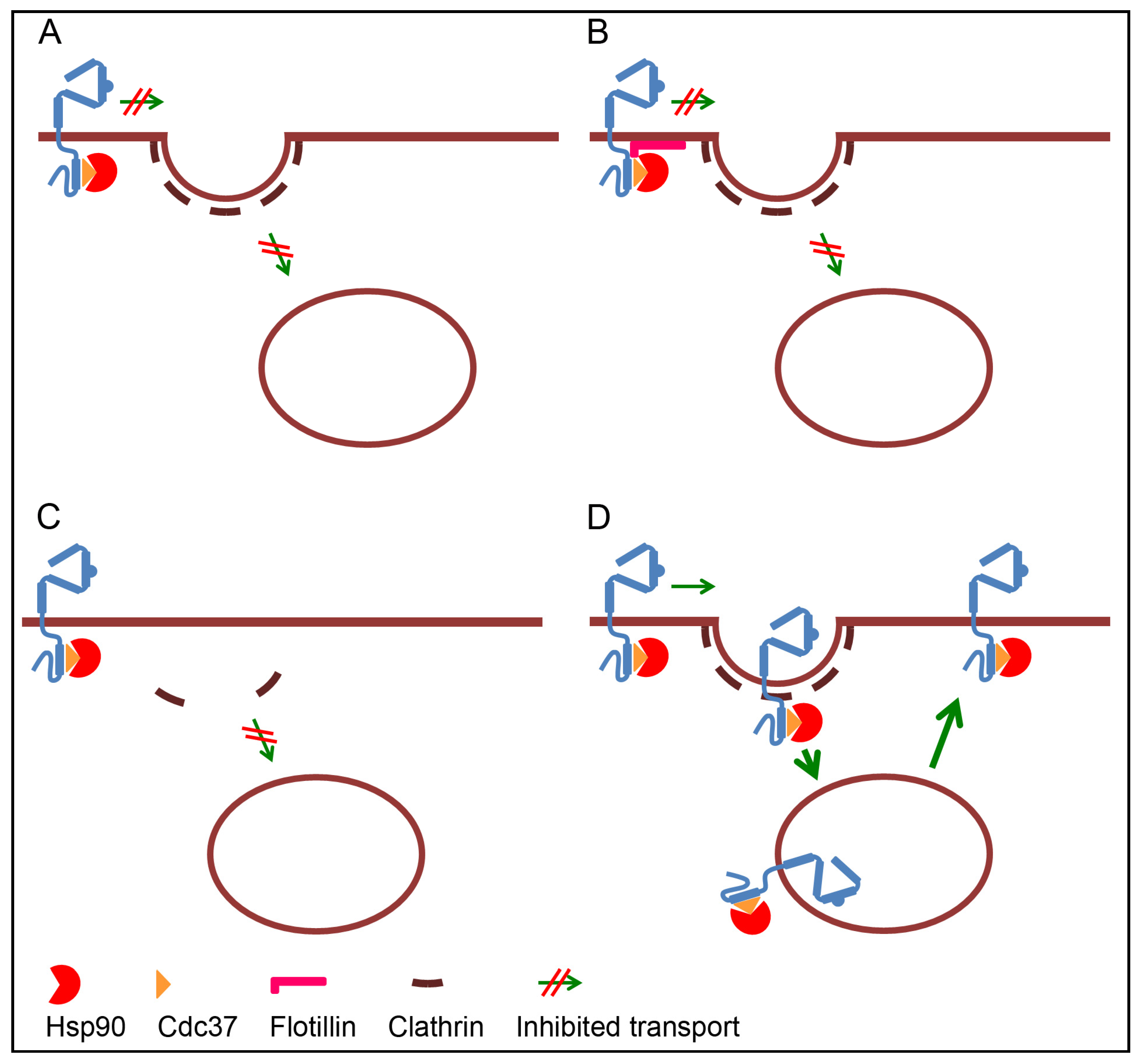
3.1. Retention of ErbB2 at the Plasma Membrane
3.2. Lack of Internalization Signals
3.3. Inhibited Formation of Clathrin Coated Pits
3.4. Rapid Recycling
4. Down-Regulation of ErbB2 upon Inhibition of Hsp90
4.1. Internalization Pathways
4.2. Ubiquitination as Internalization Signal
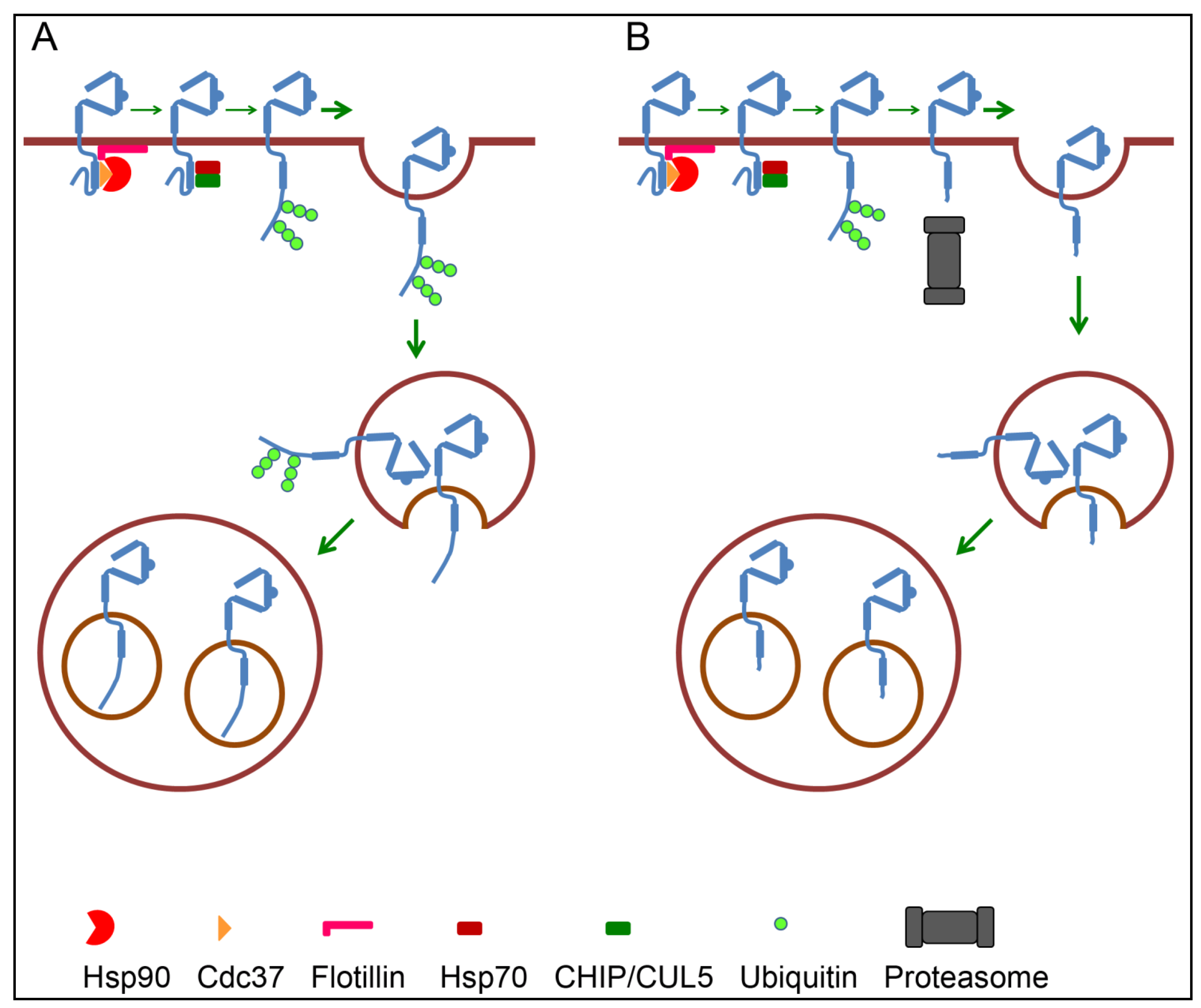
4.3. Endosomal Sorting of ErbB2
5. Effects of Anti-ErbB2 Antibodies on ErbB2 Trafficking
6. Nuclear Trafficking of ErbB2
7. Conclusions
Abbreviations
| BED | Blocking ErbB2 Degradation |
| CHIP | C-terminus of Hsc70-interacting protein |
| CLASP | Clathrin-associated sorting protein |
| CTF | Carboxyterminal fragment |
| ECD | Extracellular domain |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| ESCRT | Endosomal sorting complex required for transport |
| GA | Geldanamycin |
| ICD | Intracellular domain |
| ILV | Intraluminal vesicle |
| MVB | Multivesicular body |
| RTK | Receptor tyrosine kinase |
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Citri, A.; Skaria, K.B.; Yarden, Y. The deaf and the dumb: The biology of ErbB-2 and ErbB-3. Exp. Cell Res. 2003, 284, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, A.W.; Cho, H.S.; Eigenbrot, C.; Ferguson, K.M.; Garrett, T.P.; Leahy, D.J.; Lemmon, M.A.; Sliwkowski, M.X.; Ward, C.W.; Yokoyama, S. An open-and-shut case? Recent insights into the activation of EGF/ErbB receptors. Mol. Cell 2003, 12, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, T.P.; McKern, N.M.; Lou, M.; Elleman, T.C.; Adams, T.E.; Lovrecz, G.O.; Kofler, M.; Jorissen, R.N.; Nice, E.C.; Burgess, A.W.; et al. The crystal structure of a truncated ErbB2 ectodomain reveals an active conformation, poised to interact with other ErbB receptors. Mol. Cell 2003, 11, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roepstorff, K.; Grovdal, L.; Grandal, M.; Lerdrup, M.; van Deurs, B. Endocytic downregulation of ErbB receptors: Mechanisms and relevance in cancer. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 129, 563–578. [Google Scholar]
- Sorkin, A.; Goh, L.K. Endocytosis and intracellular trafficking of ErbBs. Exp. Cell Res. 2009, 315, 683–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gureasko, J.; Shen, K.; Cole, P.A.; Kuriyan, J. An allosteric mechanism for activation of the kinase domain of epidermal growth factor receptor. Cell 2006, 125, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, C.; Gauchez, A.S.; Jacot, W.; Lamy, P.J. HER2 shedding and serum HER2 extracellular domain: Biology and clinical utility in breast cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2012, 38, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagozdzon, R.; Gallagher, W.M.; Crown, J. Truncated HER2: Implications for HER2-targeted therapeutics. Drug Discov. Today 2011, 16, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.C.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Covington, M.; Wynn, R.; Huber, R.; Hillman, M.; Yang, G.; Ellis, D.; Marando, C.; et al. Identification of ADAM10 as a major source of HER2 ectodomain sheddase activity in HER2 overexpressing breast cancer cells. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2006, 5, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.; Fu, H.J.; Jia, L.T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Jin, B.Q.; Yao, L.B.; Chen, S.Y.; Yang, A.G. HER2-mediated upregulation of MMP-1 is involved in gastric cancer cell invasion. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 499, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anido, J.; Scaltriti, M.; Bech Serra, J.J.; Santiago Josefat, B.; Todo, F.R.; Baselga, J.; Arribas, J. Biosynthesis of tumorigenic HER2 C-terminal fragments by alternative initiation of translation. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 3234–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandarlapaty, S.; Scaltriti, M.; Angelini, P.; Ye, Q.; Guzman, M.; Hudis, C.A.; Norton, L.; Solit, D.B.; Arribas, J.; Baselga, J.; et al. Inhibitors of HSP90 block p95-HER2 signaling in Trastuzumab-resistant tumors and suppress their growth. Oncogene 2010, 29, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taipale, M.; Jarosz, D.F.; Lindquist, S. HSP90 at the hub of protein homeostasis: Emerging mechanistic insights. Nat. Rev. 2010, 11, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trepel, J.; Mollapour, M.; Giaccone, G.; Neckers, L. Targeting the dynamic HSP90 complex in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearl, L.H. Hsp90 and Cdc37—A chaperone cancer conspiracy. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2005, 15, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, P.J., Jr.; Prince, T.; Cheng, J.; Stevenson, M.A.; Calderwood, S.K. Targeting the oncogene and kinome chaperone CDC37. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnitz, L.M.; Felts, S.J. Cdc37 regulation of the kinome: When to hold 'em and when to fold 'em. Sci. STKE 2007, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.R.; Workman, P. Targeting CDC37: An alternative, kinase-directed strategy for disruption of oncogenic chaperoning. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, S.M.; Clubb, R.J.; Ortega-Cava, C.; Williams, S.H.; Bailey, T.A.; Duan, L.; Zhao, X.; Reddi, A.L.; Nyong, A.M.; Natarajan, A.; et al. Anticancer activity of Celastrol in combination with ErbB2-targeted therapeutics for treatment of ErbB2-overexpressing breast cancers. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2011, 11, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.R.; de Billy, E.; Hobbs, S.; Powers, M.; Prodromou, C.; Pearl, L.; Clarke, P.A.; Workman, P. Restricting direct interaction of CDC37 with HSP90 does not compromise chaperoning of client proteins. Oncogene 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhomirov, O.; Carpenter, G. Identification of ErbB-2 kinase domain motifs required for geldanamycin-induced degradation. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Yuan, X.; Xiang, Z.; Mimnaugh, E.; Marcu, M.; Neckers, L. Surface charge and hydrophobicity determine ErbB2 binding to the Hsp90 chaperone complex. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2005, 12, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citri, A.; Gan, J.; Mosesson, Y.; Vereb, G.; Szollosi, J.; Yarden, Y. Hsp90 restrains ErbB-2/HER2 signalling by limiting heterodimer formation. EMBO Rep. 2004, 5, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yuan, X.; Beebe, K.; Xiang, Z.; Neckers, L. Loss of Hsp90 association up-regulates Src-dependent ErbB2 activity. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Sahu, D.; Tsen, F. Secreted heat shock protein-90 (Hsp90) in wound healing and cancer. Biochim. Et biophys. Acta 2012, 1823, 730–741. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Tsen, F.; Sahu, D.; Bhatia, A.; Chen, M.; Multhoff, G.; Woodley, D.T. Extracellular Hsp90 (eHsp90) as the actual target in clinical trials: Intentionally or unintentionally. Int. Rev. Cell mol. Biol. 2013, 303, 203–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidera, K.; Patsavoudi, E. Extracellular HSP90: Conquering the cell surface. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 1564–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsumi, S.; Neckers, L. Extracellular heat shock protein 90: A role for a molecular chaperone in cell motility and cancer metastasis. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 1536–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hamidieh, A.; Grammatikakis, N.; Patsavoudi, E. Cell surface Cdc37 participates in extracellular HSP90 mediated cancer cell invasion. PLoS One 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidera, K.; Gaitanou, M.; Stellas, D.; Matsas, R.; Patsavoudi, E. A critical role for HSP90 in cancer cell invasion involves interaction with the extracellular domain of HER-2. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 2031–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sak, M.M.; Szymanska, M.; Bertelsen, V.; Hasmann, M.; Madshus, I.H.; Stang, E. Pertuzumab counteracts the inhibitory effect of ErbB2 on degradation of ErbB3. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 2031–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrott, J.; Haystead, T.A.J. Hsp90, an unlikely ally in the war on cancer. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 1381–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Mimnaugh, E.; Rosser, M.F.; Nicchitta, C.; Marcu, M.; Yarden, Y.; Neckers, L. Sensitivity of mature Erbb2 to geldanamycin is conferred by its kinase domain and is mediated by the chaperone protein Hsp90. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 3702–3708. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Marcu, M.; Yuan, X.; Mimnaugh, E.; Patterson, C.; Neckers, L. Chaperone-dependent E3 ubiquitin ligase CHIP mediates a degradative pathway for c-ErbB2/Neu. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 12847–12852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Fernandes, N.; Dodge, I.L.; Reddi, A.L.; Rao, N.; Safran, H.; DiPetrillo, T.A.; Wazer, D.E.; Band, V.; Band, H. ErbB2 degradation mediated by the co-chaperone protein CHIP. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 13829–13837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, E.S.; Wang, T.; Luo, K.; Xiao, Z.; Niewiadomska, A.M.; Martinez, T.; Xu, W.; Neckers, L.; Yu, X.F. Regulation of Hsp90 client proteins by a Cullin5-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 20330–20335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samant, R.S.; Clarke, P.A.; Workman, P. E3 ubiquitin ligase Cullin-5 modulates multiple molecular and cellular responses to heat shock protein 90 inhibition in human cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 6834–6839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigismund, S.; Algisi, V.; Nappo, G.; Conte, A.; Pascolutti, R.; Cuomo, A.; Bonaldi, T.; Argenzio, E.; Verhoef, L.G.; Maspero, E.; et al. Threshold-controlled ubiquitination of the EGFR directs receptor fate. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 2140–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksen, L.; Grandal, M.V.; Knudsen, S.L.; van Deurs, B.; Grovdal, L.M. Internalization mechanisms of the epidermal growth factor receptor after activation with different ligands. PLoS One 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roepstorff, K.; Grandal, M.V.; Henriksen, L.; Knudsen, S.L.; Lerdrup, M.; Grovdal, L.; Willumsen, B.M.; van Deurs, B. Differential effects of EGFR ligands on endocytic sorting of the receptor. Traffic 2009, 10, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longva, K.E.; Blystad, F.D.; Stang, E.; Larsen, A.M.; Johannessen, L.E.; Madshus, I.H. Ubiquitination and proteasomal activity is required for transport of the EGF receptor to inner membranes of multivesicular bodies. J. Cell Biol. 2002, 156, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sak, M.M.; Breen, K.; Ronning, S.B.; Pedersen, N.M.; Bertelsen, V.; Stang, E.; Madshus, I.H. The oncoprotein ErbB3 is endocytosed in the absence of added ligand in a clathrin-dependent manner. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, W.H.; Simion, C.; Sweeney, C.; Carraway, K.L., 3rd. Quantity control of the ErbB3 receptor tyrosine kinase at the endoplasmic reticulum. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2011, 31, 3009–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hommelgaard, A.M.; Lerdrup, M.; van Deurs, B. Association with membrane protrusions makes ErbB2 an internalization-resistant receptor. Mol. Biol. Cell 2004, 15, 1557–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yeung, T.K.; Chen, X. Endocytosis deficiency of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor-ErbB2 heterodimers in response to EGF stimulation. Mol. Biol. Cell 1999, 10, 1621–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haslekas, C.; Breen, K.; Pedersen, K.W.; Johannessen, L.E.; Stang, E.; Madshus, I.H. The inhibitory effect of ErbB2 on epidermal growth factor-induced formation of clathrin-coated pits correlates with retention of epidermal growth factor receptor-ErbB2 oligomeric complexes at the plasma membrane. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 5832–5842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorkin, A.; di Fiore, P.P.; Carpenter, G. The carboxyl terminus of epidermal growth factor receptor/erbB-2 chimerae is internalization impaired. Oncogene 1993, 8, 3021–3028. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, N.M.; Madshus, I.H.; Haslekas, C.; Stang, E. Geldanamycin-induced down-regulation of ErbB2 from the plasma membrane is clathrin dependent but proteasomal activity independent. Mol. Cancer Res. 2008, 6, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerdrup, M.; Bruun, S.; Grandal, M.V.; Roepstorff, K.; Kristensen, M.M.; Hommelgaard, A.M.; van Deurs, B. Endocytic down-regulation of ErbB2 is stimulated by cleavage of its C-terminus. Mol. Biol. Cell 2007, 18, 3656–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerdrup, M.; Hommelgaard, A.M.; Grandal, M.; van Deurs, B. Geldanamycin stimulates internalization of ErbB2 in a proteasome-dependent way. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pust, S.; Klokk, T.I.; Musa, N.; Jenstad, M.; Risberg, B.; Erikstein, B.; Tcatchoff, L.; Liestol, K.; Danielsen, H.E.; van Deurs, B.; et al. Flotillins as regulators of ErbB2 levels in breast cancer. Oncogene 2013, 32, 3443–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harari, D.; Yarden, Y. Molecular mechanisms underlying ErbB2/HER2 action in breast cancer. Oncogene 2000, 19, 6102–6114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, B.S.; Opresko, L.K.; Wiley, H.S.; Lauffenburger, D. Coregulation of epidermal growth factor receptor/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) levels and locations: Quantitative analysis of HER2 overexpression effects. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 1130–1137. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, C.D.; de Maziere, A.M.; Pisacane, P.I.; van Dijk, S.M.; Eigenbrot, C.; Sliwkowski, M.X.; Klumperman, J.; Scheller, R.H. Endocytosis and sorting of ErbB2 and the site of action of cancer therapeutics trastuzumab and geldanamycin. Mol. Biol. Cell 2004, 15, 5268–5282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortese, K.; Howes, M.T.; Lundmark, R.; Tagliatti, E.; Bagnato, P.; Petrelli, A.; Bono, M.; McMahon, H.T.; Parton, R.G.; Tacchetti, C. The HSP90 inhibitor geldanamycin perturbs endosomal structure and drives recycling ErbB2 and transferrin to modified MVBs/lysosomal compartments. Mol. Biol. Cell 2013, 24, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, P.; Vereb, G.; Sebestyen, Z.; Horvath, G.; Lockett, S.J.; Damjanovich, S.; Park, J.W.; Jovin, T.M.; Szollosi, J. Lipid rafts and the local density of ErbB proteins influence the biological role of homo- and heteroassociations of ErbB2. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 4251–4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raina, D.; Uchida, Y.; Kharbanda, A.; Rajabi, H.; Panchamoorthy, G.; Jin, C.; Kharbanda, S.; Scaltriti, M.; Baselga, J.; Kufe, D. Targeting the MUC1-C oncoprotein downregulates HER2 activation and abrogates trastuzumab resistance in breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2014, 33, 3422–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staubach, S.; Razawi, H.; Hanisch, F.G. Proteomics of MUC1-containing lipid rafts from plasma membranes and exosomes of human breast carcinoma cells MCF-7. Proteomics 2009, 9, 2820–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, C.; Tosoni, D.; Comai, R.; Rabellino, A.; Segat, D.; Caneva, F.; Luzzi, P.; Di Fiore, P.P.; Tacchetti, C. Relationships between EGFR signaling-competent and endocytosis-competent membrane microdomains. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 2704–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhomirov, O.; Carpenter, G. Geldanamycin induces ErbB-2 degradation by proteolytic fragmentation. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 26625–26631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhomirov, O.; Carpenter, G. Caspase-dependent cleavage of ErbB-2 by geldanamycin and staurosporin. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 33675–33680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Lin, Q.; Childress, C.; Yang, W. Identification of the domain in ErbB2 that restricts ligand-induced degradation. Cell Signal 2008, 20, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traub, L.M.; Bonifacino, J.S. Cargo recognition in clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, L.K.; Huang, F.; Kim, W.; Gygi, S.; Sorkin, A. Multiple mechanisms collectively regulate clathrin-mediated endocytosis of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 189, 871–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baulida, J.; Kraus, M.H.; Alimandi, M.; Di Fiore, P.P.; Carpenter, G. All ErbB receptors other than the epidermal growth factor receptor are endocytosis impaired. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 5251–5257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannessen, L.E.; Pedersen, N.M.; Pedersen, K.W.; Madshus, I.H.; Stang, E. Activation of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor induces formation of EGF receptor- and Grb2-containing clathrin-coated pits. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longva, K.E.; Pedersen, N.M.; Haslekas, C.; Stang, E.; Madshus, I.H. Herceptin-induced inhibition of ErbB2 signaling involves reduced phosphorylation of Akt but not endocytic down-regulation of ErbB2. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 116, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, D.J.; Ostermeyer-Fay, A.G.; Matundan, R.A.; Brown, D.A. Clathrin-independent endocytosis of ErbB2 in geldanamycin-treated human breast cancer cells. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 3155–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polo, S.; Di Fiore, P.P.; Sigismund, S. Keeping EGFR signaling in check: Ubiquitin is the guardian. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 681–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madshus, I.H.; Stang, E. Internalization and intracellular sorting of the EGF receptor: A model for understanding the mechanisms of receptor trafficking. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 3433–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haglund, K.; Dikic, I. The role of ubiquitylation in receptor endocytosis and endosomal sorting. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anania, V.G.; Pham, V.C.; Huang, X.; Masselot, A.; Lill, J.R.; Kirkpatrick, D.S. Peptide level immunoaffinity enrichment enhances ubiquitination site identification on individual proteins. Mol. Cell Proteomics 2014, 13, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, C.; Held, J.M.; Gibson, B.W.; Benz, C.C. ErbB2 trafficking and degradation associated with K48 and K63 polyubiquitination. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 3709–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, T.T.; Berger, C.; Bertelsen, V.; Rodland, M.S.; Stang, E.; Madshus, I.H. Preubiquitinated chimeric ErbB2 is constitutively endocytosed and subsequently degraded in lysosomes. Exp. Cell Res. 2013, 319, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Kasus, T.; Schechter, B.; Lavi, S.; Yarden, Y.; Sela, M. Persistent elimination of ErbB-2/HER2-overexpressing tumors using combinations of monoclonal antibodies: Relevance of receptor endocytosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3294–3299. [Google Scholar]
- Klapper, L.N.; Waterman, H.; Sela, M.; Yarden, Y. Tumor-inhibitory antibodies to HER-2/ErbB-2 may act by recruiting c-Cbl and enhancing ubiquitination of HER-2. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 3384–3388. [Google Scholar]
- Meijer, I.M.J.; van Leeuwen, J.E.M. ERBB2 is a target for USP8-mediated deubiquitination. Cell. Signal. 2011, 23, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, I.M.J.; van Rotterdam, W.; van Zoelen, E.J.J.; van Leeuwen, J.E.M. Recycling of EGFR and ErbB2 is associated with impaired Hrs tyrosine phosphorylation and decreased deubiquitination by AMSH. Cell. Signal. 2012, 24, 1981–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junttila, T.T.; Akita, R.W.; Parsons, K.; Fields, C.; Lewis Phillips, G.D.; Friedman, L.S.; Sampath, D.; Sliwkowski, M.X. Ligand-independent HER2/HER3/PI3K complex is disrupted by trastuzumab and is effectively inhibited by the PI3K inhibitor GDC-0941. Cancer Cell 2009, 15, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agus, D.B.; Akita, R.W.; Fox, W.D.; Lewis, G.D.; Higgins, B.; Pisacane, P.I.; Lofgren, J.A.; Tindell, C.; Evans, D.P.; Maiese, K.; et al. Targeting ligand-activated ErbB2 signaling inhibits breast and prostate tumor growth. Cancer Cell 2002, 2, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, M.C.; Carey, K.D.; Vajdos, F.F.; Leahy, D.J.; de Vos, A.M.; Sliwkowski, M.X. Insights into ErbB signaling from the structure of the ErbB2-pertuzumab complex. Cancer Cell 2004, 5, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, M.A.; Codony-Servat, J.; Albanell, J.; Rojo, F.; Arribas, J.; Baselga, J. Trastuzumab (herceptin), a humanized anti-Her2 receptor monoclonal antibody, inhibits basal and activated Her2 ectodomain cleavage in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 4744–4749. [Google Scholar]
- Baselga, J.; Albanell, J.; Molina, M.A.; Arribas, J. Mechanism of action of trastuzumab and scientific update. Semin. Oncol. 2001, 28, 4–11. [Google Scholar]
- Cuello, M.; Ettenberg, S.A.; Clark, A.S.; Keane, M.M.; Posner, R.H.; Nau, M.M.; Dennis, P.A.; Lipkowitz, S. Down-regulation of the erbB-2 receptor by trastuzumab (herceptin) enhances tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-mediated apoptosis in breast and ovarian cancer cell lines that overexpress erbB-2. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 4892–4900. [Google Scholar]
- Hudziak, R.M.; Lewis, G.D.; Winget, M.; Fendly, B.M.; Shepard, H.M.; Ullrich, A. p185HER2 monoclonal antibody has antiproliferative effects in vitro and sensitizes human breast tumor cells to tumor necrosis factor. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1989, 9, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Okollie, B.; Artemov, D. Controlled internalization of Her-2/ neu receptors by cross-linking for targeted delivery. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2007, 6, 1960–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.B.; Rodland, M.S.; Hasmann, M.; Madshus, I.H.; Stang, E. Pertuzumab Increases 17-AAG-Induced Degradation of ErbB2, and This Effect Is Further Increased by Combining Pertuzumab with Trastuzumab. Pharmaceuticals 2012, 5, 674–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahta, R.; Hung, M.C.; Esteva, F.J. The HER-2-targeting antibodies trastuzumab and pertuzumab synergistically inhibit the survival of breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 2343–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, L.M.; Rinon, A.; Schechter, B.; Lyass, L.; Lavi, S.; Bacus, S.S.; Sela, M.; Yarden, Y. Synergistic down-regulation of receptor tyrosine kinases by combinations of mAbs: Implications for cancer immunotherapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 1915–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, L.A.; Xu, F.J.; Hester, S.; Boyer, C.M.; McKenzie, S.; Bruskin, A.M.; Argon, Y.; Bast, R.C., Jr. Requirements for the internalization of a murine monoclonal antibody directed against the HER-2/neu gene product c-erbB-2. Cancer Res. 1991, 51, 5361–5369. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, C.; Madshus, I.H.; Stang, E. Cetuximab in combination with anti-human IgG antibodies efficiently down-regulates the EGF receptor by macropinocytosis. Exp. Cell Res. 2012, 318, 2578–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R.; Narasanna, A.; Wang, S.E.; Liu, S.; Chakrabarty, A.; Balko, J.M.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Mills, G.B.; Penuel, E.; Winslow, J.; et al. Trastuzumab has preferential activity against breast cancers driven by HER2 homodimers. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 1871–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheer, J.M.; Sandoval, W.; Elliott, J.M.; Shao, L.; Luis, E.; Lewin-Koh, S.C.; Schaefer, G.; Vandlen, R. Reorienting the Fab domains of trastuzumab results in potent HER2 activators. PLoS One 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, L.M.; Murray, J.C.; Shuptrine, C.W. Antibody-based immunotherapy of cancer. Cell 2012, 148, 1081–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, G.; Liao, H.J. Receptor tyrosine kinases in the nucleus. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect Biol. 2013, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.N.; Hung, M.C. Nuclear functions and subcellular trafficking mechanisms of the epidermal growth factor receptor family. Cell Biosci. 2012, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koumakpayi, I.H.; Le Page, C.; Delvoye, N.; Saad, F.; Mes-Masson, A.M. Macropinocytosis inhibitors and Arf6 regulate ErbB3 nuclear localization in prostate cancer cells. Mol. Carcinog. 2011, 50, 901–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccione, E.C.; Lieu, T.J.; Gentile, C.F.; Williams, T.R.; Connolly, A.J.; Godwin, A.K.; Koong, A.C.; Wong, A.J. A novel epidermal growth factor receptor variant lacking multiple domains directly activates transcription and is overexpressed in tumors. Oncogene 2012, 31, 2953–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.J.; Carpenter, G. Regulated intramembrane cleavage of the EGF receptor. Traffic 2012, 13, 1106–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.J.; Carpenter, G. Role of the Sec61 translocon in EGF receptor trafficking to the nucleus and gene expression. Mol. Biol. Cell 2007, 18, 1064–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.Y.; Makino, K.; Xia, W.; Matin, A.; Wen, Y.; Kwong, K.Y.; Bourguignon, L.; Hung, M.C. Nuclear localization of EGF receptor and its potential new role as a transcription factor. Nature Cell Biol. 2001, 3, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.J.; Carpenter, G. Cetuximab/C225-induced intracellular trafficking of epidermal growth factor receptor. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 6179–6183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis Campos, A.C.; Rodrigues, M.A.; de Andrade, C.; de Goes, A.M.; Nathanson, M.H.; Gomes, D.A. Epidermal growth factor receptors destined for the nucleus are internalized via a clathrin-dependent pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 412, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, P.Z.; Gunn, P.; Gleeson, P.A. Cargo trafficking between endosomes and the trans-Golgi network. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 140, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.N.; Wang, H.; Yamaguchi, H.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, H.H.; Hung, M.C. COPI-mediated retrograde trafficking from the Golgi to the ER regulates EGFR nuclear transport. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 399, 498–504. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, H.W.; Ali-Seyed, M.; Wu, Y.; Bartholomeusz, G.; Hsu, S.C.; Hung, M.C. Nuclear-cytoplasmic transport of EGFR involves receptor endocytosis, importin beta1 and CRM1. J. Cell. Biochem. 2006, 98, 1570–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.C.; Hung, M.C. Characterization of a novel tripartite nuclear localization sequence in the EGFR family. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 10432–10440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.N.; Yamaguchi, H.; Huo, L.; Du, Y.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, H.H.; Wang, H.; Hsu, J.M.; Hung, M.C. The translocon Sec61beta localized in the inner nuclear membrane transports membrane-embedded EGF receptor to the nucleus. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 38720–38729. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, W.; Liu, Z.; Zong, R.; Liu, L.; Zhao, S.; Bacus, S.S.; Mao, Y.; He, J.; Wulfkuhle, J.D.; Petricoin, E.F., 3rd.; et al. Spector, Truncated ErbB2 expressed in tumor cell nuclei contributes to acquired therapeutic resistance to ErbB2 kinase inhibitors. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 1367–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaltriti, M.; Verma, C.; Guzman, M.; Jimenez, J.; Parra, J.L.; Pedersen, K.; Smith, D.J.; Landolfi, S.; Ramony Cajal, S.; Arribas, J.; et al. Lapatinib, a HER2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor, induces stabilization and accumulation of HER2 and potentiates trastuzumab-dependent cell cytotoxicity. Oncogene 2009, 28, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Martin, A.; Oliveras-Ferraros, C.; Cufi, S.; Del Barco, S.; Martin-Castillo, B.; Menendez, J.A. Lapatinib, a dual HER1/HER2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor, augments basal cleavage of HER2 extracellular domain (ECD) to inhibit HER2-driven cancer cell growth. J. Cell. Physiol. 2010, 226, 52–57. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.P.; Yoon, Y.K.; Kim, J.W.; Han, S.W.; Hur, H.S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.H.; Oh, D.Y.; Im, S.A.; Bang, Y.J.; et al. Lapatinib, a dual EGFR and HER2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor, downregulates thymidylate synthase by inhibiting the nuclear translocation of EGFR and HER2. PLoS One 2009, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, D.K.; Ali-Seyed, M.; Li, L.Y.; Lee, D.F.; Ling, P.; Bartholomeusz, G.; Wang, S.C.; Hung, M.C. Endosomal transport of ErbB-2: Mechanism for nuclear entry of the cell surface receptor. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 11005–11018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.C.; Lien, H.C.; Xia, W.; Chen, I.F.; Lo, H.W.; Wang, Z.; Ali-Seyed, M.; Lee, D.F.; Bartholomeusz, G.; Ou-Yang, F.; et al. Binding at and transactivation of the COX-2 promoter by nuclear tyrosine kinase receptor ErbB-2. Cancer Cell 2004, 6, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.N.; Lee, H.H.; Lee, H.J.; Du, Y.; Yamaguchi, H.; Hung, M.C. Membrane-bound trafficking regulates nuclear transport of integral epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and ErbB-2. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 16869–16879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beguelin, W.; Diaz Flaque, M.C.; Proietti, C.J.; Cayrol, F.; Rivas, M.A.; Tkach, M.; Rosemblit, C.; Tocci, J.M.; Charreau, E.H.; Schillaci, R.; et al. Progesterone receptor induces ErbB-2 nuclear translocation to promote breast cancer growth via a novel transcriptional effect: ErbB-2 function as a coactivator of Stat3. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010, 30, 5456–5472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.B.; Berger, C.; Rodland, M.S.; Hasmann, M.; Stang, E.; Madshus, I.H. Pertuzumab increases epidermal growth factor receptor down-regulation by counteracting epidermal growth factor receptor-ErbB2 heterodimerization. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 1885–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kancha, R.K.; Bartosch, N.; Duyster, J. Analysis of conformational determinants underlying HSP90-kinase interaction. PLoS One 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Bertelsen, V.; Stang, E. The Mysterious Ways of ErbB2/HER2 Trafficking. Membranes 2014, 4, 424-446. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes4030424
Bertelsen V, Stang E. The Mysterious Ways of ErbB2/HER2 Trafficking. Membranes. 2014; 4(3):424-446. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes4030424
Chicago/Turabian StyleBertelsen, Vibeke, and Espen Stang. 2014. "The Mysterious Ways of ErbB2/HER2 Trafficking" Membranes 4, no. 3: 424-446. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes4030424
APA StyleBertelsen, V., & Stang, E. (2014). The Mysterious Ways of ErbB2/HER2 Trafficking. Membranes, 4(3), 424-446. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes4030424