Investigations on the Particle Fouling and Backwash Efficiency During Microplastic Microfiltration–Particle Size Aspects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of MP Particle–Water Suspensions
2.2. Microfiltration Experiments and Backwash Procedure
2.3. Characterization of the Particle Fouling
2.4. Microscopy
2.5. Water Contact Angle Measurement
2.6. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.7. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
3. Results
3.1. Preparation of the Suspension
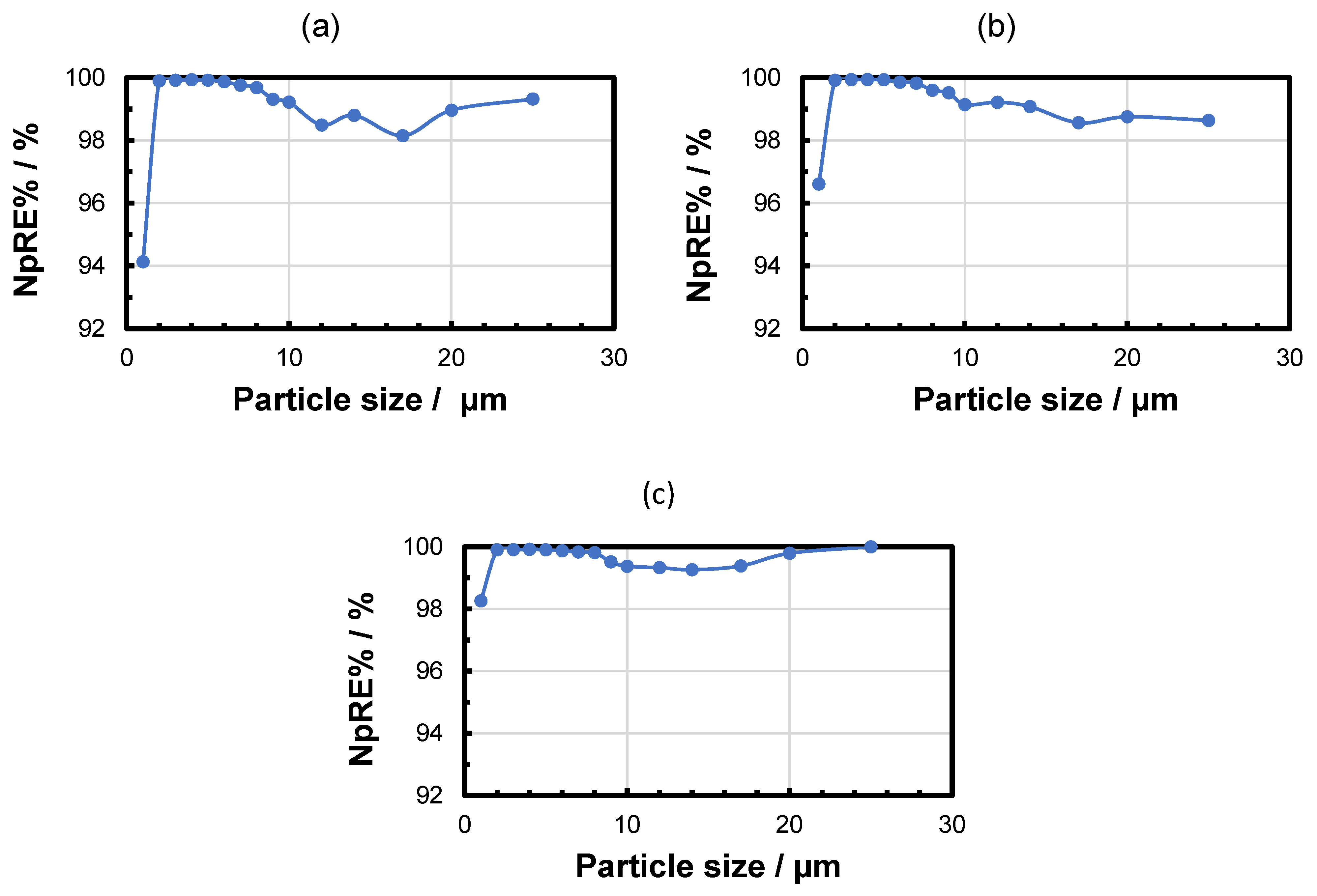
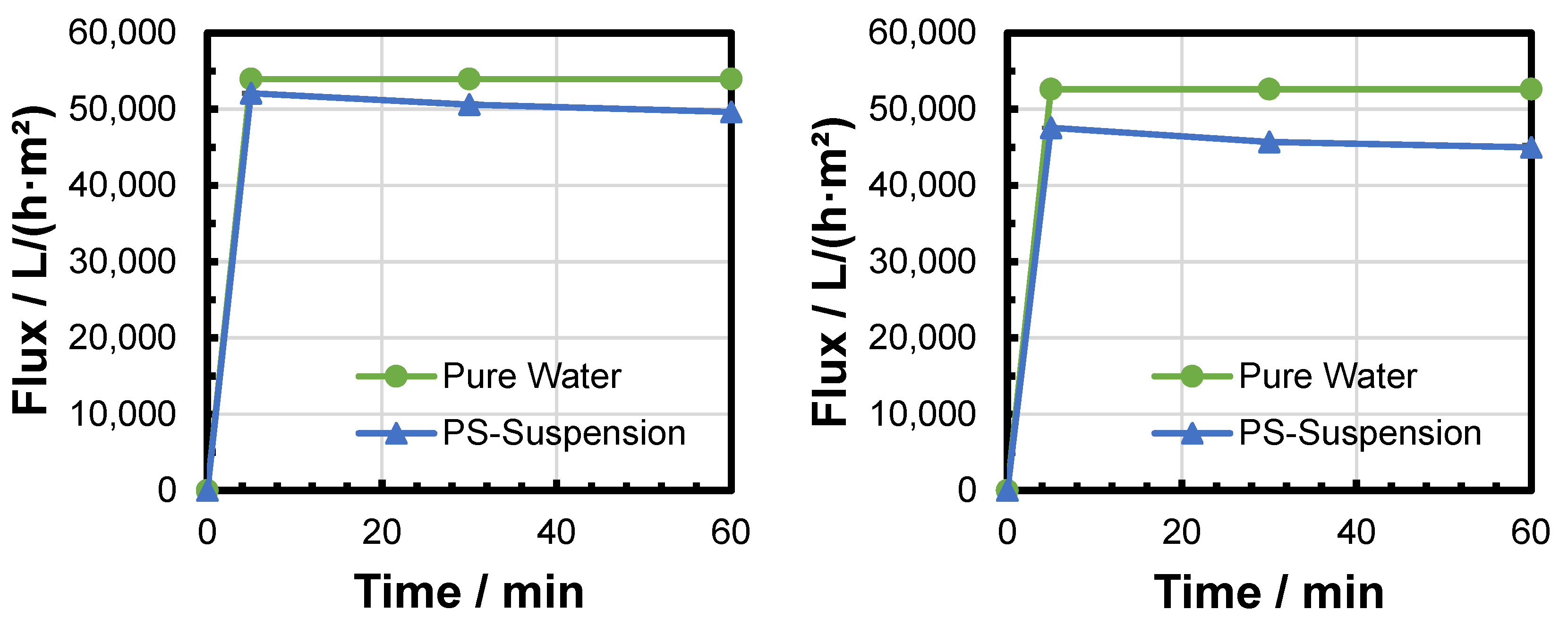
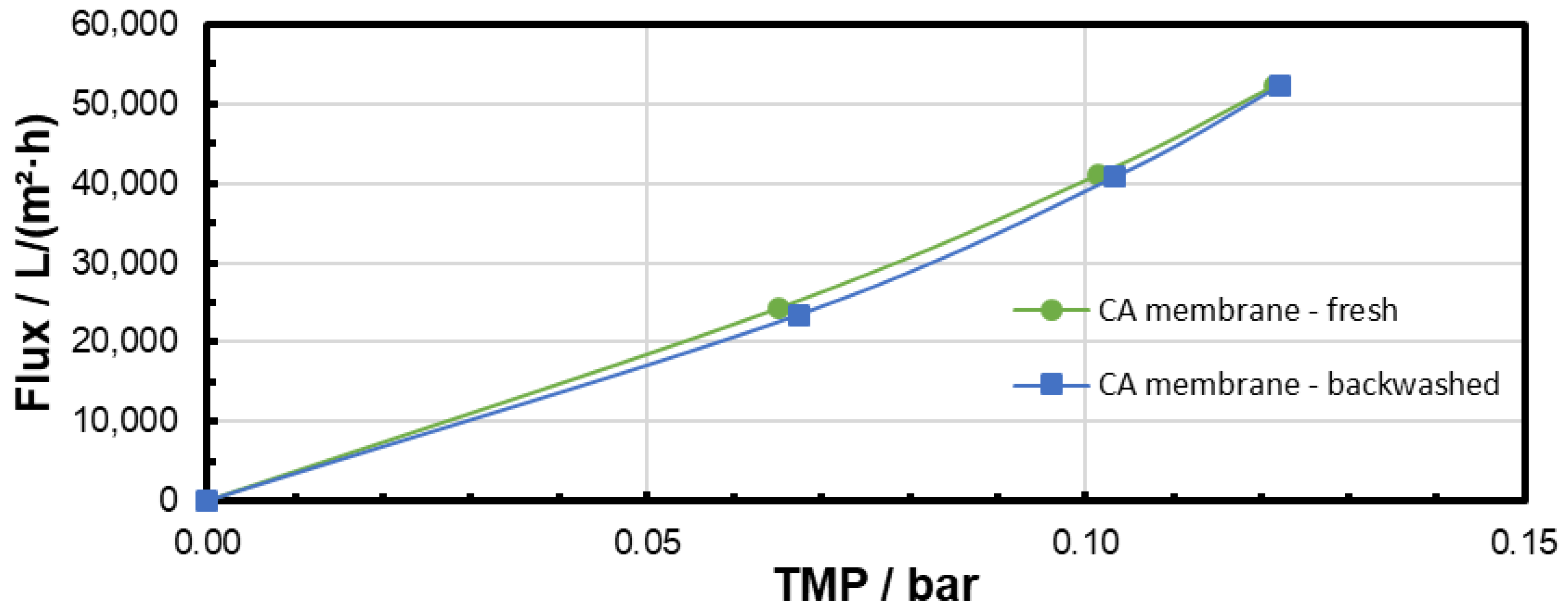
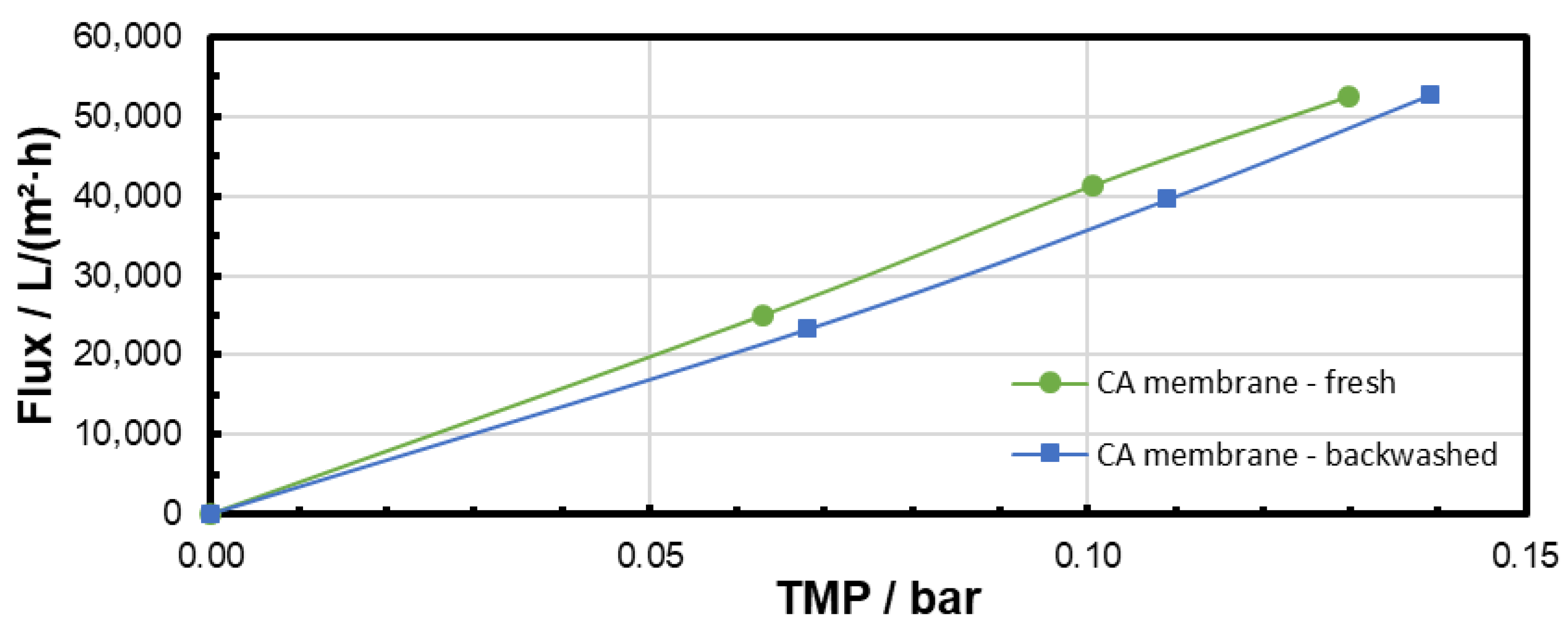
3.2. Microfiltration Experiments
3.3. Backwashing Experiments
3.4. Particle-Fouling Analysis
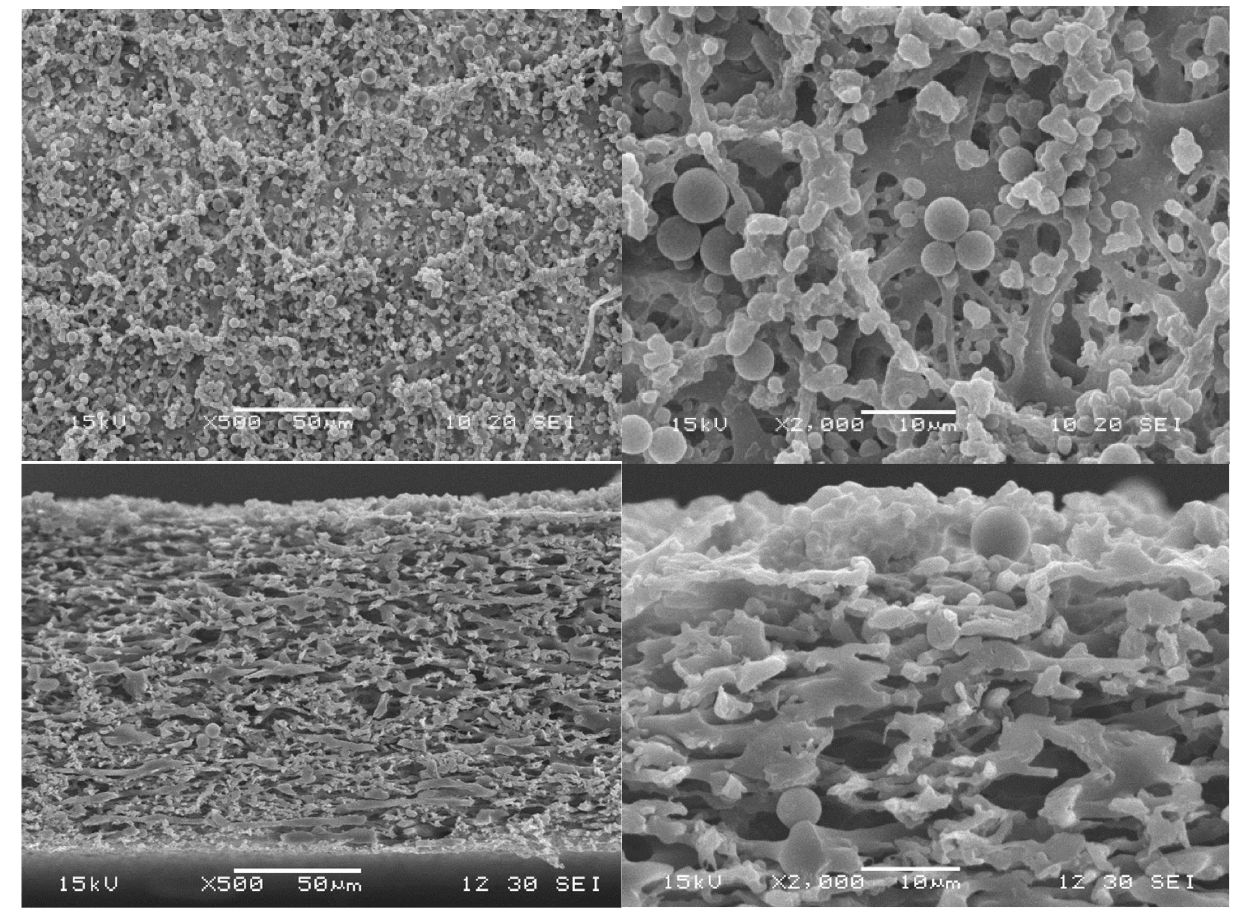
3.5. Particle-Fouling Analysis by SEM and Light Microscopy
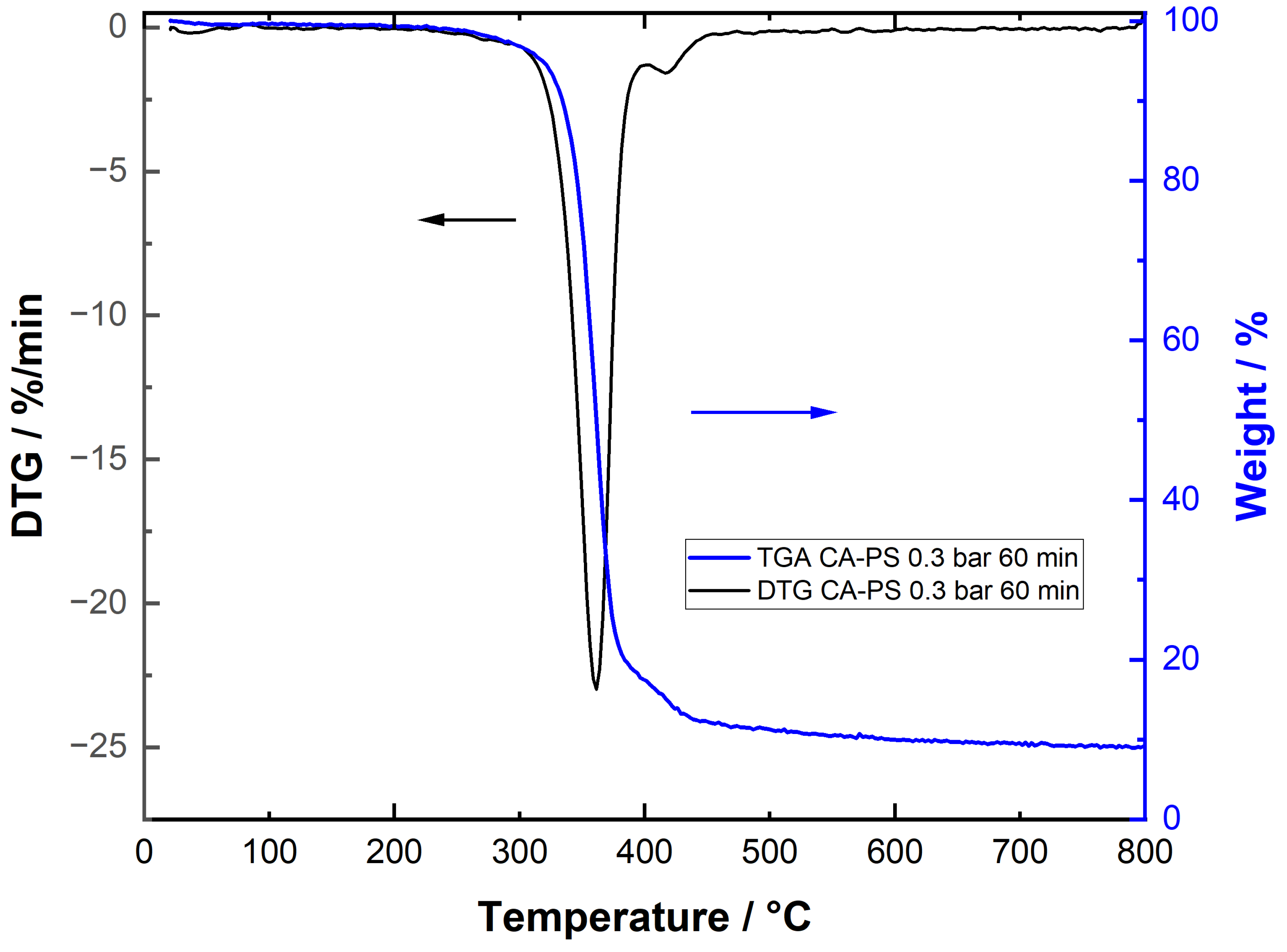
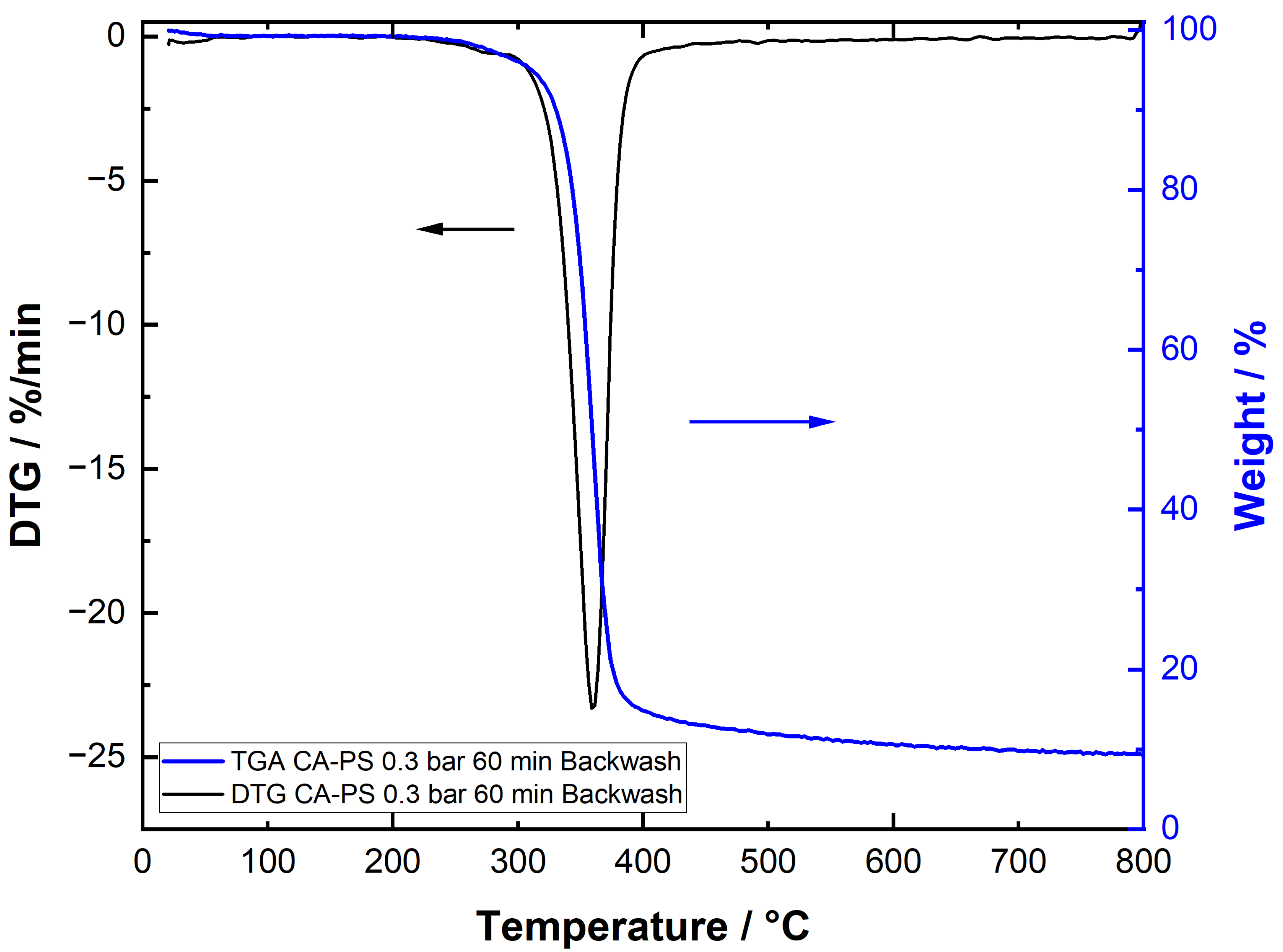
3.6. Particle-Fouling Analysis by TGA
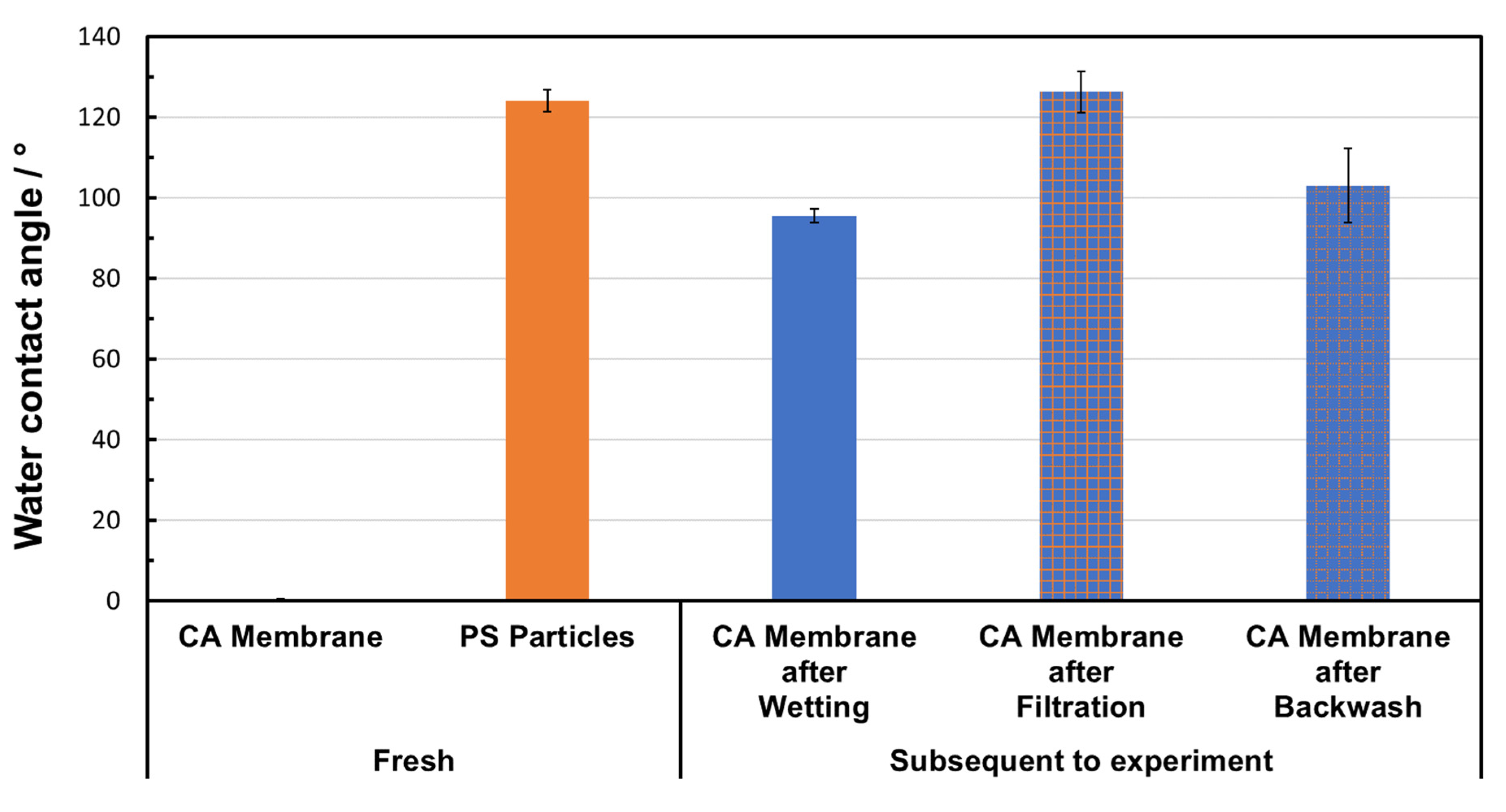
3.7. Particle-Fouling Analysis by Water Contact Angle Measurements
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tajwara, M.; Gazi, M.J.; Sahaa, S.K. Characterization and Spatial Abundance of Microplastics in the Coastal Regions of Cox’s Bazar, Bangladesh: An Integration of Field, Laboratory, and GIS Techniques. Soil Sediment Contam. Int. J. 2021, 31, 57–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Park, B. Review of Microplastic Distribution, Toxicity, Analysis Methods, and Removal Technologies. Water 2021, 13, 2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ou, Q.; Wang, X.; van der Hoek, J.P.; Liu, G. Mass Concentration and Removal Characteristics of Microplastics and Nanoplastics in a Drinking Water Treatment Plant. ACS EST Water 2024, 4, 3348–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Xue, W.; Ding, Y.; Hu, C.; Liu, H.; Qu, J. Removal characteristics of microplastics by Fe-based coagulants during drinking water treatment. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 78, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acarer, S. A review of microplastic removal from water and wastewater by membrane technologies. Water Sci. Technol. 2023, 88, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bella, G.; Corsino, S.F.; De Marines, F.; Lopresti, F.; La Carrubba, V.; Torregrossa, M.; Viviani, G. Occurrence of Microplastics in Waste Sludge of Wastewater Treatment Plants: Comparison between Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) and Conventional Activated Sludge (CAS) Technologies. Membranes 2022, 12, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egea-Corbacho, A.; Martín-García, A.P.; Franco, A.A.; Quiroga, J.M.; Andreasen, R.R.; Jørgensen, M.K.; Christensen, M.L. Occurrence, identification and removal of microplastics in a wastewater treatment plant compared to an advanced MBR technology: Full-scale pilot plant. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rius-Ayra, O.; Biserova-Tahchieva, A.; LLorca-Isern, N. Surface-functionalised materials for microplastic removal. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 167, 112335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, A.; Örmeci, B. Removal Effectiveness of Nanoplastics (<400 nm) with Separation Processes Used for Water and Wastewater Treatment. Water 2020, 12, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akrsu, C.; Kumbur, H.; Kideys, A.E. Removal of microplastics from wastewater through electrocoagulation-electroflotation and membrane filtration processes. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 84, 1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Tan, X.; Mustafa, G.; Gao, J.; Peng, C.; Naz, I.; Duan, Z.; Zhu, R.; Ruan, Y. Removal of micro- and nanoplastics by filtration technology: Performance and obstructions to market penetrations. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 470, 143305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, A.; Shetti, N.P.; Basu, S.; Reddy, R.R.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Identification and removal of micro- and nano-plastics: Efficient and cost-effective methods. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 421, 129816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, B.; Chen, Z.; Ma, B.; Chen, J.B. Ultrafiltration membrane fouling by microplastics with raw water: Behaviors and alleviation methods. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 410, 128174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golgoli, M.; Khiadani, M.; Shafieian, A.; Sen, T.K.; Hartanto, Y.; Johns, M.L.; Zargar, M. Microplastics fouling and interaction with polymeric membranes: A review. Chemosphere 2021, 283, 131185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, S.; Hu, T.; Zheng, K.; Wang, Y.; Lian, J.; Meng, G. Recent advances on micro/nanoplastic pollution and membrane fouling during water treatment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 881, 163467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemi, S.; Yan, B.; Zargar, M.; Ling, N.N.A.; Fridjonsson, E.O.; Johns, M.L. Impact of microplastics on organic fouling of hollow fiber membranes. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 467, 143320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enfrin, M.; Wang, J.; Merenda, A.; Dumèe, L.F.; Lee, J. Mitigation of membrane fouling by nano/microplastics via surface chemistry control. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 633, 119379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enfrin, M.; Lee, J.; Fane, A.G.; Dumée, L.F. Mitigation of membrane particulate fouling by nano/microplastics via physical cleaning strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzichetti, A.R.P.; Pablos, C.; Alvarez-Fernandez, C.; Reynolds, K.; Stanley, S.; Marugan, J. Evaluation of membranes performance for microplastic removal in a simple and low-cost filtration system. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 3, 100075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzichetti, A.R.P.; Pablos, C.; Alvarez-Fernandez, C.; Reynolds, K.; Stanley, S.; Marugan, J. Kinetic and mechanistic analysis of membrane fouling in microplastics removal from water by dead-end microfiltration. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slejko, E.A.; Tuan, A.; Scuor, N. From waste to value: Characterization of recycled cellulose acetate for sustainable waste management. Waste Manag. Bull. 2024, 1, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.D.; Uddin, F.J.; Rashid, T.U.; Shahruzzaman, M. Cellulose acetate-based membrane for wastewater treatment—A state-of-the-art review. Mater. Adv. 2023, 4, 4054–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peonemann, K.-V.; Nunes, S.P. Membranes for Water Treatment; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Zhanga, R.; Liua, Y.; Hea, M.; Sua, Y.; Gaob, C.; Jianga, Z. Antifouling membrane surface construction: Chemistry plays a critical role. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 551, 145–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, J.-H.; Liu, J.; Sun, D.D. Quantification of membrane fouling using thermogravimetric method. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 217, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarudin, D.; Hashim, N.A.; Ong, B.H.; Faried, M.; Suga, K.; Umakoshi, H.; Mahari, W.A.W. Alternative fouling analysis of PVDF UF membrane for surface water treatment: The credibility of silver nanoparticles. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 661, 120865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Conceicao, M.; Lucena, C.; de Alencar, A.E.V.; Mazzeto, S.E.; Soares, S.A. The effect of additives on the thermal degradation of cellulose acetate. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2003, 80, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, H.M.; Anis, A.; Poulose, A.M.; Al-Zahrani, S.M.; Madhar, N.A.; Alhamidi, A.; Aldeligan, S.H.; Alsubaie, F.S. Synthesis and Characterization of Cellulose Triacetate Obtained from Date Palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) Trunk Mesh-Derived Cellulose. Molecules 2022, 27, 1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcilla, A.; Beltrán, M. Kinetic Study of the thermal decomposition of polystyrene and polyethylene-vinyl acetate graft copolymers by thermogravimetric analysis. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1995, 50, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faravelli, T.; Pinciroli, M.; Pisano, F.; Bozzano, G.; Dente, M.; Ranzi, E. Thermal degradation of polystyrene. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2001, 60, 103–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, B.N.; Wilkie, C.A. The thermal degradation of polystyrene nanocomposite. Polymer 2005, 46, 2933–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corami, F.; Rosso, B.; Bravo, B.; Gambaro, A.; Barbante, C. A novel method for purification quantitative analysis and characterization of microplastic fibers using Micro-FTIR. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, N.; Hakkarainen, M. Degradation of Cellulose Acetate in Simulated Aqueous Environments: One-Year Study. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2022, 307, 2100951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackley, M.R.; Sherman, N.E. Cross-Flow Cake Filtration Mechanism and Kinetics. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1992, 47, 3067–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyasa, H.K.; Mawsona, A.J.; Bennett, R.J.; Marshall, A.D. A new method for estimating cake height and porosity during crossflow filtration of particulate suspensions. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 176, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellam, S.; Xu, W. Blocking laws analysis of dead-end constant flux microfiltration of compressible cakes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 301, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dersoir, B.; Schofield, A.B.; Robert de Saint Vincent, M.; Tabuteau, H. Dynamics of pore fouling by colloidal particles at the particle level. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 573, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Mat Yasin, N.H.; Derek, C.J.C.; Lim, J.K. Microfiltration of Chlorella sp.: Influence of material and membrane pore size. Membr. Water Treat. 2013, 4, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

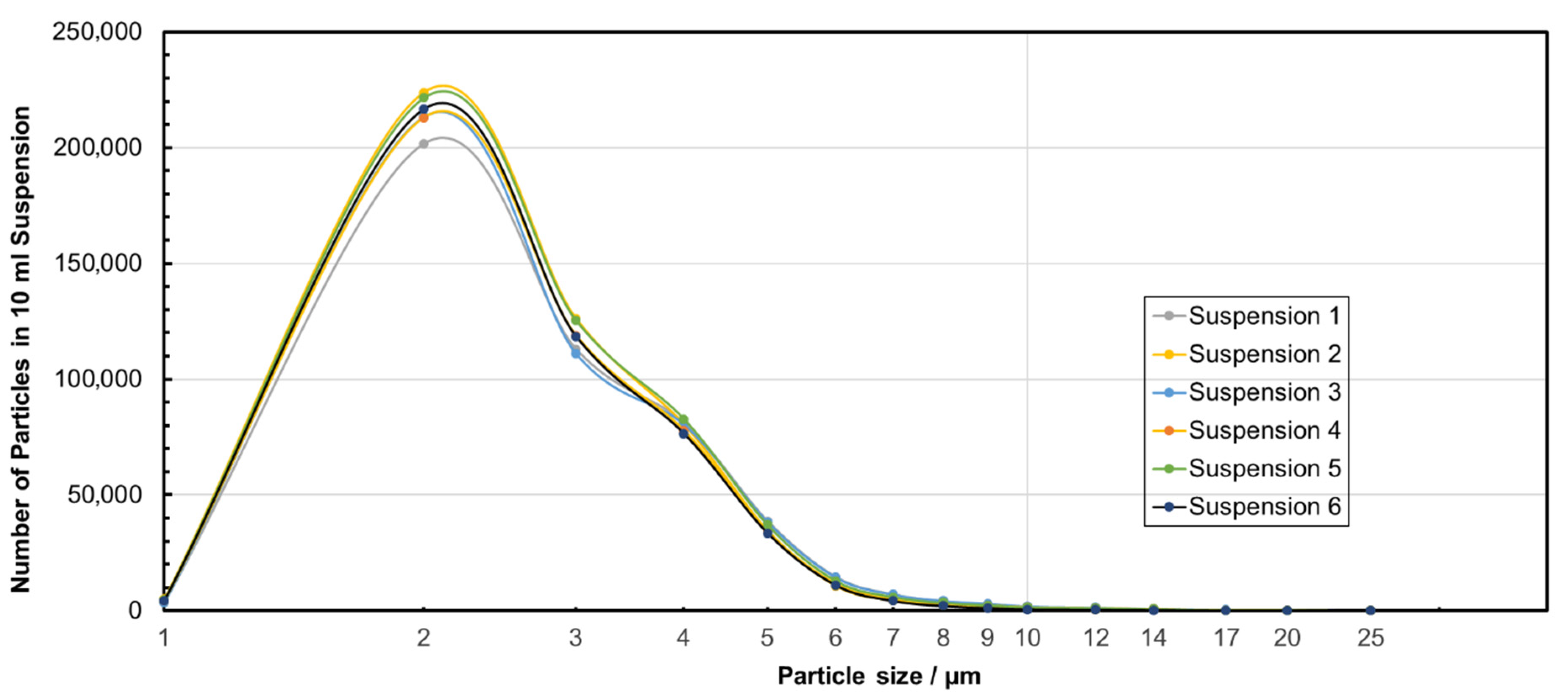
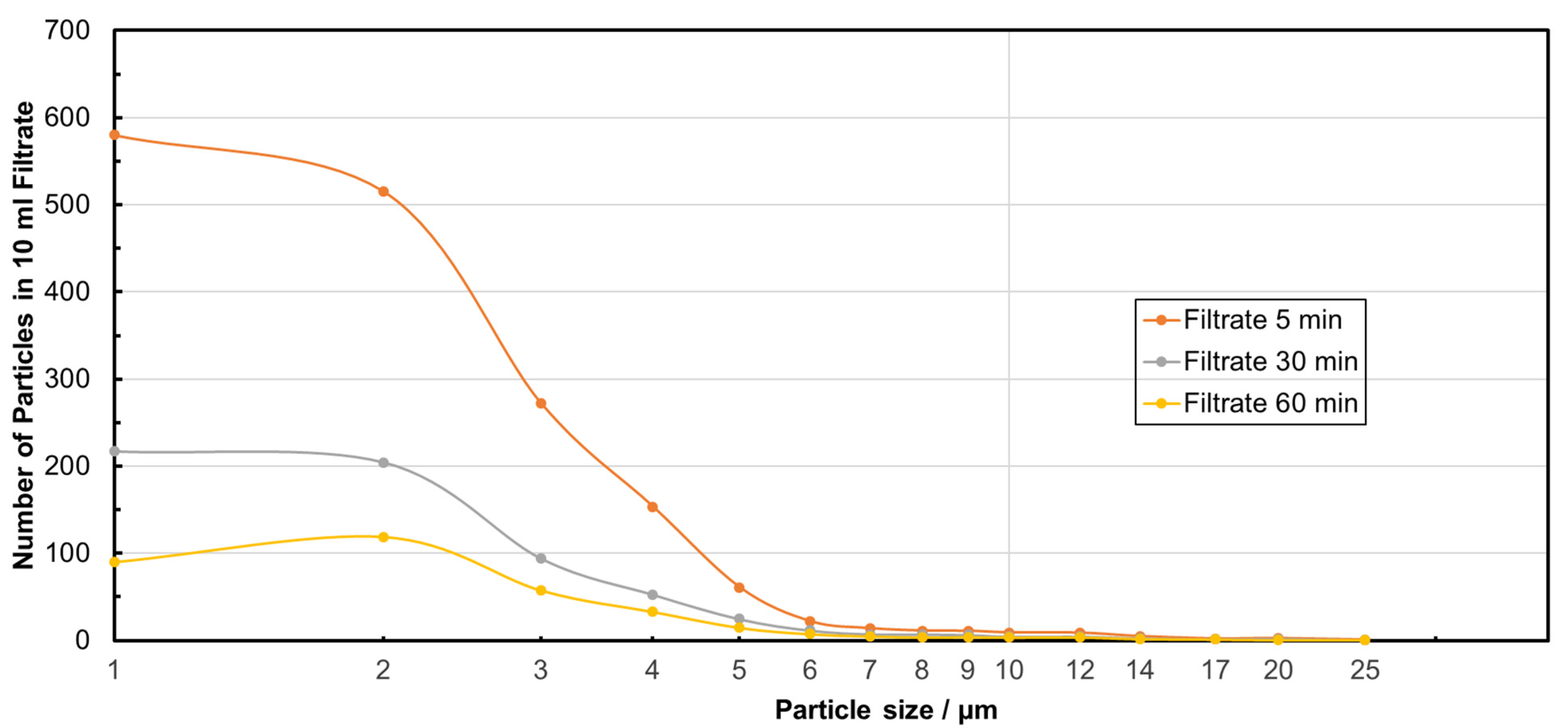
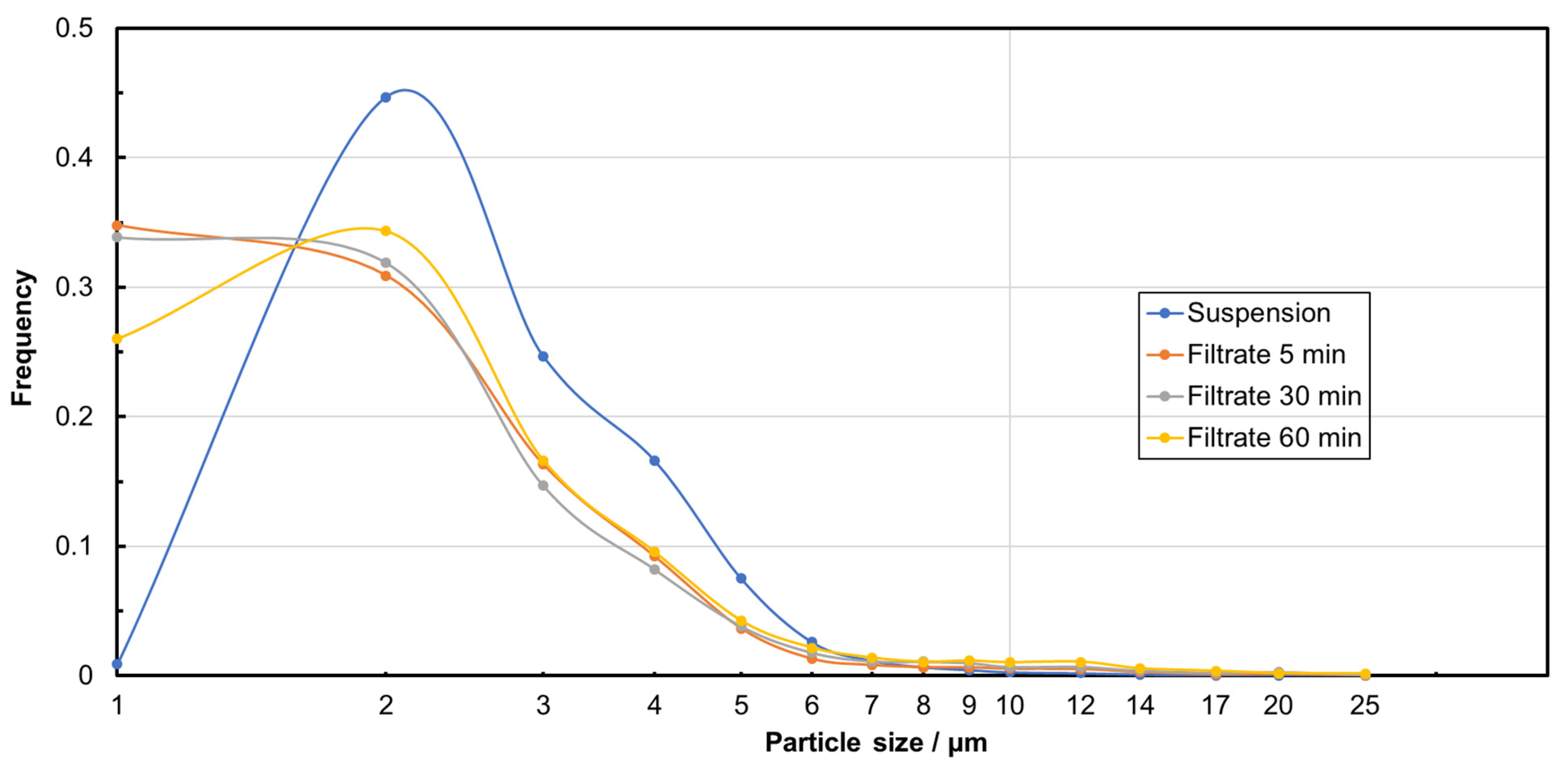
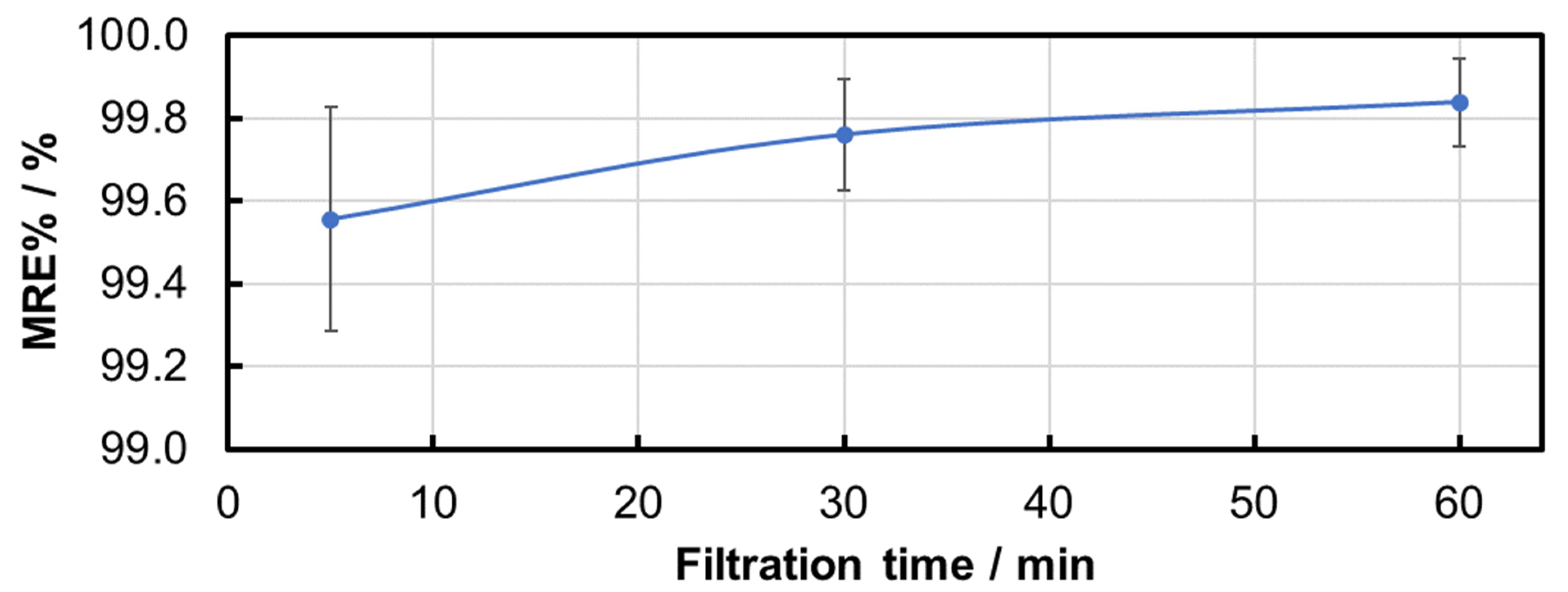




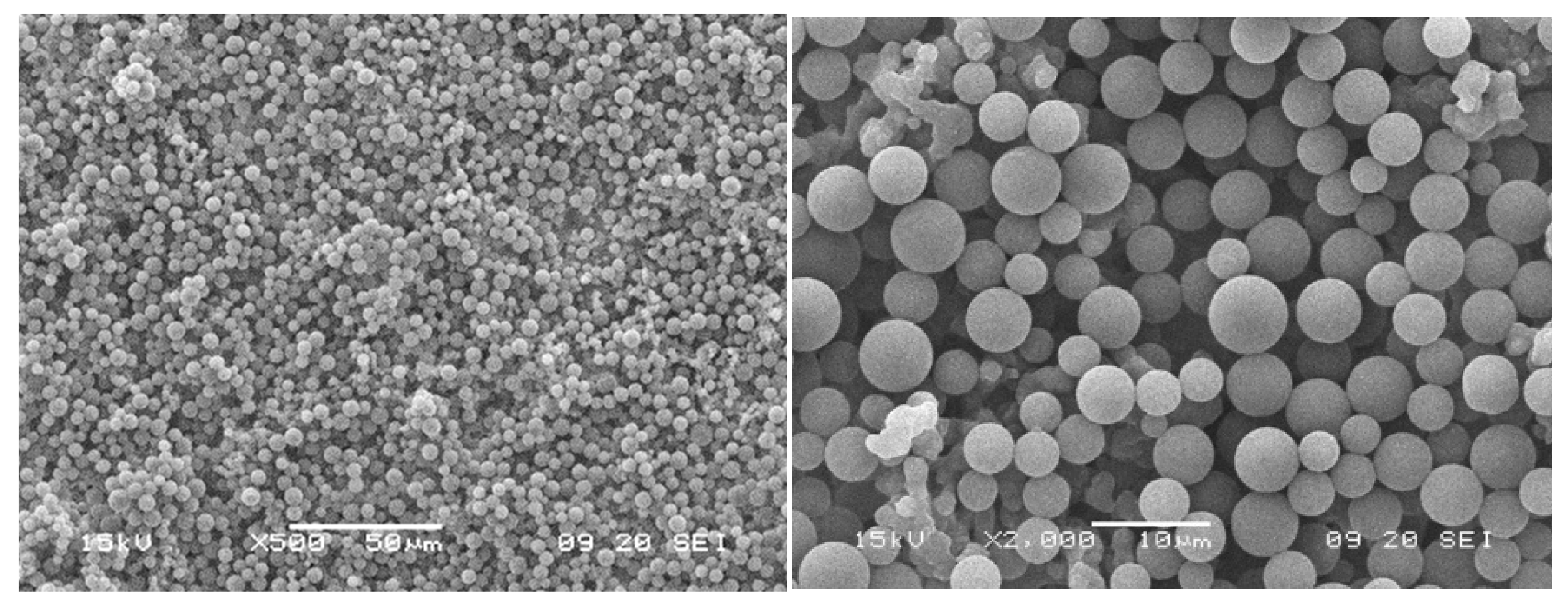
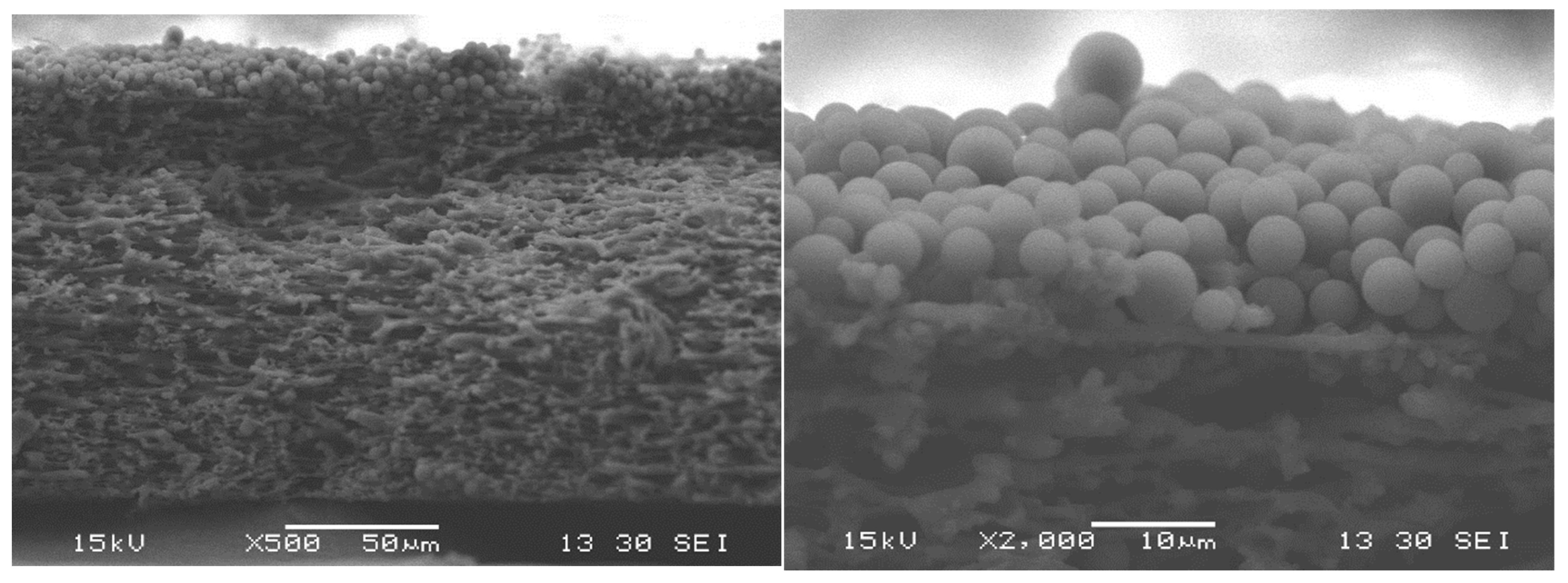
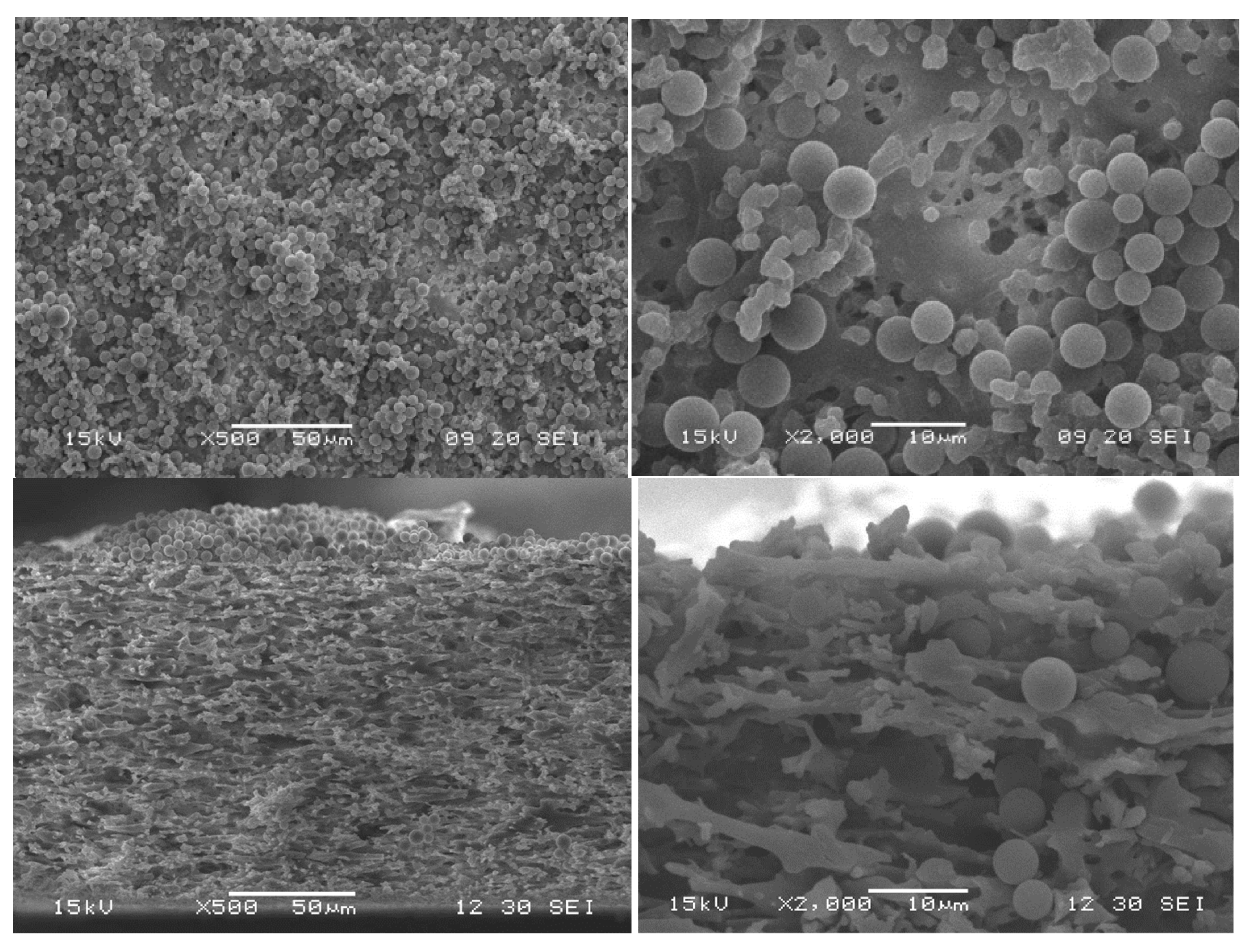
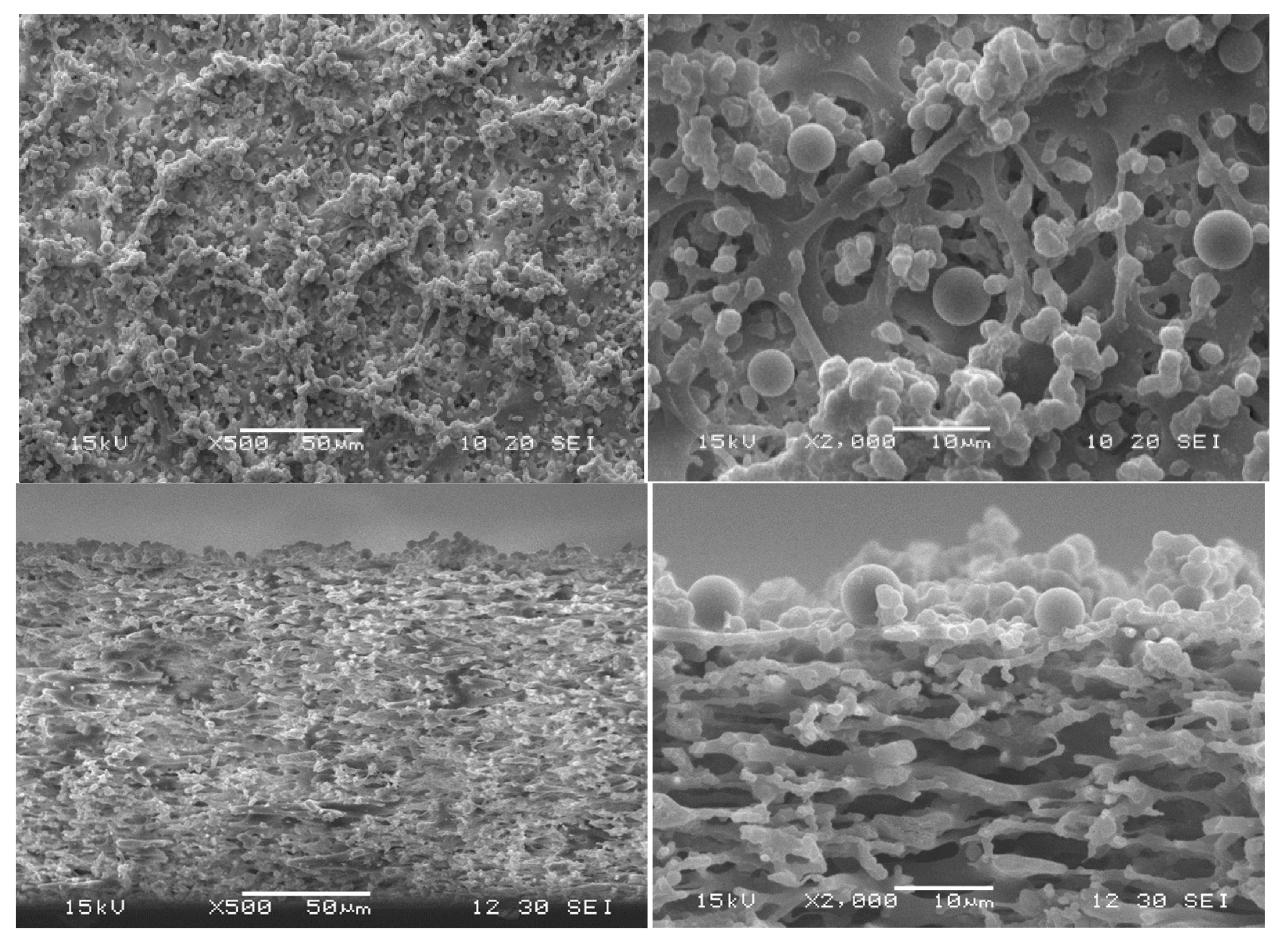
| Suspension ID | Average Particle Size/µm | Standard Deviation of Particle Size Distribution/µm | Turbidity/NTU |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.20 | 1.60 | 2.74 ± 0.04 |
| 2 | 3.02 | 1.41 | 2.52 ± 0.04 |
| 3 | 3.20 | 1.71 | 2.92 ± 0.03 |
| 4 | 3.11 | 1.60 | 2.83 ± 0.04 |
| 5 | 3.12 | 1.58 | 3.09 ± 0.09 |
| 6 | 3.00 | 1.36 | 2.71 ± 0.02 |
| Sample | Median Particle Size/µm | MRE% | NpRE% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Feed suspension | 3.00 | / | / |
| Filtrate after 5 min | 2.00 | 99.56 ± 0.27 | 99.65 ± 0.45 |
| Filtrate after 30 min | 2.00 | 99.76 ± 0.14 | 99.87 ± 0.09 |
| Filtrate after 60 min | 2.33 | 99.84 ± 0.11 | 99.93 ± 0.04 |
| Filtration Experiment | Pressure/bar | Flux Decline After 5 min/% | Flux Decline After 30 min/% | Flux Decline After 60 min/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filtration 1 | 0.1 | −22.2 | −29.7 | −31.4 |
| Filtration 2 | 0.1 | −9.1 | −17.4 | −19.7 |
| Filtration 3 | 0.2 | −10.2 | −13.1 | −15.4 |
| Filtration 4 | 0.2 | −13.3 | −18.4 | −19.9 |
| Filtration 5 | 0.3 | −3.4 | −6.2 | −8.0 |
| Filtration 6 | 0.3 | −9.6 | −13.2 | −14.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saremi, S.; Scheer, L.M.; Braun, G.; Koch, M.; Gallei, M.; Faust, M. Investigations on the Particle Fouling and Backwash Efficiency During Microplastic Microfiltration–Particle Size Aspects. Membranes 2025, 15, 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15090272
Saremi S, Scheer LM, Braun G, Koch M, Gallei M, Faust M. Investigations on the Particle Fouling and Backwash Efficiency During Microplastic Microfiltration–Particle Size Aspects. Membranes. 2025; 15(9):272. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15090272
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaremi, Saeedeh, Leonie Marie Scheer, Gerhard Braun, Marcus Koch, Markus Gallei, and Matthias Faust. 2025. "Investigations on the Particle Fouling and Backwash Efficiency During Microplastic Microfiltration–Particle Size Aspects" Membranes 15, no. 9: 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15090272
APA StyleSaremi, S., Scheer, L. M., Braun, G., Koch, M., Gallei, M., & Faust, M. (2025). Investigations on the Particle Fouling and Backwash Efficiency During Microplastic Microfiltration–Particle Size Aspects. Membranes, 15(9), 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15090272







