1. Introduction
The global human population continues to grow, and projections indicate that this trend will persist [
1]. With the rising number of inhabitants, demands for a higher standard of living are also increasing. In many coastal regions, people have begun constructing desalination plants to process seawater for the production of clean drinking water. These facilities primarily utilize membrane technologies, especially reverse osmosis (RO) [
2]. However, processing seawater through RO generates a waste stream with a high concentration of dissolved salts, several times higher than in the original seawater [
3,
4].
Table 1 shows a comparison of cation concentrations between sea water and different types of exhausted brines.
Approximately 140 million m
3 of brine are produced globally each day by reverse osmosis or mining [
7]. Common methods for brine disposal include discharging into the ocean [
8], surface water [
9], and sewage system [
10], which poses significant environmental problems. These methods often involve high costs and environmental risks, underscoring the need for more sustainable and cost-effective solutions [
11].
The European Union annually determines a list of critical raw materials that are in high demand on the European market and carry a high risk of supply disruption to the EU. Among these are substances found in brines [
12]. One such valuable material is magnesium, [
13,
14]. Magnesium, in the form of magnesium hydroxide, has a wide range of industrial applications. It can be used not only as a flame-retardant [
15,
16,
17] but also as an antibacterial agent [
18] or for reducing water pollution caused by heavy metals [
19,
20,
21].
Research into the reactive crystallization of magnesium hydroxide from magnesium chloride solution with sodium hydroxide as a precipitating agent began almost 50 years ago [
22,
23]. These early experiments showed that direct contact between magnesium chloride solution and precipitating agent produces very fine particles, which tend to agglomerate, forming a gelatinous suspension that is difficult to separate. In subsequent years, studies explored the effects of operational conditions on reactive crystallization to achieve the smallest possible agglomerates [
5,
24,
25].
Cipollina et al. [
4] proposed a desalination process concept for exhausted brine from saltworks in Trapani, Italy, which included the precipitation of magnesium in the form of Mg(OH)
2. The authors then continued their research using a semi-batch crystallizer and a continuous crystallizer [
26]. However, purity of produced Mg(OH)
2 crystals is significantly impacted by co-precipitation. The precipitation of Mg(OH)
2 may be accompanied by the precipitation of calcium in the form of Ca(OH)
2, occurring at a higher pH within the same process. Vassallo et al. [
6] tested a pilot plant for the crystallization of magnesium and calcium. But in reactive crystallization, the direct contact between the processed brine and the precipitating agent can cause unintended issues in the precipitation process, such as co-precipitation, of calcium in the form of Ca(OH)
2, occurring at a higher pH within the same process which affects the product’s quality [
27].
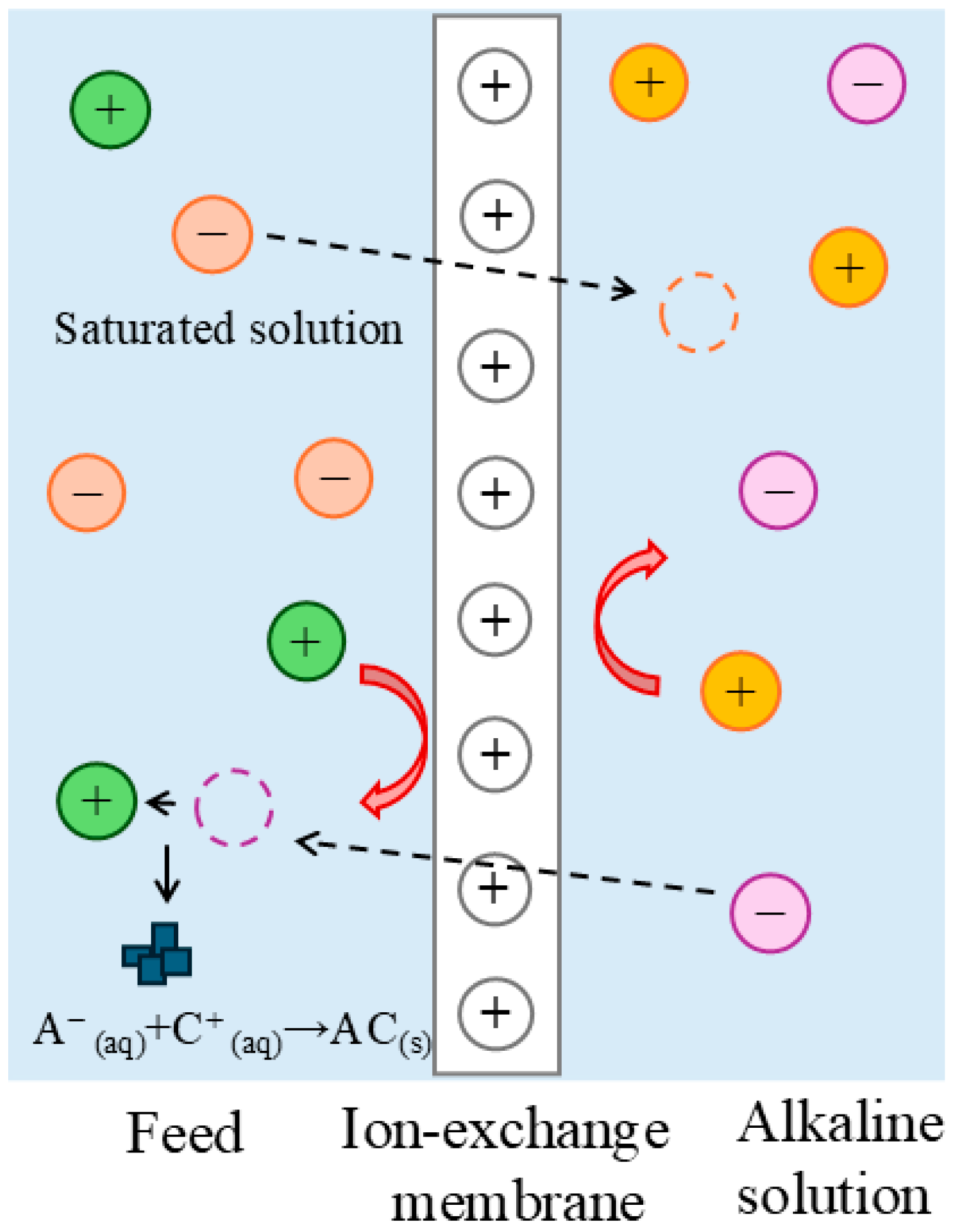
Membrane technologies, such as electrodialysis using ion-exchange membranes, are also employed for the valorization of raw materials from waste brines. This led to the idea of combining membrane technology with the precipitation crystallization process for magnesium recovery, which has been patented by La Corte et al. [
27] as an ion-exchange membrane crystallizer. This ion-exchange membrane crystallizer consisted of a flat-sheet anion-exchange membrane that separated the brine from the alkaline reactant which flowed through the serpentine channel on opposite sides of the membrane. The basic principle of the process operation is depicted in
Figure 1. The anion-exchange membrane selectively allowed only anions to pass through, causing hydroxide anions to migrate to the side of the brine rich in magnesium cations. Supersaturation of the solution with OH
− ions was achieved rapidly, and at a pH of approximately 9.8 [
6,
28] an immediate reaction occurred between the hydroxide ions according to the following reaction:
At the same time, chloride anions from the brine migrated to the alkaline reactant side to maintain electroneutrality. In general, it is assumed that ions with the same charge as the membrane were repelled based on the Donnan exclusion theory [
29,
30]. Ion transport across the membrane occurs not only due to the concentration gradient within it, but also due to the electrochemical potential gradient, which arises from the maintenance of Donnan equilibrium at the membrane-solution interface [
28].
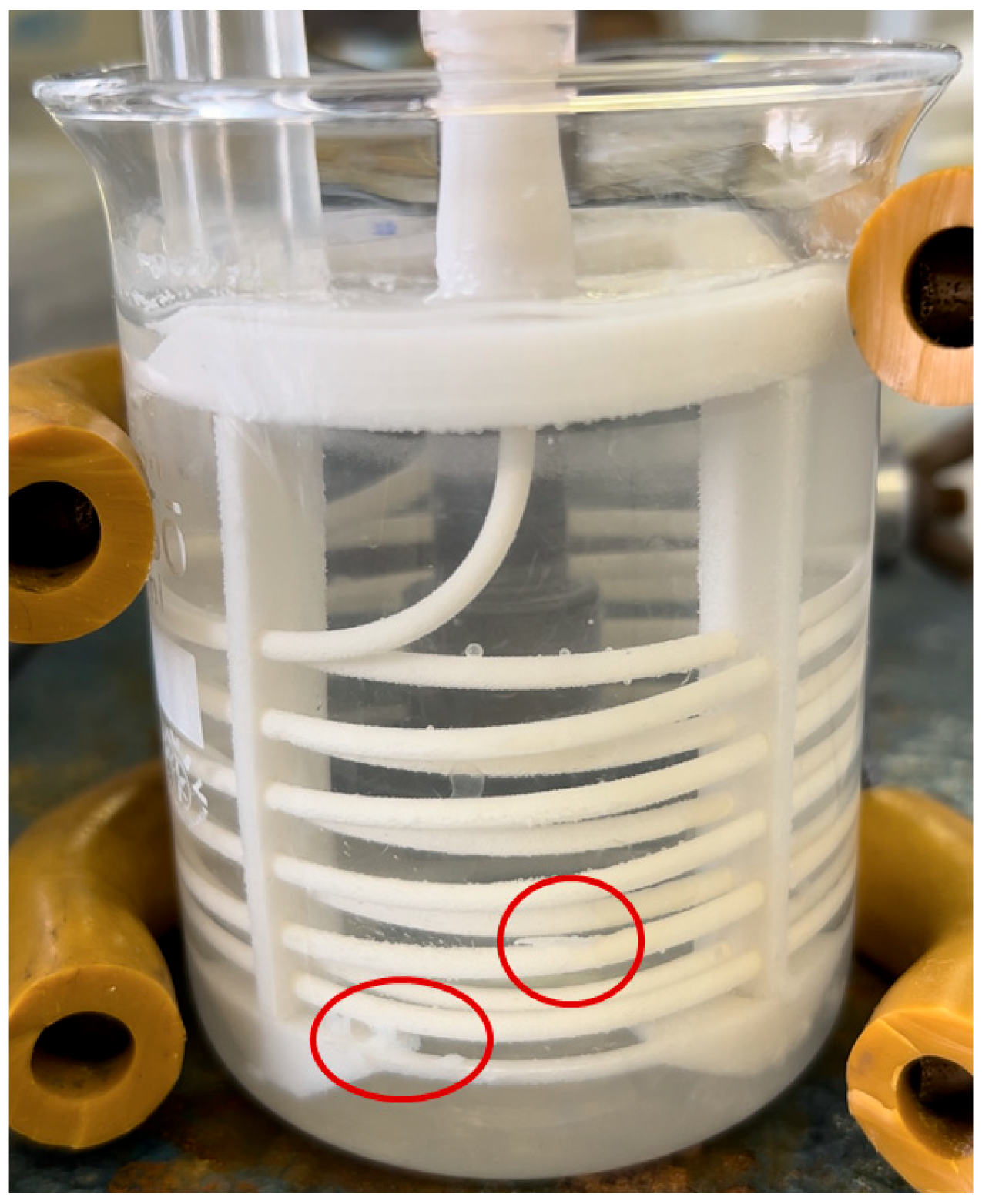
One of the significant advantages of membrane crystallization is that there is no direct contact between the alkaline solution and the brine, thus preventing the co-precipitation of other substances that could contaminate the product and affect its final quality. The second advantage is decreasing brine conductivity and salinity due to the crystallization of magnesium ions. In contrast, the direct addition of a precipitating agent to the brine also introduces sodium ions. Furthermore, the integration of membrane crystallization with electrodialysis using bipolar membranes could enhance the sustainability of the process by enabling the regeneration of the precipitating agent while simultaneously producing hydrochloric acid, which is also required for the proposed membrane crystallization process. Although studies report achieving high magnesium recovery efficiency, the issue of membrane fouling is only marginally mentioned. Upon reaching supersaturation of the solution with OH- ions, most magnesium cations react with hydroxide anions near the membrane surface, where the supersaturation is highest. Consequently, most of the product may remain trapped on the membrane rather than forming in the solution. La Corte et al. [
27] achieved with their membrane crystallizer high magnesium recovery efficiency and high product purity, while also reporting that a thin layer of magnesium hydroxide was attached to the membrane. They concluded that the formed layer did not affect the subsequent experiments, which were performed without previous cleaning of the membrane. Vassallo et al. [
28] also mentioned the issue of membrane fouling but mitigated it by positioning the membrane module horizontally and adding cleaning balls, which were circulating in the brine channel, whose purpose was to hinder the formation of scaling during the experimental run.
Membrane fouling has been extensively investigated, primarily in the context of membrane crystallization using membrane distillation, whereas reactive membrane crystallization remains largely unexplored in this regard. Fouling mitigation strategies employed in membrane crystallization with membrane distillation include pre-treatment, membrane bubbling, flushing, backflow application, chemical cleaning, and membrane modification [
31]. The application of pre-treatment methods depends on the brine composition and works on the principle of reducing the concentration of species that cause fouling. These methods include processes such as low-pressure membrane filtration, coagulation and flocculation, adsorption, pH adjustment, and the addition of anti-scalants. Gas bubbling can mitigate external fouling by increasing the shear rate and enhancing fluid dynamics on the membrane surface [
32]. Membrane flushing commonly uses deionized water to remove solutes from the membrane surface [
31]. The application of backflow reverses the driving force of the process, thereby reducing surface interactions between the membrane and scalants [
33]. Chemical cleaning is commonly employed to disrupt foulant–membrane interactions [
32]. Membrane distillation crystallization relies on strongly hydrophobic membranes that inherently resist fouling; thus, surface modification offers an effective strategy to further minimize scaling. An interesting approach is the development of self-cleaning membranes capable of sustaining stable separation for multiple cycles [
34]. Since reactive membrane crystallization with ion-exchange membranes operates differently from membrane distillation, fouling mitigation should primarily rely on removing scale deposits from the external surface, as ions of the same charge are repelled by the membrane and thus the formation of crystals inside the membrane is unlikely. An alternative approach could be to prevent the formation of scales in the first place, through improved control of nucleation, which could be significantly altered by changing the volume-to-surface ratio, as shown by Odua et al. [
35] for membrane distillation crystallization.
Previous studies have confirmed that magnesium can be separated in the form of magnesium hydroxide crystals with high purity and high recovery efficiency, or with high conversion rates, through reactive membrane crystallization. They also reported that crystals form on the other surface of the membrane but do not significantly impede the anion-exchange process. However, these studies do not report the percentage of crystals present in the suspension and therefore do not provide insight into the extent of membrane fouling that may occur during the process. In this work, an experimental hollow fiber anion exchange membrane is applied within the reactive membrane crystallization setup. The main objective is not only to recover magnesium hydroxide from model solution but also to investigate in situ cleaning methods for removing crystals from the membrane surface, thereby increasing their yield in suspension. These methods incorporate chemical cleaning with hydrochloric acid solution and demineralized water, which was delivered directly inside the hollow fiber in a backflow configuration, meaning that the protons needed to diffuse from the internal membrane surface through the anion-exchange membrane itself to the external membrane surface, where partial dissolution of deposited Mg(OH)2 occurs.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
In this work, the solution of magnesium chloride was used as a model solution of brine. Magnesium chloride hexahydrate MgCl2·6H2O (technical grade, purity > 98%), NaOH pellets (technical grade) and 6 M solution of HCl were all supplied by CentralChem, Slovakia. The experimental apparatus was built from Eppendorf (Eppendorf SE, Hamburg, Germany) BioFlo® 320 control unit, multimeter Thermo Scientic (Waltham, MA, USA) PC Eutech 450 for pH measurement, laboratory scale KERN PCB 3000-2, IKA MICROSTAR 15 control equipped with Rushton turbine for solution mixing.
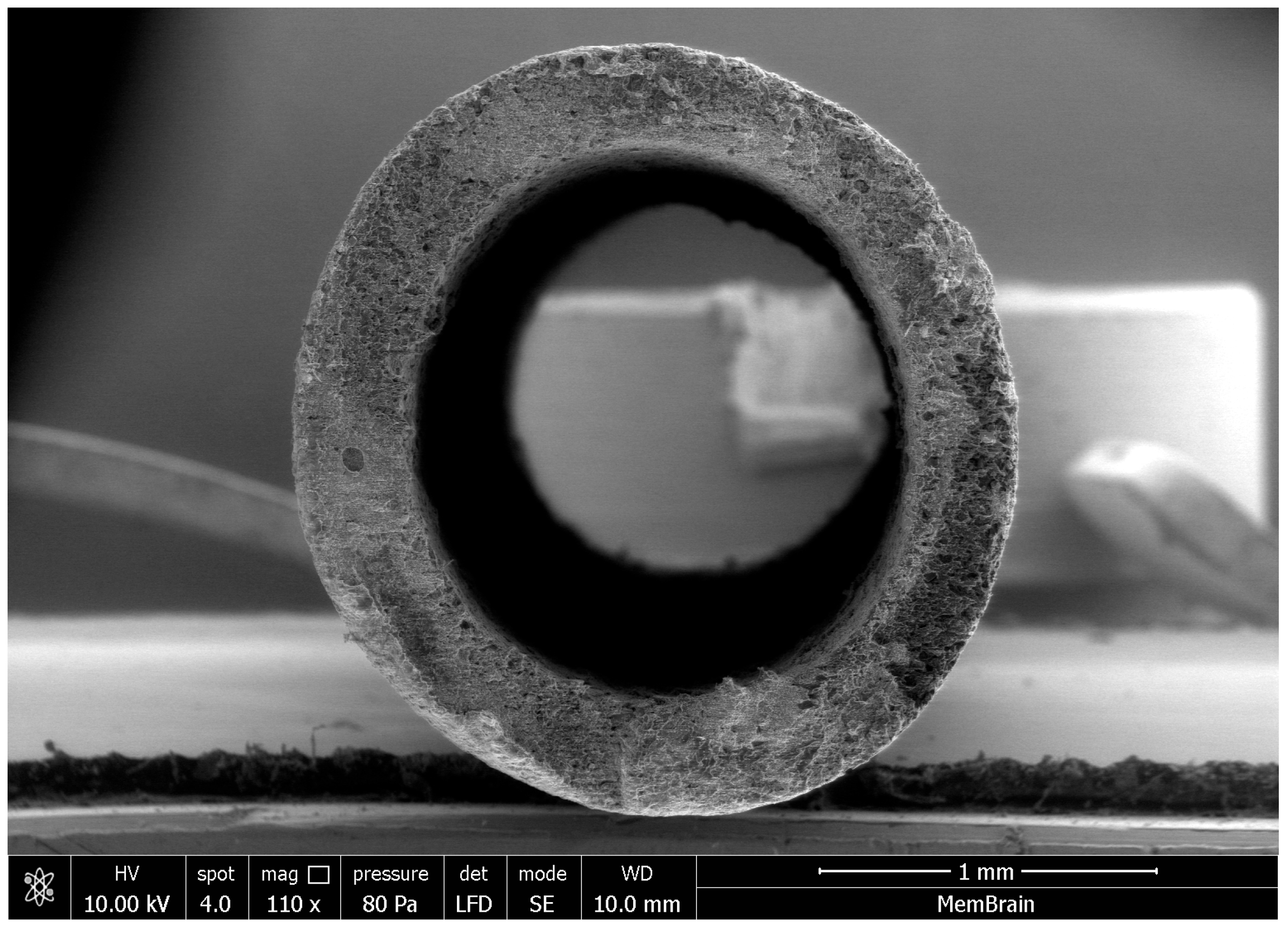
Experimental, commercially unavailable anion-exchange membranes in the form of hollow fibers, developed by MemBrain s.r.o. (Stráž pod Ralskem, Czech Republic), were used in this study. Their fabrication is similar to that of flat-sheet RALEX
® membranes: the ion-exchange resin is ground, mixed with polyethylene, homogenized, and melted to prepare a granulate consisting of a uniform mixture of both components. This granulate is then fed to the extrusion head in a melt-spinning process, producing hollow fiber membranes generally regarded as dense. A scanning electron microscope (SEM) image of the cross-section of the experimental anion-exchange hollow fiber membrane is shown in
Figure 2.
These membranes present a promising option for large-scale commercial implementation, as their cost per square meter is only half that of flat-sheet membranes produced by MemBrain s.r.o. The membrane module consists of a single hollow fiber membrane with a length of 1.5 m. The properties of the membrane are shown in
Table 2.
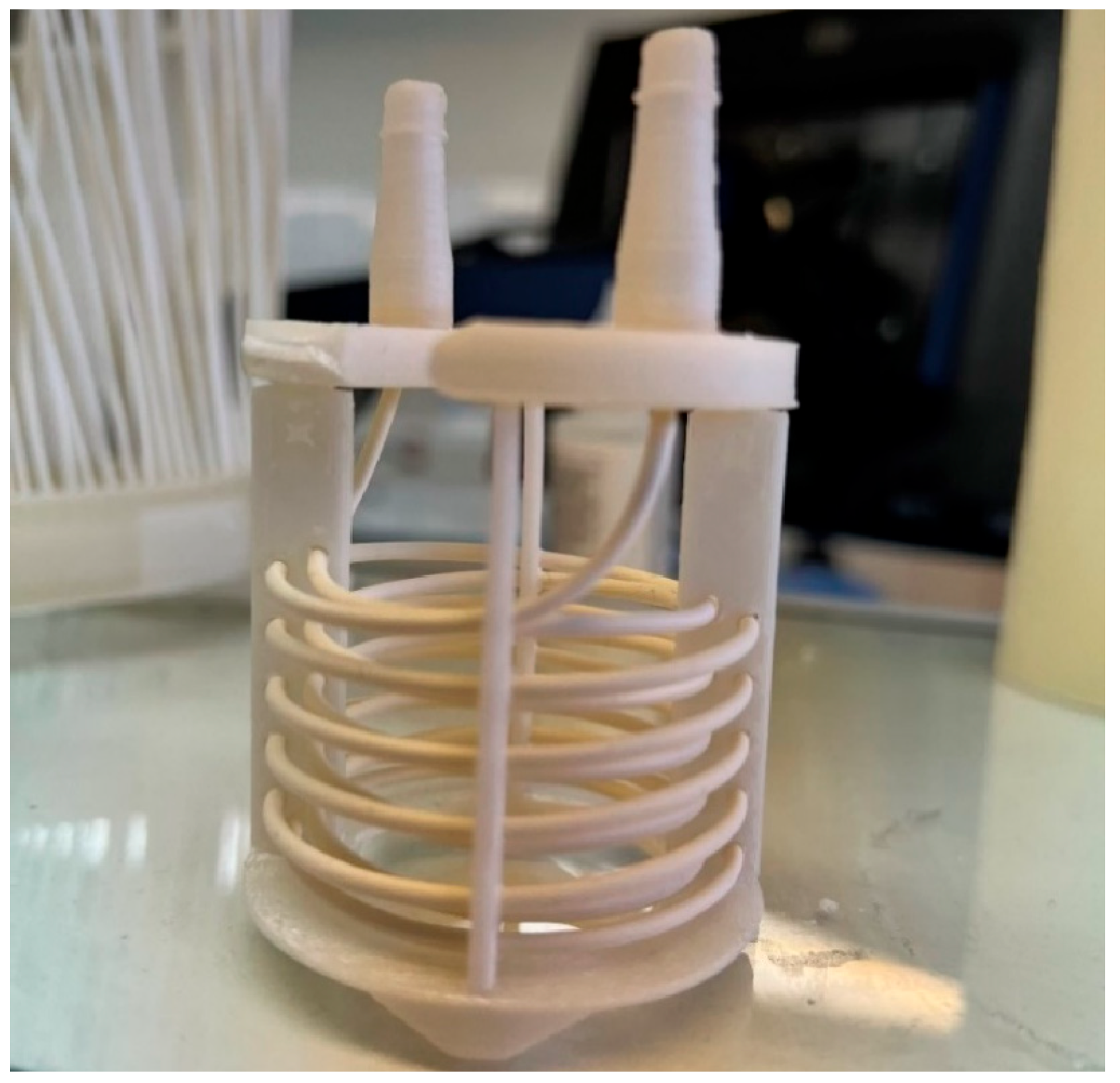
All other components of the membrane module were fabricated from polypropylene using a BambuLab 3D printer. The membrane module used in presented experiments is shown in
Figure 3 and it consisted of a single hollow fiber wound around custom 3D-printed supports.
2.2. Setup Description
Before use, the membrane module was soaked in water for one hour to allow the membrane to swell, followed by activation. Activation of the membrane module consisted of submerged into the 0.5 mol/L HCl for one hour.
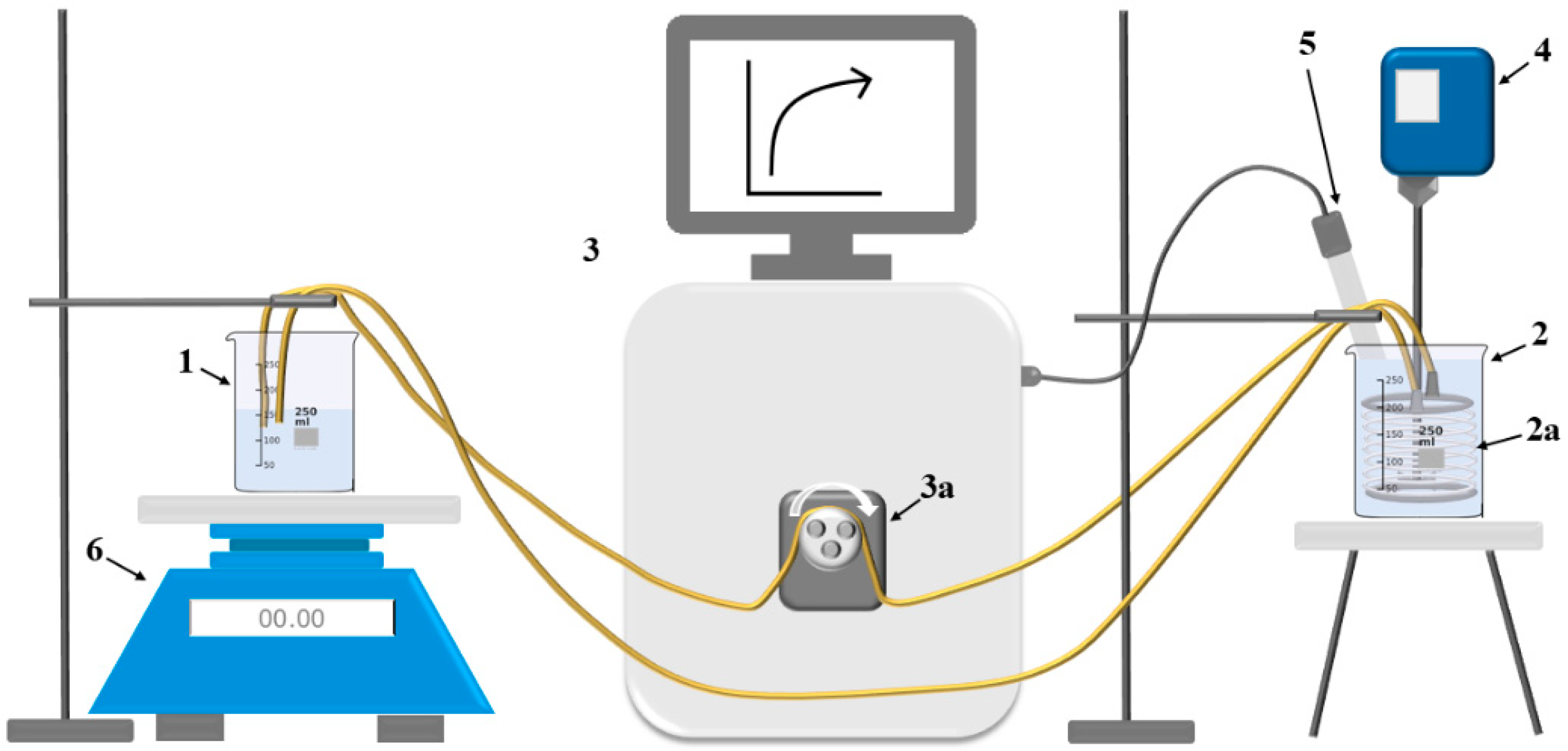
Magnesium hydroxide membrane crystallization was studied using the apparatus depicted in the simplified scheme in
Figure 4. The model brine solution located in reactor (No. 2) in which the membrane module was submerged (No. 2a) was continuously stirred throughout the process by overhead stirrer (No. 4). This improved the transfer of OH
− ions across the laminar layer on the brine side, leading to the reaction between OH
− ions and Mg
2+ ions according to Equation (1).
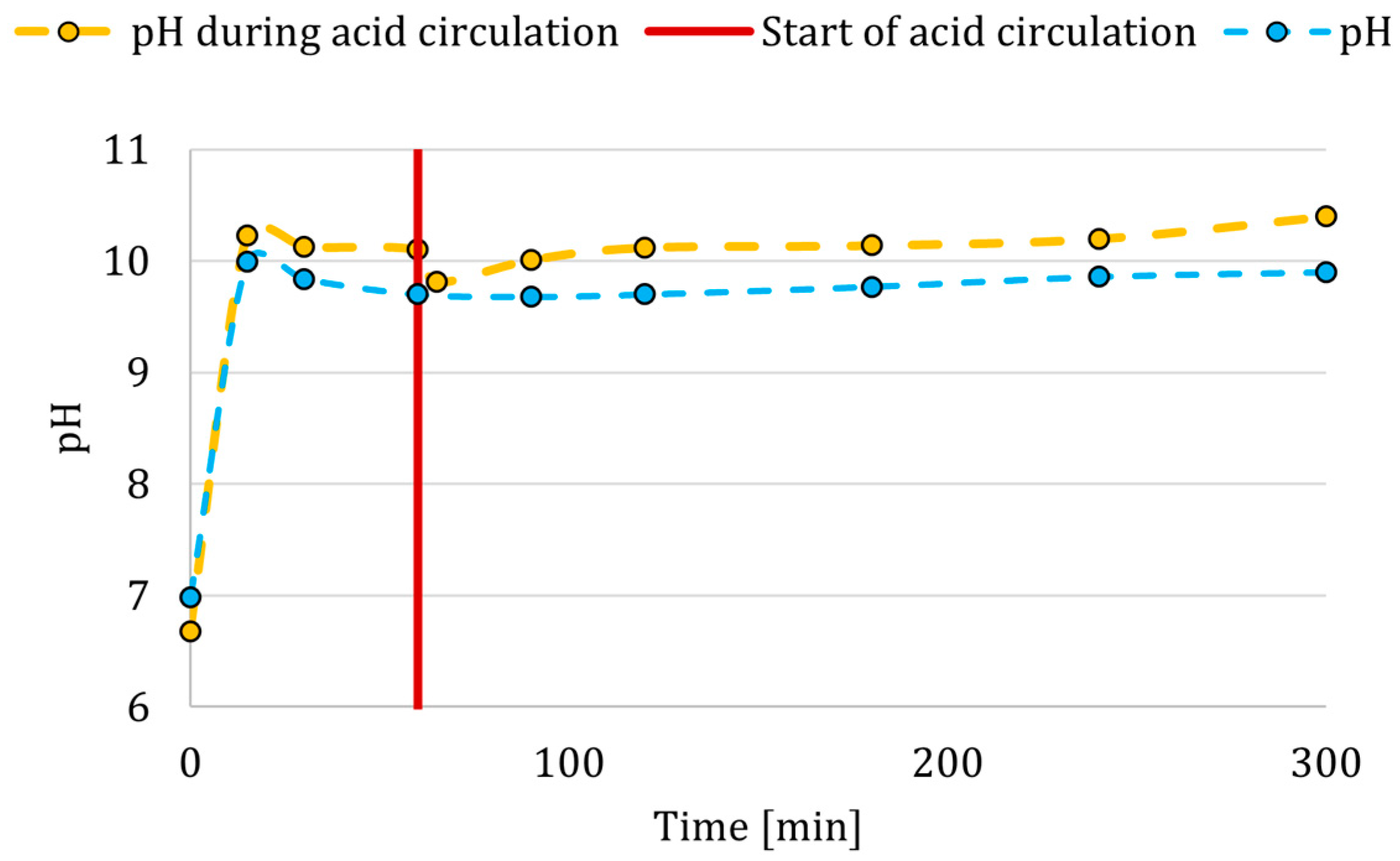
The pH of the model brine solution in the reactor was continuously monitored during the process by pH probe (No. 4) as the crystallization of Mg(OH)
2 is highly sensitive to pH, occurring within the pH range of 9.8 to approximately 10.4 [
28]. After reaching the pH value of 10.4, it was assumed that complete conversion of Mg
2+ ions occurred [
36].
On the other hand, if pH values were higher than 10.4, it could lead to co-precipitation of other components found in real brine, e.g., co-precipitation of Ca
2+ in the form of Ca(OH)
2. Co-precipitation of other components or ion sorption into the crystal structure could degrade the quality of the product [
28].
The weight of the alkaline solution (No. 1) was periodically recorded using scales, No. 6, to verify the functionality of the module and ensure that no damage occurred, which would result in direct contact between the model brine solution and the alkaline solution. If the module was damaged, allowing direct contact between the two solutions, this would be reflected in a significant rise in pH values. Otherwise, the weight of the reservoir changed minimally, within a range of 5 g. These small changes could be attributed either to evaporation of the alkaline solution or the formation of bubbles in the silicone tubes.
2.3. Experimental Procedure
All experiments were conducted with a model solution, consisting only of dissolved MgCl
2 and representing the brine, which was placed in the reactor containing the hollow fiber anion-exchange membrane module. The alkaline NaOH solution, serving as the precipitating agent, was held in the reservoir. The 125% excess of OH- ions was selected based on our previous studies, in which a high excess of OH- ions ensured a more stable driving force for mass transfer in batch configuration. Experimental conditions are presented in
Table 3.
The alkaline solution was pumped from the reservoir into the membrane module through silicone tubing using a peristaltic pump at a flow rate of 14 mL/min. The outgoing precipitating agent was recirculated back to the reservoir. Chosen initial concentrations of MgCl
2 were selected based on the published work by Cipollina [
26]. The reactor and the reservoir were mechanically stirred at 600 rpm and 100 rpm, respectively. The pH values and flow rates were recorded and controlled using an Eppendorf BioFlo
® 320 control unit. Additionally, the mass inside the reservoir was monitored. The duration of each experiment was 5 h.
The regeneration process of the membrane module after each experiment involved submerging the membrane module in 125 mL 0.5 mol/L HCl and circulating it through the system for one hour, followed by multiple rinsing procedures with 125 mL demineralized water. The demineralized water in the rector was exchanged until the conductivity of demineralized water dropped below 1 mS/cm.
2.4. Methodology
The entire process was divided into three stages. The first stage consisted of the membrane crystallization of Mg(OH)
2. The process parameters for the first stage remained unchanged throughout all experiments and the parameters are presented in
Table 2. The following two stages were introduced in order to study their application for removal of crystals from the membrane surface. The second stage involved the circulation of HCl through the membrane module and the third stage involved the circulation of demineralized water through the membrane module. Variations in the process parameters were made in the second and third stage in order to examine the effect of these process parameters on the crystal yield in the suspension. Throughout all three stages the suspension and the membrane module remained in the reactor. Process parameter changes were made only in one stage in individual experiments in order to evaluate their effects.
Circulation of the concentrated HCl through the hollow fiber causes the repulsive forces of the anion-exchange groups in the membrane to be insufficient to repel cations, which results in the membrane starting to lose its selectivity, therefore allowing these co-ions to pass through the membrane [
30]. The introduction of HCl was intended to remove a thin layer of the crystals closest to the membrane surface, according to Equation (2), allowing the upper layer of crystals to be released into the suspension. This would increase the crystal yield in the suspension and simultaneously generate potential crystal nuclei in the suspension that could continue to grow.
The third stage involved the circulation of demineralized water in the membrane module, which aimed to dislodge crystals in the vicinity of the membrane surface into the suspension. Demineralized water was pumped through the fiber placed in the reactor and due to osmosis and hydrodynamic pressure inside the fiber water was transported through the membrane to the reactor.
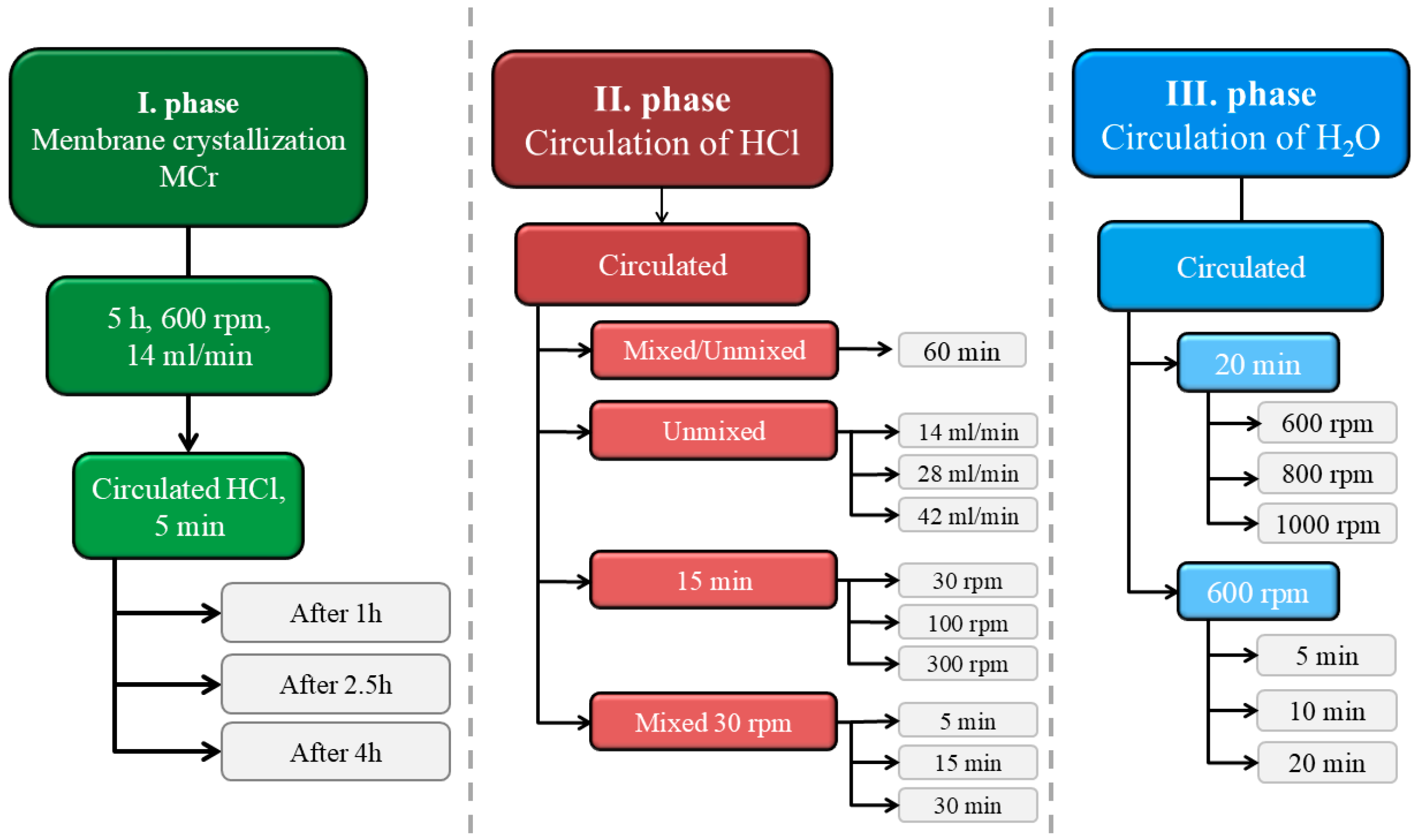
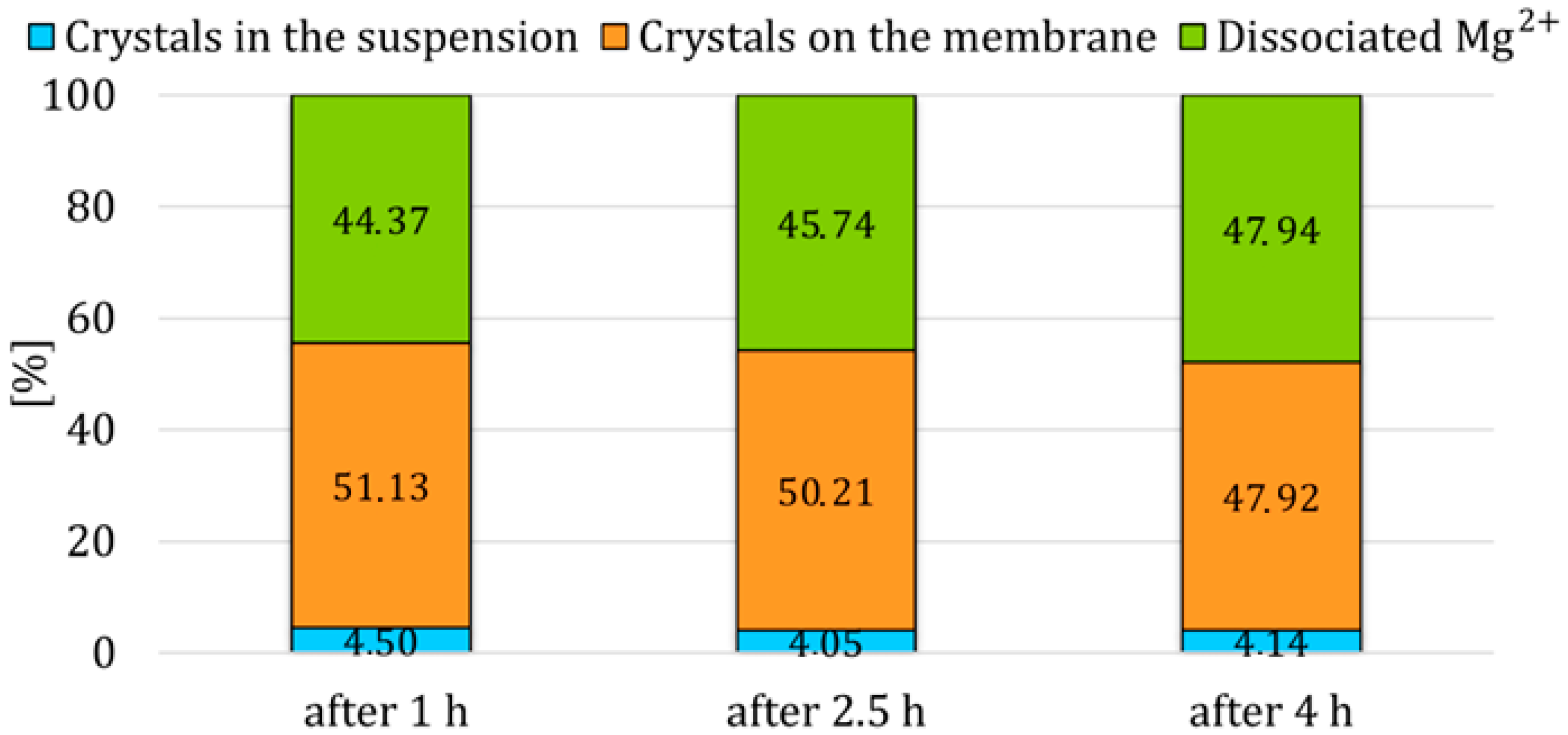
2.4.1. Modification in the First Stage
As mentioned above, the process parameters of the first stage which were presented in
Table 2 were not altered. However, in this set of experiments the effect of 2 mol/l HCl circulation on the crystal yield in the suspension of HCl was investigated if the acid was introduced for a short period of time during the first stage. The introduction of HCl during the first stage occurred at different times from the beginning of the experiment—after 1 h, after 2.5 h, or after 4 h, see
Figure 5.
2.4.2. Modifications in the Second Stage
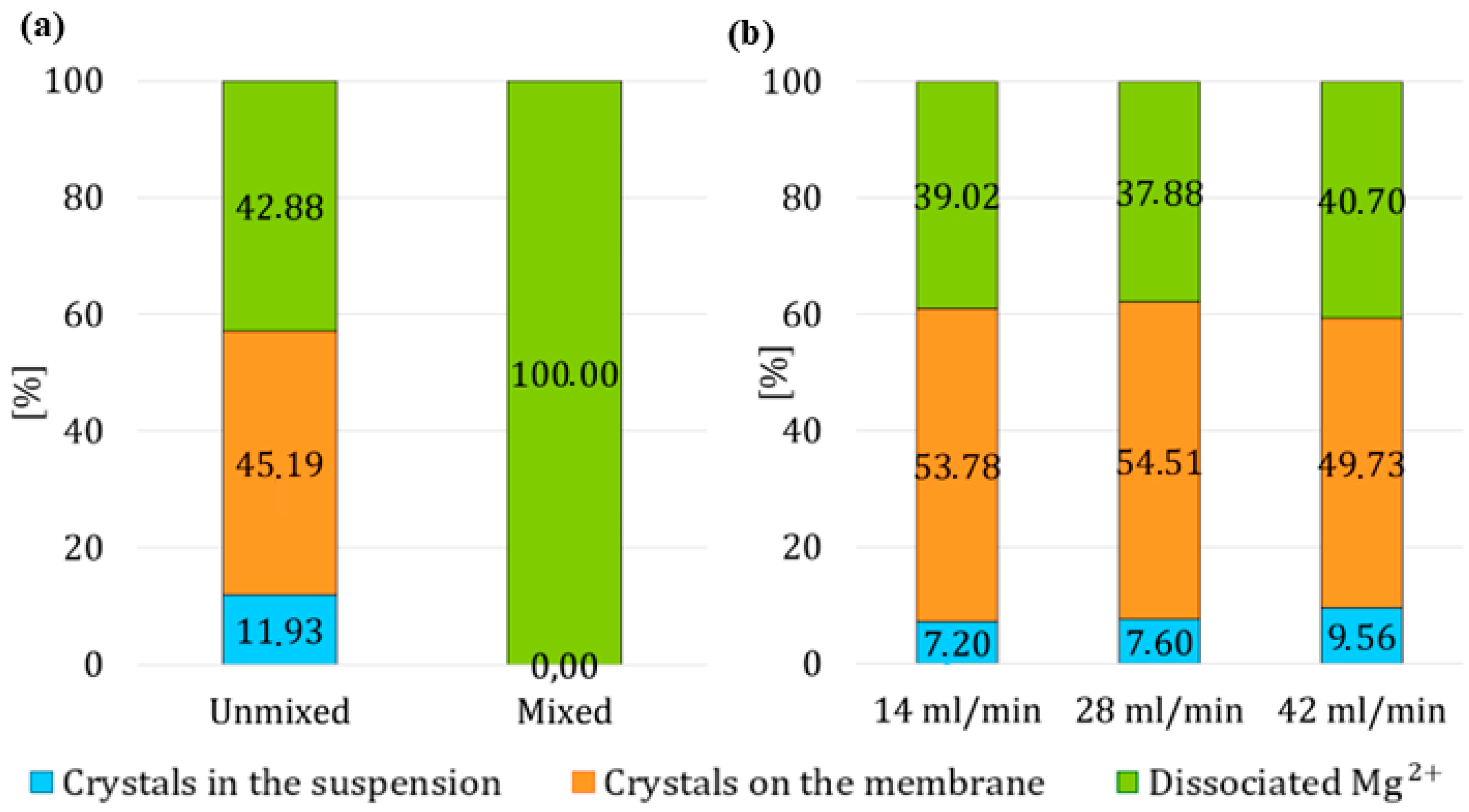
In the second stage, four sets of experiments were conducted, see
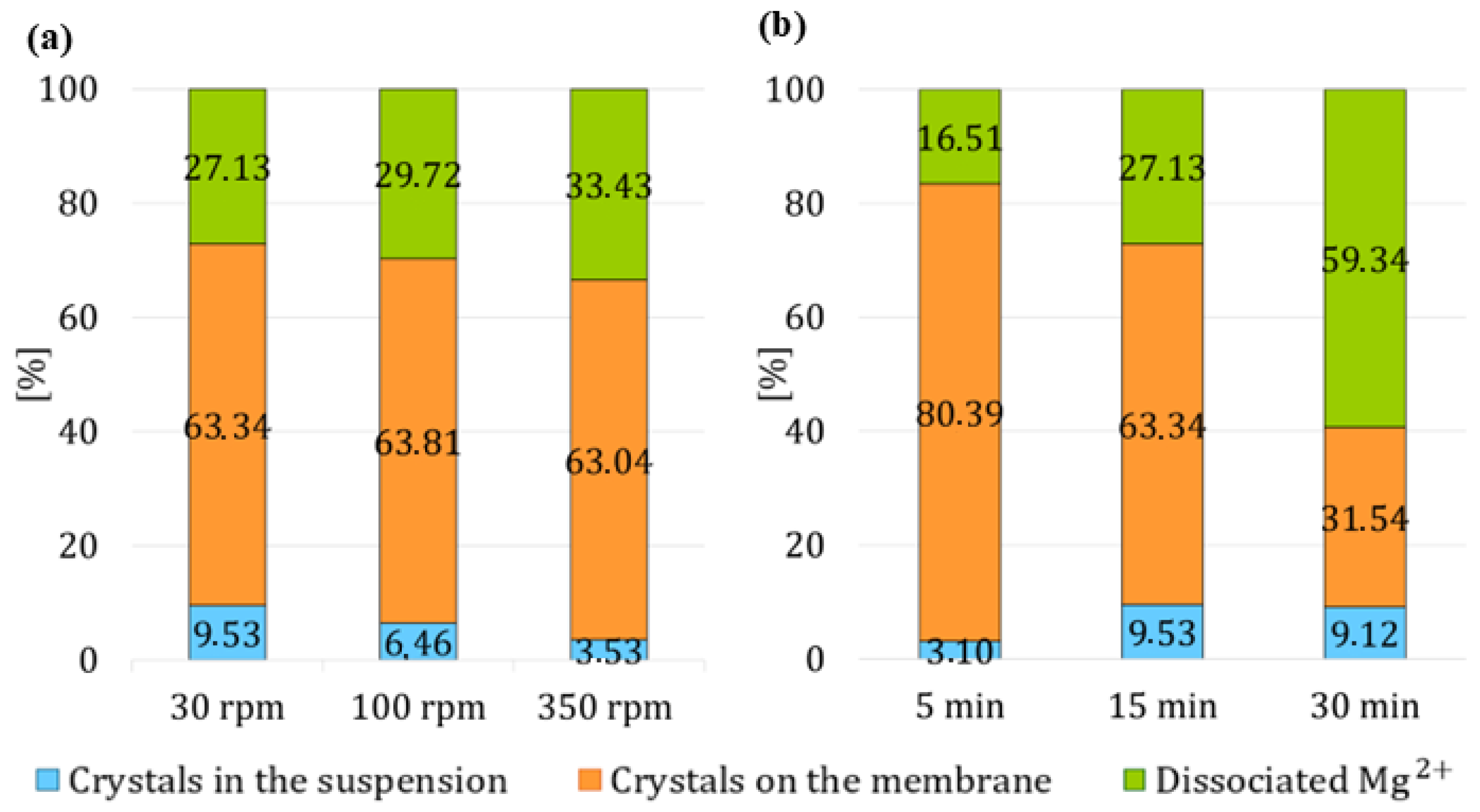
Figure 5. In the first set of experiments, two extremes were examined: stirring the reactor at 600 rpm or not stirring the reactor at all, both for a duration of 60 min. In the second set of experiments, the effect of varying the volumetric flow rate of HCl on the crystal yield in the suspension was investigated. In this set, the suspension was not stirred, and HCl was circulated in the system for 15 min, with the volumetric flow rate of HCl increasing from 14 mL/min to 28 mL/min and then to 42 mL/min. In the third set of experiments, HCl was circulated in the system for 15 min, and the effect of changing the suspension stirring speed inside the reactor on the crystal yield was examined. The stirring speed varied from 30 rpm to 100 rpm, and then to 350 rpm. In the final set of experiments, the suspension was stirred at the lowest possible stirring frequency, 30 rpm, and the effect of varying the circulation time in the system was investigated, with HCl circulating for either 5 min, 15 min, or 30 min. At these low mixing speeds, significant local concentration gradients could have occurred, which might have affected the results after the second stage. The actual outcome of the second stage will only be confirmed in the third stage, which is why the third stage is also displayed in the final graphs.
2.4.3. Modifications in the Third Stage
In the third stage, the effects of the circulation time of demineralized water in the membrane module and the intensity of suspension stirring on the crystal yield in the suspension were investigated, see
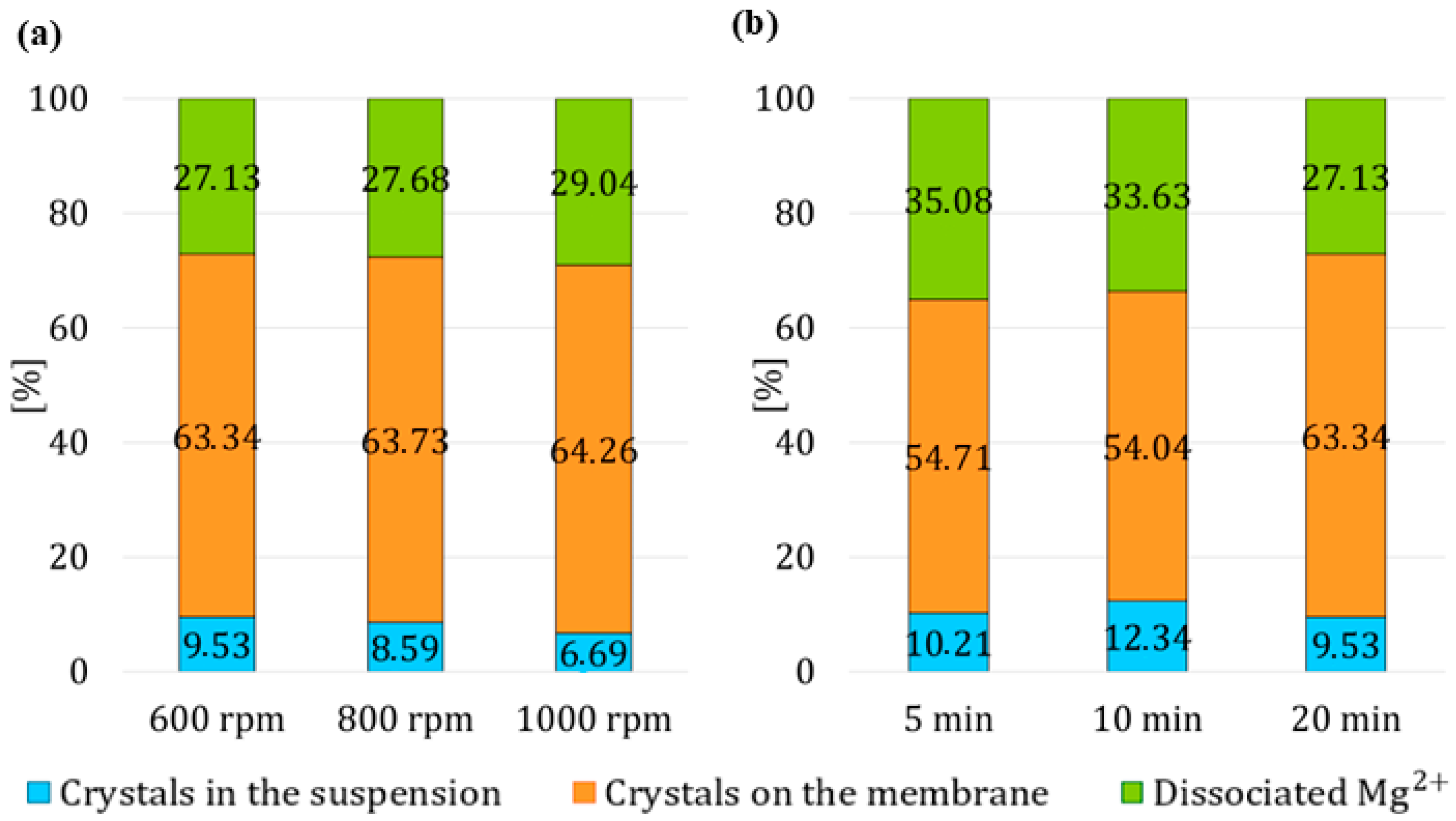
Figure 5. In the first set of experiments, demineralized water circulated in the system for 20 min, with three tests conducted at different stirring speeds of 600 rpm, 800 rpm, and 1000 rpm. In the second set of experiments, the suspension was stirred at 600 rpm, while demineralized water circulated in the system for either 5 min, 10 min, or 20 min.
2.5. Data Collection and Sampling Procedure
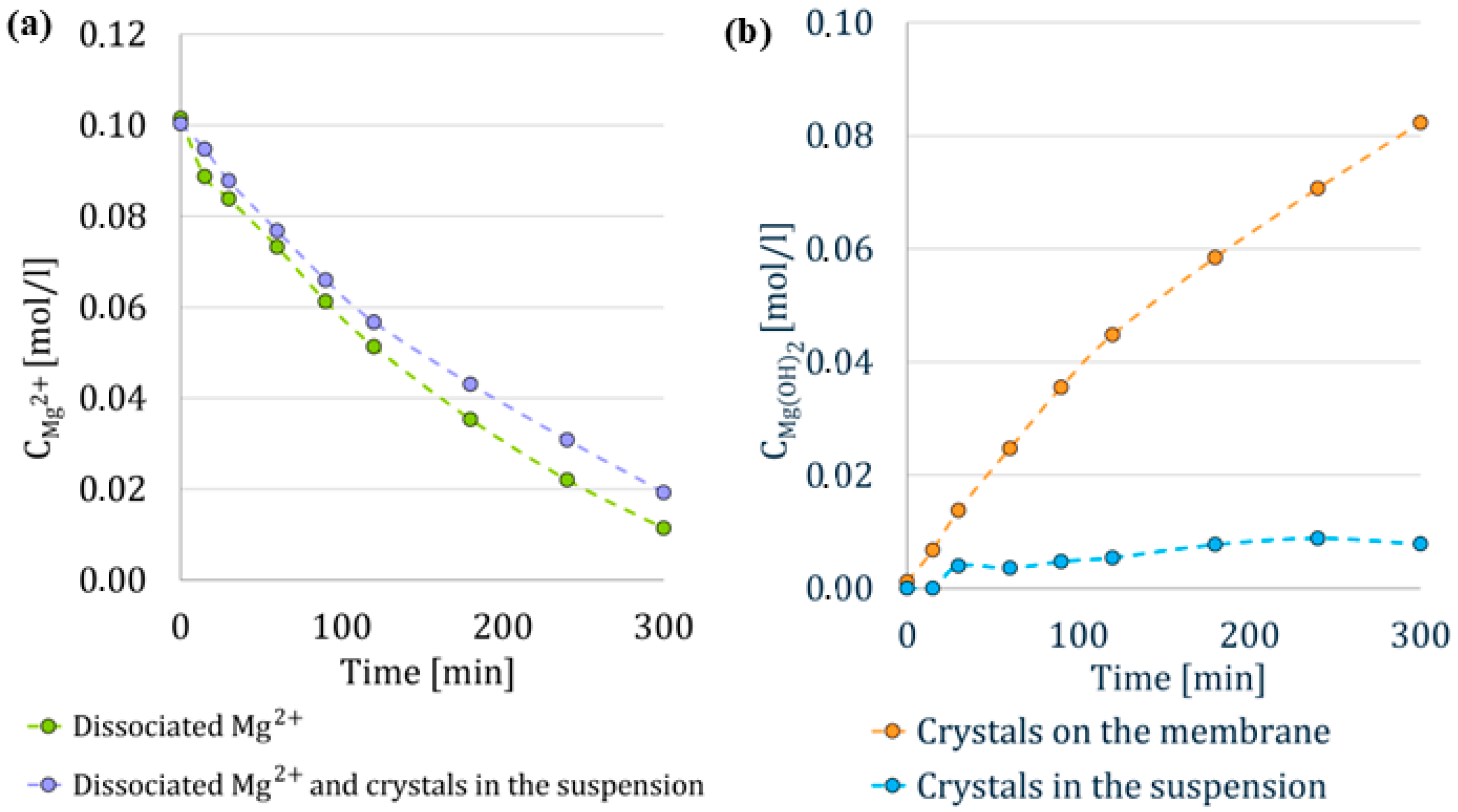
To determine the efficiency of membrane crystallization, it was necessary not only to collect samples but also to gather and record data. The collected data included pH values, which were automatically recorded by the Eppendorf BioFlo® 320 control unit and additionally logged at each sampling point. During the first half of the first stage, samples were collected more frequently—every 30 min. In the second half of the first stage, samples were taken every hour. During the second and third stages, samples were again collected more frequently, every 5 min.
The samples were diluted to fall within the calibration range. Two types of samples were taken every hour. Type I was used for determination of the free dissociated Mg2+ ions. This sample was first filtered through a 0.45 µm syringe filter and then diluted with demineralized water. Type II was used for the determination of all Mg2+ ions present in the suspension. This sample was diluted with 0.5 mol/L HCl, whose role was to dissolve any formed crystals of Mg(OH)2 and thus convert the magnesium back to the dissociated form.
From the analysis of these two sample types, we were able to determine the concentration of crystals in the suspension according to Equation (3).
represents the concentration of magnesium hydroxide in the suspension, is the total concentration of Mg2+ ions present in the suspension at a given sample time (sample type II), and refers to the concentration of free Mg2+ ions at a given sample time (sample type I).
The concentration of all Mg(OH)
2 crystals (in the suspension and on the membrane)
was calculated as the difference between the initial concentration of Mg
2+ ions in the model solution
and the concentration of free Mg
2+ ions in the suspension (sample type I) according to Equation (4).
The recovery of Mg(OH)
2 crystals in the suspension
was calculated as the difference between the concentration of all Mg
2+ ions present in the suspension (sample type II) and the concentration of free Mg
2+ ions (sample type I), divided by the initial concentration of Mg
2+ ions in the model brine solution as defined by Equation (5). Similarly, the percentage of Mg(OH)
2 crystals on the membrane
can be determined with the known concentration of Mg(OH)
2 crystals in the suspension using Equation (6). Overall conversion to Mg(OH)
2, referred to as
, was calculated according to Equation (7), using the initial concentration and the concentration of free Mg
2+ ions (sample type I).
Aqueous samples containing dissociated magnesium were analyzed using an Agilent Infinity 1260 system (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) equipped with a cation-exchange column Hamilton PRP-X-800, 4.1 mm × 250 mm, 7 µm, and each sample was analyzed in triplicate. HPLC was employed for indirect absorbance detection at 220 nm with a reference wavelength of 360 nm. The mobile phase consisted of a 1.5 mmol/L CuSO4 aqueous solution with 0.3 mmol/l H2SO4, and volumetric flow of mobile phase was 1 mL/min.
4. Conclusions
The presented study investigated methods to enhance the efficiency of magnesium hydroxide reactive membrane crystallization using a hollow fiber anion-exchange membrane, with the aim of increasing the yield of crystals in the suspension, thereby minimizing membrane fouling and improving product recovery. The membrane crystallization process demonstrated potential for magnesium recovery, achieving a conversion consistently over 85%. However, the majority of produced crystals remained attached on the membrane surface. At the end of the membrane crystallization stage, the suspension contained, on average, only 1% magnesium hydroxide crystals, indicating significant product scaling. To address this, the experiments were designed as batch processes, each consisting of three consecutive stages. The first stage involved 5 h of membrane crystallization under controlled conditions. This was followed by a second stage in which hydrochloric acid was circulated through the membrane to dissolve part of the adhered crystal layer and facilitate detachment. Finally, a third stage involved the circulation of demineralized water to assess further removal and redistribution of the crystals into the suspension. Throughout all three stages, operational parameters such as acid circulation duration and suspension mixing intensity were varied to evaluate their influence on the yield of suspended crystals. This approach allowed for a systematic investigation into in situ methods for scale removal and product recovery, offering practical insight into optimizing membrane crystallization for applications in resource recovery and zero-liquid discharge systems.
The results demonstrated that the timing, duration and intensity of process modifications in each stage significantly influenced the distribution of magnesium species between the membrane, suspension, and its dissociated forms. Introducing HCl in the later stages of the first stage resulted in increased detachment of crystals from the membrane without excessively increasing the concentration of dissociated magnesium ions. In the second stage, moderate conditions for acid circulation of 15 min and low stirring intensity resulted in the highest crystal yield in suspension (9.53%) while minimizing dissolution. Excessively long acid exposure or vigorous mixing promoted undesired dissolution of both membrane-bound and suspended crystals, resulting in more than a twofold increase in the concentration of dissociated magnesium. Similarly, in the third stage, a moderate water circulation time of 10 min at a controlled stirring intensity of 600 rpm achieved the highest overall magnesium hydroxide yield in the suspension: 12.34%. However, a compromise is desired between maximizing suspended crystal recovery and minimizing dissociated magnesium concentration in the solution.
The study confirms that targeted manipulation of process parameters can lead to greater product recovery in the bulk stage. While the demonstrated methods resulted in an approximate 10% increase in the proportion of suspended crystals, it is important to note that the experiments were conducted in batch mode at small scale, using magnesium concentrations typical of desalination brines. As a result, the absolute yield of product was relatively low. However, the findings validate the potential of in situ scale removal strategies and provide a foundation for optimizing reactive membrane crystallization systems—not only for magnesium hydroxide but potentially for other valuable salts in high-salinity streams.
Future work will focus on scaling up the process to continuous operation, using multi-fiber membrane modules. The flux per unit membrane area will be the same. The challenge will be to ensure that all fibers in the module are effectively utilized. In this envisioned setup, a dedicated membrane crystallization stage would be followed by a crystal harvesting stage, enabling sustained operation and higher overall product recovery. Additional strategies, such as integrating gas bubbling into the suspension, will also be explored to further enhance crystal detachment and improve system efficiency at scale.