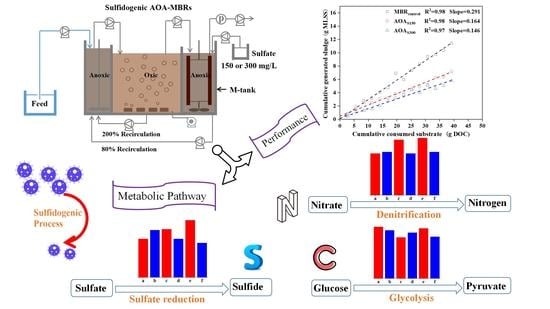
In-Situ Sludge Reduction Performance and Mechanism in Sulfidogenic Anoxic–Oxic–Anoxic Membrane Bioreactors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
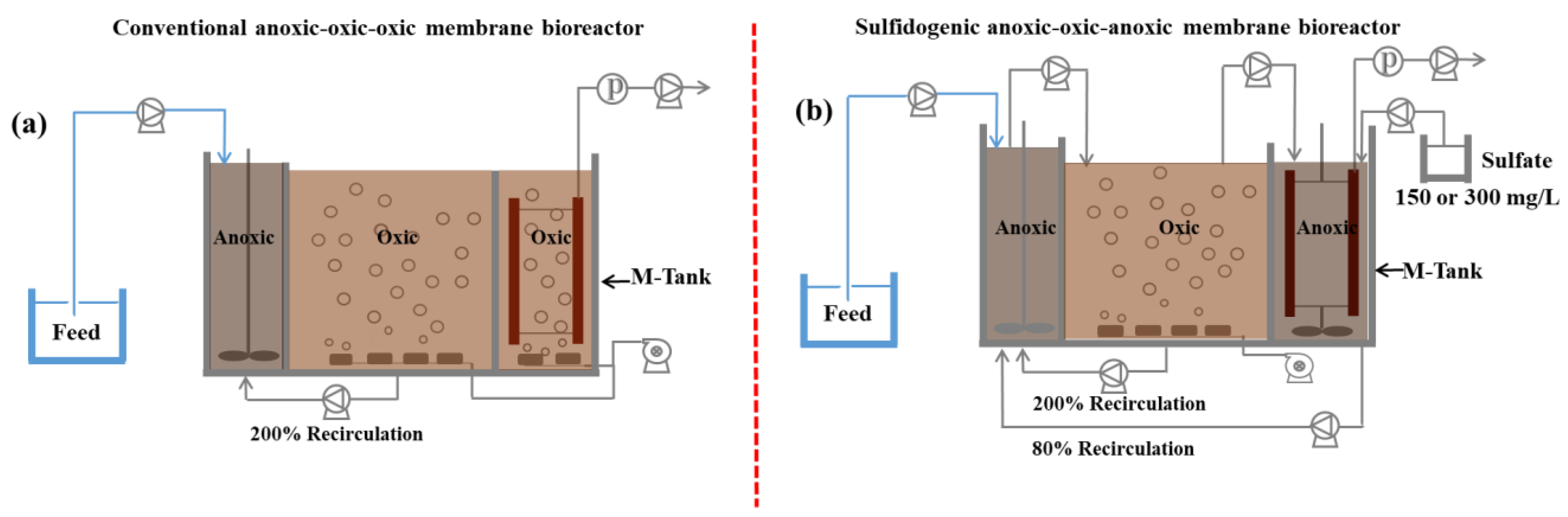
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Analytical Characterization
2.3. 16S rRNA Amplicon Sequencing and Metagenomics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Basic Water-Quality Parameters
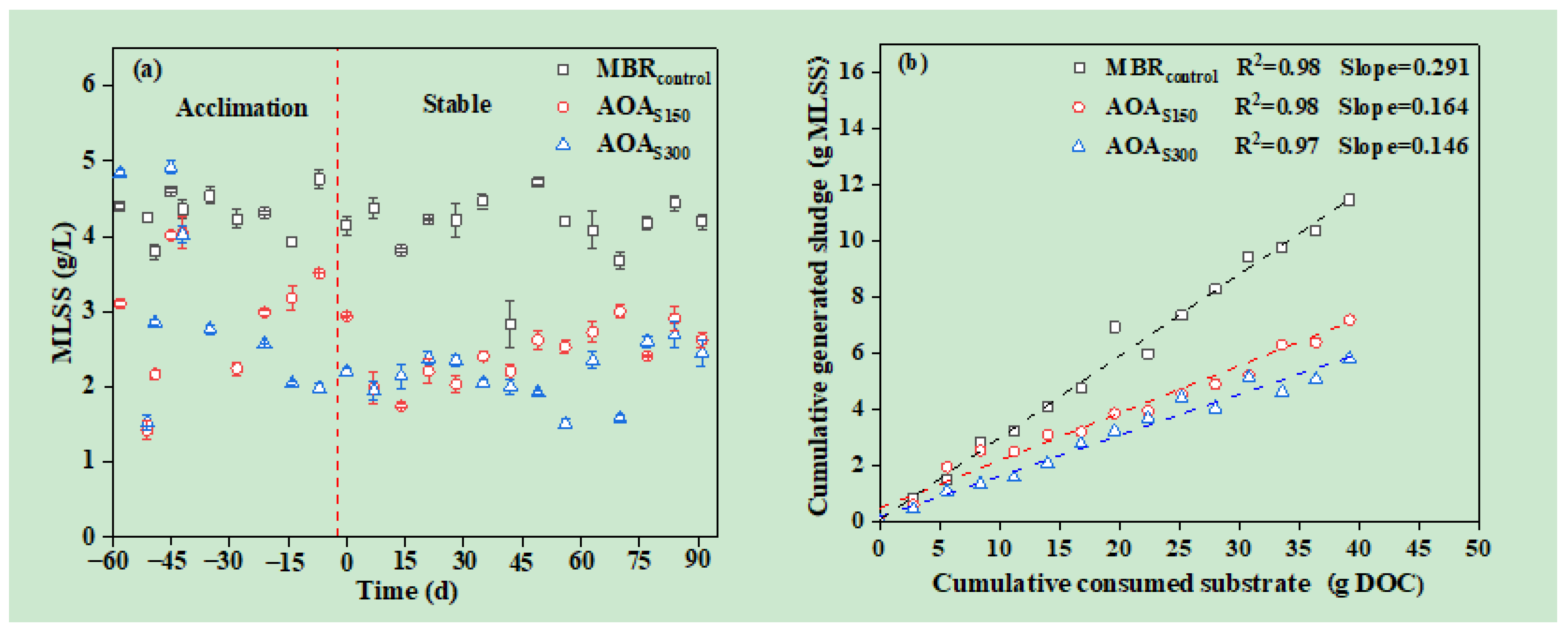
3.2. Sludge Reduction
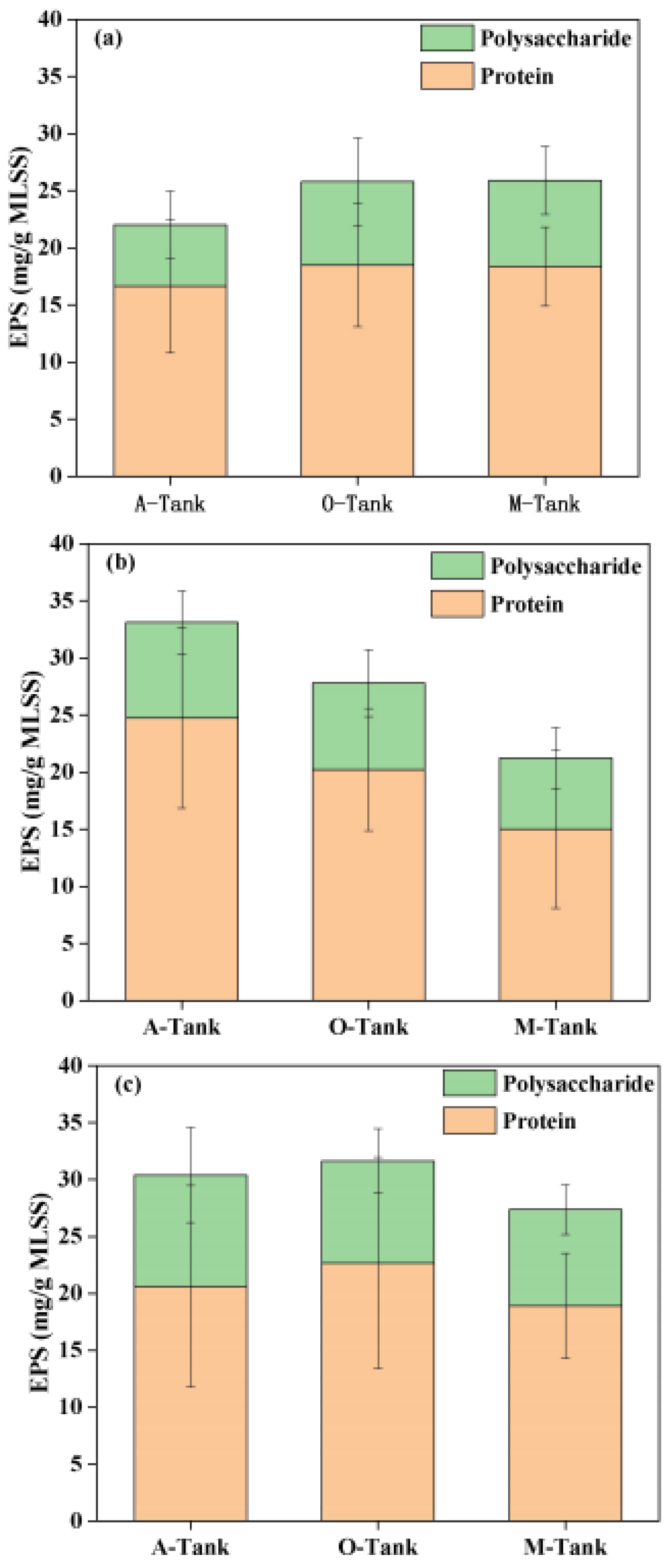
3.3. SMP and EPS Dynamics in AOA Bioreactors
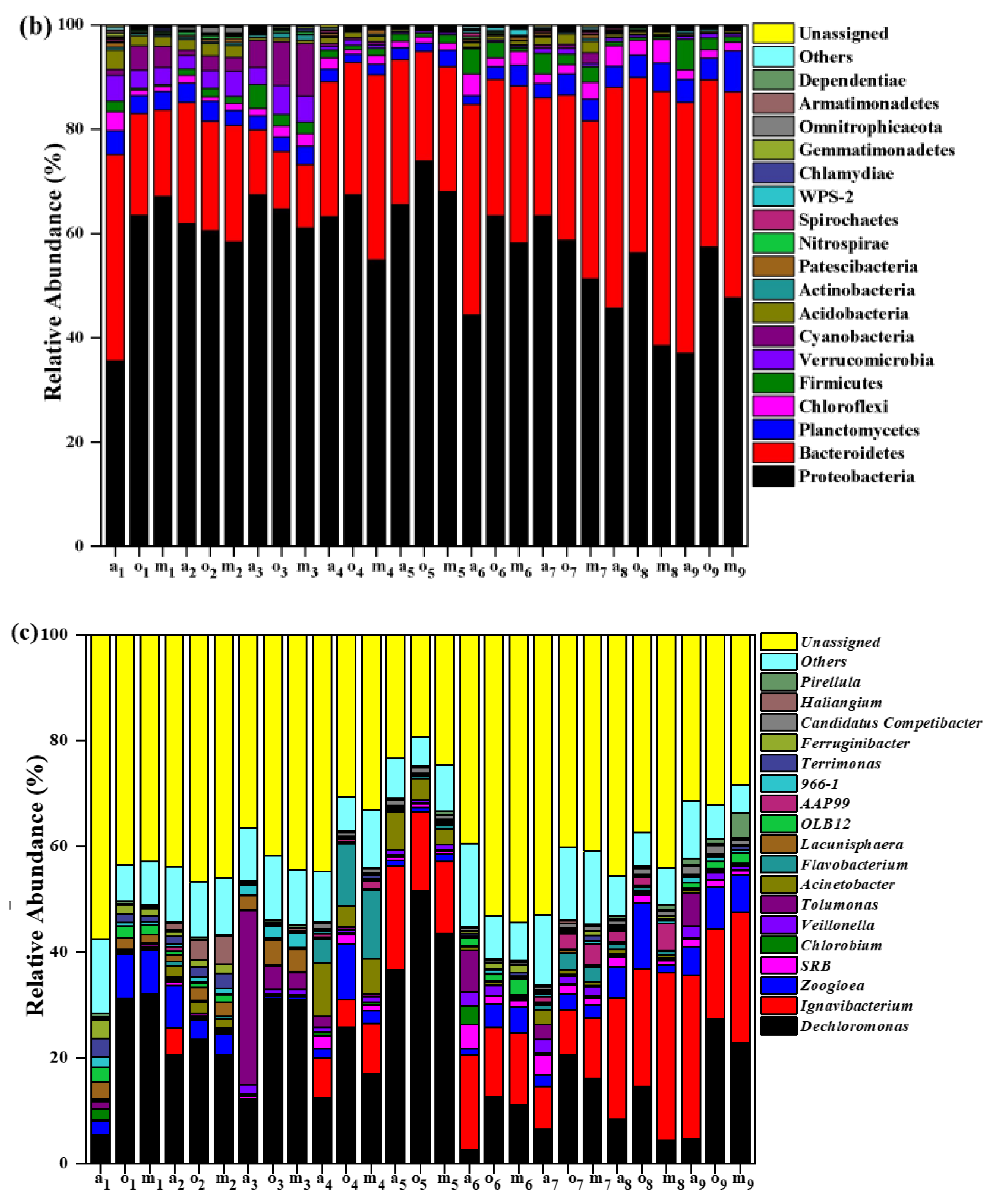
3.4. Microbial Community
3.5. Metabolic Response Pathways
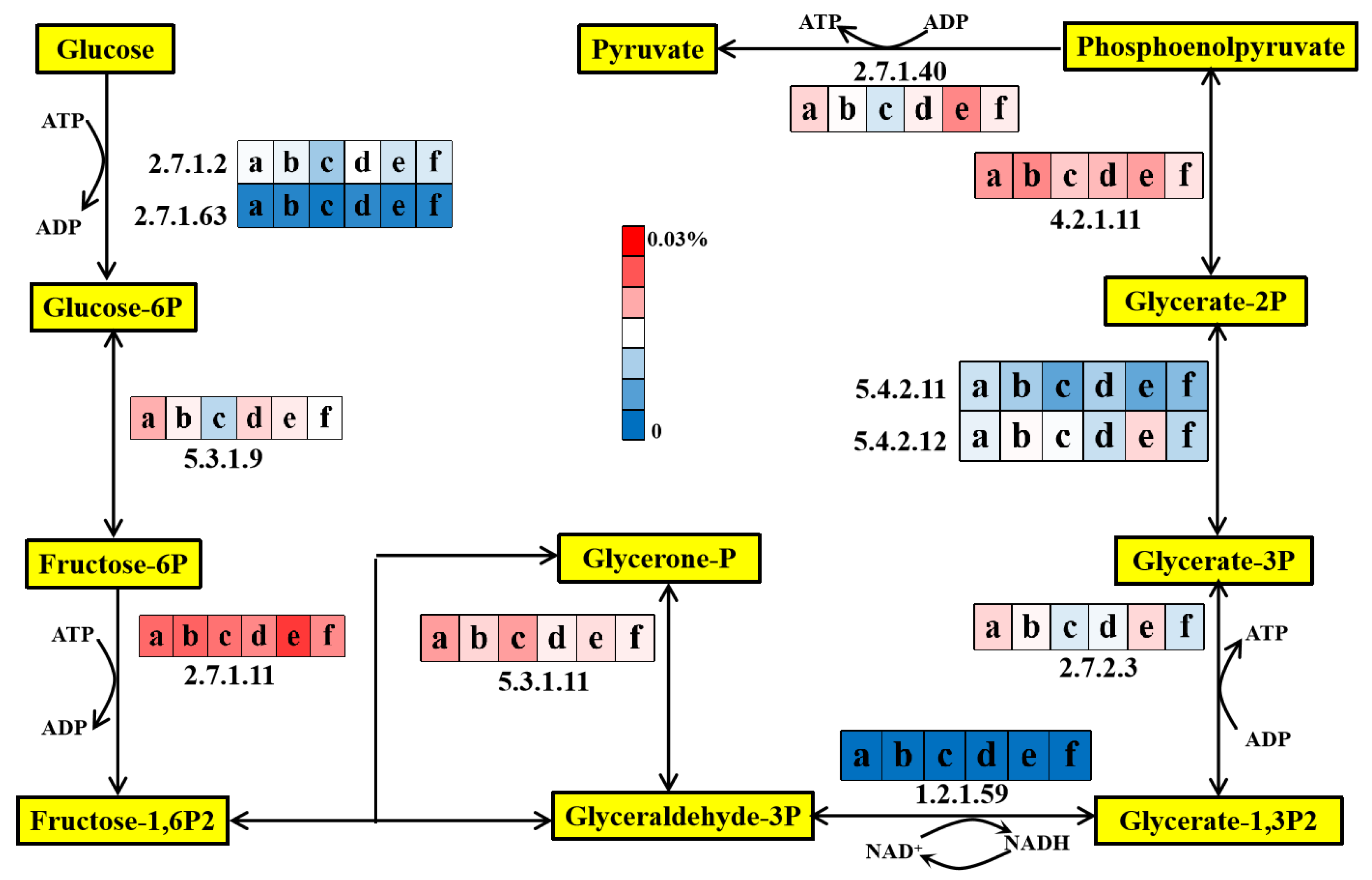
3.5.1. Glycolysis Pathway
3.5.2. Nitrogen Metabolic Pathway
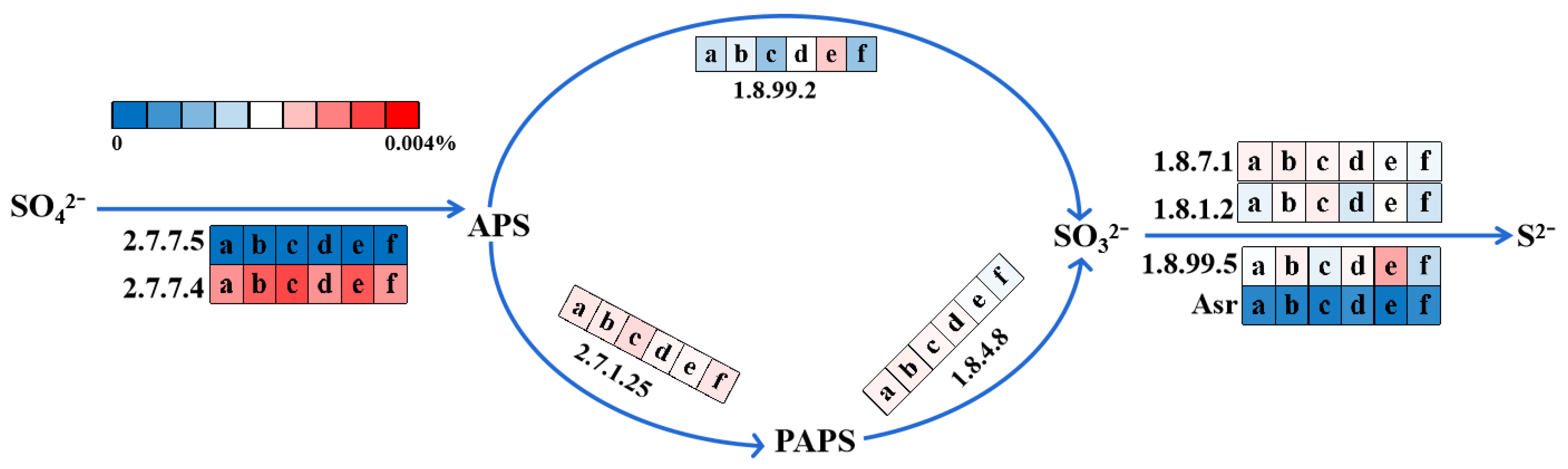
3.5.3. Sulfate Reduction Pathway
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, W.-Q.; Yang, S.-S.; Xiang, W.-S.; Wang, X.-J.; Ren, N.-Q. Minimization of excess sludge production by in-situ activated sludge treatment processes—A comprehensive review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 1386–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, H.; Sun, Y.; Wan, D.; Abbasi, H.N.; Guo, Z.; Geng, H.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y. Simultaneous denitrification and phosphorus removal: A review on the functional strains and activated sludge processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 835, 155409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y. Chemically reduced excess sludge production in the activated sludge process. Chemosphere 2003, 50, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mtrquez, P.; Gutiérrez, M.C.; Toledo, M.; Alhama, J.; Micháich, C.; Martín, M.A. Activated sludge process versus rotating biological contactors in WWTPs: Evaluating the influence of operation and sludge bacterial content on their odor impact. Process. Saf. Environ. 2022, 160, 775–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed-Hassan, S.S.A.; Wang, Y.; Hu, S.; Su, S.; Xiang, J. Thermochemical processing of sewage sludge to energy and fuel: Fundamentals, challenges and considerations. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2017, 80, 888–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Qi, Y.; Yue, Q.; Gao, B.; Gao, Y.; Fan, C.; He, S. Preparation of ceramic filler from reusing sewage sludge and application in biological aerated filter for soy protein secondary wastewater treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raheem, A.; Sikarwar, V.S.; He, J.; Dastyar, W.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Wang, W.; Zhao, M. Opportunities and challenges in sustainable treatment and resource reuse of sewage sludge: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 337, 616–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, A.; Zhang, R.; Ngo, H.H.; He, X.; Ma, J.; Nan, J.; Li, G. Life cycle assessment of sewage sludge treatment and disposal based on nutrient and energy recovery: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 144451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrentino, R.; Andreottola, G. Investigation of sludge solubilization and phosphorous release in anaerobic side-stream reactor with a low pressure swirling jet hydrodynamic cavitation treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.S.; Fang, F.; Yan, P.; Chen, Y.P. Sludge reduction based on microbial metabolism for sustainable wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrentino, R.; Langone, M.; Merzari, F.; Tramonte, L.; Andreottola, G. A review of anaerobic side-stream reactor for excess sludge reduction: Configurations, mechanisms, and efficiency. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 46, 382–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Zhou, Z.; Niu, T.; An, Y.; Shen, X.; Pan, W.; Chen, Z.; Liu, J. Effects of side-stream ratio on sludge reduction and microbial structures of anaerobic side-stream reactor coupled membrane bioreactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 234, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, H.; Zhou, Z.; Niu, T.; Jiang, L.-M.; Chen, G.; Xu, B.; Jiang, L.; Qiu, Z. Sludge reduction and microbial structures of aerobic, micro-aerobic and anaerobic side-stream reactor coupled membrane bioreactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 268, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, J.; Jiang, L.M.; Jiang, J. Sludge reduction and microbial structures in MBRs: Features influencing the sustainable adoption of MBRs. In Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhou, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Jiang, J.; Huang, J.; Qiang, J.; An, Y.; Jiang, L.; Jiang, L.-M.; Wang, Z. Understanding mechanisms of sludge in situ reduction in anaerobic side-stream reactor coupled membrane bioreactors packed with carriers at different filling fractions. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 316, 123925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Cheng, C.; Zhou, Z.; Pang, H.; Chen, L.; Jiang, L.M. Insight into the roles of packing carriers and ultrasonication in anaerobic side-stream reactor coupled membrane bioreactors: Sludge reduction performance and mechanism. Water Res. 2019, 155, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.; Zhou, Z.; Qiu, Z.; Yang, J.; Wu, W.; Pang, H. Enhancement of sludge reduction by ultrasonic pretreatment and packing carriers in the anaerobic side-stream reactor: Performance, sludge characteristics and microbial community structure. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 249, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Ekama, G.A.; Biswal, B.K.; Dai, J.; Jiang, F.; Chen, G.H.; Wu, D. A new sulfidogenic oxic-settling anaerobic (SOSA) process: The effects of sulfur-cycle bioaugmentation on the operational performance, sludge properties and microbial communities. Water Res. 2019, 162, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, F.; Hao, T. Sulfate in anaerobic co-digester accelerates methane production from food waste and waste activated sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 298, 122536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tabassum, S. Simultaneous removal of ammonia nitrogen and sulfide by coupled anammox and sulfur autotrophic denitrification process from industrial wastewater. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2022, 8, 100469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Deng, Y.F.; Zeng, Q.; Heynderickx, P.M.; Chen, G.; Wu, D. Integrating electrochemical pretreatment (EPT) and side-stream sulfidogenesis with conventional activated sludge process: Performance, microbial community and sludge reduction mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 433, 133678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, J.; Sui, X.; Lin, M.; Zhao, W.; Zhen, Y.; Bing, X.; Lin, J. Response of the reactor performances and bacterial communities to the evolution of sulfide-based mixotrophic denitrification processes from nitrate-type to nitrite-type. Biochem. Eng. J. 2021, 173, 108069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Maqbool, T.; Kang, H.; Zhang, Z. In-Situ Sludge Reduction in Membrane-Controlled Anoxic-Oxic-Anoxic Bioreactor: Performance and Mechanism. Membranes 2022, 12, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Ye, X.; Huang, J.; Jiang, L.; Chen, G.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z. Identifying microbial community evolution in membrane bioreactors coupled with anaerobic side-stream reactor, packing carriers and ultrasonication for sludge reduction by linear discriminant analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 291, 121920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Qiao, W.; Xing, C.; An, Y.; Shen, X.; Ren, W.; Jiang, L.; Wang, L. Microbial community structure of anoxic-oxic-settling-anaerobic sludge reduction process revealed by 454-pyrosequencing. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 266, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrentino, R.; Langone, M.; Gandolfi, I.; Bertolini, V.; Franzetti, A.; Andreottola, G. Shift in microbial community structure of anaerobic side-stream reactor in response to changes to anaerobic solid retention time and sludge interchange ratio. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 221, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzosa, E.A.; Hsu, T.; Sirota-Madi, A.; Shafquat, A.; Abu-Ali, G.; Morgan, X.C.; Huttenhower, C. Sequencing and beyond: Integrating molecular ‘omics’ for microbial community profiling. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 360–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federation, W.E.; Aph Association. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association (APHA): Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Leslie, G.L.; Waite, T.D. Effect of ferric and ferrous iron addition on phosphorus removal and fouling in submerged membrane bioreactors. Water Res. 2015, 69, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X. Coupling in-situ ozonation with ferric chloride addition for ceramic ultrafiltration membrane fouling mitigation in wastewater treatment: Quantitative fouling analysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 555, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X. Integration of ferrate (VI) pretreatment and ceramic membrane reactor for membrane fouling mitigation in reclaimed water treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 552, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z. Fe(II)-dosed ceramic membrane bioreactor for wastewater treatment: Nutrient removal, microbial community and membrane fouling analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Liu, C.M.; Luo, R.; Sadakane, K.; Lam, T.W. Megahit: An ultra-fast single-node solution for large and complex metagenomics assembly via succinct de Bruijn graph. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1674–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyatt, D.; Chen, G.L.; LoCascio, P.F.; Land, M.L.; Larimer, F.W.; Hauser, L.J. Prodigal: Prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site identification. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinegger, M.; Söding, J. Clustering huge protein sequence sets in linear time. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M. KEGG as a reference resource for gene and protein annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D457–D462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, T.S.; Corsino, S.F.; Di Trapani, D.; Torregrossa, M.; Viviani, G. Biological minimization of excess sludge in a membrane bioreactor: Effect of plant configuration on sludge production, nutrient removal efficiency and membrane fouling tendency. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 259, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Trapani, D.; Mannina, G.; Viviani, G. Membrane Bioreactors for wastewater reuse: Respirometric assessment of biomass activity during a two year survey. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 202, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foladori, P.; Velho, V.F.; Costa, R.H.R.; Bruni, L.; Quaranta, A.; Andreottola, G. Concerning the role of cell lysis-cryptic growth in anaerobic side-stream reactors: The single-cell analysis of viable, dead and lysed bacteria. Water Res. 2015, 74, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, P.H.; Keiding, K. Disintegration of activated sludge flocs in presence of sulfide. Water Res. 1998, 32, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Ekama, G.; Deng, Y.F.; Chen, G.H.; Wu, D. Identifying the mechanisms of sludge reduction in the sulfidogenic oxic-settling anaerobic (SOSA) process: Side-stream sulfidogenesis-intensified sludge decay and mainstream extended aeration. Water Res. 2021, 189, 116608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suopajärvi, T.; Liimatainen, H.; Hormi, O.; Niinimäki, J. Coagulation-flocculation treatment of municipal wastewater based on anionized nanocelluloses. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 231, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chon, K.; Ren, X.; Kou, Y.; Chae, K.J.; Piao, Y. Effects of beneficial microorganisms on nutrient removal and excess sludge production in an anaerobic-anoxic/oxic (A2O) process for municipal wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 281, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izadi, P.; Izadi, P.; Eldyasti, A. Holistic insights into extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) in anammosx bacterial matrix and the potential sustainable biopolymer recovery: A review. Chemosphere 2021, 274, 129703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, A.F.R.; Magalhães, N.C.; Cunha, P.V.M.; Amaral, M.C.S.; Koch, K. Influence of COD/SO42− ratio on vinasse treatment performance by two-stage anaerobic membrane bioreactor. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 259, 110034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriques, I.D.S.; Love, N.G. The role of extracellular polymeric substances in the toxicity response of activated sludge bacteria to chemical toxins. Water Res. 2007, 41, 4177–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhen, Y.; Li, N.; Wang, H.; Lin, M.; Sui, X.; Zhao, W.; Guo, P.; Lin, J. Sulfur transformation and bacterial community dynamics in both desulfurization-denitrification biofilm and suspended activated sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 343, 126108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.H.; An, K.J.; Saby, S.; Brois, E.; Djafer, M. Possible cause of excess sludge reduction in an oxic-settling-anaerobic activated sludge process (OSA process). Water Res. 2003, 37, 3855–3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Feng, Y.; Li, J.; Guo, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, S. Insight into the aggregation capacity of anammox consortia during reactor start-up. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3685–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Geng, J.; Zhou, Z.; Yu, Q.; Gao, R.; Shi, Y.; Wang, L.; Ren, H. A novel anoxic/aerobic process coupled with micro-aerobic/anaerobic side-stream reactor filled with packing carriers for in-situ sludge reduction. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 311, 127192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; An, Y.; Huang, J.; Sun, X.; Yang, A.; Zhou, Z. Elucidating the intensifying effect of introducing influent to an anaerobic side-stream reactor on sludge reduction of the coupled membrane bioreactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 342, 125931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Chon, K.; Ren, X.; Lee, Y.; Kou, Y.; Wu, Y.; Shen, M.; Hwang, M.H.; Chae, K.J. Contributions of enhanced endogenous microbial metabolism via inoculation with a novel microbial consortium into an anoxic side-stream reactor to in-situ sludge reduction for landfill leachate treatment. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 295, 113088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, D.; Miao, J.; Wu, G.; Zhan, X. Nitrogen removal, microbial community and electron transport in an integrated nitrification and denitrification system for ammonium-rich wastewater treatment. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 2018, 133, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuerst, J.A.; Sagulenko, E. Beyond the bacterium: Planctomycetes challenge our concepts of microbial structure and function. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Peng, L.; Tang, X.; Lin, Y.; Yang, D.; Geng, G.; Ren, H.; Xu, K. Performance evaluation and mechanism of nitrogen removal in a packed bed reactor using micromagnetic carriers at different carbon to nitrogen ratios. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 341, 125747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Melo Pirete, L.; Camargo, F.P.; Grosseli, G.M.; Sakamoto, I.K.; Fadini, P.S.; Silva, E.L.; Varesche, M.B.A. Influence of ethanol and nitrate on ibuprofen removal in batch reactors under denitrifying conditions. Process. Saf. Environ. 2022, 160, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xiang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Ma, H.; Shao, Z.; Chai, H. Insight into thiosulfate-driven denitrification and anammox process: Bigger aggregates driving better nitrite utilization on ammonium and nitrate contained wastewater. J. Water Process. Eng. 2022, 47, 102669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.J.; Chen, C.; Wang, A.J.; Yu, H.; Zhou, X.; Guo, H.L.; Yuan, Y.; Lee, D.J.; Zhou, J.; Ren, N.Q. Bioreactor performance and functional gene analysis of microbial community in a limited-oxygen fed bioreactor for co-reduction of sulfate and nitrate with high organic input. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 278, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Khanal, S.K.; Shu, H.; Zhang, H.; Chen, G.H.; Lu, H. Ciprofloxacin degradation in anaerobic sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) sludge system: Mechanism and pathways. Water Res. 2018, 136, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, T.; He, Q.; Xu, J.; Yin, F.; Li, H.; Ai, H. A conceptual method to simultaneously inhibit methane and hydrogen sulfide production in sewers: The carbon metabolic pathway and microbial community shift. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 246, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Liu, C.Q.; Li, X.D.; Ding, S.; Cui, G.; Teng, H.H.; Lv, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Guan, T. Carbon-sulfur coupling in a seasonally hypoxic, high-sulfate reservoir in SW China: Evidence from stable CS isotopes and sulfate-reducing bacteria. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 828, 154537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, F.; Xia, Y.; Guo, F.; Wang, Z.P.; Zhang, T. Taxonomic relatedness shapes bacterial assembly in activated sludge of globally distributed wastewater treatment plants. Environ. Micro. 2014, 16, 2421–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.; Chen, S.; Huang, T.; Li, B.; Li, N.; Liu, K.; Zong, R.; Miao, Y.; Huang, X. Community compositions of phytoplankton and eukaryotes during the mixing periods of a drinking water reservoir: Dynamics and interactions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, J.; Hiras, J.; Hanson, T.E. Sulfite oxidation in Chlorobaculum tepidum. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, K.; Baskaran, V.; Nemati, M. Bacteria of the sulphur cycle: An overview of microbiology, biokinetics and their role in petroleum and mining industries. Biochem. Eng. J. 2009, 44, 73–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, N.; Feng, C.; Deng, Y. Insights into heterotrophic denitrification diversity in wastewater treatment systems: Progress and future prospects based on different carbon sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, B.; Wang, S.; Peng, Y. Short-chain fatty acids production and microbial community in sludge alkaline fermentation: Long-term effect of temperature. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 211, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maughan, R. Carbohydrate metabolism. Surgery 2009, 27, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, C.; Hou, J.; Wang, P.; Miao, L. Effects of Ag NPs on denitrification in suspended sediments via inhibiting microbial electron behaviors. Water Res. 2020, 171, 115436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Guo, F.; Liu, X.; Su, X.; He, Q. Metagenomic analysis of the biotoxicity of titanium dioxide nanoparticles to microbial nitrogen transformation in constructed wetlands. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Su, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wan, R.; Liu, K.; Li, M.; Yin, D. Zinc oxide nanoparticles cause inhibition of microbial denitrification by affecting transcriptional regulation and enzyme activity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 13800–13807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; He, Q. Impacts of chlorothalonil on denitrification and N2O emission in riparian sediments: Microbial metabolism mechanism. Water Res. 2019, 148, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhao, X.; Sun, X.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, A.; An, Y.; Wang, Z. Repurposing hydrolysis acidification tank in municipal wastewater treatment plants for sludge reduction and biological nutrient removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 396, 125327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liang, Y.; Miao, Y.; Wang, D.; Jia, S.; Liu, C.H. Metagenomic insights into aniline effects on microbial community and biological sulfate reduction pathways during anaerobic treatment of high-sulfate wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 742, 140537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.H.; Luo, G.; Li, J.; Li, W.T.; Li, Y.; Li, A.M. Substrate competition and microbial function in sulfate-reducing internal circulation anaerobic reactor in the presence of nitrate. Chemosphere 2021, 280, 130937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neculita, C.M.; Zagury, G.J.; Bussière, B. Passive treatment of acid mine drainage in bioreactors using sulfate-reducing bacteria: Critical review and research needs. J. Environ. Qual. 2007, 36, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Maqbool, T.; Kang, H.; Zhang, Z. In-Situ Sludge Reduction Performance and Mechanism in Sulfidogenic Anoxic–Oxic–Anoxic Membrane Bioreactors. Membranes 2022, 12, 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12090865
Li C, Maqbool T, Kang H, Zhang Z. In-Situ Sludge Reduction Performance and Mechanism in Sulfidogenic Anoxic–Oxic–Anoxic Membrane Bioreactors. Membranes. 2022; 12(9):865. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12090865
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Chengyue, Tahir Maqbool, Hongyu Kang, and Zhenghua Zhang. 2022. "In-Situ Sludge Reduction Performance and Mechanism in Sulfidogenic Anoxic–Oxic–Anoxic Membrane Bioreactors" Membranes 12, no. 9: 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12090865
APA StyleLi, C., Maqbool, T., Kang, H., & Zhang, Z. (2022). In-Situ Sludge Reduction Performance and Mechanism in Sulfidogenic Anoxic–Oxic–Anoxic Membrane Bioreactors. Membranes, 12(9), 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12090865