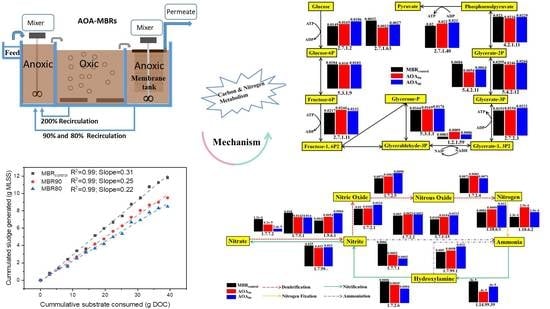
In-Situ Sludge Reduction in Membrane-Controlled Anoxic-Oxic-Anoxic Bioreactor: Performance and Mechanism
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Experimental Setups
2.2. Extraction and Characterization of EPS and SMP
2.3. Analytical Characterization
2.4. PARAFAC Modeling
2.5. 16S rRNA Amplicon Sequencing and Metagenomics Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Basic Water Quality Parameters
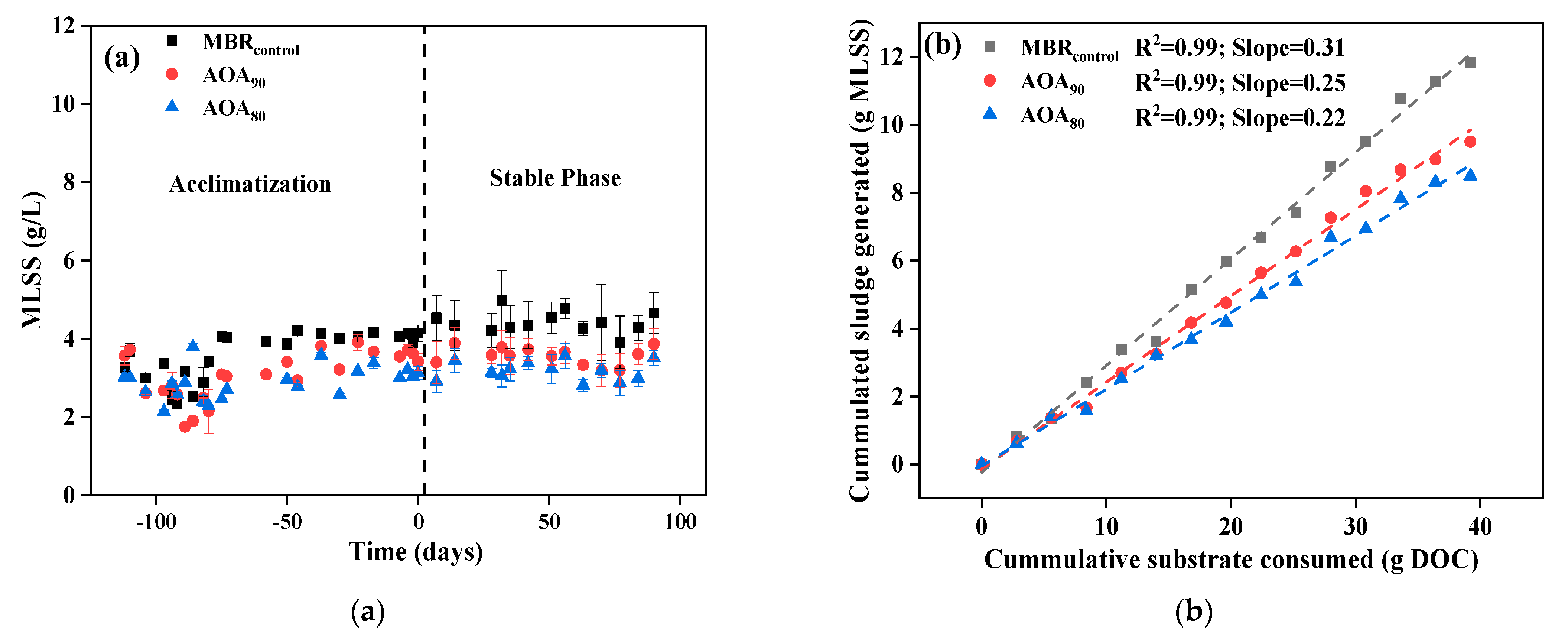
3.2. Sludge Reduction
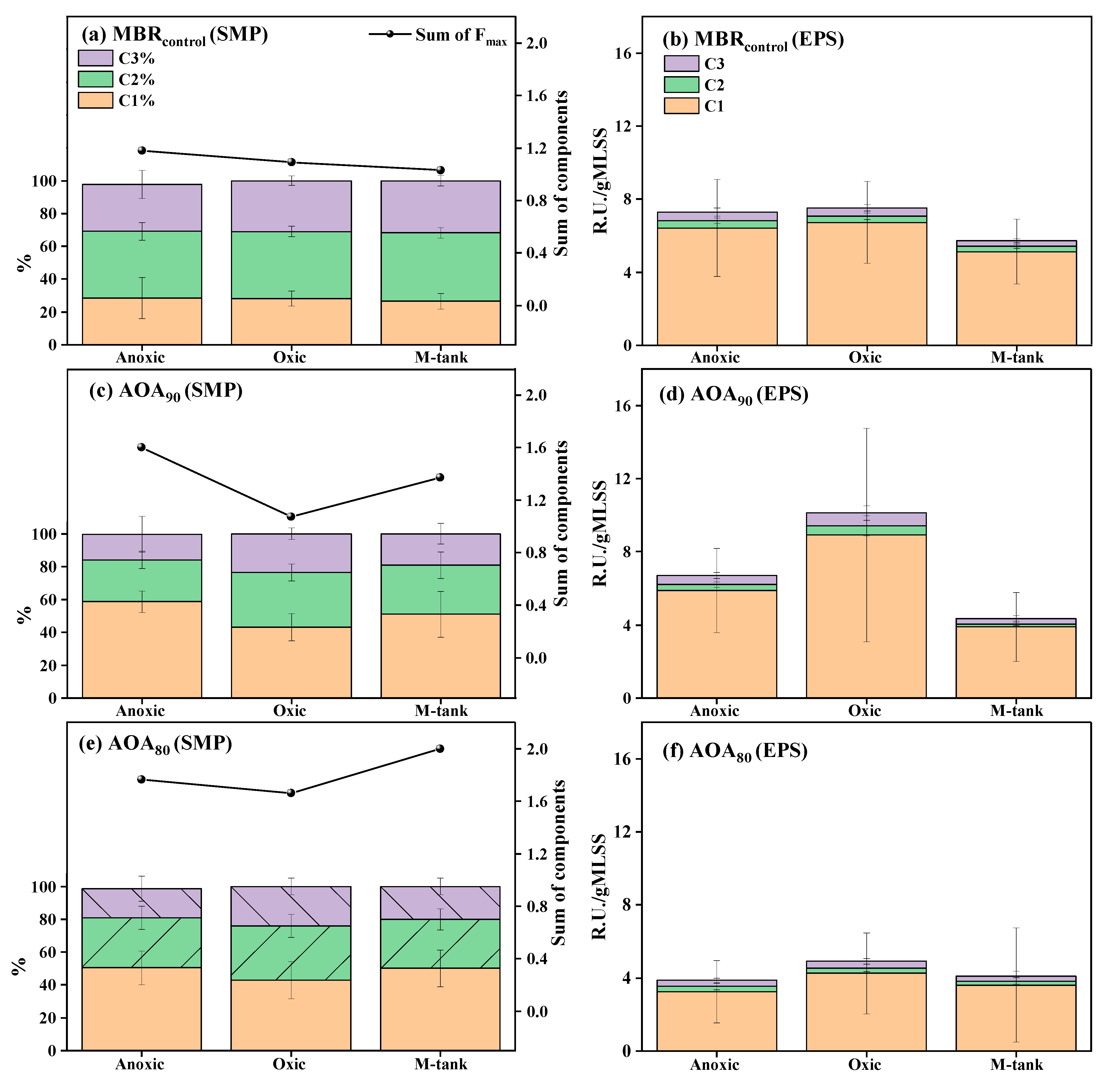
3.3. Dynamics of EPS and SMP in AOA Bioreactors
3.4. Microbial Community
3.5. Metabolic Response Pathways
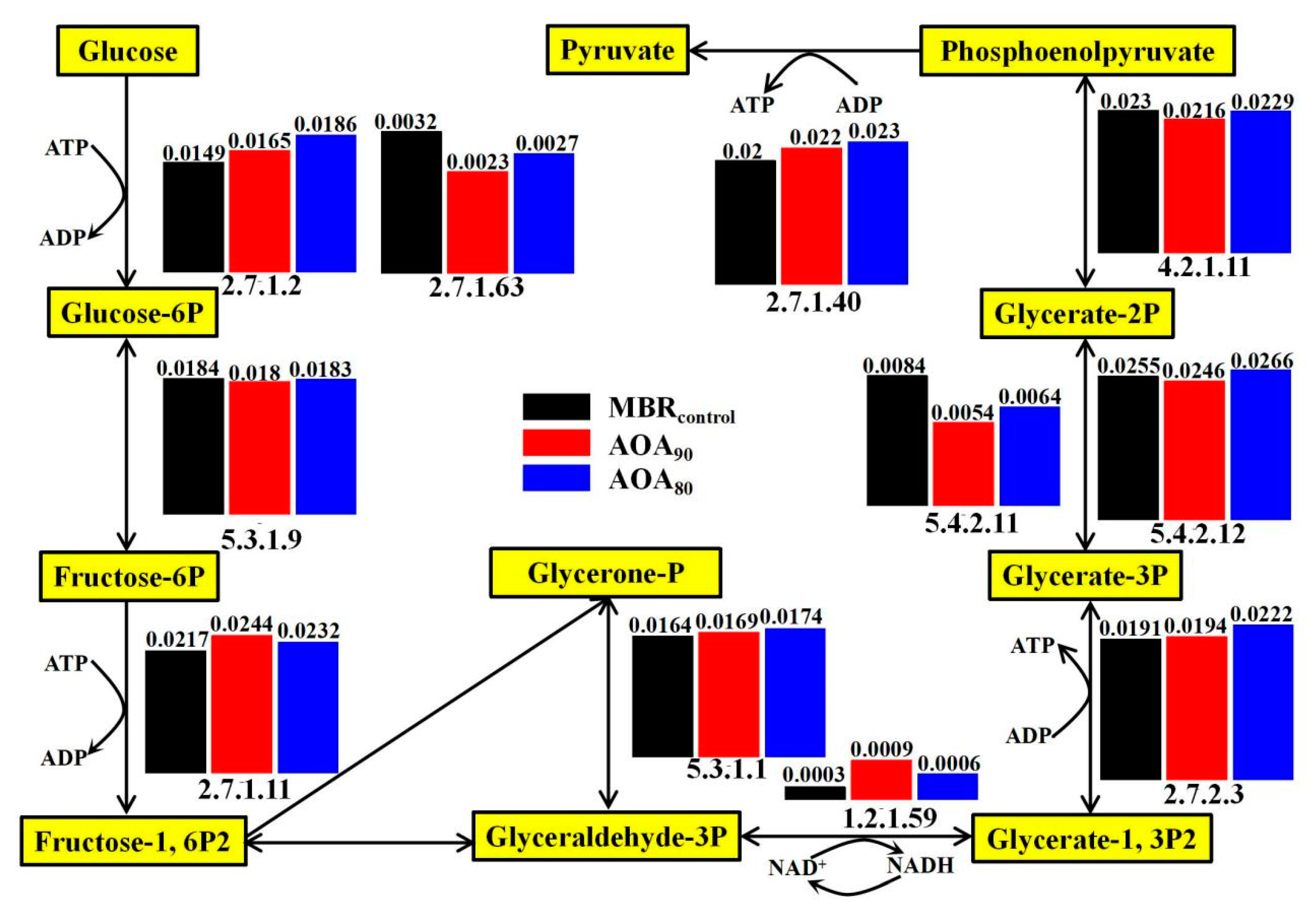
3.5.1. Carbohydrate Metabolic Analysis and Functional Genes
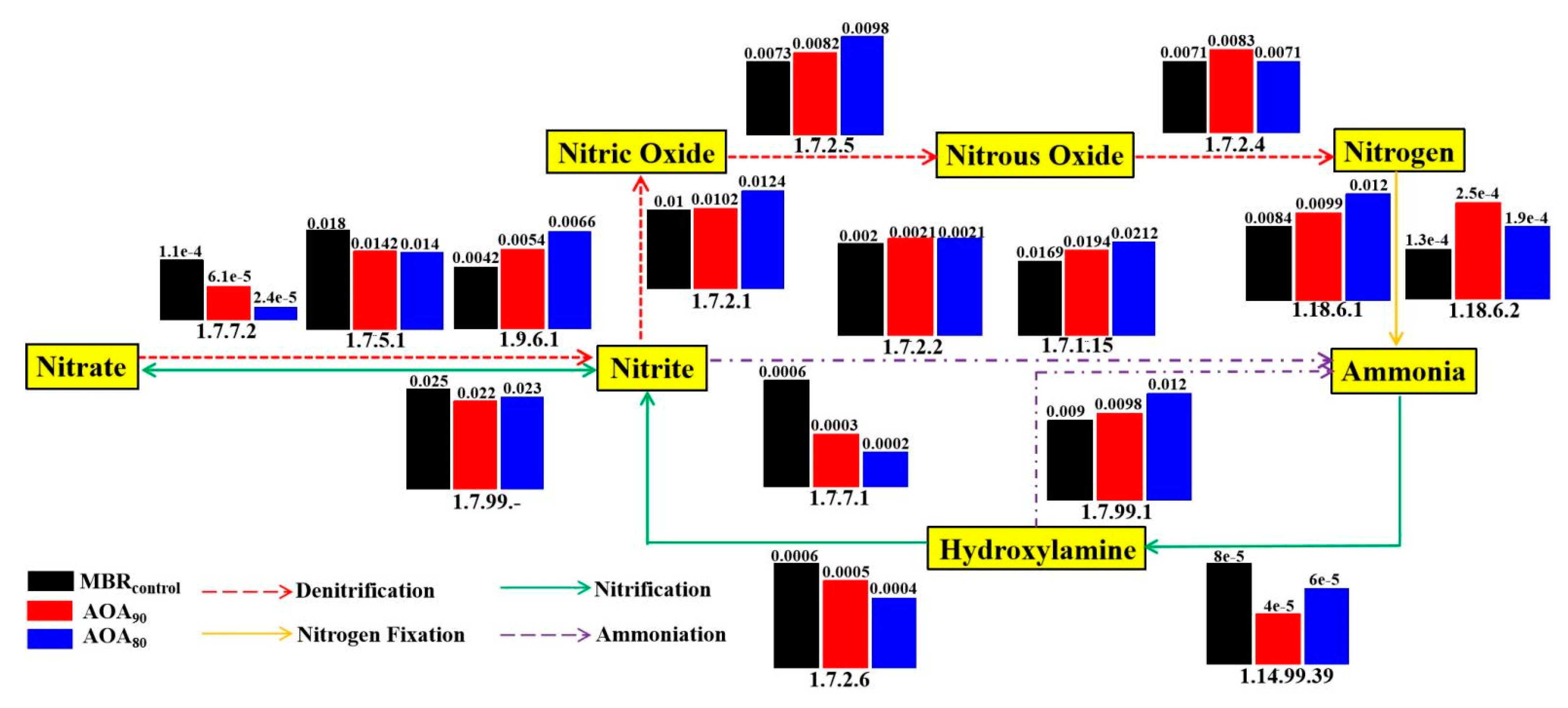
3.5.2. Nitrogen Metabolic Analysis and Functional Genes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Q.; Wei, W.; Gong, Y.; Yu, Q.; Li, Q.; Sun, J.; Yuan, Z. Technologies for reducing sludge production in wastewater treatment plants: State of the art. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 587, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Li, X.; Xu, G.; Yu, H. Overview of strategies for enhanced treatment of municipal/domestic wastewater at low temperature. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Li, J.; Peng, Y. Impact of starvation conditions on the nitrifying performance and sludge properties in SBR system with a limited filamentous bulking state. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 797, 148997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Geng, J.; Hu, H.; Shi, Y.; Gao, R.; Wang, X.; Ren, H. In-situ sludge reduction performance and mechanism in an anoxic/aerobic process coupled with alternating aerobic/anaerobic side-stream reactor. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 145856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Fan, Y.; Li, H.; Ren, Z.; Kou, L.; Guo, X.; Jia, H.; Wang, T.; Zhu, L. Excess sludge disintegration by discharge plasma oxidation: Efficiency and underlying mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, A.; Lin, W.; Chen, R.L.; Ngo, H.H.; Zhang, R.R.; He, X.; Nan, J.; Li, G.B.; Ma, J. Improvement of sludge dewaterability by energy uncoupling combined with chemical re-flocculation: Reconstruction of floc, distribution of extracellular polymeric substances, and structure change of proteins. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 816, 151646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Luo, J.; Chen, Y. Dilemma of Sewage Sludge Treatment and Disposal in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 4781–4782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.-Q.; Yang, S.-S.; Xiang, W.-S.; Wang, X.-J.; Ren, N.-Q. Minimization of excess sludge production by in-situ activated sludge treatment processes-A comprehensive review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 1386–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semblante, G.U.; Hai, F.I.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; You, S.-J.; Price, W.E.; Nghiem, L.D. Sludge cycling between aerobic, anoxic and anaerobic regimes to reduce sludge production during wastewater treatment: Performance, mechanisms, and implications. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 155, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pang, H.; Zhou, Z.; Niu, T.; Jiang, L.-M.; Chen, G.; Xu, B.; Jiang, L.; Qiu, Z. Sludge reduction and microbial structures of aerobic, micro-aerobic and anaerobic side-stream reactor coupled membrane bioreactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 268, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhou, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Jiang, J.; Huang, J.; Qiang, J.; An, Y.; Jiang, L.; Jiang, L.-M.; Wang, Z. Understanding mechanisms of sludge in situ reduction in anaerobic side-stream reactor coupled membrane bioreactors packed with carriers at different filling fractions. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 316, 123925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrentino, R.; Langone, M.; Gandolfi, I.; Bertolini, V.; Franzetti, A.; Andreottola, G. Shift in microbial community structure of anaerobic side-stream reactor in response to changes to anaerobic solid retention time and sludge interchange ratio. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 221, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, T.; Zhou, Z.; Shen, X.; Qiao, W.; Jiang, L.-M.; Pan, W.; Zhou, J. Effects of dissolved oxygen on performance and microbial community structure in a micro-aerobic hydrolysis sludge in situ reduction process. Water Res. 2016, 90, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.-S.; Fang, F.; Yan, P.; Chen, Y.-P. Sludge reduction based on microbial metabolism for sustainable wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, J.; Jiang, L.M.; Jiang, J. Sludge reduction and microbial structures in MBRs: Features influencing the sustainable adoption of MBRs. In Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Jiang, J.; Zhou, Z. Responses of microbial structures, functions and metabolic pathways for nitrogen removal to different hydraulic retention times in anoxic side-stream reactor coupled membrane bioreactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 329, 124903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, X.; Yang, Q.; Seow, W.Y.; Zhu, W.; Zhou, Y. Variations in physical, chemical and biological properties in relation to sludge dewaterability under Fe (II)—Oxone conditioning. Water Res. 2017, 109, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.; Rosebrough, N.; Farr, L.; Randall, R. Protein Measurement woth the folin phenol reagent. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 1951, 1, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuBois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric Method for Determination of Sugars and Related Substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apha, A. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA; American Water Works Association: Washington, DC, USA; Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; Volume 21, pp. 258–259. [Google Scholar]
- Lawaetz, A.J.; Stedmon, C.A. Fluorescence Intensity Calibration Using the Raman Scatter Peak of Water. Appl. Spectrosc. 2009, 63, 936–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqbool, T.; Li, C.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, J.; Asif, M.B.; Zhang, Z. A year-long cyclic pattern of dissolved organic matter in the tap water of a metropolitan city revealed by fluorescence spectroscopy. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 77, 144850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z. Fe(II)-dosed ceramic membrane bioreactor for wastewater treatment: Nutrient removal, microbial community and membrane fouling analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.-W.; Sheng, G.-P.; Zeng, R.J.; Liu, X.-W.; Yu, H.-Q. China’s wastewater discharge standards in urbanization. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 1422–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Ong, S.L.; Ng, H.Y. Performance of submerged anaerobic membrane bioreactor at different SRTs for domestic wastewater treatment. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 164, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Wu, X.; Cai, D.; Chen, G.; Li, D.; Yu, Y.; Petrik, L.F.; Liu, G. Linking solids retention time to the composition, structure, and hydraulic resistance of biofilms developed on support materials in dynamic membrane bioreactors. J. Memb. Sci. 2019, 581, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Qiao, W.; Xing, C.; Wang, C.; Jiang, L.-M.; Gu, Y.; Wang, L. Characterization of dissolved organic matter in the anoxic–oxic-settling-anaerobic sludge reduction process. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 259, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Ekama, G.; Deng, Y.-F.; Chen, G.-H.; Wu, D. Identifying the mechanisms of sludge reduction in the sulfidogenic oxic-settling anaerobic (SOSA) process: Side-stream sulfidogenesis-intensified sludge decay and mainstream extended aeration. Water Res. 2021, 189, 116608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Liu, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Qi, L.; Xu, X.; Wang, J.; He, Y.; Li, Q.; et al. Sludge characteristics, system performance and microbial kinetics of ultra-short-SRT activated sludge processes. Environ. Int. 2020, 143, 105973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Hu, Z.; Tu, X.; Wu, K.; Chen, G.; Chai, X.-S. In-situ determination of the observed yield coefficient of aerobic activated sludge by headspace gas chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1610, 460560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, K.J.; Oh, S.E.; Lee, S.T.; Bae, J.W.; Kim, I.S. The optimum substrate to biomass ratio to reduce net biomass yields and inert compounds in biological leachate treatment under pure-oxygen conditions. Bioprocess Eng. 2000, 23, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramdani, A.; Dold, P.; Déléris, S.; Lamarre, D.; Gadbois, A.; Comeau, Y. Biodegradation of the endogenous residue of activated sludge. Water Res. 2010, 44, 2179–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wang, J. Modeling effects of DO and SRT on activated sludge decay and production. Water Res. 2015, 80, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Iaconi, C.; De Sanctis, M.; Altieri, V.G. Full-scale sludge reduction in the water line of municipal wastewater treatment plant. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 269, 110714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Wu, W.; Xu, J.; Wang, Z. An anaerobic dynamic membrane bioreactor for enhancing sludge digestion: Impact of solids retention time on digestion efficacy. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 329, 124864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Li, A.; Ma, F. Formation of soluble microbial products and their contribution as electron donors for denitrification. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 326, 1159–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J. Research on rapid cultivation of aerobic granular sludge (AGS) with different feast-famine strategies in continuous flow reactor and achieving high-level denitrification via utilization of soluble microbial product (SMP). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 786, 147237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqbool, T.; Cho, J.; Hur, J. Changes in spectroscopic signatures in soluble microbial products of activated sludge under different osmotic stress conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 255, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Westerhoff, P.; Leenheer, J.A.; Booksh, K. Fluorescence Excitation-Emission Matrix Regional Integration to Quantify Spectra for Dissolved Organic Matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 5701–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.H.; He, P.J.; Shao, L.M. Novel insights into sludge dewaterability by fluorescence excitation-emission matrix combined with parallel factor analysis. Water Res. 2010, 44, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.R.; Hambly, A.; Singh, S.; Henderson, R.K.; Baker, A.; Stuetz, R.; Khan, S.J. Organic matter fluorescence in municipal water recycling schemes: Toward a unified PARAFAC model. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 2909–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, S.K.L.; Boyer, T.H. Behavior of reoccurring parafac components in fluorescent dissolved organic matter in natural and engineered systems: A critical review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 2006–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Liu, C.; Yu, X.; Wang, Y.; Song, J.; Xiao, X.; Meng, F.; Cai, Y.; Ji, W.; Xie, Y.; et al. Insight into binding characteristics of copper (II) with water-soluble organic matter emitted from biomass burning at various pH values using EEM-PARAFAC and two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy analysis. Chemosphere 2021, 278, 130439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Li, D.; Yu, Z.; Meng, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhao, S.; Meng, F. Biochemical characteristics and membrane fouling behaviors of soluble microbial products during the lifecycle of Escherichia coli. Water Res. 2021, 192, 116835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinta, É.; Pacheco-Forés, S.I.; Wallace, E.P.; Knudson, K.J. Provenancing wood used in the Norse Greenlandic settlements: A biogeochemical study using hydrogen, oxygen, and strontium isotopes. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2021, 131, 105407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Zhou, Z.; Pang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, L.; Jiang, L.-M.; Zhao, X. Correlation of microbial community structure with pollutants removal, sludge reduction and sludge characteristics in micro-aerobic side-stream reactor coupled membrane bioreactors under different hydraulic retention times. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 260, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Jiang, X.; Xiao, K.; Shen, N.; Zeng, R.J.; Zhou, Y. Enhanced volatile fatty acids (VFAs) production in a thermophilic fermenter with stepwise pH increase-Investigation on dissolved organic matter transformation and microbial community shift. Water Res. 2017, 112, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.J.; Su, C.Y.; Wang, A.L. Comparative study of oxic granular sludge with different carbon sources: Effluent nitrogen forms and microbial community. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 43, 102211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Si, D.; Chen, Q. Evolution of microbial community along with increasing solid concentration during high-solids anoxic digestion of sewage sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 216, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, P.; Wang, H.; Qiu, Y.; Ren, L.; Jiang, B. Microbial characteristics in anoxic digestion process of food waste for methane production—A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 248, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Xu, W.; Sontag, P.; Li, X.; Xue, G.; Liu, T.; Sun, W. Correlating microbial community compositions with environmental factors in activated sludge from four full-scale municipal wastewater treatment plants in Shanghai, China. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 4663–4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwanza, E.P.; Westhuizen, W.; Boucher, C.E.; Charimba, G.; Hugo, C. Heterologous expression and characterisation of a keratinase produced by chryseobacterium carnipullorum. Protein Expres. Purif. 2021, 186, 105926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Zhou, Z.; Niu, T.; An, Y.; Shen, X.; Pan, W.; Chen, Z.; Liu, J. Effects of side-stream ratio on sludge reduction and microbial structures of anaerobic side-stream reactor coupled membrane bioreactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 234, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Cheng, C.; Zhou, Z. Insight into the roles of packing carriers and ultrasonication in anoxic side-stream reactor coupled membrane bioreactors: Sludge reduction performance and mechanism. Water Res. 2019, 155, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, F.; Xia, Y.; Guo, F.; Wang, Z.P.; Zhang, T. Taxonomic relatedness shapes bacterial assembly in activated sludge of globally distributed wastewater treatment plants. Environ. Micro. 2014, 16, 2421–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.Y.; An, Y.; Huang, J.; Sun, X.; Yang, A.; Zhou, Z. Elucidating the intensifying effect of introducing influent to an anoxic side-stream reactor on sludge reduction of the coupled membrane bioreactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 342, 125931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świątczak, P.; Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A.; Zielińska, M. Treatment of the liquid phase of digestate from a biogas plant for water reuse. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 276, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Guo, W.; Ngo, S.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y. Application of a specific membrane fouling control enhancer in membrane bioreactor for real municipal wastewater treatment: Sludge characteristics and microbial community. Bioresour Technol. 2020, 312, 123612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Geng, J.; Zhou, Z.; Yu, Q.; Gao, R.; Shi, Y.; Wang, L.; Ren, H. A novel anoxic/aerobic process coupled with micro-aerobic/anaerobic side-stream reactor filled with packing carriers for in-situ sludge reduction. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 311, 127192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, T.; Chen, S.; Quan, X. Accelerating anaerobic hydrolysis acidification of dairy wastewater in integrated floating-film and activated sludge (IFFAS) by using zero-valent iron (ZVI) composite carriers. Biochem. Eng. J. 2022, 177, 108226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y.; Moreau, J.W. Bacterial predation limits microbial sulfate-reduction in a coastal acid sulfate soil (CASS) ecosystem. Soil Biol. Bioch. 2020, 148, 107930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Dai, X.; Chai, X. Effect of different carbon sources on denitrification performance, microbial community structure and denitrification genes. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 364, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Quan, X.; Zhuo, M.; Zhang, X.; Quan, Y. In-situ formation and self-immobilization of biogenic Fe oxides in anaerobic granular sludge for enhanced performance of acidogenesis and methanogenesis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 787, 147400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maughan, R. Carbohydrate metabolism. Surgery 2009, 27, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Guo, F.; Liu, X.; Su, X.; He, Q. Metagenomic analysis of the biotoxicity of titanium dioxide nanoparticles to microbial nitrogen transformation in constructed wetlands. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Qiao, W.; Xing, C.; An, Y.; Shen, X.; Ren, W.; Jiang, L.-M.; Wang, L. Microbial community structure of anoxic-oxic-settling-anaerobic sludge reduction process revealed by 454-pyrosequencing. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 266, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanuel, S.A.; Sul, W.J.; Seong, H.J.; Rhee, C.; Koh, S.C. Metagenomic analysis of relationships between the denitrification process and carbon metabolism in a bioaugmented full-scale tannery wastewater treatment plant. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 149, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Maqbool, T.; Kang, H.; Zhang, Z. In-Situ Sludge Reduction in Membrane-Controlled Anoxic-Oxic-Anoxic Bioreactor: Performance and Mechanism. Membranes 2022, 12, 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12070659
Li C, Maqbool T, Kang H, Zhang Z. In-Situ Sludge Reduction in Membrane-Controlled Anoxic-Oxic-Anoxic Bioreactor: Performance and Mechanism. Membranes. 2022; 12(7):659. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12070659
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Chengyue, Tahir Maqbool, Hongyu Kang, and Zhenghua Zhang. 2022. "In-Situ Sludge Reduction in Membrane-Controlled Anoxic-Oxic-Anoxic Bioreactor: Performance and Mechanism" Membranes 12, no. 7: 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12070659
APA StyleLi, C., Maqbool, T., Kang, H., & Zhang, Z. (2022). In-Situ Sludge Reduction in Membrane-Controlled Anoxic-Oxic-Anoxic Bioreactor: Performance and Mechanism. Membranes, 12(7), 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12070659