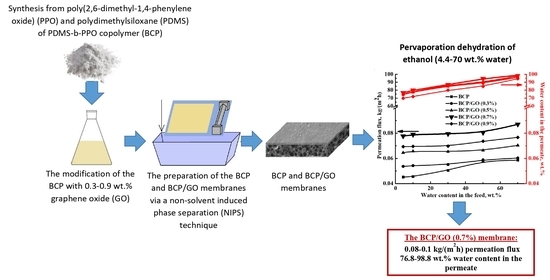
Novel PDMS-b-PPO Membranes Modified with Graphene Oxide for Efficient Pervaporation Ethanol Dehydration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
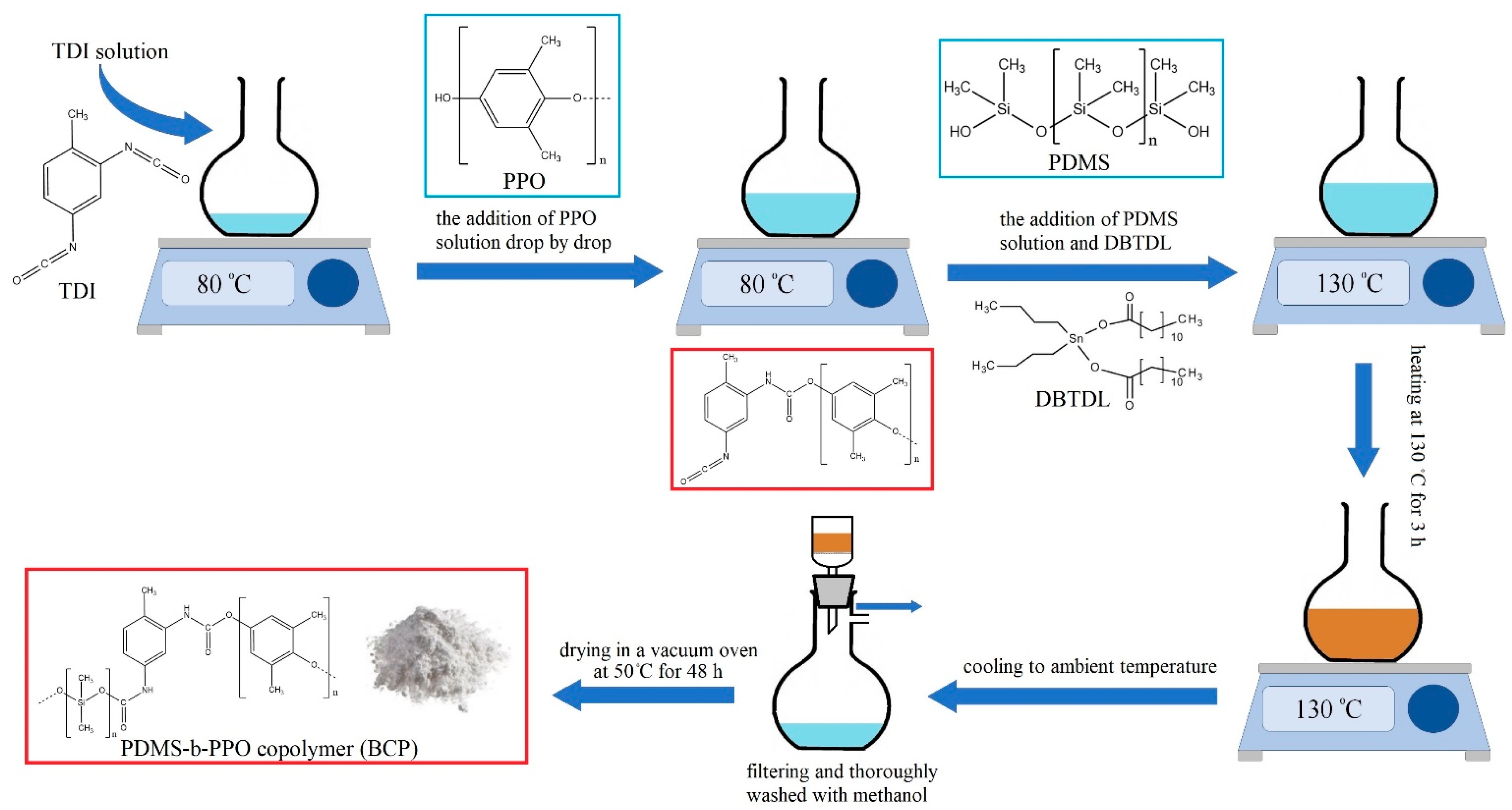
2.2. Synthesis of the PDMS-b-PPO Copolymer
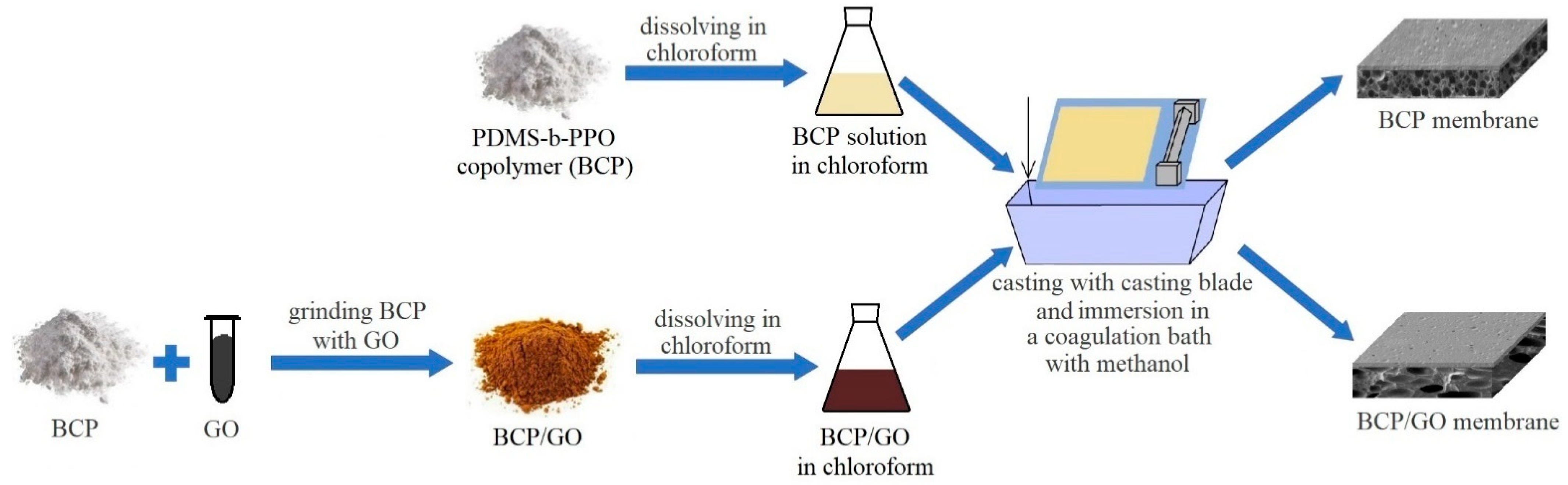
2.3. Membrane Preparation
2.4. Pervaporation
2.5. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.6. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)
2.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.8. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
2.9. Contact Angle Measurements
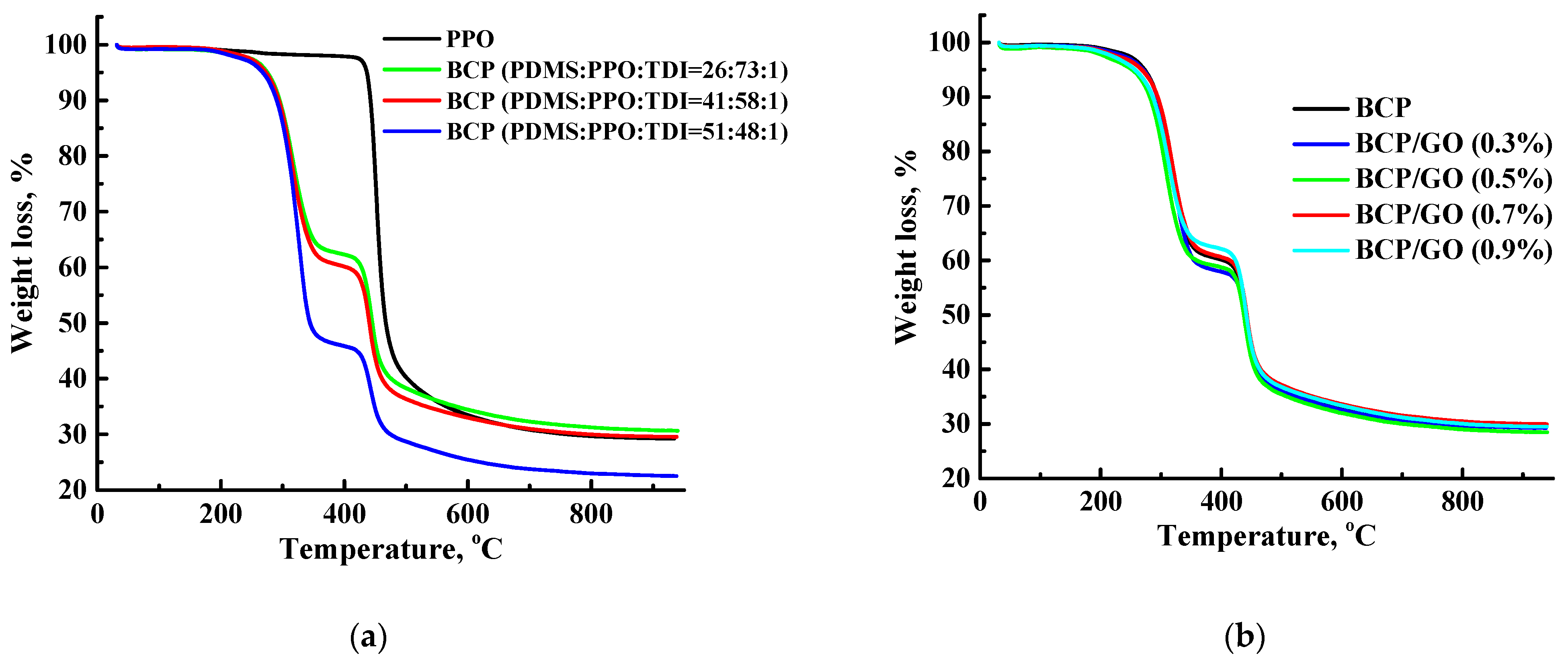
2.10. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
3. Results and Discussion
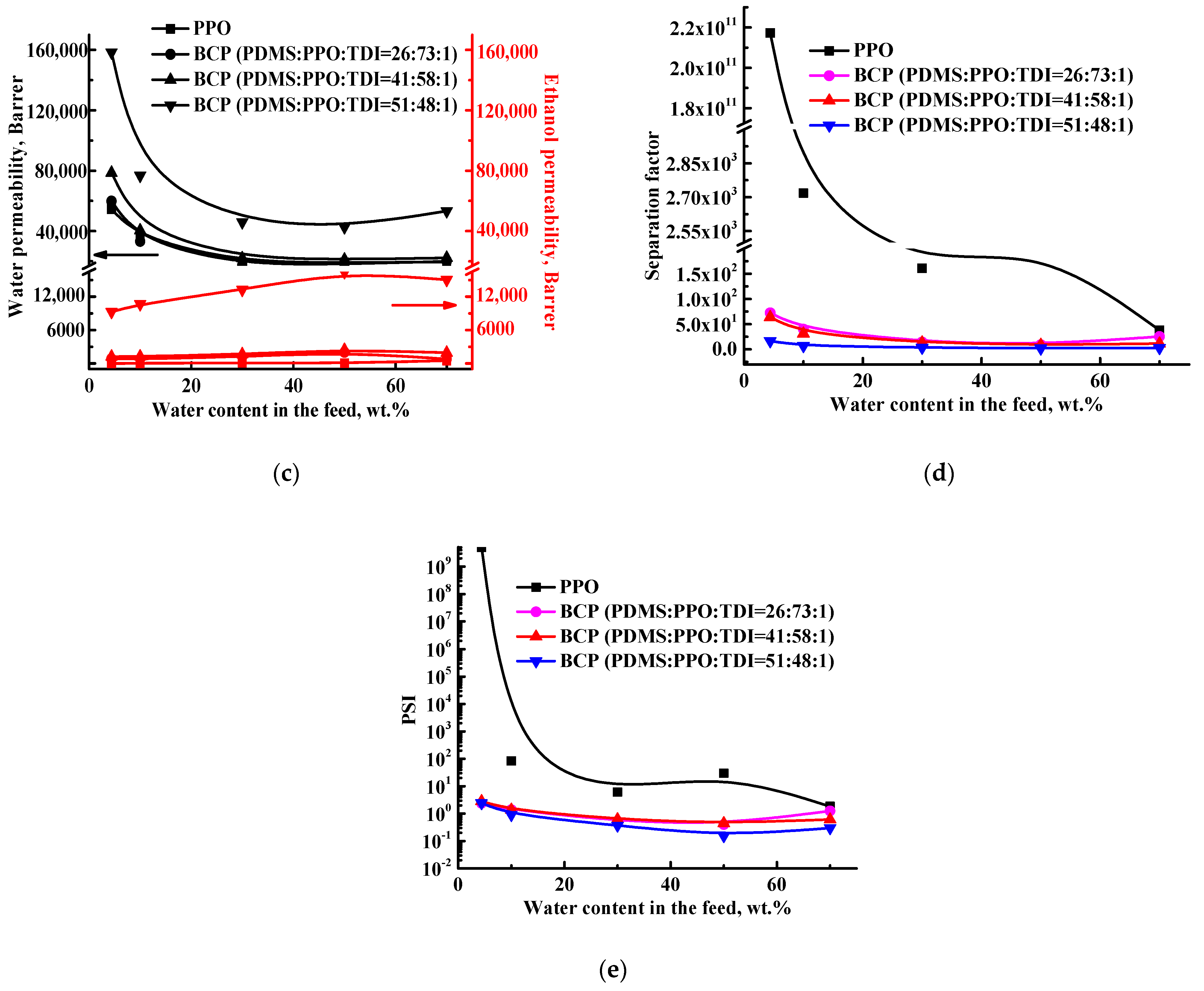
3.1. Transport Properties of the BCP-Based Membranes
3.2. Characterization of the BCP-Based Membranes
3.3. Comparison of Membrane Performance in the Pervaporation Dehydration of Ethanol
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dhabhai, R.; Niu, C.H.; Dalai, A.K. Agricultural byproducts-based biosorbents for purification of bioalcohols: A review. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2018, 5, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madero-Castro, R.M.; Calero, S.; Yazaydin, A.O. The role of hydrogen bonding in the dehydration of bioalcohols in hydrophobic pervaporation membranes. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 340, 117297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishov, A.; Penkova, A.; Zabrodin, A.; Nikolaev, K.; Dmitrenko, M.; Ermakov, S.; Bulatov, A. Vapor permeation-stepwise injection simultaneous determination of methanol and ethanol in biodiesel with voltammetric detection. Talanta 2016, 148, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, C.H.; Baylak, T.; Wilson, D.I.; Zhang, M. Pelletisation of canola meal by extrusion–spheronisation for ethanol dehydration. Biomass Bioenergy 2014, 66, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolkova, A.K.; Raeva, V.M. Bioethanol dehydration: State of the art. Theor. Found. Chem. Eng. 2010, 44, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burts, K.S.; Plisko, T.V.; Prozorovich, V.G.; Melnikova, G.B.; Ivanets, A.I.; Bildyukevich, A.V. Development and Study of PVA–SiO2/poly(AN-co-MA) Dynamic Nanocomposite Membranes for Ethanol Dehydration via Pervaporation. Membr. Membr. Technol. 2022, 4, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, R.H.; Linzmeyer, P.; Franco, C.M.B.; Souza, O.; Sellin, N.; Medeiros, S.H.W.; Marangoni, C. Pervaporation of ethanol produced from banana waste. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 1501–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzminova, A.I.; Dmitrenko, M.E.; Poloneeva, D.Y.; Selyutin, A.A.; Mazur, A.S.; Emeline, A.V.; Mikhailovskii, V.Y.; Solovyev, N.D.; Ermakov, S.S.; Penkova, A.V. Sustainable composite pervaporation membranes based on sodium alginate modified by metal organic frameworks for dehydration of isopropanol. J. Memb. Sci. 2021, 626, 119194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitrenko, M.; Liamin, V.; Kuzminova, A.; Mazur, A.; Lahderanta, E.; Ermakov, S.; Penkova, A. Novel Mixed Matrix Sodium Alginate–Fullerenol Membranes: Development, Characterization, and Study in Pervaporation Dehydration of Isopropanol. Polymers 2020, 12, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitrenko, M.E.; Penkova, A.V.; Atta, R.R.; Zolotarev, A.A.; Plisko, T.V.; Mazur, A.S.; Solovyev, N.D.; Ermakov, S.S. The development and study of novel membrane materials based on polyphenylene isophthalamide-Pluronic F127 composite. Mater. Des. 2019, 165, 107596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitrenko, M.E.; Penkova, A.V.; Missyul, A.B.; Kuzminova, A.I.; Markelov, D.A.; Ermakov, S.S.; Roizard, D. Development and investigation of mixed-matrix PVA-fullerenol membranes for acetic acid dehydration by pervaporation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 187, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitrenko, M.E.; Penkova, A.V.; Kuzminova, A.I.; Atta, R.R.; Zolotarev, A.A.; Mazur, A.S.; Vezo, O.S.; Lahderanta, E.; Markelov, D.A.; Ermakov, S.S. Development and investigation of novel polyphenylene isophthalamide pervaporation membranes modified with various fullerene derivatives. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 226, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, M.; Bin, T.; Nakao, S. Selective ethanol extraction from fermentation broth using a silicalite membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2002, 27, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Guo, H.X.; Ji, S.L.; Niu, H.J.; Li, J.R. A new PDMS-b-PPO block copolymer membrane with novel non-perforated structure towards high flux for alcohol permselective pervaporation. Express Polym. Lett. 2015, 9, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimon, C.; Elharfi, A. Plasma-modified poly (vinyl alcohol) membranes for the dehydration of ethanol. Polym. Int. 2003, 1229, 1222–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenes, M.L.; Liu, L.; Feng, X. Sericin/poly (vinyl alcohol) blend membranes for pervaporation separation of ethanol/water mixtures. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 295, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.S.V.K.; Subha, M.C.S.; Sairam, M.; Mallikarjuna, N.N.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Blend membranes of chitosan and poly(vinyl alcohol) in pervaporation dehydration of isopropanol and tetrahydrofuran. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 103, 1918–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, G.; Fang, Y.; Wang, X. Maleic anhydride surface-modification of crosslinked chitosan membrane and its pervaporation performance. J. Memb. Sci. 2007, 295, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Cui, Y.; Yan, Y.; Jiang, W. The effect of structure on pervaporation of chitosan membrane. J. Memb. Sci. 2000, 165, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurkuri, M.D.; Toti, U.S.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Syntheses and Characterization of Blend Membranes of Sodium Alginate and Poly (vinyl alcohol) for the Pervaporation Separation of Water + Isopropanol Mixtures. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 86, 3642–3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyani, S.; Smitha, B.; Sridhar, S.; Krishnaiah, A. Separation of Ethanol−Water Mixtures by Pervaporation Using Sodium Alginate/Poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) Blend Membrane Crosslinked with Phosphoric Acid. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 9088–9095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeom, C.K.; Lee, K.-H. Characterization of sodium alginate and poly(vinyl alcohol) blend membranes in pervaporation separation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1998, 67, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, W.-Y.; Lin, Y.-H. Properties of modified polyacrylonitrile membranes prepared by copolymerization with hydrophilic monomers for water-ethanol mixture separation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 90, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumarnaidu, B.; Sairam, M.; Raju, K.; Aminabhavi, T. Pervaporation separation of water+isopropanol mixtures using novel nanocomposite membranes of poly(vinyl alcohol) and polyaniline. J. Memb. Sci. 2005, 260, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.-H.; Ng, C.-F.; Lam-Leung, S.-Y.; He, X.; Cheung, O.-C. Water-alcohol separation by pervaporation through poly(amide-sulfonamide)s (PASAs) membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1997, 65, 1113–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-R.; Chen, R.-Y.; Lai, J.-Y. Plasma deposition of vinyl acetate onto Nylon-4 membrane for pervaporation and evapomeation separation of aqueous alcohol mixtures. J. Memb. Sci. 1992, 75, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaluenga, J.P.G.; Godino, P.; Khayet, M.; Seoane, B.; Mengual, J.I. Pervaporation of Alcohols and Methyl tert-Butyl Ether through a Dense Poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide) Membrane. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2004, 43, 2548–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alentiev, A.Y.; Chirkov, S.V.; Nikiforov, R.Y.; Levin, I.A.; Kechekyan, A.S.; Kechekyan, P.A.; Belov, N.A. Poly(2,6-Dimethyl-1,4-Phenylene Oxide) as a Polymer-Polymer Nanocomposite: Mechanical and Gas Transport Characteristics. Membr. Membr. Technol. 2022, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polotskaya, G.A.; Penkova, A.V.; Toikka, A.M.; Pientka, Z.; Brozova, L.; Bleha, M. Transport of small molecules through polyphenylene oxide membranes modified by fullerene. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2007, 42, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitrenko, M.; Chepeleva, A.; Liamin, V.; Mazur, A.; Semenov, K.; Solovyev, N.; Penkova, A. Novel Mixed Matrix Membranes Based on Polyphenylene Oxide Modified with Graphene Oxide for Enhanced Pervaporation Dehydration of Ethylene Glycol. Polymers 2022, 14, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, C.-Y.; Chen, S.-H.; Liou, R.-M.; Lai, J.-Y.; Chang, J.-S. Pervaporation separation of water/ethanol mixture by poly(phenylene oxide) and sulfonated poly(phenylene oxide) membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 105, 1566–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimune, M.; Mizoguchi, K.; Haraya, K. Alcohol dehydration by pervaporation using a carbon hollow fiber membrane derived from sulfonated poly(phenylene oxide). J. Memb. Sci. 2013, 425–426, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polotskaya, G.A.; Gladchenko, S.V.; Pen’kova, A.V.; Kuznetsov, V.M.; Toikka, A.M. Synthesis of fullerene-polyphenylene oxide membranes for separating aqueous-organic mixtures. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2005, 78, 1468–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otvagina, K.; Penkova, A.; Dmitrenko, M.; Kuzminova, A.; Sazanova, T.; Vorotyntsev, A.; Vorotyntsev, I. Novel Composite Membranes Based on Chitosan Copolymers with Polyacrylonitrile and Polystyrene: Physicochemical Properties and Application for Pervaporation Dehydration of Tetrahydrofuran. Membranes 2019, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penkova, A.V.; Acquah, S.F.; Piotrovskiy, L.B.; Markelov, D.A.; Semisalova, A.S.; Kroto, H.W. Fullerene derivatives as nano-additives in polymer composites. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2017, 86, 530–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummers, W.S.; Offeman, R.E. Preparation of Graphitic Oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penkova, A.V.; Dmitrenko, M.E.; Ermakov, S.S.; Toikka, A.M.; Roizard, D. Novel green PVA-fullerenol mixed matrix supported membranes for separating water-THF mixtures by pervaporation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 25, 20354–20362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.W. Membrane Technology and Applications; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, R.W.; Wijmans, J.G.; Huang, Y. Permeability, permeance and selectivity: A preferred way of reporting pervaporation performance data. J. Memb. Sci. 2010, 348, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekala, M.; Neerudi, B.; Are, P.R.; Surakasi, R.; Manikandan, G.; Kakara, V.R.; Dhumal, A.A. Water Removal from an Ethanol-Water Mixture at Azeotropic Condition by Adsorption Technique. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2022, 2022, 8374471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halakoo, E.; Feng, X. Self-assembled membranes from polyethylenimine and graphene oxide for pervaporation dehydration of ethylene glycol. J. Memb. Sci. 2020, 616, 118583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhalim, A.O.E.; Sharoyko, V.V.; Meshcheriakov, A.A.; Luttsev, M.D.; Potanin, A.A.; Iamalova, N.R.; Zakharov, E.E.; Ageev, S.V.; Petrov, A.V.; Vasina, L.V.; et al. Synthesis, characterisation and biocompatibility of graphene–L-methionine nanomaterial. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 314, 113605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhalim, A.O.E.; Sharoyko, V.V.; Meshcheriakov, A.A.; Martynova, S.D.; Ageev, S.V.; Iurev, G.O.; Al Mulla, H.; Petrov, A.V.; Solovtsova, I.L.; Vasina, L.V.; et al. Reduction and functionalization of graphene oxide with L-cysteine: Synthesis, characterization and biocompatibility. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2020, 29, 102284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagendra, B.; Cozzolino, A.; Daniel, C.; Rizzo, P.; Guerra, G.; Auriemma, F.; De Rosa, C.; D’Alterio, M.C.; Tarallo, O.; Nuzzo, A. Two Nanoporous Crystalline Forms of Poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene)oxide and Related Co-Crystalline Forms. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 9646–9656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitrenko, M.; Kuzminova, A.; Zolotarev, A.; Liamin, V.; Plisko, T.; Burts, K.; Bildyukevich, A.; Ermakov, S.; Penkova, A. Novel High Flux Poly(m-phenylene isophtalamide)/TiO2 Membranes for Ultrafiltration with Enhanced Antifouling Performance. Polymers 2021, 13, 2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manshad, S.; Sazegar, M.R.; Mohd Nawawi, M.G.; bin Hassan, H. Fabrication of nanohybrid polyetherimide/graphene oxide membranes: Biofuel dehydration by pervaporation process. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 103888–103894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Wahab, M.S.; Rahman, S.A.; Samah, R.A. Hydrophilic enhancement of Polysulfone membrane via Graphene Oxide embedded thin film nanocomposite for Isopropanol dehydration. Vacuum 2020, 180, 109569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostovtseva, V.; Pulyalina, A.; Rudakova, D.; Vinogradova, L.; Polotskaya, G. Strongly Selective Polymer Membranes Modified with Heteroarm Stars for the Ethylene Glycol Dehydration by Pervaporation. Membranes 2020, 10, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-H.; Chua, S.-P.; Wang, D.-M.; Lee, K.-R.; Lai, J.-Y. Pervaporation Separation of Water/Ethanol Mixtures through Polycarbonate/Cobalt(III) Acetylacetonate Membranes. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1998, 33, 1955–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mali, M.; Walekar, L.; Mhamane, D.; Mali, G.; Pawar, S.; Patil, V.; Parbat, H.; Gokavi, G. Fabrication of ternary polyvinyl alcohol/tetraethyl orthosilicate/silicotungstic acid hybrid membranes for pervaporation dehydration of alcohol. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 652, 129741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalad, V.T.; Gokavi, G.S.; Raju, K.V.S.N.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Mixed matrix blend membranes of poly(vinyl alcohol)–poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) loaded with phosphomolybdic acid used in pervaporation dehydration of ethanol. J. Memb. Sci. 2010, 354, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalad, V.T.; Supale, A.R.; Maradur, S.P.; Gokavi, G.S.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Preyssler type heteropolyacid-incorporated highly water-selective sodium alginate-based inorganic–organic hybrid membranes for pervaporation dehydration of ethanol. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 159, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunitha, K.; Satyanarayana, S.V.; Sridhar, S. Phosphorylated chitosan membranes for the separation of ethanol–water mixtures by pervaporation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 1569–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uragami, T.; Banno, M.; Miyata, T. Dehydration of an ethanol/water azeotrope through alginate-DNA membranes cross-linked with metal ions by pervaporation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 134, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyani, S.; Smitha, B.; Sridhar, S.; Krishnaiah, A. Pervaporation separation of ethanol–water mixtures through sodium alginate membranes. Desalination 2008, 229, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanse, N.G.; Dawande, S.D.; Dhanke, P.B. Effect of Feed Temperature and Solution Concentration on Pervaporation for separation of Azeotropic Mixtures. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 3541–3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


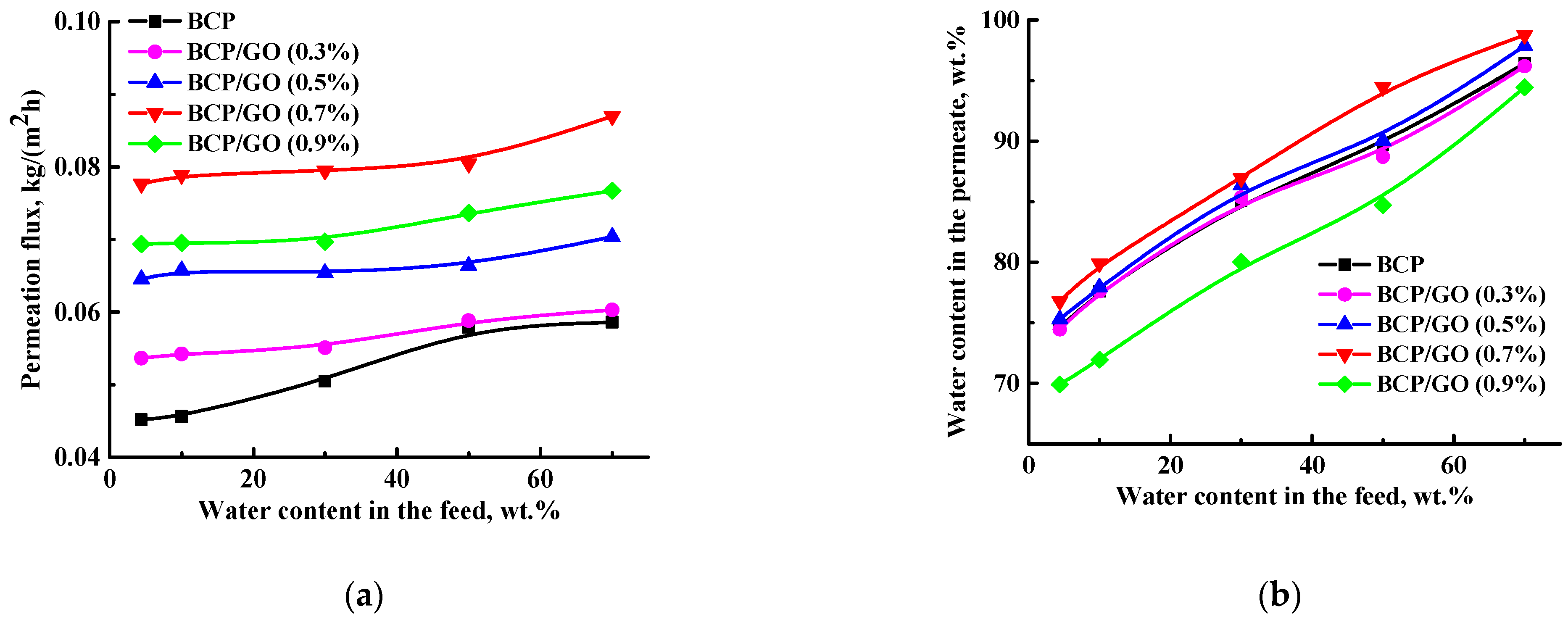
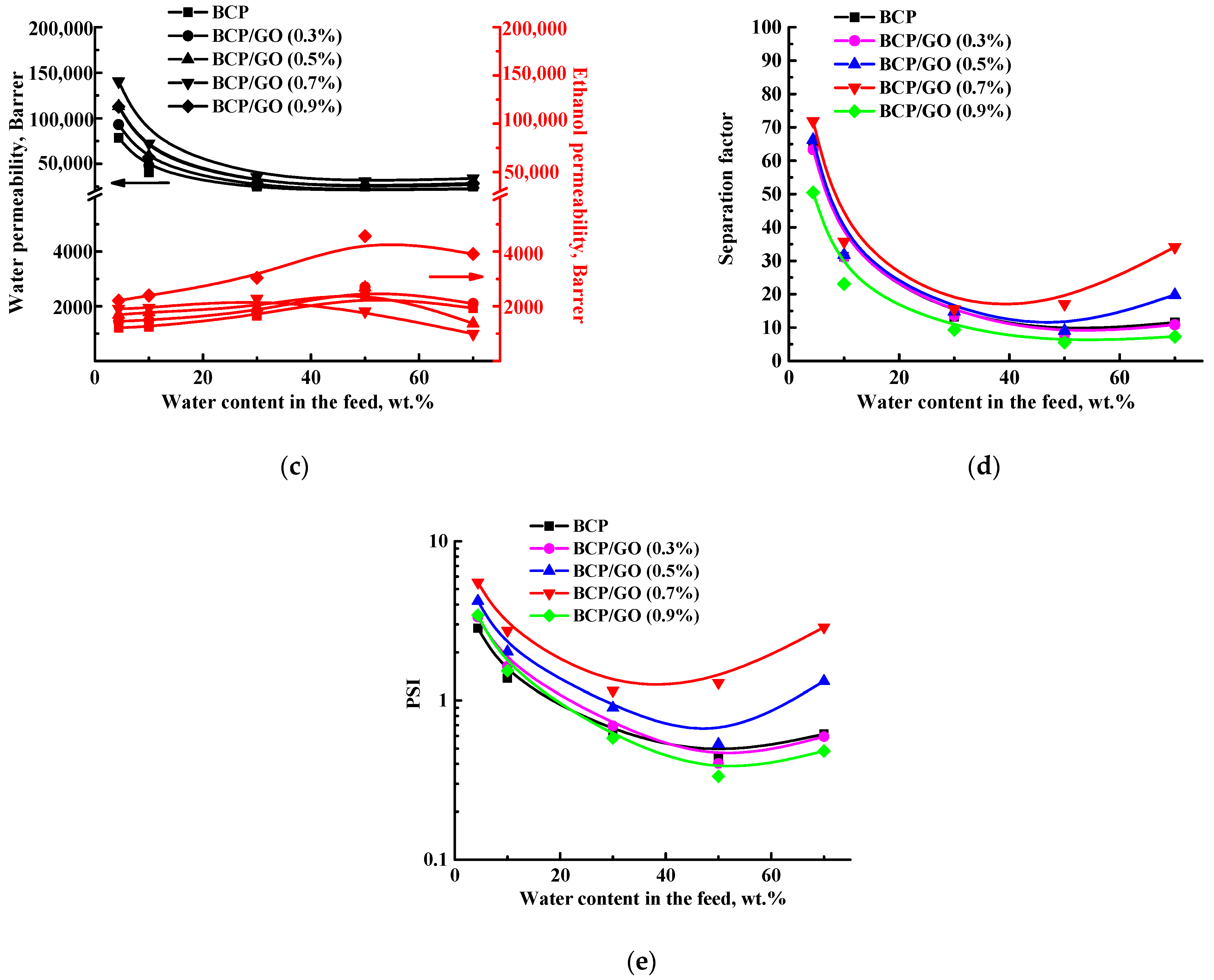

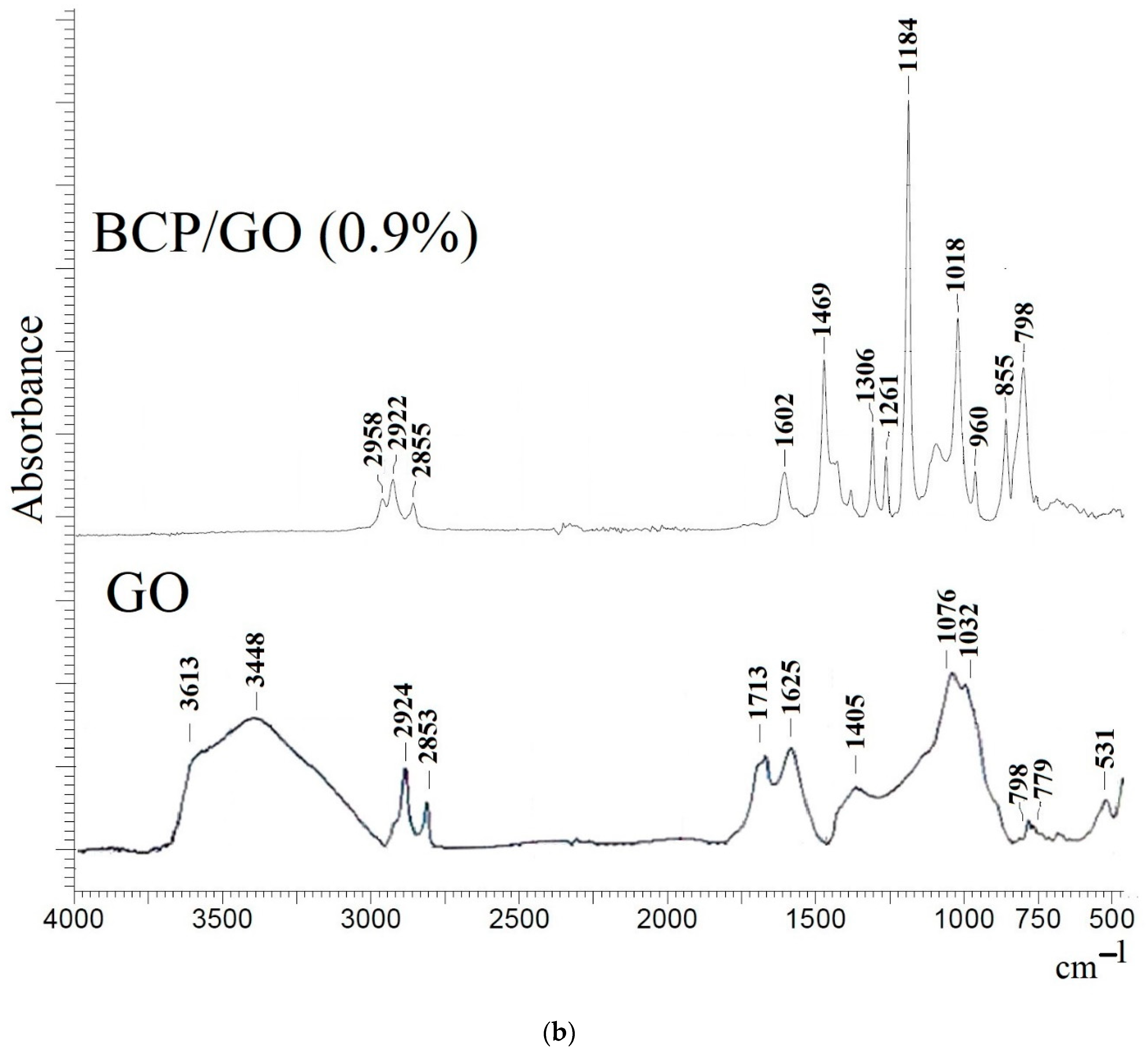
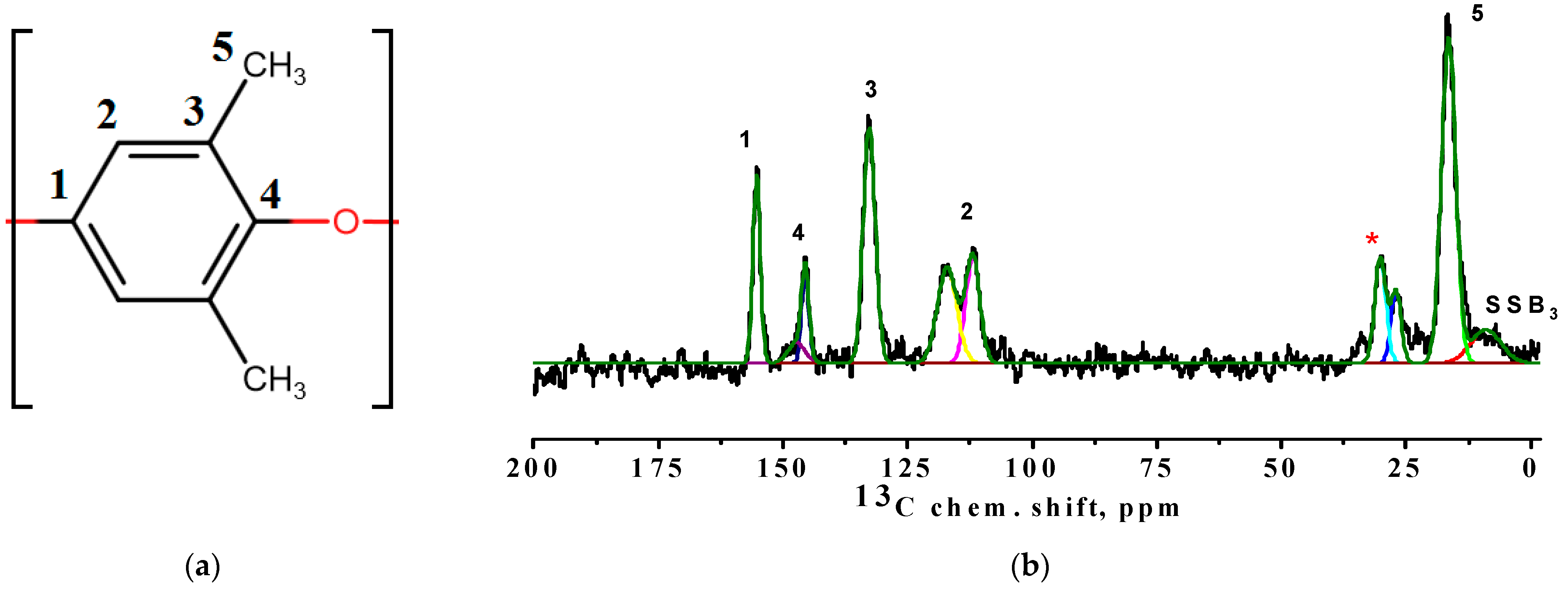



| Membrane | Surface Parameters | Contact Angle of Water, ° | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ra, nm | Rq, nm | ||
| PPO | 4.0 | 5.2 | 89 ± 2 |
| BCP (PDMS:PPO:TDI = 26:73:1) | 28.1 | 38.0 | 91 ± 2 |
| BCP (PDMS:PPO:TDI = 41:58:1) | 33.0 | 58.0 | 95 ± 2 |
| BCP (PDMS:PPO:TDI = 51:48:1) | 41.6 | 64.9 | 98 ± 2 |
| BCP/GO (0.3%) | 33.4 | 52.5 | 95 ± 2 |
| BCP/GO (0.5%) | 37.3 | 58.9 | 94 ± 2 |
| BCP/GO (0.7%) | 35.5 | 61.8 | 93 ± 2 |
| BCP/GO (0.9%) | 34.0 | 53.2 | 92 ± 2 |
| Membrane | Feed-Water Content, wt.% | Temperature, °C | Permeation Flux, g/(m2h) | Separation Factor (β) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCP/GO (0.7%) | 4.4 | 22 | 79 | 72 | This study |
| PVA/TEOS | 4 | RT | 30 | 375 | [50] |
| PVA/TEOS/STA (5%) | 4 | RT | 40 | 2949 | |
| PVA/TEOS/STA (10%) | 4 | RT | 52 | 5377 | |
| PVA/TEOS/STA (15%) | 4 | RT | 67 | 8622 | |
| PVA/PVP/PMA (4%) | 4 | 27 | 100 | 10 | [51] |
| NaAlg/HPA (6%) | 4 | 30 | 170 | 60 | [52] |
| P-CS | 3.5 | 30 | 250 | 670 | [53] |
| Alg/DNA-Ca2+ | 3.5 | 40 | 10 | 5500 | [54] |
| Alg/DNA-Mg2+ | 3.5 | 40 | 10 | 6500 | |
| P-SA | 5.2 | 30 | 240 | 2182 | [55] |
| PVA | 6.25 | 45 | 22 | 1143 | [56] |
| PVA/PES | 6.25 | 45 | 33 | 950 |
| Membrane | Temperature, °C | Permeation Flux, g/(m2h) | Separation Factor (β) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCP/GO (0.7%) | 22 | 79 | 36 | This study |
| PPO | 50 | 700 | 13 | [33] |
| PPO/C60 (1%) | 50 | 920 | 16 | |
| PPO/C60 (2%) | 50 | 1100 | 21 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dmitrenko, M.; Chepeleva, A.; Liamin, V.; Kuzminova, A.; Mazur, A.; Semenov, K.; Penkova, A. Novel PDMS-b-PPO Membranes Modified with Graphene Oxide for Efficient Pervaporation Ethanol Dehydration. Membranes 2022, 12, 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12090832
Dmitrenko M, Chepeleva A, Liamin V, Kuzminova A, Mazur A, Semenov K, Penkova A. Novel PDMS-b-PPO Membranes Modified with Graphene Oxide for Efficient Pervaporation Ethanol Dehydration. Membranes. 2022; 12(9):832. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12090832
Chicago/Turabian StyleDmitrenko, Mariia, Anastasia Chepeleva, Vladislav Liamin, Anna Kuzminova, Anton Mazur, Konstantin Semenov, and Anastasia Penkova. 2022. "Novel PDMS-b-PPO Membranes Modified with Graphene Oxide for Efficient Pervaporation Ethanol Dehydration" Membranes 12, no. 9: 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12090832
APA StyleDmitrenko, M., Chepeleva, A., Liamin, V., Kuzminova, A., Mazur, A., Semenov, K., & Penkova, A. (2022). Novel PDMS-b-PPO Membranes Modified with Graphene Oxide for Efficient Pervaporation Ethanol Dehydration. Membranes, 12(9), 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12090832