Surface of CuO Nanoparticles Modified by p-Benzoquinone for N2-Selective Membrane
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Membrane Preparation
2.2.2. Material Characterization
2.2.3. Gas Separation Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Separation Test
3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3.3. FT-IR Spectroscopy
3.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis
3.5. UV–Vis
3.6. XPS (X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy)
3.7. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chuzhi, H.; Xianjin, H. Characteristics of carbon emission in China and analysis on its cause. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2008, 18, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revelle, R.; Suess, H.E. Carbon dioxide exchange between atmosphere and ocean and the question of an increase of atmospheric CO2 during the past decades. Tellus 1957, 9, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mondal, M.K.; Balsora, H.K.; Varshney, P. Progress and trends in CO2 capture/separation technologies: A review. Energy 2012, 46, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmalensee, R.; Stoker, T.M.; Judson, R.A. World carbon dioxide emissions: 1950–2050. Rev. Econ. Stat. 1998, 80, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigley, T.; Jones, P.D. Influences of precipitation changes and direct CO2 effects on streamflow. Nature 1985, 314, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essa, W.K.; Yasin, S.A.; Saeed, I.A.; Ali, G.A. Nanofiber-based face masks and respirators as COVID-19 protection: A review. Membranes 2021, 11, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Gan, S.; Bao, Y.; Zhong, L.; Xu, J.; Wang, W.; Niu, L. Solid-contact ion-selective electrodes: Response mechanisms, transducer materials and wearable sensors. Membranes 2020, 10, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webley, P.A. Adsorption technology for CO2 separation and capture: A perspective. Adsorption 2014, 20, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomé, L.C.; Mecerreyes, D.; Freire, C.S.R.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Marrucho, I.M. Pyrrolidinium-based polymeric ionic liquid materials: New perspectives for CO2 separation membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 428, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaron, D.; Tsouris, C. Separation of CO2 from flue gas: A review. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2005, 40, 321–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Liang, F.; Yang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Liu, W. An improved CO2 separation and purification system based on cryogenic separation and distillation theory. Energies 2014, 7, 3484–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santos, E.; Albo, J.; Irabien, A. Acetate based Supported Ionic Liquid Membranes (SILMs) for CO2 separation: Influence of the temperature. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 452, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Guo, R.; Hou, J.; Wei, Z.; Li, X. Mixed-matrix membranes containing carbon nanotubes composite with hydrogel for efficient CO2 separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 29044–29051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norahim, N.; Yaisanga, P.; Faungnawakij, K.; Charinpanitkul, T.; Klaysom, C. Recent membrane developments for CO2 separation and capture. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2018, 41, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Noble, R.D.; Gin, D.L.; Zhang, X.; Deng, L. Combination of ionic liquids with membrane technology: A new approach for CO2 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 497, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jindaratsamee, P.; Ito, A.; Komuro, S.; Shimoyama, Y. Separation of CO2 from the CO2/N2 mixed gas through ionic liquid membranes at the high feed concentration. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 423, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Ansaloni, L.; Deng, L. Recent advances in multi-layer composite polymeric membranes for CO2 separation: A review. Green Energy Environ. 2016, 1, 102–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, S.; Wang, Z.; Qiao, Z.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. Improvement of CO2/N2 separation characteristics of polyvinylamine by modifying with ethylenediamine. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 378, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Jawad, Z.A.; Low, S.C.; Zein, S.H.S. A cellulose acetate/multi-walled carbon nanotube mixed matrix membrane for CO2/N2 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 451, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuah, C.Y.; Lee, J.; Song, J.; Bae, T. CO2/N2 separation properties of polyimide-based mixed-matrix membranes comprising UiO-66 with various functionalities. Membranes 2020, 10, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nellepalli, P.; Tome, L.C.; Vijayakrishna, K.; Marrucho, I.M. Imidazolium-based copoly (ionic liquid) membranes for CO2/N2 separation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 2017–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahurin, S.M.; Lee, J.S.; Baker, G.A.; Luo, H.; Dai, S. Performance of nitrile-containing anions in task-specific ionic liquids for improved CO2/N2 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 353, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Kang, S.W. Effect of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid on CO2 separation performance of poly (ethylene oxide) membrane. Macromol. Res. 2016, 24, 1111–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.S.; Ha, C.; Kang, S.W. Highly permeable ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazoliumtetrafluoroborate (BMIMBF 4)/CuO composite membrane for CO2 separation. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 33568–33571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, K.W.; Kim, H.; Kang, Y.S.; Kang, S.W. 1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate/zinc oxide composite membrane for high CO2 separation performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 320, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.J.; Kang, S.W. Composites of poly (vinyl pyrrolidone) and polarized Ag nanoparticles for CO2 separation. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 39, 2542–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

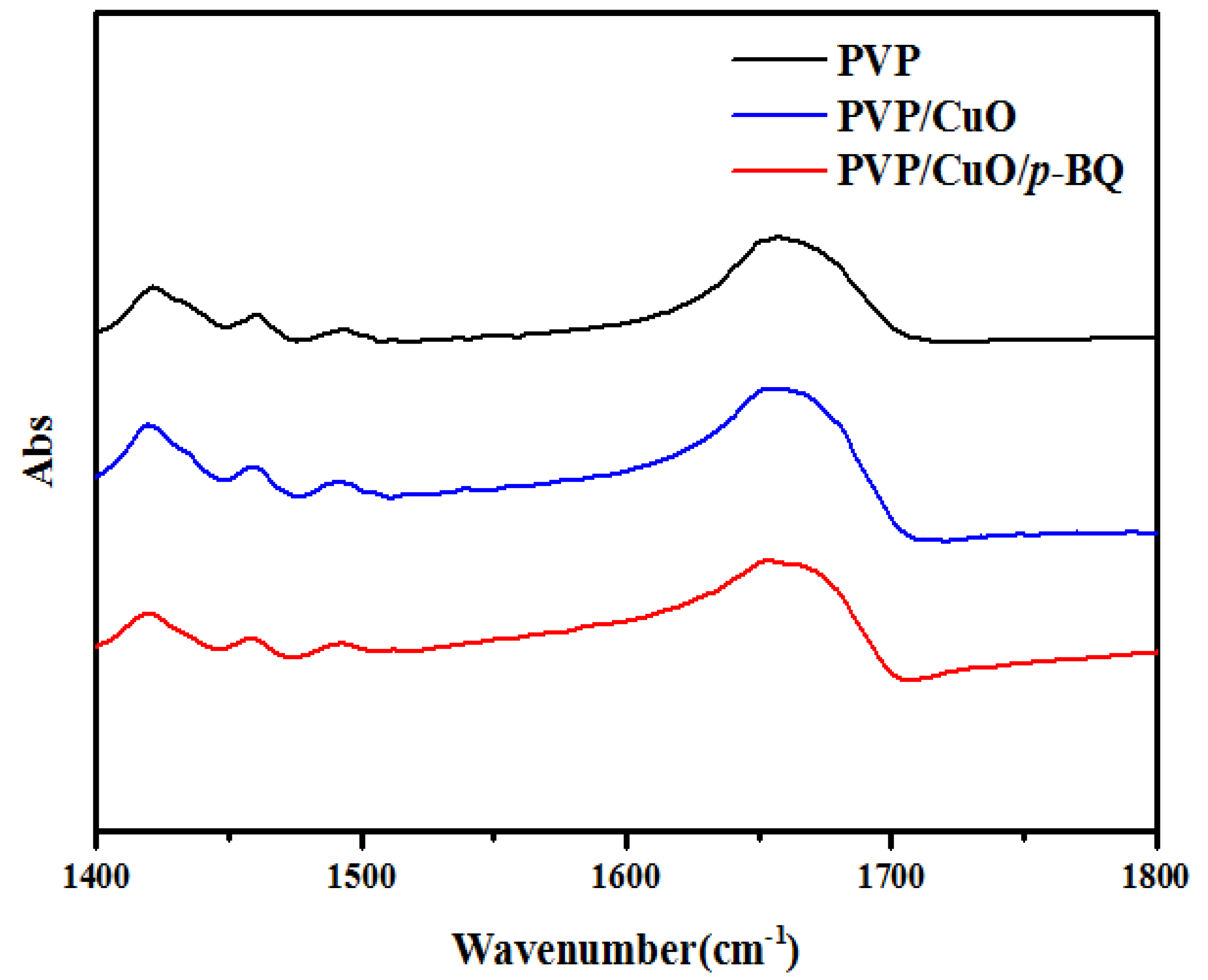
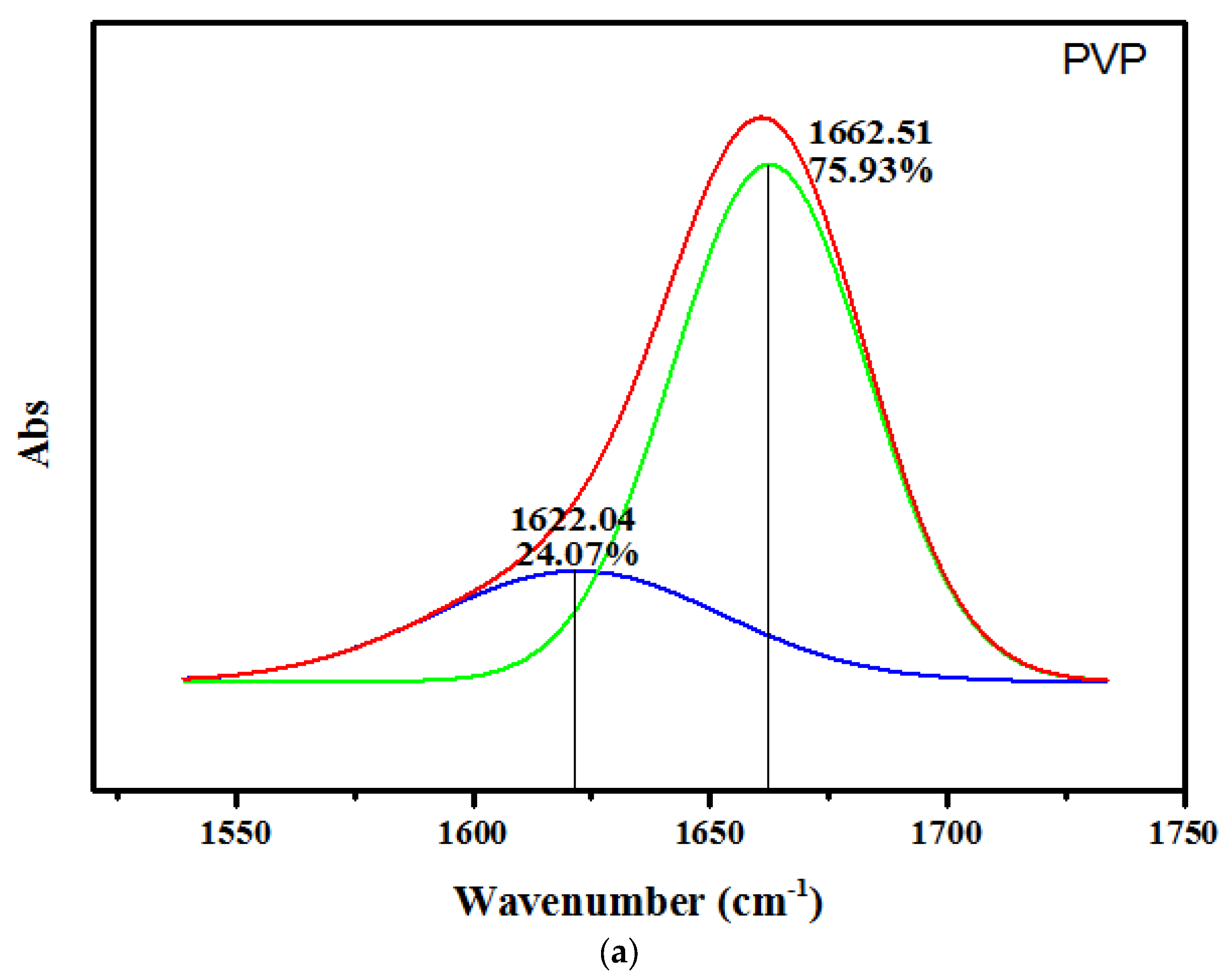
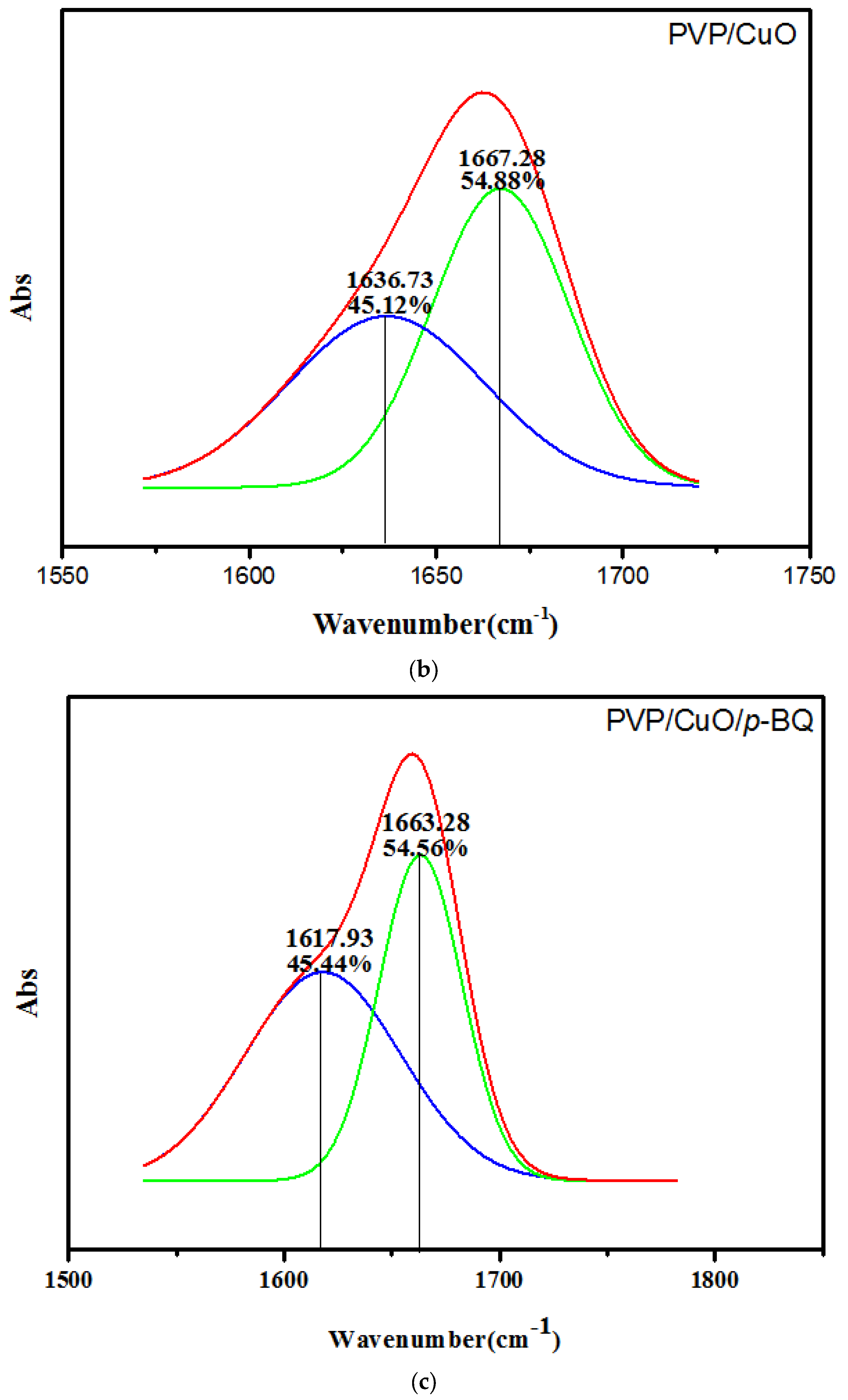





| N2/CO2 Selectivity | N2 Permeance (GPU) | |
|---|---|---|
| Neat PVP | Not measurable | Not measurable |
| PVP/CuO | 0.9 | 13.8 |
| PVP/CuO/p-BQ | 23.1 ± 1.8 | 13.3 ± 0.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.; Sohn, H.; Kang, S.W. Surface of CuO Nanoparticles Modified by p-Benzoquinone for N2-Selective Membrane. Membranes 2022, 12, 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12121229
Lee J, Sohn H, Kang SW. Surface of CuO Nanoparticles Modified by p-Benzoquinone for N2-Selective Membrane. Membranes. 2022; 12(12):1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12121229
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Juyeong, Hiesang Sohn, and Sang Wook Kang. 2022. "Surface of CuO Nanoparticles Modified by p-Benzoquinone for N2-Selective Membrane" Membranes 12, no. 12: 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12121229
APA StyleLee, J., Sohn, H., & Kang, S. W. (2022). Surface of CuO Nanoparticles Modified by p-Benzoquinone for N2-Selective Membrane. Membranes, 12(12), 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12121229






