Structure, Thermal Properties and Proton Conductivity of the Sulfonated Polyphenylquinoxalines
Abstract
1. Introduction
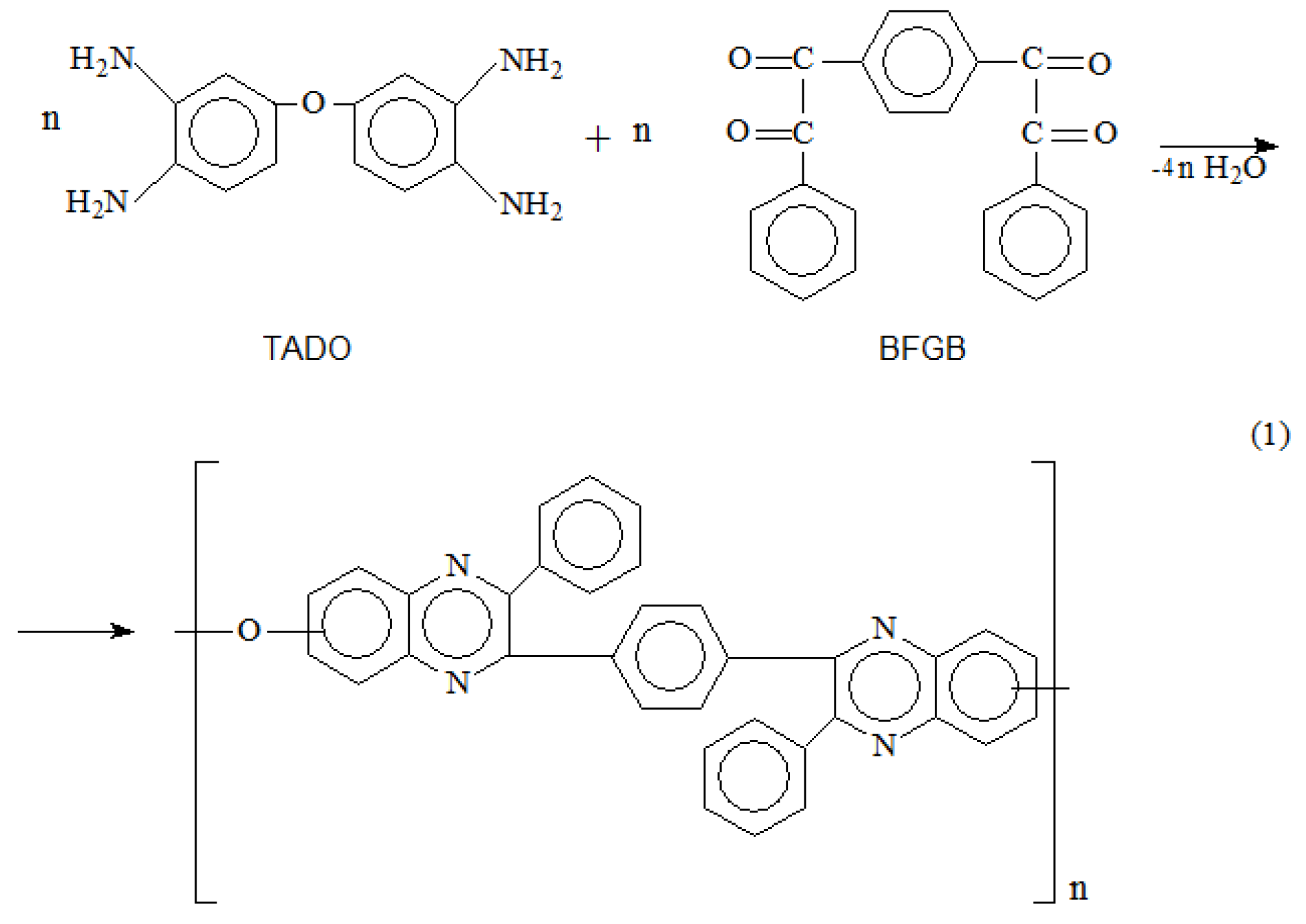
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
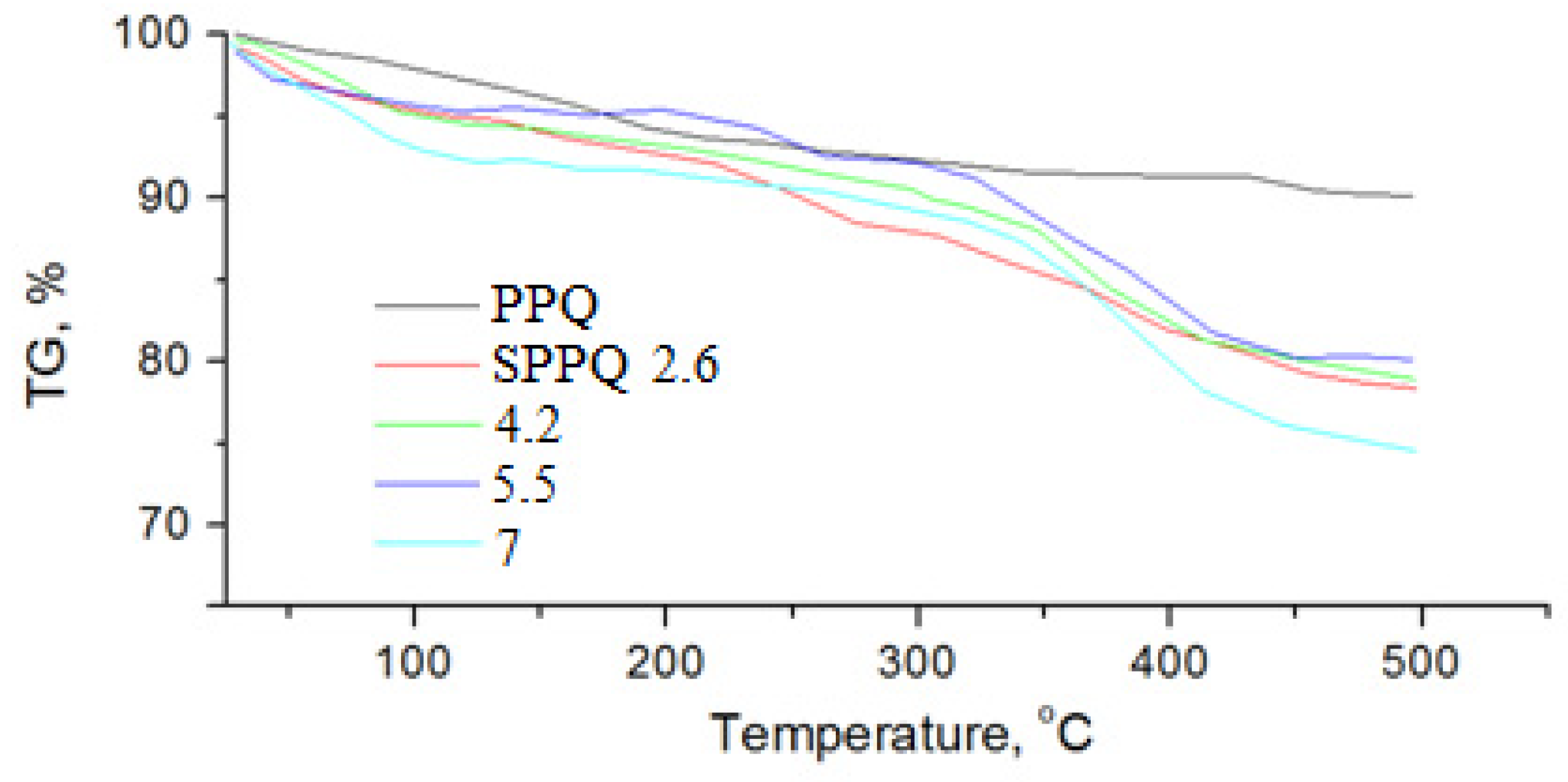
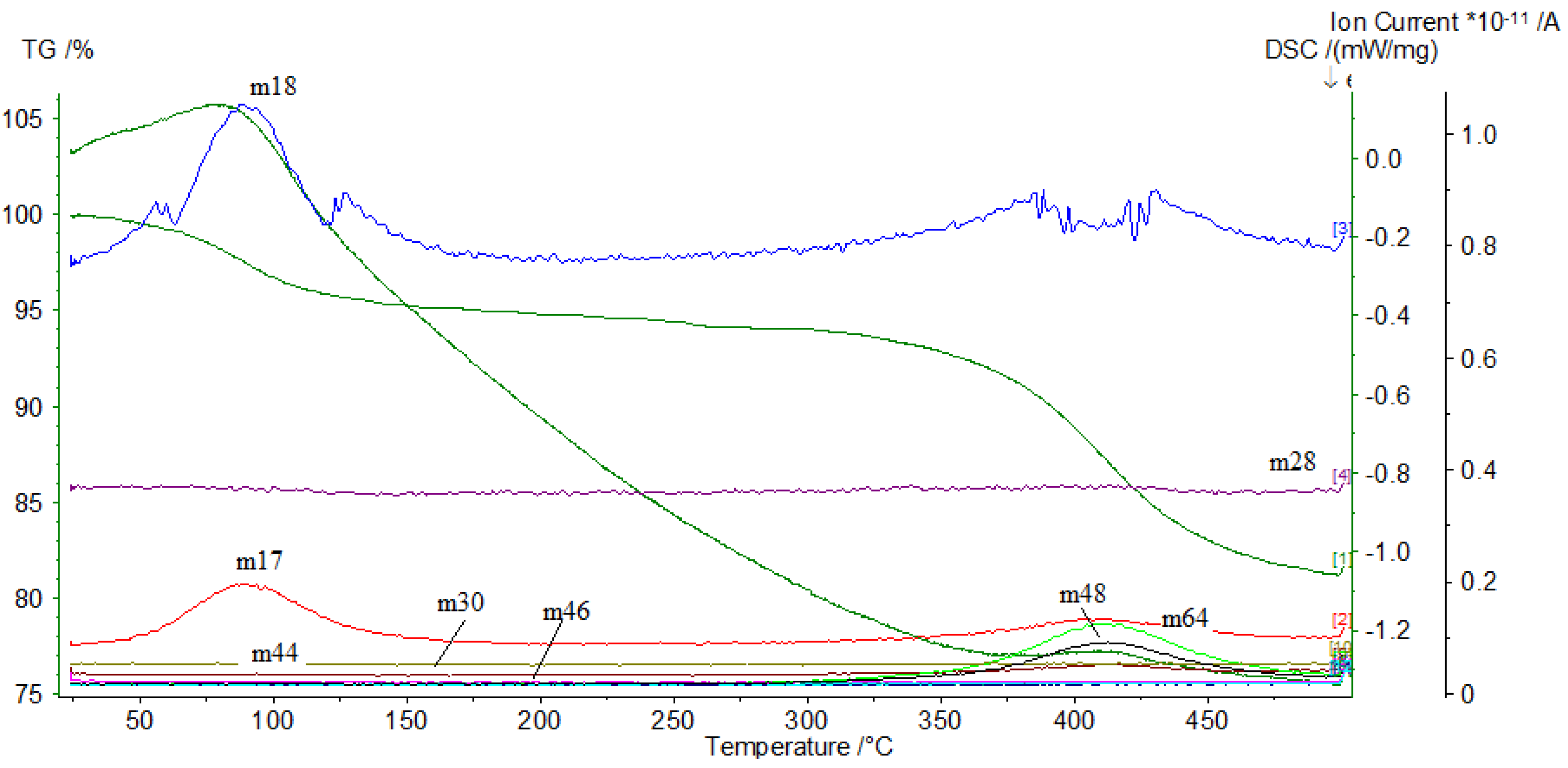
3.1. Thermal Analysis
3.2. Water Sorption
3.3. Molecular Weight
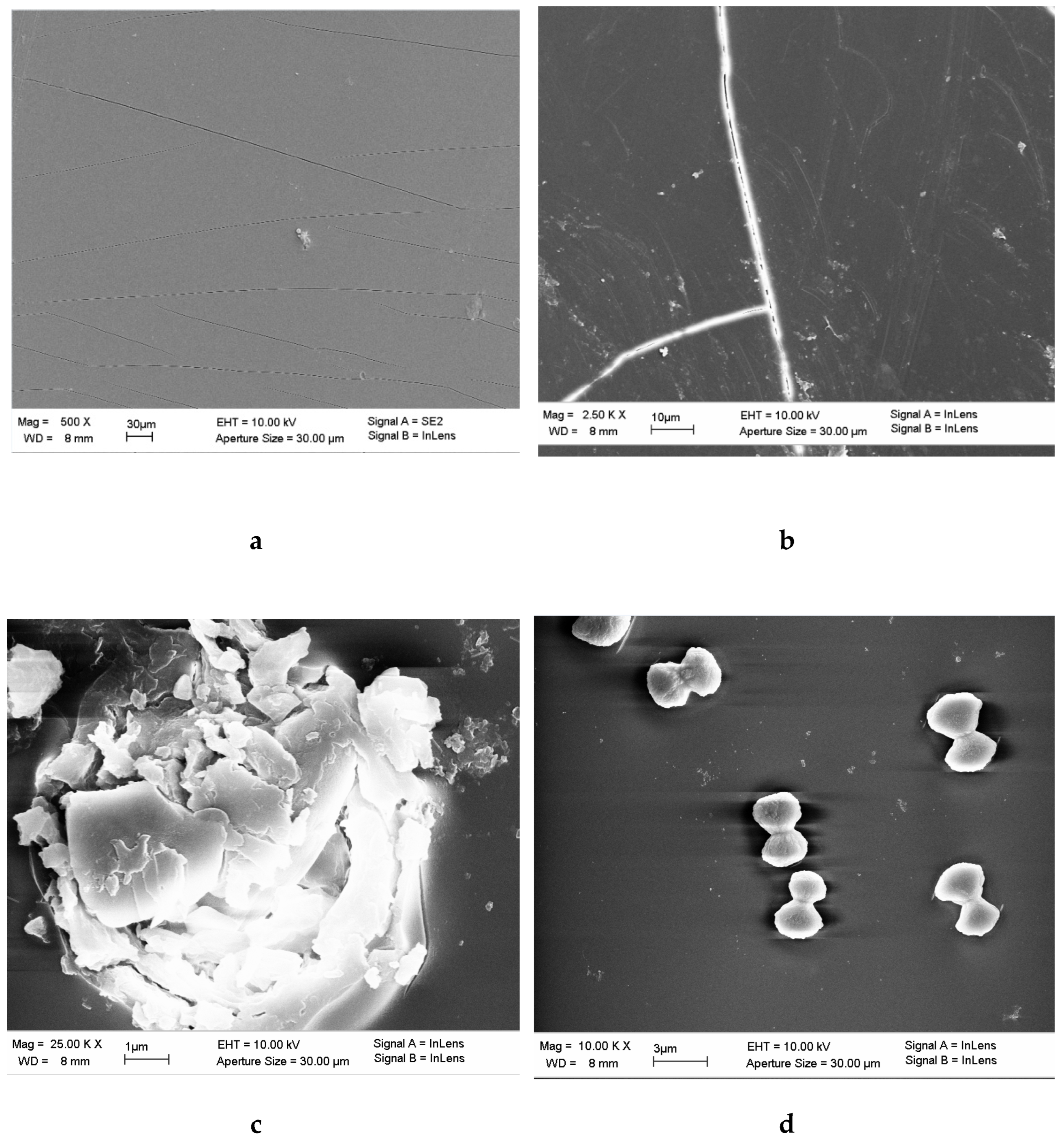
3.4. Scanning Electronic Microscopy
3.5. IR Spectroscopy
3.6. Quantum Chemical Simulation of Structure of SPPQ
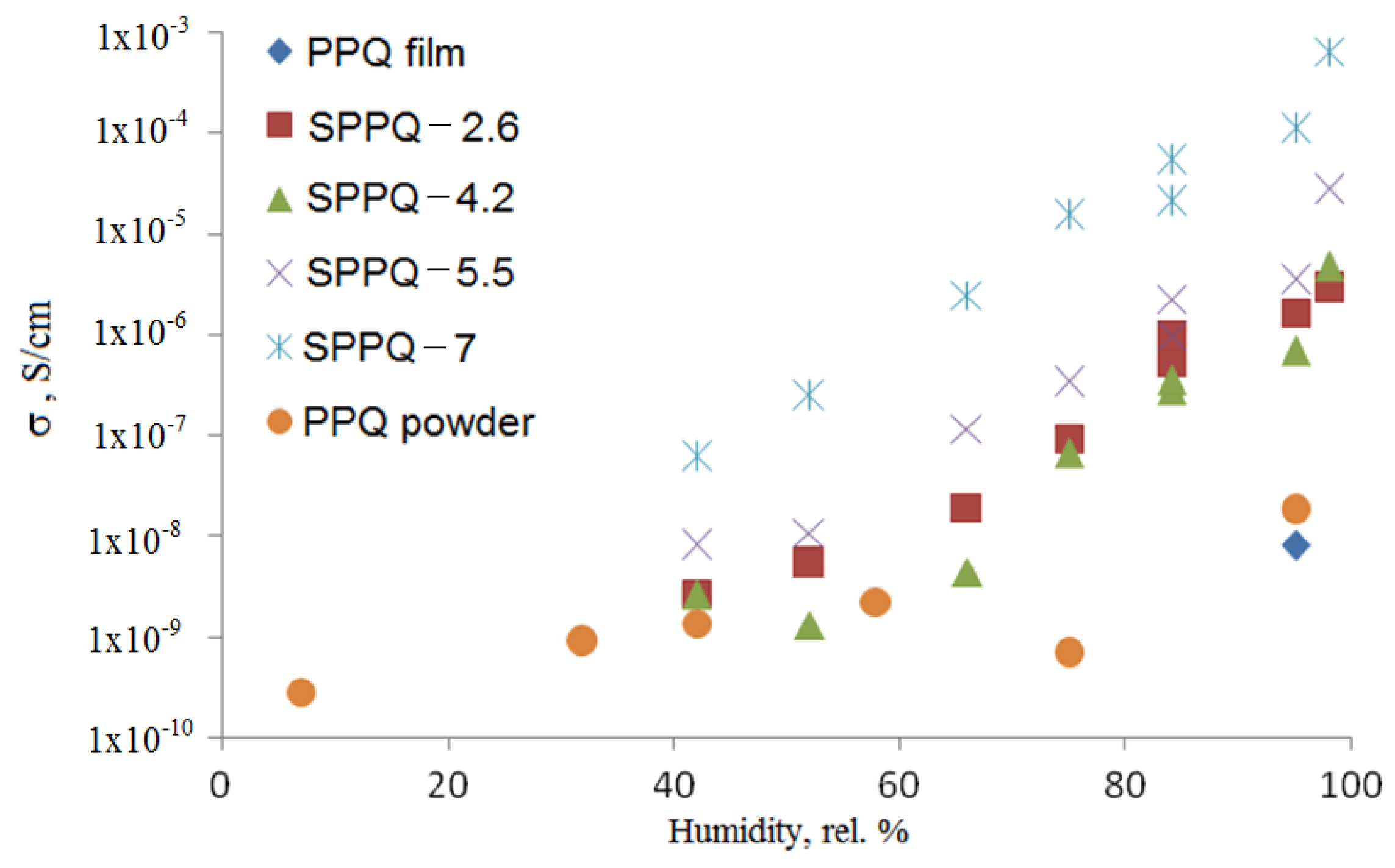
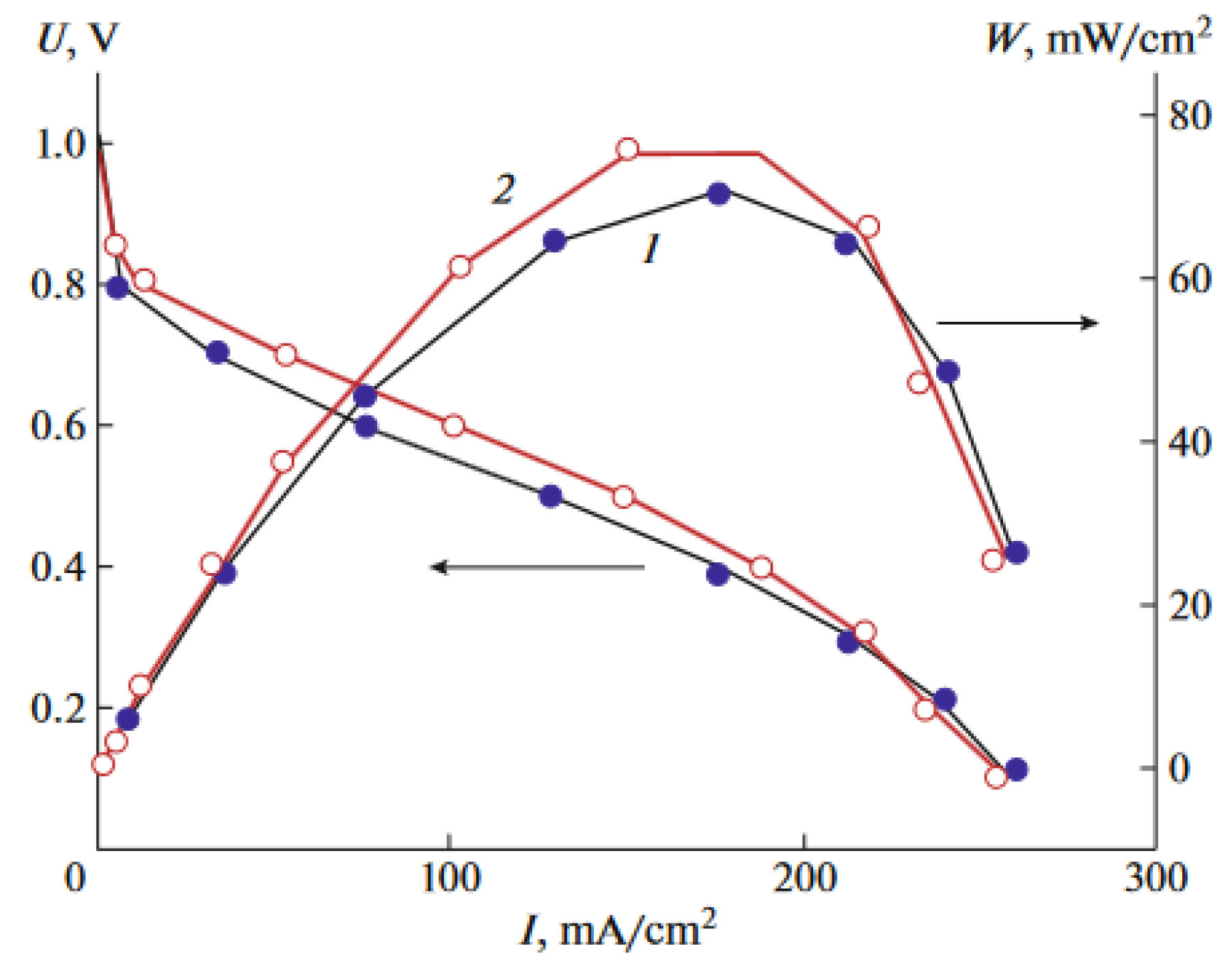
3.7. Impedance Spectroscopy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rikukawa, M.; Sanui, K. Proton-conducting polymer electrolyte membranes based on hydrocarbon polymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2000, 25, 1463–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerres, J.A. Development of ionomer membranes for fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 185, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smitha, B.; Sridhar, S.; Khan, A.A. Solid polymer electrolyte membranes for fuel cell applications-a review. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 259, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrovolsky, Y.A.; Jannasch, P.; Lafitte, B.; Belomoina, N.M.; Rusanov, A.L.; Likhachev, D.Y. Achievements in the field of proton-conductive portion electrolyte membranes. Russ. J. Electrochem. 2007, 43, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusanov, A.L.; Likhatchev, D.; Kostoglodov, P.; Mullen, K.; Klapper, M. Proton-exchanging electrolyte membranes based on aromatic condensation polymers. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2005, 179, 83–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusanov, A.L.; Likhachev, D.Y.; Mullen, K. Electrolytic proton-conducting membranes based on aromatic condensation polymers. UspekhiKhimii 2002, 71, 761–774. [Google Scholar]
- Rusanov, A.L.; Komarova, L.G.; Bulycheva, E.G.; Bugaenko, M.G.; Begunov, R.S.; Valyaeva, A.N. Poly(arylene oxides) Containing Sulfo Acid Groups: Synthesis, Properties, and Application. Polymer Sci. Ser. B 2010, 52, 499–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.P.; Zholobko, O.; Wu, X.F.; Aulich, T.; Thakare, J.; Hurley, J. Polybenzimidazole-Based Polymer Electrolyte Membranes for High-Temperature Fuel Cells: Current Status and Prospects. Energies 2021, 14, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korshak, V.V.; Pavlova, S.A.; Gribkova, P.N.; Vlasova, I.V.; Berlin, A.M.; Krongauz, E.S. Thermal-degradation of polyphenylquinoxalines. Vysokomol. Soed. Ser. A 1975, 17, 2407–2410. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voloshchuk, K.A.; Tseitlin, G.M.; Blyumenfeld, A.B.; Zabelnikov, N.S.; Atrushkevich, A.A. Thermal transformations of polyphenylquinoxalines. Vysokomol. Soed. Ser. A 1989, 32, 295–300. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Korshak, V.V.; Pavlova, S.A.; Gribkova, P.N.; Vlasova, I.V.; Berlin, A.M.; Krongauz, E.S.; Kofman, N.M. Thermal-oxidative degradation of polyphenylquinoxalines. Vysokomol. Soed. Ser. A 1977, 19, 638–642. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kopitzke, R.W.; Linkous, C.A.; Nelson, G.L. Sulfonation of a poly(phenylquinoxaline) film. J. Polymer Sci. Part A 1998, 36, 1197–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusanov, A.L.; Belomoina, N.M.; Bulycheva, E.G.; Yanul, N.A.; Likhatchev, D.Y.; Dobrovolskii, Y.A.; Iojoiu, C.; Sanchez, J.Y.; Voytekunas, V.Y.; Abadie, M.J.M. Preparation and Characterization of Sulfonated Polyphenylquinoxalines. High Perform. Polym. 2008, 20, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulycheva, E.G.; Belomoina, N.M.; Vasiliev, V.G.; Elmanovich, I.V.; Wasserman, L.A.; Hsu, S.L.C.; Cheng, P.Y. Structure formation of sulfonated polyphenylquinoxalines in solution and in the solid state. Dokl. Phys. Chem. 2016, 471, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belomoina, N.M.; Rusanov, A.L.; Yanul, N.A.; Kirsh, Y.E. Thermoreactive sulfur-containing poly(phenylquinoxaline)s. Vysokomol. Soed. Ser. B 1996, 38, 355–358. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Vasil’ev, V.G.; Buzin, M.I.; Nikiforova, G.G.; Belomoina, N.M.; Bulycheva, E.G.; Papkov, V.S. Ionomers of a new type based on sulfonated polyphenylquinoxalines. Dokl. Phys. Chem. 2014, 458, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belomoina, N.M.; Rusanov, A.L.; Bruma, M. Modified phenylquinoxaline-containing polymers and materials on their basis. Polymer Sci. Ser. C 2007, 49, 386–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.M.; Liu, J.G.; Yang, S.Y. A review on recent progress of R&D for high-temperature resistant polymer dielectrics and their applications in electrical and electronic insulation. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2016, 46, 22–38. [Google Scholar]
- Seel, D.C.; Benicewicz, B.C. Polyphenylquinoxaline-based proton exchange membranes synthesized via the PPA Process for high temperature fuel cell systems. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 405, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.L.C.; Liu, C.W.; Tu, C.H.; Chuang, H.Y.; Bulycheva, E.; Belomoina, N. Synthesis and properties of ABPPQ for high-temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Polymer Bull. 2018, 75, 5321–5331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.H.; Hsu, S.L.C.; Bulycheva, E.; Belomoina, N. Novel crosslinked AB-type polyphenylquinoxaline membranes for high-temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Polymer Engin. Sci. 2019, 59, 2169–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belomoina, N.M.; Rusanov, A.L.; Yanul, N.A.; Kirsh, Y.E. Electrochemical properties of cation-exchange membranes made of sulfonate-containing polyphenylquinoxalines. Russ. J. Electrochem. 1996, 32, 151–153. [Google Scholar]
- Kopitzke, R.W.; Linkous, C.A.; Anderson, H.R.; Nelson, G.L. Conductivity and water uptake of aromatic-based proton exchange membrane electrolyte. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2000, 147, 1677–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linkous, C.A.; Anderson, H.R.; Kopitzke, R.W.; Nelson, G.L. Development of new proton exchange membrane electrolytes for water electrolysis at higher temperatures. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 1998, 23, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, F.X.; Li, N.W.; Zhang, S.B. Synthesis and properties of novel sulfonated poly(phenylquinoxaline)s as proton exchange membranes. Polymer 2009, 50, 6001–6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusanov, A.L.; Dobrovolsky, Y.A.; Gerasimova, E.V.; Belomoina, N.M.; Bulycheva, E.G. Proton-Conducting Membranes on the Basis of Sulfonated PolyphenylquinoxalinesInUnique Properties of Polymers and Composites: Pure and Applied Science Today and Tomorrow; Bubnov, Y.N., Vasnev, V.A., Askaskii, A.A., Zaikov, G.E., Eds.; Nova Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 2, pp. 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Belomoina, N.M.; Bulycheva, E.G.; Pisarev, R.V.; Gerasimova, E.V.; Pisareva, A.V.; Dobrovol’skii, Y.A. Sulfonated Polyphenylquinoxalines: Synthesis, Thermal Stability, and Proton Conductivity. Polymer Sci. Ser. C 2020, 62, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.L.; Wan, M.X.; Lu, F.C. Conducting films of polyphenylquinoxaline. Polymer 1994, 35, 2977–2979. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, D.; Wu, Q.; Shi, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, K. Novel Side-Chain type Sulfonated Poly(phenylquinoxaline) Proton Exchange Membranes for Direct Methanol Fuel Cells. Membranes 2022, 12, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lai, Z.G.; Lu, F.C. Conducting polyphenylquinoxaline. Polymer 1991, 32, 3075–3079. [Google Scholar]
- Templier, F.; Torres, J.; Clarisse, C.; Palleau, J. Protonation effects on PPQ polymer during HF lift-off process used in multichip module fabrication. Mater. Sci. High Temp. Polym. Microelectron. 1991, 227, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, M.A.; Clarisse, C.; Templier, F. Electrochemical properties of polyphenylquinoxaline films. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1993, 140, 2498–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, E.H.; Paik, W.K. Properties of polyphenylquinoxaline acid complex as an electrode material. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1998, 145, 1193–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donald, A.M.; Kramer, E.J. The competition between shear deformation and crazing in glassy polymers. J. Mater. Sci. 1982, 17, 1871–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.J.; Shen, J.S.; Lu, F.C.; Xu, M. Effect of physical aging on fracture behavior of polyphenylquinoxaline films. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2000, 78, 1275–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.J.; Shen, J.S.; Lu, F.C.; Xu, M. Tensile crazing and thermal history of polyphenylquinoxaline films. Polymer J. 2000, 32, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.J.; Shen, J.S.; Wang, Z.; Lu, F.C.; Xu, M. The deformation mechanism of polyphenylquinoxaline films. Polymer 2001, 42, 7461–7464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikol’skii, O.G.; Ponomarev, I.I.; Martirosov, V.A.; Obolonkova, E.S.; Volkova, Y.A.; Rusanov, A.L.; Vinogradova, S.V. New block copolymers based on rigid- and flexible-chain polyheteroarylenes. Polymer Sci. Ser. A 2004, 46, 369–376. [Google Scholar]
- Korshak, V.V.; Krongauz, E.S.; Berlin, A.M.; Raubah, H. USSR copyright certificate 483409. Bull. Invent. 1975, 33, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, B.; Kawamura, S.; Miyatake, K.; Watanabe, M. Synthesis and properties of sulfonated poly(arylene ether)s containing azole groups. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2011, 49, 3863–3873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becke, A.D. Density-functional thermochemistry. 3. The role of exact exchange. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 5648–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.G.; Gill, P.M.W.; Pople, J.A. The performance of a family of density functional methods. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 5612–5626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaussian Inc. Gaussian 09 Revision B.01; Gaussian Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bukun, N.G.; Ukshe, A.E.; Ukshe, E.A. Frequency-analysis of the impedance and determination of the elements of equivalent-circuits in systems with solid electrolytes. Russ. J. Electrochem. 1993, 29, 146–155. [Google Scholar]
- Sverdlov, L.M.; Kovner, M.A.; Kraynov, E.P. Vibrational Spectra of Polyatomic Molecules; Moscow Science: Moscow, Russia, 1970; 559p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Zundel, G. Hydration and Intermolecular Interaction: Infrared Investigations with Polyelectrolyte Membranes; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]



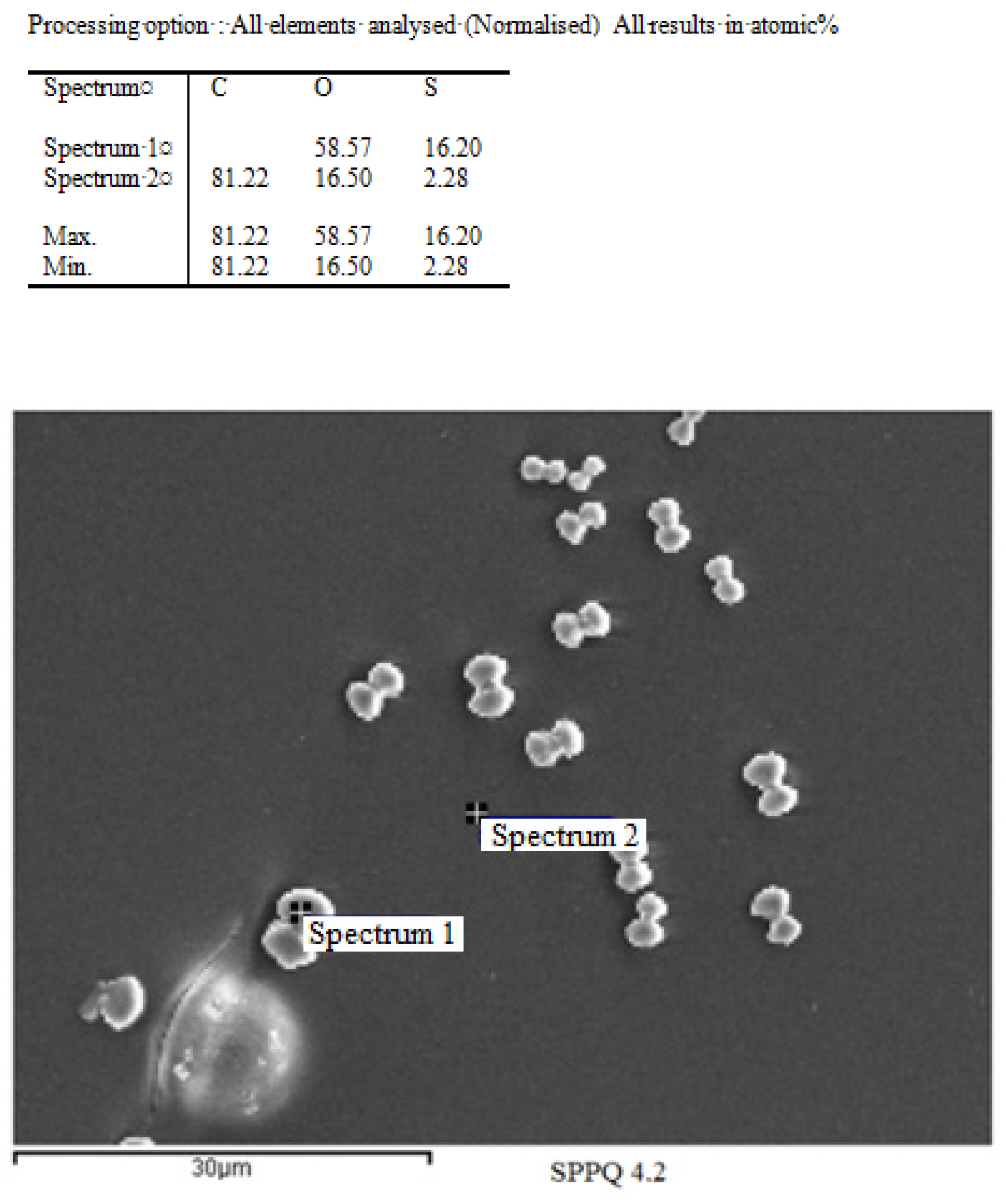

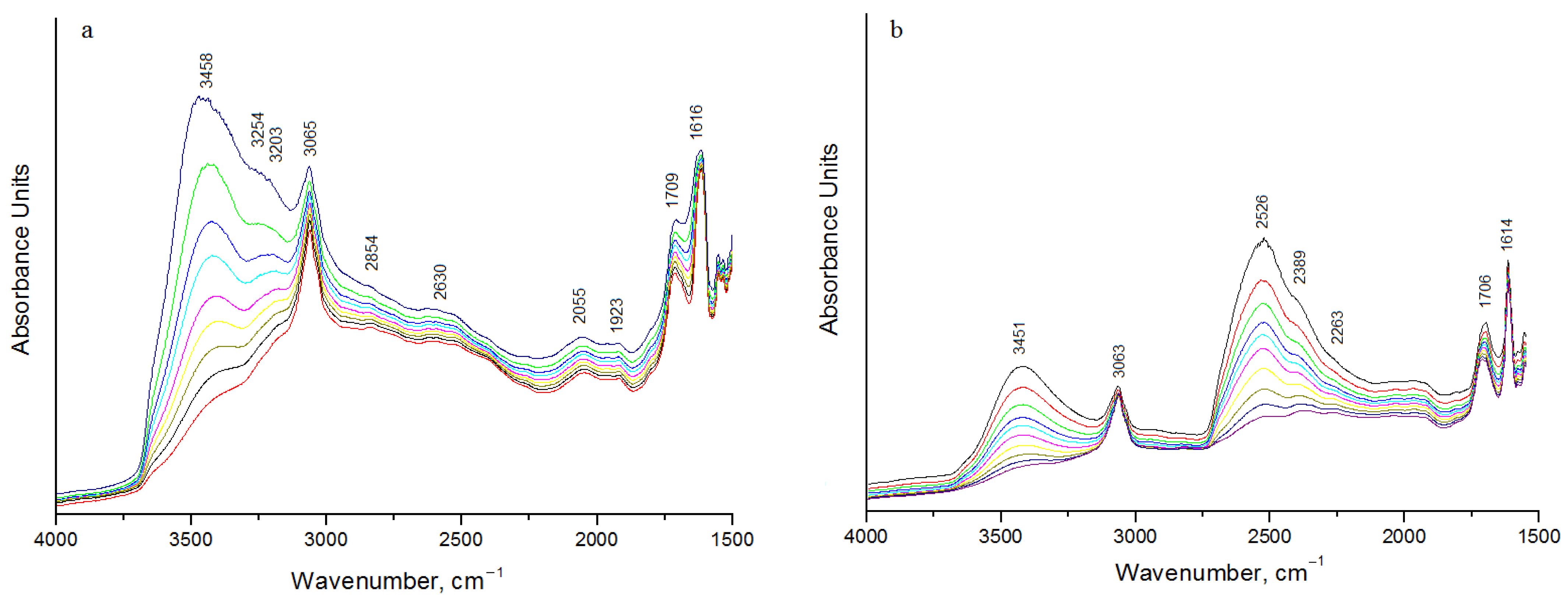

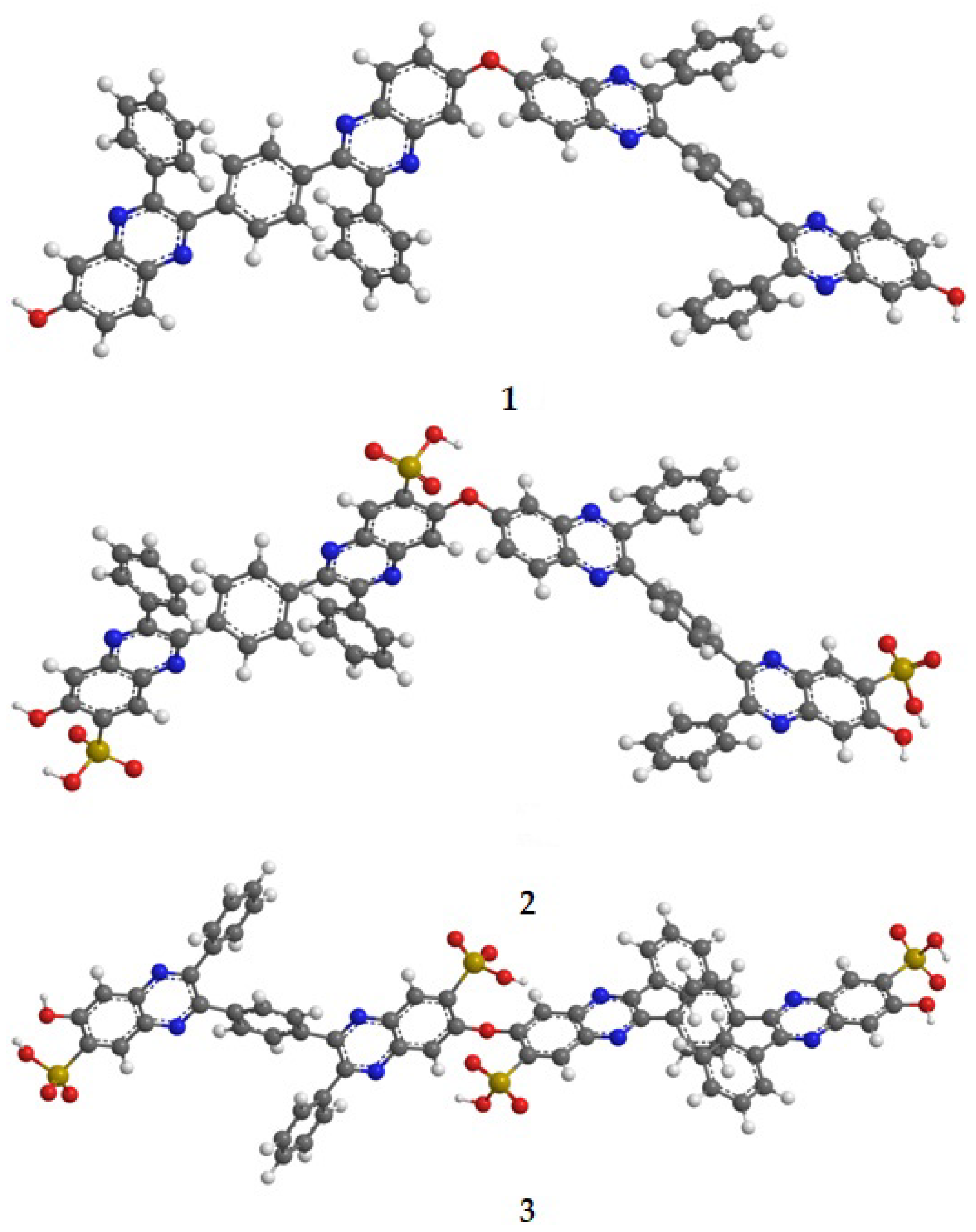
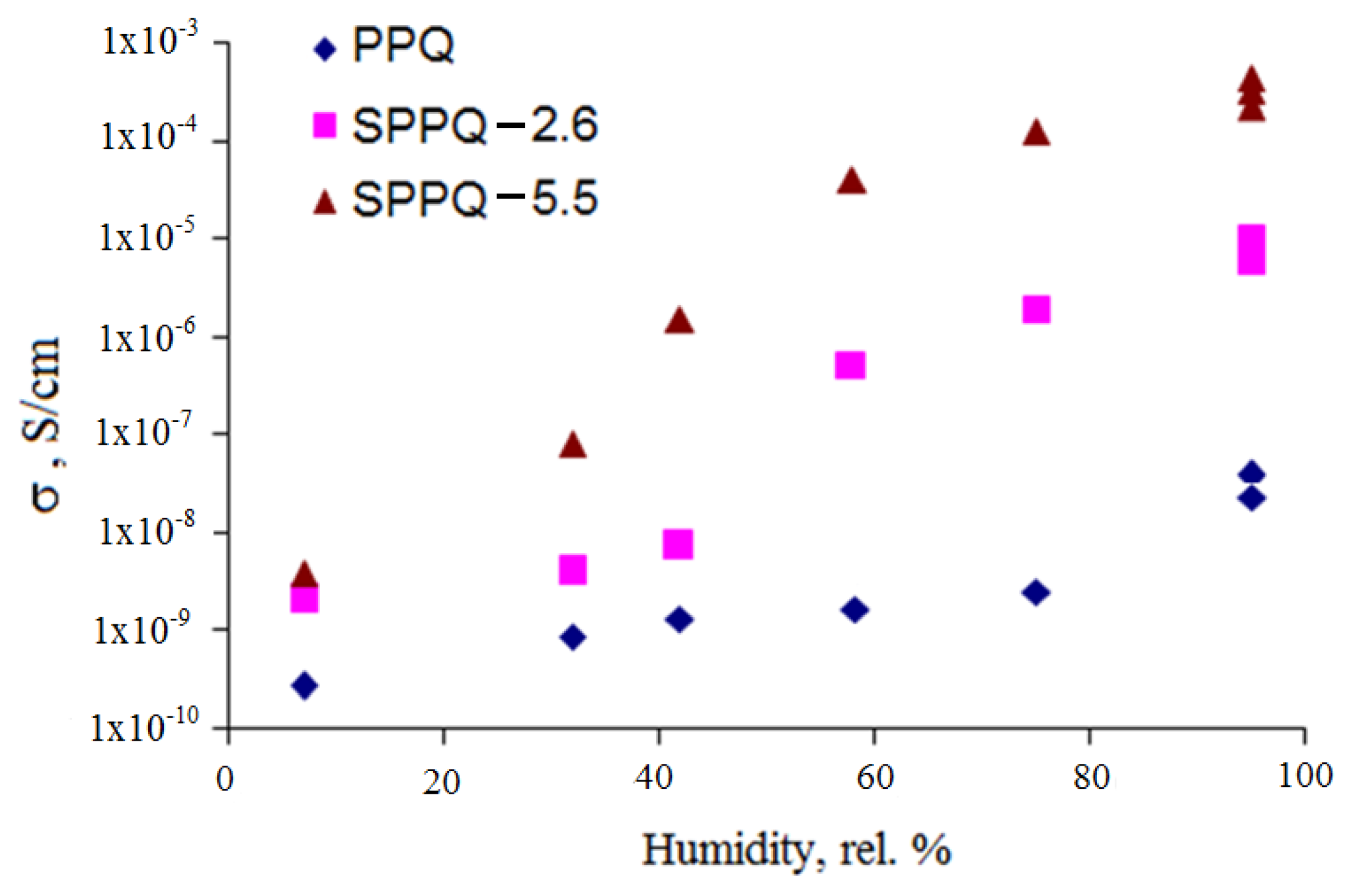
| SPPQ, Mass. % S | 0 | 2.6 | 4.2 | 5.5 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature, °C | |||||
| 100 | 0.6 | 4.2 | 4.1 | 5.6 | 4.5 |
| 150 | 1 | 5.4 | 5.6 | 7 | 5.1 |
| 250 | 2.3 | 8.5 | 7.1 | 9 | 5.6 |
| 300 | 3.3 | 10 | 8 | 10.5 | 7.5 |
| SPPQ, %S | Mw | Mn | Mw/Mn |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 45,840 | 17,303 | 2.649 |
| 4 | 146,846 | 90,339 | 1.625 |
| 7 | 93,578 | 48,273 | 1.939 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pisareva, A.V.; Belomoina, N.M.; Bulycheva, E.G.; Ilyin, M.M.; Postnova, E.Y.; Pisarev, R.V.; Zyubina, T.S.; Zyubin, A.S.; Karelin, A.I.; Dobrovolsky, Y.A. Structure, Thermal Properties and Proton Conductivity of the Sulfonated Polyphenylquinoxalines. Membranes 2022, 12, 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12111095
Pisareva AV, Belomoina NM, Bulycheva EG, Ilyin MM, Postnova EY, Pisarev RV, Zyubina TS, Zyubin AS, Karelin AI, Dobrovolsky YA. Structure, Thermal Properties and Proton Conductivity of the Sulfonated Polyphenylquinoxalines. Membranes. 2022; 12(11):1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12111095
Chicago/Turabian StylePisareva, Anna V., Nataliya M. Belomoina, Elena G. Bulycheva, Mikhail M. Ilyin, Evgeniya Y. Postnova, Rostislav V. Pisarev, Tatiana S. Zyubina, Alexander S. Zyubin, Alexander I. Karelin, and Yury A. Dobrovolsky. 2022. "Structure, Thermal Properties and Proton Conductivity of the Sulfonated Polyphenylquinoxalines" Membranes 12, no. 11: 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12111095
APA StylePisareva, A. V., Belomoina, N. M., Bulycheva, E. G., Ilyin, M. M., Postnova, E. Y., Pisarev, R. V., Zyubina, T. S., Zyubin, A. S., Karelin, A. I., & Dobrovolsky, Y. A. (2022). Structure, Thermal Properties and Proton Conductivity of the Sulfonated Polyphenylquinoxalines. Membranes, 12(11), 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12111095







