Tanning Wastewater Treatment by Ultrafiltration: Process Efficiency and Fouling Behavior
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characteristics of Tanning Wastewater
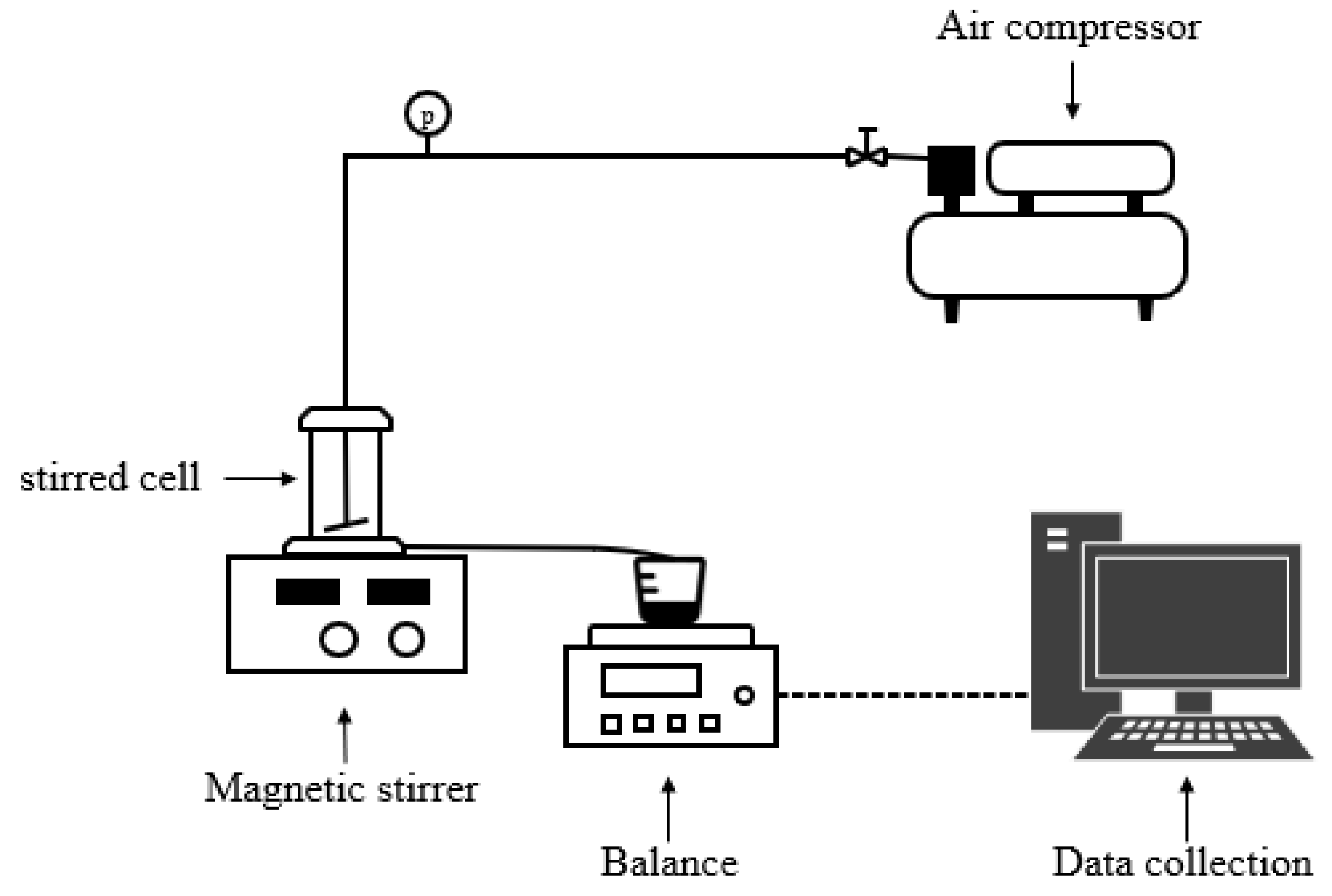
2.2. Ultrafiltration Membranes and Experimental Setup
2.3. Calculated Parameters
2.4. Models of Membrane Fouling Analysis
2.4.1. Resistance-In-Series Model
2.4.2. Membrane Fouling Propensity Model
2.4.3. Membrane Pore Blocking Model
3. Results and Discussion
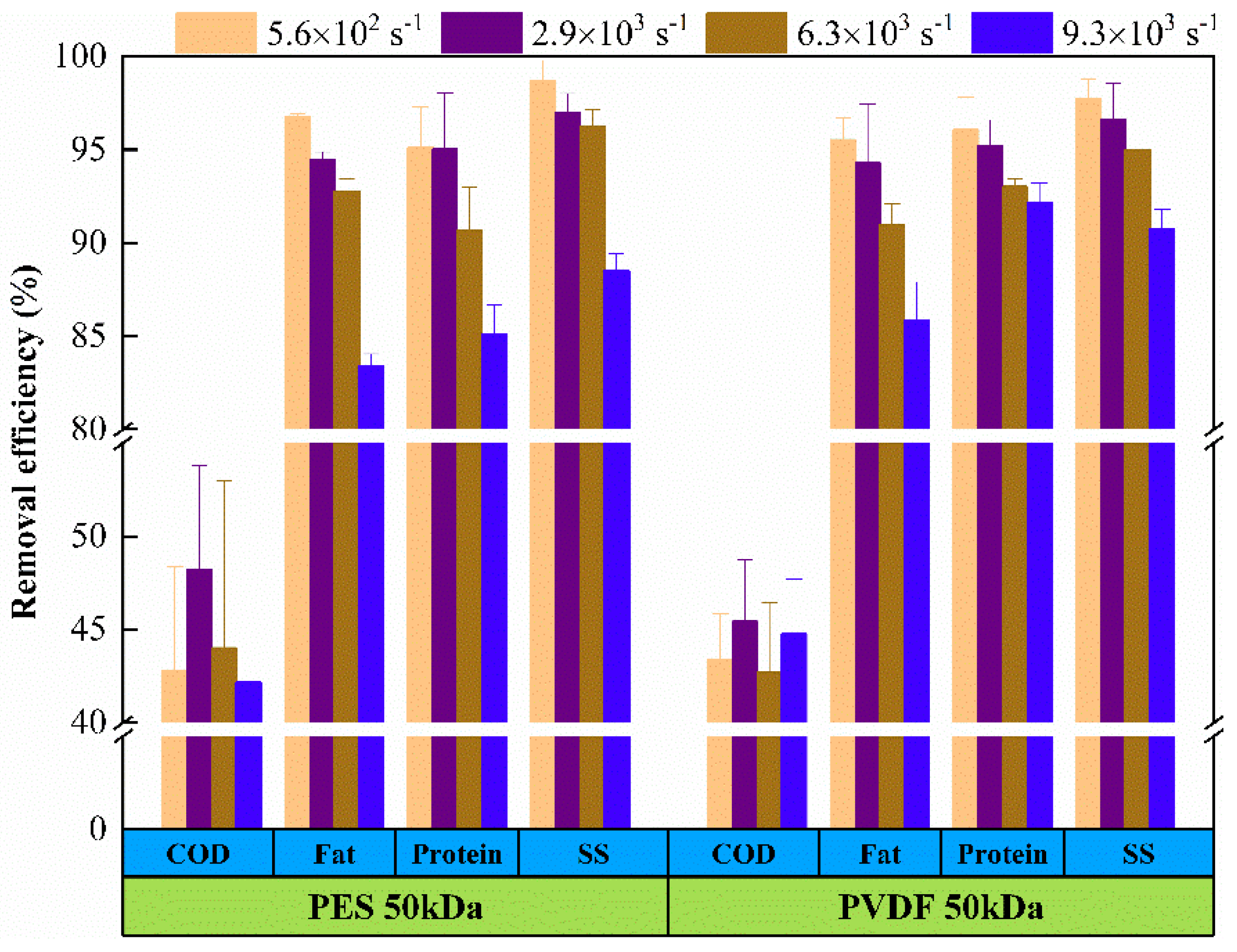
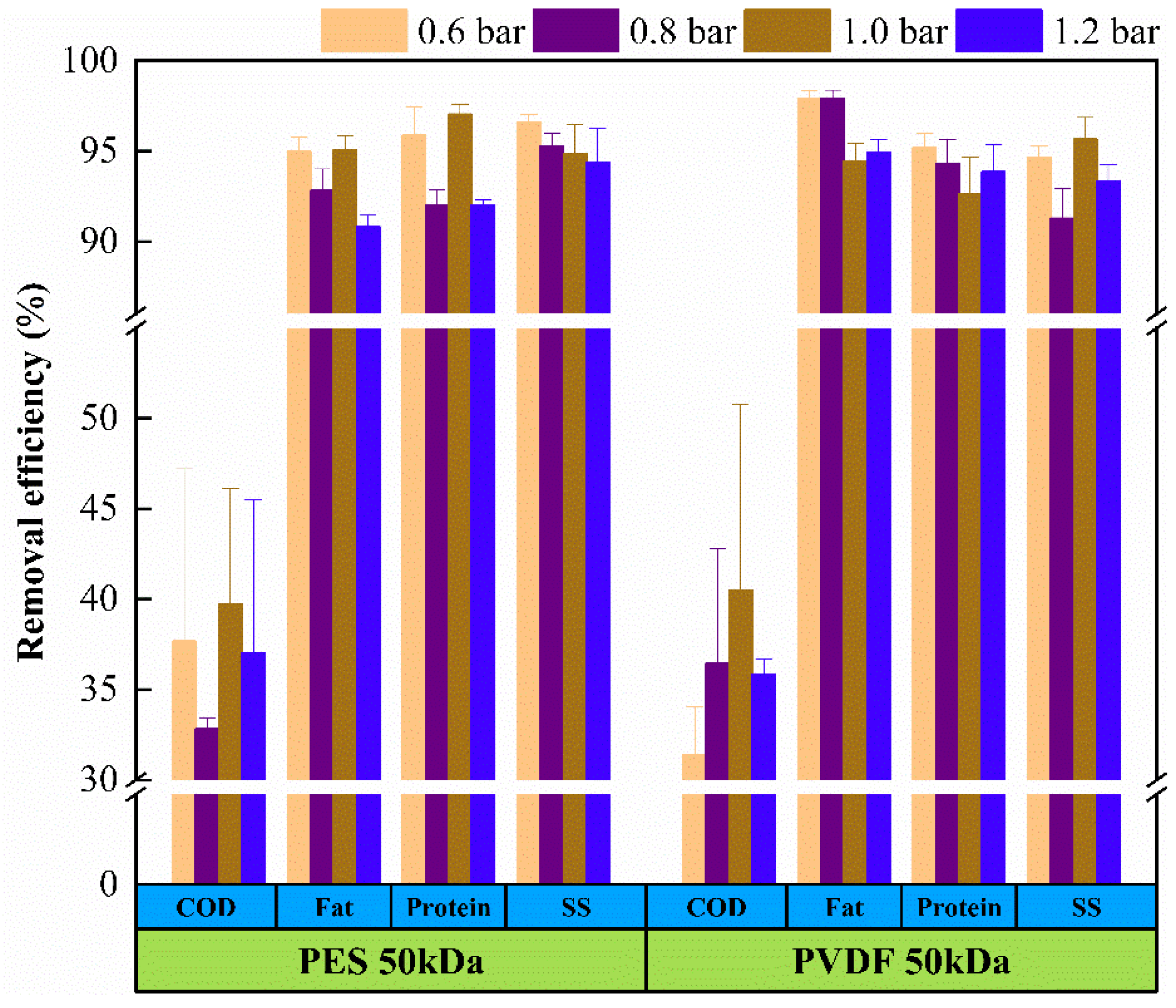
3.1. Pollutant Removal Efficiency
3.2. Permeation Efficiency
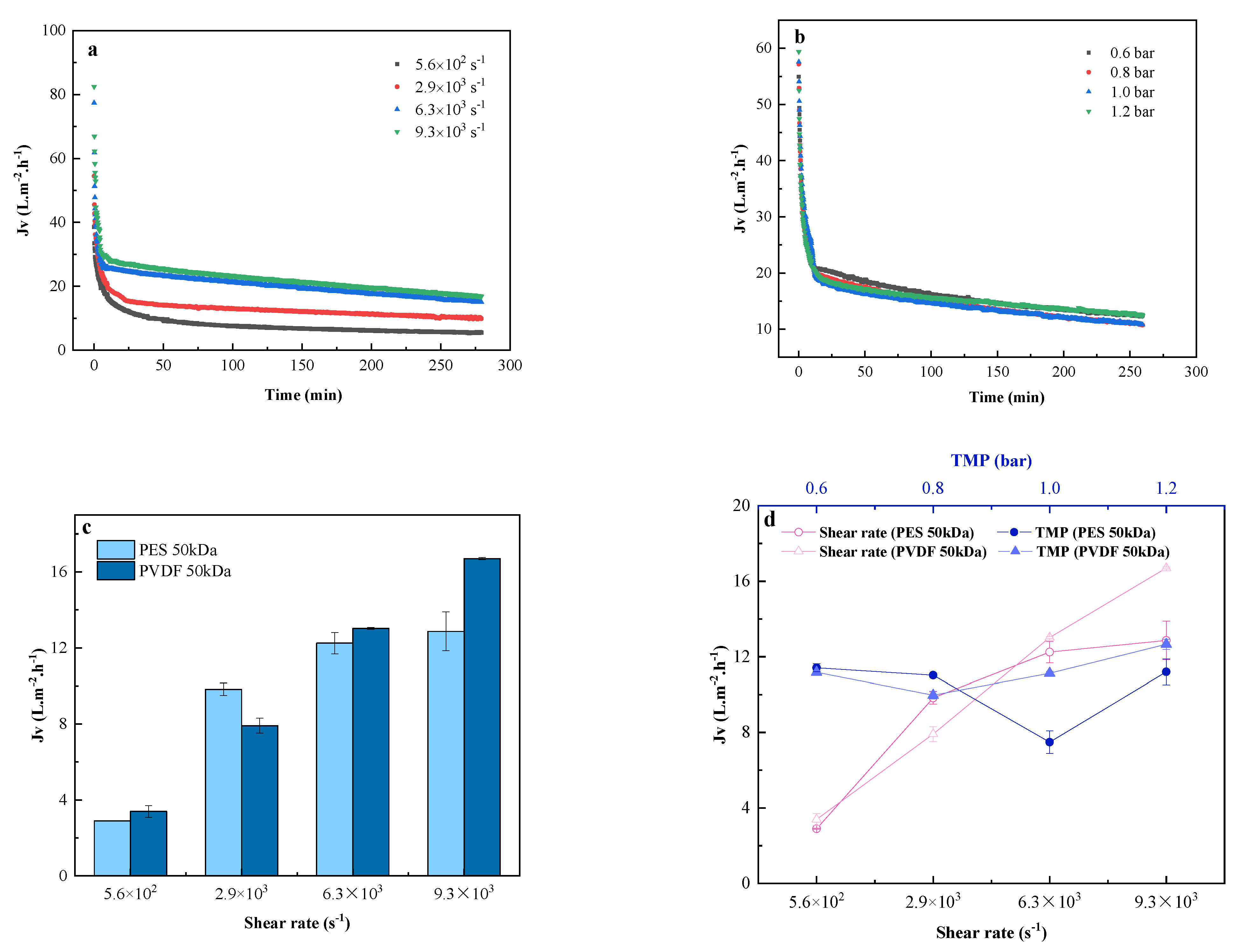
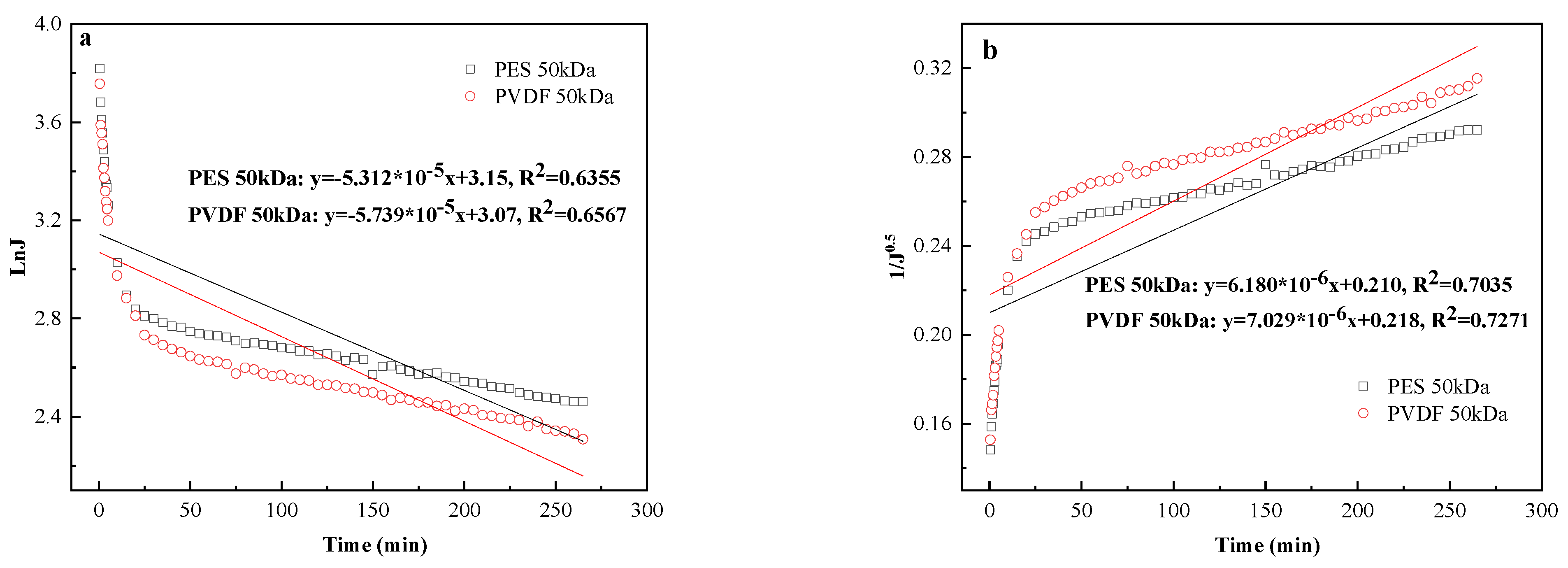
3.2.1. Permeate Flux Evolution
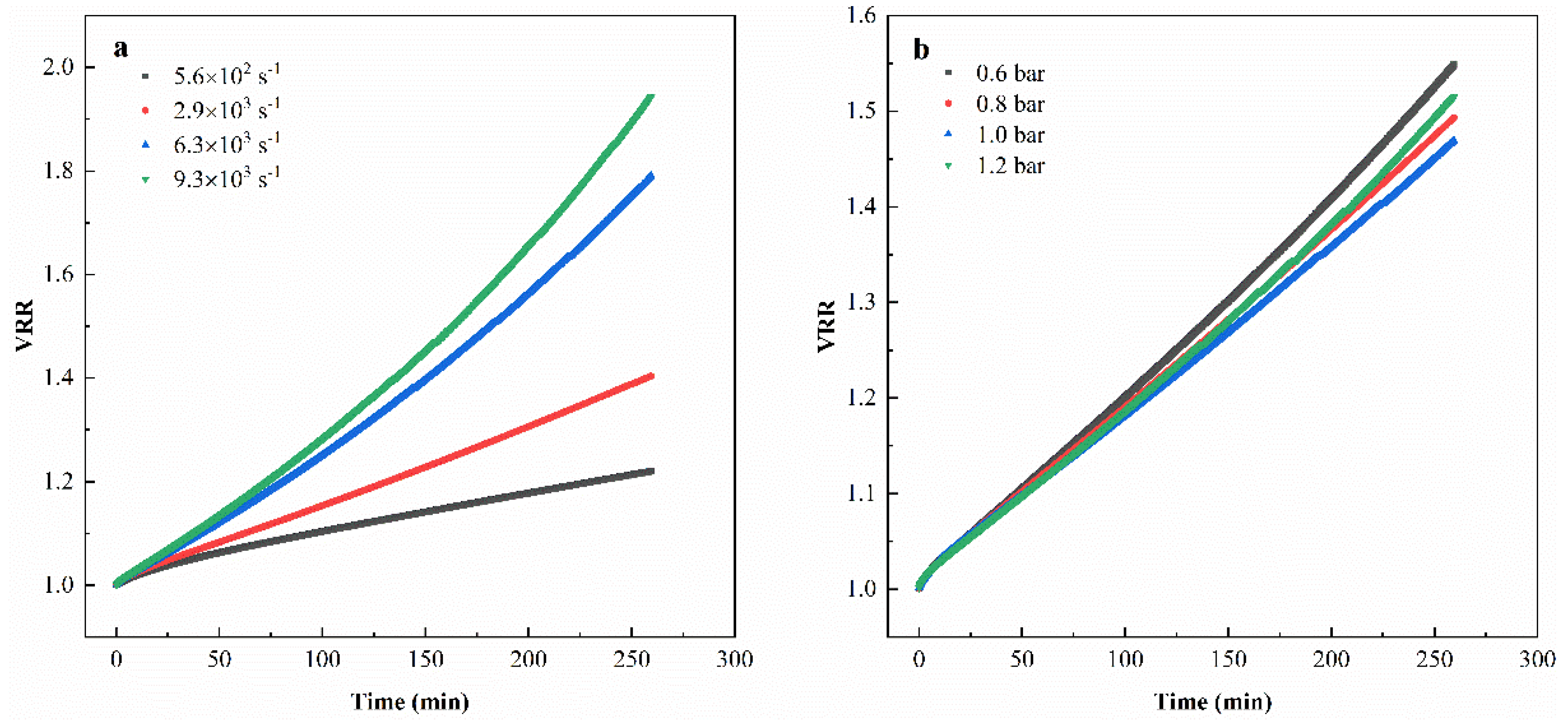
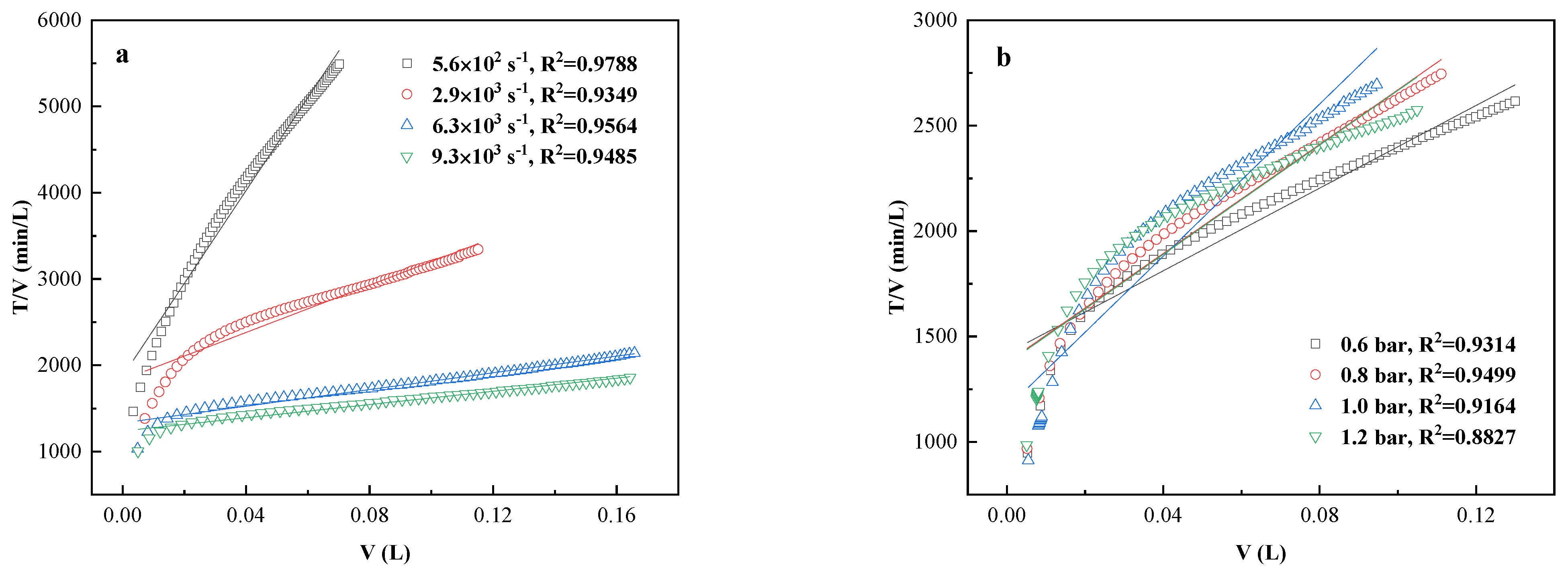
3.2.2. Cumulative Infiltrate Volume
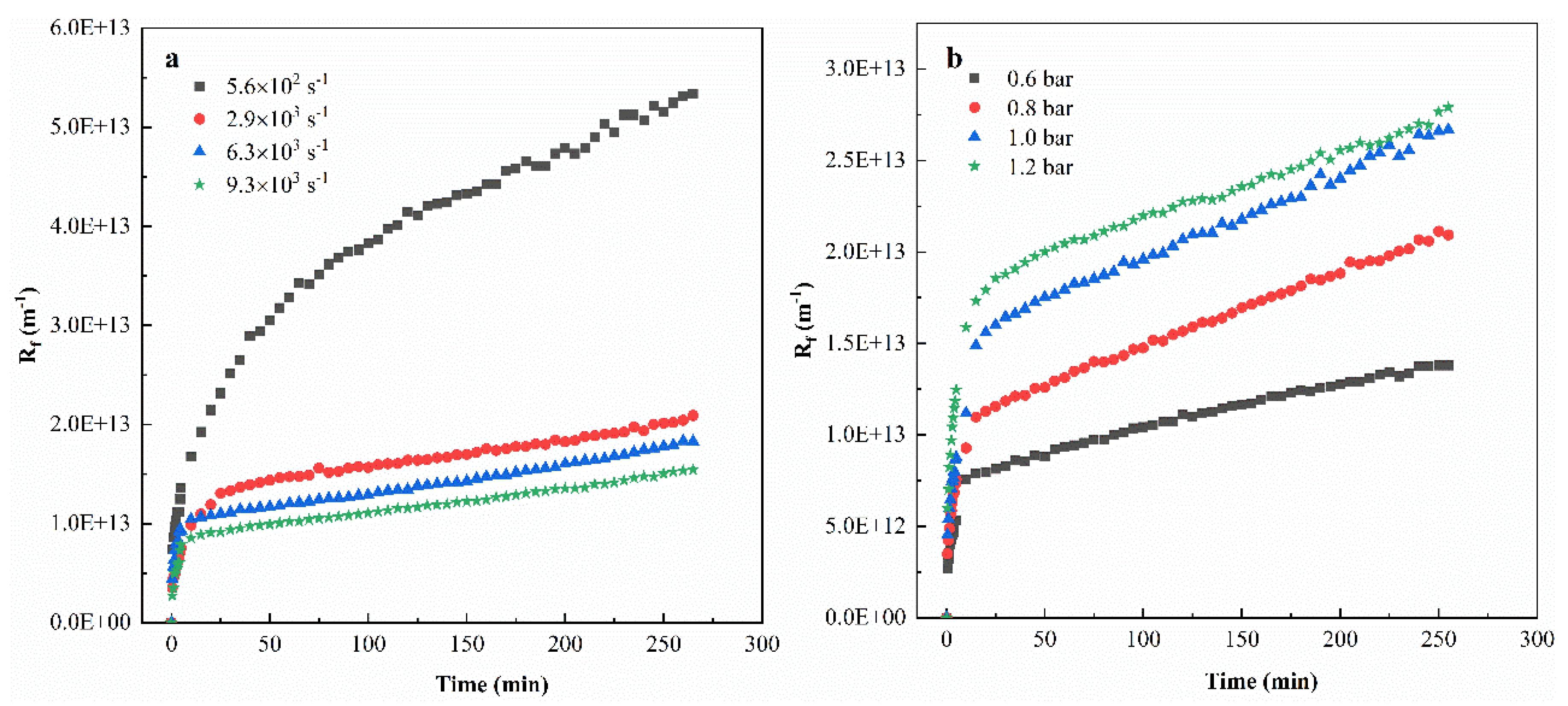
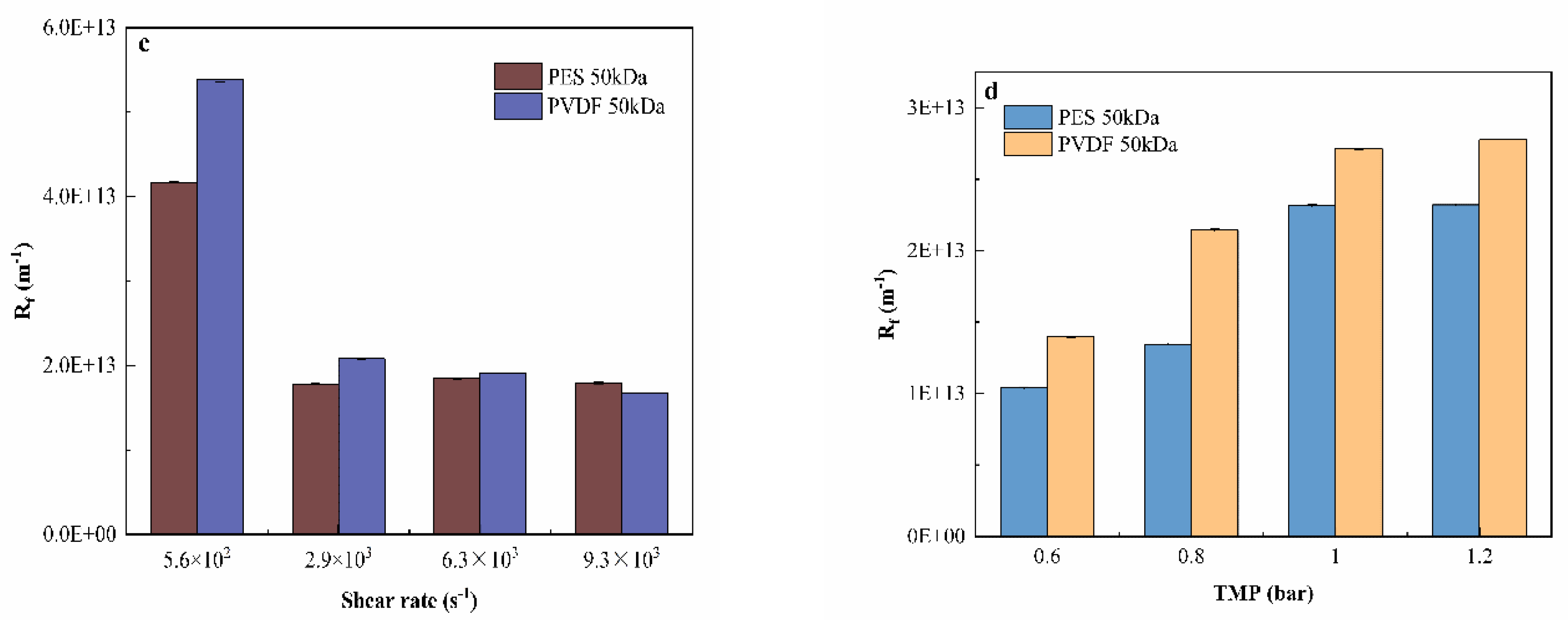
3.3. Filtration Resistance
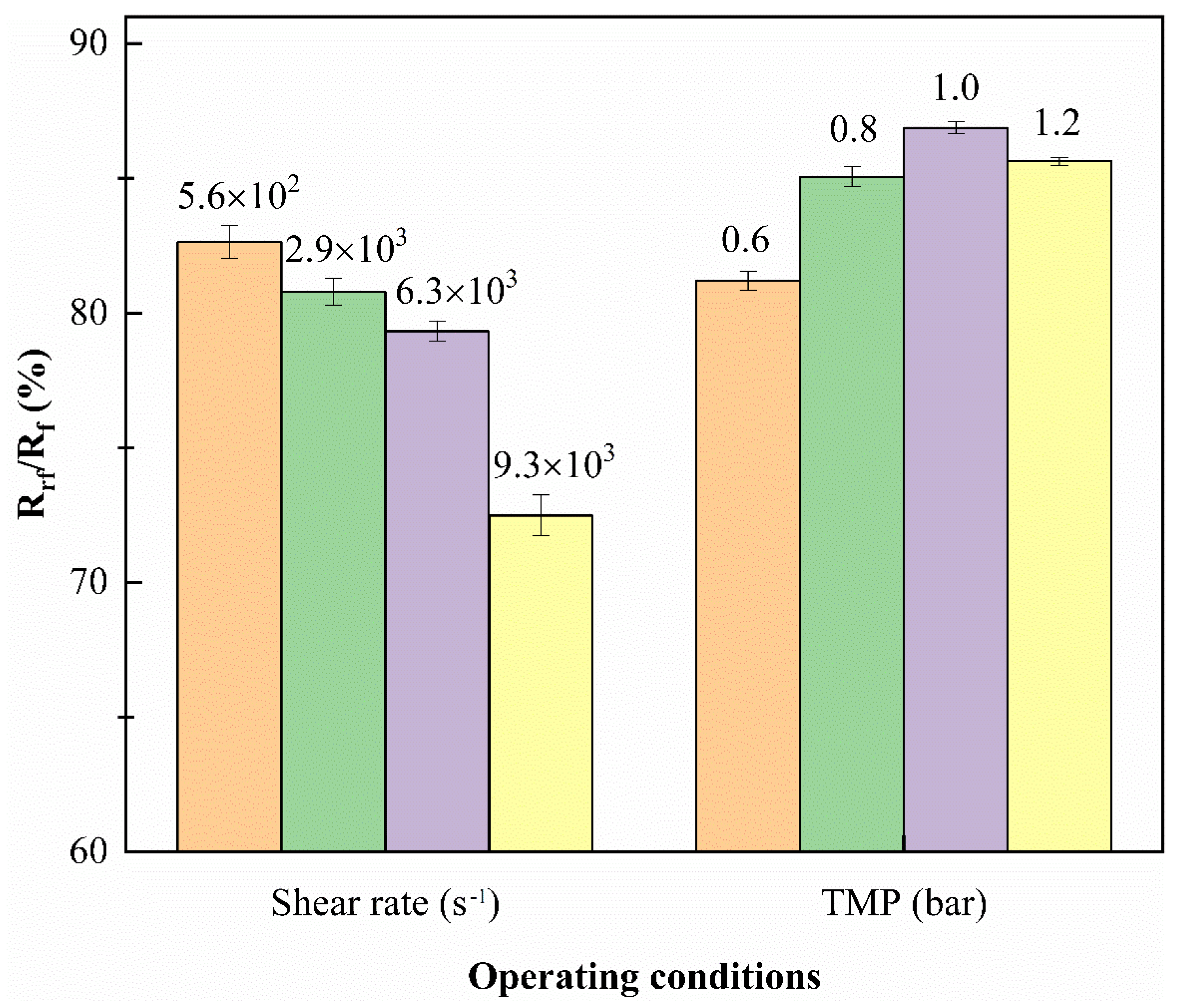
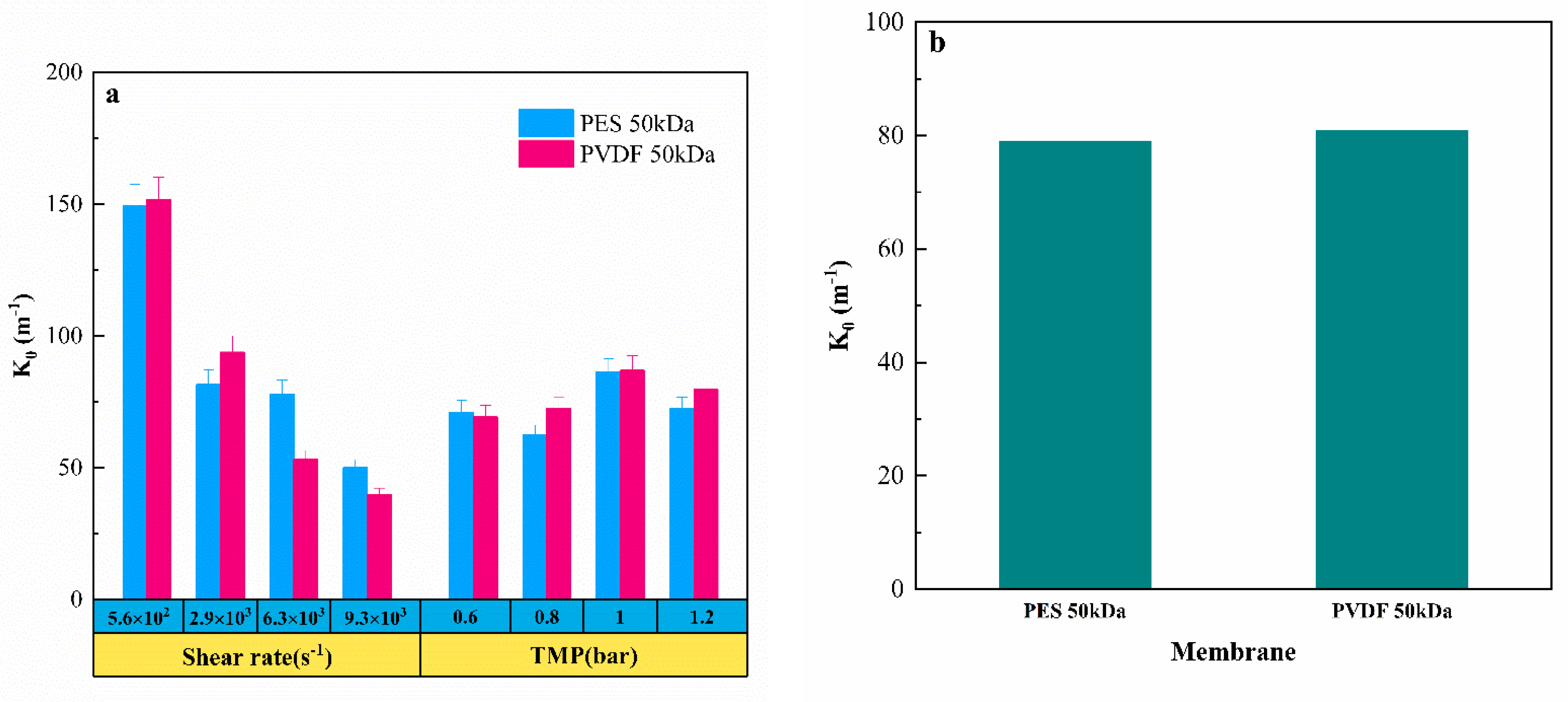
3.4. Fouling Propensity
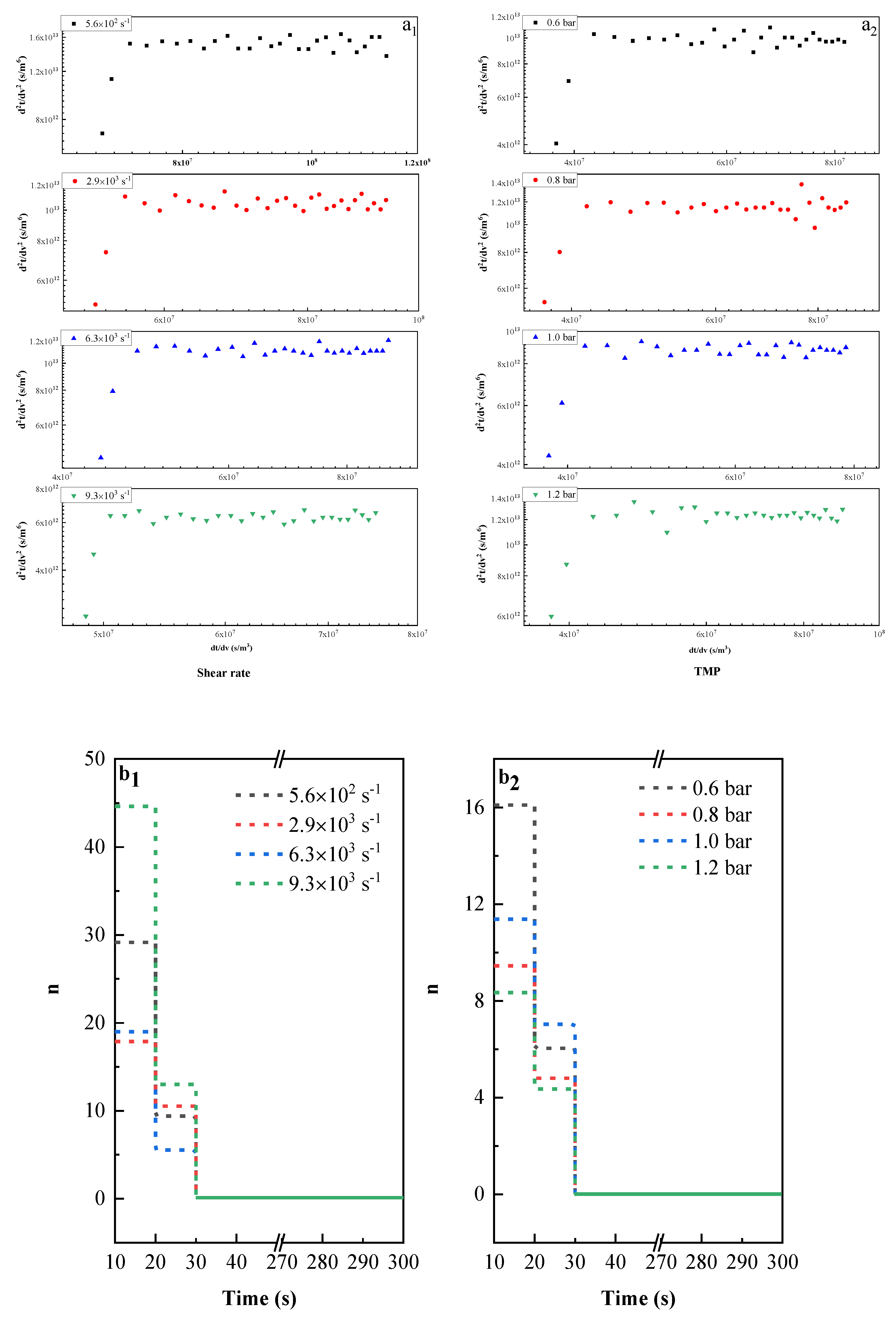
3.5. Pore Blocking Mechanism
3.5.1. Effect of Membrane Material on Pore Blocking Mechanism
3.5.2. Effect of Operating Conditions on Pore Blocking Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cassano, A.; Molinari, R.; Romano, M.; Drioli, E. Treatment of aqueous effluents of the leather industry by membrane processes: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 181, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şengil, İ.A.; Kulaç, S.; Özacar, M. Treatment of tannery liming drum wastewater by electrocoagulation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 940–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achouri, O.; Panico, A.; Bencheikh-Lehocine, M.; Derbal, K.; Pirozzi, F. Effect of chemical coagulation pretreatment on anaerobic digestion of tannery wastewater. J. Environ. Eng. 2017, 143, 04017039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Módenes, A.N.; Espinoza-Quiñones, F.R.; Borba, F.H.; Manenti, D.R. Performance evaluation of an integrated Photo-Fenton–electrocoagulation process applied to pollutant removal from tannery effluent in batch system. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 197, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbricino, M.; Naviglio, B.; Tortora, G.; d’Antonio, L. An environmental friendly cycle for Cr(III) removal and recovery from tannery wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 117, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, S.; Cavaco, S.A.; Quina, M.J.; Gando-Ferreira, L.M. Nanofiltration process for separating Cr(III) from acid solutions: Experimental and modelling analysis. Desalination 2010, 254, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannucci, A.; Munz, G.; Mori, G.; Lubello, C. Anaerobic treatment of vegetable tannery wastewaters: A review. Desalination 2010, 264, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, S.K.; Meshram, P.; Pandey, B.D.; Kumar, V.; Mankhand, T.R. Removal of Chromium(III) by cation exchange resin, indion 790 for tannery waste treatment. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 99, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamasco, R.; Konradt-Moraes, L.C.; Vieira, M.F.; Fagundes-Klen, M.R.; Vieira, A.M.S. Performance of a coagulation–ultrafiltration hybrid process for water supply treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 166, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molinari, R.; Buonomenna, M.G.; Cassano, A.; Drioli, E. Recovery and recycle of tannins in the leather industry by nanofiltration membranes. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2004, 79, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassano, A.; Adzet, J.; Molinari, R.; Buonomenna, M.G.; Roig, J.; Drioli, E. Membrane treatment by nanofiltration of exhausted vegetable tannin liquors from the leather industry. Water Res. 2003, 37, 2426–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munz, G.; De Angelis, D.; Gori, R.; Mori, G.; Casarci, M.; Lubello, C. The role of tannins in conventional and membrane treatment of tannery wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamersit, S.; Bouhidel, K.-E.; Zidani, Z. Investigation of Electrodialysis Anti-Fouling Configuration for Desalting and Treating Tannery Unhairing Wastewater: Feasibility of by-Products Recovery and Water Recycling. J. Environ. Manage. 2018, 207, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghadhban, M.Y.; Majdi, H.S.; Rashid, K.T.; Alsalhy, Q.F.; Lakshmi, D.S.; Salih, I.K.; Figoli, A. Removal of Dye from a Leather Tanning Factory by Flat-Sheet Blend Ultrafiltration (UF) Membrane. Membranes 2020, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maria Romero-Dondiz, E.; Emilio Almazan, J.; Beatriz Rajal, V.; Fani Castro-Vidaurre, E. Comparison of the Performance of Ultrafiltration and Nanofiltration Membranes for Recovery and Recycle of Tannins in the Leather Industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 135, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mert, K.B.; Kestioglu, K. Application of Nanofiltration and Reverse Osmosis for Tanning Wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2014, 8, 789–798. [Google Scholar]
- Saraswathi, M.S.S.A.; Rana, D.; Alwarappan, S.; Gowrishankar, S.; Vijayakumar, P.; Nagendran, A. Polydopamine layered poly (ether imide) ultrafiltration membranes tailored with silver nanoparticles designed for better permeability, selectivity and antifouling. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 76, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Hengl, N.; Baup, S.; Maitrejean, G.; Pignon, F. Modeling and analysis of concentration profiles obtained by in-situ SAXS during cross-flow ultrafiltration of colloids. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 528, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, Y.; Choi, Y.; Cho, H.; Shin, Y.; Lee, S. Comparison of fouling behaviors of hydrophobic microporous membranes in pressure- and temperature-driven separation processes. Desalination 2018, 428, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marke, H.S.; Breil, M.P.; Hansen, E.B.; Pinelo, M.; Krühne, U. Investigation of the velocity factor in a rotational dynamic microfiltration system. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 220, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Ismail, A.F. Fouling control on microfiltration/ultrafiltration membranes: Effects of morphology, hydrophilicity, and charge. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babel, S.; Takizawa, S. Microfiltration membrane fouling and cake behavior during algal filtration. Desalination 2010, 261, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lv, K.; Zhuo, M.; Han, Y.; Lu, Y. Investigation of the PES microfiltration membrane fouling characteristics for five substances. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2020, 207, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas, I.; Collado, S.; Gutiérrez, A.; Díaz, M. Fouling mechanisms of pseudomonas putida on PES microfiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 465, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego-Molina, A.; Mendoza-Roca, J.A.; Aguado, D.; Galiana-Aleixandre, M.V. Reducing pollution from the deliming–bating operation in a tannery. Wastewater reuse by microfiltration membranes. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2013, 91, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.-Y.; Qiu, Y.-R. Removal of copper(II) ions from aqueous solutions by complexation–ultrafiltration using rotating disk membrane and the shear stability of PAA–Cu complex. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 136, 712–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Huang, J.; Zhou, R.; Wu, C.; Jin, Y. Microfiltration of raw soy sauce: Membrane fouling mechanisms and characterization of physicochemical, aroma and shelf-life properties. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 2928–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De la Garza, F.; Boulton, R. The modeling of wine filtrations. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1984, 35, 189–195. [Google Scholar]
- Gökmen, V.; Çetinkaya, Ö. Effect of pretreatment with gelatin and bentonite on permeate flux and fouling layer resistance during apple juice ultrafiltration. J. Food Eng. 2007, 80, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Luo, J.; Ding, L.; Bals, O.; Jaffrin, M.Y.; Vorobiev, E. Chicory juice clarification by membrane filtration using rotating disk module. J. Food Eng. 2013, 115, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Luo, X.; Yin, F.; Li, S.; He, J. Clarification of jerusalem artichoke extract using ultra-filtration: Effect of membrane pore size and operation conditions. Food Bioprocess. Technol. 2018, 11, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Prudente, A.; Sathivel, S. Purification of soluble rice bran fiber using ultrafiltration technology. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Li, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhou, R.; Wu, C.; Jin, Y. Microfiltration of soy sauce: Efficiency, resistance and fouling mechanism at different operating stages. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 240, 116656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.-M.; Liu, J.; Liu, M.; Shen, C.-H.; Yu, X.-C.; Wu, C.-D.; Huang, J.; Zhou, R.-Q.; Jin, Y. Fouling analysis and permeate quality evaluation of mulberry wine in microfiltration process. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhattacharya, P.K.; Todi, R.K.; Tiwari, M.; Bhattacharjee, C.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Datta, S. Studies on ultrafiltration of spent sulfite liquor using various membranes for the recovery of lignosulphonates. Desalination 2005, 174, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Dondiz, E.M.; Almazán, J.E.; Rajal, V.B.; Castro-Vidaurre, E.F. Removal of vegetable tannins to recover water in the leather industry by ultrafiltration polymeric membranes. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2015, 93, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Rayess, Y.; Albasi, C.; Bacchin, P.; Taillandier, P.; Mietton-Peuchot, M.; Devatine, A. Analysis of membrane fouling during cross-flow microfiltration of wine. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2012, 16, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, S.; Xing, W.; Wong, F.-S. Resistance analysis for ceramic membrane microfiltration of raw soy sauce. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 299, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piry, A.; Heino, A.; Kühnl, W.; Grein, T.; Ripperger, S.; Kulozik, U. Effect of membrane length, membrane resistance, and filtration conditions on the fractionation of milk proteins by microfiltration. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 1590–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charfi, A.; Ben Amar, N.; Harmand, J. Analysis of fouling mechanisms in anaerobic membrane bioreactors. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2637–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parameter | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| pH | - | 5.11 |
| Chemical oxygen demand (COD) | mg/L | 21,305 ± 150.58 |
| Fat | mg/L | 1297 ± 38.30 |
| Suspended solids (SS) | mg/L | 4831 ± 131.16 |
| Protein | mg/L | 675 ± 5.93 |
| Conductivity | mS/cm | 38.67 ± 0.51 |
| Designation | PES 50 kDa | PVDF 50 kDa |
| Manufacturer | SEPRO (USA) | Synder (USA) |
| Polymer type | Poly ether sulfone | Poly vinylidene fluoride |
| Molecular weight cut-off | 50 kDa | 50 kDa |
| Operating pressure | <6 bar | <8 bar |
| Operating pH | 4–10 | 2–10 |
| Maximum temperature | 60 °C | 60 °C |
| Pore Blocking Models | Model Equations | Physical Concept |
|---|---|---|
| Complete blocking (n = 2) | Formation of a surface deposit | |
| Standard blocking (n = 1.5) | Pore adsorption | |
| Intermediate blocking (n = 1.5) | Pore constriction + surface deposit | |
| Cake filtration (n = 0) | Pore blocking + surface deposit |
| Operating Conditions | Fouling Resistance (×1010 m−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shear rate | 5.6 × 102 s−1 | 236 | 5650 | 4669 | 745 |
| 2.9 × 103 s−1 | 181 | 2269 | 1833 | 254 | |
| 6.3 × 103 s−1 | 168 | 2057 | 1499 | 391 | |
| 9.3 × 103 s−1 | 226 | 1841 | 1335 | 281 | |
| TMP | 0.6 bar | 109 | 1503 | 1220 | 174 |
| 0.8 bar | 158 | 2313 | 1968 | 188 | |
| 1.0 bar | 162 | 2879 | 2501 | 216 | |
| 1.2 bar | 186 | 2965 | 2539 | 240 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, F.; Huang, Z.; Huang, J.; Wu, C.; Zhou, R.; Jin, Y. Tanning Wastewater Treatment by Ultrafiltration: Process Efficiency and Fouling Behavior. Membranes 2021, 11, 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11070461
Yang F, Huang Z, Huang J, Wu C, Zhou R, Jin Y. Tanning Wastewater Treatment by Ultrafiltration: Process Efficiency and Fouling Behavior. Membranes. 2021; 11(7):461. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11070461
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Fu, Zhengkun Huang, Jun Huang, Chongde Wu, Rongqing Zhou, and Yao Jin. 2021. "Tanning Wastewater Treatment by Ultrafiltration: Process Efficiency and Fouling Behavior" Membranes 11, no. 7: 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11070461
APA StyleYang, F., Huang, Z., Huang, J., Wu, C., Zhou, R., & Jin, Y. (2021). Tanning Wastewater Treatment by Ultrafiltration: Process Efficiency and Fouling Behavior. Membranes, 11(7), 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11070461







