Oxidative Imbalance and Kidney Damage in Cafeteria Diet-Induced Rat Model of Metabolic Syndrome: Effect of Bergamot Polyphenolic Fraction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Diets and Supplement
2.4. Blood and Tissue Collection
2.5. Blood Analysis
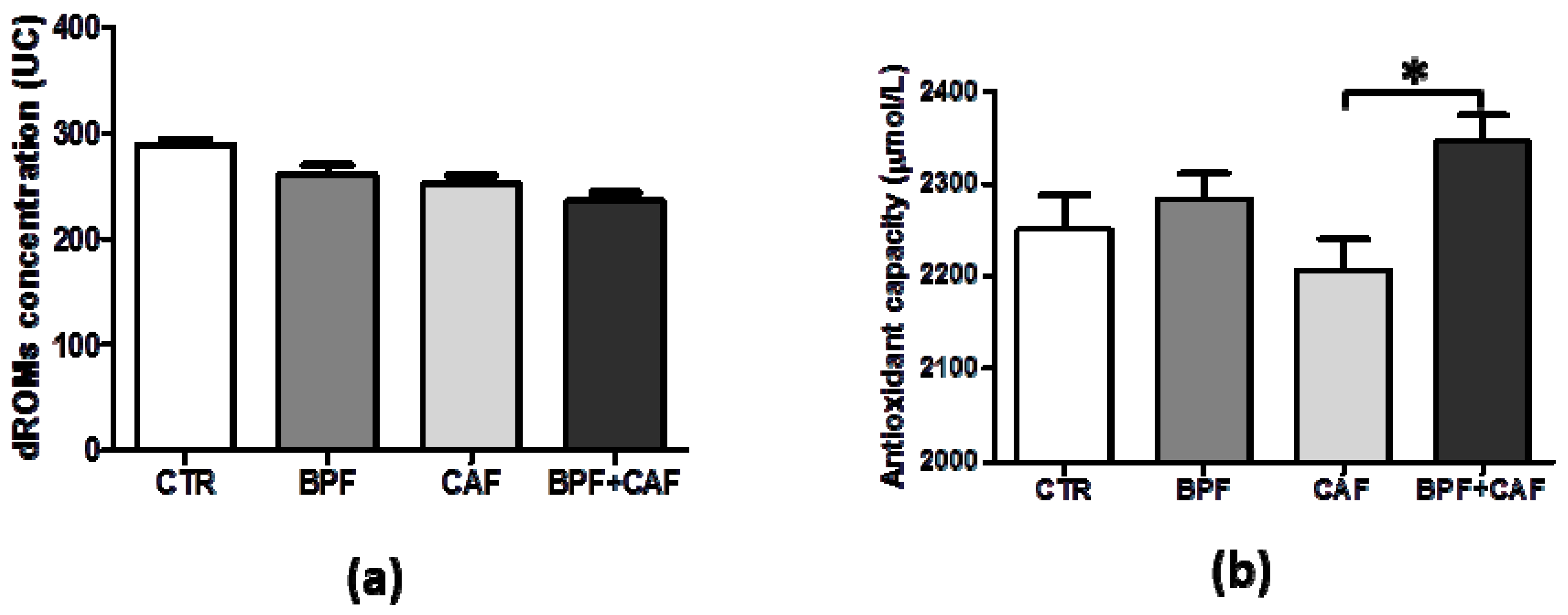
2.6. Measurement of Plasma Oxidative Status
2.7. Western Blot and Densitometric Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of CAF Diet and BPF Treatment on Obesity and Blood Parameters
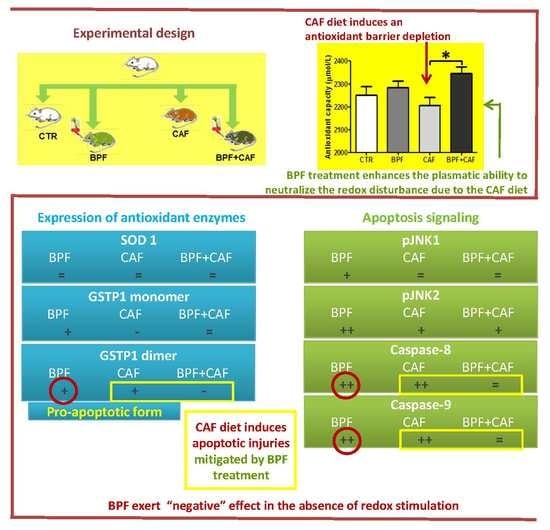
3.2. Plasmatic Oxidative Status
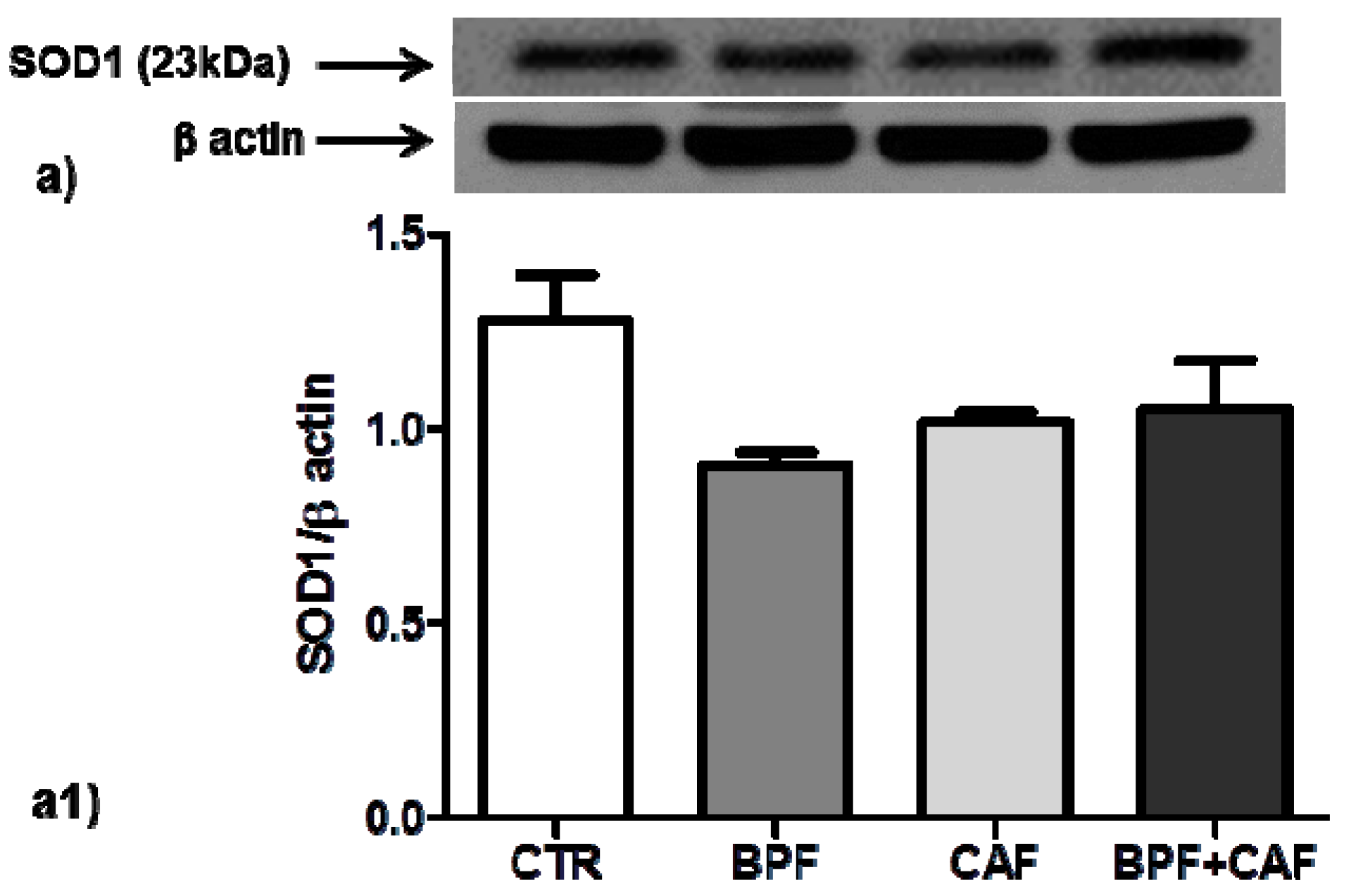
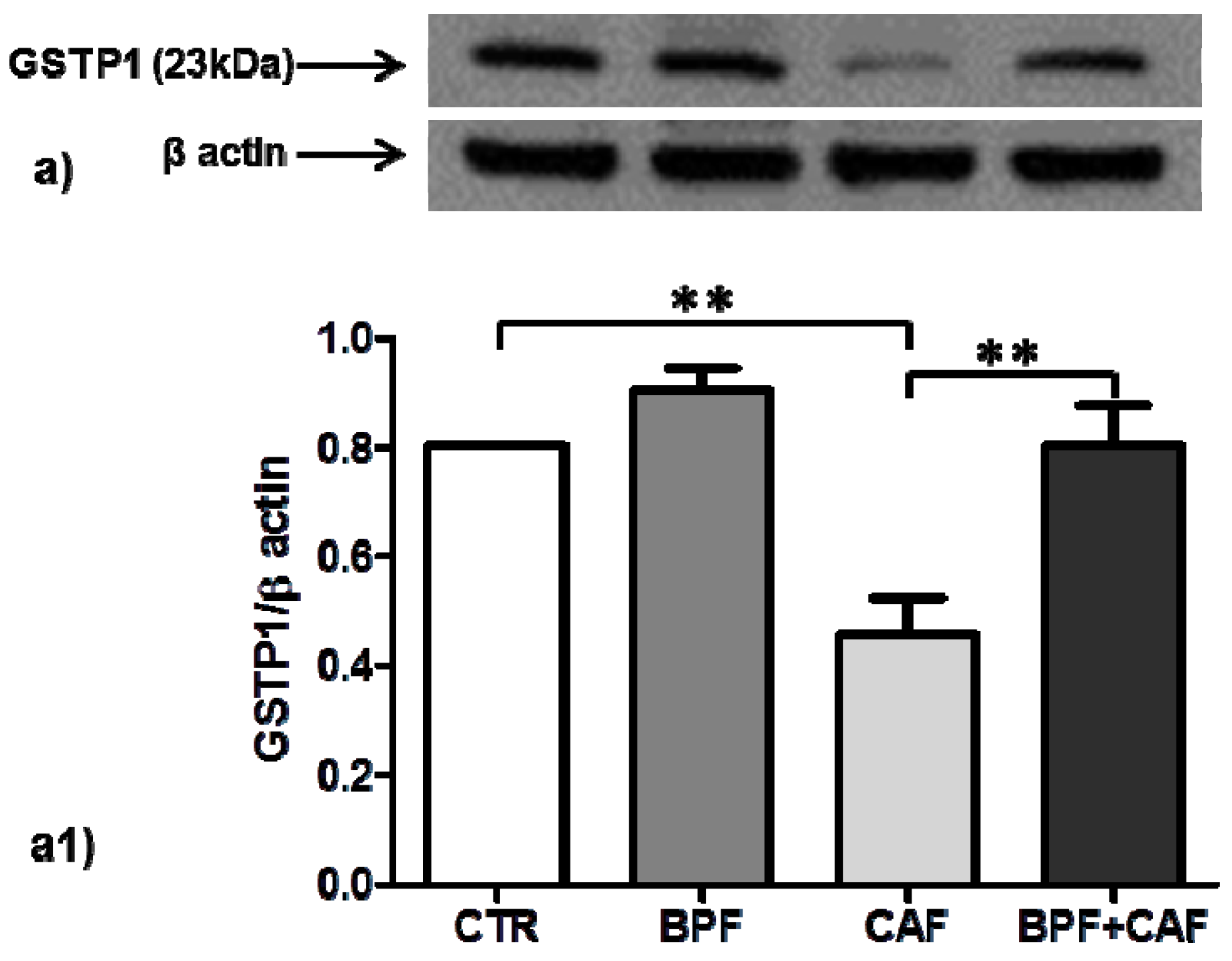
3.3. Antioxidant Enzymes’ Expression
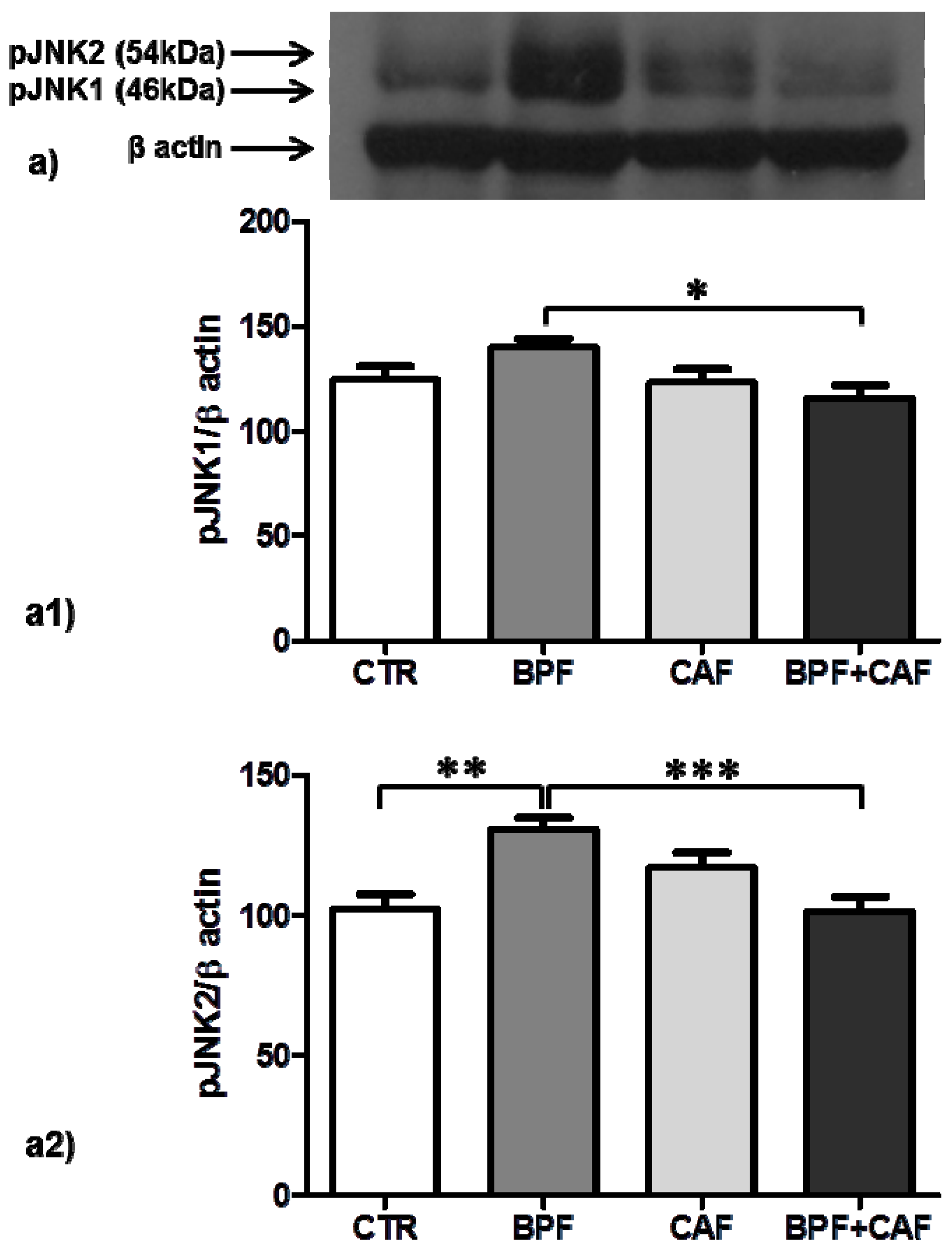
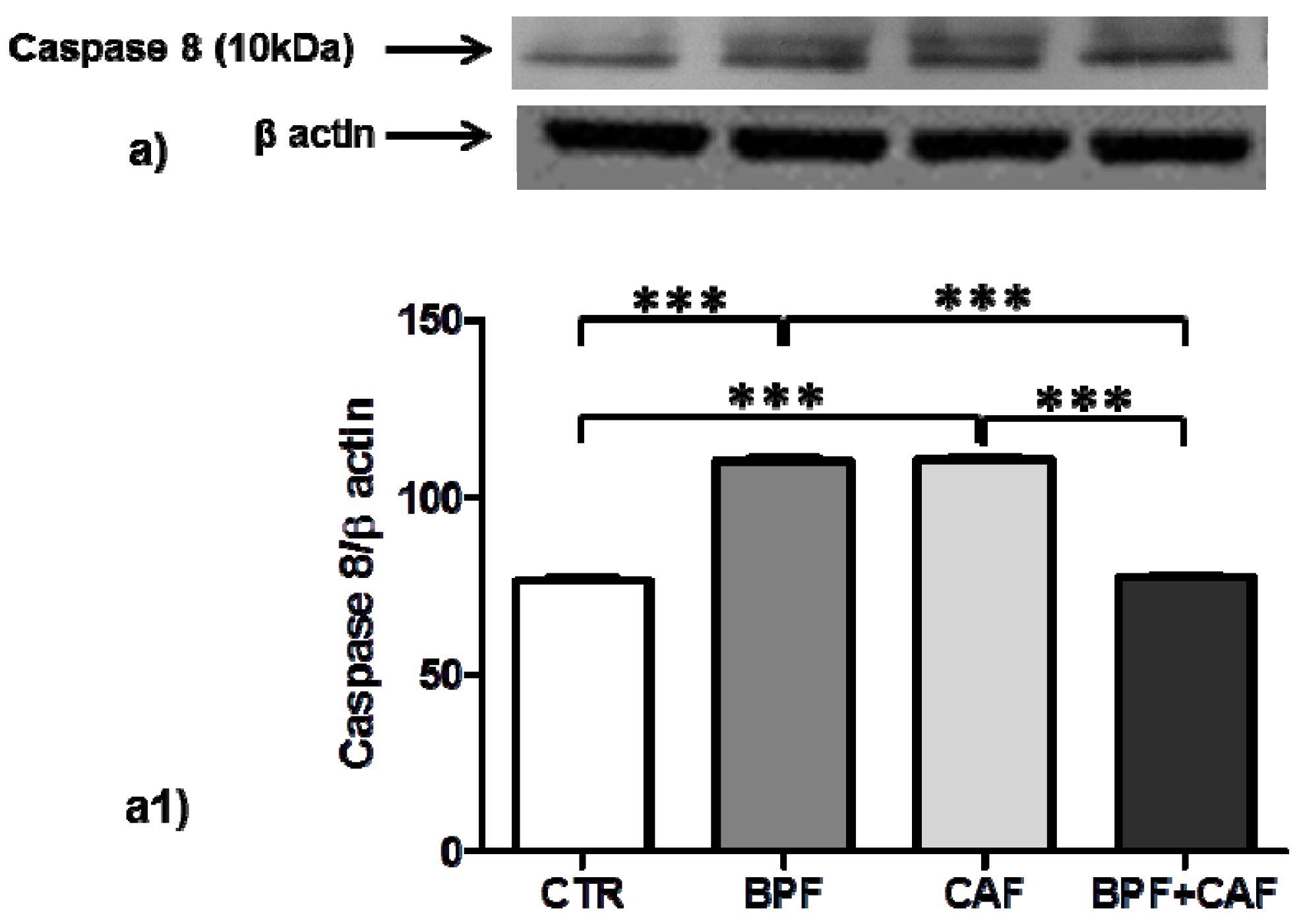
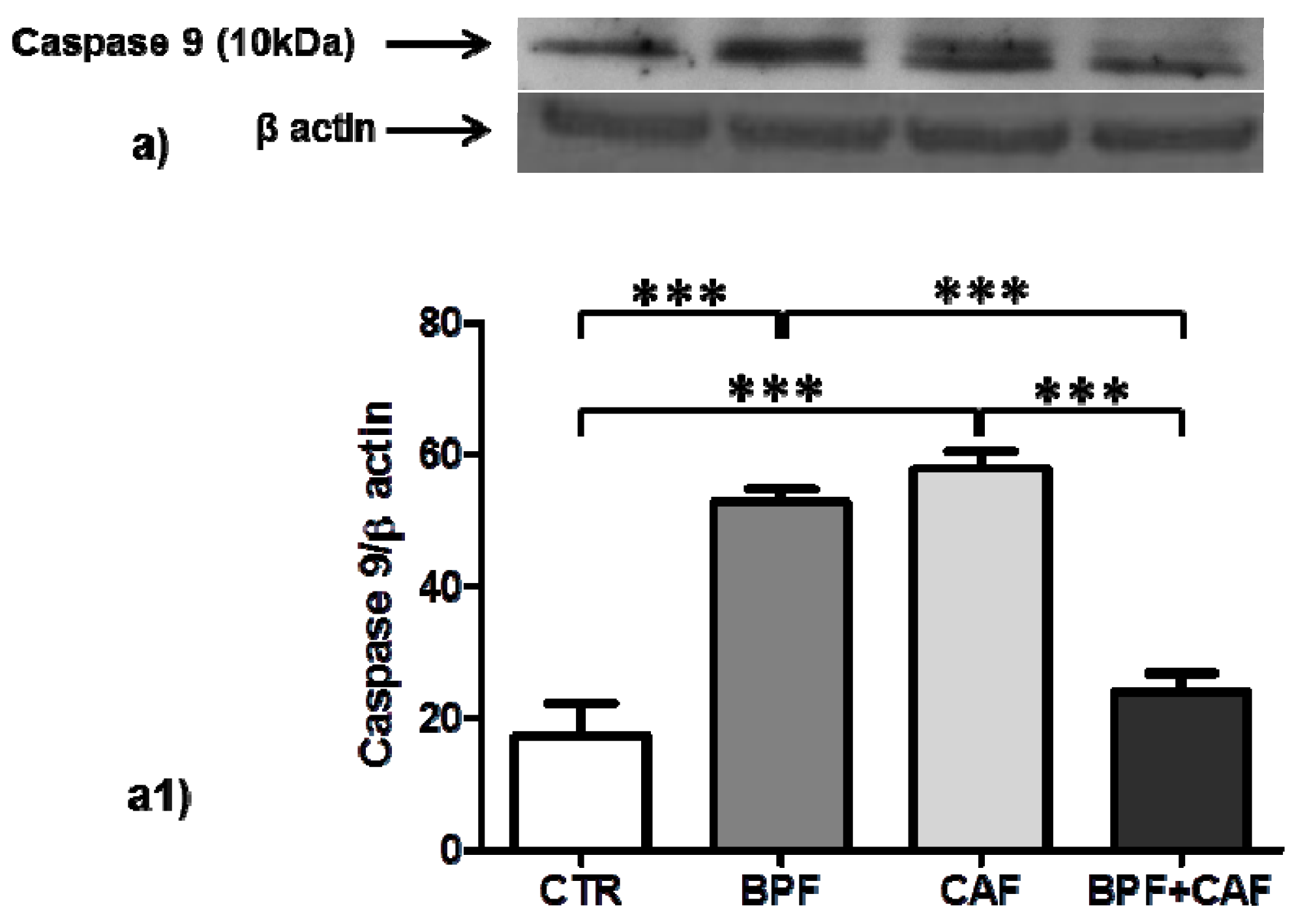
3.4. Apoptotic Pathways
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Clinical Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2015 Obesity Collaborators; Afshin, A.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Reitsma, M.B.; Sur, P.; Estep, K.; Lee, A.; Marczak, L.; Mokdad, A.H.; Moradi-Lakeh, M.; et al. Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity in 195 Countries over 25 Years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 37, 13–27. [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo, A.; Monasta, L.; Stamatakis, E.; Lioret, S.; Castetbon, K.; Frenken, F.; Manios, Y.; Moschonis, G.; Savva, S.; Zaborskis, A.; et al. Overweight and obesity in infants and pre-school children in the European Union: A review of existing data. Obes. Rev. 2010, 11, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, G.M.; Danaei, G.; Farzadfar, F.; Stevens, G.A.; Woodward, M.; Wormser, D.; Kaptoge, S.; Whitlock, G.; Qiao, Q.; Lewington, S.; et al. The age-specific quantitative effects of metabolic risk factors on cardiovascular diseases and diabetes: A pooled analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collaboration, E.R.F.; Wormser, D.; Kaptoge, S.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Wood, A.M.; Pennells, L.; Thompson, A.; Sarwar, N.; Kizer, J.R.; Lawlor, D.A.; et al. Separate and combined associations of body-mass index and abdominal adiposity with cardiovascular disease: Collaborative analysis of 58 prospective studies. Lancet 2011, 377, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauby-Secretan, B.; Scoccianti, C.; Loomis, D. Body Fatness and Cancer—Viewpoint of the IARC Working Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovesdy, C.P.; Furth, S.; Zoccali, C. Obesity and kidney disease: Hidden consequences of the epidemic. Indian J. Nephrol. 2017, 27, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsayed, E.F.; Sarnak, M.J.; Tighiouart, H.; Griffith, J.L.; Kurth, T.; Salem, D.N.; Levey, A.S.; Weiner, D.E. Waist-to-Hip Ratio, Body Mass Index, and Subsequent Kidney Disease and Death. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2008, 52, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimoto, T.; Sairenchi, T.; Iso, H.; Irie, F.; Yamagishi, K.; Watanabe, H.; Tanaka, K.; Muto, T.; Ota, H. The Dose-Response Relationship between Body Mass Index and the Risk of Incident Stage ≥3 Chronic Kidney Disease in a General Japanese Population: The Ibaraki Prefectural Health Study (IPHS). J. Epidemiol. 2014, 24, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiuchi, M.G.; Mion, D. Chronic kidney disease and risk factors responsible for sudden cardiac death: A whiff of hope? Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2016, 35, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Ryu, S.; Choi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cho, J.; Kwon, M.J.; Hyun, Y.Y.; Lee, K.B.; Kim, H.; Jung, H.S.; et al. Metabolically healthy obesity and development of chronic kidney disease: A cohort study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2016, 164, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postorino, M.; Marino, C.; Tripepi, G.; Zoccali, C. Abdominal Obesity and All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality in End-Stage Renal Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 53, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovesdy, C.P.; Czira, M.E.; Rudas, A.; Ujszaszi, A.; Rosivall, L.; Novak, M.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Molnar, M.Z.; Mucsi, I. Body mass index, waist circumference and mortality in kidney transplant recipients. Am. J. Transplant. 2010, 10, 2644–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, M.C.; Hwang, S.J.; Massaro, J.M.; Hoffmann, U.; Deboer, I.H.; Robins, S.J.; Vasan, R.S.; Fox, C.S. Association of subcutaneous and visceral adiposity with albuminuria: The framingham heart study. Obesity 2011, 19, 1284–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinn, D.H.; Kang, D.; Jang, H.R.; Gu, S.; Cho, S.J.; Paik, S.W.; Ryu, S.; Chang, Y.; Lazo, M.; Guallar, E.; et al. Development of chronic kidney disease in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A cohort study. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 1274–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, M.; Shimomura, I. Increased oxidative stress in obesity: Implications for metabolic syndrome, diabetes, hypertension, dyslipidemia, atherosclerosis, and cancer. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2013, 7, e330–e341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, L.F.; Shintani, A.; Ikizler, T.A.; Himmelfarb, J. Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Are Associated with Adiposity in Moderate to Severe CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suen, J.; Thomas, J.; Kranz, A.; Vun, S.; Miller, M. Effect of Flavonoids on Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Adults at Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: A Systematic Review. Healthcare 2016, 4, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, J.A.; Kasum, C.M. Dietary flavonoids: Bioavailability, metabolic effects, and safety. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2002, 22, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlazzo, N.; Visalli, G.; Smeriglio, A.; Cirmi, S.; Lombardo, G.E.; Campiglia, P.; Di Pietro, A.; Navarra, M. Flavonoid Fraction of Orange and Bergamot Juices Protect Human Lung Epithelial Cells from Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Oxidative Stress. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 957031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiva-Blanch, G.; Badimon, L. Effects of Polyphenol Intake on Metabolic Syndrome: Current Evidences from Human Trials. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 5812401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosso, G.; Godos, J.; Lamuela-Raventos, R.; Ray, S.; Micek, A.; Pajak, A.; Sciacca, S.; D’Orazio, N.; Del Rio, D.; Galvano, F. A comprehensive meta-analysis on dietary flavonoid and lignan intake and cancer risk: Level of evidence and limitations. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1600930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Rio, D.; Rodriguez-Mateos, A.; Spencer, J.P.E.; Tognolini, M.; Borges, G.; Crozier, A. Dietary (Poly)phenolics in Human Health: Structures, Bioavailability, and Evidence of Protective Effects Against Chronic Diseases. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 18, 1818–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosso, G.; Micek, A.; Godos, J.; Pajak, A.; Sciacca, S.; Galvano, F.; Giovannucci, E.L. Dietary Flavonoid and Lignan Intake and Mortality in Prospective Cohort Studies: Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 185, 1304–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Ouyang, Y.Y.; Liu, J.; Zhao, G. Flavonoid intake and risk of CVD: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 111, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomé-Carneiro, J.; Visioli, F. Polyphenol-based nutraceuticals for the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease: Review of human evidence. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 1145–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, R.; Janda, E.; Mollace, V. The Use of Bergamot-Derived Polyphenol Fraction in Cardiometabolic Risk Prevention and its Possible Mechanisms of Action. Polyphen. Hum. Health Dis. 2013, 2, 1087–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Janda, E.; Lascala, A.; Martino, C.; Ragusa, S.; Nucera, S.; Walker, R.; Gratteri, S.; Mollace, V. Molecular mechanisms of lipid- and glucose-lowering activities of bergamot flavonoids. PharmaNutrition 2016, 4, S8–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollace, V.; Sacco, I.; Janda, E.; Malara, C.; Ventrice, D.; Colica, C.; Visalli, V.; Muscoli, S.; Ragusa, S.; Muscoli, C.; et al. Hypolipemic and hypoglycaemic activity of bergamot polyphenols: From animal models to human studies. Fitoterapia 2011, 82, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gliozzi, M.; Walker, R.; Muscoli, S.; Vitale, C.; Gratteri, S.; Carresi, C.; Musolino, V.; Russo, V.; Janda, E.; Ragusa, S.; et al. Bergamot polyphenolic fraction enhances rosuvastatin-induced effect on LDL-cholesterol, LOX-1 expression and protein kinase B phosphorylation in patients with hyperlipidemia. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 170, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parafati, M.; Lascala, A.; Morittu, V.M.; Trimboli, F.; Rizzuto, A.; Brunelli, E.; Coscarelli, F.; Costa, N.; Britti, D.; Ehrlich, J.; et al. Bergamot polyphenol fraction prevents nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via stimulation of lipophagy in cafeteria diet-induced rat model of metabolic syndrome. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 26, 938–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lascala, A.; Martino, C.; Parafati, M.; Salerno, R.; Oliverio, M.; Pellegrino, D.; Mollace, V.; Janda, E. Analysis of proautophagic activities of Citrus flavonoids in liver cells reveals the superiority of a natural polyphenol mixture over pure flavones. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 58, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parafati, M.; Lascala, A.; La Russa, D.; Mignogna, C.; Trimboli, F.; Morittu, V.M.; Riillo, C.; Macirella, R.; Mollace, V.; Brunelli, E.; et al. Bergamot Polyphenols Boost Therapeutic Effects of the Diet on Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) Induced by “Junk Food”: Evidence for Anti-Inflammatory Activity. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forman, H.J.; Davies, K.J.A.; Ursini, F. How do nutritional antioxidants really work: Nucleophilic tone and para-hormesis versus free radical scavenging in vivo. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 66, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, H.A. CalcDose: A software for drug dosage conversion using metabolically active mass of animals. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2003, 26, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Russa, D.; Brunelli, E.; Pellegrino, D. Oxidative imbalance and kidney damage in spontaneously hypertensive rats: Activation of extrinsic apoptotic pathways. Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 1419–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunelli, E.; Domanico, F.; La Russa, D.; Pellegrino, D. Sex differences in oxidative stress biomarkers. Curr. Drug Targets 2014, 15, 811–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunelli, E.; La Russa, D.; Pellegrino, D. Impaired oxidative status is strongly associated with cardiovascular risk factors. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 6480145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Russa, D.; Pellegrino, D.; Montesanto, A.; Gigliotti, P.; Perri, A.; la Russa, A.; Bonofiglio, R. Oxidative Balance and Inflammation in Hemodialysis Patients: Biomarkers of Cardiovascular Risk? Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 8567275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novelli, E.L.B.; Diniz, Y.S.; Galhardi, C.M.; Ebaid, G.M.X.; Rodrigues, H.G.; Mani, F.; Fernandes, A.A.H.; Cicogna, A.C.; Novelli Filho, J.L.V.B. Anthropometrical parameters and markers of obesity in rats. Lab. Anim. 2007, 41, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeeni, N.; Dagher-Hamalian, C.; Dimassi, H.; Faour, W.H. Cafeteria diet-fed mice is a pertinent model of obesity-induced organ damage: A potential role of inflammation. Inflamm. Res. 2015, 64, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.J.; Lu, C.; Su, L.Y.; Sharma, A.M.; Lee, R.M.K.W. Modulation of vascular function by perivascular adipose tissue: The role of endothelium and hydrogen peroxide. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 151, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira-Lancha, L.O.; Coelho, D.F.; De Campos-Ferraz, P.L.; Lancha, A.H.; Pereira-Lancha, L.O.; Coelho, D.F.; de Campos-Ferraz, P.L. Body fat regulation: Is it a result of a simple energy balance or a high fat intake? J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2010, 29, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafat, A.; Murray, B.; Rumsey, D. Energy density in cafeteria diet induced hyperphagia in the rat. Appetite 2009, 52, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothwell, N.J.; Stock, M.J. The cafeteria diet as a tool for studies of thermogenesis. J. Nutr. 1988, 118, 925–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, E.N.; Stampfer, M.J.; Curhan, G.C. Obesity, weight gain, and the risk of kidney stones. JAMA 2005, 293, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskaran, K.; Douglas, I.; Forbes, H.; Dos-Santos-Silva, I.; Leon, D.A.; Smeeth, L. Body-mass index and risk of 22 specific cancers: A population-based cohort study of 5·24 million UK adults. Lancet 2014, 384, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, M.; Pandeya, N.; Byrnes, G.; Renehan, A.G.; Stevens, G.A.; Ezzati, M.; Ferlay, J.; Miranda, J.J.; Romieu, I.; Dikshit, R.; et al. Global burden of cancer attributable to high body-mass index in 2012: A population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renehan, A.G.; Tyson, M.; Egger, M.; Heller, R.F.; Zwahlen, M. Body-mass index and incidence of cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective observational studies. Lancet 2008, 371, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.L.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Ma, J.Z.; Quarles, L.D.; Kovesdy, C.P. Association of body mass index with outcomes in patients with CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 2088–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovesdy, C.P.; Anderson, J.E.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Paradoxical Association between Body Mass Index and Mortality in Men with CKD Not Yet on Dialysis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2007, 49, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Kuwae, N.; Wu, D.Y.; Shantouf, R.S.; Fouque, D.; Anker, S.D.; Block, G.; Kopple, J.D. Associations of body fat and its changes over time with quality of life and prospective mortality in hemodialysis patients. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beddhu, S.; Pappas, L.M.; Ramkumar, N.; Samore, M. Effects of body size and body composition on survival in hemodialysis patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, 2366–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keaney, J.F.; Larson, M.G.; Vasan, R.S.; Wilson, P.W.F.; Lipinska, I.; Corey, D.; Massaro, J.M.; Sutherland, P.; Vita, J.A.; Benjamin, E.J. Obesity and systemic oxidative stress: Clinical correlates of oxidative stress in the Framingham study. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Nong, S.; Huang, X.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Lin, Y.; Man, Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, J.; Li, J. The effects of palmitate on hepatic insulin resistance are mediated by NADPH oxidase 3-derived reactive oxygen species through JNK and p38MAPKpathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 29965–29973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumashiro, N.; Tamura, Y.; Uchida, T.; Ogihara, T.; Fujitani, Y.; Hirose, T.; Mochizuki, H.; Kawamori, R.; Watada, H. Impact of oxidative stress and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator-1α in hepatic insulin resistance. Diabetes 2008, 57, 2083–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuzawa, N.; Takamura, T.; Kurita, S.; Misu, H.; Ota, T.; Ando, H.; Yokoyama, M.; Honda, M.; Zen, Y.; Nakanuma, Y.; et al. Lipid-induced oxidative stress causes steatohepatitis in mice fed an atherogenic diet. Hepatology 2007, 46, 1392–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, S.; Takamura, T.; Matsuzawa-Nagata, N.; Takayama, H.; Misu, H.; Noda, H.; Nabemoto, S.; Kurita, S.; Ota, T.; Ando, H.; et al. Palmitate induces insulin resistance in H4IIEC3 hepatocytes through reactive oxygen species produced by mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 14809–14818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.; Ballinger, S.W.; Messina, J.L. Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in Injury-Induced Insulin Resistance. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 25, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, N.C.; Croft, K.D. Hypertension and oxidative stress. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2006, 33, 872–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demerdash, H.M. Role of Oxidative Stress and Associated Alteration in Enzyme Activities in Obesity Comorbidities. Obes. Res. Open J. 2017, 4, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, S.; Fujita, T.; Shimabukuro, M.; Iwaki, M.; Yamada, Y.; Nakajima, Y.; Nakayama, O.; Makishima, M.; Matsuda, M.; Shimomura, I. Increased oxidative stress in obesity and its impact on metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 1752–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carillon, J.; Romain, C.; Bardy, G.; Fouret, G.; Feillet-Coudray, C.; Gaillet, S.; Lacan, D.; Cristol, J.P.; Rouanet, J.M. Cafeteria diet induces obesity and insulin resistance associated with oxidative stress but not with inflammation: Improvement by dietary supplementation with a melon superoxide dismutase. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 65, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigo, R.; Libuy, M.; Feliú, F.; Hasson, D. Oxidative stress-related biomarkers in essential hypertension and ischemia-reperfusion myocardial damage. Dis. Markers 2013, 35, 773–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassègue, B.; Griendling, K.K. Reactive oxygen species in hypertension: An update. Am. J. Hypertens. 2004, 17, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, A.R.; Wilkerson, M.D.; Sampey, B.P.; Troester, M.A.; Hayes, D.N.; Makowski, L. Cafeteria diet-induced obesity causes oxidative damage in white adipose. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 473, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, V. Regulation of JNK signaling by GSTp. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 1321–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tew, K.D.; Ronai, Z. GST function in drug and stress response. Drug Resist. Updat. 1999, 2, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranganathan, P.N.; Whalen, R.; Boyer, T.D. Characterization of the molecular forms of glutathione S-transferase P1 in human gastric cancer cells (Kato III) and in normal human erythrocytes. Biochem. J. 2005, 386, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K.; Uysal, K.T.; Hotamisligil, G.S.; Chang, L.; Tuncman, G.; Görgün, C.Z.; Hirosumi, J.; Karin, M. A central role for JNK in obesity and insulin resistance. Nature 2002, 420, 333–336. [Google Scholar]
- Solinas, G.; Becattini, B. JNK at the crossroad of obesity, insulin resistance, and cell stress response. Mol. Metab. 2017, 6, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmore, S. Apoptosis: A Review of Programmed Cell Death. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanasekaran, D.N.; Reddy, E.P. JNK signaling in apoptosis. Oncogene 2008, 27, 6245–6251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Goeddel, D.V. TNF-R1 signaling: A beautiful pathway. Science 2002, 296, 1634–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Nijhawan, D.; Budihardjo, I.; Srinivasula, S.M.; Ahmad, M.; Alnemri, E.S.; Wang, X. Cytochrome c and dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an apoptotic protease cascade. Cell 1997, 91, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.C.; Peng, C.C.; Hsieh, C.L.; Peng, R.Y. Exercise ameliorates renal cell apoptosis in chronic kidney disease by intervening in the intrinsic and the extrinsic apoptotic pathways in a rat model. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 368450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas, F.; Romecín, P.; García-Guillén, A.I.; Wangesteen, R.; Vargas-Tendero, P.; Paredes, M.D.; Atucha, N.M.; García-Estañ, J. Flavonoids in kidney health and disease. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, N.O.A.; Ahmed, L.A.; Abdallah, D.M.; El-Sayeh, B.M. Nephro-toxic effects of intraperitoneally injected EGCG in diabetic mice: Involvement of oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.H.; Sweet, D.H.; Lin, S.P.; Yu, C.P.; Chao, P.D.L.; Hou, Y.C. Green tea inhibited the elimination of nephro-cardiovascular toxins and deteriorated the renal function in rats with renal failure. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlberg, C.J.; Ou, J.J.; Babish, J.G.; Lamb, J.J.; Eliason, S.; Brabazon, H.; Gao, W.; Kaadige, M.R.; Tripp, M.L. A 13-week low glycemic load diet and lifestyle modification program combining low glycemic load protein shakes and targeted nutraceuticals improved weight loss and cardio-metabolic risk factors. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2017, 95, 1414–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babish, J.G.; Dahlberg, C.J.; Ou, J.J.; Keller, W.J.; Gao, W.; Kaadige, M.R.; Brabazon, H.; Lamb, J.; Soudah, H.C.; Kou, X.; et al. Synergistic in vitro antioxidant activity and observational clinical trial of F105, a phytochemical formulation including Citrus bergamia, in subjects with moderate cardiometabolic risk factors. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2016, 186, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernarelli, J.A.; Lambert, J.D. Flavonoid intake is inversely associated with obesity and C-reactive protein, a marker for inflammation, in US adults. Nutr. Diabetes 2017, 7, e276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Body Weight and Biochemical Profiles | CTR | BPF | CAF | BPF + CAF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body weight (g) | 466.0 ± 34.1 | 460.4 ± 49.6 | 615.0 ± 29.3 ** | 556.7 ± 55.7 # |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 230.0 ± 27.6 | 266.5 ± 28.4 | 350.86 ± 30.2 ** | 310.4 ± 47.6 # |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 57.0 ± 18.7 | 55.0 ± 23.6 | 86.3 ± 14.6 * | 61.9 ± 14.6 ## |
| Cholesterol, total (mg/dL) | 92.8 ± 12.2 | 89.2 ± 12.0 | 90.5 ± 11.8 | 73 ± 11.7 # |
| HDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 63.6 ± 11.2 | 63.4 ± 12.0 | 61.6 ± 9.3 | 50.8 ± 4.9 # |
| LDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 25.2 ± 9.2 | 19 ± 7.9 * | 18.1 ± 5.7 * | 13.1 ± 4.7 # |
| Creatinin (mg/dL) | 0.8 ± 0.12 | 0.74 ± 0.11 | 0.8 ± 0.08 | 0.8 ± 0.07 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
La Russa, D.; Giordano, F.; Marrone, A.; Parafati, M.; Janda, E.; Pellegrino, D. Oxidative Imbalance and Kidney Damage in Cafeteria Diet-Induced Rat Model of Metabolic Syndrome: Effect of Bergamot Polyphenolic Fraction. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8030066
La Russa D, Giordano F, Marrone A, Parafati M, Janda E, Pellegrino D. Oxidative Imbalance and Kidney Damage in Cafeteria Diet-Induced Rat Model of Metabolic Syndrome: Effect of Bergamot Polyphenolic Fraction. Antioxidants. 2019; 8(3):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8030066
Chicago/Turabian StyleLa Russa, Daniele, Francesca Giordano, Alessandro Marrone, Maddalena Parafati, Elzbieta Janda, and Daniela Pellegrino. 2019. "Oxidative Imbalance and Kidney Damage in Cafeteria Diet-Induced Rat Model of Metabolic Syndrome: Effect of Bergamot Polyphenolic Fraction" Antioxidants 8, no. 3: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8030066
APA StyleLa Russa, D., Giordano, F., Marrone, A., Parafati, M., Janda, E., & Pellegrino, D. (2019). Oxidative Imbalance and Kidney Damage in Cafeteria Diet-Induced Rat Model of Metabolic Syndrome: Effect of Bergamot Polyphenolic Fraction. Antioxidants, 8(3), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8030066