Physical Exercise Alleviates Oxidative Stress and Autonomic Dysregulation in a Rat Model of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Ethical Approval
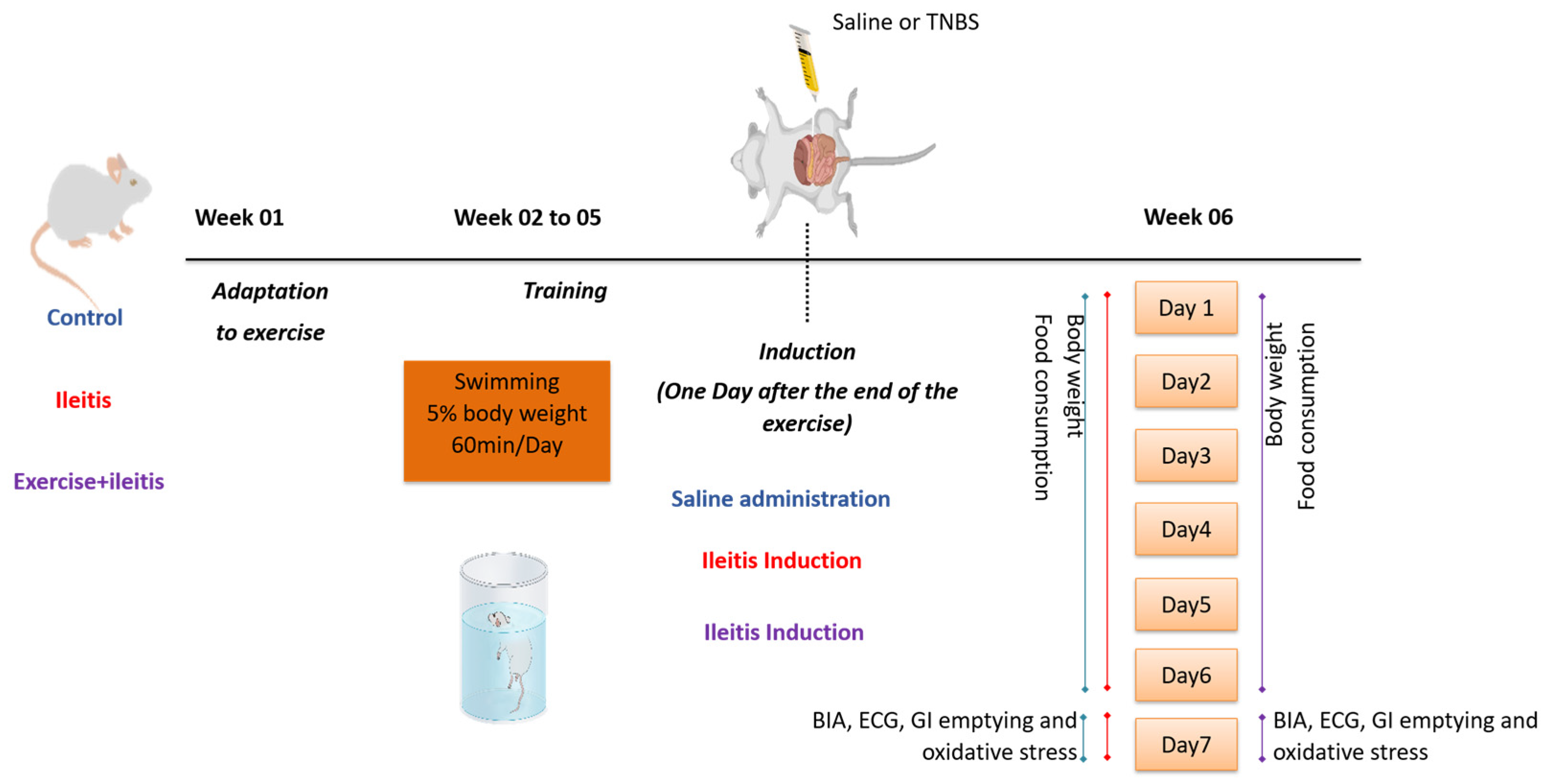
2.2. Physical Exercise Protocol
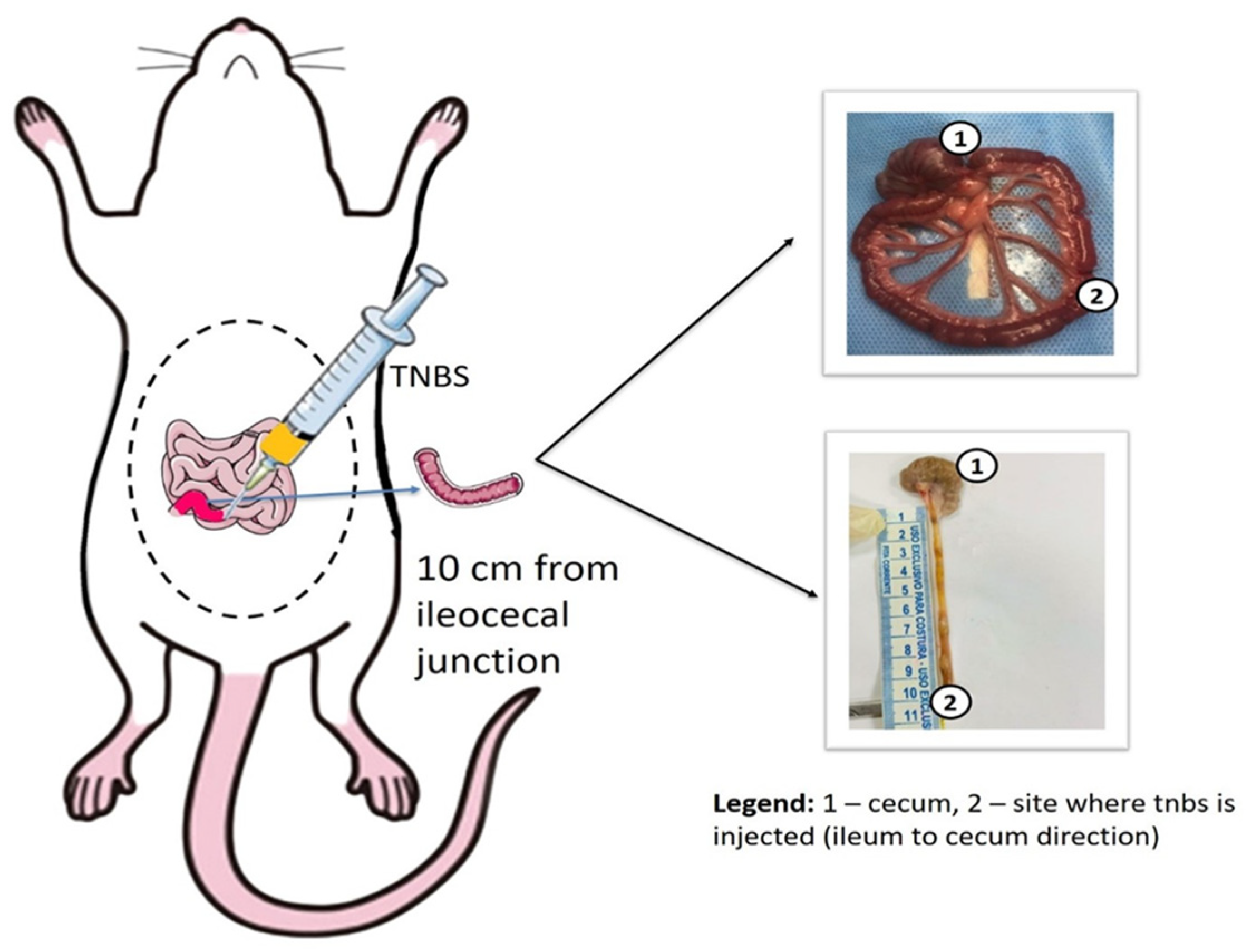
2.3. Ileitis Induction Model
2.4. Assessment of Feed Intake Behavior
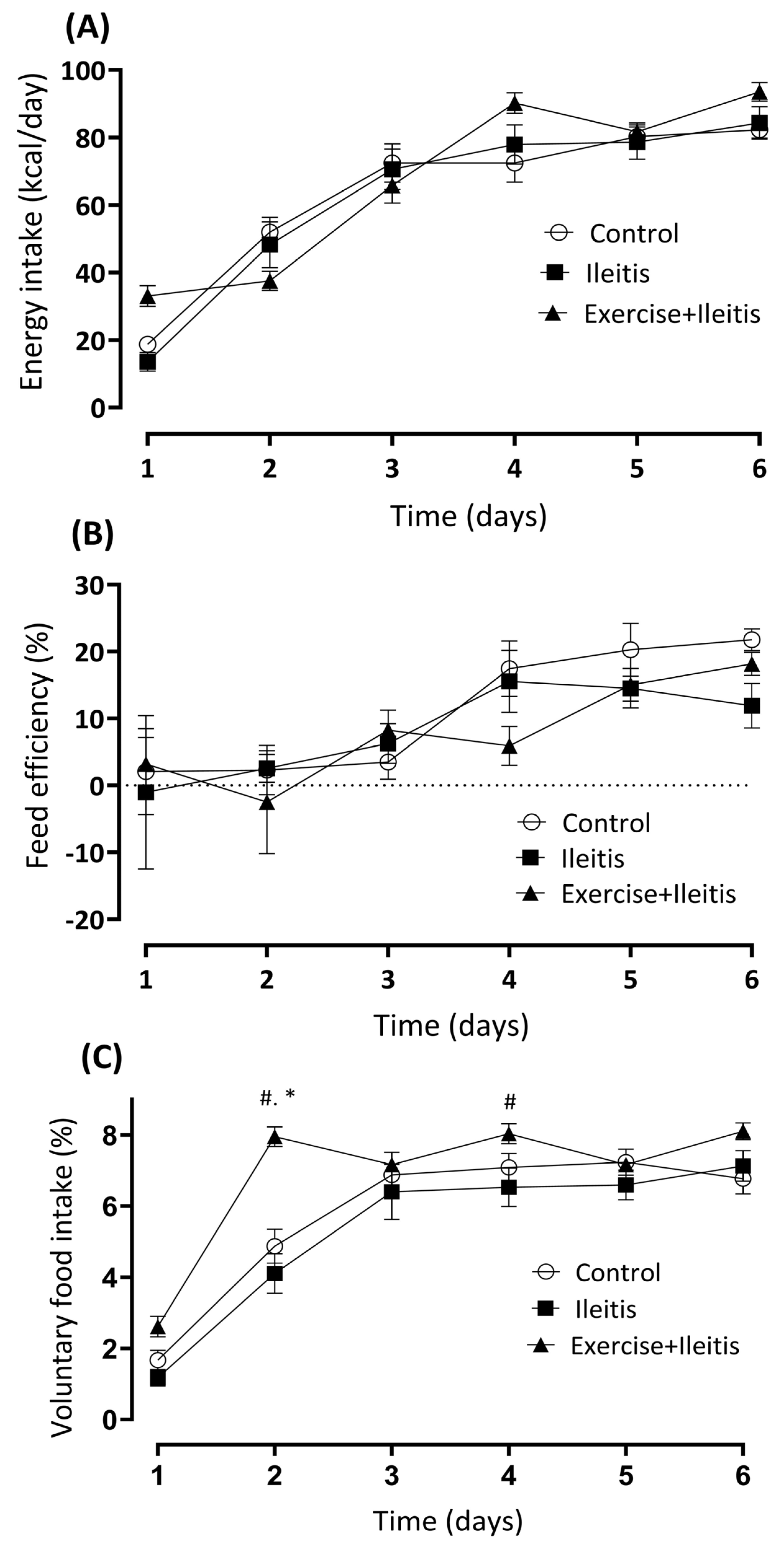
- Energy intake (EI, kcal/day) = average food consumption (g) × dietary metabolizable energy (kcal);
- Feed efficiency (FE, %) = (average body weight gain (g) × 100)/energy intake (kcal/day);
- Voluntary food intake (VFI, %) = (average food intake × 100)/average body weight.
2.5. Body Composition Assessment
2.6. Assessment of Gastrointestinal Motility
2.7. Malondialdehyde (MDA) Assessment
2.8. Glutathione (GSH) Analysis
2.9. Nitrite/Nitrate (NOx) Evaluation
2.10. Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) Levels
2.11. Assessment of the Weight of Organs and Tissues
2.12. Cardiac Activity and HRV Assessment
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
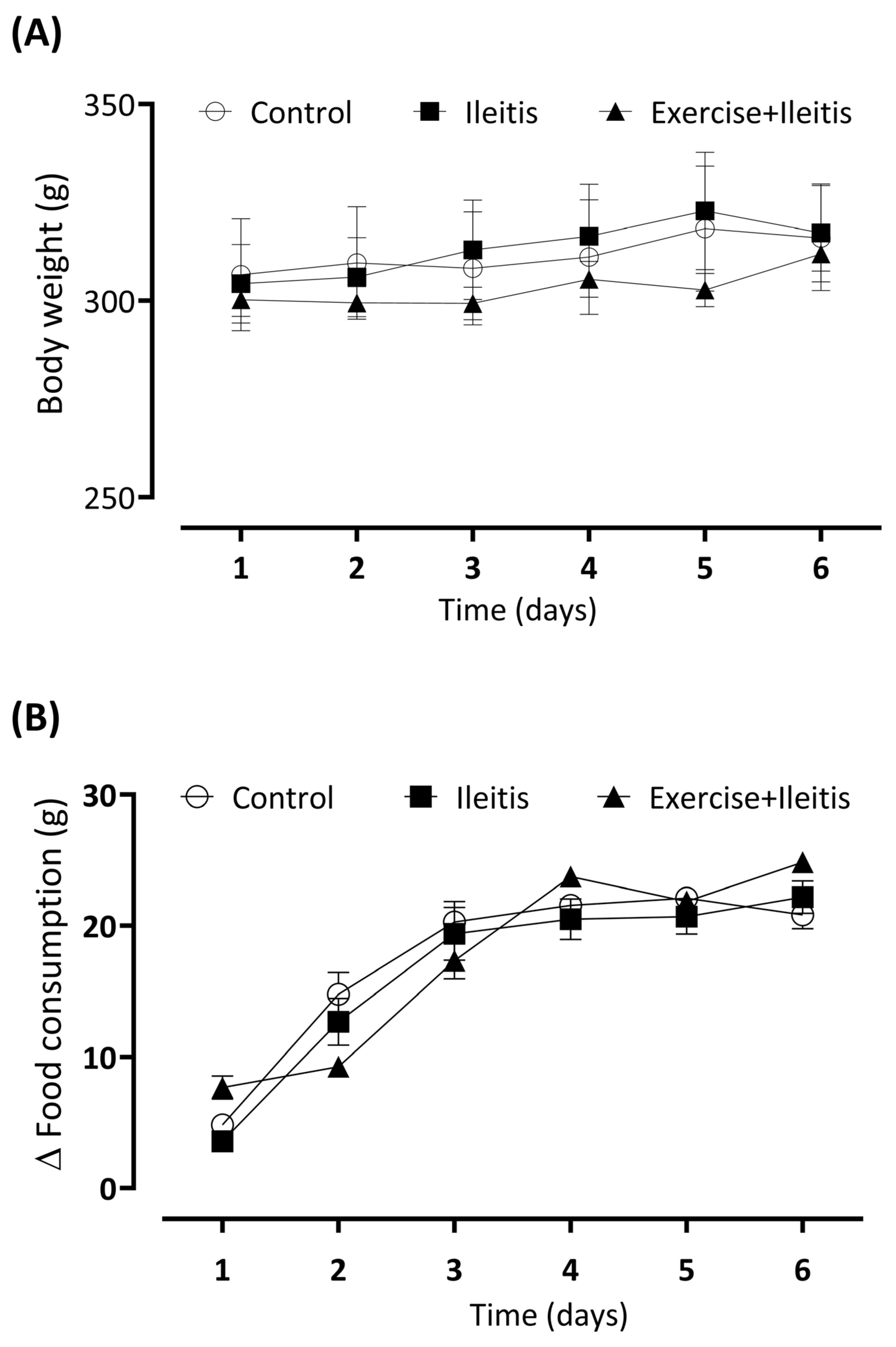
3.1. Body Weight and Daily Consumption
3.2. Nutritional Parameters
3.3. Body Composition Assessment
3.4. Gastrointestinal Parameters
3.5. Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress
3.6. Weight of the Gastrointestinal Tissue and Heart
3.7. Electrocardiogram (ECG)
3.8. Heart Rate Variability (HRV)
3.9. Linear Correlation of Heart Rate Variability and Gastrointestinal Motility
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IBD | Inflammatory bowel disease |
| GI | Gastrointestinal |
| TNBS | 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid |
| ECG | Electrocardiogram |
| TBW | Total body water |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| FFM | Fat-free mass |
| GIT | Gastrointestinal tract |
| UC | Ulcerative colitis |
| CD | Crohn’s disease |
| HPA | Hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal |
| ANS | Autonomic nervous system |
| ENS | Enteric nervous system |
| SNS | Sympathetic nervous system |
| PNS | Parasympathetic nervous system |
| HRV | Heart rate variability |
| CEUA | Ethics Committee on Animal Use |
| EI | Energy intake |
| FE | Feed efficiency |
| VFI | Voluntary food intake |
| BIS | Bioimpedance spectroscopy |
| FM | Fat mass |
| ECF | Extracellular fluid |
| ICF | Intracellular fluid |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| NPSH | Non-protein sulfhydryl |
| TCA | Trichloroacetic acid |
| DTNB | Dithiol-nitrobenzoic acid |
| NOx | Nitrite/nitrate |
| KCl | Potassium chloride |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| FFT | Fourier transformation |
| LF | Low frequency |
| HF | High frequency |
| RMSSD | Square root of the mean squares of the differences between adjacent regular RR intervals |
| SDRR | Standard deviation of regular RR intervals |
| GPx | Glutathione peroxidase |
| HR | Heart rate |
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| DOAJ | Directory of open access journals |
| TLA | Three letter acronym |
| LD | Linear dichroism |
References
- Arosa, L.; Camba-Gómez, M.; Golubnitschaja, O.; Conde-Aranda, J. Predictive, preventive and personalised approach as a conceptual and technological innovation in primary and secondary care of inflammatory bowel disease benefiting affected individuals and populations. EPMA J. 2024, 15, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd-Price, J.; Arze, C.; Ananthakrishnan, A.N.; Schirmer, M.; Avila-Pacheco, J.; Poon, T.W.; Andrews, E.; Ajami, N.J.; Bonham, K.S.; Brislawn, C.J.; et al. Multi-omics of the gut microbial ecosystem in inflammatory bowel diseases. Nature 2019, 569, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavakoli, P.; Vollmer-Conna, U.; Hadzi-Pavlovic, D.; Grimm, M.C. A review of inflammatory bowel disease: A model of microbial, immune and neuropsychological integration. Public Health Rev. 2021, 42, 1603990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severo, J.S.; Barros, V.J.S.; Mendes, P.H.M.; Santos, B.L.B.; Silva, A.C.A.; Oliveira, K.B.V.; Moura, M.S.B.; Viola, P.C.A.F.; Nogueira, N.N.; Parente, J.M.L.; et al. Phase angle values and ultra-processed food consumption are associated with changes in oxidative stress in inflammatory bowel disease patients. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2023, 57, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaz, B.; Sinniger, V.; Pellissier, S. Therapeutic potential of vagus nerve stimulation for inflammatory bowel diseases. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 650971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallrapp, A.; Isaac, M.C. Neuroimmune Interactions in the Intestine. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2024, 42, 489–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Collen, L.V.; Mowat, C.; Isaacs, K.L.; Singh, S.; Kane, S.V.; Farraye, F.A.; Snapper, S.; Jneid, H.; Lavie, C.J.; et al. Inflammatory bowel disease and cardiovascular diseases. Am. J. Med. 2022, 135, 1453–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaz, B.; Bernstein, C.N. Brain-gut interactions in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Guo, J.; Liu, J.; Lyu, B.; Foreman, R.D.; Yin, J.; Shi, Z.; Chen, J.D.Z. Anti-inflammatory effects and mechanisms of vagal nerve stimulation combined with electroacupuncture in a rodent model of TNBS-induced colitis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2017, 313, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciesielczyk, K.; Furgała, A.; Dobrek, Ł.; Juszczak, K.; Thor, P. Altered sympathovagal balance and pain hypersensitivity in TNBS-induced colitis. Arch. Med. Sci. 2017, 13, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowski, A.; Dunlap, C.; Lacombe, A.; Hanes, D. Alterations in Heart Rate Variability Associated With Irritable Bowel Syndrome or Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2020, 12, e00275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaskova, E.; Velganova-Veghova, M.; Geryk, M.; Foltenova, H.; Kucerova, V.; Karasek, D. Role of Adipose Tissue in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadgar, N.; Altemus, J.; Li, Y.; Lightner, A.L. Effect of Crohn’s disease mesenteric mesenchymal stem cells and their extracellular vesicles on T-cell immunosuppressive capacity. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 4924–4939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Si, X.; Yang, L.; Wang, H.; Sun, Y.; Liu, N. Association between intestinal microbiota and inflammatory bowel disease. Anim. Model. Exp. Med. 2022, 5, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, F.; de Souza, H.S.P. Dietary Composition and Effects in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawley, J.A.; Forster, S.C.; Giles, E.M. Exercise, Gut Microbiome, and Gastrointestinal Diseases: Therapeutic Impact and Molecular Mechanisms. Gastroenterology 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zholos, A.V.; Melnyk, M.I.; Dryn, D.O. Molecular mechanisms of cholinergic neurotransmission in visceral smooth muscles with a focus on receptor-operated TRPC4 channel and impairment of gastrointestinal motility by general anaesthetics and anxiolytics. Neuropharmacology 2024, 242, 109776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.O.; Cardoso, G.S.; Lima, L.C.; Cavalcante, M.L.S.; Silva, M.S.; Cavalcante, A.K.M.; Severo, J.S.; Sousa, F.B.M.; Pacheco, G.; Alves, E.H.P.; et al. L-glutamine and physical exercise prevent intestinal inflammation and oxidative stress without improving gastric dysmotility in rats with ulcerative colitis. Inflammation 2021, 44, 617–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, T.C.; Barbosa, M.A.; Costa, D.C.; Becker, L.K.; Cardoso, L.M.; Alzamora, A.C. Fitness is improved by adjustments in muscle intracellular signaling in rats with renovascular hypertension 2K1C undergoing voluntary physical exercise. Life Sci. 2020, 250, 117549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, C.; Magalhães-Cardoso, M.T.; Ferreirinha, F.; Silva, I.; Dias, A.S.; Pelletier, J.; Sévigny, J.; Correia-de-Sá, P. Feed-forward inhibition of CD73 and upregulation of adenosine deaminase contribute to the loss of adenosine neuromodulation in postinflammatory ileitis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 254640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, C.; Ferreirinha, F.; Magalhães-Cardoso, M.T.; Silva, I.; Marques, P.; Correia-de-Sá, P. Post-inflammatory Ileitis Induces Non-neuronal Purinergic Signaling Adjustments of Cholinergic Neurotransmission in the Myenteric Plexus. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontell, L.; Castelucci, P.; Bagyánszki, M.; Jovic, T.; Thacker, M.; Nurgali, K.; Bron, R.; Furness, J.B. Structural changes in the epithelium of the small intestine and immune cell infiltration of enteric ganglia following acute mucosal damage and local inflammation. Virchows Arch. 2009, 455, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, W.L.L.; da Silva Pinheiro, C.; de Oliveira Santos, R.; da Silva, A.C.A.; Severo, J.S.; Mendes, P.H.M.; de Sousa, L.C.; de Sousa, O.M.C.; dos Santos, B.L.B.; de Oliveira, K.B.V.; et al. Physical exercise alleviates oxidative stress in brown adipose tissue and causes changes in body composition and nutritional behavior in rats with polycystic ovary syndrome. Life Sci. 2023, 325, 121754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.; Johnson, M., Jr.; Nagy, T. Precision and accuracy of bioimpedance spectroscopy for determination of in vivo body composition in rats. Int. J. Body Compos. Res. 2009, 7, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Reynell, P.C.; Spray, G.H. The simultaneous measurement of absorption and transit in the gastro-intestinal tract of the rat. J. Physiol. 1956, 131, 452–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, P.P.; Christensen, R.D.; Rothstein, G. Cellular and extracellular myeloperoxidase in pyogenic inflammation. Blood 1982, 60, 618–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlak, J.; Lindsay, R.H. Estimation of total, protein-bound, and nonprotein sulfhydryl groups in tissue with Ellman’s reagent. Anal. Biochem. 1968, 25, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapil, V.; Khambata, R.S.; Jones, D.A.; Rathod, K.; Primus, C.; Massimo, G.; Fukuto, J.M.; Ahluwalia, A. The Noncanonical Pathway for In Vivo Nitric Oxide Generation: The Nitrate-Nitrite-Nitric Oxide Pathway. Pharmacol. Rev. 2020, 72, 692–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, N.S.; Grisham, M.B. Methods to detect nitric oxide and its metabolites in biological samples. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 43, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, J.F.; Janero, D.R. Microplate superoxide dismutase assay employing a nonenzymatic superoxide generator. Anal. Biochem. 1995, 232, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, E.B.; Oliveira, L.C.S.; Cardoso, G.S.; Telles, P.V.N.; Lima, L.C.; Sousa, J.F.R.; Araújo, R.P.N.; Oliveira, A.P.; Santos, R.F.; Santos, A.A.; et al. Moderate-intensity exercise and renin-angiotensin system blockade improve renovascular hypertension (2K1C)-induced gastric dysmotility in rats. Life Sci. 2018, 1, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Ojaimi, Y.; Khachab, M.; Bazzi, S.; Bahr, G.M.; Echtay, K.S. Mitochondrial bioenergetics, uncoupling protein-2 activity, and reactive oxygen species production in the small intestine of a TNBS-induced colitis rat model. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2020, 470, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Arthur, S.; Sundaram, U. Mechanisms of Regulation of Transporters of Amino Acid Absorption in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Com. Physiol. 2020, 10, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, G.W.; Thapaliya, G. The Gut-Brain Axis and Its Role in Controlling Eating Behavior in Intestinal Inflammation. Nutrients 2021, 13, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourad, F.H.; Barada, K.A.; Saade, N.E. Impairment of Small Intestinal Function in Ulcerative Colitis: Role of Enteric Innervation. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2017, 11, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, J.; Beglinger, C.; Holst, J.J.; Andresen, V.; Layer, P. Mechanisms of gastric emptying disturbances in chronic and acute inflammation of the distal gastrointestinal tract. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2009, 297, G861–G868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nóbrega, A.C.; Ferreira, B.R.; Oliveira, G.J.; Sales, K.M.; Santos, A.A.; Souza, M.A.N.E.; Braga, L.L.B.C.B.; Troncon, L.E.A.; Souza, M.H.L.P. Dyspeptic symptoms and delayed gastric emptying of solids in patients with inactive Crohn’s disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 2012, 12, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales, K.M.O.; Cavalcanti, R.F.; Nobre, E.; Souza, M.A.; Saraiva, L.G.M.; Braga, L.L.B.C.; Castro, M.; Oliveira, R.B.; Souza, M.H.L.P. Gastroduodenal Symptoms in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Are Correlated with Gastric Emptying and Serum Levels of Active Ghrelin. Dig. Dis. 2019, 37, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damião, A.O.; Sipahi, A.M.; Vezozzo, D.P.; Gonçalves, P.L.; Laudanna, A.A. Measurement of gastric emptying time by real-time ultrasonography in patients with Crohn’s disease. Rev. Hosp. Das Clin. 1996, 51, 154–156. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, J.; Binnewies, U.; Rösch, M.; Juul Holst, J.; Beglinger, C.; Andresen, V.; Layer, P. Gastric emptying and disease activity in inflammatory bowel disease. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 45, 1234–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassotti, G.; Antonelli, E.; Villanacci, V.; Nascimbeni, R.; Dore, M.P.; Pes, G.M.; Maconi, G. Abnormal gut motility in inflammatory bowel disease: An update. Tech. Coloproctology 2020, 24, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, R.K.; Guo, Y.; Mashimo, H. Advances in the physiology of gastric emptying. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2019, 31, e13546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakin, R.; Guzman, C.; Izaddoustdar, F.; Polidovitch, N.; Goodman, J.M.; Backx, P.H. Changes in Heart Rate and Its Regulation by the Autonomic Nervous System Do Not Differ Between Forced and Voluntary Exercise in Mice. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, D.K.; Heilmann, R.M.; Paital, B.; Patel, A.; Yadav, V.K.; Wong, D.; Jergens, A.E. Oxidative stress, hormones, and effects of natural antioxidants on intestinal inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1217165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgonje, A.R.; Feelisch, M.; Faber, K.N.; Pasch, A.; Dijkstra, G.; van Goor, H. Oxidative Stress and Redox-Modulating Therapeutics in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Trends Mol. Med. 2020, 26, 1034–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakutis, F.S.; Nishitokukado, I.; Dos Santos, F.M.; Ortiz-Agostinho, C.L.; de Alencar, D.T.; Achtschin, C.G.; Nunes, V.S.; Leite, A.Z.A.; Sipahi, A.M. Evaluation of oxidative stress in an experimental model of Crohn’s disease treated with hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Clinics 2023, 78, 100305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, A.M.; Bon-Frauches, A.C.; Keszthelyi, D.; Melotte, V.; Boesmans, W. The enteric nervous system in gastrointestinal disease etiology. Cell Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2021, 78, 4713–4733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamalian, A.; Asl, M.S.; Dolatshahi, M.; Afshari, K.; Shamshiri, S.; Roudsari, N.M.; Momtaz, S.; Rahimi, R.; Abdollahi, M.; Abdolghaffari, A.H. Interventions of natural and synthetic agents in inflammatory bowel disease, modulation of nitric oxide pathways. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 3365–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, S.A.; Mirza, U.A.; Patrick, J.M. Influence of sex and sedentary conditions on sympathetic burst characteristics in prepubertal, postpubertal, and young adult rats. J. Appl. Physiol. 2024, 136, 1170–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, J.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, C.; Hu, J.; Liu, C. Effects of Physical Exercise on the Microbiota in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.; Zhu, C.; Zhou, X.; Zeng, Q.; Huang, L.; Cao, X.; Zhou, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Huang, J.; Liu, J.; et al. Effect of Physical Activity on the Association Between Diet and Constipation: Evidence From the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007-2010. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2024, 30, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falz, R.; Bischoff, C.; Thieme, R.; Lässing, J.; Mehdorn, M.; Stelzner, S.; Busse, M.; Gockel, I. Effects and duration of exercise-based rehabilitation in surgical therapy of colon and rectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 148, 2187–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.C.; Compton, S.L.E.; Meyerhardt, J.A.; Spielmann, G.; Yang, S. The dose-response effect of aerobic exercise on inflammation in colon cancer survivors. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1257767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.N.; Yao, Y.; Ju, S.Y. Heart rate variability and inflammatory bowel disease in humans: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2020, 99, e23430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghdasi-Bornaun, H.; Kutluk, G.; Keskindemirci, G.; Öztarhan, K.; Dedeoğlu, R.; Yılmaz, N.; Tosun, Ö. Evaluation of autonomic nervous system functions in the frame of heart rate variability in children with inflammatory bowel disease in remission. Turk. J. Pediatr. 2018, 60, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunterberg, V.; Simrén, M.; Öhman, L.; Friberg, P.; Jones, M.P.; Van Oudenhove, L.; Strid, H. Autonomic nervous system function predicts the inflammatory response over three years in newly diagnosed ulcerative colitis patients. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2016, 11, 1655–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornaro, R.; Actis, G.C.; Caviglia, G.P.; Pitoni, D.; Ribaldone, D.G. Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Role of Vagus Nerve Stimulation. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Makharia, G.K.; Ahuja, V.; Dwivedi, S.N.; Deepak, K.K. Autonomic dysfunctions in patients with inflammatory bowel disease in clinical remission. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2009, 54, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coruzzi, P.; Castiglioni, P.; Parati, G.; Brambilla, V.; Brambilla, L.; Gualerzi, M.; Cademartiri, F.; Franzè, A.; De Angelis, G.; Di Rienzo, M.; et al. Autonomic cardiovascular regulation in quiescent ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 37, 964–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirillo, G.; Negrete-Diaz, F.; Daniela, Y.; Virtuoso, A.; Korai, S.A.; Luca, C.D.; Kaniusas, E.; Papa, M.; Panetsos, F. Vagus Nerve Stimulation: A Personalized Therapeutic Approach for Crohn’s and Other Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Cells 2022, 24, 4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eser, P.; Jaeger, E.; Marcin, T.; Herzig, D.; Trachsel, L.D.; Wilhelm, M. Acute and chronic effects of high-intensity interval and moderate-intensity continuous exercise on heart rate and its variability after recent myocardial infarction: A randomized controlled trial. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2022, 65, 101444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, C.F.; Filippone, R.T.; Stavely, R.; Bornstein, J.C.; Apostolopoulos, V.; Nurgali, K. Neuroinflammation as an etiological trigger for depression comorbid with inflammatory bowel disease. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pergolizzi, S.; Alesci, A.; Centofanti, A.; Aragona, M.; Pallio, S.; Magaudda, L.; Cutroneo, G.; Lauriano, E.R. Role of Serotonin in the Maintenance of Inflammatory State in Crohn’s Disease. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilski, J.; Mazur-Bialy, A.I.; Brzozowski, B.; Magierowski, M.; Jasnos, K.; Krzysiek-Maczka, G.; Urbanczyk, K.; Ptak-Belowska, A.; Zwolinska-Wcislo, M.; Mach, T.; et al. Moderate exercise training attenuates the severity of experimental rodent colitis: The importance of crosstalk between adipose tissue and skeletal muscles. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 605071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.Y.; Hsieh, P.L.; Hsiao, S.F.; Chien, M.Y. Effects of Exercise Training on Autonomic Function in Chronic Heart Failure: Systematic Review. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 591708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
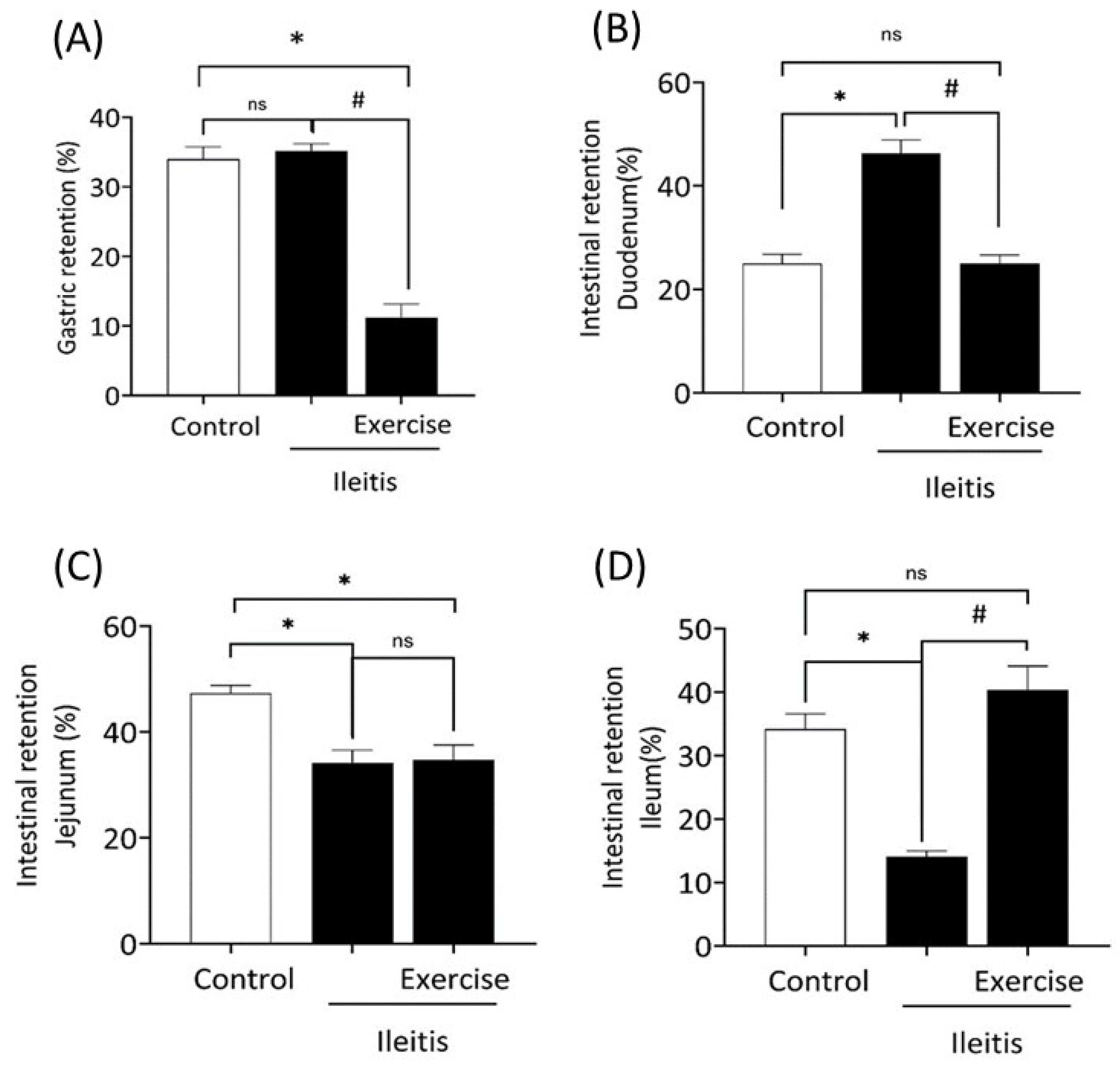

 ). In boxes (A,B), LF correlation between gastric retention in all groups; in boxes (C,D) HF correlation between gastric retention in all groups; and in boxes (E,F) LF/HF correlation between gastric retention in all groups. Each data point indicates one animal. Pearson correlation was used for r and p values.
). In boxes (A,B), LF correlation between gastric retention in all groups; in boxes (C,D) HF correlation between gastric retention in all groups; and in boxes (E,F) LF/HF correlation between gastric retention in all groups. Each data point indicates one animal. Pearson correlation was used for r and p values.
 ). In boxes (A,B), LF correlation between gastric retention in all groups; in boxes (C,D) HF correlation between gastric retention in all groups; and in boxes (E,F) LF/HF correlation between gastric retention in all groups. Each data point indicates one animal. Pearson correlation was used for r and p values.
). In boxes (A,B), LF correlation between gastric retention in all groups; in boxes (C,D) HF correlation between gastric retention in all groups; and in boxes (E,F) LF/HF correlation between gastric retention in all groups. Each data point indicates one animal. Pearson correlation was used for r and p values.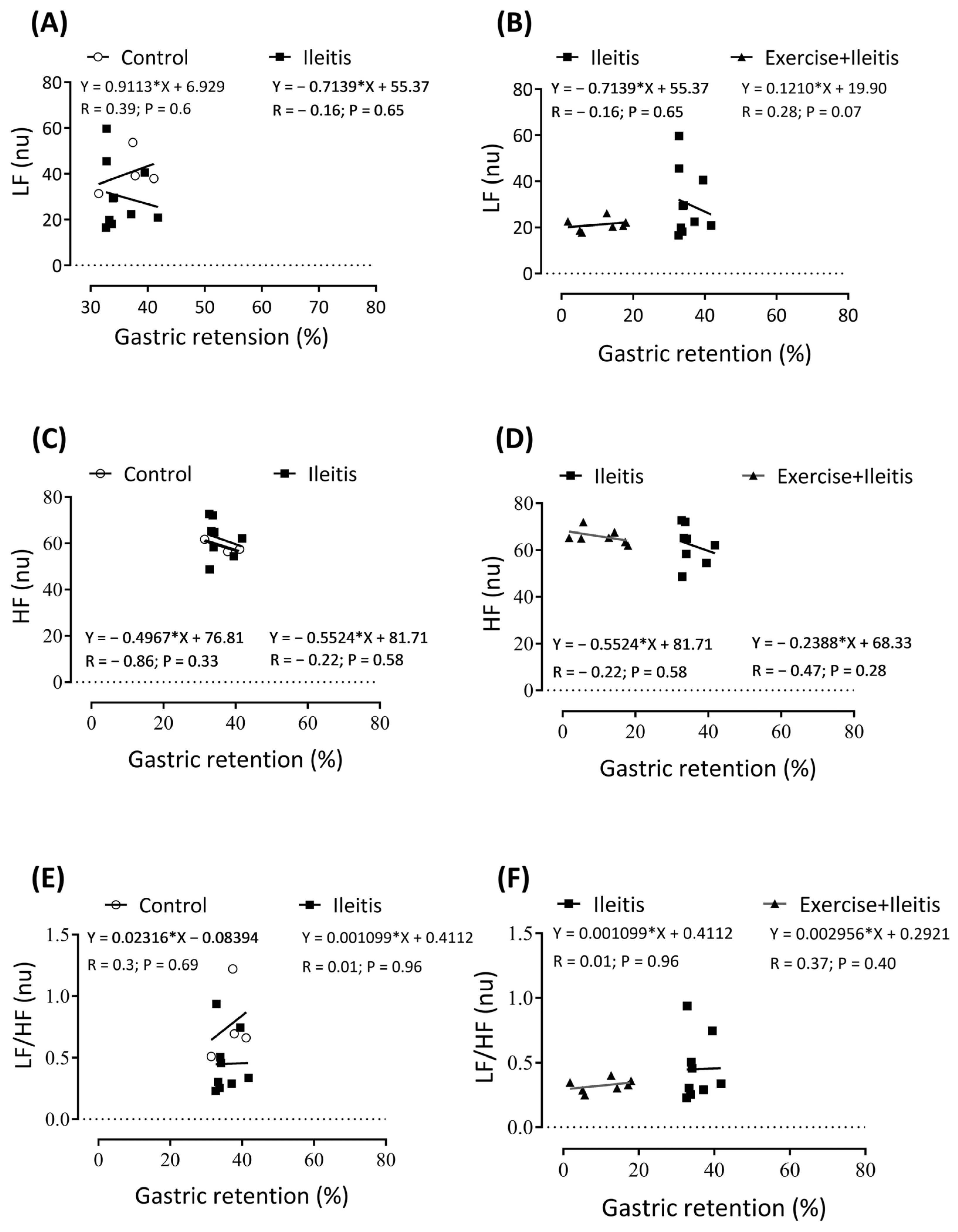
 ). In boxes (A,B) LF correlation between intestinal retention duodenum in all groups, in boxes (C,D) HF correlation between intestinal retention duodenum in all groups, and boxes (E,F) LF/HF correlation between intestinal retention duodenum in all groups. Each data point indicates one individual. Sinificance was found in (C,D) at p < 0.05. Pearson correlation was used for r and p values.
). In boxes (A,B) LF correlation between intestinal retention duodenum in all groups, in boxes (C,D) HF correlation between intestinal retention duodenum in all groups, and boxes (E,F) LF/HF correlation between intestinal retention duodenum in all groups. Each data point indicates one individual. Sinificance was found in (C,D) at p < 0.05. Pearson correlation was used for r and p values.
 ). In boxes (A,B) LF correlation between intestinal retention duodenum in all groups, in boxes (C,D) HF correlation between intestinal retention duodenum in all groups, and boxes (E,F) LF/HF correlation between intestinal retention duodenum in all groups. Each data point indicates one individual. Sinificance was found in (C,D) at p < 0.05. Pearson correlation was used for r and p values.
). In boxes (A,B) LF correlation between intestinal retention duodenum in all groups, in boxes (C,D) HF correlation between intestinal retention duodenum in all groups, and boxes (E,F) LF/HF correlation between intestinal retention duodenum in all groups. Each data point indicates one individual. Sinificance was found in (C,D) at p < 0.05. Pearson correlation was used for r and p values.
 ). In boxes (A,B) is the LF correlation between intestinal retention jejunum in all groups, in boxes (C,D) HF correlation between intestinal retention jejunum in all groups, and in boxes (E,F) LF/HF correlation between intestinal retention jejunum in all groups. Each data point indicates one individual. Significance was found in (D) at p < 0.05. Pearson correlation was used for r and p values.
). In boxes (A,B) is the LF correlation between intestinal retention jejunum in all groups, in boxes (C,D) HF correlation between intestinal retention jejunum in all groups, and in boxes (E,F) LF/HF correlation between intestinal retention jejunum in all groups. Each data point indicates one individual. Significance was found in (D) at p < 0.05. Pearson correlation was used for r and p values.
 ). In boxes (A,B) is the LF correlation between intestinal retention jejunum in all groups, in boxes (C,D) HF correlation between intestinal retention jejunum in all groups, and in boxes (E,F) LF/HF correlation between intestinal retention jejunum in all groups. Each data point indicates one individual. Significance was found in (D) at p < 0.05. Pearson correlation was used for r and p values.
). In boxes (A,B) is the LF correlation between intestinal retention jejunum in all groups, in boxes (C,D) HF correlation between intestinal retention jejunum in all groups, and in boxes (E,F) LF/HF correlation between intestinal retention jejunum in all groups. Each data point indicates one individual. Significance was found in (D) at p < 0.05. Pearson correlation was used for r and p values.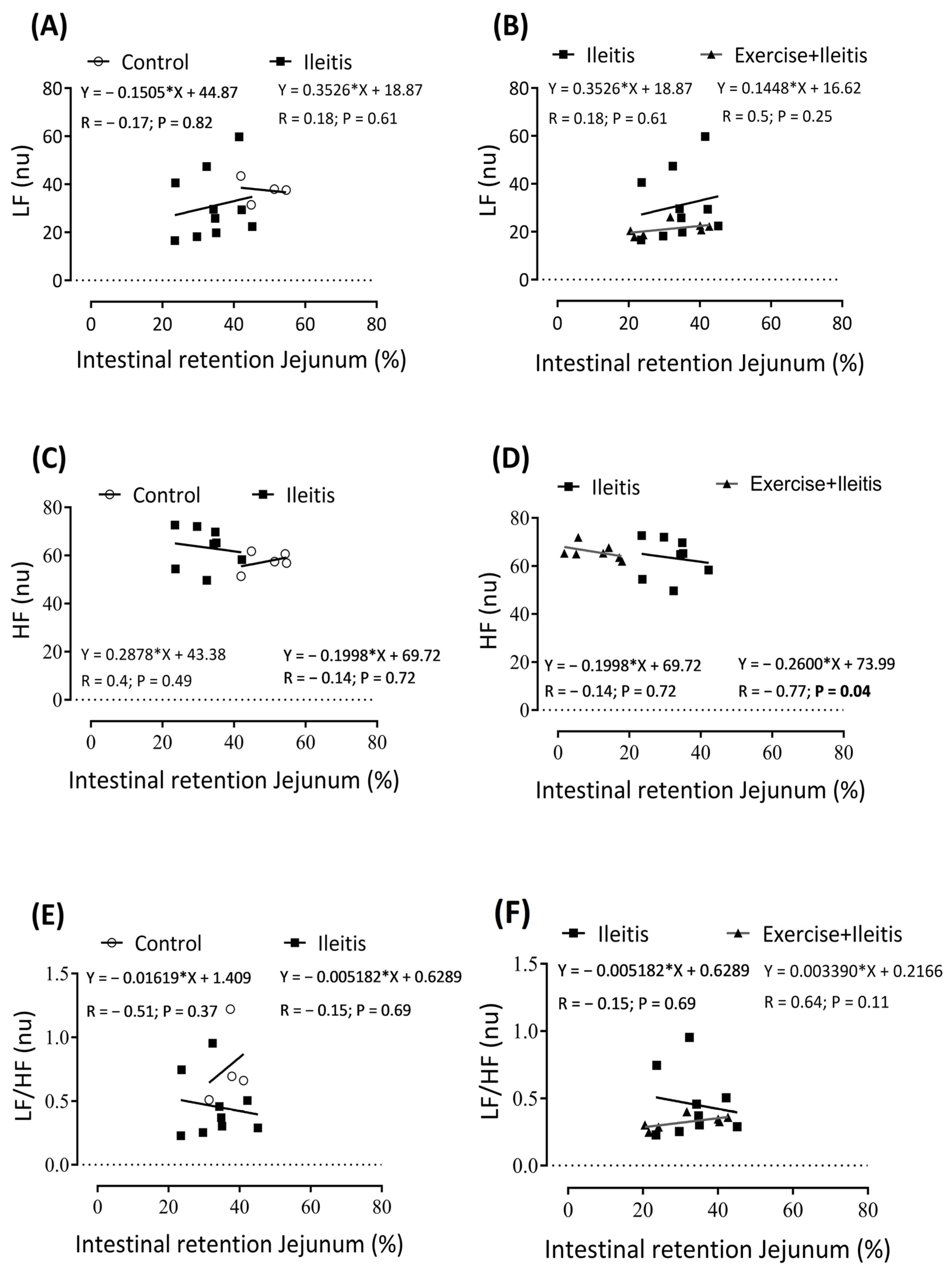
 ). In boxes (A,B) L, LF correlation between intestinal retention ileum in all groups; in boxes (C,D), HF correlation between intestinal retention ileum in all groups; and in boxes (E,F), LF/HF correlation between intestinal retention ileum in all groups. Each data point indicates one individual. Significance was found in (LF) in the ileitis group (A,B) at p < 0.05. Pearson correlation was used for r and p values.
). In boxes (A,B) L, LF correlation between intestinal retention ileum in all groups; in boxes (C,D), HF correlation between intestinal retention ileum in all groups; and in boxes (E,F), LF/HF correlation between intestinal retention ileum in all groups. Each data point indicates one individual. Significance was found in (LF) in the ileitis group (A,B) at p < 0.05. Pearson correlation was used for r and p values.
 ). In boxes (A,B) L, LF correlation between intestinal retention ileum in all groups; in boxes (C,D), HF correlation between intestinal retention ileum in all groups; and in boxes (E,F), LF/HF correlation between intestinal retention ileum in all groups. Each data point indicates one individual. Significance was found in (LF) in the ileitis group (A,B) at p < 0.05. Pearson correlation was used for r and p values.
). In boxes (A,B) L, LF correlation between intestinal retention ileum in all groups; in boxes (C,D), HF correlation between intestinal retention ileum in all groups; and in boxes (E,F), LF/HF correlation between intestinal retention ileum in all groups. Each data point indicates one individual. Significance was found in (LF) in the ileitis group (A,B) at p < 0.05. Pearson correlation was used for r and p values.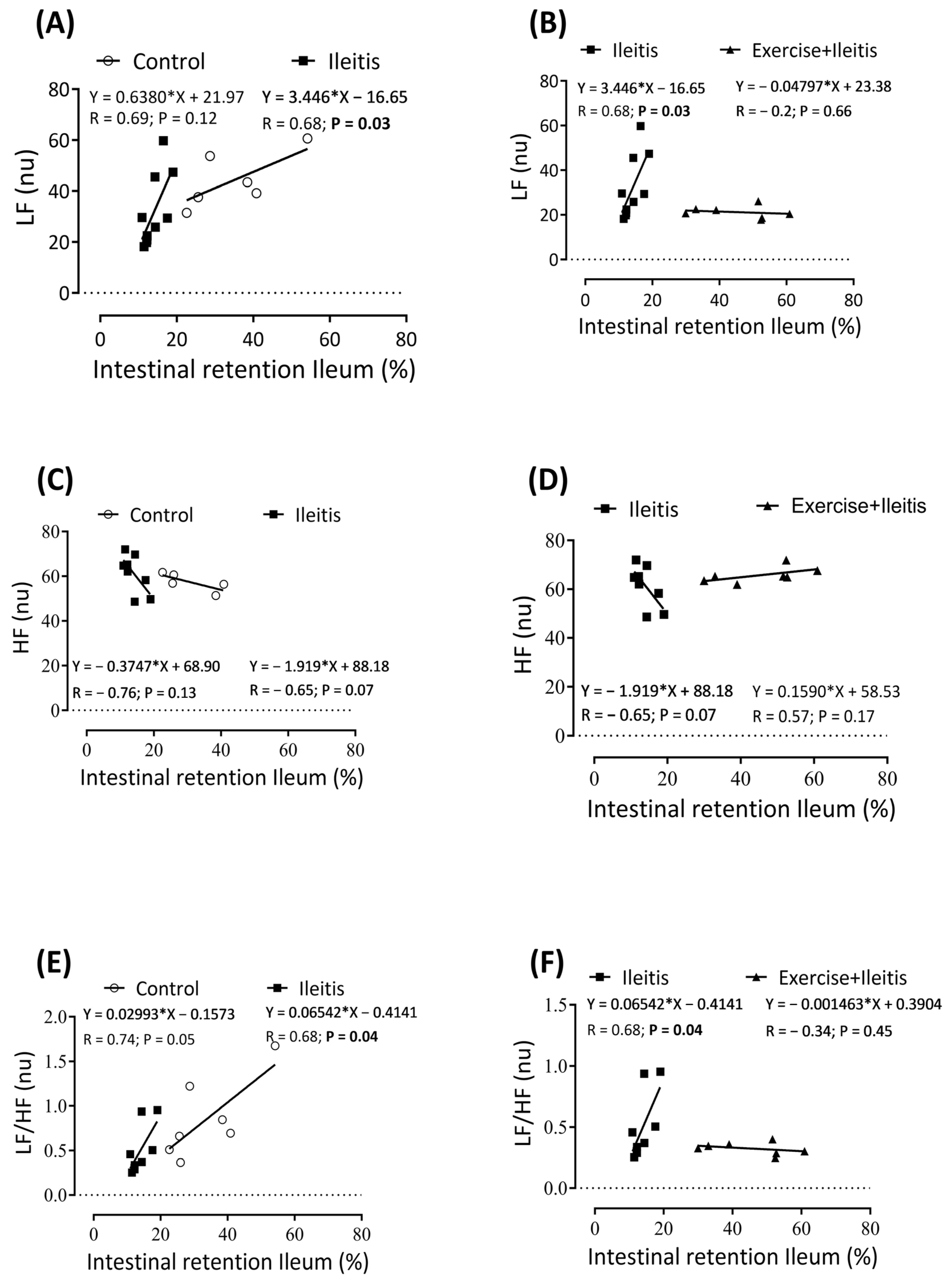
| Parameters | Control | Ileitis | Exercise+Ileitis |
|---|---|---|---|
| TBW (mL) | 130.60 ± 28.23 | 216.80 ± 11.44 * | 91.33 ± 12.33 # |
| ECF (mL) | 52.19 ± 15.75 | 96.32 ± 5.16 * | 38.99 ± 7.49 # |
| ICF (mL) | 78.37 ± 12.56 | 120.50 ± 6.60 * | 52.34 ± 5.58 # |
| FFM (g) | 193.00 ± 42.21 | 287.10 ± 14.66 * | 133.80 ± 16.82 # |
| FM (g) | 172.40 ± 7.61 | 152.80 ± 11.82 | 174.90 ± 15.35 |
| BMI (g/cm2) | 16.38 ± 2.50 | 24.09 ± 2.15 * | 11.73 ± 0.47 # |
| Tissue | Control | Ileitis | Exercise+Ileitis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heart (g/100 g) | 0.3530 ± 0.022 | 0.3453 ± 0.02 | 0.6176 ± 0.084 *# |
| Duodenum (g/100 g) | 0.223 ± 0.0177 | 0.256 ± 0.03 | 0.4855 ± 0.031 *# |
| Ileum (g/100 g) | 0.3687 ± 0.024 | 0.5034 ± 0.037 * | 0.3563 ± 0.046 # |
| Colon (g/100 g) | 0.513 ± 0.034 | 0.574 ± 0.026 | 1.385 ± 0.118 *# |
| Parameters | Control | Ileitis | Exercise+Ileitis |
|---|---|---|---|
| HR (bpm) | 391.1 ± 10.06 | 368.6 ± 8.315 | 342 ± 5.235 *# |
| R-R” Interval (s) | 0.154 ± 0.003 | 0.164 ± 0.003 | 0.176 ± 0.002 *# |
| PR Interval (s) | 0.049 ± 0.001 | 0.047 ± 0.001 | 0.044 ± 0.001 * |
| Duration P (s) | 0.015 ± 0.001 | 0.013 ± 0.001 | 0.011 ± 0.001 * |
| QRS Interval (s) | 0.016 ± 0.001 | 0.016 ± 0.001 | 0.0161 ± 0.001 |
| QTc Interval (s) | 0.057 ± 0.002 | 0.053 ± 0.001 | 0.052 ± 0.001 |
| QT Interval (s) | 0.021 ± 0.001 | 0.021 ± 0.001 | 0.022 ± 0.001 |
| ST height (mV) | 0.001 ± 0.006 | 0.003 ± 0.002 | 0.01 ± 0.003 |
| Parameters | Control | Ileitis | Exercise+Ileitis |
|---|---|---|---|
| VLF (%) | 39.32 ± 8.0 | 47.07 ± 7.45 | 52.14 ± 5.90 |
| LF (%) | 24.44 ± 2.07 | 14.42 ± 1.59 * | 11.53 ± 1.19 * |
| LF (nu) | 43.43 ± 3.86 | 31.32 ± 3.99 * | 19.85 ± 0.82 #,* |
| HF (%) | 37.70 ± 4.35 | 33.54 ± 5.52 | 30.75 ± 4.12 |
| HF (nu) | 57.41 ± 1.49 | 61.75 ± 2.77 | 67.38 ± 1.26 |
| LF/HF (%) | 0.70 ± 0.10 | 0.48 ± 0.08 | 0.34 ± 0.03 * |
| RMSSD (ms) | 4.57 ± 0.61 | 4.49 ± 0.71 | 6.32 ± 0.92 |
| SDRR (ms) | 8.27 ± 1.10 | 6.50 ± 0.78 | 8.30 ± 0.83 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
dos Santos, B.L.B.; da Silva, A.C.A.; Severo, J.S.; de Sousa Barbosa, B.; de Sousa, M.C.; dos Santos Moreira, F.A.; de Sousa, L.E.; Soares, H.S.; de Freitas, A.K.L.; Torres-Leal, F.L.; et al. Physical Exercise Alleviates Oxidative Stress and Autonomic Dysregulation in a Rat Model of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14030328
dos Santos BLB, da Silva ACA, Severo JS, de Sousa Barbosa B, de Sousa MC, dos Santos Moreira FA, de Sousa LE, Soares HS, de Freitas AKL, Torres-Leal FL, et al. Physical Exercise Alleviates Oxidative Stress and Autonomic Dysregulation in a Rat Model of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(3):328. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14030328
Chicago/Turabian Styledos Santos, Brenda Lois Barros, Alda Cássia Alves da Silva, Juliana Soares Severo, Bruno de Sousa Barbosa, Maisa Campêlo de Sousa, Francisco Assis dos Santos Moreira, Lucas Estevão de Sousa, Heron Silva Soares, Antônio Klingem Leite de Freitas, Francisco Leonardo Torres-Leal, and et al. 2025. "Physical Exercise Alleviates Oxidative Stress and Autonomic Dysregulation in a Rat Model of Inflammatory Bowel Disease" Antioxidants 14, no. 3: 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14030328
APA Styledos Santos, B. L. B., da Silva, A. C. A., Severo, J. S., de Sousa Barbosa, B., de Sousa, M. C., dos Santos Moreira, F. A., de Sousa, L. E., Soares, H. S., de Freitas, A. K. L., Torres-Leal, F. L., Correia-de-Sá, P., dos Santos, A. A., & da Silva, M. T. B. (2025). Physical Exercise Alleviates Oxidative Stress and Autonomic Dysregulation in a Rat Model of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Antioxidants, 14(3), 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14030328








