Effects of Different Levels of Lycium barbarum Flavonoids on Growth Performance, Immunity, Intestinal Barrier and Antioxidant Capacity of Meat Ducks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Animal Care
2.2. Experimental Design and Animal Management
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Indices Measured by Enzyme-Linked Immunoassay (ELISA)
2.5. Antioxidative Indices in Jejunum and Ileum
2.6. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis
2.7. Analysis of Western Blotting
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth Performance
3.2. Organ Index
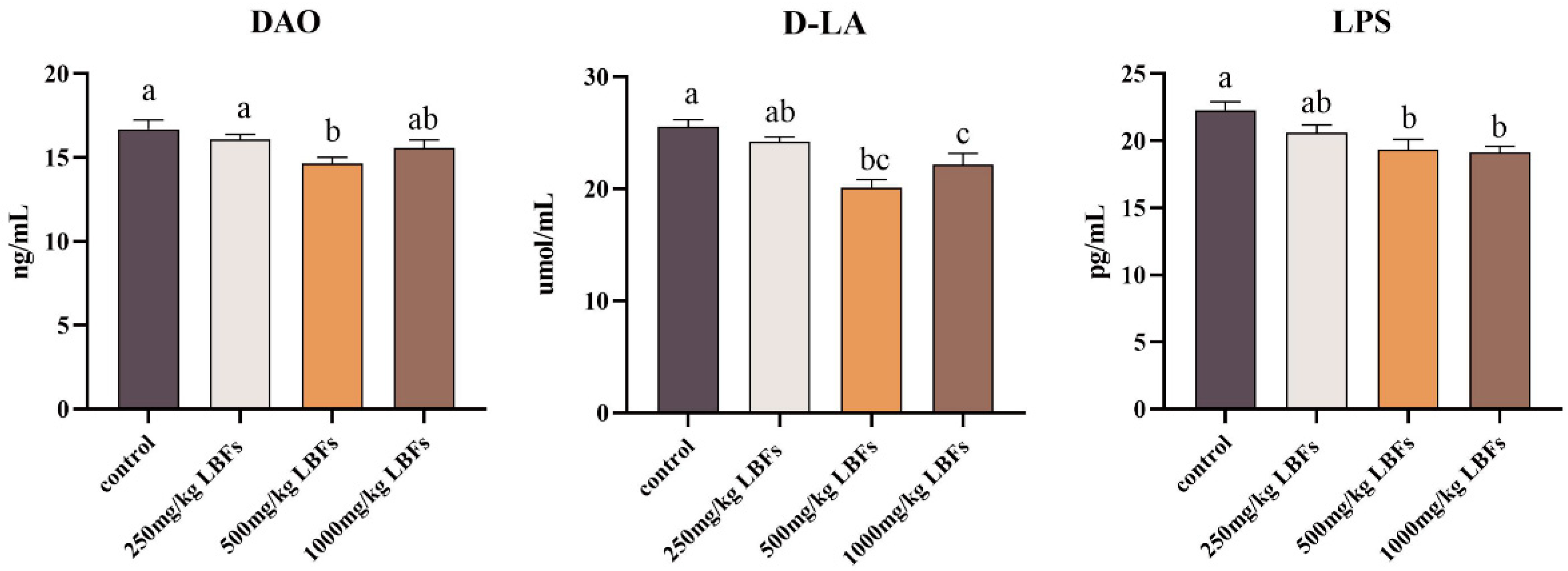
3.3. Intestinal Tract Permeability
3.4. Antioxidant Status in Intestinal Mucosa
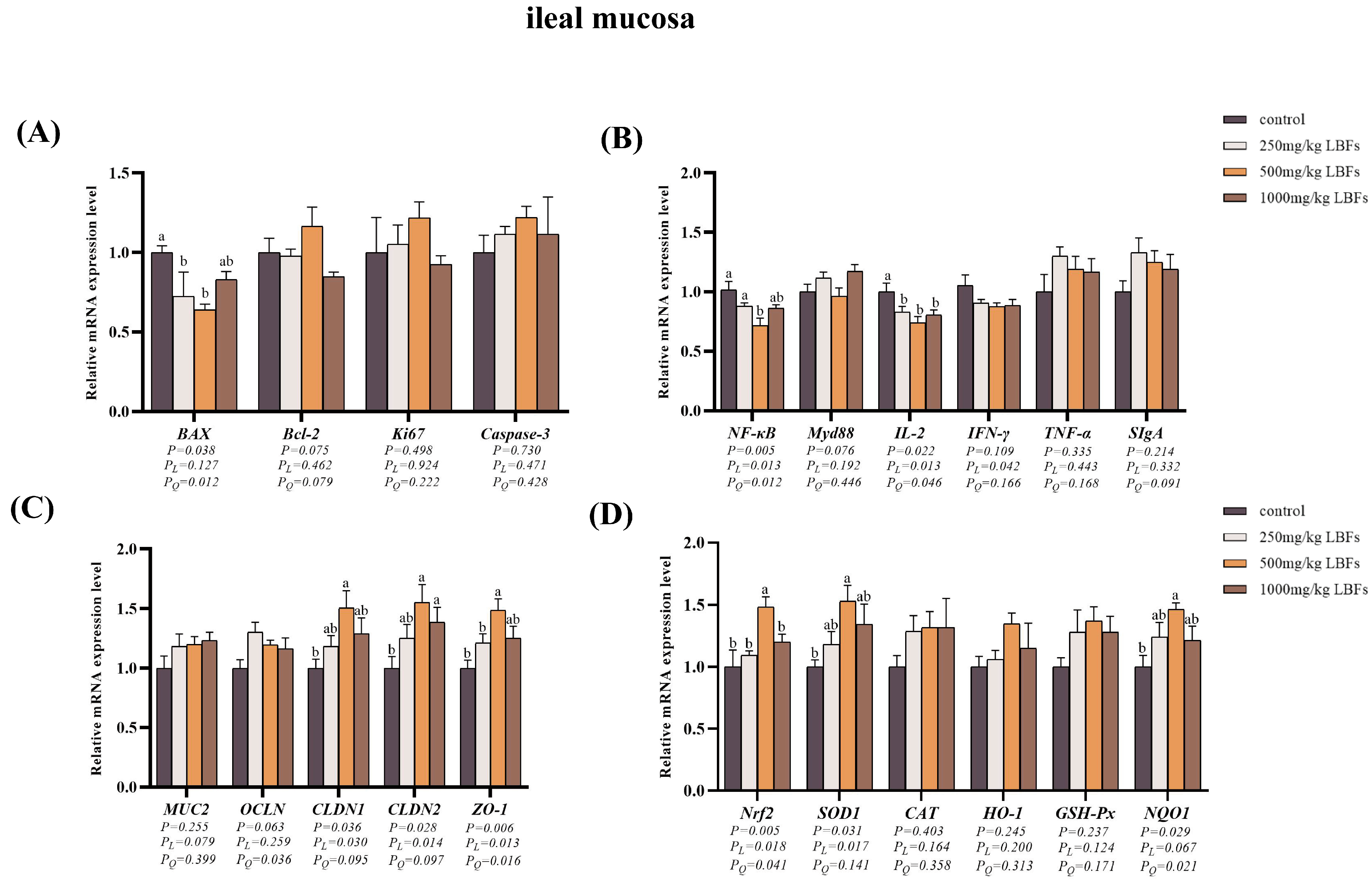
3.5. Cell Apoptosis-Related Genes Expression in Intestinal Mucosa
3.6. Immune-Related Gene Expression in Intestinal Mucosa
3.7. Intestinal Barrier-Related Gene Expression in Intestinal Mucosa
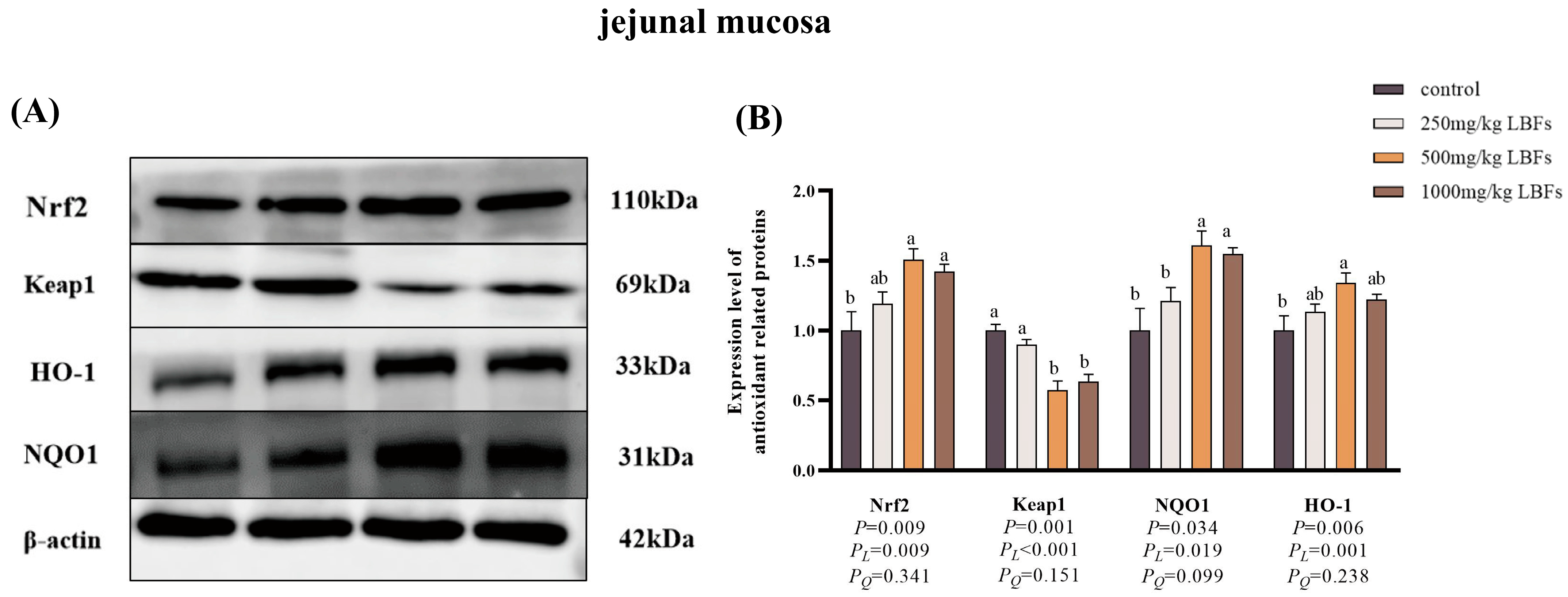
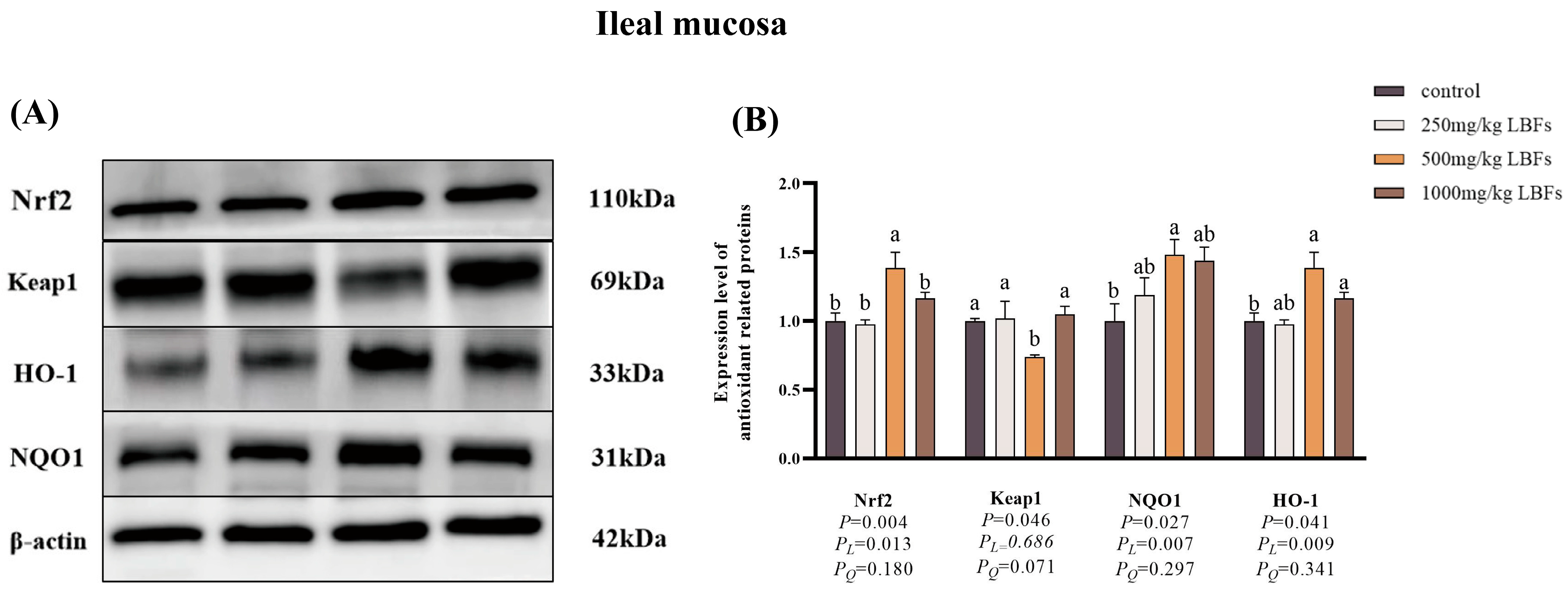
3.8. Antioxidant-Related Gene and Protein Expression in Intestinal Mucosa
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, D.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Liu, T.; Guo, Z.; Fan, W.; Wang, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhang, B.; Liu, H.; et al. Metabolome-based genome-wide association study of duck meat leads to novel genetic and biochemical insights. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2300148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abo-Al-Ela, H.G.; El-Kassas, S.; El-Naggar, K. Stress and immunity in poultry: Light management and nanotechnology as effective immune enhancers to fight stress. Cell Stress Chaperones 2021, 26, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, B.; Jha, R. Oxidative stress in the poultry gut: Potential challenges and interventions. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajput, D.S.; Zeng, D.; Khalique, A.; Rajput, S.S.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, N.; Ni, X. Pretreatment with probiotics ameliorate gut health and necrotic enteritis in broiler chickens, a substitute to antibiotics. AMB Express 2020, 10, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Hunkapiller, A.A.; Layton, A.C.; Chang, Y.J.; Robbins, K.R. Response of intestinal microbiota to antibiotic growth promoters in chickens. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2013, 10, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Yan, F.; Yang, C.; Yang, X. Effects of encapsulated organic acids and essential oils on intestinal barrier, microbial count, and bacterial metabolites in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 2858–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, X.; Kim, I.H. Effects of grape seed extract on performance, immunity, antioxidant capacity, and meat quality in Pekin ducks. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 2078–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Huang, X.; Zhang, X.; Deng, P.; Jiang, G.; Dai, Q. Effects of rosemary extract supplementation in feed on growth performance, meat quality, serum biochemistry, antioxidant capacity, and immune function of meat ducks. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, F.; Silva, A.M.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Rodrigues, F. Lycium barbarum berries (solanaceae) as source of bioactive compounds for healthy purposes: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, X.; Xia, T.; Geng, B.; Zhao, M.; Li, X.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, M. Bioactive components of Lycium barbarum and deep-processing fermentation products. Molecules 2023, 28, 8044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhang, B.; Chen, J.; Ou, H.; He, R.R.; So, K.F.; Zhang, L. Lycium barbarum (Wolfberry) glycopeptide prevents stress-induced anxiety disorders by regulating oxidative stress and ferroptosis in the medial prefrontal cortex. Phytomedicine 2023, 116, 154864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Y.; Chen, J.; Fan, Y.; Kou, T. Effect of flavonoids from Lycium barbarum leaves on the oxidation of myofibrillar proteins in minced mutton during chilled storage. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 1766–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Hu, Y.; Yan, Y. Characterization and evaluation of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of flavonoids from the fruits of Lycium barbarum. Foods 2022, 11, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, F.; Chen, Z. Lycium barbarum: A traditional chinese herb and a promising anti-aging agent. Aging Dis. 2017, 8, 778–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Ying, Z.; He, J.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, X.; Wang, T. Effects of dietary zinc oxide nanoparticles on growth, diarrhea, mineral deposition, intestinal morphology, and barrier of weaned piglets. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2018, 185, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Ma, L.; Wang, T.; Wang, C. Effects of dietary nano-zinc oxide supplementation on meat quality, antioxidant capacity and cecal microbiota of intrauterine growth retardation finishing pigs. Foods 2023, 12, 1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, C.J.C.; Hosseintabar-Ghasemabad, B.; Gorlov, I.F.; Slozhenkina, M.I.; Mosolov, A.A.; Seidavi, A. Immunomodulatory effects of natural feed additives for meat chickens. Life 2023, 13, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, T.C.; Dias, M.I.; Barros, L.; Calhelha, R.C.; Alves, M.J.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Phenolic compounds profile, nutritional compounds and bioactive properties of Lycium barbarum L.: A comparative study with stems and fruits. Ind. Crop Prod. 2018, 122, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Latif, M.A.; Elbestawy, A.R.; El-Far, A.H.; Noreldin, A.E.; Emam, M.; Baty, R.S.; Albadrani, G.M.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Abd El-Hamid, H.S. Quercetin Dietary Supplementation Advances Growth Performance, Gut Microbiota, and Intestinal mRNA Expression Genes in Broiler Chickens. Animals 2021, 11, 2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, B.; Zhuang, S.; He, X.; Wang, T.; Wang, C. Effects of different levels of rutin on growth performance, immunity, intestinal barrier and antioxidant capacity of broilers. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2022, 21, 1390–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.H.; Qian, Z.C.; Song, J.; Luan, Z.S.; Zuo, A.Y. Effects of zinc oxide-montmorillonite hybrid on growth performance, intestinal structure, and function of broiler chicken. Poult. Sci. 2013, 92, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, G.P. Stress-induced gastrointestinal barrier dysfunction and its inflammatory effects. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 87, E101–E108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Wang, S.; Qiu, Y.; Jiang, E.; Du, G.; Wang, W.; Xu, P.; Yang, H.; Hu, M.; Xiao, W. Screening for and combining serum intestinal barrier-related biomarkers to predict the disease severity of AECOPD. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2021, 10, 1548–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.P.; Yang, M.X.; Zhang, L.L.; Lu, Z.X.; Zhou, Y.M.; Wang, T. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens supplementation alleviates immunological stress in lipopolysaccharide-challenged broilers at early age. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 1504–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietschel, E.T.; Kirikae, T.; Schade, F.U.; Mamat, U. Bacterial endotoxin: Molecular relationships of structure to activity and function. FASEB J. 1994, 8, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Li, Z.; Ma, H.; Yue, Y.; Hao, K.; Li, J.; Xiang, Y.; Min, Y. Quercetin alleviates intestinal inflammation and improves intestinal functions via modulating gut microbiota composition in LPS-challenged laying hens. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretó, M.; Pérez-Bosque, A. Dietary plasma proteins, the intestinal immune system, and the barrier functions of the intestinal mucosa. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 87, E92–E100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulluwishewa, D.; Anderson, R.C.; McNabb, W.C.; Moughan, P.J.; Wells, J.M.; Roy, N.C. Regulation of tight junction permeability by intestinal bacteria and dietary components. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, S.; Tanabe, S.; Suzuki, T. Differential effects of flavonoids on barrier integrity in human intestinal Caco-2 cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 4628–4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Lai, Y.; Hua, Z.C. Apoptosis and apoptotic body: Disease message and therapeutic target potentials. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20180992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHenry, M.W.; Shi, P.; Camara, C.M.; Cohen, D.T.; Rettenmaier, T.J.; Adhikary, U.; Gygi, M.A.; Yang, K.; Gygi, S.P.; Wales, T.E.; et al. Covalent inhibition of pro-apoptotic BAX. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2024, 20, 1022–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spitz, A.Z.; Gavathiotis, E. Physiological and pharmacological modulation of BAX. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 43, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahim, A.S.; Sabbagh, H.; Liddane, A.; Raufi, A.; Kandouz, M.; Al-Katib, A. Hematologic malignancies: Newer strategies to counter the BCL-2 protein. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 142, 2013–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, D.T.; Korsmeyer, S.J. BCL-2 family: Regulators of cell death. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1998, 16, 395–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.-R.; Kang, Y.-J.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, H.T.; Cho, S.-G. Modulation of apoptosis in HaCaT keratinocytes via differential regulation of ERK signaling pathway by flavonoids. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 31498–31507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, Z.U.; Meng, C.; Sun, Y.; Safdar, A.; Pasha, R.H.; Munir, M.; Ding, C. Oxidative Stress in Poultry: Lessons from the Viral Infections. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 5123147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estévez, M. Oxidative damage to poultry: From farm to fork. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 1368–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Deng, D.; Chen, W. Inhibitors and Activators of SOD, GSH-Px, and CAT. Enzym. Inhib. Act. 2017, 29, 207–224. [Google Scholar]
- Chanput W, Krueyos N and Ritthiruangdej P, Anti-oxidative assays as markers for anti-inflammatory activity of flavonoids. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 40, 170–175. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, K.; Liu, G.; Yang, M.; Luan, Y.; Zhao, Z. Protective effect of allyl methyl disulfide on acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016, 249, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedi, A.; Ghobadi, H.; Sharghi, A.; Iranpour, S.; Fazlzadeh, M.; Aslani, M.R. Effect of saffron supplementation on oxidative stress markers (MDA, TAC, TOS, GPx, SOD, and pro-oxidant/antioxidant balance): An updated systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1071514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, T.; Qiang, X.; Geng, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Meng, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, M. Changes in the Phytochemical and Bioactive Compounds and the Antioxidant Properties of Wolfberry during Vinegar Fermentation Processes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilić, T.; Dodevska, M.; Marčetić, M.; Božić, D.; Kodranov, I.; Vidović, B. Chemical Characterization, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties of Goji Berries Cultivated in Serbia. Foods 2020, 9, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Tie, H.; Tian, W.; Zhao, Y.; Qin, L.; Guo, S.; Li, Q.; Bao, C. Eriodictyol regulated ferroptosis, mitochondrial dysfunction, and cell viability via Nrf2/HO-1/NQO1 signaling pathway in ovarian cancer cells. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2023, 37, e23368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Qian, Y.; Wang, B.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; Chen, C.; Feng, L.; Chen, J.; Dong, N. Glycyrrhizin protects against particulate matter-induced lung injury via regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress and NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis through Nrf2/HO-1/NQO1 signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 120, 110371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, P.H.; Lin, S.Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Chen, W.Y.; Chuang, Y.H.; Wu, C.C.; Chen, C.J. Protective effects of rutin on liver injury induced by biliary obstruction in rats. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 73, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.S.; Um, K.H.; Park, S.O.; Zammit, V.A. Effect of stocking density on behavioral traits, blood biochemical parameters and immune responses in meat ducks exposed to heat stress. Arch. Anim. Breed. 2018, 61, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.L.; Gomez-Cabrera, M.C.; Steinhafel, N.; Vina, J. Acute exercise activates nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB signaling pathway in rat skeletal muscle. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 1499–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Qin, T.; Gao, S.; Yue, Y.; Wang, S. TNF-a is a potent stimulator of Tc9-cell differentiation. J. Immunother. 2020, 43, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, H.; Zhou, T.; Luo, J.; Wang, J.; Han, C.; Hu, J.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Y. Duck IL-2 promoter cloning and the effects of methylation status on mRNA levels in immune tissues. Cent. Eur. J. Immunol. 2018, 43, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Jobin, C. The flavonoid luteolin prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced NF-kappaB signalling and gene expression by blocking IkappaB kinase activity in intestinal epithelial cells and bone-marrow derived dendritic cells. Immunology 2005, 115, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, C.H.; Choi, Y.H.; Moon, S.K.; Kim, W.J.; Kim, G.Y. Quercetin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production in BV2 microglial cells by suppressing the NF-κB pathway and activating the Nrf2-dependent HO-1 pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2013, 17, 808–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Item | Starter Period (1~21 d) | Grower Period (22~42 d) |
|---|---|---|
| Ingredient (%) | ||
| Corn | 66.7 | 68.98 |
| Soybean meal | 20.4 | 20.1 |
| Rice bran | 4.33 | 4.09 |
| Corn gluten meal | 3.70 | 1.70 |
| Dicalcium phosphate | 1.87 | 1.98 |
| Limestone | 1.08 | 1.07 |
| L-Lysine | 0.32 | 0.42 |
| DL-Methionine | 0.30 | 0.36 |
| Sodium chloride | 0.30 | 0.30 |
| Premix A | 1 | 1 |
| Total | 100 | 100 |
| Nutrient B | ||
| ME (MJ·kg−1) C | 12.48 | 12.39 |
| Crude protein (%) | 21.79 | 18.15 |
| Lysine (%) | 1.39 | 1.25 |
| Methionine (%) | 0.68 | 0.65 |
| Calcium (%) | 0.96 | 1.00 |
| Total phosphorus (%) | 0.67 | 0.72 |
| Gene A | Accession No. | Primers Sequence (5′→3′) | Products Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| β-actin | NM_205518.1 | F: TGCTGTGTTCCCATCTATCG | 150 |
| R: TTGGTGACAATACCGTGTTCA | |||
| Nrf2 | XM_027460922.2 | F:CAGCTCAGCGCATTCAGTCA | 165 |
| R:ATGCAGCTGAAGAAGCCTCA | |||
| NQO1 | XM_027466610.2 | F:GATCTGATCATCTTCCAGTTCCCA | 161 |
| R:GTGGTGAATGACAGCATGGC | |||
| SOD1 | XM_027449207.2 | F:TCGGCAACGTGACTGCTAAA | 163 |
| R:TTCCCAGTTAGCGTGCTCTC | |||
| GSH-Px | KU_048803.1 | F:CAGTACATCATCTGGTCGCC | 127 |
| R:CCTGGATCTTGATGGTTTCG | |||
| HO-1 | KU_048806.1 | F:CCCATGCCTACACTCGCTAT | 217 |
| R:GCCTCCTCCAAGACTCGTTT | |||
| CAT | KU_048802.1 | F:CTGTTGAGGAAGCAGGAAGG | 101 |
| R:GAAAGACCAGGATGGGTAGTTG | |||
| TNF-α | XM_027471963.2 | F:CTCACGGACAAGGAAGGTTGG | 135 |
| R:GGCTTCTGCCATCAGCTCTT | |||
| Myd88 | NM_001310832.1 | F:AGCTTATAGAAAGGAGGTGTCGG | 131 |
| R:AATCAGCCGCTTGAGACGAG | |||
| IL-2 | NM_001310373.1 | F:AGTGCAGCTGGCAAACTCTG | 156 |
| R:TTCCTGGGGGAATTAGGTCCATA | |||
| IFN-γ | NM_001310417.1 | F:CAGGTCCACGAGGTCTTT | 146 |
| R:TGAGCCAGATTGTTTCCC | |||
| NF-κB | XM_027465251.2 | F:TTCATGGGATGCAGATACGGC | 101 |
| R:CAAGGGACGAGCTCGAATGT | |||
| SlgA | U27222.1 | F:TCGCTCAAGGAACCCATCGT | 174 |
| R:GCGGGACCACGAGAACTTCA | |||
| MUC2 | XM_005024513.2 | F:GGGCGCTCAATTCAACATAAGTA | 150 |
| R:TAAACTGATGGCTTCTTATGCGG | |||
| CLDN1 | XM_013108556.1 | F:TCATGGTATGGCAACAGAGTGG | 146 |
| R:CGGGTGGGTGGATAGGAAGT | |||
| CLDN2 | XM_005009661.2 | F:CTCCTCCTTGTTCACCCTCATC | 160 |
| R:GAACTCGCTCTTGGGTTTGTG | |||
| OCLN | XM_013109403.1 | F:GGCTTCCTCATCGTCCTCTTG | 160 |
| R:TCTCGTACTGCGACTCGTCCAC | |||
| ZO-1 | XM_013104936.1 | F:ACGCTGGTGAAATCAAGGAAGAA | 255 |
| R:AGGGACATTCAACAGCGTGGC | |||
| BAX | XM_013106199.3 | F:AAGGCCTGCCTTGCTTTTGA | 127 |
| R:CAGTGCTTCCAGCAGGGTAAAT | |||
| Bcl-2 | XM_005028719.1 | F:ACCTGGTTCTGAATAAGTGGGAT | 187 |
| R:GGTTGTCTTCTCAGTGTTGCCT | |||
| Ki67 | XM_038180817.1 | F:CCTCTGAAGCACGGAGATGT | 132 |
| R:CTGAACATGAAGAACCTGCCG | |||
| Caspase3 | XM_021279218.3 | F:TTGTCAGCCTCGCAGTTGAT | 198 |
| R:ACACACTCTCCCATCTCTGGA |
| Item A | Dietary Treatments B | SEM C | p Value D | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 250 | 500 | 1000 | p | L | Q | ||
| Body weight | ||||||||
| 1 d (g) | 51.42 | 51.50 | 51.33 | 51.50 | 0.224 | 0.994 | 0.969 | 0.932 |
| 21 d (kg) | 1.11 | 1.12 | 1.12 | 1.16 | 0.007 | 0.143 | 0.066 | 0.244 |
| 42 d (kg) | 2.69 c | 2.77 b | 2.84 ab | 2.86 a | 0.023 | 0.001 | <0.001 | 0.222 |
| ADG, g/d | ||||||||
| 1~21 d | 50.61 | 50.92 | 50.69 | 52.55 | 0.342 | 0.142 | 0.065 | 0.243 |
| 21~42 d | 74.80 b | 78.45 ab | 82.30 a | 81.03 a | 0.863 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.080 |
| 1~42 d | 62.70 c | 64.69 b | 66.49 ab | 66.79 a | 0.463 | 0.001 | <0.001 | 0.222 |
| ADFI, g/d | ||||||||
| 1~21 d | 81.34 a | 76.98 b | 78.49 b | 77.07 b | 0.568 | 0.011 | 0.013 | 0.130 |
| 21~42 d | 172.88 b | 169.36 bc | 185.49 a | 161.65 c | 2.418 | 0.001 | 0.271 | 0.008 |
| 1~42 d | 127.11 b | 123.17 bc | 131.99 a | 119.36 c | 1.244 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.0016 |
| FCR | ||||||||
| 1~21 d | 1.61 a | 1.51 b | 1.55 ab | 1.47 b | 0.017 | 0.017 | 0.007 | 0.825 |
| 21~42 d | 2.31 a | 2.16 ab | 2.26 a | 1.99 b | 0.037 | 0.006 | 0.004 | 0.369 |
| 1~42 d | 2.02 a | 1.91 bc | 1.98 b | 1.79 c | 0.025 | <0.001 | 0.001 | 0.277 |
| Item | Dietary Treatments A | SEM B | p Value C | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 250 | 500 | 1000 | p | L | Q | ||
| Pectoral muscles | 85.67 | 102.70 | 90.63 | 87.77 | 3.043 | 0.197 | 0.826 | 0.103 |
| Liver | 25.37 | 24.51 | 24.43 | 23.37 | 0.488 | 0.706 | 0.266 | 0.966 |
| Pancreas | 2.51 | 2.27 | 2.03 | 1.90 | 0.103 | 0.161 | 0.028 | 0.779 |
| Spleen | 1.03 | 0.75 | 0.86 | 0.78 | 0.106 | 0.820 | 0.529 | 0.668 |
| Bursa | 1.16 | 1.08 | 1.03 | 1.04 | 0.040 | 0.677 | 0.278 | 0.600 |
| Abdominal fat | 11.42 | 11.81 | 13.03 | 10.92 | 0.502 | 0.520 | 0.956 | 0.235 |
| Item A | Dietary Treatments B | SEM C | p Value D | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 250 | 500 | 1000 | p | L | Q | ||
| GSH (umoL/gprot) | 288.71 | 296.40 | 298.88 | 291.04 | 3.280 | 0.702 | 0.418 | 0.992 |
| CAT (U/mgprot) | 20.01 b | 20.07 b | 22.42 a | 21.26 ab | 0.328 | 0.014 | 0.016 | 0.389 |
| T-AOC (U/mgprot) | 1.34 b | 1.42 ab | 1.51 a | 1.46 a | 0.019 | 0.010 | 0.006 | 0.048 |
| T-SOD (U/mgprot) | 19.26 | 19.80 | 20.87 | 20.39 | 0.618 | 0.831 | 0.975 | 0.983 |
| MDA (nmoL/mgprot) | 2.64 | 1.96 | 1.60 | 1.95 | 0.177 | 0.209 | 0.126 | 0.141 |
| GSH-Px (U/mgprot) | 90.10 b | 95.29 ab | 100.85 a | 100.31 a | 1.352 | 0.007 | 0.001 | 0.197 |
| Item A | Dietary Treatments B | SEM C | p Value D | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 250 | 500 | 1000 | p | L | Q | ||
| GSH (umol/gprot) | 191.75 b | 237.94 a | 252.05 a | 230.51 a | 6.327 | 0.001 | 0.005 | 0.001 |
| CAT (U/mgprot) | 19.85 | 20.58 | 20.76 | 20.66 | 0.176 | 0.252 | 0.104 | 0.237 |
| T-AOC (U/mgprot) | 1.33 c | 1.39 bc | 1.49 a | 1.44 ab | 0.019 | 0.010 | 0.021 | 0.009 |
| T-SOD (U/mgprot) | 14.12 b | 16.36 ab | 17.63 a | 17.16 a | 0.511 | 0.061 | 0.028 | 0.344 |
| MDA (nmol/mgprot) | 1.54 b | 1.41 ab | 1.18 a | 1.16 a | 0.545 | 0.021 | 0.003 | 0.556 |
| GSH-Px (U/mgprot) | 79.71 | 82.16 | 85.05 | 84.86 | 1.131 | 0.302 | 0.220 | 0.558 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tu, M.; Cai, G.; Ma, L.; Yan, L.; Wang, T.; Shi, Z.; Wang, C.; Chen, Z. Effects of Different Levels of Lycium barbarum Flavonoids on Growth Performance, Immunity, Intestinal Barrier and Antioxidant Capacity of Meat Ducks. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14010067
Tu M, Cai G, Ma L, Yan L, Wang T, Shi Z, Wang C, Chen Z. Effects of Different Levels of Lycium barbarum Flavonoids on Growth Performance, Immunity, Intestinal Barrier and Antioxidant Capacity of Meat Ducks. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(1):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14010067
Chicago/Turabian StyleTu, Minhang, Gentan Cai, Longfei Ma, Leyan Yan, Tian Wang, Zhendan Shi, Chao Wang, and Zhe Chen. 2025. "Effects of Different Levels of Lycium barbarum Flavonoids on Growth Performance, Immunity, Intestinal Barrier and Antioxidant Capacity of Meat Ducks" Antioxidants 14, no. 1: 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14010067
APA StyleTu, M., Cai, G., Ma, L., Yan, L., Wang, T., Shi, Z., Wang, C., & Chen, Z. (2025). Effects of Different Levels of Lycium barbarum Flavonoids on Growth Performance, Immunity, Intestinal Barrier and Antioxidant Capacity of Meat Ducks. Antioxidants, 14(1), 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14010067








