Exploring Potential Complement Modulation Strategies for Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury in Kidney Transplantation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Complement System
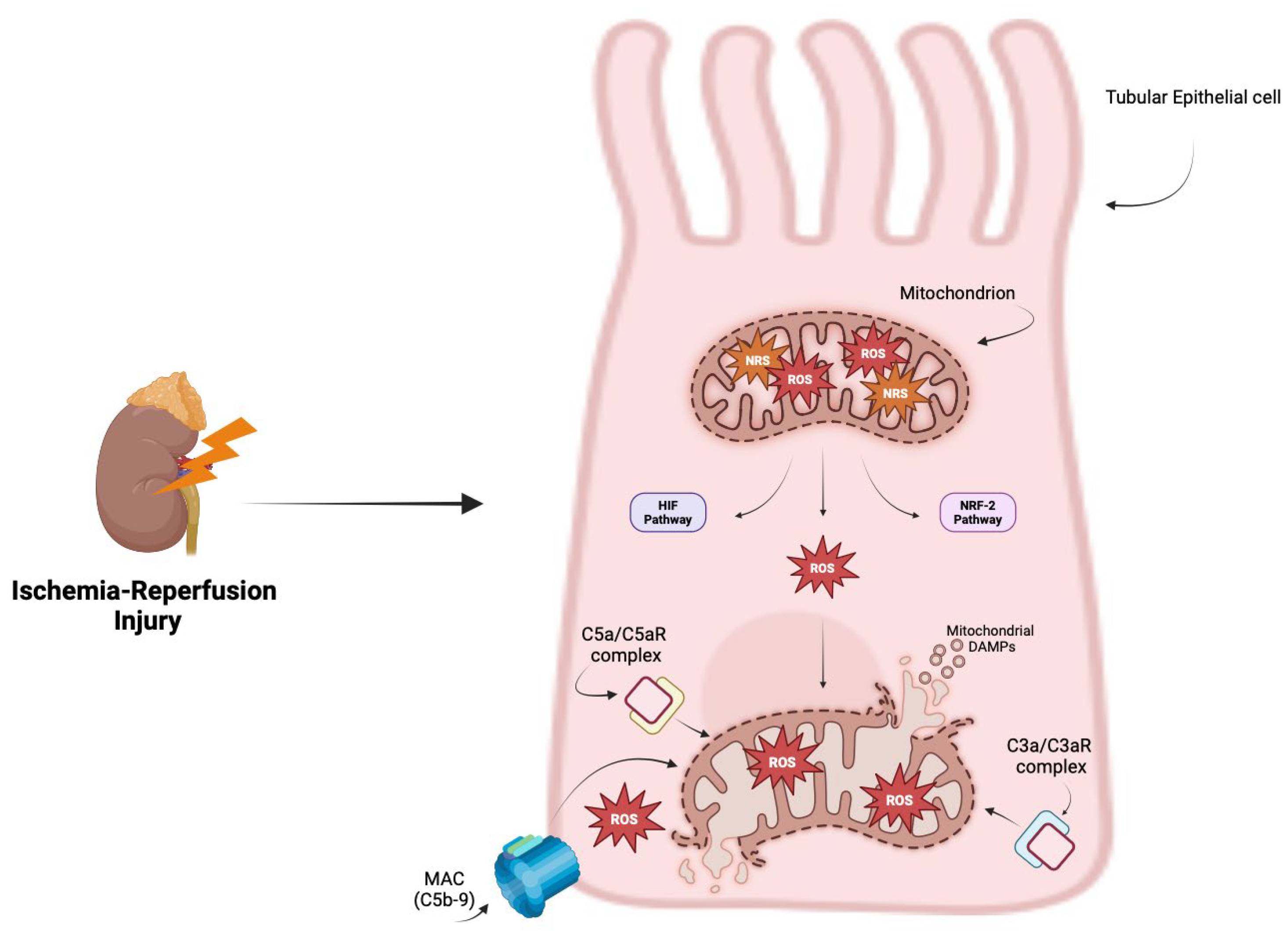
3. Oxidative Stress and Complement System
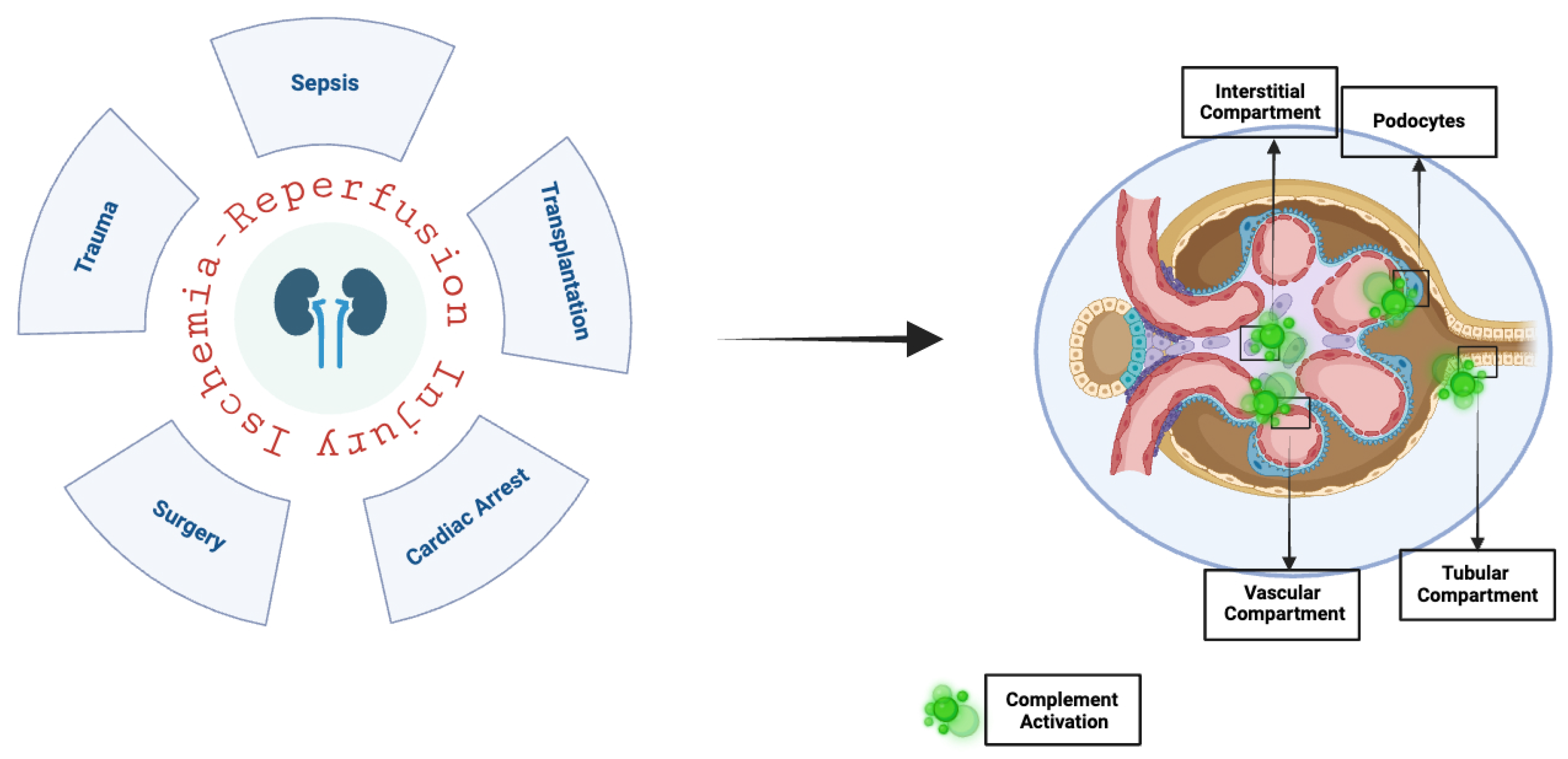
4. The Complement System in Renal Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury
5. Potential Therapeutic Strategies
5.1. Targeting Complement C5 and C3
5.2. Targeting Complement Receptors and Regulatory Proteins
5.3. Targeting Complement Factors B and D
6. Conclusions and Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Biglarnia, A.-R.; Huber-Lang, M.; Mohlin, C.; Ekdahl, K.N.; Nilsson, B. The multifaceted role of complement in kidney transplantation. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 767–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troise, D.; Infante, B.; Mercuri, S.; Piccoli, C.; Lindholm, B.; Stallone, G. Hypoxic Inducible Factor Stabilization in Pericytes beyond Erythropoietin Production: The Good and the Bad. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongoni, A.K.; Lu, B.; Salvaris, E.J.; Roberts, V.; Fang, D.; McRae, J.L.; Fisicaro, N.; Dwyer, K.M.; Cowan, P.J. Overexpression of Human CD55 and CD59 or Treatment with Human CD55 Protects against Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Mice. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 4837–4845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Farrar, C.A.; Abe, K.; Pratt, J.R.; Marsh, J.E.; Wang, Y.; Stahl, G.L.; Sacks, S.H. Predominant role for C5b-9 in renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 105, 1363–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stea, E.D.; D’Ettorre, G.; Mitrotti, A.; Gesualdo, L. The complement system in the pathogenesis and progression of kidney diseases: What doesn’t kill you makes you older. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2024, 124, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, M.C.; Nauser, C.L.; Farrar, C.A.; Sacks, S.H. Correction to: Complement in ischaemia–reperfusion injury and transplantation. Semin. Immunopathol. 2022, 44, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, M.W.; Woodruff, T.M. Complement: Bridging the innate and adaptive immune systems in sterile inflammation. J. Leucoc. Biol. 2020, 108, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenawy, H.I.; Boral, I.; Bevington, A. Complement-Coagulation Cross-Talk: A Potential Mediator of the Physiological Activation of Complement by Low pH. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafilou, M.; Hughes, T.R.; Morgan, B.P.; Triantafilou, K. Complementing the inflammasome. Immunology 2016, 147, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajishengallis, G.; Lambris, J.D. Crosstalk pathways between Toll-like receptors and the complement system. Trends Immunol. 2010, 31, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipfel, P.F.; Skerka, C. Complement regulators and inhibitory proteins. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauser, C.L.; Farrar, C.A.; Sacks, S.H. Complement Recognition Pathways in Renal Transplantation. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 2571–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, T.R.; Beischel, L.S.; Frenzke, M.; Witte, D. Regulated expression of complement factor B in the human kidney. Kidney Int. 1996, 50, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooimans, R.A.; Stegmann, A.P.; van Dorp, W.T.; van der Ark, A.A.; van der Woude, F.J.; van Es, L.; Daha, M.R.A. Interleukin 2 mediates stimulation of complement C3 biosynthesis in human proximal tubular epithelial cells. J. Clin. Investig. 1991, 88, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mühlig, A.K.; Keir, L.S.; Abt, J.C.; Heidelbach, H.S.; Horton, R.; Welsh, G.I.; Meyer-Schwesinger, C.; Licht, C.; Coward, R.J.; Fester, L.; et al. Podocytes Produce and Secrete Functional Complement C3 and Complement Factor H. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzin, R.; Stasi, A.; Fiorentino, M.; Stallone, G.; Cantaluppi, V.; Gesualdo, L.; Castellano, G. Inflammaging and Complement System: A Link Between Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Graft Damage. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netti, G.S.; Franzin, R.; Stasi, A.; Spadaccino, F.; Strologo, A.D.; Infante, B.; Gesualdo, L.; Castellano, G.; Ranieri, E.; Stallone, G. Role of complement in regulating inflammation processes in renal and prostate cancers. Cells 2021, 10, 2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, R.; Qin, W. Role of Complement System in Kidney Transplantation: Stepping From Animal Models to Clinical Application. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 811696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petr, V.; Thurman, J.M. The role of complement in kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2023, 19, 771–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, E.E.; Kunz, N.; Kemper, C. Complement and human T cell metabolism: Location, location, location. Immunol. Rev. 2020, 295, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Wu, X.; Song, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wan, J. Complement C3 exacerbates renal interstitial fibrosis by facilitating the M1 macrophage phenotype in a mouse model of unilateral ureteral obstruction. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2019, 317, F1171–F1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stallone, G.; Netti, G.S.; Cormio, L.; Castellano, G.; Infante, B.; Pontrelli, P.; Divella, C.; Selvaggio, O.; Spadaccino, F.; Ranieri, E.; et al. Modulation of complement activation by pentraxin-3 in prostate cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H. Complement regulation: Physiology and disease relevance. Korean J. Pediatr. 2015, 58, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keragala, C.B.; Draxler, D.F.; McQuilten, Z.K.; Medcalf, R.L. Haemostasis and innate immunity—A complementary relationship. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 180, 782–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amara, U.; Flierl, M.A.; Rittirsch, D.; Klos, A.; Chen, H.; Acker, B.; Brückner, U.B.; Nilsson, B.; Gebhard, F.; Lambris, J.D.; et al. Molecular Intercommunication between the Complement and Coagulation Systems. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 5628–5636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heurich, M.; McCluskey, G. Complement and coagulation crosstalk—Factor H in the spotlight. Immunobiology 2023, 228, 152707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, J.H.; Walton, B.L.; Aleman, M.M.; O’Byrne, A.M.; Lei, V.; Harrasser, M.; Foley, K.A.; Wolberg, A.S.; Conway, E.M. Complement Activation in Arterial and Venous Thrombosis is Mediated by Plasmin. EBioMedicine 2016, 5, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelmann, B.; Massberg, S. Thrombosis as an intravascular effector of innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stallone, G.; Pontrelli, P.; Rascio, F.; Castellano, G.; Gesualdo, L.; Grandaliano, G. Coagulation and Fibrinolysis in Kidney Graft Rejection. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajishengallis, G.; Lambris, J.D. More than complementing Tolls: Complement–Toll-like receptor synergy and crosstalk in innate immunity and inflammation. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 274, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, M.R.; Hoffman, S.M.; Tomlinson, S.; Fleming, S.D. Complement regulates TLR4-mediated inflammatory responses during intestinal ischemia reperfusion. Mol. Immunol. 2010, 48, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lin, L.; Rao, S.; Tao, X.; Cui, J.; Wan, J. Complement C3 mediates podocyte injury through TLR4/NFΚB-P65 signaling during ischemia–reperfusion acute kidney injury and post-injury fibrosis. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichida, S.; Yuzawa, Y.; Okada, H.; Yoshioka, K.; Matsuo, S. Localization of the complement regulatory proteins in the normal human kidney. Kidney Int. 1994, 46, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurman, J.M. Altered renal tubular expression of the complement inhibitor Crry permits complement activation after ischemia/reperfusion. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnum, S.R. Therapeutic Inhibition of Complement: Well Worth the Risk. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 38, 503–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe-Kusunoki, K.; Anders, H.-J. Balancing efficacy and safety of complement inhibitors. J. Autoimmun. 2024, 145, 103216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karp, D.R.; Holers, V.M. Complement in Health and Disease. In Goldman’s Cecil Medicine; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohebnasab, M.; Eriksson, O.; Persson, B.; Sandholm, K.; Mohlin, C.; Huber-Lang, M.; Keating, B.J.; Ekdahl, K.N.; Nilsson, B. Current and Future Approaches for Monitoring Responses to Anti-complement Therapeutics. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troise, D.; Infante, B.; Mercuri, S.; Netti, G.S.; Ranieri, E.; Gesualdo, L.; Stallone, G.; Pontrelli, P. Hypoxic State of Cells and Immunosenescence: A Focus on the Role of the HIF Signaling Pathway. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carcy, R.; Cougnon, M.; Poet, M.; Durandy, M.; Sicard, A.; Counillon, L.; Blondeau, N.; Hauet, T.; Tauc, M.; Pisani, D.F. Targeting oxidative stress, a crucial challenge in renal transplantation outcome. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 169, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzin, R.; Stasi, A.; Fiorentino, M.; Simone, S.; Oberbauer, R.; Castellano, G.; Gesualdo, L. Renal Delivery of Pharmacologic Agents During Machine Perfusion to Prevent Ischaemia-Reperfusion Injury: From Murine Model to Clinical Trials. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 673562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collard, C.D.; Lekowski, R.; Jordan, J.E.; Agah, A.; Stahl, G.L. Complement activation following oxidative stress. Mol. Immunol. 1999, 36, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.S.; Jeon, H.; Yoo, S.-M.; Lee, M.-S. Activation of the Complement System on Human Endothelial Cells by Urban Particulate Matter Triggers Inflammation-Related Protein Production. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collard, C.D.; Väkevä, A.; Büküsoglu, C.; Zünd, G.; Sperati, C.J.; Colgan, S.P.; Stahl, G.L. Reoxygenation of Hypoxic Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells Activates the Classic Complement Pathway. Circulation 1997, 96, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, S.; Baker, P.J.; Johnson, R.J.; Ochi, R.F.; Pritzl, P.; Couser, W.G. Complement membrane attack complex stimulates production of reactive oxygen metabolites by cultured rat mesangial cells. J. Clin. Investig. 1986, 77, 762–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Qi, J.; Zhou, M.; Pan, T.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, Y.; Han, H.; Han, Y. Upregulation of Nrf2 Attenuates Oxidative Stress–Induced, Complement Activation–Associated Endothelial Injury and Apoptosis in Transplant-Associated Thrombotic Microangiopathy. Transpl. Cell Ther. 2021, 27, 758.e1–758.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, M.; Rohrer, B. Anaphylatoxin C5a receptor signaling induces mitochondrial fusion and sensitizes retinal pigment epithelial cells to oxidative stress. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Gen. Subj. 2023, 1867, 130374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, M.; Beeson, G.; Beeson, C.; Rohrer, B. Mitochondrial C3a Receptor Activation in Oxidatively Stressed Epithelial Cells Reduces Mitochondrial Respiration and Metabolism. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 628062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbore, G.; West, E.E.; Spolski, R.; Robertson, A.A.B.; Klos, A.; Rheinheimer, C.; Dutow, P.; Woodruff, T.M.; Yu, Z.X.; O’neill, L.A.; et al. T helper 1 immunity requires complement-driven NLRP3 inflammasome activity in CD4+ T cells. Science 2016, 352, aad1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, I.-J.; Lin, W.-C.; Yang, Y.-H.; Tseng, Y.-L.; Lin, Y.-H.; Chou, C.-H.; Tsau, Y.-K. High Concentration of C5a-Induced Mitochondria-Dependent Apoptosis in Murine Kidney Endothelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simone, S.; Lin, W.-C.; Yang, Y.-H.; Tseng, Y.-L.; Lin, Y.-H.; Chou, C.-H.; Tsau, Y.-K. Complement-dependent NADPH oxidase enzyme activation in renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 74, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, S.; Rascio, F.; Castellano, G.; Divella, C.; Chieti, A.; Ditonno, P.; Battaglia, M.; Crovace, A.; Staffieri, F.; Oortwijn, B.; et al. Oxidative Stress and Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Kidney Transplantation: Focus on Ferroptosis, Mitophagy and New Antioxidants. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detsika, M.G.; Lianos, E.A. Regulation of Complement Activation by Heme Oxygenase-1 (HO-1) in Kidney Injury. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ahn, H.; Chang, M.; Narasimhan, P.; Chan, P.H.; Song, Y.S. Complement component 3 inhibition by an antioxidant is neuroprotective after cerebral ischemia and reperfusion in mice. J. Neurochem. 2013, 124, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijveldt, R.J.; van Nood, E.; van Hoorn, D.E.; Boelens, P.G.; van Norren, K.; van Leeuwen, P.A. Flavonoids: A review of probable mechanisms of action and potential applications. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 74, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, R.O.S.; Losada, D.M.; Jordani, M.C.; Évora, P.; Castro-e-Silva, O. Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Revisited: An Overview of the Latest Pharmacological Strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaura, I.F.; Gao, Q.; Anwar, I.J.; Abraham, N.; Kahan, R.; Hartwig, M.G.; Barbas, A.S. Complement-targeting therapeutics for ischemia-reperfusion injury in transplantation and the potential for ex vivo delivery. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1000172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppelaars, F.; Seelen, M.A. Complement-mediated inflammation and injury in brain dead organ donors. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 84, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoszek, D.; Mazanowska, O.; Kościelska-Kasprzak, K.; Kamińska, D.; Lepiesza, A.; Chudoba, P.; Myszka, M.; Żabińska, M.; Klinger, M. Functional Activity of the Complement System in Deceased Donors in Relation to Kidney Allograft Outcome. Transpl. Proc. 2018, 50, 1697–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, B.; Connelly, C.; Moldakhmetova, S.; Sheerin, N.S. Complement activation and kidney transplantation; a complex relationship. Immunobiology 2023, 228, 152396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casiraghi, F.; Azzollini, N.; Todeschini, M.; Fiori, S.; Cavinato, R.A.; Cassis, P.; Solini, S.; Pezzuto, F.; Mister, M.; Thurman, J.M.; et al. Complement Alternative Pathway Deficiency in Recipients Protects Kidney Allograft From Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury and Alloreactive T Cell Response. Am. J. Transplant. 2017, 17, 2312–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Cabrales, C.; Rodriguez-Garcia, E.; Gimeno, J.; Benito, D.; Pérez-Sáez, M.J.; Redondo-Pachón, D.; Buxeda, A.; Burballa, C.; Crespo, M.; Riera, M.; et al. Role of C5aR1 and C5L2 Receptors in Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiser, M.R.; Rodriguez-Garcia, E.; Gimeno, J.; Benito, D.; Pérez-Sáez, M.J.; Redondo-Pachón, D.; Buxeda, A.; Burballa, C.; Crespo, M.; Riera, M.; et al. Reperfusion injury of ischemic skeletal muscle is mediated by natural antibody and complement. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 183, 2343–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurman, J.M.; Ljubanovic, D.; Edelstein, C.L.; Gilkeson, G.S.; Holers, V.M. Lack of a Functional Alternative Complement Pathway Ameliorates Ischemic Acute Renal Failure in Mice. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 1517–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renner, B.; Ferreira, V.P.; Cortes, C.; Goldberg, R.; Ljubanovic, D.; Pangburn, M.K.; Pickering, M.C.; Tomlinson, S.; Holland-Neidermyer, A.; Strassheim, D.; et al. Binding of factor H to tubular epithelial cells limits interstitial complement activation in ischemic injury. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller-Kristensen, M.; Wang, W.; Ruseva, M.; Thiel, S.; Nielsen, S.; Takahashi, K.; Shi, L.; Ezekowitz, A.; Jensenius, J.C.; Gadjeva, M. Mannan-Binding Lectin Recognizes Structures on Ischaemic Reperfused Mouse Kidneys and is Implicated in Tissue Injury. Scand. J. Immunol. 2005, 61, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Werkhoven, M.B.; Damman, J.; van Dijk, M.C.R.F.; Daha, M.R.; de Jong, I.J.; Leliveld, A.; Krikke, C.; Leuvenink, H.G.; van Goor, H.; van Son, W.J.; et al. Complement Mediated Renal Inflammation Induced by Donor Brain Death: Role of Renal C5a-C5aR Interaction. Am. J. Transplant. 2013, 13, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damman, J.; Seelen, M.A.; Moers, C.; Daha, M.R.; Rahmel, A.; Leuvenink, H.G.; Paul, A.; Pirenne, J.; Ploeg, R.J. Systemic Complement Activation I n Deceased Donors Is Associated With Acute Rejection After Renal Transplantation in the Recipient. Transplantation 2011, 92, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, B.; Köhl, J.; Leclercq, W.K.G.; Wolfs, T.G.A.M.; van Bijnen, A.A.J.H.M.; Heeringa, P.; Buurman, W.A. Complement Factor C5a Mediates Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Independent from Neutrophils. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 3883–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, T.V.; Shiels, I.A.; Strachan, A.J.; Abbenante, G.; Fairlie, D.P.; Taylor, S.M. A small molecule C5a receptor antagonist protects kidneys from ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Kidney Int. 2003, 63, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurman, J.M.; Lenderink, A.M.; Royer, P.A.; Coleman, K.E.; Zhou, J.; Lambris, J.D.; Nemenoff, R.A.; Quigg, R.J.; Holers, V.M. C3a Is Required for the Production of CXC Chemokines by Tubular Epithelial Cells after Renal Ishemia/Reperfusion. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 1819–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budkowska, M.; Ostrycharz, E.; Serwin, N.M.; Nazarewski, Ł.; Cecerska-Heryć, E.; Poręcka, M.; Rykowski, P.; Pietrzak, R.; Zieniewicz, K.; Siennicka, A.; et al. Biomarkers of the Complement System Activation (C3a, C5a, sC5b-9) in Serum of Patients before and after Liver Transplantation. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrar, C.A.; Asgari, E.; Schwaeble, W.J.; Sacks, S.H. Which pathways trigger the role of complement in ischaemia/reperfusion injury? Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaban, V.; Nakstad, E.R.; Stær-Jensen, H.; Schjalm, C.; Seljeflot, I.; Vaage, J.; Lundqvist, C.; Benth, J.; Sunde, K.; Mollnes, T.E.; et al. Complement activation is associated with poor outcome after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Resuscitation 2021, 166, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, D.; Yoder, M. Renal Endothelial Dysfunction in Acute Kidney Ischemia Reperfusion Injury. Cardiovasc. Hematol. Disord. Drug Targets 2014, 14, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, M.; Li, H.; Yang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, X.; Xing, G. Endothelial-derived complement factor D contributes to endothelial dysfunction in malignant nephrosclerosis via local complement activation. Hypertens. Res. 2023, 46, 1759–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongoni, A.; McRae, J.; Salvaris, E.; Fisicaro, N.; Kiss, B.; Pál, G.; Gál, P.; Cowan, P. 228.4: Treatment with a specific inhibitor of the complement lectin pathway is protective against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Transplantation 2024, 108, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwenhuijs-Moeke, G.J.; Pischke, S.E.; Berger, S.P.; Sanders, J.S.F.; Pol, R.A.; Struys, M.M.R.F.; Ploeg, R.J.; Leuvenink, H.G.D. Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury in Kidney Transplantation: Relevant Mechanisms in Injury and Repair. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rother, R.P.; Rollins, S.A.; Mojcik, C.F.; Brodsky, R.A.; Bell, L. Discovery and development of the complement inhibitor eculizumab for the treatment of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1256–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandsema, J.F.; Ginsberg, M.; Hoshino, H.; Mimaki, M.; Nagata, S.; Rao, V.K.; Ruzhansky, K.; Suresh, N.; Tiongson, E.; Yamanouchi, H.; et al. Eculizumab in Adolescent Patients With Refractory Generalized Myasthenia Gravis: A Phase 3, Open-Label, Multicenter Study. Pediatr. Neurol. 2024, 156, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringelstein, M.; Asseyer, S.; Lindenblatt, G.; Fischer, K.; Pul, R.; Skuljec, J.; Revie, L.; Giglhuber, K.; Häußler, V.; Karenfort, M.; et al. Eculizumab Use in Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorders. Neurology 2024, 103, e209888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, A.N.R.; Asgari, E.; Chowdhury, P.; Sacks, S.H.; Dorling, A.; Mamode, N. The use of eculizumab in renal transplantation. Clin. Transpl. 2013, 27, E216–E229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoli, G.; Strologo, A.D.; Grandaliano, G.; Pesce, F. Updates on C3 Glomerulopathy in Kidney Transplantation: Pathogenesis and Treatment Options. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, E.A.; Cohen, A.F. Eculizumab. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2009, 68, 318–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaabak, M.; Babenko, N.; Kuznetsov, O.; Matveev, A.; Minina, M.; Platova, E.; Morozova, M.; Novozhilova, T. Eculizumab reverses the potentially fatal effects of kidney graft reperfusion injury. Pediatr. Transpl. 2014, 18, E44–E47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaabak, M.; Babenko, N.; Shapiro, R.; Zokoyev, A.; Dymova, O.; Kim, E. A prospective randomized, controlled trial of eculizumab to prevent ischemia-reperfusion injury in pediatric kidney transplantation. Pediatr. Transpl. 2018, 22, e13129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröppel, B.; Akalin, E.; Baweja, M.; Bloom, R.D.; Florman, S.; Goldstein, M.; Haydel, B.; Hricik, D.E.; Kulkarni, S.; Levine, M.; et al. Peritransplant eculizumab does not prevent delayed graft function in deceased donor kidney transplant recipients: Results of two randomized controlled pilot trials. Am. J. Transplant. 2020, 20, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; de Fontbrune, F.S.; Lee, L.W.L.; Pessoa, V.; Gualandro, S.; Füreder, W.; Ptushkin, V.; Rottinghaus, S.T.; Volles, L.; Shafner, L.; et al. Ravulizumab (ALXN1210) vs eculizumab in adult patients with PNH naive to complement inhibitors: The 301 study. Blood 2019, 133, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winterberg, P.; Solinsky, C.; LI, G.; Smith, W. #3259 Artemis: A Phase 3 Study Of Ravulizumab To Protect Patients With Ckd Undergoing Cardiac Surgery From Aki And Subsequent Major Adverse Kidney Events. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2023, 38, i1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuzawa, T.; Sampei, Z.; Haraya, K.; Ruike, Y.; Shida-Kawazoe, M.; Shimizu, Y.; Gan, S.W.; Irie, M.; Tsuboi, Y.; Tai, H.; et al. Long lasting neutralization of C5 by SKY59, a novel recycling antibody, is a potential therapy for complement-mediated diseases. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolucci, P.; Ataga, K.I.; Callaghan, M.U.; De Franceschi, L.; Minniti, C.; Alexandrou, A.; Imbs, D.-C.; Fox, R.; Patel, H.; Sostelly, A.; et al. Trial in Progress: The Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase Ib CROSSWALK-a Trial Evaluating the Safety of Crovalimab for the Management of Acute Uncomplicated Vaso-Occlusive Episodes (VOEs) in Patients with Sickle Cell Disease (SCD). Blood 2021, 138, 3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivarelli, M.; Barratt, J.; Beck, L.H.; Fakhouri, F.; Gale, D.P.; de Jorge, E.G.; Mosca, M.; Noris, M.; Pickering, M.C.; Susztak, K.; et al. The role of complement in kidney disease: Conclusions from a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Controversies Conference. Kidney Int. 2024, 106, 369–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frémeaux-Bacchi, V.; Legendre, C.M. The emerging role of complement inhibitors in transplantation. Kidney Int. 2015, 88, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Estebanez, B.T.; Bomback, A.S. C3 Glomerulopathy: Novel Treatment Paradigms. Kidney Int. Rep. 2024, 9, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhouri, F.; Bomback, A.; Kavanagh, D.; Remuzzi, G.; Sunder-Plassmann, G.; Kanellis, J.; Daina, E.; Walker, P.; Wang, Z.; Ahmad, Z. #1467 Pegcetacoplan for post-transplant recurrent C3 glomerulopathy or immune complex membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis in NOBLE: 12-week evolution. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2024, 39, i727–i728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notaro, R.; Luzzatto, L. Breakthrough Hemolysis in PNH with Proximal or Terminal Complement Inhibition. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooden, B.; Tarragon, B.; Navarro-Torres, M.; Bomback, A.S. Complement inhibitors for kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2023, 38, ii29–ii39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Zhang, H.; Pedagogos, E.; Ma, J.; Zhou, H.; Rabe, M.; Hart, A.; Yue, C.; Yan, A.; Tsui, P.; et al. WCN23-1154 TRIAL IN PROGRESS: AN OPEN-LABEL, PHASE 2 STUDY TO EVALUATE EFFICACY, SAFETY, PK, PD OF KP104, A BIFUNCTIONAL COMPLEMENT INHIBITOR, IN IGAN AND C3G SUBJECTS. Kidney Int. Rep. 2023, 8, S230–S231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricklin, D.; Mastellos, D.C.; Reis, E.S.; Lambris, J.D. The renaissance of complement therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 26–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Dairaghi, D.J.; Powers, J.P.; Ertl, L.S.; Baumgart, T.; Wang, Y.; Seitz, L.C.; Penfold, M.E.; Gan, L.; Hu, P.; et al. C5a Receptor (CD88) Blockade Protects against MPO-ANCA GN. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Li, G.-Q.; He, Q.-H.; Li, Y.; Tang, M.; Zheng, Q.-Y.; Xu, G.-L.; Zhang, K.-Q. C5a/C5aR pathway accelerates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury by downregulating PGRN expression. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 53, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Li, G.-Q.; He, Q.-H.; Li, Y.; Tang, M.; Zheng, Q.-Y.; Xu, G.-L.; Zhang, K.-Q. The C5a/C5aR1 axis promotes progression of renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis in a mouse model of renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Kidney Int. 2019, 96, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levien, T.L.; Baker, D.E. Avacopan. Hosp. Pharm. 2023, 58, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlap, C.; Zhao, N.; Ertl, L.S.; Schall, T.J.; Sullivan, K.M.C. C5aR expression in kidney tubules, macrophages and fibrosis. J. Histotechnol. 2024, 11, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buelli, S.; Imberti, B.; Morigi, M. The Complement C3a and C5a Signaling in Renal Diseases: A Bridge between Acute and Chronic Inflammation. Nephron 2024, 148, 712–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, A.; Liaquat, A.; Shabbir, S.; Bokhari, S.A.; Tariq, Z.; Furrukh, Z.; Raja, A.A.; Khan, M.J. High level of lactate dehydrogenase and ischaemia–reperfusion injury regulate the multiple organ dysfunction in patients with COVID-19. Postgrad. Med. J. 2023, 99, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongoni, A.K.; Vikstrom, I.B.; McRae, J.L.; Salvaris, E.J.; Fisicaro, N.; Pearse, M.J.; Wymann, S.; Rowe, T.; Morelli, A.B.; Hardy, M.P.; et al. A potent truncated form of human soluble CR1 is protective in a mouse model of renal ischemia–reperfusion injury. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassimatis, T.; Greenlaw, R.; Hunter, J.P.; Douiri, A.; Flach, C.; Rebollo-Mesa, I.; Nichols, L.L.; Qasem, A.; Danzi, G.; Olsburgh, J.; et al. Ex vivo delivery of Mirococept: A dose-finding study in pig kidney after showing a low dose is insufficient to reduce delayed graft function in human kidney. Am. J. Transplant. 2021, 21, 1012–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Praska, C.E.; Tamburrini, R.; Danobeitia, J.S. Innate immune modulation in transplantation: Mechanisms, challenges, and opportunities. Front. Transplant. 2023, 2, 1277669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, G.; Melchiorre, R.; Loverre, A.; Ditonno, P.; Montinaro, V.; Rossini, M.; Divella, C.; Battaglia, M.; Lucarelli, G.; Annunziata, G.; et al. Therapeutic Targeting of Classical and Lectin Pathways of Complement Protects from Ischemia-Reperfusion-Induced Renal Damage. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 176, 1648–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danobeitia, J.S.; Ziemelis, M.; Ma, X.; Zitur, L.J.; Zens, T.; Chlebeck, P.J.; Van Amersfoort, E.S.; Fernandez, L.A. Complement inhibition attenuates acute kidney injury after ischemia-reperfusion and limits progression to renal fibrosis in mice. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponticelli, C.; Reggiani, F.; Moroni, G. Delayed Graft Function in Kidney Transplant: Risk Factors, Consequences and Prevention Strategies. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, S.C.; Choi, J.; Aubert, O.; Haas, M.; Loupy, A.; Huang, E.; Peng, A.; Kim, I.; Louie, S.; Ammerman, N.; et al. A phase I/II, double-blind, placebo-controlled study assessing safety and efficacy of C1 esterase inhibitor for prevention of delayed graft function in deceased donor kidney transplant recipients. Am. J. Transplant. 2018, 18, 2955–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renner, B.; Laskowski, J.; Poppelaars, F.; Ferreira, V.P.; Blaine, J.; Antonioli, A.H.; Hannan, J.P.; Kovacs, J.M.; van Kooten, C.; You, Z.; et al. Factor H related proteins modulate complement activation on kidney cells. Kidney Int. 2022, 102, 1331–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, L.; Laskowski, J.; Renner, B.; Pickering, M.C.; Kulik, L.; Klawitter, J.; Stites, E.; Christians, U.; van der Vlag, J.; Ravichandran, K.; et al. Complement factor H protects mice from ischemic acute kidney injury but is not critical for controlling complement activation by glomerular IgM. Eur. J. Immunol. 2018, 48, 791–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnabolk, G.; Parsons, N.; Obert, E.; Annamalai, B.; Nasarre, C.; Tomlinson, S.; Lewin, A.S.; Rohrer, B. Delivery of CR2-fH Using AAV Vector Therapy as Treatment Strategy in the Mouse Model of Choroidal Neovascularization. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2018, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudler, T.; Yaseen, S.; Cummings, W.J. Development and characterization of narsoplimab, a selective MASP-2 inhibitor, for the treatment of lectin-pathway–mediated disorders. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1297352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Brodsky, R.A.; Nishimura, J.-I.; Kulasekararaj, A.G. The role of the alternative pathway in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria and emerging treatments. Expert. Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 15, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Chetlapalli, K.; Wang, D.; Potnis, K.C.; Richmond, R.; Krumholz, H.; Lee, A.I.; Cuker, A.; Goshua, G. Cost-effectiveness of iptacopan for paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood J. 2024, 145, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jager, N.M.; van Zanden, J.E.; Subías, M.; Leuvenink, H.G.D.; Daha, M.R.; de Córdoba, S.R.; Poppelaars, F.; Seelen, M.A. Blocking Complement Factor B Activation Reduces Renal Injury and Inflammation in a Rat Brain Death Model. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amura, C.R.; Renner, B.; Lyubchenko, T.; Faubel, S.; Simonian, P.L.; Thurman, J.M. Complement activation and toll-like receptor-2 signaling contribute to cytokine production after renal ischemia/reperfusion. Mol. Immunol. 2012, 52, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Stahl, G.L.; Xu, Y.; Hao, L.; Miller, M.; Buras, J.A.; Fung, M.; Zhao, H. Role for the Alternative Complement Pathway in Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 162, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Miwa, T.; Sato, S.; Golla, M.; Song, W.-C. Expansion of Anticomplement Therapy Indications from Rare Genetic Disorders to Common Kidney Diseases. Annu. Rev. Med. 2024, 75, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risitano, A.M.; Kulasekararaj, A.G.; Lee, J.W.; Maciejewski, J.P.; Notaro, R.; Brodsky, R.; Huang, M.; Geffner, M.; Browett, P. Danicopan: An oral complement factor D inhibitor for paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Haematologica 2020, 106, 3188–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browett, P.J.; Kulasekararaj, A.; Notaro, R.; Ogawa, M.; Risitano, A.; Yu, J.; Lee, J.W. Vemircopan (ALXN2050) Monotherapy in Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria: Interim Data from a Phase 2 Open-Label Proof-of-Concept Study. Blood 2022, 140, 717–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, I.J.; DeLaura, I.; Ladowski, J.; Gao, Q.; Knechtle, S.J.; Kwun, J. Complement-targeted therapies in kidney transplantation—Insights from preclinical studies. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 984090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Troise, D.; Allegra, C.; Cirolla, L.A.; Mercuri, S.; Infante, B.; Castellano, G.; Stallone, G. Exploring Potential Complement Modulation Strategies for Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury in Kidney Transplantation. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14010066
Troise D, Allegra C, Cirolla LA, Mercuri S, Infante B, Castellano G, Stallone G. Exploring Potential Complement Modulation Strategies for Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury in Kidney Transplantation. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(1):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14010066
Chicago/Turabian StyleTroise, Dario, Costanza Allegra, Luciana Antonia Cirolla, Silvia Mercuri, Barbara Infante, Giuseppe Castellano, and Giovanni Stallone. 2025. "Exploring Potential Complement Modulation Strategies for Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury in Kidney Transplantation" Antioxidants 14, no. 1: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14010066
APA StyleTroise, D., Allegra, C., Cirolla, L. A., Mercuri, S., Infante, B., Castellano, G., & Stallone, G. (2025). Exploring Potential Complement Modulation Strategies for Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury in Kidney Transplantation. Antioxidants, 14(1), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14010066







