Evaluating the Impact of Age, Acoustic Exposure, and Electrical Stimulation on Binaural Sensitivity in Adult Bilateral Cochlear Implant Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Age-Related Factors
1.2. Acoustic and Impaired Experience/Exposure Factors
1.3. Experience with Electric Hearing
1.4. Understanding Binaural Sensitivity in Bilateral Cochlear Implant Users
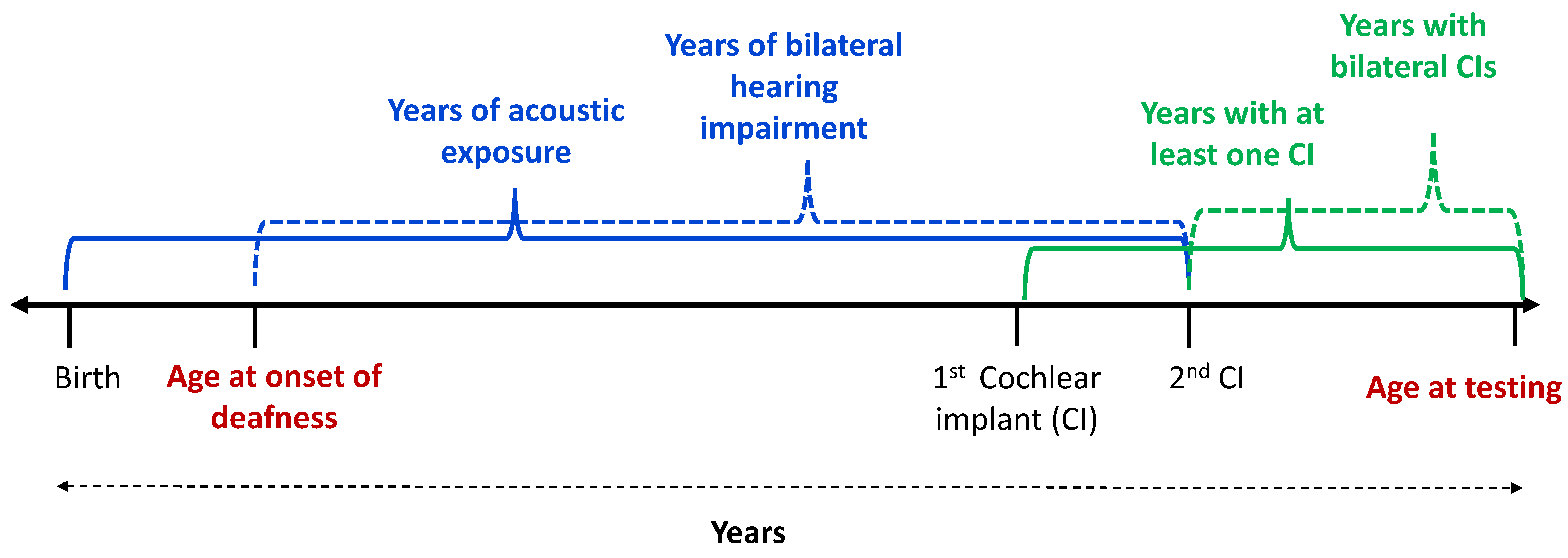
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Listeners
2.2. Equipment and Stimuli
2.3. Mapping
2.4. Pitch Matching
2.5. Tasks
2.5.1. ILD Discrimination
2.5.2. ITD Discrimination
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Electrode Pair Location on JNDs
3.2. Effect of Etiological Factors on ILD and ITD JNDs
3.2.1. ILD Just-Noticeable Differences
3.2.2. ITD Just-Noticeable Differences
3.3. Categorical Analysis of Age-Related Factors
3.4. Relationship between ILD and ITD Sensitivity
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of Age-Related Factors
4.2. Impact of Acoustic and Impaired Experience/Exposure
4.3. Impact of Electric Hearing
4.4. Relationship between Binaural Cue Types
5. Conclusions and Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Litovsky, R.Y. Development of the auditory system. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2015, 129, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, B.S.; Dorman, M.F. Cochlear implants: A remarkable past and a brilliant future. Hear. Res. 2008, 242, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, B.S.; Finley, C.C.; Lawson, D.T.; Wolford, R.D.; Eddington, N.K.; Rabinowitz, W.M. Better speech recognition with cochlear implants. Nature 1991, 352, 236–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sousa, A.F.; Couto, M.I.V.; Martinho-Carvalho, A.C.; De Carvalho, A.C.M. Quality of life and cochlear implant: Results in adults with postlingual hearing loss. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2018, 84, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aronoff, J.M.; Yoon, Y.-S.; Freed, D.J.; Vermiglio, A.J.; Pal, I.; Soli, S.D. The use of interaural time and level difference cues by bilateral cochlear implant users. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2010, 127, EL87–EL92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, H.G.; Kan, A.; Litovsky, R.Y. Comparing sound localization deficits in bilateral cochlear-implant users and vocoder simulations with normal-hearing listeners. Trends Hear. 2014, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeber, B.U.; Fastl, H. Localization cues with bilateral cochlear implants. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 123, 1030–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laback, B.; Pok, S.-M.; Baumgartner, W.-D.; Deutsch, W.A.; Schmid, K. Sensitivity to interaural level and envelope time differences of two bilateral cochlear implant listeners using clinical sound processors. Ear Hear. 2004, 25, 488–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grantham, D.W.; Ashmead, D.H.; Ricketts, T.; Labadie, R.F.; Haynes, D.S. Horizontal-plane localization of noise and speech signals by postlingually deafened adults fitted with bilateral cochlear implants. Ear Hear. 2007, 28, 524–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litovsky, R.Y.; Goupell, M.J.; Godar, S.; Grieco-Calub, T.; Jones, G.L.; Garadat, S.N.; Agrawal, S.; Kan, A.; Todd, A.; Hess, C.; et al. Studies on Bilateral Cochlear Implants at the University of Wisconsin’s Binaural Hearing and Speech Laboratory. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2012, 23, 476–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litovsky, R.Y.; Goupell, M.J.; Kan, A.; Landsberger, D.M. Use of Research Interfaces for Psychophysical Studies With Cochlear-Implant Users. Trends Hear. 2017, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hoesel, R.J.; Jones, G.L.; Litovsky, R.Y. Interaural Time-Delay Sensitivity in Bilateral Cochlear Implant Users: Effects of Pulse Rate, Modulation Rate, and Place of Stimulation. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2009, 10, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, A.; Litovsky, R.Y. Binaural hearing with electrical stimulation. Hear. Res. 2015, 322, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laback, B.; Egger, K.; Majdak, P. Perception and coding of interaural time differences with bilateral cochlear implants. Hear. Res. 2015, 322, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litovsky, R.Y.; Jones, G.L.; Agrawal, S.; Van Hoesel, R. Effect of age at onset of deafness on binaural sensitivity in electric hearing in humans. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2010, 127, 400–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, Y.; Buechel, B.D.; Sunwoo, W.; Wagner, J.D.; Delgutte, B. Neural ITD Sensitivity and Temporal Coding with Cochlear Implants in an Animal Model of Early-Onset Deafness. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2019, 20, 37–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddins, A.C.; Ozmeral, E.J.; Eddins, D.A. How aging impacts the encoding of binaural cues and the perception of auditory space. Hear. Res. 2018, 369, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.R.; Easter, K.; Goupell, M.J. Effects of rate and age in processing interaural time and level differences in normal-hearing and bilateral cochlear-implant listeners. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2019, 146, 3232–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strouse, A.; Ashmead, D.H.; Ohde, R.N.; Grantham, D.W. Temporal processing in the aging auditory system. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1998, 104, 2385–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichora-Fuller, M.K.; Schneider, B.A. Masking-level differences in older adults: The effect of the level of the masking noise. Percept. Psychophys. 1998, 60, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dubno, J.R.; Ahlstrom, J.B.; Horwitz, A.R. Binaural Advantage for Younger and Older Adults with Normal Hearing. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2008, 51, 539–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babkoff, H.; Muchnik, C.; Ben-David, N.; Furst, M.; Even-Zohar, S.; Hildesheimer, M. Mapping lateralization of click trains in younger and older populations. Hear. Res. 2002, 165, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, G.E.; Warren, L.R.; Wagener, J.W. Auditory Lateralization: Age Differences in Sensitivity to Dichotic Time and Amplitude Cues. J. Gerontol. 1977, 32, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozmeral, E.J.; Eddins, D.A.; Eddins, A.C. Reduced temporal processing in older, normal-hearing listeners evident from electrophysiological responses to shifts in interaural time difference. J. Neurophysiol. 2016, 116, 2720–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blamey, P.; Artières, F.; Başkent, D.; Bergeron, F.; Beynon, A.; Burke, E.; Dillier, N.; Dowell, R.; Fraysse, B.; Gallego, S.; et al. Factors Affecting Auditory Performance of Postlinguistically Deaf Adults Using Cochlear Implants: An Update with 2251 Patients. Audiol. Neurotol. 2013, 18, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vollmer, M. Neural Processing of Acoustic and Electric Interaural Time Differences in Normal-Hearing Gerbils. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 6949–6966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kral, A.; Tillein, J.; Heid, S.; Hartmann, R.; Klinke, R. Postnatal Cortical Development in Congenital Auditory Deprivation. Cereb. Cortex 2005, 15, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polonenko, M.; Papsin, B.C.; Gordon, K.A. Delayed access to bilateral input alters cortical organization in children with asymmetric hearing. NeuroImage Clin. 2017, 17, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, K.A.; Henkin, Y.; Kral, A. Asymmetric Hearing During Development: The Aural Preference Syndrome and Treatment Options. Pediatrics 2015, 136, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillein, J.; Hubka, P.; Kral, A. Monaural Congenital Deafness Affects Aural Dominance and Degrades Binaural Processing. Cereb. Cortex 2016, 26, 1762–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, K.A.; Wong, D.D.; Papsin, B.C. Bilateral input protects the cortex from unilaterally-driven reorganization in children who are deaf. Brain 2013, 136, 1609–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorodensky, J.H.; Alemu, R.Z.; Gill, S.S.; Sandor, M.T.; Papsin, B.C.; Cushing, S.L.; Gordon, K.A. Binaural hearing is impaired in children with hearing loss who use bilateral hearing aids. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2019, 146, 4352–4362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salloum, C.A.M.; Valero, J.; Wong, D.D.E.; Papsin, B.C.; Van Hoesel, R.; Gordon, K.A. Lateralization of Interimplant Timing and Level Differences in Children Who Use Bilateral Cochlear Implants. Ear Hear. 2010, 31, 441–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litovsky, R.Y.; Gordon, K. Bilateral cochlear implants in children: Effects of auditory experience and deprivation on auditory perception. Hear. Res. 2016, 338, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, K.A.; Deighton, M.R.; Abbasalipour, P.; Papsin, B.C. Perception of Binaural Cues Develops in Children Who Are Deaf through Bilateral Cochlear Implantation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, B.R.; Litovsky, R.; Parkinson, A.; Lake, J. Importance of Age and Postimplantation Experience on Speech Perception Measures in Children With Sequential Bilateral Cochlear Implants. Otol. Neurotol. 2007, 28, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlers, E.; Goupell, M.J.; Zheng, Y.; Godar, S.P.; Litovsky, R.Y. Binaural sensitivity in children who use bilateral cochlear implants. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2017, 141, 4264–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easwar, V.; Yamazaki, H.; Deighton, M.; Papsin, B.; Gordon, K.A. Cortical Representation of Interaural Time Difference Is Impaired by Deafness in Development: Evidence from Children with Early Long-term Access to Sound through Bilateral Cochlear Implants Provided Simultaneously. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 2349–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, A.; Stoelb, C.; Litovsky, R.Y.; Goupell, M.J. Effect of mismatched place-of-stimulation on binaural fusion and lateralization in bilateral cochlear-implant users. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 134, 2923–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, T.; Kan, A.; Jones, H.G.; Litovsky, R.Y. Mixed stimulation rates to improve sensitivity of interaural timing differences in bilateral cochlear implant listeners. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2018, 143, 1428–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, A.; Litovsky, R.Y.; Goupell, M.J. Effects of interaural pitch matching and auditory image centering on binaural sensitivity in cochlear implant users. Ear Hear. 2015, 36, e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, A.; Jones, H.G.; Litovsky, R.Y. Effect of multi-electrode configuration on sensitivity to interaural timing differences in bilateral cochlear-implant users. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2015, 138, 3826–3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Dietz, M. Comparison of Interaural Electrode Pairing Methods for Bilateral Cochlear Implants. Trends Hear. 2015, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, C.J.; Eddington, N.K.; Colburn, H.S.; Rabinowitz, W.M. Binaural sensitivity as a function of interaural electrode position with a bilateral cochlear implant user. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2003, 114, 1565–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goupell, M.J.; Cosentino, S.; Stakhovskaya, O.A.; Bernstein, J.G.W. Interaural Pitch-Discrimination Range Effects for Bilateral and Single-Sided-Deafness Cochlear-Implant Users. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2019, 20, 187–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, B.B.; Eddington, N.K.; Noel, V.; Colburn, H.S. Sensitivity to interaural time difference with bilateral cochlear implants: Development over time and effect of interaural electrode spacing. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2009, 126, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichmann, F.A.; Hill, N.J. The psychometric function: I. Fitting, sampling, and goodness of fit. Percept. Psychophys. 2001, 63, 1293–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitt, H. Transformed Up-Down Methods in Psychoacoustics. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1971, 49, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grantham, D.W. Discrimination of dynamic interaural intensity differences. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1984, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yost, W.A.; Dye, R.H., Jr. Discrimination of interaural differences of level as a function of frequency. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1988, 83, 1846–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, L.R. Detection of interaural delay in high-frequency noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1982, 71, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadden, D.; Pasanen, E.G. Lateralization at high frequencies based on interaural time differences. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1976, 59, 634–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klumpp, R.G.; Eady, H.R. Some Measurements of Interaural Time Difference Thresholds. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1956, 28, 859–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuetzel, J.M.; Hafter, E.R. Discrimination of interaural delays in complex waveforms: Spectral effects. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1981, 69, 1112–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.R.; Burnham, K.P. Avoiding Pitfalls When Using Information-Theoretic Methods. J. Wildl. Manag. 2002, 66, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Ewert, S.D.; McAlpine, D.; Dietz, M. Differences in the temporal course of interaural time difference sensitivity between acoustic and electric hearing in amplitude modulated stimuli. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2017, 141, 1862–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitton, J.P.; Polley, D.B. Evaluating the Perceptual and Pathophysiological Consequences of Auditory Deprivation in Early Postnatal Life: A Comparison of Basic and Clinical Studies. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2011, 12, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, K.E.; Noel, V.; Ryugo, D.K.; Delgutte, B. Neural coding of interaural time differences with bilateral cochlear implants: Effects of congenital deafness. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 14068–14079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashmead, D.H.; Clifton, R.K.; Perris, E.E. Precision of auditory localization in human infants. Dev. Psychol. 1987, 23, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litovsky, R.Y. Developmental changes in the precedence effect: Estimates of minimum audible angle. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1997, 102, 1739–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlers, E.; Kan, A.; Winn, M.B.; Stoelb, C.; Litovsky, R.Y. Binaural hearing in children using Gaussian enveloped and transposed tones. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2016, 139, 1724–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, A.E.; Goupell, M.J.; Litovsky, R.Y. The Relationship Between Intensity Coding and Binaural Sensitivity in Adults With Cochlear Implants. Ear Hear. 2017, 38, e128–e141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Godar, S.P.; Litovsky, R.Y. Development of Sound Localization Strategies in Children with Bilateral Cochlear Implants. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grieco-Calub, T.M.; Litovsky, R.Y. Spatial acuity in 2-to-3-year-old children with normal acoustic hearing, unilateral cochlear implants, and bilateral cochlear implants. Ear Hear. 2012, 33, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieco-Calub, T.M.; Litovsky, R.Y. Sound Localization Skills in Children Who Use Bilateral Cochlear Implants and in Children with Normal Acoustic Hearing. Ear Hear. 2010, 31, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Deun, L.; Van Wieringen, A.; Bogaert, T.V.D.; Scherf, F.; Offeciers, F.E.; Van De Heyning, P.; Desloovere, C.; Dhooge, I.; Deggouj, N.; De Raeve, L.; et al. Sound Localization, Sound Lateralization, and Binaural Masking Level Differences in Young Children with Normal Hearing. Ear Hear. 2009, 30, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killan, C.; Scally, A.; Killan, E.; Totten, C.; Raine, C. Factors Affecting Sound-Source Localization in Children With Simultaneous or Sequential Bilateral Cochlear Implants. Ear Hear. 2019, 40, 870–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullington, H.; Bele, D.; Brinton, J.C.; Cooper, S.; Daft, M.; Harding, J.; Hatton, N.; Humphries, J.; Lutman, M.E.; Maddocks, J.; et al. United Kingdom national paediatric bilateral project: Demographics and results of localization and speech perception testing. Cochlea Implant. Int. 2016, 18, 2–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, A.; Peng, Z.E.; Moua, K.; Litovsky, R.Y. A systematic assessment of a cochlear implant processor’s ability to encode interaural time differences. In Proceedings of the Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA ASC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 12–15 November 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, K.E.; Chung, Y.; Delgutte, B. Congenital and Prolonged Adult-Onset Deafness Cause Distinct Degradations in Neural ITD Coding with Bilateral Cochlear Implants. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2013, 14, 393–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, Z.; Delgutte, B. Sensitivity to interaural time differences in the inferior colliculus with bilateral cochlear implants. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 6740–6750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgärtel, R.M.; Hu, H.; Kollmeier, B.; Dietz, M. Extent of lateralization at large interaural time differences in simulated electric hearing and bilateral cochlear implant users. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2017, 141, 2338–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freigang, C.; Rübsamen, R.; Richter, N. Pre-attentive cortical processing of behaviorally perceptible spatial changes in older adults—a mismatch negativity study. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shannon, R.V. Advances in auditory prostheses. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2012, 25, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kral, A.; Dorman, M.F.; Wilson, B.S. Neuronal Development of Hearing and Language: Cochlear Implants and Critical Periods. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 42, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polonenko, M.; Gordon, K.A.; Cushing, S.L.; Papsin, B.C. Cortical organization restored by cochlear implantation in young children with single sided deafness. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polonenko, M.; Papsin, B.C.; Gordon, K.A. Limiting asymmetric hearing improves benefits of bilateral hearing in children using cochlear implants. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easwar, V.; Yamazaki, H.; Deighton, M.; Papsin, B.; Gordon, K. Cortical Processing of Level Cues for Spatial Hearing is Impaired in Children with Prelingual Deafness Despite Early Bilateral Access to Sound. Brain Topogr. 2017, 31, 270–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churchill, T.H.; Kan, A.; Goupell, M.J.; Litovsky, R.Y. Spatial hearing benefits demonstrated with presentation of acoustic temporal fine structure cues in bilateral cochlear implant listeners. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2014, 136, 1246–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, N.J.; Hawley, M.L.; Colburn, H.S. Relating interaural difference sensitivities for several parameters measured in normal-hearing and hearing-impaired listeners. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2016, 140, 1783–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Listener ID | Apex-EL | Apex-ER | Mid-EL | Mid-ER | Base-EL | Base-ER | Etiology | Age at Onset of Deafness | Age at Testing |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IAG | 18 | 22 | 12 | 18 | 4 | 10 | Congenital | 2 | 56 |
| IAJ | 19 | 21 | 14 | 14 | 6 | 8 | Unknown; progressive since early childhood | 5 | 65 |
| IAZ | 20 | 20 | 13 | 14 | 4 | 4 | Hereditary | 55 | 76 |
| IBA | 20 | 16 | 12 | 14 | 8 | 8 | Unknown; progressive since birth | 0 | 75 |
| IBB | 20 | 22 | 12 | 15 | 4 | 4 | Unknown | 23 | 44 |
| IBD | 22 | 20 | 12 | 12 | 4 | 4 | Meniere’s; hereditary | 36 | 81 |
| IBF | 20 | 22 | 12 | 13 | 4 | 6 | Hereditary | 38 | 59 |
| IBJ | 21 | 20 | 12 | 13 | 4 | 4 | Unknown | 8 | 26 |
| IBK | 18 | 22 | 14 | 13 | 6 | 6 | Hereditary; noise exposure | 53 | 70 |
| IBL | 20 | 20 | 12 | 12 | 4 | 4 | Unknown | 12 | 64 |
| IBM | 20 | 20 | 12 | 12 | 4 | 4 | Hereditary | 30 | 56 |
| IBN | 18 | 18 | 12 | 16 | 4 | 8 | Unknown; progressive since childhood | 0 | 65 |
| IBO | -- | -- | 12 | 12 | -- | -- | Otosclerosis first followed by sudden bilateral loss | 20 | 46 |
| IBP | 20 | 19 | 12 | 15 | 4 | 4 | Meningitis in adulthood | 54 | 61 |
| IBQ | 20 | 11 | 14 | 7 | 8 | 1 | Meniere’s Disease-left ear Unknown-right ear | 44 | 80 |
| IBR | 18 | 17 | 12 | 12 | -- | -- | Unknown | 28 | 57 |
| IBU | 20 | 20 | 12 | 12 | 6 | 6 | Hereditary | 20 | 56 |
| IBV | 20 | 19 | 12 | 10 | 4 | 5 | Unknown illness which caused ringing in both ears | 16 | 69 |
| IBW | 22 | 20 | 14 | 14 | 6 | 6 | Ototoxic medication | 13 | 56 |
| IBX | 20 | 22 | 12 | 13 | 4 | 4 | Suspected ototoxic medication | 40 | 70 |
| IBY | 19 | 17 | 12 | 12 | 4 | 7 | Unknown | 41 | 48 |
| IBZ | 18 | 16 | 12 | 12 | 4 | 4 | Unknown; sudden loss | 30 | 44 |
| ICA | 20 | 20 | 14 | 14 | 3 | 4 | Childhood illnesses | 13 | 53 |
| ICB | 18 | 19 | 12 | 12 | 4 | 4 | Heredity | 9 | 61 |
| ICC | 20 | 20 | 12 | 14 | 4 | 5 | Unknown; progressive since birth | 2 | 66 |
| ICD | 20 | 18 | 12 | 10 | 4 | 2 | Enlarged vestibular aqueduct | 3 | 54 |
| ICE | 20 | 21 | 12 | 14 | 4 | 6 | Unknown | 66 | 72 |
| ICF | 20 | 16 | 12 | 10 | 4 | 8 | Otosclerosis | 21 | 70 |
| ICG | 20 | 18 | 12 | 10 | 6 | 8 | Unknown; progressive since birth | 2 | 50 |
| ICH | 20 | 20 | 12 | 14 | 4 | 4 | Enlarged vestibular aqueduct | 2 | 32 |
| ICI | 18 | 18 | 12 | 16 | 4 | 6 | Unknown | 31 | 54 |
| ICJ | 20 | 16 | 12 | 12 | 4 | 6 | Unknown | 13 | 63 |
| ICK | 20 | 20 | 12 | 13 | 6 | 9 | Noise exposure | 30 | 69 |
| ICL | 20 | 19 | 12 | 18 | 4 | 6 | German Measles | 3 | 45 |
| ICM | 20 | 20 | 12 | 14 | 4 | 5 | Unknown | 20 | 59 |
| ICN | 16 | 17 | 12 | 14 | 8 | 12 | Unknown; progressive since birth | 4 | 40 |
| ICO | 18 | 18 | 12 | 12 | 4 | 4 | Unknown; progressive since early childhood | 4 | 32 |
| ICP | 20 | 22 | 12 | 14 | 4 | 10 | Unknown; progressive since early childhood | 3 | 50 |
| ICQ | 18 | 20 | 12 | 13 | 4 | 8 | Meningitis in childhood | 4 | 19 |
| ICR | 18 | 20 | 12 | 14 | 4 | 4 | Radiation | 27 | 59 |
| ICS | 18 | 19 | 12 | 12 | 4 | 5 | Unknown | 68 | 85 |
| ICT | 20 | 20 | 12 | 12 | 4 | 5 | Car wreck; traumatic injury | 18 | 20 |
| ICV | 20 | 20 | 12 | 14 | 4 | 7 | Unknown; progressive since childhood | 7 | 58 |
| ICW | 20 | 19 | 12 | 9 | 4 | 2 | Congenital | 0 | 21 |
| ICX | 18 | 15 | 12 | 10 | 8 | 9 | Progressive since childhood; Meniere’s in adulthood | 0 | 74 |
| (A) Multicollinearity of the ILD JND Dataset | |||
| Row | Column | Correlation Coefficient | p-Value |
| Years of acoustic exposure | Age at testing | 0.98 | <0.05 * |
| Years of acoustic exposure | Years with one CI | −0.14 | 0.45 |
| Age at testing | Years with one CI | −0.06 | 0.74 |
| Years of acoustic exposure | Years with bilateral CIs | 0.18 | 0.34 |
| Age at testing | Years with bilateral CIs | 0.35 | 0.05 |
| Years with one CI | Years with bilateral CIs | 0.35 | 0.05 |
| Years of acoustic exposure | Age at Onset | 0.56 | <0.05 * |
| Age at Testing | Age at Onset | 0.54 | <0.05 * |
| Years with one CI | Age at Onset | −0.16 | 0.39 |
| Years with bilateral CIs | Age at Onset | 0.08 | 0.65 |
| Years of acoustic exposure | Years with bilateral hearing impairment | 0.27 | 0.14 |
| Age at testing | Years with bilateral hearing impairment | 0.28 | 0.12 |
| Years with one CI | Years with bilateral hearing impairment | 0.06 | 0.73 |
| Years with bilateral CIs | Years with bilateral hearing impairment | 0.08 | 0.67 |
| Age at Onset | Years with bilateral hearing impairment | −0.64 | <0.05 * |
| (B) Multicollinearity of ITD JND Dataset | |||
| Row | Column | Correlation Coefficient | p-Value |
| Years of acoustic exposure | Age at testing | 0.98 | <0.05 * |
| Years of acoustic exposure | Years with one CI | −0.13 | 0.42 |
| Age at testing | Years with one CI | −0.05 | 0.75 |
| Years of acoustic exposure | Years with bilateral CIs | 0.13 | 0.40 |
| Age at testing | Years with bilateral CIs | 0.30 | 0.05 |
| Years with one CI | Years with bilateral CIs | 0.39 | <0.05 * |
| Years of acoustic exposure | Age at Onset | 0.53 | <0.05 * |
| Age at Testing | Age at Onset | 0.51 | <0.05 * |
| Years with one CI | Age at Onset | −0.12 | 0.44 |
| Years with bilateral CIs | Age at Onset | 0.05 | 0.75 |
| Years of acoustic exposure | Years with bilateral hearing impairment | 0.35 | <0.05* |
| Age at testing | Years with bilateral hearing impairment | 0.36 | <0.05* |
| Years with one CI | Years with bilateral hearing impairment | 0.02 | 0.89 |
| Years with bilateral CIs | Years with bilateral hearing impairment | 0.08 | 0.62 |
| Age at Onset | Years with bilateral hearing impairment | −0.61 | <0.05 * |
| Model Coefficients | Std. Error | t-Value | p-Value | VIF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 4.24 | 0.56 | 7.59 | <0.001 * | |
| Years with one CI | −0.15 | 0.11 | −1.41 | 0.17 | 1.04 |
| Years with bilateral hearing impairment | −0.04 | 0.04 | −1.13 | 0.27 | 1.21 |
| Years of acoustic exposure | 0.14 | 0.05 | 2.96 | <0.05 * | 1.89 |
| Years with bilateral hearing impairment: years of acoustic exposure | −0.006 | <0.05 | −2.60 | <0.05 * | 1.72 |
| Model Coefficients | Std. Error | t-Value | p-Value | VIF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 4.28 | 0.56 | 7.67 | <0.001 * | |
| Years with one CI | −0.20 | 0.11 | −1.86 | 0.07 | 1.01 |
| Years with bilateral hearing impairment | −0.04 | 0.03 | −1.16 | 0.26 | 1.20 |
| Age at testing | 0.14 | 0.04 | 3.06 | <0.05 * | 1.87 |
| Age at testing: years with bilateral hearing impairment | <−0.05 | <0.001 | −2.64 | <0.05 * | 1.72 |
| Model Coefficients | Std. Error | t-Value | p-Value | VIF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 429.29 | 46.79 | 9.17 | <0.001 * | |
| Years with bilateral hearing impairment | −3.37 | 2.88 | −1.12 | 0.25 | 1.01 |
| Years with one CI | 11.10 | 10.30 | 1.10 | 0.29 | 1.00 |
| Years with bilateral hearing impairment: years with one CI | −1.90 | 0.72 | −2.63 | <0.05 * | 1.01 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thakkar, T.; Anderson, S.R.; Kan, A.; Litovsky, R.Y. Evaluating the Impact of Age, Acoustic Exposure, and Electrical Stimulation on Binaural Sensitivity in Adult Bilateral Cochlear Implant Patients. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060406
Thakkar T, Anderson SR, Kan A, Litovsky RY. Evaluating the Impact of Age, Acoustic Exposure, and Electrical Stimulation on Binaural Sensitivity in Adult Bilateral Cochlear Implant Patients. Brain Sciences. 2020; 10(6):406. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060406
Chicago/Turabian StyleThakkar, Tanvi, Sean R. Anderson, Alan Kan, and Ruth Y. Litovsky. 2020. "Evaluating the Impact of Age, Acoustic Exposure, and Electrical Stimulation on Binaural Sensitivity in Adult Bilateral Cochlear Implant Patients" Brain Sciences 10, no. 6: 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060406
APA StyleThakkar, T., Anderson, S. R., Kan, A., & Litovsky, R. Y. (2020). Evaluating the Impact of Age, Acoustic Exposure, and Electrical Stimulation on Binaural Sensitivity in Adult Bilateral Cochlear Implant Patients. Brain Sciences, 10(6), 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060406





