Focus on Clozapine Withdrawal- and Misuse-Related Cases as Reported to the European Medicines Agency (EMA) Pharmacovigilance Database
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Pharmacodynamic Considerations
1.2. Clozapine Abuse Issues and Substance Use Disorders
1.3. Aims
2. Methods
2.1. Data Source and Acquisition
2.2. Data Analysis
2.3. Ethics’ Issues
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations
4.2. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khokhar, J.; Henricks, A.M.; Sullivan, E.D.; Green, A.I. Unique Effects of Clozapine: A Pharmacological Perspective. Adv. Pharmacol. 2018, 82, 137–162. [Google Scholar]
- Warnez, S.; Alessi-Severini, S. Clozapine: A review of clinical practice guidelines and prescribing trends. BMC Psychiatry 2014, 14, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ArrayExpress—A database of functional genomics experiments. Available online: http://www. ebi.ac.uk/arrayexpress/ (accessed on 12 November 2012).
- Stahl, S.M. Stahl’s Essential Psychopharmacology-Prescriber’s Guide, 6th ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mauri, M.C.; Paletta, S.; Maffini, M.; Colasanti, A.; Dragogna, F.; Di Pace, C.; Altamura, A. Clinical pharmacology of atypical antipsychotics: An update. EXCLI J. 2014, 13, 1163–1191. [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence, R.E.; First, M.B.; Lieberman, J.A. Schizophrenia and Other Psychoses; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; Volume 1, pp. 791–856. [Google Scholar]
- O Kalkman, H.; Loetscher, E. alpha2C-Adrenoceptor blockade by clozapine and other antipsychotic drugs. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 462, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fjalland, B.; Boeck, V. Neuroleptic Blockade of the Effect of Various Neurotransmitter Substances. Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1978, 42, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilbily, J.; Mccollum, B.; De Leon, J. Catatonia Secondary to Sudden Clozapine Withdrawal: A Case with Three Repeated Episodes and a Literature Review. Case Rep. Psychiatry 2017, 2017, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, E.; Schembri, F.; Green, D.M.; Burns, J. Serotonin Syndrome Associated with Clozapine Withdrawal. JAMA Neurol. 2013, 70, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meltzer, H.Y. An overview of the mechanism of action of clozapine. J. Clin. Psychiatry 1994, 55. [Google Scholar]
- Schwieler, L.; Engberg, G.; Erhardt, S. Clozapine modulates midbrain dopamine neuron firing via interaction with the NMDA receptor complex. Synapse 2004, 52, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Ikeda, K.; Kumanishi, T. Effects of clozapine on the delta- and kappa- opioid receptors and the G-protein-activated K+ (GIRK) channel expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 123, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronson, J.K. Clozapine. In Meyler’s Side Effects of Drugs (Sixteenth Edition): The International Encyclopedia of Adverse Drug Reactions and Interactions; Elsevier: Kidlington, UK, 2016; pp. 443–477. [Google Scholar]
- Trenton, A.J.; Currier, G.W.; Zwemer, F.L. Fatalities associated with therapeutic use and overdose of atypical antipsychotics. CNS Drugs 2003, 17, 307–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khokhar, J.; Dwiel, L.L.; Henricks, A.M.; Doucette, W.T.; Green, A.I. The link between schizophrenia and substance use disorder: A unifying hypothesis. Schizophr. Res. 2018, 194, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olianas, M.C.; Dedoni, S.; Ambu, R.; Onali, P.L. Agonist activity of N-desmethylclozapine at δ-opioid receptors of human frontal cortex. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 607, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundram, S.; Copolov, D.; Dean, B. Clozapine decreases [3H] CP 55940 binding to the cannabinoid1 receptor in the rat nucleus accumbens. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2005, 371, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, P.C.S.; Kieffer, B.L. Delta opioid receptors in brain function and diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 140, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schifano, F.; Chiappini, S.; Corkery, J.M.; Guirguis, A. Abuse of Prescription Drugs in the Context of Novel Psychoactive Substances (NPS): A Systematic Review. Brain Sci. 2018, 8, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bersani, F.S.; Corazza, O.; Simonato, P.; Mylokosta, A.; Levari, E.; Lovaste, R.; Schifano, F. Drops of madness? Recreational misuse of tropicamide collyrium; early warning alerts from Russia and Italy. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2013, 35, 571–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Blichowski, M.; Daskalakis, Z.J.; Wu, Z.; Liu, C.C.; Cortez, M.A.; Snead, O.C. Evidence that clozapine directly interacts on the GABAB receptor. NeuroReport 2011, 22, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Gil, X.; Artigas, F.; Adell, A. Unraveling monoamine receptors involved in the action of typical and atypical antipsychotics on glutamatergic and serotonergic transmission in prefrontal cortex. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 502–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schifano, F.; Orsolini, L.; Papanti, G.D.; Corkery, J.M. Novel psychoactive substances of interest for psychiatry. World Psychiatry 2015, 14, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schifano, F.; Napoletano, F.; Arillotta, D.; Zangani, C.; Gilgar, L.; Guirguis, A.; Corkery, J.M.; Vento, A. The clinical challenges of synthetic cathinones. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmet, S.V.; Strous, R.D.; Burgess, E.S.; Kohnstamm, S.; Green, A.I. Effects of clozapine on substance use in patients with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder: A retrospective survey. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2000, 20, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, M.; Huhn, M.; Schneider-Thoma, J.; Bighelli, I.; Gutsmiedl, K.; Leucht, S. Efficacy, acceptability and tolerability of antipsychotics in patients with schizophrenia and comorbid substance use. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019, 29, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunette, M.F.; Drake, R.E.; Xie, H.; McHugo, G.J.; Green, A.I. Clozapine Use and Relapses of Substance Use Disorder Among Patients with Co-occurring Schizophrenia and Substance Use Disorders. Schizophr. Bull. 2006, 32, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okhuijsen-Pfeifer, C.; Sterk, A.Y.; Horn, I.M.; Terstappen, J.; Kahn, R.S.; Luykx, J.J. Demographic and clinical features as predictors of clozapine response in patients with schizophrenia spectrum disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 111, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Kim, S.; Lee, G.; Kim, E.; Jung, H. Quetiapine misuse and abuse: Is it an atypical paradigm of drug seeking behavior? J. Res. Pharm. Pr. 2017, 6, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiappini, S.; Schifano, F. Is There a Potential of Misuse for Quetiapine? Literature Review and Analysis of the European Medicines Agency/European Medicines Agency Adverse Drug Reactions’ Database. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2018, 38, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evoy, K.; Teng, C.; Encarnacion, V.G.; Frescas, B.; Hakim, J.; Saklad, S.; Frei, C.R. Comparison of Quetiapine Abuse and Misuse Reports to the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System with Other Second-Generation Antipsychotics. Subst. Abus. Res. Treat. 2019, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vento, A.E.; Kotzalidis, G.D.; Cacciotti, M.; Papanti, G.D.; Orsolini, L.; Rapinesi, C.; Savoja, V.; Calabrò, G.; Del Casale, A.; Piacentino, D.; et al. Quetiapine Abuse Fourteen Years Later: Where Are We Now? A Systematic Review. Subst. Use Misuse 2019, 55, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Guideline on good pharmacovigilance practices, Module VI—Collection, management and submission of reports of suspected adverse reactions to medicinal products (Rev 2). Available online: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Regulatory_and_procedural_guideline/2017/08/WC500232767.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2019).
- MedDRA. Version 21. 2018. Available online: https://www.meddra.org/sites/default/files/guidance/file/smq_intguide_21_0_english.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2019).
- Schifano, F.; Chiappini, S.; Corkery, J.M.; Guirguis, A. Assessing the 2004–2018 Fentanyl Misusing Issues Reported to an International Range of Adverse Reporting Systems. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schifano, F.; Chiappini, S.; Corkery, J.M.; Guirguis, A. An Insight into Z-Drug Abuse and Dependence: An Examination of Reports to the European Medicines Agency Database of Suspected Adverse Drug Reactions. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019, 22, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schifano, F.; Chiappini, S. Is there such a thing as a ’lope’ dope? Analysis of loperamide-related European Medicines Agency (EMA) pharmacovigilance database reports. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schifano, F.; Chiappini, S. Is There a Potential of Misuse for Venlafaxine and Bupropion? Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Note for Guidance—EudraVigilance Human—Processing of Safety Messages and Individual Case Safety Reports (ICSRs) (EMA/H/20665/04/Final Rev. 2). Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/regulatory-procedural-guideline/note-guidance-eudravigilance-human-processing-safety-messages-individual-case-safety-reports-icsrs_en.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2019).
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). EudraVigilance Working Group (EV-EWG). Guideline on the Use of Statistical Signal Detection Methods in the EudraVigilance Data Analysis System. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/regulatory-procedural-guideline/draft-guideline-use-statistical-signal-detection-methods-eudravigilance-data-analysis-system_en.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2019).
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). ICH Guideline E2B (R3) on Electronic Transmission of Individual Case Safety Reports (ICSRs)—Data Elements and Message Specification—Implementation Guide. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/international-conference-harmonisation-technical-requirements-registration-pharmaceuticals-human-use_en-4.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2019).
- Bastiampillai, T.; Forooziya, F.; Dhillon, R. Clozapine-withdrawal catatonia. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2013, 43, 283–284. [Google Scholar]
- Goudie, A.J.; Smith, J.A.; Robertson, A.; Cavanagh, C. Clozapine as a drug of dependence. Psychopharmacology 1999, 142, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ines, S.; Mahal, A.; Hoss, J.; Gaertner, H.J. Intoxication with clozapine: Plasma levels above 9000 ng/mL. Typical clinical picture diagnostic confusion (abstract). Neuropsychopharmacology 1994, 10, 122S. [Google Scholar]
- Le Blaye, I.; Donatini, B.; Hall, M. Acute over dosage with clozapine: A review of the available clinical experience. Pharm. Med. 1992, 6, 169–178. [Google Scholar]
- Piccini, G.; Ceroni, P.; Marchesi, C.; Maggini, C.; Maestri, G. Acute clozapine overdosage. Br. J. Psychiatry 1997, 170, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worm, K.; Kringsholm, B.; Steentoft, A. Clozapine cases with fatal, toxic or therapeutic concentrations. Int. J. Leg. Med. 1993, 106, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niehues, G.D.; Balan, A.B.; Prá, V.B.; Pellizzaro, R.S.; Da Silva, P.R.A.; Schwarzbold, M.L.; Diaz, A.P.; Costa, A.P. Trends in the prescription of clozapine in a psychiatric hospital: A 5-year observational study. Trends Psychiatry Psychother. 2017, 39, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nielsen, J.; Røge, R.; Schjerning, O.; Sørensen, H.J.; Taylor, D. Geographical and temporal variations in clozapine prescription for schizophrenia. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2012, 22, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdoux, H.; Pambrun, E.; Cortaredona, S.; Coldefy, M.; Le Neindre, C.; Tournier, M.; Verger, P. Geographical disparities in prescription practices of lithium and clozapine: A community-based study. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2016, 133, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, A.; Genov, G.; Spooner, A.; Raine, J.; Arlett, P. Promoting and Protecting Public Health: How the European Union Pharmacovigilance System Works. Drug Saf. 2017, 40, 855–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galova, A.; Berney, P.; Desmeules, J.; Sergentanis, I.; Besson, M. A case report of cholinergic rebound syndrome following abrupt low-dose clozapine discontinuation in a patient with type I bipolar affective disorder. BMC Psychiatry 2019, 19, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lander, M.; Bastiampillai, T.; Sareen, J. Review of withdrawal catatonia: What does this reveal about clozapine? Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koychev, I.; Hadjiphilippou, S.; Lynch, J.; Whelan, P.; MacCabe, J. Sudden-Onset Catatonia Following Clozapine Withdrawal: A Case Report. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2016, 77, e899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncrieff, J. Does antipsychotic withdrawal provoke psychosis? Review of the literature on rapid onset psychosis (supersensitivity psychosis) and withdrawal-related relapse. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2006, 114, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, S.; Chetia, D.; Raha, B.; Agarwal, G. Clozapine withdrawal emergent dystonia, oculogyric crisis and rebound psychosis in a single patient. Ther. Adv. Psychopharmacol. 2015, 6, 145–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shore, D.; Matthews, S.; Cott, J.; Lieberman, J.A. Clinical implications of clozapine discontinuation: Report of a NIMH workshop. Schizophr Bull. 1995, 21, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, B.Z.; Gupta, A.; Bastiampillai, T.; Sani, F. Recurrent clozapine and lorazepam withdrawal psychosis with catatonia. Aust. New Zealand J. Psychiatry 2012, 46, 795–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breen, E.G. Clozapine withdrawal syndrome. BJPsych Bull. 2017, 41, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Sur, S.; Singh, A. Catatonia Following Abrupt Stoppage of Clozapine. Aust. New Zealand J. Psychiatry 2011, 45, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiovitz, T.M.; Welke, T.L.; Tigel, P.D.; Anand, R.; Hartman, R.D.; Sramek, J.J.; Kurtz, N.M.; Cutler, N.R. Cholinergic Rebound and Rapid Onset Psychosis Following Abrupt Clozapine Withdrawal. Schizophr. Bull. 1996, 22, 591–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, A.W.-C.; Lee, J.W.Y.; Cheng, T.-C.; Wen, J.-K.; Chen, W.-H. Clozapine withdrawal catatonia associated with cholinergic and serotonergic rebound hyperactivity: A case report. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2004, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadekar, M.; Syed, S. Clozapine-Withdrawal Catatonia. Psychosomatics 2010, 51, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerjav-Lacombe, S.; Dewan, V. Possible serotonin syndrome associated with clomipramine after withdrawal of clozapine. Ann. Pharmacother. 2001, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.F.; Tan, Y.Y.; Huang, X.; Wang, Q. Effect of chronic treatment with clozapine and haloperidol on 5-HT2A and 2C receptor mRNA expression in the rat brain. Neurosci. Res. 2007, 59, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, M.K.; Bastiampillai, T.; Mohan, T. Managing clozapine discontinuation—Acute and chronic maintenance strategies. Aust. New Zealand J. Psychiatry 2012, 46, 1104–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meltzer, H.Y.; Alphs, L.; Green, A.I.; Altamura, A.C.; Anand, R.; Bertoldi, A.; Bourgeois, M.; Chouinard, G.; Islam, M.Z.; Kane, J.; et al. International Suicide Prevention Trial Study Group. Clozapine treatment for suicidality in schizophrenia: International Suicide Prevention Trial (InterSePT). Arch. Gen. Psychiatry. 2003, 60, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fava, G.A.; Gatti, A.; Belaise, C.; Guidi, J.; Offidani, E. Withdrawal Symptoms after Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor Discontinuation: A Systematic Review. Psychother. Psychosom. 2015, 84, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, M.; Sharma, V. Antidepressant discontinuation syndrome. CMAJ 2017, 189, E747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schatzberg, A.F.; Haddad, P.; Kaplan, E.M.; Lejoyeux, M.; Rosenbaum, J.F.; Young, A.H.; Zajecka, J. Serotonin reuptake inhibitor discontinuation syndrome: A hypothetical definition. Discontinuation Consensus panel. J. Clin. Psychiatry 1997, 58, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shelton, R. The nature of the discontinuation syndrome associated with antidepressant drugs. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2006, 67, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Szafrański, T.; Gmurkowski, K. Clozapine withdrawal. Psychiatr. Pol. 1999, 33, 51–67. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, L.; Bangh, S.; Cole, J.B. Intentional Recreational Abuse of Quetiapine Compared to Other Second-generation Antipsychotics. West. J. Emerg. Med. 2016, 18, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, A.A.; Befort, K.; Nozaki, C.; Gavériaux, C.; Kieffer, B.L. The delta opioid receptor: An evolving target for the treatment of brain disorders. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 32, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solismaa, A.; Kampman, O.; Lyytikäinen, L.-P.; Seppälä, N.; Viikki, M.; Mononen, N.; Lehtimaki, T.; Leinonen, E. Genetic Polymorphisms Associated with Constipation and Anticholinergic Symptoms in Patients Receiving Clozapine. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2018, 38, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrents, R.; Ferré, J.F.; Konareff, A.; Hemery, P.; Sherwin, K.; Lassalle, C.; Simon, N.; Scerra, S. Misuse of Trihexyphenidyl (Artane) on Réunion Island. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2018, 38, 250–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farren, C.; Hameedi, F.A.; Rosen, M.A.; Woods, S.; Jatlow, P.; Kosten, T.R. Significant interaction between clozapine and cocaine in cocaine addicts. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2000, 59, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency (EMA); Committee for Proprietary Medicinal Products (CPMP). Summary information on referral opinion following arbitration pursuant to Article 30 of Council Directive 2001/83/EC for Leponex and associated names. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/referrals/leponex (accessed on 24 July 2019).
- Kasckow, J.; Felmet, K.; Zisook, S. Managing suicide risk in patients with schizophrenia. CNS Drugs 2011, 25, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- He, J.-L.; Xiang, Y.-T.; Li, W.-B.; Cai, Z.-J.; Ungvari, G.S. Hemoperfusion in the Treatment of Acute Clozapine Intoxication in China. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2007, 27, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broich, K.; Heinrich, S.; Marneros, A. Acute Clozapine Overdose: Plasma Concentration and Outcome. Pharmacopsychiatry 1998, 31, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, I.; Rauber-Lüthy, C.; Kupferschmidt, H. Minimal dose for severe poisoning and influence factors in acute human clozapine intoxication: A 13-year retrospective study. Clin. Neuropharm. 2011, 33, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulrich, S.; Baumann, B.; Wolf, R.; Lehmann, D.; Peters, B.; Bogerts, B.; Meyer, F. Therapeutic drug monitoring of clozapine and relapse—A retrospective study of routine clinical data. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 41, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipriani, A.; Boso, M.; Barbui, C. Clozapine combined with different antipsychotic drugs for treatment resistant schizophrenia. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2009, CD006324. [Google Scholar]
- Pandarakalam, J.P. The art of clozapine therapy and “clozaphobia”. BMJ 2019, 364, l484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
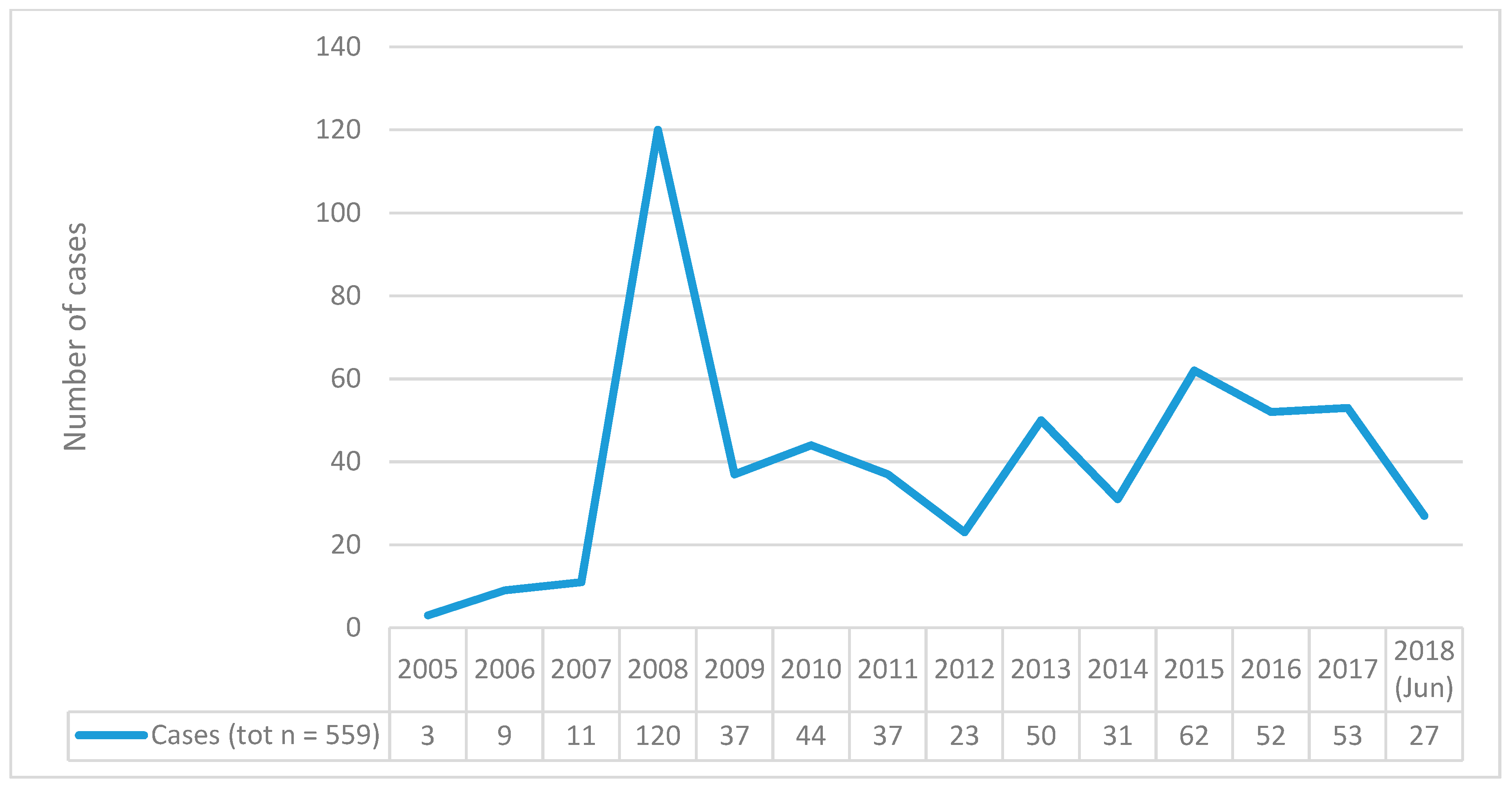
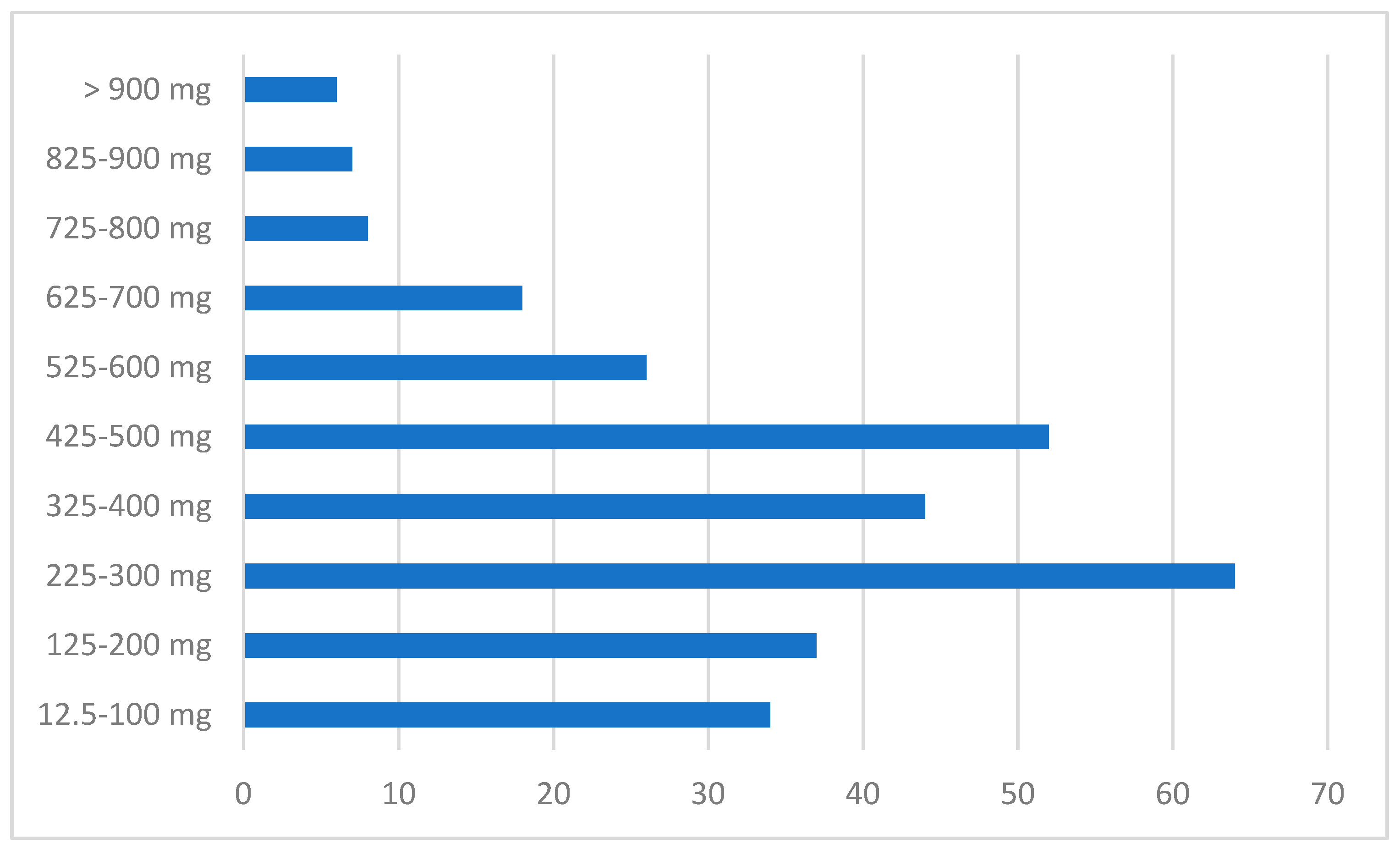
| EudraVigilance (EV) Clozapine-Related Misuse/Abuse/Dependence and Withdrawal ADRs (2005–June 2018) | n |
|---|---|
| Total “suspect” clozapine-related ADRs | 11,847 |
| Clozapine-related ‘abuse, dependence and withdrawal’ ADRs | 599 (CI 95% 595–603) (n individual cases = 559) |
| Drug abuse | 198 |
| Drug abuser | 1 |
| Substance abuse | 42 |
| Dependence | 7 |
| Drug dependence | 6 |
| Drug diversion | 1 |
| Intentional product misuse | 80 |
| Product use issue | 4 |
| Drug withdrawal convulsions | 1 |
| Drug withdrawal neonatal syndrome | 1 |
| Drug withdrawal syndrome | 91 |
| Withdrawal syndrome | 165 |
| Further issues emerging from the analysis of clozapine ADRs’ dataset | |
| Intentional overdose | 12 |
| Overdose | 17 |
| Completed suicide | 9 |
| Intentional self-injury | 4 |
| Suicidal behavior | 1 |
| Suicidal ideation | 4 |
| Suicide attempt | 7 |
| Self-injurious ideation | 4 |
| Clozapine-Related Misuse, Abuse, Dependence and Withdrawal Cases | n of Unique Patients |
|---|---|
| 559 | |
| Age range (years) | 3 neonates, 1 child (5 years), 2 adolescents (15–16 years), 78 adults (18–65 years), 1 elderly (67 years), 474 Not specified |
| Gender | 171 F, 379 M, 9 Not Specified |
| Sender | 241 Regulatory authority, 303 Pharmaceutical company, 9 Other (distributor, study sponsor, contract research organization), 6 Not Specified |
| Outcome | |
| Resulted in death | 46 Y, 448 N, 65 Not Specified |
| Life threatening | 35 Y, 447 N, 77 Not Specified |
| Required a prolonged hospitalization | 298 Y, 219 N, 42 Not Specified |
| Disabling | 8 Y, 467 N, 84 Not Specified |
| Clozapine-Related Misuse, Abuse, Dependence and Withdrawal Cases Recorded by the EudraVigilance (EV) Dataset | Tot (n = 559) |
|---|---|
| Clozapine ingested as a lone drug | 387 (69.2%) |
| Clozapine identified in combination with remaining drugs | 172 (30.7%) |
| Prescribing drugs | |
| Other antipsychotics | 55 |
| Benzodiazepines | 54 |
| Antidepressants | 33 |
| Mood stabilizers | 20 |
| Z-drugs | 4 |
| Recreational drugs | |
| Opioids | 15 |
| Amphetamine derivatives | 10 |
| Cannabis | 7 |
| Alcohol | 7 |
| Cocaine | 4 |
| Ketamine | 1 |
| Clozapine Dosage (mg) | Concomitant Drugs | Medical History | Reactions according to the MedDRA Dictionary (Preferred Terms-PT) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M, Adult (30 yy) | 200 mg | Benzodiazepines Alcohol | Intentional product misuse; Antipsychotic drug level increased (clozapine plasmatic 1.1 mg/mL); Blood pressure decreased; Loss of consciousness; Poisoning; Dysarthria; Loss of consciousness; Blood alcohol increased | |
| 2 | M, Adult (48 yy) | N/A | Cocaine Opioids Z-drugs | Hypertension; Schizophrenia; Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; Arteriosclerosis | Substance abuse; Toxicity to various agents |
| 3 | M, Adult (25 yy) | 300 mg | Benzodiazepines Opioids | Cardiac arrest; Arrhythmia Toxicity to various agents (methadone and clozapine); Drug abuse; Drug level increased (methadone and clozapine) | |
| 4 | M, Adult (44 yy) | N/A | Opioids | Hypertension; Alcoholism; Depression; Epigastric discomfort; Anxiety | Pulmonary embolism; Drug abuse |
| 5 | M, Adult | 400 mg | Alcohol | Liver function test abnormal; Blood alkaline phosphatase increased; Gamma-glutamyl transferase increased; Asphyxia; Alcohol abuse; Drug abuse (heroin) | |
| 6 | M, Adult (24yy) | N/A | Alcohol | Anemia | Drug abuse (Clozaril abuse) |
| 7 | F | 300 mg | Alcoholism; Mental impairment; Depression; Treatment noncompliance; Deep vein thrombosis | Death; Withdrawal syndrome; Acute psychosis; Cognitive disorder; Amnesia; Speech disorder; Gait disturbance; Chills | |
| 8 | F, Adult (54yy) | 350 mg | Benzodiazepines | Withdrawal syndrome; Insomnia; Completed suicide | |
| 9 | M, Adult (66 yy) | N/A | Completed suicide; Drug abuse | ||
| 10 | F, Adult (25yy) | N/A | Antidepressants | Completed suicide; Drug abuse | |
| 11. | M, Adult (31yy) | N/A | Completed suicide; Drug abuse | ||
| 12 | M | N/A | Obesity; Gastroesophageal reflux; Drug abuse | Drug abuse; Death | |
| 13 | F | N/A | Cocaine Benzodiazepines Opioids | Drug dependence | Drug abuse (cocaine, leponex and probably benzodiazepines); Death; Hyperthermia malignant; Cardiac arrest; Circulatory collapse; Delirium |
| 14 | M | N/A | Hepatitis | Drug abuse (possible use of non-prescribed drugs); Death | |
| 15 | M | N/A | Salivary hypersecretion; Drug abuse (crack cocaine, marijuana, alcohol); Extrapyramidal disorder | Nonspecific reaction; Treatment noncompliance; Drug abuse (mixed polysubstance abuse); Death | |
| 16 | F | N/A | Mood stabilizers Antipsychotics | Drug abuse | |
| 17 | M | 1000 mg | Hypercholesterolemia; Substance abuse; Hypertension; Schizophrenia; Gastro-esophageal reflux disease | Hematemesis; Drug abuse; Cardiac arrest; Completed suicide; Toxicity to various agents; Intentional overdose; Resuscitation; Seizure; Tachycardia | |
| 18 | F, Adult (27yy) | N/A | Drug abuse | ||
| 19 | M, Adult (30yy) | N/A | Myocardial infarction; Drug abuse; Eye swelling; Glossodynia; Tongue coated; Swollen tongue | ||
| 20 | F | N/A | Intentional self-injury; Meningioma; Drug abuse; Hypoglycemia; Peripheral venous disease; Hepatic steatosis; Scar; Pneumonia; Bronchitis; Arteriosclerosis coronary artery; Purulent discharge; Pulmonary congestion; Death | ||
| 21 | M, Adult (26yy) | 800 mg | Coronary artery disease; Drug abuse; Hallucination, auditory; Epilepsy; Depressed mood | ||
| 22 | M, Adult (31yy) | N/A | Death; Substance abuse | ||
| 23 | M | N/A | Surgery; Intentional self-injury; Bipolar disorder | Agitation; Death; Drug abuse; Suicidal ideation; Nasal septum deviation | |
| 24 | M, Adult (30yy) | N/A | Autonomic nervous system imbalance; Catatonia; Drug withdrawal syndrome; Dyskinesia; Neuroleptic malignant syndrome; Psychotic disorder | ||
| 25 | M, Adult (36yy) | N/A | Alcohol abuse; Drug abuse; Myocardial infarction; Coronary artery disease | ||
| 26 | M | 200 mg | Drug abuse; Obesity | ||
| 27 | M, Adult (34yy) | 350 mg | Circulatory collapse; Intentional product misuse; Cardiopulmonary failure | ||
| 28 | M, Adult (33yy) | N/A | Benzodiazepines Opioids | Death; Drug abuse (heroin, temazepam) | |
| 29 | N/A | Arm amputation; Drug dependence (including cannabis, benzodiazepines and heroin); Limb reduction defect; Alcohol use | Drug abuse; Loss of consciousness; Hypothermia | ||
| 30 | M, Adult (31yy) | N/A | Abnormal behavior; Myocardial infarction; Drug abuse (heroin, cocaine); Psychomotor hyperactivity; Peripheral coldness; Unresponsive to stimuli; Arteriosclerosis coronary artery; Blood glucose decreased | ||
| 31. | F, Adult (72yy) | 200 mg | Opioids | Schizophrenia; Depression; Somnolence; Anxiety | Movement disorder; Sudden death; Drug abuse |
| 32. | M, Adult (27yy) | 400 mg | Antipsychotics | Asthma; Nicotine dependence; Drug abuse; Obesity; Substance use; Diabetes mellitus; Mental disorder; Alcohol use | Asphyxia; Substance abuse |
| 33. | M, Adult (50 yy) | 550 mg | Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy; Drug abuse (cocaine); Pulmonary hemosiderosis; Pulmonary edema; Cardiac arrest; Left ventricular hypertrophy; Arteriosclerosis coronary artery; Aortic arteriosclerosis; Myocardial fibrosis; Hepatic steatosis; Spleen congestion | ||
| 34. | M, Adult (29yy) | 1000 mg | Opioids | Schizophrenia | Substance abuse (heroin) |
| 35. | F, Adult | N/A | Antidepressants | Drug abuse | |
| 36. | M, Adult (34yy) | 700 mg | Schizophrenia; Nicotine dependence; Drug abuse | Cardiac arrest; Substance abuse | |
| 37. | F, Adult (28yy) | N/A | Antidepressants | Drug abuse | |
| 38. | M | 100 mg | Blood cholesterol increased; Bipolar disorder; Gastroesophageal reflux; Schizoaffective disorder; Diabetes mellitus | Sudden death; Drug abuse (cocaine and another illicit drug) | |
| 39. | F, Adult (50yy) | N/A | Alcohol | Drug abuse; Drug dependence | Completed suicide; Toxicity to various agents; Drug abuse (propofol) |
| 40. | M | N/A | Product use issue; Psychotic disorder | Product use issue; Drug level increased (clozapine levels in the 600,000 s); Death; Adverse event; Psychotic disorder; Intentional product misuse | |
| 41. | M | N/A | Drug withdrawal syndrome; Memory impairment; Disorientation; Completed suicide | ||
| 42. | F, Adult (28yy) | N/A | Antidepressants | Toxicity to various agents; Drug abuse | |
| 43. | M, Adult (31yy) | 700 mg | Anxiety; Psychotic disorder; Depression | Completed suicide (suicide due to overdose on clozapine); Intentional product misuse; Overdose; Adverse event | |
| 44. | M | N/A | Completed suicide (patient jumped to his death); Withdrawal syndrome (periodically he would refrain from taking the medication, thus suffering withdrawal/Initially withdrawal symptoms would consist of disorientation after 2–3 days and memory impairment after 4–7 days) | ||
| 45. | M | N/A | Death; Withdrawal syndrome (withdrawal symptoms from the capsule form of Clozaril antipsychotic medication) | ||
| 46. | M, Adult (58yy) | 100 mg | Alcohol use; Hypertension | Drug abuse; Vomiting; Asphyxia; Prescription drug used without a prescription (abuse of clozapine 100 mg tablets) |
| Comments in the ADRs Reported in the Dataset | |
|---|---|
| Overdose and suicidal behaviour ADRs |
|
| Withdrawal and clozapine discontinuation ADRs |
|
| Abuse of clozapine |
|
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiappini, S.; Schifano, F.; Corkery, J.M.; Guirguis, A. Focus on Clozapine Withdrawal- and Misuse-Related Cases as Reported to the European Medicines Agency (EMA) Pharmacovigilance Database. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10020105
Chiappini S, Schifano F, Corkery JM, Guirguis A. Focus on Clozapine Withdrawal- and Misuse-Related Cases as Reported to the European Medicines Agency (EMA) Pharmacovigilance Database. Brain Sciences. 2020; 10(2):105. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10020105
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiappini, Stefania, Fabrizio Schifano, John Martin Corkery, and Amira Guirguis. 2020. "Focus on Clozapine Withdrawal- and Misuse-Related Cases as Reported to the European Medicines Agency (EMA) Pharmacovigilance Database" Brain Sciences 10, no. 2: 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10020105
APA StyleChiappini, S., Schifano, F., Corkery, J. M., & Guirguis, A. (2020). Focus on Clozapine Withdrawal- and Misuse-Related Cases as Reported to the European Medicines Agency (EMA) Pharmacovigilance Database. Brain Sciences, 10(2), 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10020105








