Contributions of Imaging to Neuromodulatory Treatment of Drug-Refractory Epilepsy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Contributions of Advanced Neuroimaging to Presurgical Evaluation of Drug-Resistant Epilepsy
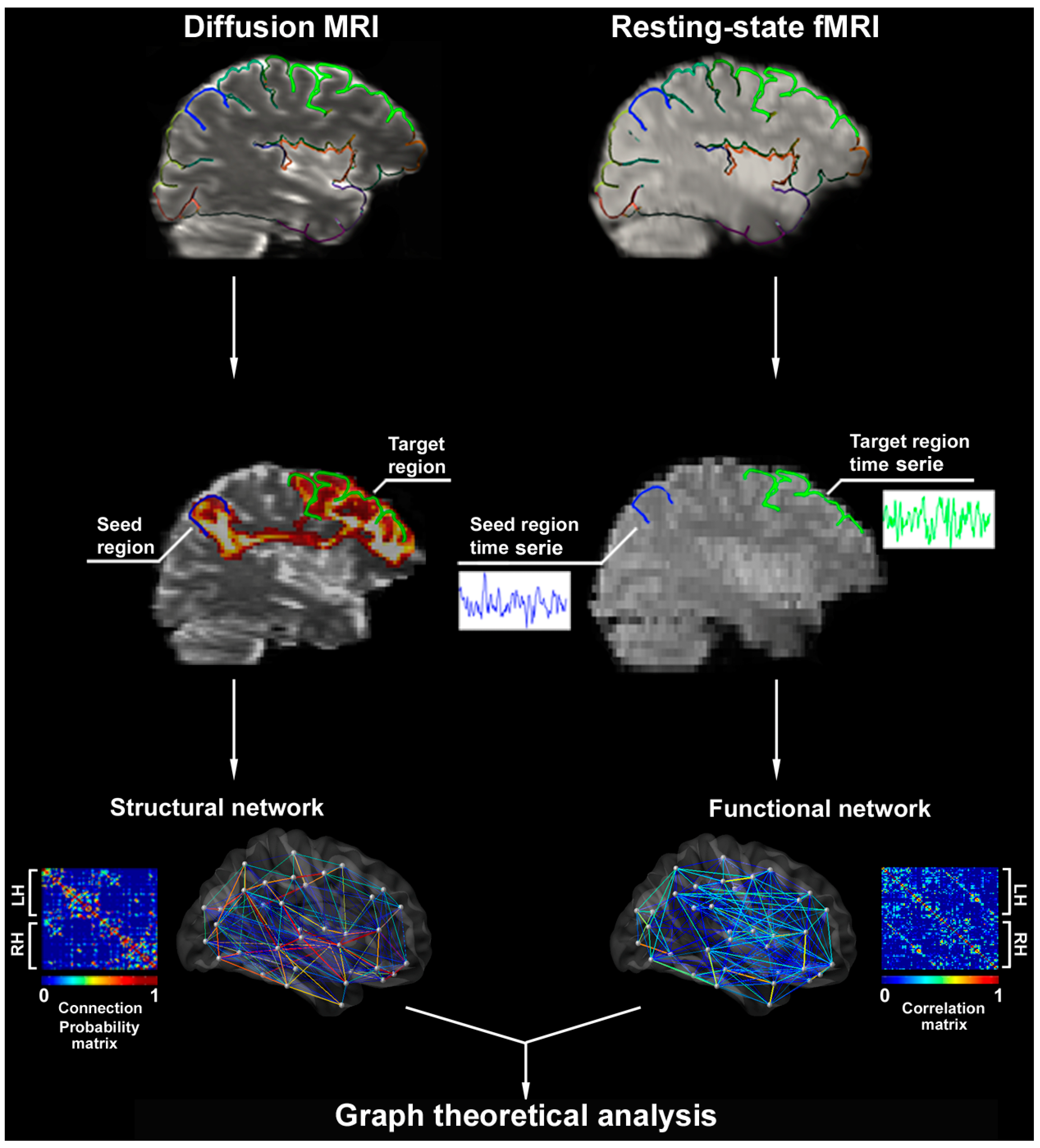
2.1. Network Modelling Using Structural and Functional MRI
2.2. Studying Networks with Graph Theory
2.3. Epilepsy as a Network Disorder
3. Imaging-Informed Neuromodulation of Drug-Resistant Epilepsy
3.1. Deep Brain Stimulation
3.2. Responsive Neurostimulation
3.3. Vagus Nerve Stimulation
| Landmark Publications in Neuromodulatory Treatment for Refractory Epilepsy | Key Findings | |
|---|---|---|
| Deep Brain Stimulation | ||
| Fisher et al. [57] | SANTE trial, Epilepsia 2010 | ANT-DBS is effectice in reducing seizure frequencies in drug-refractory patients without the option of resective surgery |
| Salanova et al. [59] | Epilepsia 2015 | Up to 76% total decrease in seizure frequency has been demonstrated in long-term follow-up of SANTE patients |
| Tröster et al. [60] | Seizure 2017 | ANT-DBS and associated reduction in seizure frequency improves executive functioning, memory, attention and mood |
| Yu et al. [66] | Brain 2018 | ANT-DBS desynchronization of seizure networks is associated with reduction of seizure frequency, supresses pathological HC activity |
| Middlebrooks et al. [70] | Neurosurgical Focus 2018 | Functional imaging-derived connectivity profiles predict treatment response to ANT-DBS |
| Schaper et al. [72] | Neurosurgery 2020 | Delivering DBS to the mamillothalamic tract junction instead of the ANT surpresses seizure activity, potential target site |
| Responsive Neurostimulation | ||
| Morrell et al. [79] | RNS trial, Neurology 2011 | Decrease in disabling partial seizures, improved quality of life in drug-refractory patients with ≤ 2 independent epileptogenic foci |
| Bergey et al. [49] | Neurology 2015 | Long-term efficacy and safety in RNS trial patients |
| Hirsch et al. [81] | Epilepsia 2020 | Long-term ambulatory EEG-sampling obtained from RNS leads provides additional information to lateralize seizures |
| Loring et al. [82] | Epilepsia 2015 | Improved cognitive functioning observed in several domains, i.e., verbal memory; overall memory |
| Nair et al. [83] | Neurology 2019 | Long-term improvement in quality of life and sustained reduction in seizure frequency, 9-year follow-up |
| Vagus Nerve Stimulation | ||
| Morris et al. [87] | AAN guidelines/Neurology 2013 | Effective and safe in patients with intractable partial or generalized seizures, ≥ 50% sustained seizure frequency reduction |
| Hachem et al. [88] | Neurosurgical Focus 2018 | Identification of the vagus-afferent network and associated brain stem nuclei |
| Mithani et al. [89] | Annals of Neurology 2018 | Connectivity profiles of insular and temporal networks and preserved white matter microstructure predict treatment response to VNS |
| Ibrahim et al. [90] | Neuroimage Clinical 2017 | Enhanced connectivity between thalamus, anterior cingulate, and insular cortices is associated with favorable VNS response |
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fiest, K.; Sauro, K.; Wiebe, S.; Patten, S.; Kwon, C.; Dykeman, J.; Pringsheim, T.; Lorenzetti, D.; Jette, N. Prevalence and incidence of epilepsy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of international studies. Neurology 2017, 88, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, P.; Arzimanoglou, A.; Berg, A.T.; Brodie, M.J.; Allen Hauser, W.; Mathern, G.; Moshé, S.L.; Perucca, E.; Wiebe, S.; French, J. Definition of drug resistant epilepsy: Consensus proposal by the ad hoc Task Force of the ILAE Commission on Therapeutic Strategies. Epilepsia 2010, 51, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blumcke, I.; Thom, M.; Aronica, E.; Armstrong, D.D.; Bartolomei, F.; Bernasconi, A.; Bernasconi, N.; Bien, C.G.; Cendes, F.; Coras, R.; et al. International consensus classification of hippocampal sclerosis in temporal lobe epilepsy: A task force report from the ilae commission on diagnostic methods. Epilepsia 2013, 54, 1315–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papayannis, C.E.; Consalvo, D.; Kauffman, M.A.; Seifer, G.; Oddo, S.; D’Alessio, L.; Saidon, P.; Kochen, S. Malformations of cortical development and epilepsy in adult patients. Seizure 2012, 21, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- West, S.; Nevitt, S.J.; Cotton, J.; Gandhi, S.; Weston, J.; Sudan, A.; Ramirez, R.; Newton, R. Surgery for epilepsy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 6, CD010541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Téllez-Zenteno, J.F.; Dhar, R.; Wiebe, S. Long-term seizure outcomes following epilepsy surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain 2005, 128, 1188–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J.; Urbach, H.; Niehusmann, P.; von Lehe, M.; Elger, C.E.; Wellmer, J. Focal cortical dysplasia type IIb: Completeness of cortical, not subcortical, resection is necessary for seizure freedom. Epilepsia 2011, 52, 1418–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.C.H.; Cook, M.J. Deep brain stimulation for drug-resistant epilepsy. Epilepsia 2018, 59, 273–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobst, B.C.; Kapur, R.; Barkley, G.L.; Bazil, C.W.; Berg, M.J.; Bergey, G.K.; Boggs, J.G.; Cash, S.S.; Cole, A.J.; Duchowny, M.S.; et al. Brain-responsive neurostimulation in patients with medically intractable seizures arising from eloquent and other neocortical areas. Epilepsia 2017, 313, 285–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakol, S.; Royer, J.; Lowe, A.J.; Bonilha, L.; Tracy, J.I.; Jackson, G.D.; Duncan, J.S.; Bernasconi, A.; Bernasconi, N.; Bernhardt, B.C. Neuroimaging and connectomics of drug-resistant epilepsy at multiple scales: From focal lesions to macroscale networks. Epilepsia 2019, 60, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, B.C.; Chen, Z.; He, Y.; Evans, A.C.; Bernasconi, N. Graph-Theoretical Analysis Reveals Disrupted Small-World Organization of Cortical Thickness Correlation Networks in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Cereb. Cortex 2011, 21, 2147–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakas Damianos, E.; Panourias, I.G.; Simpson, B.A.; Krames, E.S. An introduction to operative neuromodulation and functional neuroprosthetics, the new frontiers of clinical neuroscience and biotechnology. In Oper Neuromodulation; Funct Neuroprosthetic Surg Introd [online]; Sakas, D.E., Simpson, B.A., Krames, E.S., Eds.; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2007; Volume 1, pp. 3–10. Available online: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-211-33079-1_1 (accessed on 21 September 2020).
- Krames, E.S.; Hunter Peckham, P.; Rezai, A.; Aboelsaad, F. Chapter 1—What Is Neuromodulation? In Neuromodulation; Krames, E.S., Peckham, P.H., Rezai, A.R., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2009; pp. 3–8. Available online: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780123742483000021 (accessed on 21 September 2020).
- Sisterson, N.D.; Kokkinos, V. Neuromodulation of Epilepsy Networks. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 31, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassett, D.S.; Sporns, O. Network neuroscience. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sporns, O.; Tononi, G.; Kötter, R. The Human Connectome: A Structural Description of the Human Brain. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2005, 1, e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullmore, E.; Sporns, O. Complex brain networks: Graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional systems. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, B.C.; Bernasconi, N.; Concha, L.; Bernasconi, A. Cortical thickness analysis in temporal lobe epilepsy: Reproducibility and relation to outcome. Neurology 2010, 74, 1776–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, A.L.; Lee, J.E.; Lazar, M.; Field, A.S. Diffusion Tensor Imaging of the Brain. Neurother. J. Am. Soc. Exp. Neurother. 2007, 4, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conturo, T.E.; Lori, N.F.; Cull, T.S.; Akbudak, E.; Snyder, A.Z.; Shimony, J.S.; McKinstry, R.C.; Burton, H.; Raichle, M.E. Tracking neuronal fiber pathways in the living human brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 10422–10427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, B.C.; Hong, S.; Bernasconi, A.; Bernasconi, N. Imaging structural and functional brain networks in temporal lobe epilepsy. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 624. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3787804/ (accessed on 21 October 2013). [CrossRef]
- Alexander-Bloch, A.; Giedd, J.N.; Bullmore, E. Imaging structural co-variance between human brain regions. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 322–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernasconi, A.; Bernasconi, N.; Koepp, M. Imaging Biomarkers in Epilepsy; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Power, J.D.; Cohen, A.L.; Nelson, S.M.; Wig, G.S.; Barnes, K.A.; Church, J.A.; Vogel, A.C.; Laumann, T.O.; Miezin, F.M.; Schlaggar, B.L.; et al. Functional network organization of the human brain. Neuron 2011, 72, 665–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wykes, R.C.; Khoo, H.M.; Caciagli, L.; Blumenfeld, H.; Golshani, P.; Kapur, J.; Stern, J.M.; Bernasconi, A.; Dedeurwaerdere, S.; Bernasconi, N. WONOEP appraisal: Network concept from an imaging perspective. Epilepsia 2019, 60, 1293–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, B.B.; Mennes, M.; Zuo, X.-N.; Gohel, S.; Kelly, C.; Smith, S.M.; Beckmann, C.F.; Adelstein, J.S.; Buckner, R.L.; Colcombe, S.; et al. Toward discovery science of human brain function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4734–4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhardt, B.C.; Bonilha, L.; Gross, D.W. Network analysis for a network disorder: The emerging role of graph theory in the study of epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2015, 50, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sporns, O. The human connectome: A complex network. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1224, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullmore, E.T.; Bassett, D.S. Brain graphs: Graphical models of the human brain connectome. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2011, 7, 113–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, D.J.; Strogatz, S.H. Collective dynamics of ‘small-world’ networks. Nature 1998, 393, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colizza, V.; Flammini, A.; Serrano, M.A.; Vespignani, A. Detecting rich-club ordering in complex networks. Nat. Phys. 2006, 2, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Heuvel, M.P.; Sporns, O. A cross-disorder connectome landscape of brain dysconnectivity. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 20, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Liao, W.; Li, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, G.; Chen, H. Disrupted structural and functional rich club organization of the brain connectome in patients with generalized tonic-clonic seizure. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2016, 37, 4487–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.-J.; Bernhardt, B.C.; Gill, R.S.; Bernasconi, N.; Bernasconi, A. The spectrum of structural and functional network alterations in malformations of cortical development. Brain 2017, 140, 2133–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.-J.; Lee, H.-M.; Gill, R.; Crane, J.; Sziklas, V.; Bernhardt, B.C.; Bernasconi, N.; Bernasconi, A. A connectome-based mechanistic model of focal cortical dysplasia. Brain 2019, 142, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-Y.; Slotine, J.-J.; Barabási, A.-L. Controllability of complex networks. Nature 2011, 473, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tewarie, P.; Hillebrand, A.; van Dellen, E.; Schoonheim, M.; Barkhof, F.; Polman, C.H.; Beaulieu, C.; Gong, G.; van Dijk, B.W.; Stam, C.J. Structural degree predicts functional network connectivity: A multimodal resting-state fMRI and MEG study. NeuroImage 2014, 97, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Mo, J.-J.; Sang, L.; Zhao, B.-T.; Zhang, C.; Hu, W.-H.; Zhang, J.-G.; Shao, X.-Q.; Zhang, K. Symptomatogenic zone and network of oroalimentary automatisms in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 2019, 60, 1150–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleichgerrcht, E.; Kocher, M.; Bonilha, L. Connectomics and graph theory analyses: Novel insights into network abnormalities in epilepsy. Epilepsia 2015, 56, 1660–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, S.S. Neural networks in human epilepsy: Evidence of and implications for treatment. Epilepsia 2002, 43, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, C.L.; Chen, Z.; Beltramini, G.C.; Coan, A.C.; Morita, M.E.; Kubota, B.; Bergo, F.; Beaulieu, C.; Cendes, F.; Gross, D.W. Aberrant topological patterns of brain structural network in temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 2015, 56, 1992–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Diessen, E.; Zweiphenning, W.J.E.M.; Jansen, F.E.; Stam, C.J.; Braun, K.P.J.; Otte, W.M. Brain Network Organization in Focal Epilepsy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114606. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4262431/ (accessed on 23 September 2019). [CrossRef]
- Bernasconi, A. Connectome-based models of the epileptogenic network: A step towards epileptomics? Brain 2017, 140, 2525–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilha, L.; Helpern, J.A.; Sainju, R.; Nesland, T.; Edwards, J.C.; Glazier, S.S.; Tabesh, A. Presurgical connectome and postsurgical seizure control in temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurology 2013, 81, 1704–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, S.S.; Richardson, M.P.; O’Muircheartaigh, J.; Schoene-Bake, J.-C.; Elger, C.; Weber, B. Morphometric MRI alterations and postoperative seizure control in refractory temporal lobe epilepsy: Morphometry and Outcome in Epilepsy. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2015, 36, 1637–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonilha, L.; Jensen, J.H.; Baker, N.; Breedlove, J.; Nesland, T.; Lin, J.J.; Drane, D.L.; Saindane, A.M.; Binder, J.R.; Kuzniecky, R.I. The brain connectome as a personalized biomarker of seizure outcomes after temporal lobectomy. Neurology 2015, 84, 1846–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, R.P.D.; Concha, L.; Snyder, T.J.; Beaulieu, C.; Gross, D.W. Correlations between Limbic White Matter and Cognitive Function in Temporal-Lobe Epilepsy, Preliminary Findings. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014, 6, 142. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4075095/ (accessed on 28 November 2019). [CrossRef]
- Bonilha, L.; Keller, S.S. Quantitative MRI in refractory temporal lobe epilepsy: Relationship with surgical outcomes. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2015, 5, 204–224. [Google Scholar]
- Bergey, G.K.; Morrell, M.J.; Mizrahi, E.M.; Goldman, A.; King-Stephens, D.; Nair, D.; Srinivasan, S.; Jobst, B.; Gross, R.E.; Shields, D.C.; et al. Long-term treatment with responsive brain stimulation in adults with refractory partial seizures. Neurology 2015, 84, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gummadavelli, A.; Zaveri, H.P.; Spencer, D.D.; Gerrard, J.L. Expanding Brain–Computer Interfaces for Controlling Epilepsy Networks: Novel Thalamic Responsive Neurostimulation in Refractory Epilepsy. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 474. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6079216/ (accessed on 31 July 2020). [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, B.C.; Fadaie, F.; Liu, M.; Caldairou, B.; Gu, S.; Jefferies, E.; Smallwood, J.; Bassett, D.S.; Bernasconi, A.; Ebernasconi, N. Temporal lobe epilepsy: Hippocampal pathology modulates connectome topology and controllability. Neurology 2019, 92, e2209–e2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foit, N.A.; Bernasconi, A.; Bernasconi, N. Functional Networks in Epilepsy Presurgical Evaluation. Neurosurg. Clin. 2020, 31, 395–405. Available online: https://www.neurosurgery.theclinics.com/article/S1042-3680(20)30018-8/abstract (accessed on 29 April 2020). [CrossRef]
- Lozano, A.M.; Lipsman, N. Probing and Regulating Dysfunctional Circuits Using Deep Brain Stimulation. Neuron 2013, 77, 406–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiken, S.; Nambu, A. Mechanism of Deep Brain Stimulation: Inhibition, Excitation, or Disruption? In The Neuroscientist; SAGE PublicationsSage CA: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2015; Available online: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/1073858415581986 (accessed on 21 September 2020).
- Florence, G.; Sameshima, K.; Fonoff, E.T.; Hamani, C. Deep Brain Stimulation: More Complex than the Inhibition of Cells and Excitation of Fibers. In The Neuroscientist; SAGE PublicationsSage CA: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2015; Available online: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/1073858415591964?icid=int.sj-full-text.similar-articles.1 (accessed on 21 September 2020).
- Schulze-Bonhage, A. Brain stimulation as a neuromodulatory epilepsy therapy. Seizure 2017, 44, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, R.; Salanova, V.; Witt, T.; Worth, R.; Henry, T.; Gross, R.; Oommen, K.; Osorio, I.; Nazzaro, J.; LaBar, D.; et al. Electrical stimulation of the anterior nucleus of thalamus for treatment of refractory epilepsy. Epilepsia 2010, 51, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprengers, M.; Vonck, K.; Carrette, E.; Marson, A.G.; Boon, P. Deep brain and cortical stimulation for epilepsy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6483316/ (accessed on 14 July 2020).
- Salanova, V.; Witt, T.; Worth, R.; Henry, T.R.; Gross, R.E.; Nazzaro, J.M.; LaBar, D.; Sperling, M.R.; Sharan, A.; Sandok, E.; et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of thalamic stimulation for drug-resistant partial epilepsy. Neurology 2015, 84, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tröster, A.I.; Meador, K.J.; Irwin, C.P.; Fisher, R.S. Memory and mood outcomes after anterior thalamic stimulation for refractory partial epilepsy. Seizure 2017, 45, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, E.; Bartolomei, F.; Boon, P.; Chabardes, S.; Colon, A.J.; Eross, L.; Fabó, D.; Gonçalves-Ferreira, A.; Imbach, L.L.; van Paesschen, W.; et al. European Expert Opinion on ANT-DBS therapy for patients with drug-resistant epilepsy (a Delphi consensus). Seizure 2020, 81, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möttönen, T.; Katisko, J.; Haapasalo, J.; Tähtinen, T.; Kiekara, T.; Kāhārā, V.; Peltola, J.; Ohman, J.; Lehtimäki, K. Defining the anterior nucleus of the thalamus (ANT) as a deep brain stimulation target in refractory epilepsy: Delineation using 3 T MRI and intraoperative microelectrode recording. NeuroImage Clin. 2015, 7, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; D’Haese, P.-F.; Pallavaram, S.; Dawant, B.M.; Konrad, P.; Sharan, A.D. Variations in Thalamic Anatomy Affect Targeting in Deep Brain Stimulation for Epilepsy. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 2016, 94, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernasconi, N.; Bernasconi, A.; Caramanos, Z.; Antel, S.B.; Andermann, F.; Arnold, D.L. Mesial temporal damage in temporal lobe epilepsy: A volumetric MRI study of the hippocampus, amygdala and parahippocampal region. Brain J. Neurol. 2003, 126, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, D.S.; Tandon, N.; Lancaster, J.L.; Fox, P.T. Thalamic structural connectivity in medial temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 2014, 55, e50–e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Worrell, G.; Chauvel, P.; Ni, D.; Qiao, L.; Liu, C.; Li, L.; et al. High-frequency stimulation of anterior nucleus of thalamus desynchronizes epileptic network in humans. Brain 2018, 141, 2631–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stypulkowski, P.H.; Stanslaski, S.R.; Jensen, R.M.; Denison, T.J.; Giftakis, J.E. Brain Stimulation for Epilepsy–Local and Remote Modulation of Network Excitability. Brain Stimulat. 2014, 7, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, K.; Jech, R.; Růžička, F.; Holiga, S.; Ballarini, T.; Bezdicek, O.; Möller, H.E.; Vymazal, J.; Růžička, E.; Schroeter, M.L.; et al. Brain connectivity changes when comparing effects of subthalamic deep brain stimulation with levodopa treatment in Parkinson’s disease. NeuroImage Clin. 2018, 19, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, A.; Reich, M.; Vorwerk, J.; Li, N.; Wenzel, G.; Fang, Q.; Schmitz-Hübsch, T.; Nickl, R.; Kupsch, A.; Volkmann, J.; et al. Connectivity Predicts deep brain stimulation outcome in Parkinson disease. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 82, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middlebrooks, E.H.; Grewal, S.S.; Stead, M.; Lundstrom, B.N.; Worrell, G.A.; Gompel, J.J.V. Differences in functional connectivity profiles as a predictor of response to anterior thalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation for epilepsy: A hypothesis for the mechanism of action and a potential biomarker for outcomes. Neurosurg. Focus 2018, 45, E7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barron, D.S.; Fox, P.T.; Pardoe, H.R.; Lancaster, J.; Price, L.R.; Blackmon, K.; Berry, K.; Cavazos, J.E.; Kuzniecky, R.; Devinsky, O.; et al. Thalamic functional connectivity predicts seizure laterality in individual TLE patients: Application of a biomarker development strategy. NeuroImage Clin. 2015, 7, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaper, F.L.W.V.J.; Plantinga, B.R.; Colon, A.J.; Wagner, G.L.; Boon, P.; Blom, N.; Gommer, E.D.; Hoogland, G.; Ackermans, L.; Rouhl, R.P.W.; et al. Deep Brain Stimulation in Epilepsy: A Role for Modulation of the Mammillothalamic Tract in Seizure Control? Neurosurgery 2020. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/neurosurgery/article/doi/10.1093/neuros/nyaa141/5838842 (accessed on 30 July 2020).
- Garibay-Pulido, D.; Cendejas-Zaragoza, L.; Dawe, R.; Rossi, M.A. Parametric subtracted post-ictal diffusion tensor imaging for guiding direct neurostimulation therapy. Hippocampus 2019, 29, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerwinkle, V.L.; Cediel, E.G.; Mirea, L.; Williams, K.; Kerrigan, J.F.; Lam, S.; Raskin, J.S.; Desai, V.R.; Wilfong, A.A.; Adelson, P.D.; et al. Network-targeted approach and postoperative resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging are associated with seizure outcome. Ann. Neurol. 2019, 86, 344–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girgis, F.; Miller, J.P. White matter stimulation for the treatment of epilepsy. Seizure 2016, 37, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmi, S.; Petkoski, S.; Guye, M.; Bartolomei, F.; Jirsa, V. Controlling seizure propagation in large-scale brain networks. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, e1006805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, A.; Li, N.; Dembek, T.A.; Kappel, A.; Boulay, C.B.; Ewert, S.; Tietze, A.; Husch, A.; Perera, T.; Neumann, W.-J.; et al. Lead-DBS v2: Towards a comprehensive pipeline for deep brain stimulation imaging. NeuroImage 2019, 184, 293–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinger, N.; Mittal, S. Deep brain stimulation for seizure control in drug-resistant epilepsy. Neurosurg. Focus 2018, 45, E4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrell, M.J.; RNS System in Epilepsy Study Group. Responsive cortical stimulation for the treatment of medically intractable partial epilepsy. Neurology 2011, 77, 1295–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boon, P.; De Cock, E.; Mertens, A.; Trinka, E. Neurostimulation for drug-resistant epilepsy: A systematic review of clinical evidence for efficacy, safety, contraindications and predictors for response. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2018, 31, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, L.J.; Mirro, E.A.; Salanova, V.; Witt, T.C.; Drees, C.N.; Brown, M.-G.M.; Lee, R.W.; Sadler, T.L.; Felton, E.A.; Rutecki, P.; et al. Mesial temporal resection following long-term ambulatory intracranial EEG monitoring with a direct brain-responsive neurostimulation system. Epilepsia 2020, 61, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loring, D.W.; Kapur, R.; Meador, K.J.; Morrell, M.J. Differential neuropsychological outcomes following targeted responsive neurostimulation for partial-onset epilepsy. Epilepsia 2015, 56, 1836–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, D.R.; Laxer, K.D.; Weber, P.B.; Murro, A.M.; Park, Y.D.; Barkley, G.L.; Smith, B.J.; Gwinn, R.P.; Doherty, M.J.; Noe, K.H.; et al. Nine-year prospective efficacy and safety of brain-responsive neurostimulation for focal epilepsy. Neurology 2020, 95, e1244–e1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geller, E.B. Responsive neurostimulation: Review of clinical trials and insights into focal epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2018, 88, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.; Jo, S.; Jun, S.B.; Lee, H.W.; Lee, S. Prediction of the Seizure Suppression Effect by Electrical Stimulation via a Computational Modeling Approach. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 39. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5447012/ (accessed on 31 July 2020). [CrossRef]
- Thomas, G.P.; Jobst, B.C. Critical review of the responsive neurostimulator system for epilepsy. Med. Devices Auckl N. Z. 2015, 8, 405–411. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, G.L.; Gloss, D.; Buchhalter, J.; Mack, K.J.; Nickels, K.; Harden, C. Evidence-based guideline update: Vagus nerve stimulation for the treatment of epilepsy: Report of the Guideline Development Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2013, 81, 1453–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachem, L.D.; Wong, S.M.; Ibrahim, G.M. The vagus afferent network: Emerging role in translational connectomics. Neurosurg. Focus 2018, 45, E2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mithani, K.; Mikhail, M.; Morgan, B.R.; Wong, S.; Weil, A.G.; Deschenes, S.; Wang, S.; Bernal, B.; Guillen, M.R.; Ochi, A.; et al. Connectomic profiling Identifies responders to vagus nerve stimulation. Ann. Neurol. 2019, 86, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, G.M.; Sharma, P.; Hyslop, A.; Guillen, M.; Morgan, B.R.; Wong, S.M.; Abel, T.J.; Elkaim, L.; Cajigas, I.; Shah, A.H.; et al. Presurgical thalamocortical connectivity is associated with response to vagus nerve stimulation in children with intractable epilepsy. NeuroImage Clin. 2017, 16, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Foit, N.A.; Bernasconi, A.; Ladbon-Bernasconi, N. Contributions of Imaging to Neuromodulatory Treatment of Drug-Refractory Epilepsy. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10100700
Foit NA, Bernasconi A, Ladbon-Bernasconi N. Contributions of Imaging to Neuromodulatory Treatment of Drug-Refractory Epilepsy. Brain Sciences. 2020; 10(10):700. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10100700
Chicago/Turabian StyleFoit, Niels Alexander, Andrea Bernasconi, and Neda Ladbon-Bernasconi. 2020. "Contributions of Imaging to Neuromodulatory Treatment of Drug-Refractory Epilepsy" Brain Sciences 10, no. 10: 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10100700
APA StyleFoit, N. A., Bernasconi, A., & Ladbon-Bernasconi, N. (2020). Contributions of Imaging to Neuromodulatory Treatment of Drug-Refractory Epilepsy. Brain Sciences, 10(10), 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10100700




