Plasmonic Tweezers towards Biomolecular and Biomedical Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Optical Forces
2.1. Self-Induced Back-Action Effect
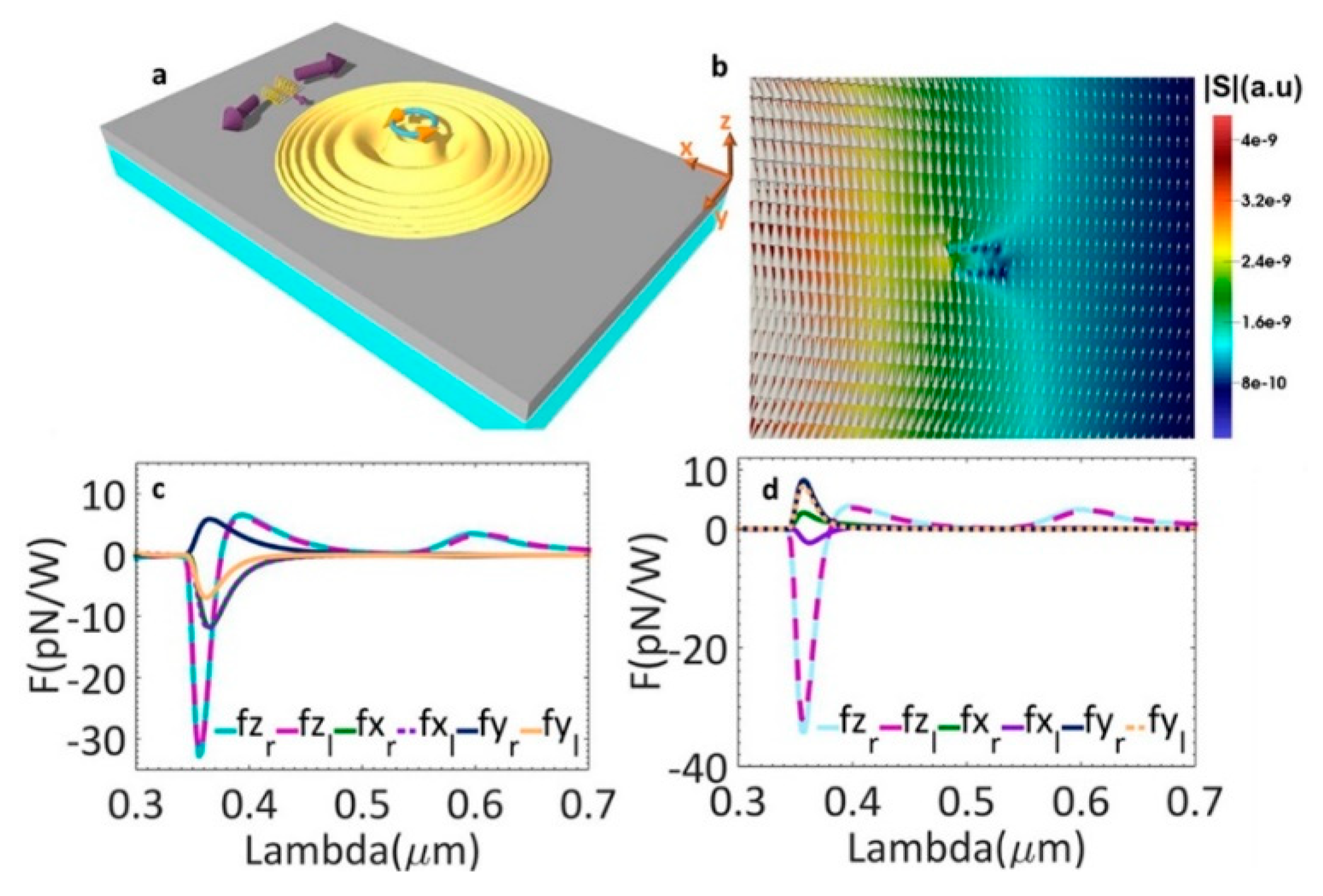
2.2. Chiral Optical Force
3. Major Designs
3.1. Single Nanoholes
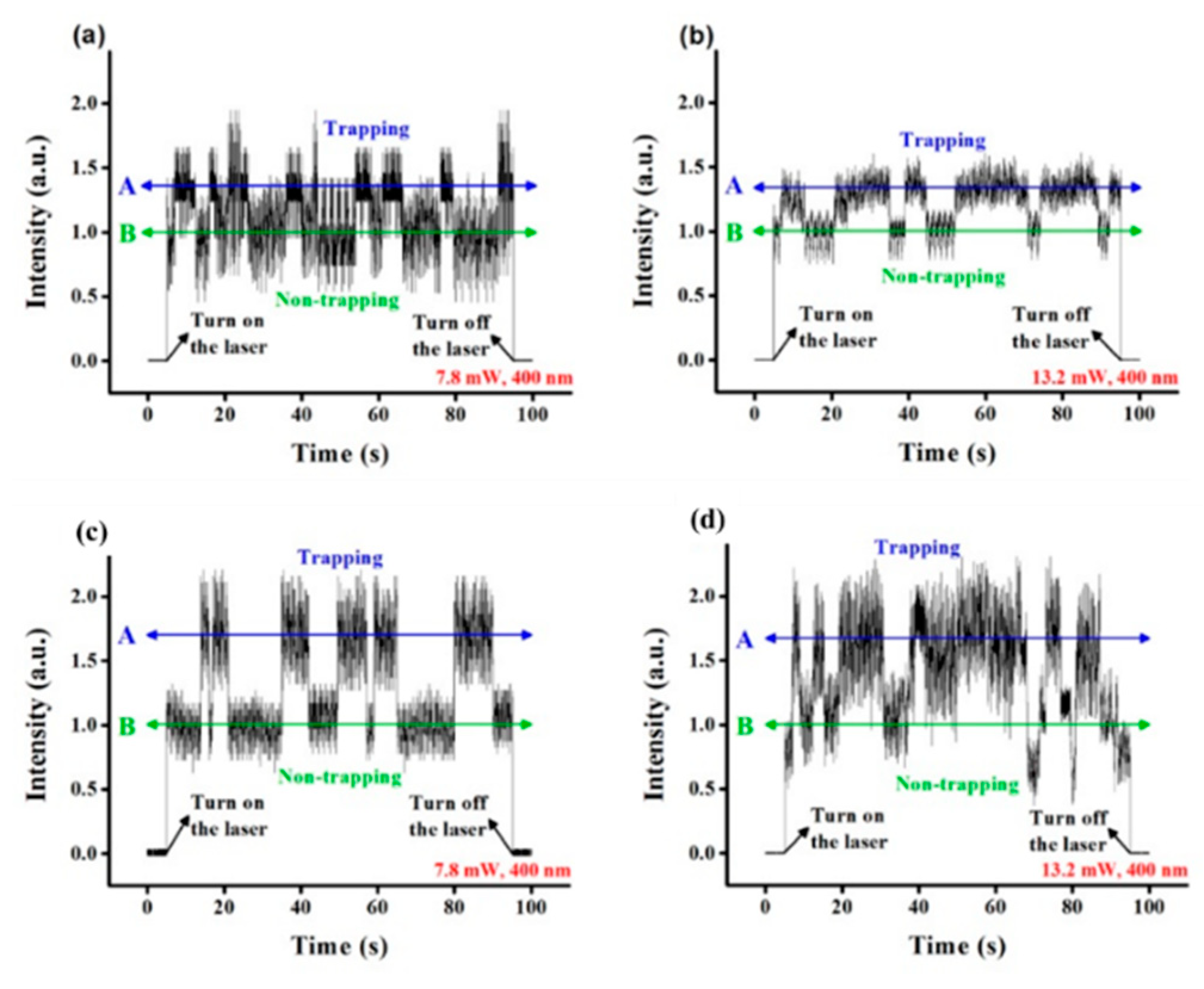
3.2. Bowtie Nano-Apertures (BNA)
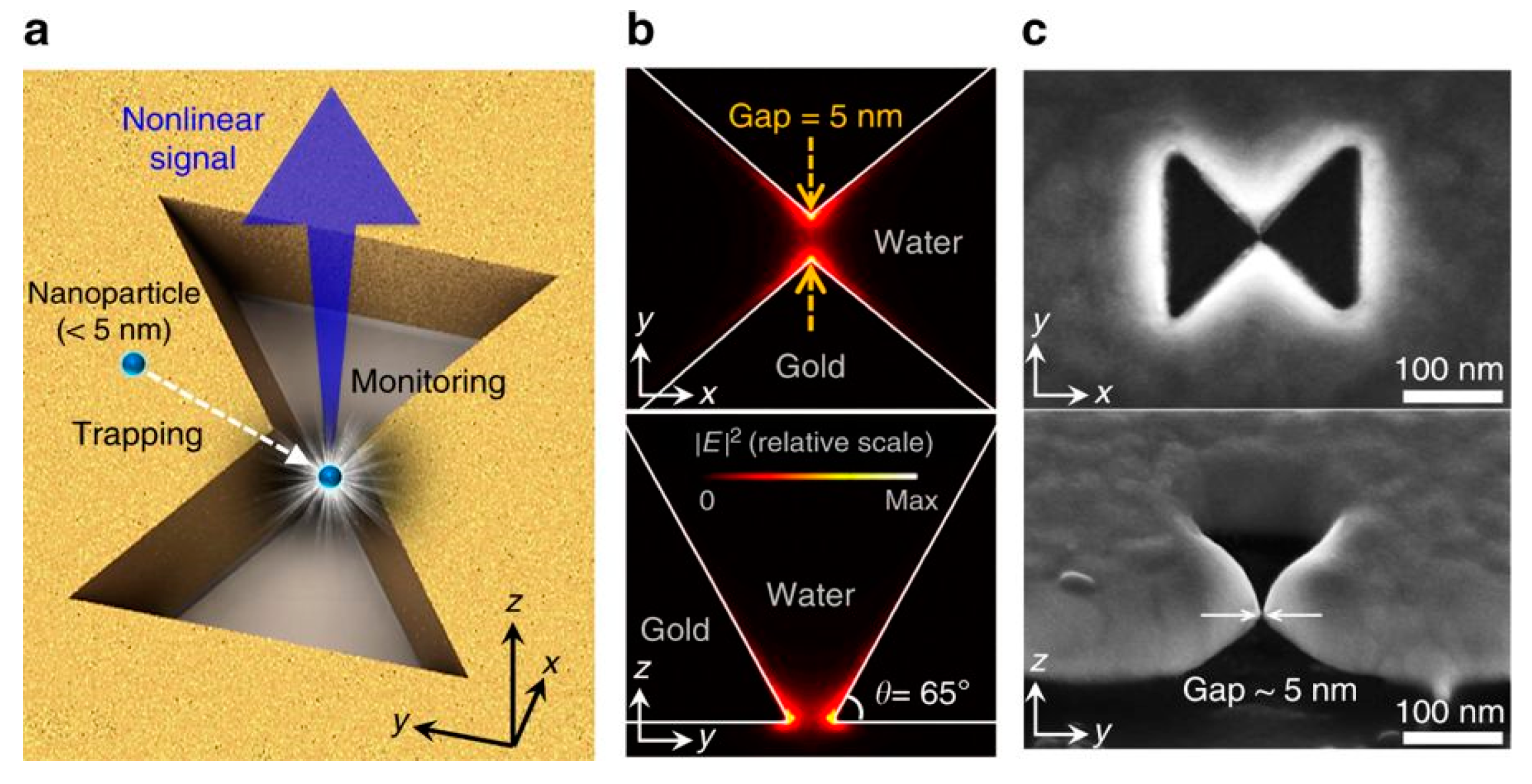
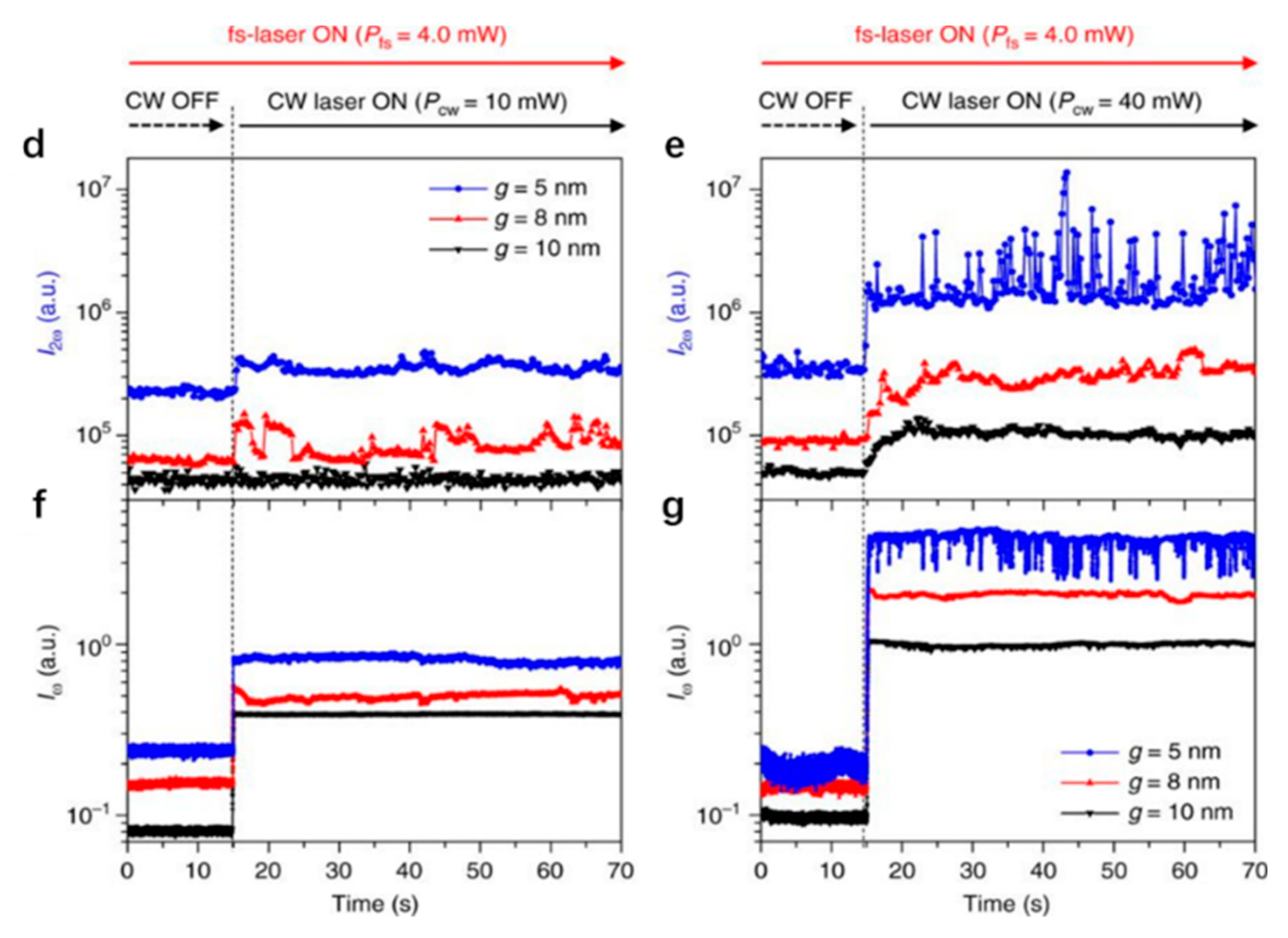
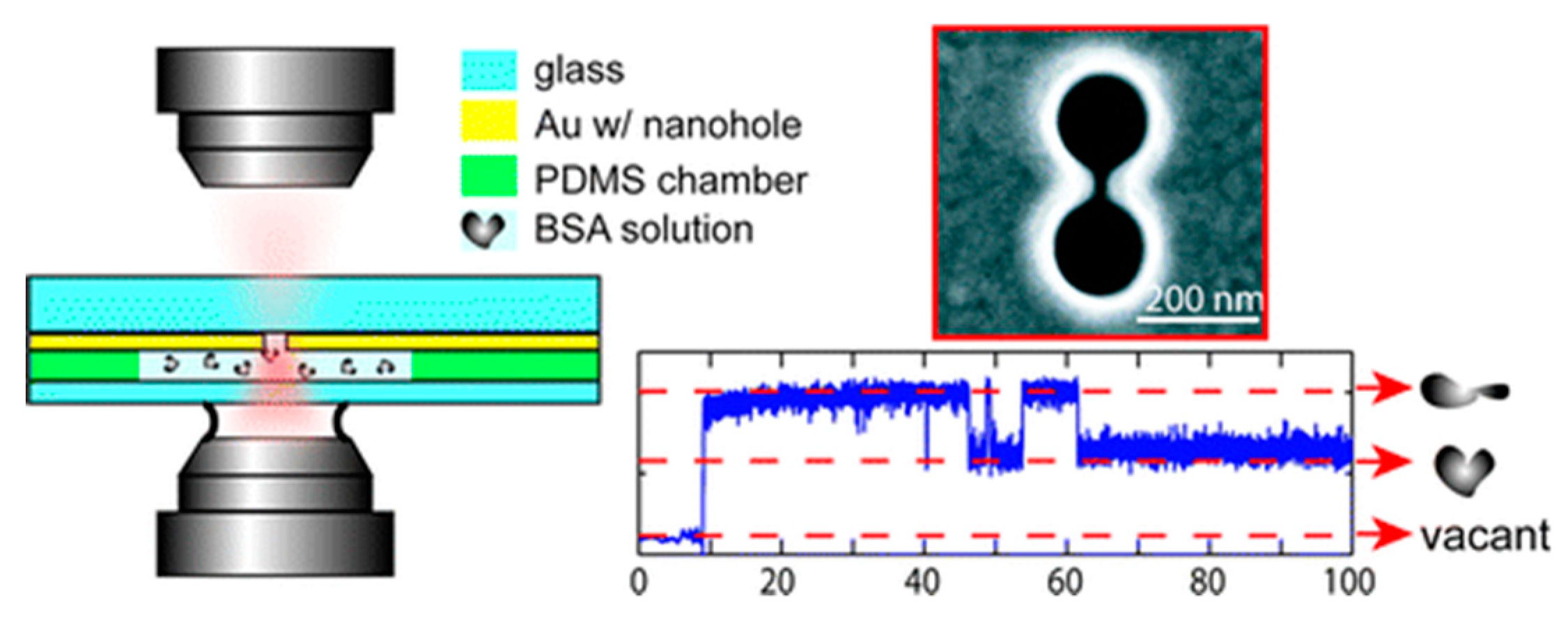
3.3. Double Nanoholes
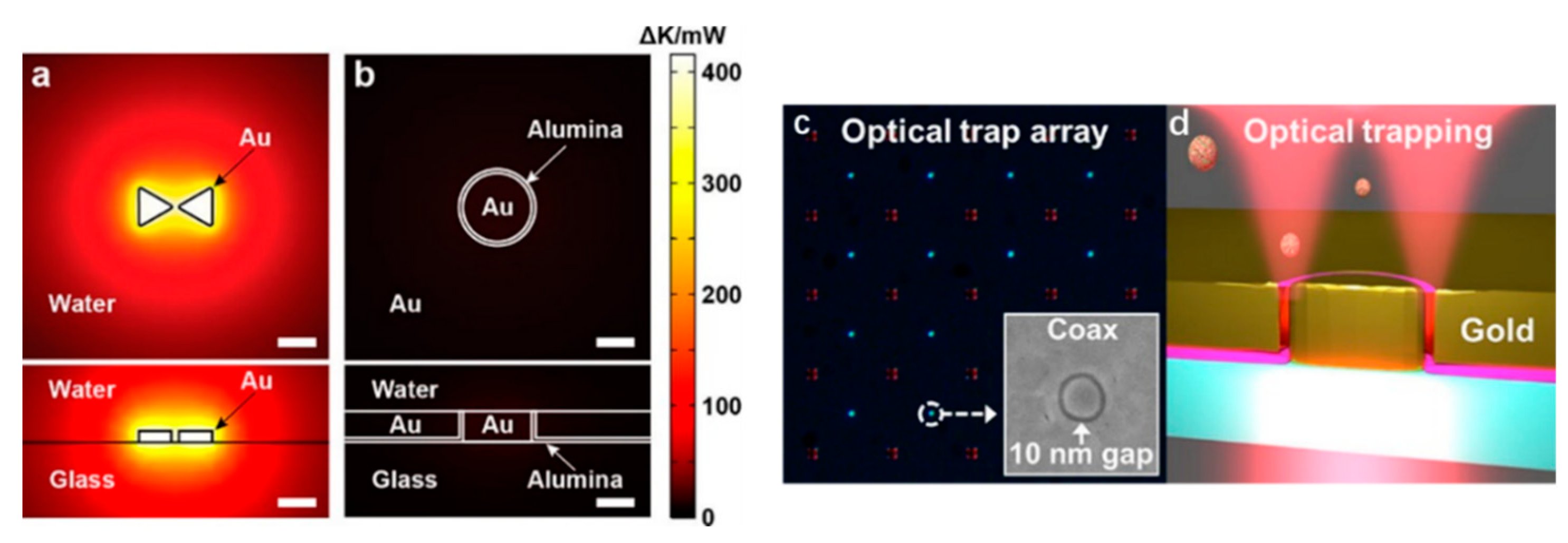
3.4. Annular Apertures
4. Outlook
4.1. Multifunctional PTs
4.2. Challenges
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ashkin, A. Acceleration and Trapping of Particles by Radiation Pressure. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1970, 24, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkin, A. Atomic-Beam Deflection by Resonance-Radiation Pressure. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1970, 25, 1321–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkin, A.; Dziedzic, J.M.; Bjorkholm, J.E.; Chu, S. Observation of a single-beam gradient force optical trap for dielectric particles. Opt. Lett. 1986, 11, 288–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashkin, A.; Dziedzic, J.M. Optical trapping and manipulation of viruses and bacteria. Science 1987, 235, 1517–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashkin, A.; Dziedzic, J.M.; Yamane, T. Optical trapping and manipulation of single cells using infrared laser beams. Nature 1987, 330, 769–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Sevilla, P.; Labrador-Páez, L.; Jaque, D.; Haro-González, P. Optical trapping for biosensing: Materials and applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 9085–9101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, D.J.; Gunn-Moore, F.; Dholakia, K. Light forces the pace: Optical manipulation for biophotonics. J. Biomed. Opt. 2010, 15, 041503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svoboda, K.; Block, S.M. Biological applications of optical forces. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 1994, 23, 247–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, S.M.; Blair, D.F.; Berg, H.C. Compliance of bacterial flagella measured with optical tweezers. Nature 1989, 338, 514–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.B.; Cui, Y.; Bustamante, C. Overstretching B-DNA: The Elastic Response of Individual Double-Stranded and Single-Stranded DNA Molecules. Science 1996, 271, 795–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante, C.; Bryant, Z.; Smith, S.B. Ten years of tension: Single-molecule DNA mechanics. Nature 2003, 421, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veigel, C.; Coluccio, L.M.; Jontes, J.D.; Sparrow, J.C.; Milligan, R.A.; Molloy, J.E. The motor protein myosin-I produces its working stroke in two steps. Nature 1999, 398, 530–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Block, S.M.; Goldstein, L.S.; Schnapp, B.J. Bead movement by single kinesin molecules studied with optical tweezers. Nature 1990, 348, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbondanzieri, E.A.; Greenleaf, W.J.; Shaevitz, J.W.; Landick, R.; Block, S.M. Direct observation of base-pair stepping by RNA polymerase. Nature 2005, 438, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shank, E.A.; Cecconi, C.; Dill, J.W.; Marqusee, S.; Bustamante, C. The folding cooperativity of a protein is controlled by its chain topology. Nature 2010, 465, 637–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.C.; Wei, X.B.; Zhou, J.H.; Wang, Z.Q.; Li, Y.M. Trapping red blood cells in living animals using optical tweezers. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favre-Bulle, I.A.; Stilgoe, A.B.; Rubinsztein-Dunlop, H.; Scott, E.K. Optical trapping of otoliths drives vestibular behaviours in larval zebrafish. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norregaard, K.; Metzler, R.; Ritter, C.M.; Berg-Sorensen, K.; Oddershede, L.B. Manipulation and Motion of Organelles and Single Molecules in Living Cells. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 4342–4375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.E.; Badman, R.P.; Wang, M.D. Nanophotonic trapping: Precise manipulation and measurement of biomolecular arrays. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 10, e1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grujic, K.; Helleso, O.G.; Hole, J.P.; Wilkinson, J.S. Sorting of polystyrene microspheres using a Y-branched optical waveguide. Opt. Express 2005, 13, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reece, P.J.; Garcés-Chávez, V.; Dholakia, K. Near-field optical micromanipulation with cavity enhanced evanescent waves. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 221116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Haumonte, J.B.; Micheau, Y.; Chon, J.W.M.; Gan, X.S. Laser trapping and manipulation under focused evanescent wave illumination. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 84, 4236–4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šiler, M.; Čižmár, T.; Šerý, M.; Zemánek, P. Optical forces generated by evanescent standing waves and their usage for sub-micron particle delivery. Appl. Phys. B 2006, 84, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schein, P.; Kang, P.; O’Dell, D.; Erickson, D. Nanophotonic force microscopy: Characterizing particle-surface interactions using near-field photonics. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 1414–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Song, W.Z.; Crozier, K.B. Optical Trapping of Nanoparticles Using All-Silicon Nanoantennas. ACS Photonics 2018, 5, 4993–5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.G.; Han, B.M.; Chang, S. Force of surface plasmon-coupled evanescent fields on Mie particles. Opt. Commun. 2001, 198, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, E.S.; Onuta, T.D.; Amarie, D.; Potyrailo, R.; Stein, B.; Jacobson, S.C.; Schaich, W.L.; Dragnea, B. Optical trapping with integrated near-field apertures. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 13607–13612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigorenko, A.N.; Roberts, N.W.; Dickinson, M.R.; Zhang, Y. Nanometric optical tweezers based on nanostructured substrates. Nat. Photonics 2008, 2, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, M.L.; Righini, M.; Quidant, R. Plasmon nano-optical tweezers. Nat. Photonics 2011, 5, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, T.; Tsuboi, Y. Plasmonic Optical Tweezers toward Molecular Manipulation: Tailoring Plasmonic Nanostructure, Light Source, and Resonant Trapping. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 2957–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, D.; Mossa, A.; Jadhav, M.; Cecconi, C. Bio-Molecular Applications of Recent Developments in Optical Tweezers. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.H.; Kim, K.; Ee, H.S.; Lee, Y.H.; Yoon, T.Y.; Seo, M.K.; Park, H.G. Low-power nano-optical vortex trapping via plasmonic diabolo nanoantennas. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoji, T.; Saitoh, J.; Kitamura, N.; Nagasawa, F.; Murakoshi, K.; Yamauchi, H.; Ito, S.; Miyasaka, H.; Ishihara, H.; Tsuboi, Y. Permanent fixing or reversible trapping and release of DNA micropatterns on a gold nanostructure using continuous-wave or femtosecond-pulsed near-infrared laser light. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 6643–6648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Righini, M.; Ghenuche, P.; Cherukulappurath, S.; Myroshnychenko, V.; Garcia de Abajo, F.J.; Quidant, R. Nano-optical trapping of Rayleigh particles and Escherichia coli bacteria with resonant optical antennas. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 3387–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galloway, C.M.; Kreuzer, M.P.; Acimovic, S.S.; Volpe, G.; Correia, M.; Petersen, S.B.; Neves-Petersen, M.T.; Quidant, R. Plasmon-Assisted Delivery of Single Nano-Objects in an Optical Hot Spot. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 4299–4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andres-Arroyo, A.; Wang, F.; Toe, W.J.; Reece, P. Intrinsic heating in optically trapped Au nanoparticles measured by dark-field spectroscopy. Biomed. Opt. Express 2015, 6, 3646–3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.J.; Lee, Y.G. Comparison of plasmonic structures in terms of temperature increase under equivalent maximal trapping forces. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 119, 083108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, R.W.; Padgett, M.J. Optical trapping and binding. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2013, 76, 026401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuman, K.C.; Block, S.M. Optical trapping. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2004, 75, 2787–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieminen, T.A.; du Preez-Wilkinson, N.; Stilgoe, A.B.; Loke, V.L.Y.; Bui, A.A.M.; Rubinsztein-Dunlop, H. Optical tweezers: Theory and modelling. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2014, 146, 59–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draine, B.T. The Discrete-Dipole Approximation and Its Application to Interstellar Graphite Grains. Astrophys. J. 1988, 333, 848–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albaladejo, S.; Marques, M.I.; Laroche, M.; Saenz, J.J. Scattering forces from the curl of the spin angular momentum of a light field. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 113602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, J.P.; Alexander, D.R.; Schaub, S.A. Theoretical determination of net radiation force and torque for a spherical particle illuminated by a focused laser beam. J. Appl. Phys. 1989, 66, 4594–4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivinskaya, A.; Petrov, M.I.; Bogdanov, A.A.; Shishkin, I.; Ginzburg, P.; Shalin, A.S. Plasmon-assisted optical trapping and anti-trapping. Light-Sci. Appl. 2017, 6, e16258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Truong, V.G.; Thomas, P.S.; Chormaic, S.N. Sequential trapping of single nanoparticles using a gold plasmonic nanohole array. Photonics Res. 2018, 6, 981–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolf, D.; Kats, M.A.; Capasso, F. Spoof surface plasmon waveguide forces. Opt. Lett. 2014, 39, 517–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.F.; Song, G.; Yu, L. Optical trapping of single quantum dots for cavity quantum electrodynamics. Photonics Res. 2018, 6, 182–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, M.; Benson, O. Manipulation of dielectric particles using photonic crystal cavities. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 253114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, M.L.; Gordon, R.; Pang, Y.J.; Eftekhari, F.; Quidant, R. Self-induced back-action optical trapping of dielectric nanoparticles. Nat. Phys. 2009, 5, 915–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descharmes, N.; Dharanipathy, U.P.; Diao, Z.; Tonin, M.; Houdre, R. Observation of backaction and self-induced trapping in a planar hollow photonic crystal cavity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 123601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestres, P.; Berthelot, J.; Acimovic, S.S.; Quidant, R. Unraveling the optomechanical nature of plasmonic trapping. Light-Sci. Appl. 2016, 5, e16092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumeier, L.; Quidant, R.; Chang, D.E. Self-induced back-action optical trapping in nanophotonic systems. New J. Phys. 2015, 17, 123008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Juan, M.L.; Li, Y.; Maes, G.; Borghs, G.; Van Dorpe, P.; Quidant, R. Enhanced optical trapping and arrangement of nano-objects in a plasmonic nanocavity. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobson, C.M. Protein folding and misfolding. Nature 2003, 426, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Saleh, A.A.E.; Dionne, J.A. Enantioselective Optical Trapping of Chiral Nanoparticles with Plasmonic Tweezers. ACS Photonics 2016, 3, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, M.H.; Reinhard, B.M. Transverse Chiral Optical Forces by Chiral Surface Plasmon Polaritons. ACS Photonics 2015, 2, 1780–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champi, H.A.A.; Bustamante, R.H.; Salcedo, W.J. Optical enantioseparation of chiral molecules using asymmetric plasmonic nanoapertures. Opt. Mater. Express 2019, 9, 1763–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Liu, X. Optical lateral forces and torques induced by chiral surface-plasmon-polaritons and their potential applications in recognition and separation of chiral enantiomers. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 1308–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendry, E.; Carpy, T.; Johnston, J.; Popland, M.; Mikhaylovskiy, R.V.; Lapthorn, A.J.; Kelly, S.M.; Barron, L.D.; Gadegaard, N.; Kadodwala, M. Ultrasensitive detection and characterization of biomolecules using superchiral fields. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 783–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotnala, A.; Gordon, R. Quantification of high-efficiency trapping of nanoparticles in a double nanohole optical tweezer. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 853–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.D.; Lee, Y.G. Trapping of a single DNA molecule using nanoplasmonic structures for biosensor applications. Biomed. Opt. Express 2014, 5, 2471–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roxworthy, B.J.; Ko, K.D.; Kumar, A.; Fung, K.H.; Chow, E.K.; Liu, G.L.; Fang, N.X.; Toussaint, K.C., Jr. Application of plasmonic bowtie nanoantenna arrays for optical trapping, stacking, and sorting. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.T.; Chu, H.Y.; Lu, T.W.; Lee, P.T. Trapping particles using waveguide-coupled gold bowtie plasmonic tweezers. Lab. A Chip 2014, 14, 4647–4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pin, C.; Ishida, S.; Takahashi, G.; Sudo, K.; Fukaminato, T.; Sasaki, K. Trapping and Deposition of Dye-Molecule Nanoparticles in the Nanogap of a Plasmonic Antenna. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 4878–4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roxworthy, B.J.; Toussaint, K.C., Jr. Plasmonic nanotweezers: Strong influence of adhesion layer and nanostructure orientation on trapping performance. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 9591–9603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, S.J.; Lee, J.; Han, S.; Kim, C.K.; Ahn, C.W.; Kim, M.K.; Lee, Y.H. Non-fluorescent nanoscopic monitoring of a single trapped nanoparticle via nonlinear point sources. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthelot, J.; Acimovic, S.S.; Juan, M.L.; Kreuzer, M.P.; Renger, J.; Quidant, R. Three-dimensional manipulation with scanning near-field optical nanotweezers. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, R.A.; Huang, I.C.; Chen, O.; Choy, J.T.; Bischof, T.S.; Loncar, M.; Bawendi, M.G. Optical Trapping and Two-Photon Excitation of Colloidal Quantum Dots Using Bowtie Apertures. ACS Photonics 2016, 3, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Balushi, A.A.; Kotnala, A.; Wheaton, S.; Gelfand, R.M.; Rajashekara, Y.; Gordon, R. Label-free free-solution nanoaperture optical tweezers for single molecule protein studies. Analyst 2015, 140, 4760–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Gordon, R. Optical trapping of a single protein. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotnala, A.; Wheaton, S.; Gordon, R. Playing the notes of DNA with light: Extremely high frequency nanomechanical oscillations. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 2295–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hacohen, N.; Ip, C.J.X.; Gordon, R. Analysis of Egg White Protein Composition with Double Nanohole Optical Tweezers. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 5266–5272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Balushi, A.A.; Gordon, R. Label-Free Free-Solution Single-Molecule Protein–Small Molecule Interaction Observed by Double-Nanohole Plasmonic Trapping. ACS Photonics 2014, 1, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Park, H.R.; Pelton, M.; Piao, X.; Lindquist, N.C.; Im, H.; Kim, Y.J.; Ahn, J.S.; Ahn, K.J.; Park, N.; et al. Atomic layer lithography of wafer-scale nanogap arrays for extreme confinement of electromagnetic waves. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, A.A.; Dionne, J.A. Toward efficient optical trapping of sub-10-nm particles with coaxial plasmonic apertures. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 5581–5586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, D.; Gurunatha, K.L.; Choi, H.K.; Mohr, D.A.; Ertsgaard, C.T.; Gordon, R.; Oh, S.H. Low-Power Optical Trapping of Nanoparticles and Proteins with Resonant Coaxial Nanoaperture Using 10 nm Gap. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 3637–3642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Serey, X.; Erickson, D. Nanomanipulation using silicon photonic crystal resonators. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.F.; Serey, X.; Sarkar, R.; Chen, P.; Erickson, D. Controlled photonic manipulation of proteins and other nanomaterials. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 1633–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Kaneda, S.; Sasaki, K. Nanostructured Potential of Optical Trapping Using a Plasmonic Nanoblock Pair. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 2146–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Liu, K.; Sun, C. Plasmonics for Biosensing. Materials 2019, 12, 1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takai, T.; Nakao, H.; Iwata, F. Three-dimensional microfabrication using local electrophoresis deposition and a laser trapping technique. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 28109–28117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadappuram, B.P.; Cadinu, P.; Barik, A.; Ainscough, A.J.; Devine, M.J.; Kang, M.; Gonzalez-Garcia, J.; Kittler, J.T.; Willison, K.R.; Vilar, R.; et al. Nanoscale tweezers for single-cell biopsies. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2019, 14, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiou, P.Y.; Ohta, A.T.; Wu, M.C. Massively parallel manipulation of single cells and microparticles using optical images. Nature 2005, 436, 370–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ertsgaard, C.T.; Wittenberg, N.J.; Klemme, D.J.; Barik, A.; Shih, W.C.; Oh, S.H. Integrated Nanogap Platform for Sub-Volt Dielectrophoretic Trapping and Real-Time Raman Imaging of Biological Nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 5946–5953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, X.; Lin, L.Y. Large dielectrophoresis force and torque induced by localized surface plasmon resonance of Au nanoparticle array. Opt. Lett. 2007, 32, 295–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, A.T.; Chiou, P.Y.; Han, T.H.; Liao, J.C.; Bhardwaj, U.; McCabe, E.R.B.; Yu, F.Q.; Sun, R.; Wu, M.C. Dynamic cell and microparticle control via optoelectronic tweezers. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2007, 16, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yuan, Y.J. A review of polystyrene bead manipulation by dielectrophoresis. Rsc Adv. 2019, 9, 4963–4981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.B.; Xia, M.; Zhang, P.; Xie, Y.H. Self-Aligned Trapping and Detecting Molecules Using a Plasmonic Tweezer with an Integrated Electrostatic Cell. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2017, 5, 1600329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Verschueren, D.; Pud, S.; Dekker, C. Integrating Sub-3 nm Plasmonic Gaps into Solid-State Nanopores. Small 2018, 14, e1703307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.Y.; Chen, W.T.; Zaidi, A.; Huang, Y.-W.; Khorasaninejad, M.; Sanjeev, V.; Qiu, C.-W.; Capasso, F. Giant intrinsic chiro-optical activity in planar dielectric nanostructures. Light Sci. Appl. 2018, 7, 17158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolotin, K.I.; Sikes, K.J.; Jiang, Z.; Klima, M.; Fudenberg, G.; Hone, J.; Kim, P.; Stormer, H.L. Ultrahigh electron mobility in suspended graphene. Solid State Commun. 2008, 146, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, R.R.; Blake, P.; Grigorenko, A.N.; Novoselov, K.S.; Booth, T.J.; Stauber, T.; Peres, N.M.; Geim, A.K. Fine structure constant defines visual transparency of graphene. Science 2008, 320, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, S.; Kim, H.; Lee, Y.; Xu, X.; Park, J.-S.; Zheng, Y.; Balakrishnan, J.; Lei, T.; Ri Kim, H.; Song, Y.I.; et al. Roll-to-roll production of 30-inch graphene films for transparent electrodes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balandin, A.A.; Ghosh, S.; Bao, W.; Calizo, I.; Teweldebrhan, D.; Miao, F.; Lau, C.N. Superior Thermal Conductivity of Single-Layer Graphene. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 902–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.D.; Lee, Y.G. Graphene-based plasmonic tweezers. Carbon 2016, 103, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Pisana, S.; Chakraborty, B.; Piscanec, S.; Saha, S.K.; Waghmare, U.V.; Novoselov, K.S.; Krishnamurthy, H.R.; Geim, A.K.; Ferrari, A.C.; et al. Monitoring dopants by Raman scattering in an electrochemically top-gated graphene transistor. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ukjin, J.; Yun Ji, K.; Yonghun, K.; Young Gon, L.; Byoung Hun, L. Extraction of the Interface State Density of Top-Gate Graphene Field-Effect Transistors. IEEE Electron. Device Lett. 2015, 36, 408–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grier, D.G.; Roichman, Y. Holographic optical trapping. Appl. Opt. 2006, 45, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korda, P.T.; Taylor, M.B.; Grier, D.G. Kinetically locked-in colloidal transport in an array of optical tweezers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 128301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villangca, M.J.; Palima, D.; Banas, A.R.; Gluckstad, J. Light-driven micro-tool equipped with a syringe function. Light: Sci. Appl. 2016, 5, e16148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butaite, U.G.; Gibson, G.M.; Ho, Y.D.; Taverne, M.; Taylor, J.M.; Phillips, D.B. Indirect optical trapping using light driven micro-rotors for reconfigurable hydrodynamic manipulation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| # | Geometry | Wavelength (nm) | Nanoparticle (Diameter) | Trap Stiffness (fN/nm) | Scaled Trap Stiffness (fN/nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1D silicon photonic crystals (2010) [77] | 1548.15 nm | 200 nm Polystyrene | Radical 2.86 | 2.86 |
| 2 | 1D silicon photonic crystals (2012) [78] | 1064 nm | 22 nm Polystyrene; | Lateral 0.17 | 0.13 |
| 3 | Silicon nano-antennas (2018) [25] | 1064 nm | 20 nm Polystyrene; | Lateral 0.10 (estimated) | 0.10 |
| 4 | Plasmonic nano pillar (2008) [28] | 1064 nm | 200 nm Polystyrene; | 0.013 | 0.013 |
| 5 | Gold nanoblock pairs (2013) [79] | 1064 nm | 100 nm Polystyrene; | Lateral 1.86 | 0.01 |
| 6 | Double nanohole (2014) [60] | 820 nm | 20 nm Polystyrene; | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| 7 | Connected circular holes (2018) [45] | 980 nm | 30 nm Polystyrene; | 0.84 | 0.25 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, X.; Sun, C. Plasmonic Tweezers towards Biomolecular and Biomedical Applications. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3596. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9173596
Han X, Sun C. Plasmonic Tweezers towards Biomolecular and Biomedical Applications. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(17):3596. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9173596
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Xue, and Changsen Sun. 2019. "Plasmonic Tweezers towards Biomolecular and Biomedical Applications" Applied Sciences 9, no. 17: 3596. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9173596
APA StyleHan, X., & Sun, C. (2019). Plasmonic Tweezers towards Biomolecular and Biomedical Applications. Applied Sciences, 9(17), 3596. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9173596





