Degradation of Trace Organic Contaminants by a Membrane Distillation—Enzymatic Bioreactor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Trace Organic Contaminants (TrOCs), Laccase and Mediators
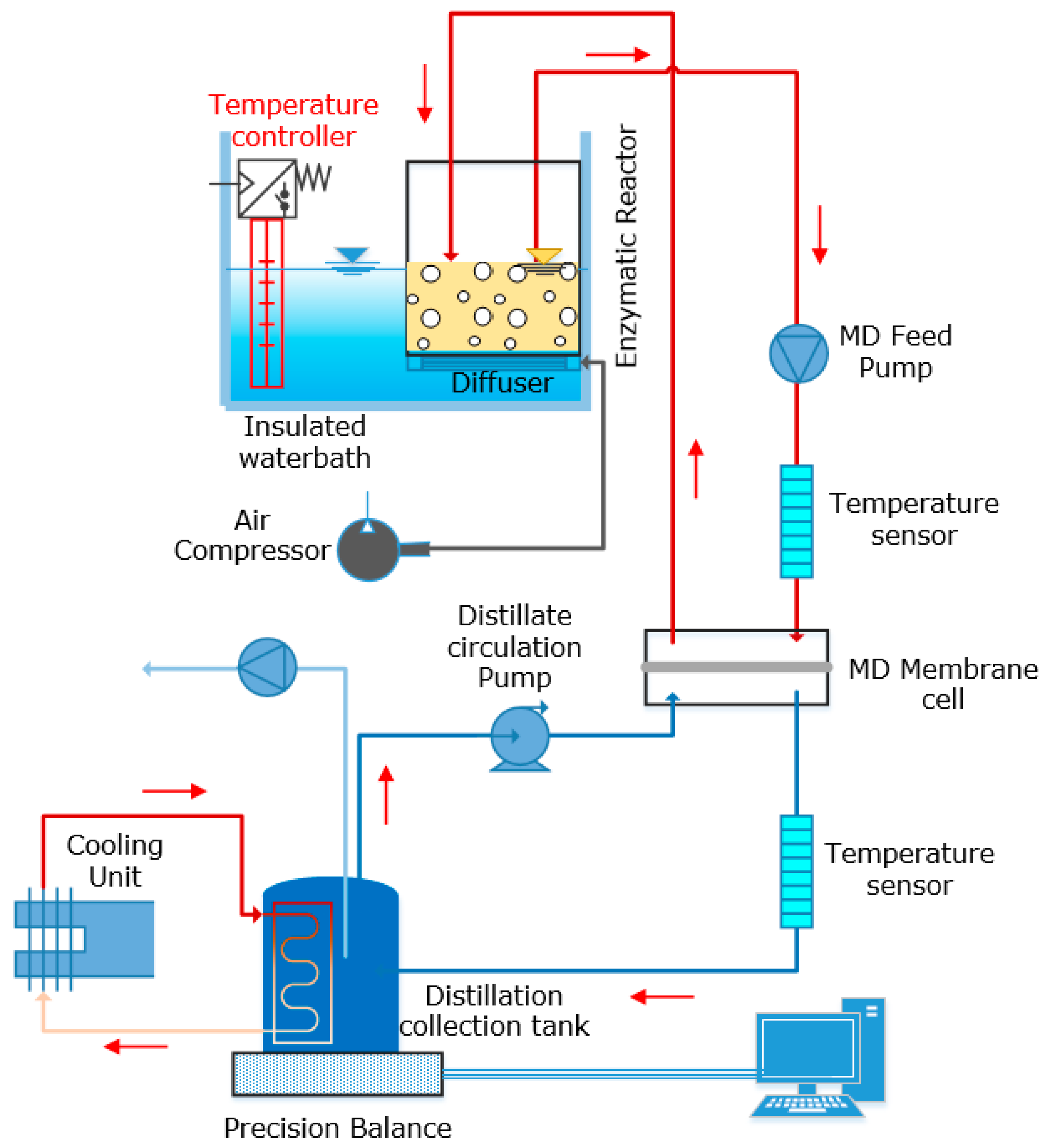
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Experimental Protocol
2.4. Analytical Methods
2.4.1. TrOC Analysis
2.4.2. Enzymatic Activity, ORP and Toxicity Assay
3. Results and Discussion
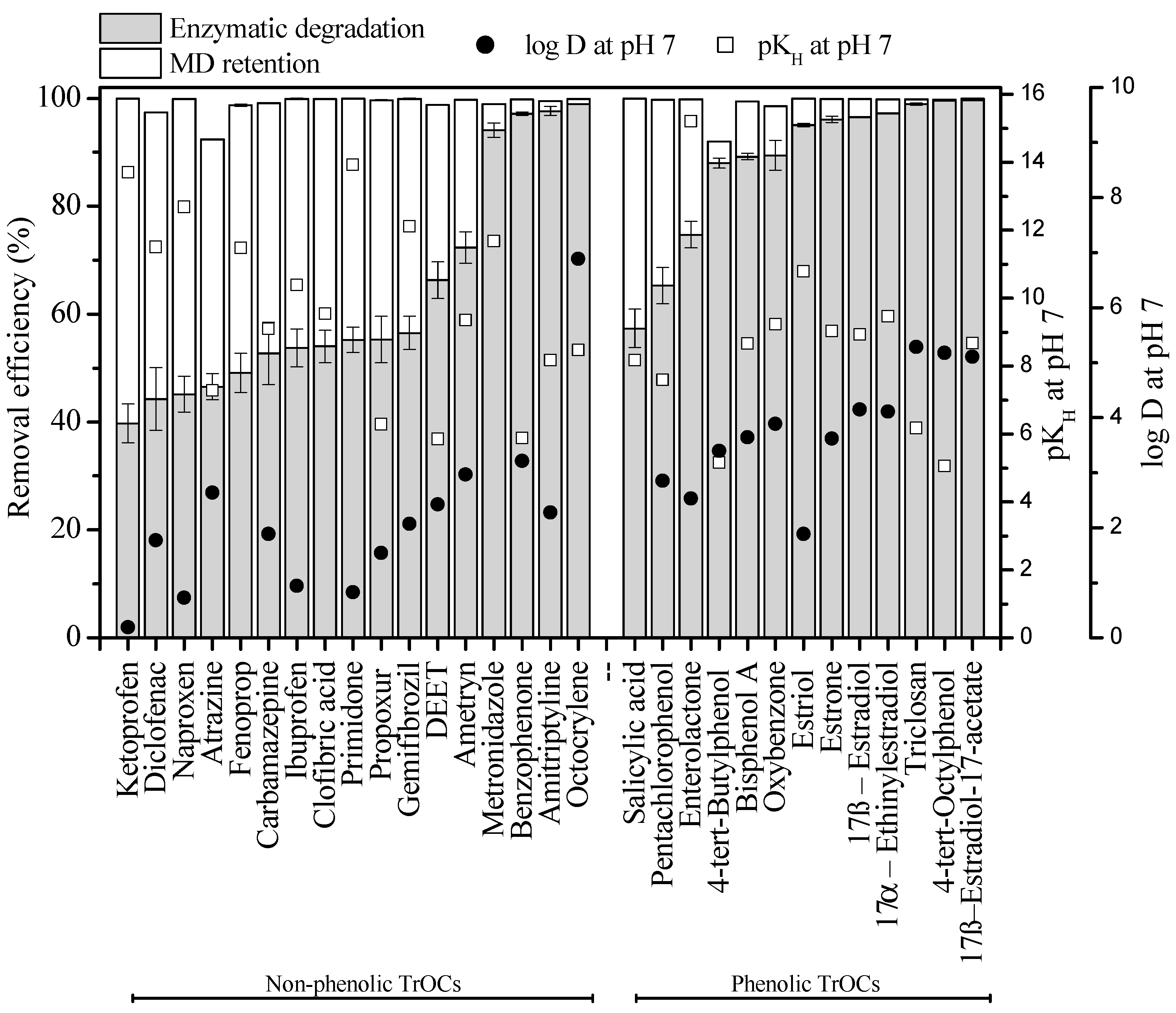
3.1. Overall Removal of TrOCs
3.2. TrOC Degradation in Enzymatic Bioreactor
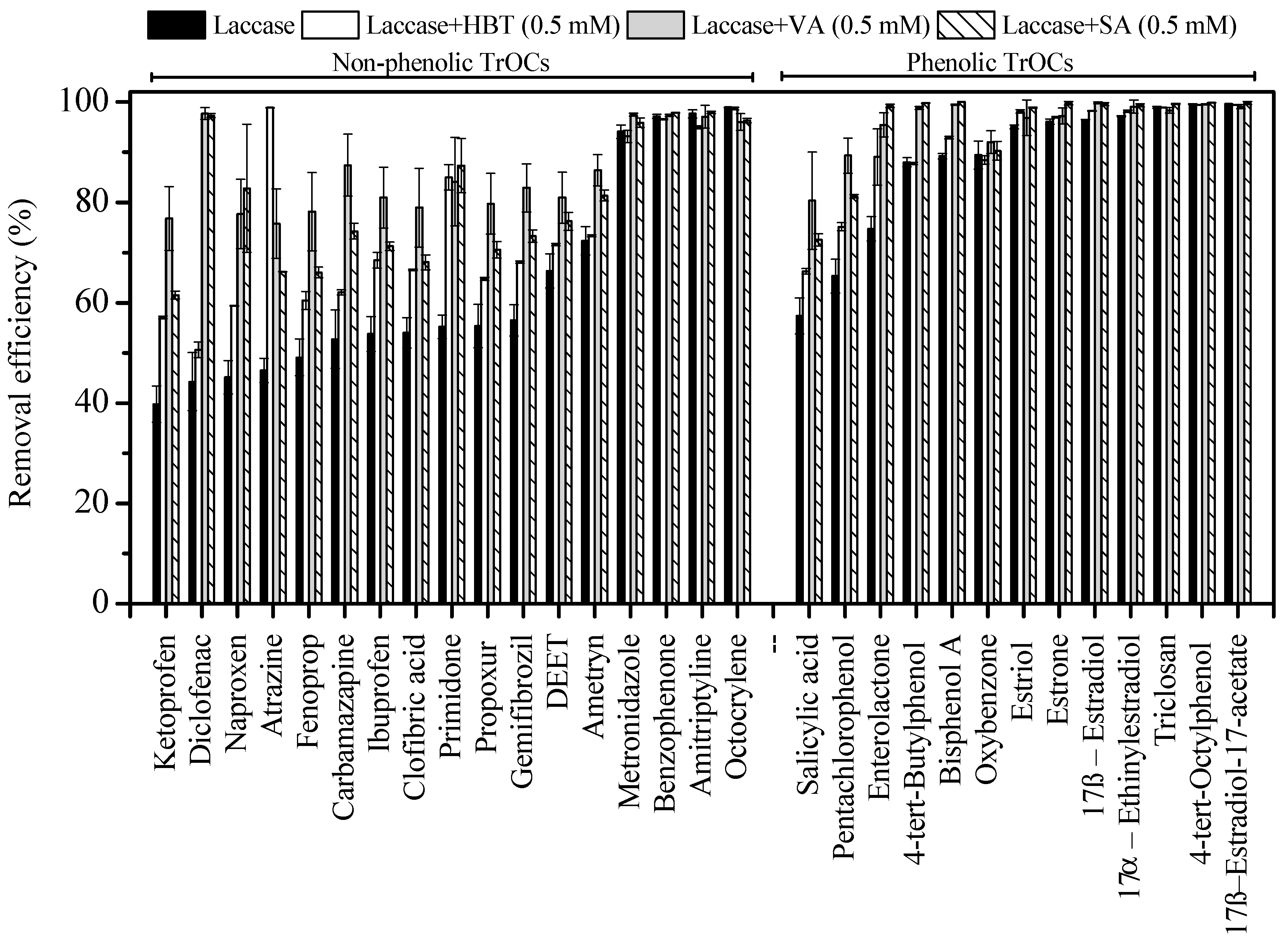
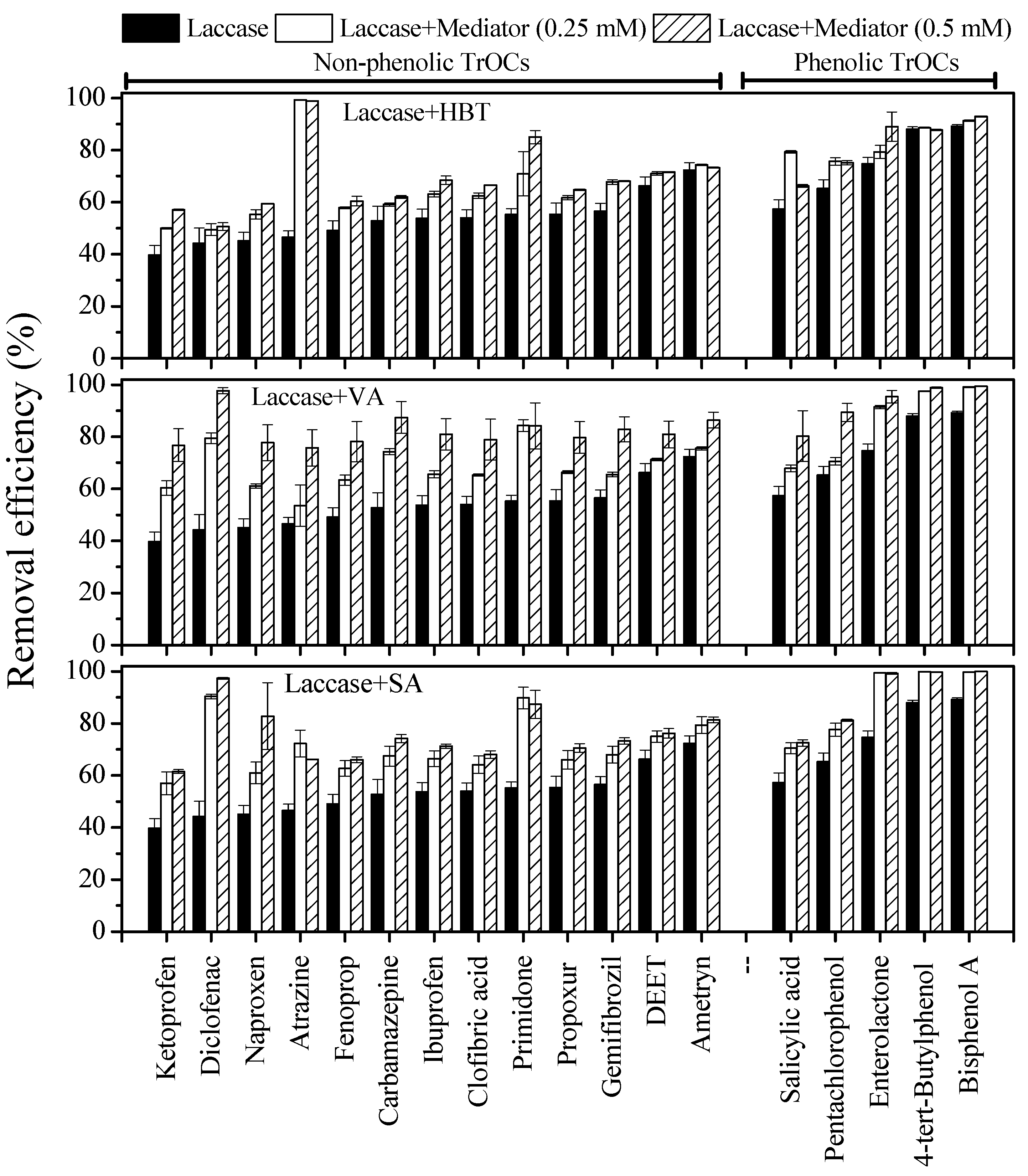
3.3. Impact of Mediator Addition on TrOC Degradation
3.3.1. Comparison of Redox-Mediators
3.3.2. Impact of Mediator Concentration
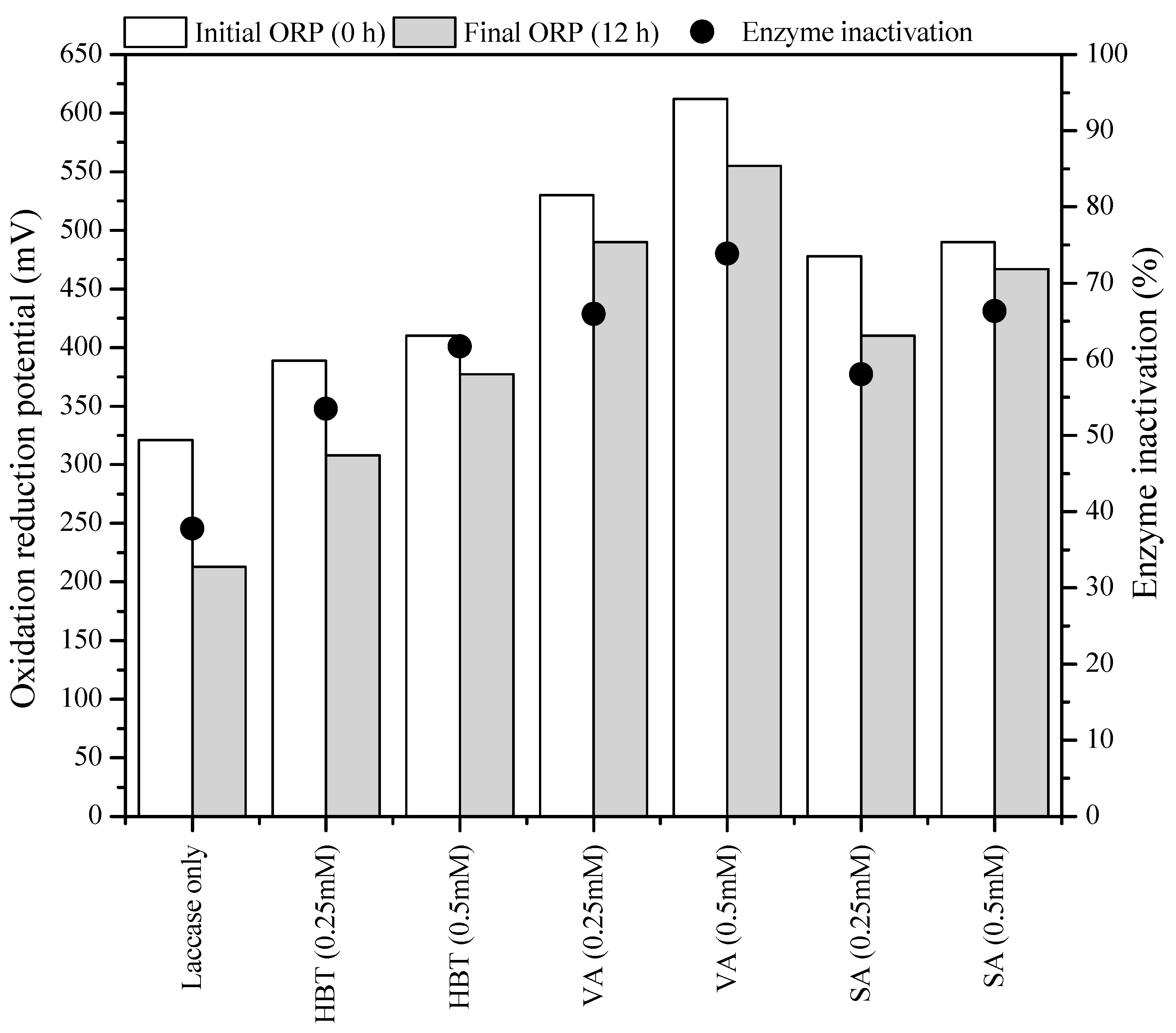
3.3.3. Effect of Mediators on Enzyme Stability
3.4. Effluent Toxicity
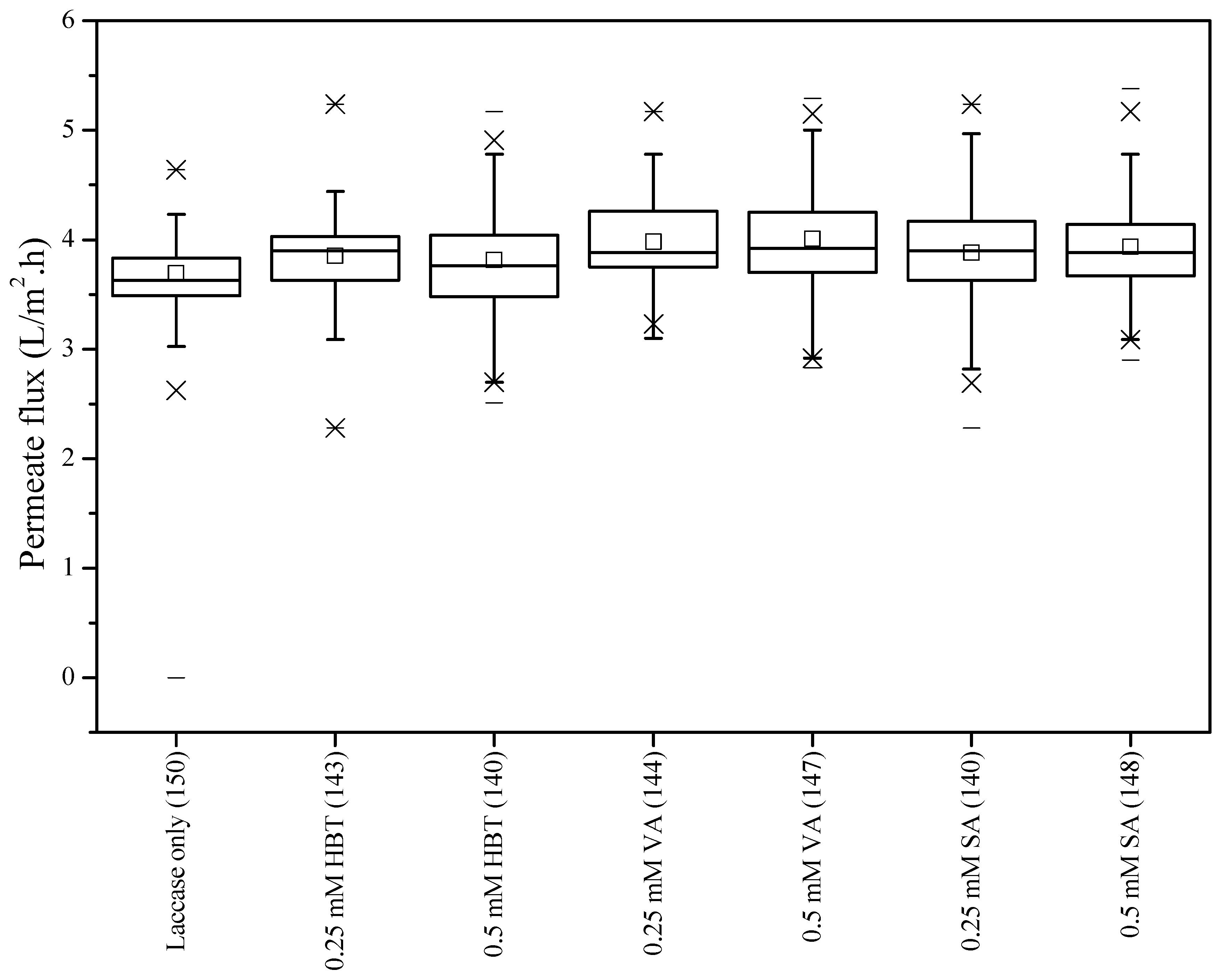
3.5. Permeate Flux
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hai, F.I.; Yamamoto, K.; Nakajima, F.; Fukushi, K. Application of a gac-coated hollow fiber module to couple enzymatic degradation of dye on membrane to whole cell biodegradation within a membrane bioreactor. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 389, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, F.I.; Yamamoto, K.; Fukushi, K. Hybrid treatment systems for dye wastewater. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 37, 315–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yan, M.; Geng, Y.; Huang, J. Laccase immobilization on poly(p-phenylenediamine)/Fe3O4 nanocomposite for reactive blue 19 dye removal. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, F.I.; Yamamoto, K.; Fukushi, K. Development of a submerged membrane fungi reactor for textile wastewater treatment. Desalination 2006, 192, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, F.I.; Yamamoto, K.; Nakajima, F.; Fukushi, K.; Nghiem, L.D.; Price, W.E.; Jin, B. Degradation of azo dye acid orange 7 in a membrane bioreactor by pellets and attached growth of Coriolus versicolour. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 141, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asif, M.B.; Hai, F.I.; Singh, L.; Price, W.E.; Nghiem, L.D. Degradation of pharmaceuticals and personal care products by white-rot fungi—A critical review. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2017, 3, 88–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.B.; Hai, F.I.; Hou, J.; Price, W.E.; Nghiem, L.D. Impact of wastewater derived dissolved interfering compounds on growth, enzymatic activity and trace organic contaminant removal of white rot fungi—A critical review. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 201, 89–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Nghiem, L.D.; Hai, F.I.; Zhang, J.; Liang, S.; Wang, X.C. A review on the occurrence of micropollutants in the aquatic environment and their fate and removal during wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473, 619–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, J.T.; Hai, F.I.; Al-aboud, T.M. Chemical coagulation-based processes for trace organic contaminant removal: Current state and future potential. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 111, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, A.; Gin, K.Y.-H.; Lin, A.Y.-C.; Reinhard, M. Impacts of emerging organic contaminants on freshwater resources: Review of recent occurrences, sources, fate and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 6062–6069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Hai, F.I.; Nghiem, L.D.; Price, W.E.; Roddick, F.; Moreira, M.T.; Magram, S.F. Understanding the factors controlling the removal of trace organic contaminants by white-rot fungi and their lignin modifying enzymes: A critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 141, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margot, J.; Maillard, J.; Rossi, L.; Barry, D.A.; Holliger, C. Influence of treatment conditions on the oxidation of micropollutants by trametes versicolor laccase. New Biotechnol. 2013, 30, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hai, F.I.; Nghiem, L.D.; Khan, S.J.; Price, W.E.; Yamamoto, K. Wastewater reuse: Removal of emerging trace organic contaminants. In Membrane Biological Reactors: Theory, Modeling, Design, Management and Applications to Wastewater Reuse; Hai, F.I., Yamamoto, K., Lee, C., Eds.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2014; pp. 165–205. ISBN 9781780400655. [Google Scholar]
- Hai, F.I.; Tadkaew, N.; McDonald, J.A.; Khan, S.J.; Nghiem, L.D. Is halogen content the most important factor in the removal of halogenated trace organics by mbr treatment? Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 6299–6303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, N.H.; Urase, T.; Kusakabe, O. Biodegradation characteristics of pharmaceutical substances by whole fungal culture trametes versicolor and its laccase. J. Water Environ. Technol. 2010, 8, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañas, A.I.; Camarero, S. Laccases and their natural mediators: Biotechnological tools for sustainable eco-friendly processes. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 694–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purich, D.L. Enzyme Kinetics: Catalysis & Control: A Reference of Theory and Best-Practice Methods; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; p. 759. ISBN 9780123809247. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, L.N.; Hai, F.I.; Price, W.E.; Kang, J.; Leusch, F.D.; Roddick, F.; van de Merwe, J.P.; Magram, S.F.; Nghiem, L.D. Degradation of a broad spectrum of trace organic contaminants by an enzymatic membrane reactor: Complementary role of membrane retention and enzymatic degradation. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 99, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloret, L.; Eibes, G.; Feijoo, G.; Moreira, M.T.; Lema, J.M. Degradation of estrogens by laccase from myceliophthora thermophila in fed-batch and enzymatic membrane reactors. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 213–214, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.N.; Hai, F.I.; Price, W.E.; Leusch, F.D.; Roddick, F.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Magram, S.F.; Nghiem, L.D. The effects of mediator and granular activated carbon addition on degradation of trace organic contaminants by an enzymatic membrane reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 167, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.; Hai, F.I.; Price, W.E.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Yamamoto, K.; Nghiem, L.D. High retention membrane bioreactors: Challenges and opportunities. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 167, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijekoon, K.C.; Hai, F.I.; Kang, J.; Price, W.E.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Cath, T.Y.; Nghiem, L.D. A novel membrane distillation–thermophilic bioreactor system: Biological stability and trace organic compound removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 159, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.; Hai, F.I.; Kang, J.; Price, W.E.; Nghiem, L.D.; Elimelech, M. The role of forward osmosis and microfiltration in an integrated osmotic-microfiltration membrane bioreactor system. Chemosphere 2015, 136, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-H.; Dockko, S.; Fukushi, K.; Yamamoto, K. A novel application of a submerged nanofiltration membrane bioreactor (NF MBR) for wastewater treatment. Desalination 2002, 146, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, F.I.; Nghiem, L.D.; Modin, O. Biocatalytic membrane reactors for the removal of recalcitrant and emerging pollutants from wastewater. In Handbook of Membrane Reactors: Reactor Types and Industrial Applications; Basile, A., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2013; Volume 2, pp. 763–807. ISBN 9780857094155. [Google Scholar]
- Modin, O.; Hai, F.I.; Nghiem, L.D.; Basile, A.; Fukushi, K. Gas-diffusion, extractive, biocatalytic and electrochemical membrane biological reactors. In Membrane Biological Reactors: Theory, Modeling, Design, Management and Applications to Wastewater Reuse; Hai, F.I., Yamamoto, K., Lee, C., Eds.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2014; pp. 299–334. ISBN 9781780400655. [Google Scholar]
- Alkhudhiri, A.; Darwish, N.; Hilal, N. Membrane distillation: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2012, 287, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qtaishat, M.R.; Banat, F. Desalination by solar powered membrane distillation systems. Desalination 2013, 308, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijekoon, K.C.; Hai, F.I.; Kang, J.; Price, W.E.; Cath, T.Y.; Nghiem, L.D. Rejection and fate of trace organic compounds (TrOCs) during membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 453, 636–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, H.C.; Duke, M.; Gray, S.; Cooper, P.; Nghiem, L.D. Membrane scaling and prevention techniques during seawater desalination by air gap membrane distillation. Desalination 2016, 397, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, J.; Sun, H.; Cheng, F.; Liu, Y. Advanced treatment of biologically treated coking wastewater by membrane distillation coupled with pre-coagulation. Desalination 2016, 380, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phattaranawik, J.; Fane, A.G.; Pasquier, A.C.; Bing, W. A novel membrane bioreactor based on membrane distillation. Desalination 2008, 223, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.B.; Nguyen, L.N.; Hai, F.I.; Price, W.E.; Nghiem, L.D. Integration of an enzymatic bioreactor with membrane distillation for enhanced biodegradation of trace organic contaminants. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashe, B.; Nguyen, L.N.; Hai, F.I.; Lee, D.-J.; van de Merwe, J.P.; Leusch, F.D.; Price, W.E.; Nghiem, L.D. Impacts of redox-mediator type on trace organic contaminants degradation by laccase: Degradation efficiency, laccase stability and effluent toxicity. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 113, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nghiem, L.D.; Cath, T. A scaling mitigation approach during direct contact membrane distillation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 80, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, F.I.; Tessmer, K.; Nguyen, L.N.; Kang, J.; Price, W.E.; Nghiem, L.D. Removal of micropollutants by membrane bioreactor under temperature variation. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 383, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.N.; van de Merwe, J.P.; Hai, F.I.; Leusch, F.D.; Kang, J.; Price, W.E.; Roddick, F.; Magram, S.F.; Nghiem, L.D. Laccase-syringaldehyde-mediated degradation of trace organic contaminants in an enzymatic membrane reactor: Removal efficiency and effluent toxicity. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Merwe, J.P.; Leusch, F.D. A sensitive and high throughput bacterial luminescence assay for assessing aquatic toxicity—The blt-screen. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2015, 17, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Acunzo, F.; Galli, C.; Gentili, P.; Sergi, F. Mechanistic and steric issues in the oxidation of phenolic and non-phenolic compounds by laccase or laccase-mediator systems. The case of bifunctional substrates. New J. Chem. 2006, 30, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, T.; Shintate, H.; Kawai, S.; Okamura, H.; Nishida, T. Elimination of carbamazepine by repeated treatment with laccase in the presence of 1-hydroxybenzotriazole. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 1175–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloret, L.; Eibes, G.; Moreira, M.; Feijoo, G.; Lema, J. On the use of a high-redox potential laccase as an alternative for the transformation of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2013, 97, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.N.; Hai, F.I.; Kang, J.; Leusch, F.D.; Roddick, F.; Magram, S.F.; Price, W.E.; Nghiem, L.D. Enhancement of trace organic contaminant degradation by crude enzyme extract from trametes versicolor culture: Effect of mediator type and concentration. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 1855–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Acunzo, F.; Baiocco, P.; Galli, C. A study of the oxidation of ethers with the enzyme laccase under mediation by two N–OH–type compounds. New J. Chem. 2003, 27, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, H.; Hirai, H.; Kawai, S.; Nishida, T. Removal of estrogenic activity of iso-butylparaben and n-butylparaben by laccase in the presence of 1-hydroxybenzotriazole. Biodegradation 2009, 20, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khlifi-Slama, R.; Mechichi, T.; Sayadi, S.; Dhouib, A. Effect of natural mediators on the stability of trametes trogii laccase during the decolourization of textile wastewaters. J. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Nicell, J.A. Impact of reaction conditions on the laccase-catalyzed conversion of bisphenol A. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1431–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marco-Urrea, E.; Pérez-Trujillo, M.; Vicent, T.; Caminal, G. Ability of white-rot fungi to remove selected pharmaceuticals and identification of degradation products of ibuprofen by trametes versicolor. Chemosphere 2009, 74, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, H.C.; Hai, F.I.; Al-Jubainawi, A.; Ma, Z.; He, T.; Nghiem, L.D. Liquid desiccant lithium chloride regeneration by membrane distillation for air conditioning. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 177, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nghiem, L.D.; Hildinger, F.; Hai, F.I.; Cath, T. Treatment of saline aqueous solutions using direct contact membrane distillation. Desalination Water Treat. 2011, 32, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, H.C.; Cooper, P.; Nelemans, B.; Cath, T.Y.; Nghiem, L.D. Optimising thermal efficiency of direct contact membrane distillation by brine recycling for small-scale seawater desalination. Desalination 2015, 374, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| TrOCs | Chemical Formula | Molecular Weight | Log D at pH = 7 | Water Solubility at 25 °C | Vapor Pressure | pKH at pH 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g/mole | mg/L | (mmHg) | ||||
| Non-Phenolic Compounds | ||||||
| Primidone | C12H14N2O | 218.25 | 0.83 | 1500 | 6.08 × 10−11 | 13.93 |
| Ketoprofen | C16H14O3 | 254.28 | 0.19 | 554,000 | 3.32 × 10−8 | 13.70 |
| Naproxen | C14H14O3 | 230.26 | 0.73 | 435,000 | 3.01 × 10−7 | 12.68 |
| Gemfibrozil | C15H22O3 | 250.33 | 2.07 | 263,000 | 6.13 × 10 −7 | 12.11 |
| Metronidazole | C6H9N3O3 | 171.15 | −0.14 | 29,000 | 2.67 × 10−7 | 11.68 |
| Diclofenac | C14H11Cl2NO2 | 296.15 | 1.77 | 20,000 | 1.59 × 10−7 | 11.51 |
| Fenoprop | C9H7Cl3O3 | 269.51 | −0.13 | 230,000 | 2.13 × 10−6 | 11.48 |
| Ibuprofen | C13H18O2 | 206.28 | 0.94 | 928,000 | 1.39 × 10−4 | 10.39 |
| Ametryn | C9H17N5S | 27.33 | 2.97 | 140 | 1.72 × 10−6 | 9.35 |
| Clofibric acid | C10H11ClO3 | 214.65 | −1.06 | 100,000 | 1.03 × 10−4 | 9.54 |
| Carbamazepine | C15H12N2O | 236.27 | 1.89 | 220 | 5.78 × 10−7 | 9.09 |
| Octocrylene | C24H27N | 361.48 | 6.89 | 0.36 | 2.56 × 10−9 | 8.47 |
| Amitriptyline | C20H23N | 277.40 | 2.28 | 83 | 1.50 × 10−6 | 8.18 |
| Atrazine | C8H14ClN5 | 215.68 | 2.64 | 69 | 1.27 × 10−5 | 7.28 |
| Propoxur | C11H15NO3 | 209.24 | 1.54 | 800 | 1.53 × 10−3 | 6.28 |
| Benzophenone | C13H10O | 182.22 | 3.21 | 150 | 8.23 × 10−4 | 5.88 |
| DEET | C12H17NO | 191.3 | 2.42 | 1000 | 5.6 × 10−3 | 5.85 |
| Phenolic Compounds | ||||||
| Enterolactone | C18H18O4 | 288.38 | 2.53 | 200 | 3.29 × 10−13 | 15.20 |
| Estriol | C18H24O3 | 298.33 | 1.89 | 32 | 1.34 × 10−9 | 10.78 |
| 17α-Ethinylestradiol | C20H24O2 | 269.40 | 4.11 | 3.9 | 3.74 × 10−9 | 9.47 |
| Oxybenzone | C14H12O3 | 228.24 | 3.89 | 2700 | 5.26 × 10−6 | 9.23 |
| Estrone | C18H22O2 | 270.37 | 3.62 | 5.9 | 1.54 × 10−8 | 9.03 |
| 17β-Estradiol | C18H24O2 | 272.38 | 4.15 | 3 | 9.82 × 10−9 | 8.93 |
| 17β-Estradiol-17-acetate | C20H26O3 | 314.42 | 5.11 | 1.9 | 9.88 × 10−9 | 8.67 |
| Bisphenol A | C15H16O2 | 228.29 | 3.64 | 73 | 5.34 × 10−7 | 8.66 |
| Salicylic acid | C7H6O3 | 138.12 | −1.13 | 2240 | 8.2 × 10−5 | 8.18 |
| Pentachlorophenol | C6HCl5O | 266.34 | 2.85 | 4800 | 3.49 × 10−4 | 7.59 |
| Triclosan | C12H7Cl3O2 | 289.54 | 5.28 | 19 | 3.26 × 10−5 | 6.18 |
| 4-tert-Butylphenol | C10H14O | 150.22 | 3.40 | 1000 | 0.0361 | 5.15 |
| 4-tert-Octylphenol | C14H22O | 206.32 | 5.18 | 62 | 1.98 × 10−3 | 5.06 |
| Reaction Mixture | Toxicity of the Reactor Mixture (rTU) | Toxicity of the Permeate (rTU) |
|---|---|---|
| TrOCs + Laccase | <1–1.8 | <1 |
| TrOCs + Laccase + HBT (0.5 mM) | <1–1.7 | <1 |
| TrOCs + Laccase + VA (0.5 mM) | 3.3–3.9 | <1 |
| TrOCs + Laccase + SA (0.5 mM) | 109–116 | <1 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Asif, M.B.; Hai, F.I.; Kang, J.; Van de Merwe, J.P.; Leusch, F.D.L.; Yamamoto, K.; Price, W.E.; Nghiem, L.D. Degradation of Trace Organic Contaminants by a Membrane Distillation—Enzymatic Bioreactor. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 879. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7090879
Asif MB, Hai FI, Kang J, Van de Merwe JP, Leusch FDL, Yamamoto K, Price WE, Nghiem LD. Degradation of Trace Organic Contaminants by a Membrane Distillation—Enzymatic Bioreactor. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(9):879. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7090879
Chicago/Turabian StyleAsif, Muhammad B., Faisal I. Hai, Jinguo Kang, Jason P. Van de Merwe, Frederic D. L. Leusch, Kazuo Yamamoto, William E. Price, and Long D. Nghiem. 2017. "Degradation of Trace Organic Contaminants by a Membrane Distillation—Enzymatic Bioreactor" Applied Sciences 7, no. 9: 879. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7090879
APA StyleAsif, M. B., Hai, F. I., Kang, J., Van de Merwe, J. P., Leusch, F. D. L., Yamamoto, K., Price, W. E., & Nghiem, L. D. (2017). Degradation of Trace Organic Contaminants by a Membrane Distillation—Enzymatic Bioreactor. Applied Sciences, 7(9), 879. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7090879







