Observer-Based Remote Conductivity Variable-Parameter Sliding Mode Control for Water–Fertilizer Integration Machines Using Recursive Least Squares Adaptive Estimation
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Remote Conductivity Control in Water–Fertilizer Integration
1.2. Challenges in PMSM Servo Systems
1.3. Advancements in Sliding Mode Control
1.4. Research Gap and Proposed Solution
1.5. Objectives
- Develop a VSMC strategy to enhance the robustness of PMSM servo systems used in water–fertilizer integration equipment.
- Design a recursive least squares (RLS)-based observer to estimate real-time system parameters, including rotational inertia and load torque.
- Adaptively adjust the sliding surface parameters in the VSMC using the observer’s output to maintain control accuracy under varying operating conditions.
- Compare two parameter derivation strategies—analytical modeling and data-driven fitting—for determining sliding mode parameters.
- Validate the proposed method through simulations and field experiments by assessing its performance in maintaining target conductivity and improving fertilizer distribution uniformity.
2. Materials and Methods
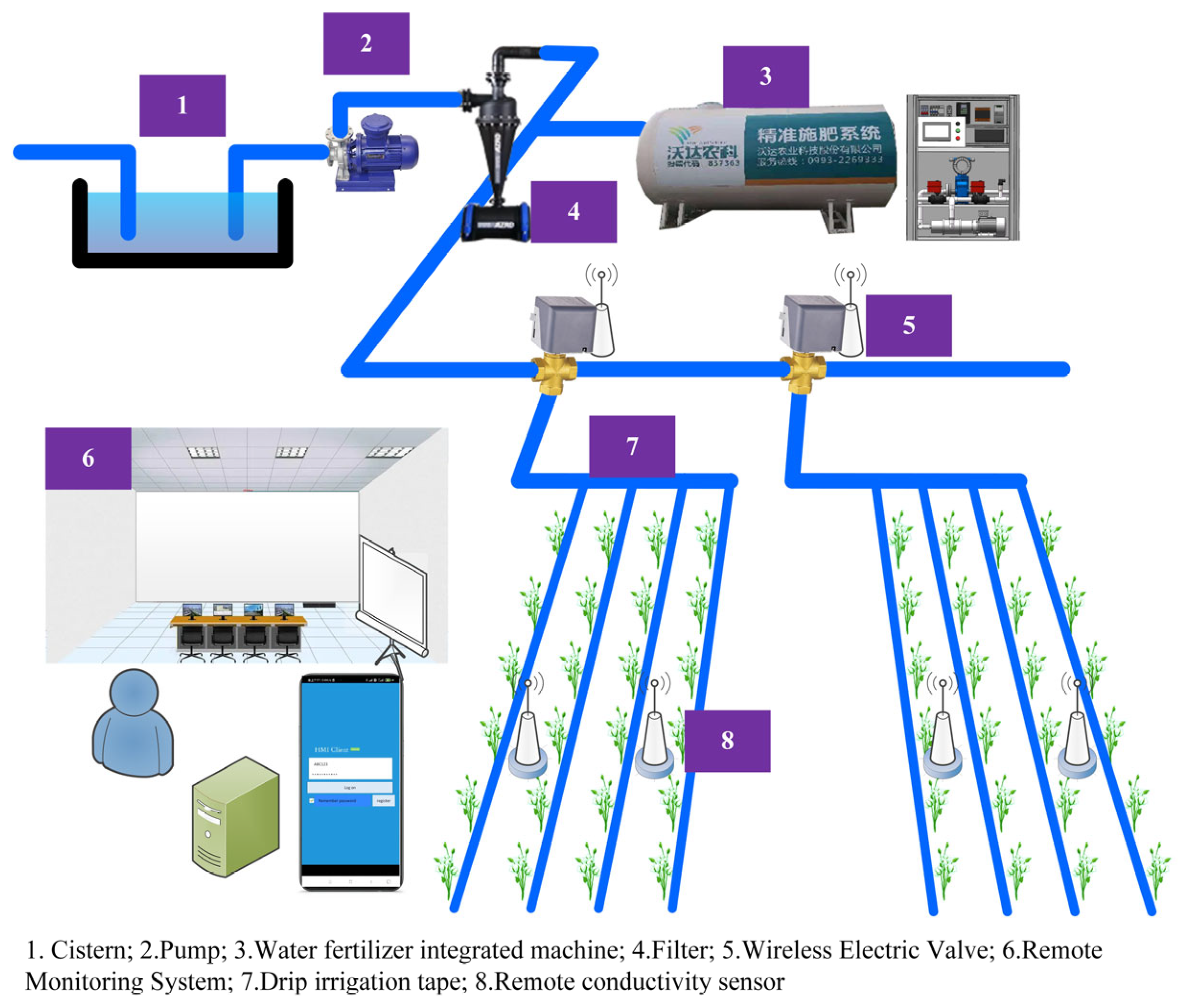
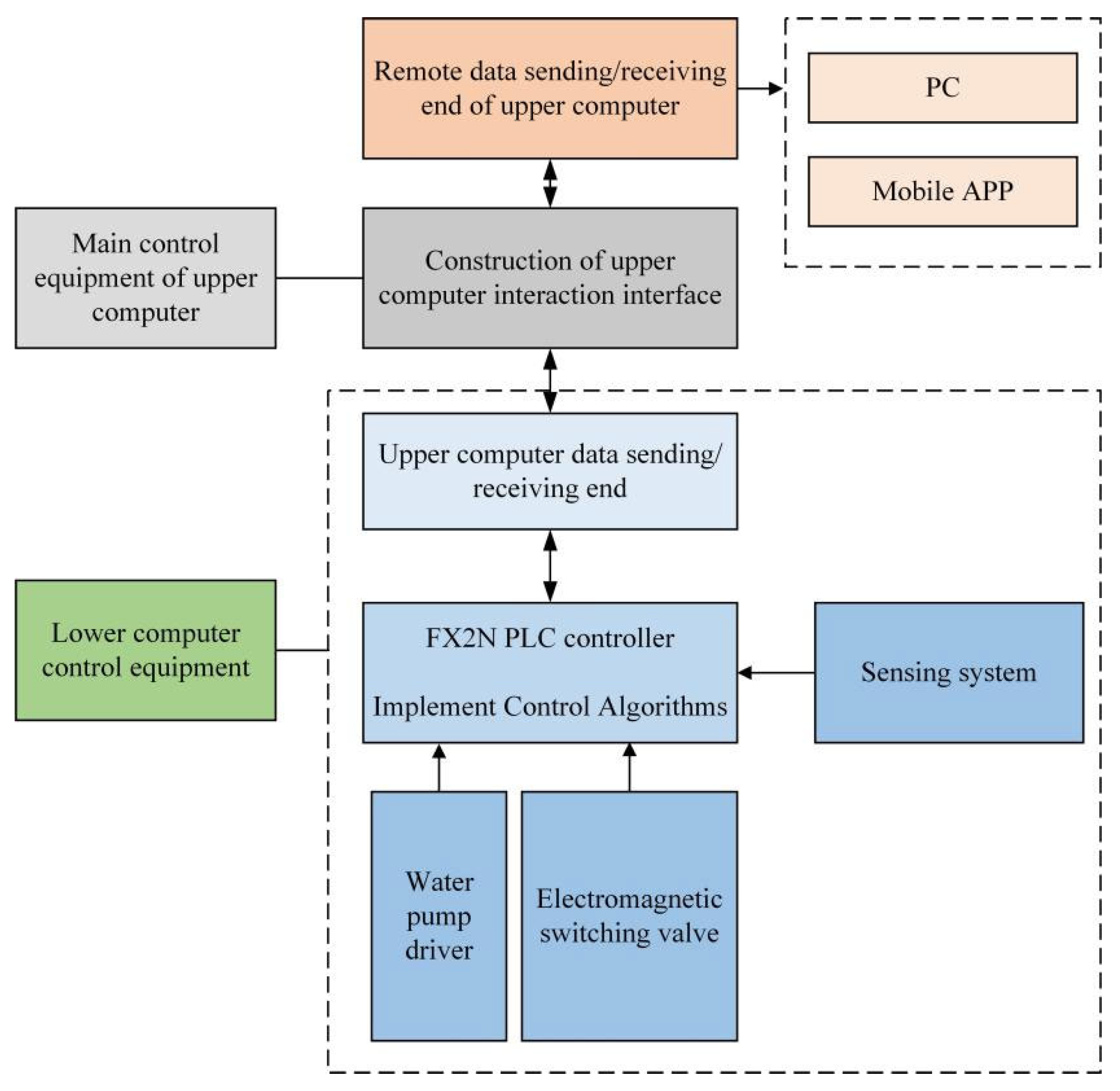
2.1. Remote Conductivity Control System for Water and Fertilizer Integration Machine
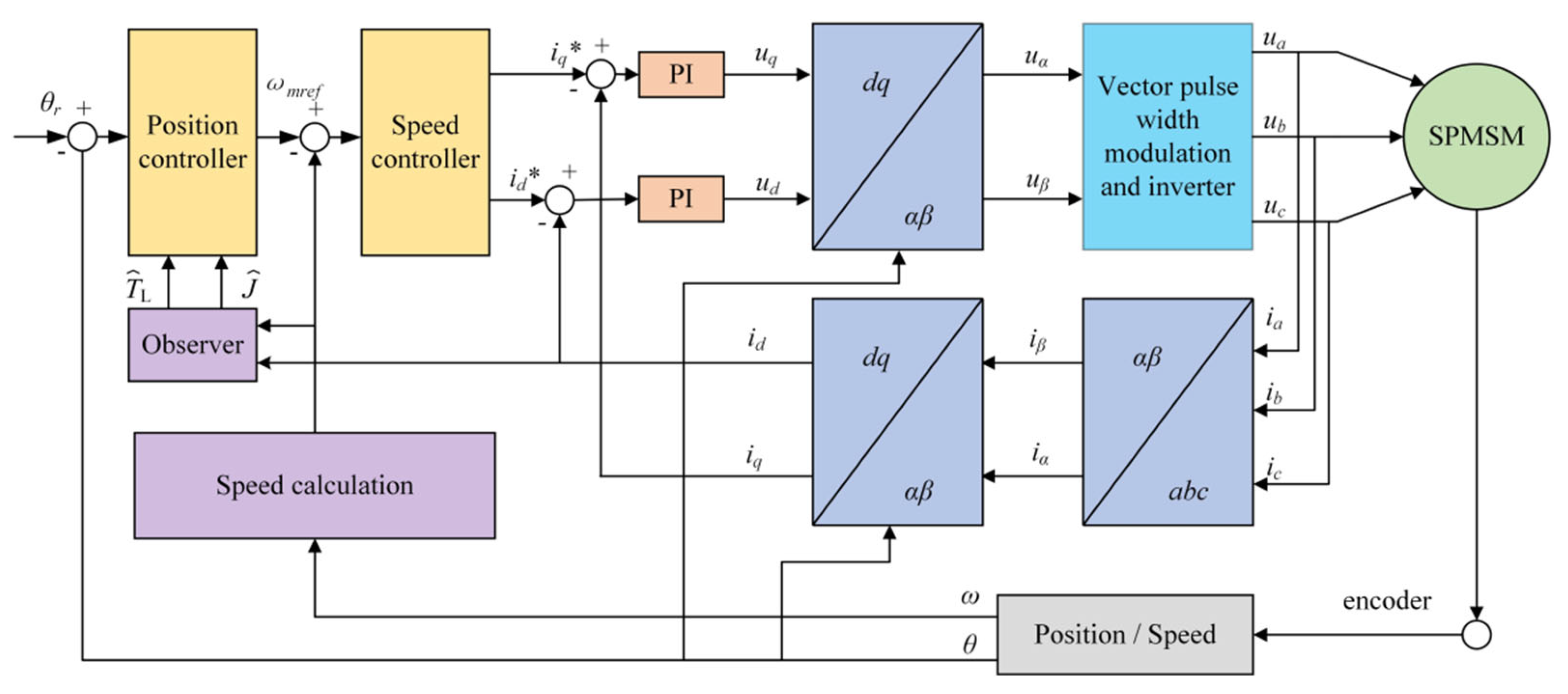
2.2. Design of the Variable-Parameter Sliding Mode Position Controller
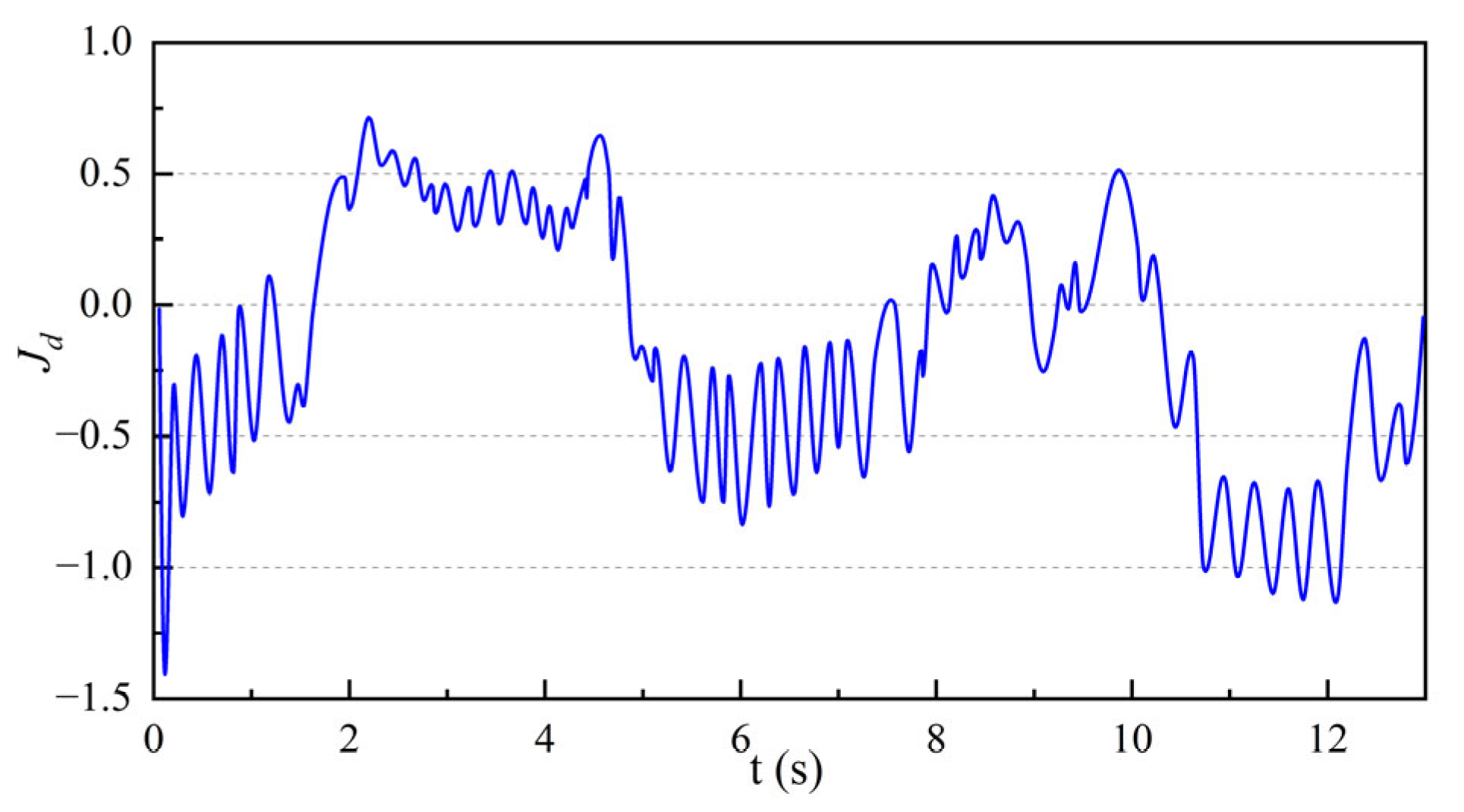
2.3. Design of the Recursive Least Squares Observer
2.4. Software and Versions
3. Results and Discussion
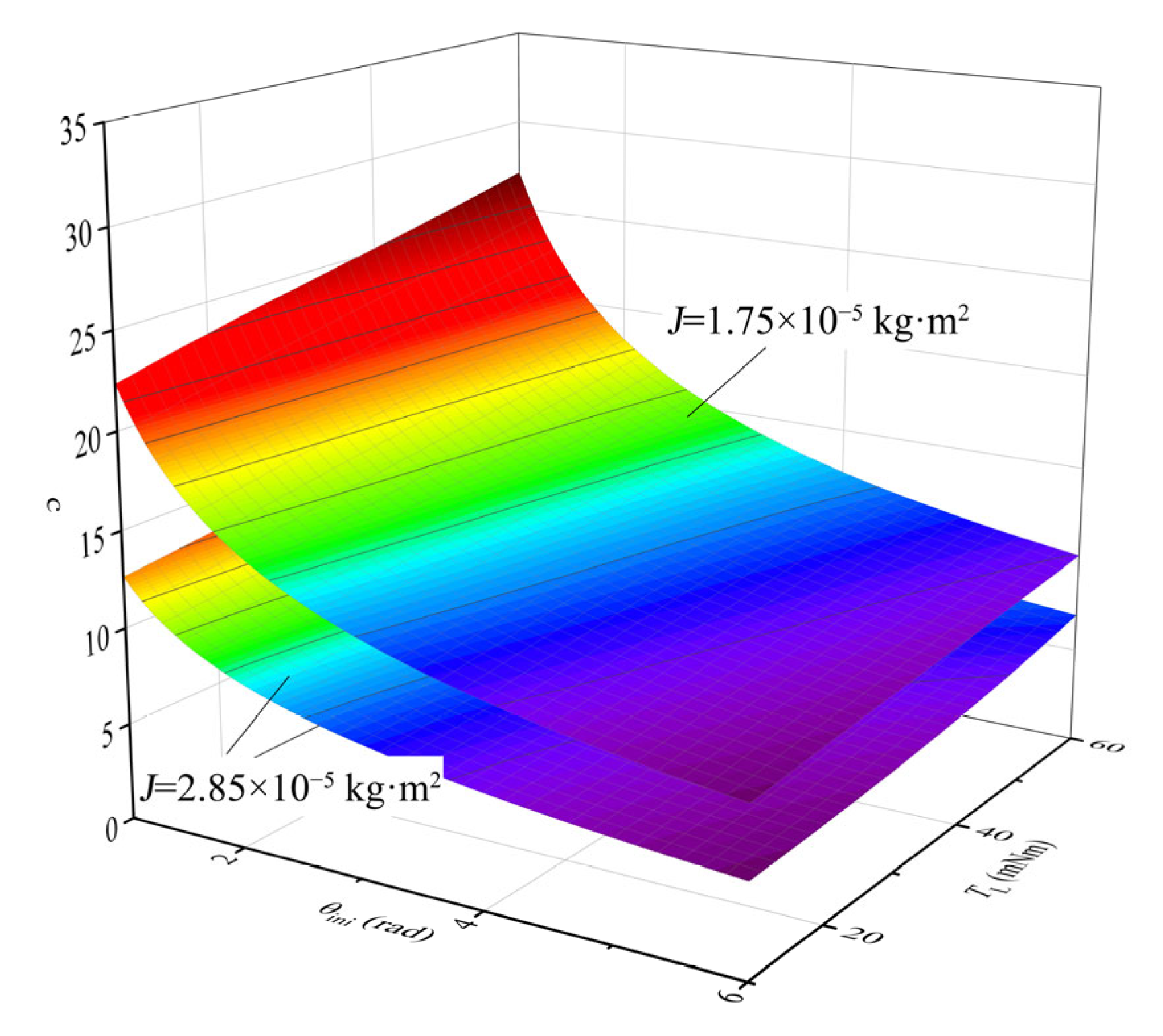
3.1. Simulation Analysis
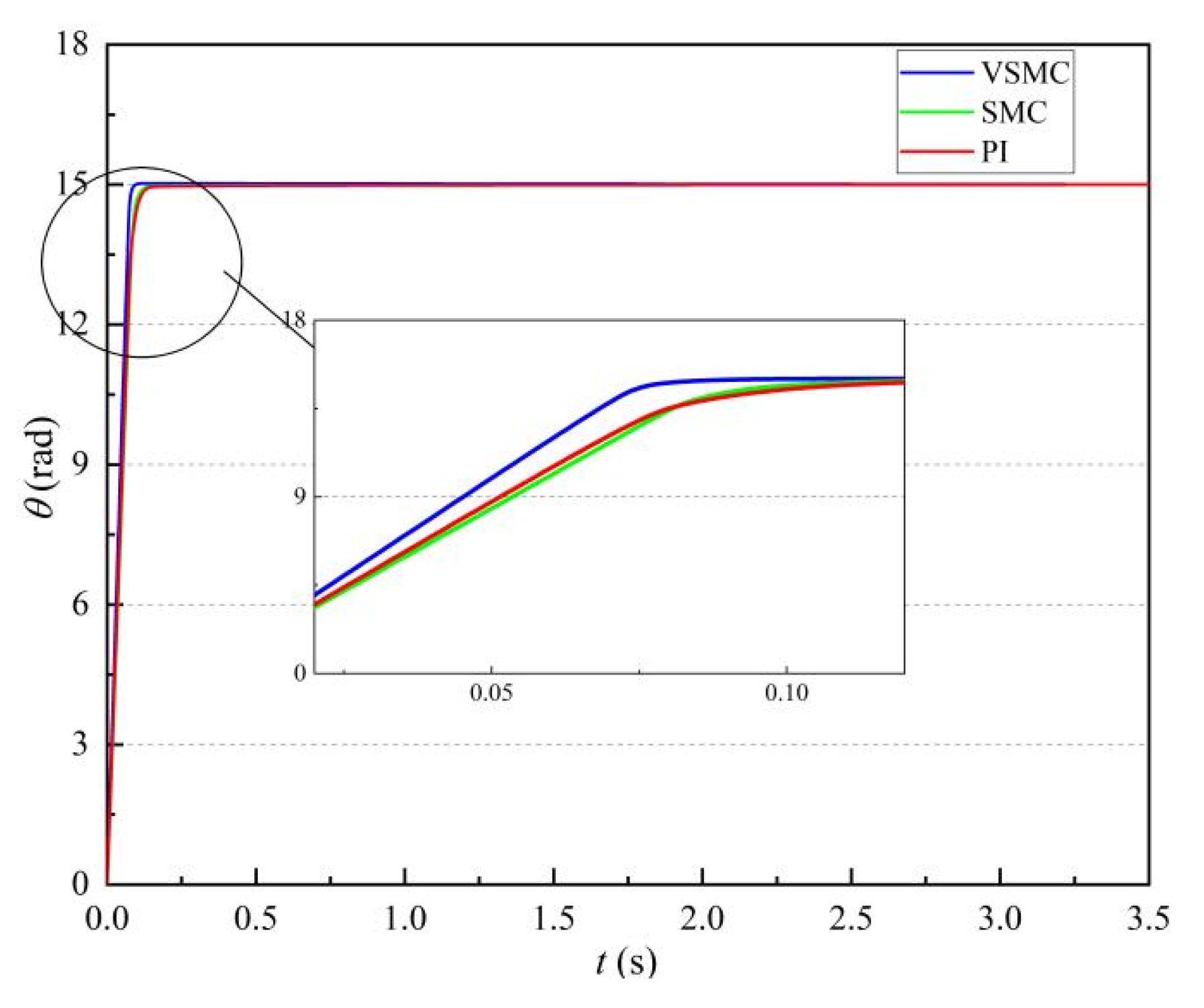
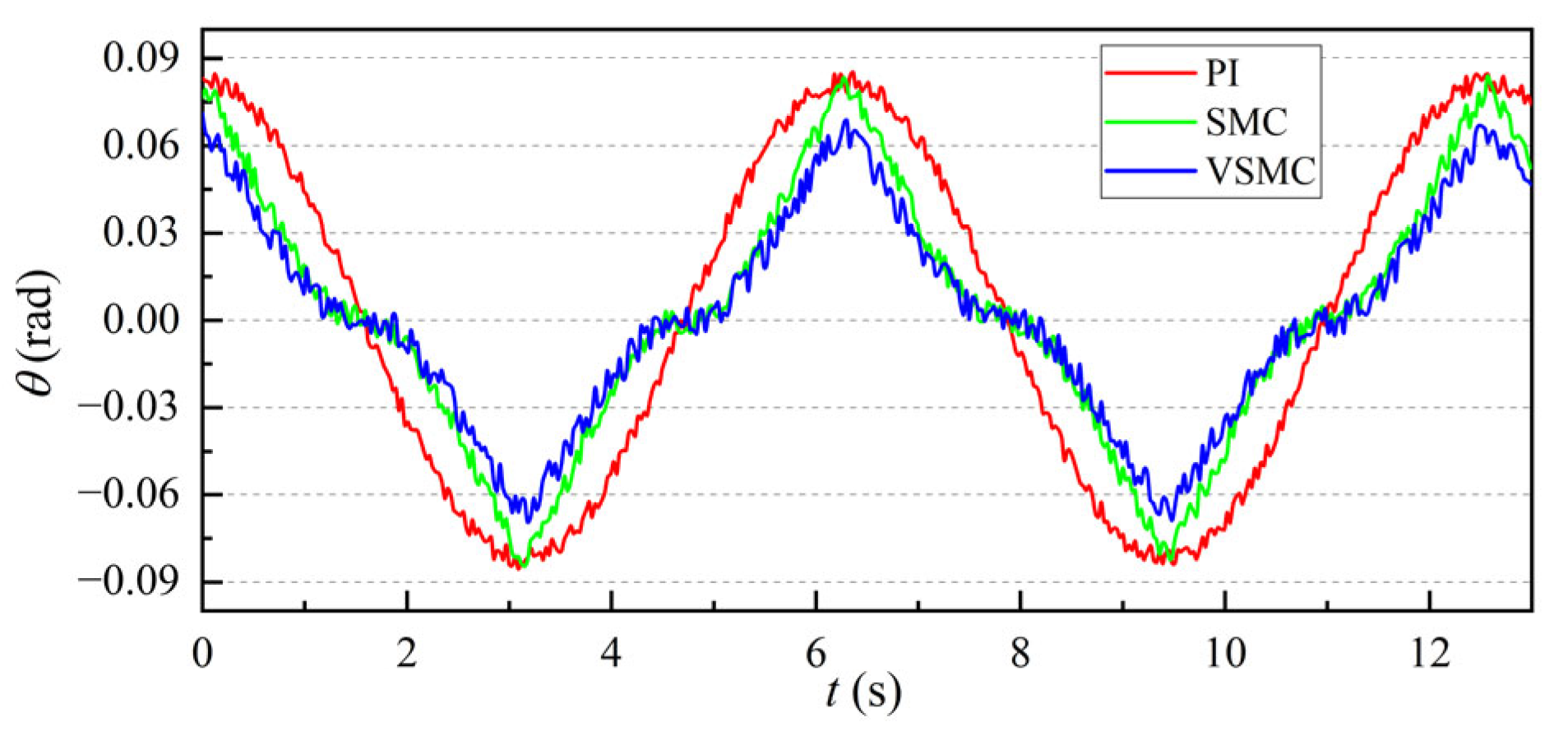
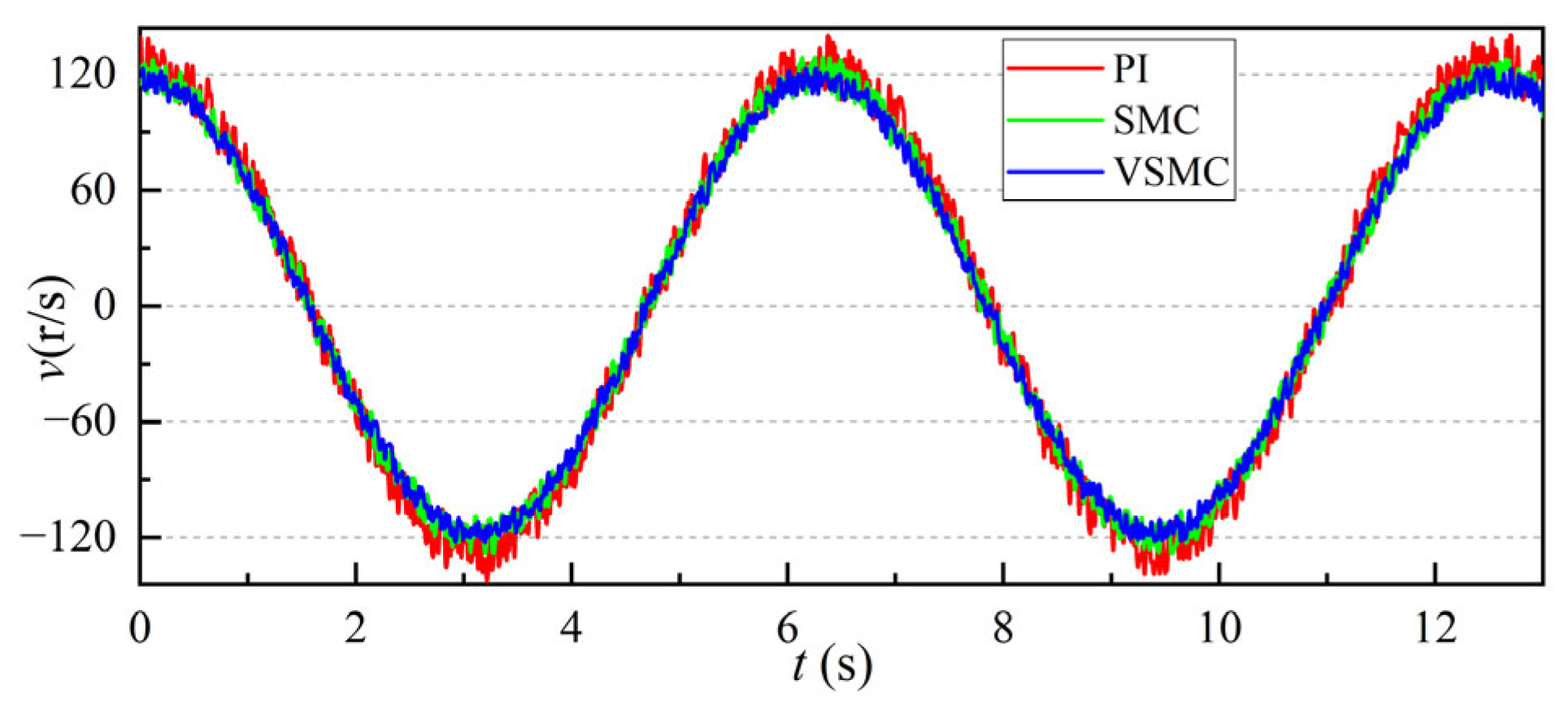
3.1.1. Response Speed Simulation Analysis
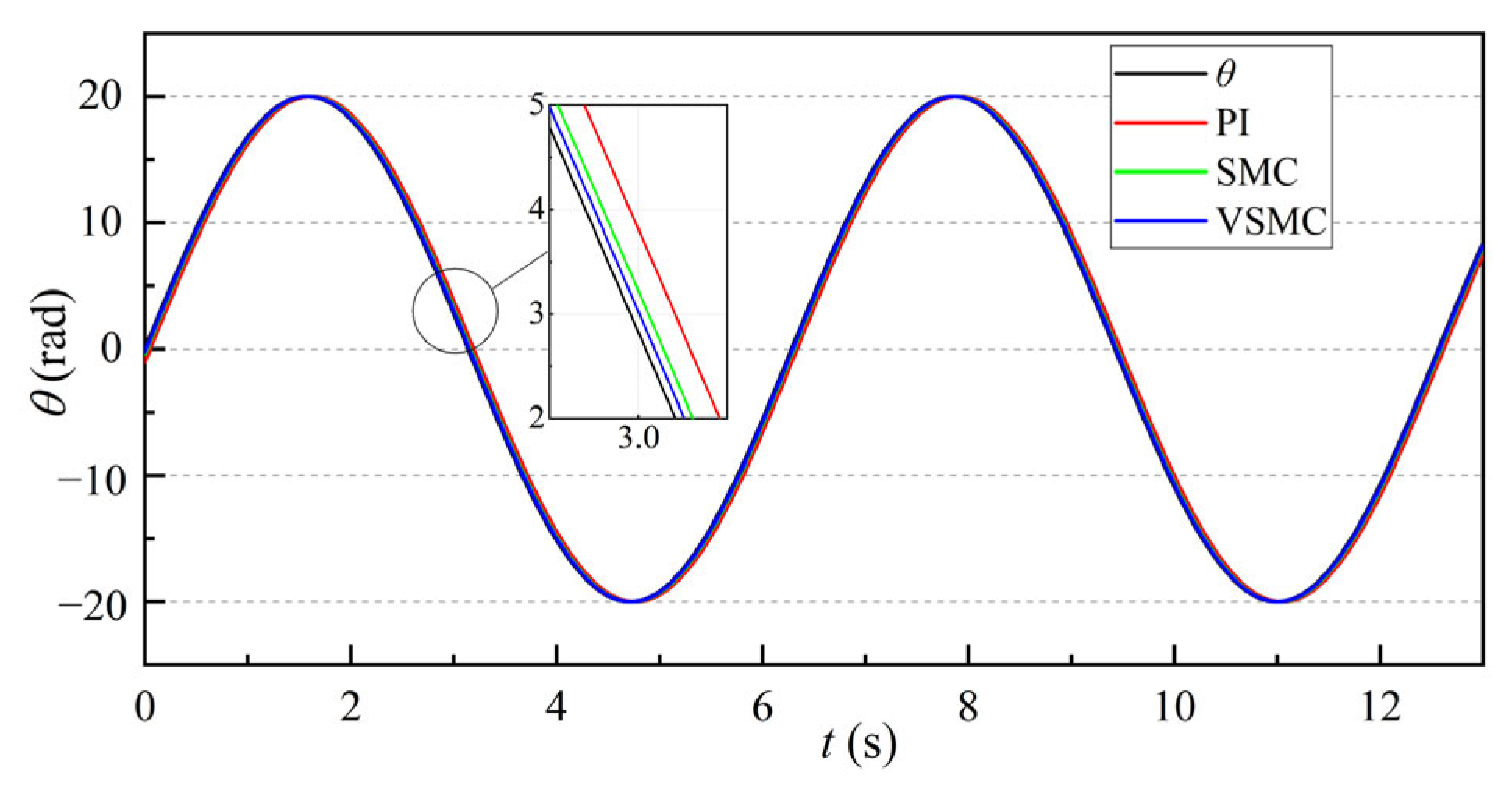
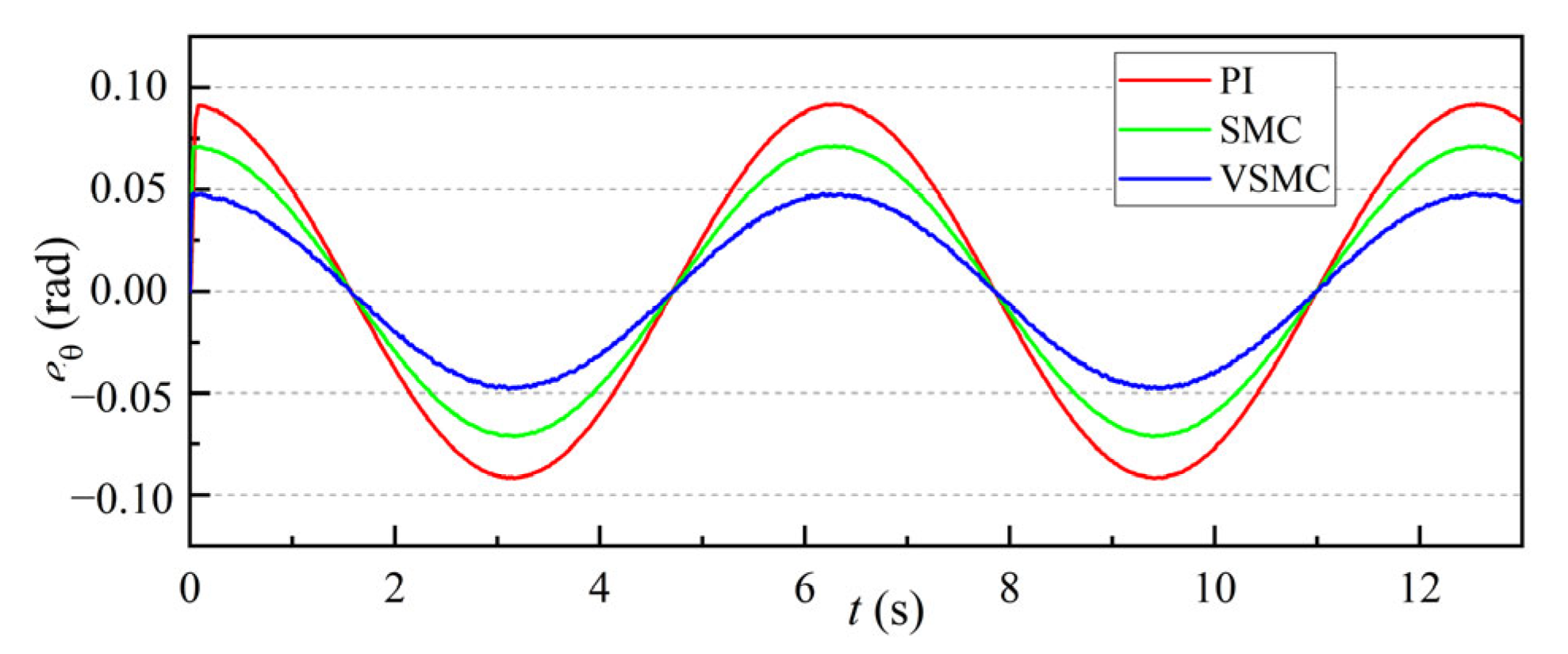
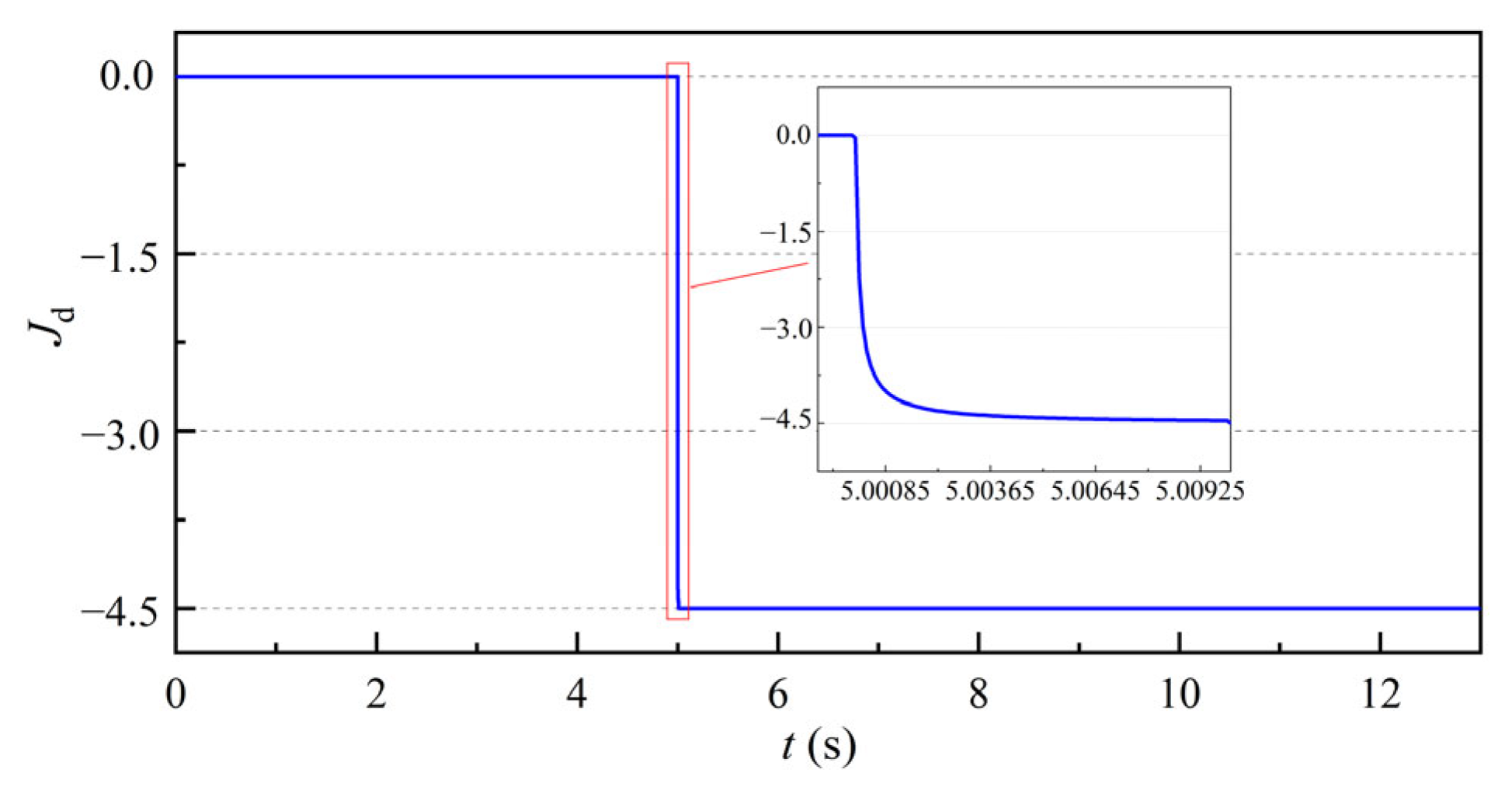
3.1.2. Motor Rotation Response Simulation Analysis
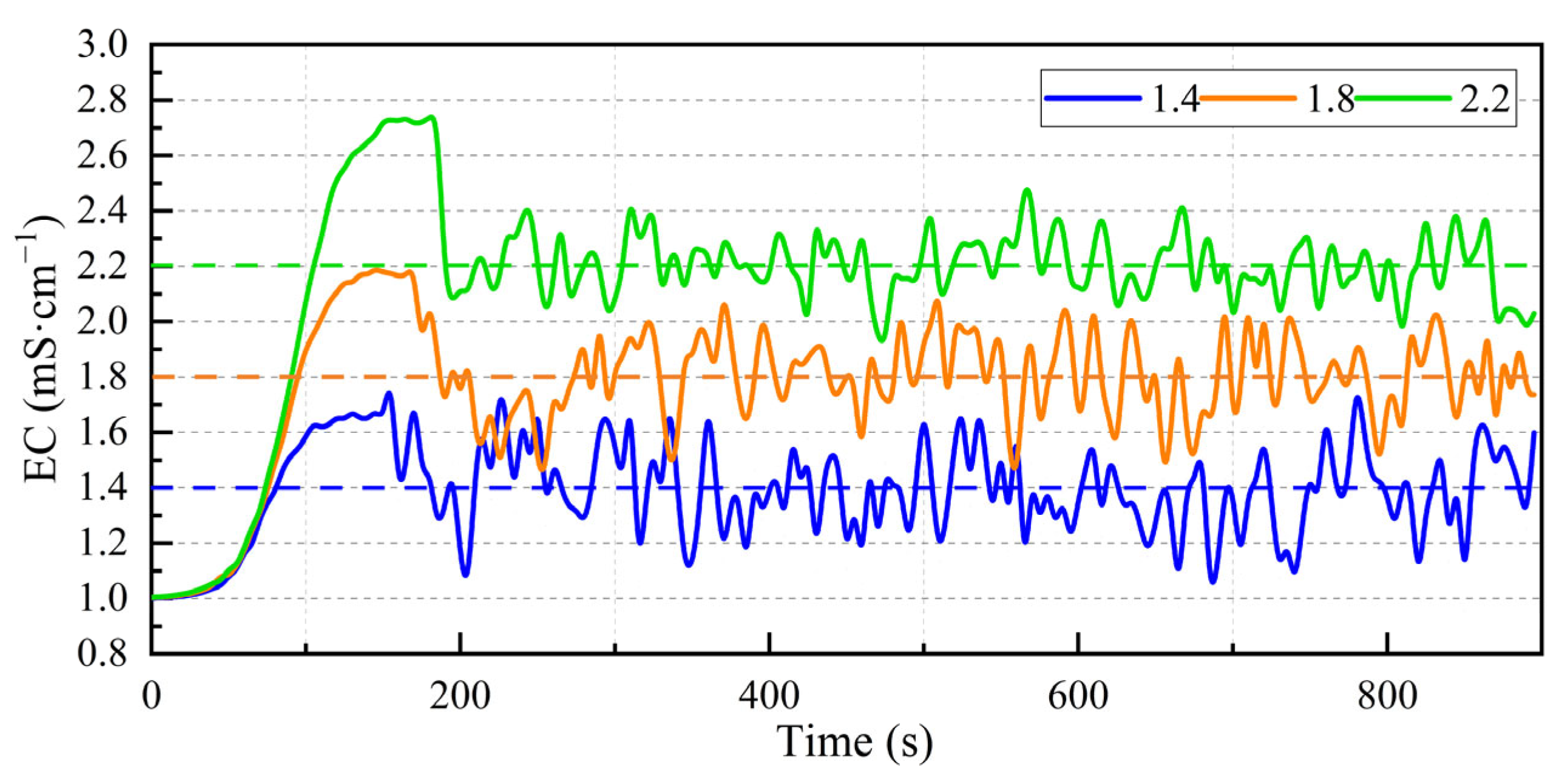
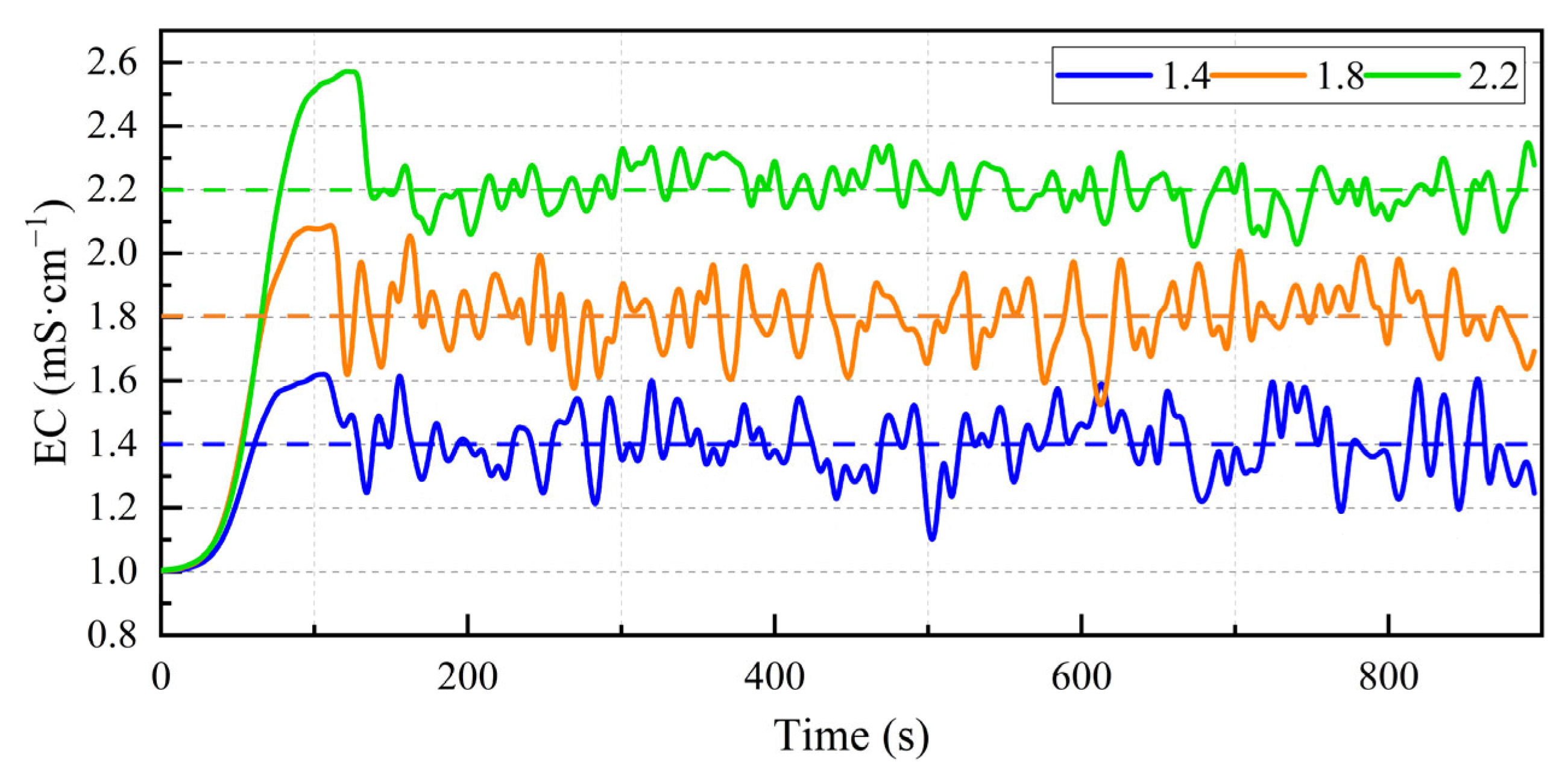
3.2. Experimental Validation
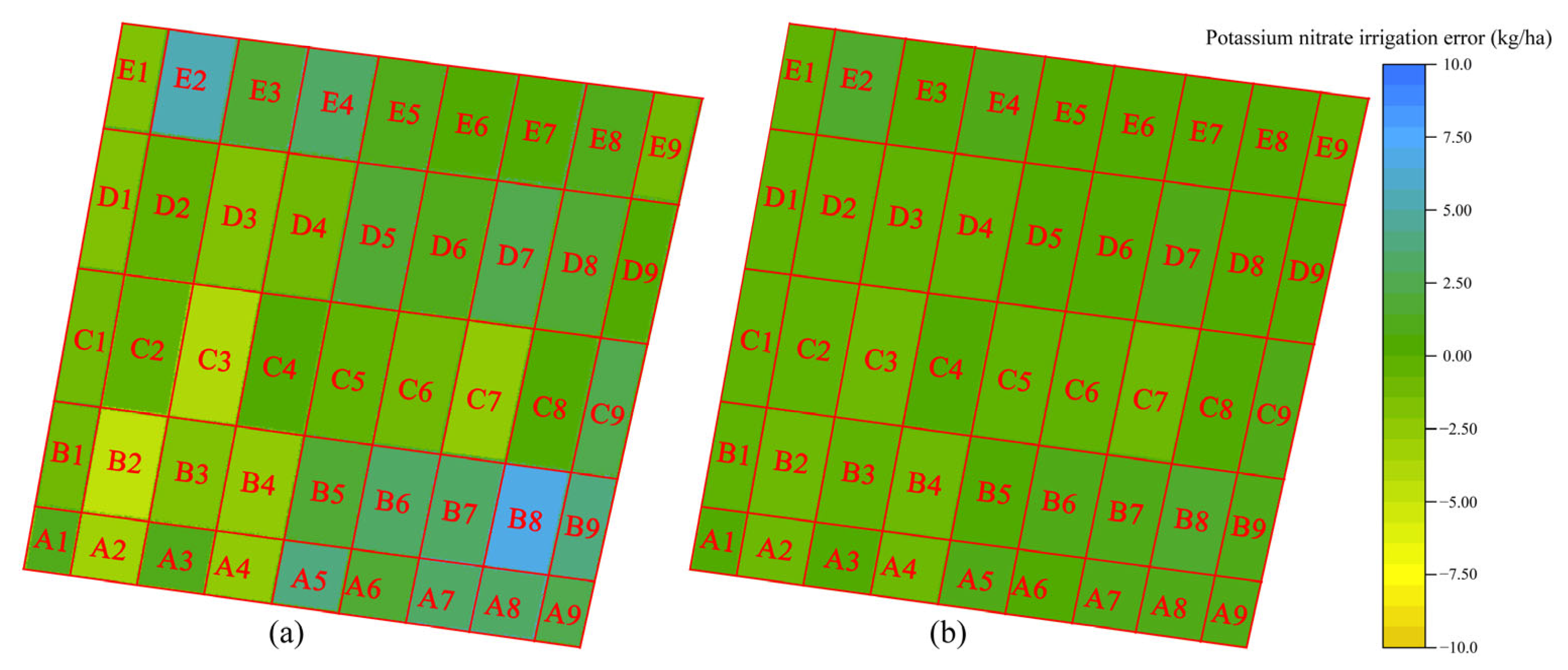
3.3. Field Performance and Adaptive Control Challenges
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liao, Q.; Nie, J.; Yin, H.; Luo, Y.; Shu, C.; Cheng, Q.; Fu, H.; Li, B.; Li, L.; Sun, Y.; et al. Can the Integration of Water and Fertilizer Promote the Sustainable Development of Rice Production in China? Agriculture 2024, 14, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, A.; Carriquiry, M.; Rosas, F. An integrated assessment model of the impacts of agricultural intensification: Trade-offs between economic benefits and water quality under uncertainty. Aust. J. Agric. Resour. Econ. 2024, 68, 315–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, T.; Zhang, J.; Du, L.; Ding, L.; Zhang, R.; Liu, X.; Ren, F.; Yin, M.; Yang, R.; Tian, P.; et al. Comprehensive evaluation of the water-fertilizer coupling effects on pumpkin under different irrigation volumes. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1386109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaser, D.R.; Barrowes, B.E.; Shubitidze, F.; Slater, L.D. Laboratory investigation of high-frequency electromagnetic induction measurements for macro-scale relaxation signatures. Geophys. J. Int. 2023, 235, 1274–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Li, W.; Gao, H.; Huang, C.; Xu, S.; Liu, W. Organic Water-Soluble Fertilizers Enhance Pesticide Degradation: Towards Reduced Residues. J. Agric. Sci. 2024, 30, 179–192. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Z.J.; Sun, Y.S.; Liu, J.X. An Integrated Parameter Identification Method of Asynchronous Motor Combined with Adaptive Load Characteristics. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2023, 18, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, H.; Cao, Z.; Chen, P.; Luo, Y.; Luo, X. Fractional-order electromagnetic modeling and identification for PMSM servo system. ISA Trans. 2024, 147, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Zhen, S.; Liu, X.; Zhong, H.; Chen, Y.H. Model-based robust servo control for permanent magnet synchronous motor with inequality constraint. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2024, 35, 017002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kökçam, E.; Tan, N.S. Comparison of Adaptation Mechanisms on MRAC. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 31862–31874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, X.; Ma, X. Application of Hyperspectral Technology Combined with Genetic Algorithm to Optimize Convolution Long- and Short-Memory Hybrid Neural Network Model in Soil Moisture and Organic Matter. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Zhu, S.; Cui, Y.; Liu, C.; Lin, X. Adaptive PI Controller for Speed Control of Electric Drives Based on Model Reference Adaptive Identification. Electronics 2024, 13, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, J.C.; González, J.; Navarro, A.; Guzmán, J.L. New Tuning Rules of PI+CI Controllers for First-Order Systems. Actuators 2024, 13, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhou, Z.; Li, J.; Song, L. Dynamic Yarn-Tension Detection Using Machine Vision Combined with a Tension Observer. Sensors 2023, 23, 3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraveas, C.; Karavas, C.-S.; Loukatos, D.; Bartzanas, T.; Arvanitis, K.G.; Symeonaki, E. Agricultural Greenhouses: Resource Management Technologies and Perspectives for Zero Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, Y. Senseless Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Based on New Fuzzy Adaptive Sliding Mode Observer. Electronics 2023, 12, 3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Yang, C.; Gui, J.; Fu, R. Sliding Mode Active Disturbance Rejection Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on Improved Genetic Algorithm. Actuators 2023, 12, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.-S.; Kim, J.-Y.; Song, K.-Y.; Cho, K.-Y.; Kim, H.-W. Slip prevention algorithm for dual-rotor PM synchronous motor. J. Power Electron. 2024, 24, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, K.; Cao, Z.; Rsetam, K.; Man, Z. Practical Adaptive Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Control for Servo Motors. Actuators 2023, 12, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadiji, A.E.; Yadav, A.N.; Santoyo, G.; Babalola, O.O. Understanding the plant-microbe interactions in environments exposed to abiotic stresses: An overview. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 271, 127368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, H.V.A.; Nam, S.; Kim, S.; Kim, Y.; Chung, W.K. Backstepping-Sliding-Mode-Based Neural Network Control for Electro-Hydraulic Actuator Subject to Completely Unknown System Dynamics. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2024, 21, 6202–6216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhou, S.-Z.; Li, X.; Chen, H.; Hu, S. Fast Transient Modulation of a Dual-Bridge Series Resonant Converter. In Proceedings of the IECON 2021—47th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Toronto, ON, Canada, 13–16 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.L.; Zhang, X.H.; Liu, S.Y. Design method of improved non-singulars terminal sliding mode control systems. In Proceedings of the 2007 Chinese Control and Decision Conference; Northeastern University Press: Shenyang, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Nippatla, V.R.; Mandava, S. Comparative vector control study on speed of PMSM drive using sensorless and machine learning techniques: Review. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2024, 46, 4381–4395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.; Mesny, L.; Chesné, S. Sliding Mode Control for Hybrid Mass Dampers: Experimental analysis on robustness. J. Sound Vib. 2024, 575, 118241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Mao, J.; Zhao, F.; Wang, W.; Jia, R. Speed-current composite loop SPMSM control based on ADR-SMC. IEICE Electron. Express 2024, 21, 20240088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, G.; Guo, Y.; Wang, P.; Cheng, G.; Zhao, D. Research on Control Method of the Power System of Stepping-Type Anchoring Equipment. Sensors 2021, 21, 7123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.H.; Zhang, J.X.; Zhang, T. Sliding mode sensorless control of wind turbine pitch motor with ESO feedforward compensation in the offshore wind power system. Sci. Technol. Energy Transit. 2024, 79, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, L.; Yu, S. Application of Disturbance Observer-Based Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Control for Asynchronous Motors in Remote Electrical Conductivity Control of Fertigation Systems. Agriculture 2024, 14, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.M.; Tippur, H.V.; Rousseau, C.E. Measurement of contact stresses using real-time shearing interferometry. Opt. Eng. 1999, 38, 1932–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonker, J.; Doorenbos, C.S.E.; Kremer, D.; Gore, E.J.; Niesters, H.G.M.; van Leer-Buter, C.; Bourgeois, P.; Connelly, M.A.; Dullaart, R.P.F.; Berger, S.P.; et al. High-Density Lipoprotein Particles and Torque Teno Virus in Stable Outpatient Kidney Transplant Recipients. Viruses 2024, 16, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Zhang, L.; Hu, X.; Zhao, J.; Meng, Z.; Zheng, Y. Research and Design of Hybrid Optimized Backpropagation (BP) Neural Network PID Algorithm for Integrated Water and Fertilizer Precision Fertilization Control System for Field Crops. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; Chen, Z.; Wang, J. Research on the dq-Axis Current Reaction Time of an Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor for Electric Vehicle. World Electr. Veh. J. 2023, 14, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| TL/Nm | c | |
|---|---|---|
| J = 1.75 × 10−5 kg·m2 | J = 2.85 × 10−5 kg·m2 | |
| 0 | 242 | 198 |
| 0.01 | 255 | 206 |
| 0.02 | 268 | 212 |
| 0.03 | 282 | 222 |
| 0.04 | 286 | 232 |
| 0.05 | 305 | 240 |
| 0.06 | 318 | 249 |
| Control Algorithm | Set EC (mS/cm) | Steady-State EC (mS/cm) | Steady-State Time (s) | Overshoot (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PI | 1.4 | 1.25~1.56 | 160 | 19.3 |
| 1.8 | 1.65~1.93 | 175 | 22.2 | |
| 2.2 | 2.10~2.30 | 190 | 25.1 | |
| SMC | 1.4 | 1.30~1.50 | 130 | 15.6 |
| 1.8 | 1.67~1.90 | 120 | 16.7 | |
| 2.2 | 2.12~2.28 | 130 | 17.2 | |
| VSMC | 1.4 | 1.18~1.60 | 95 | 14.3 |
| 1.8 | 1.60~1.98 | 100 | 15.5 | |
| 2.2 | 2.06~2.35 | 120 | 16.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, P.; Li, Z.; Hu, X.; Zhang, L. Observer-Based Remote Conductivity Variable-Parameter Sliding Mode Control for Water–Fertilizer Integration Machines Using Recursive Least Squares Adaptive Estimation. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4993. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094993
Zhang P, Li Z, Hu X, Zhang L. Observer-Based Remote Conductivity Variable-Parameter Sliding Mode Control for Water–Fertilizer Integration Machines Using Recursive Least Squares Adaptive Estimation. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(9):4993. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094993
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Peng, Zhigang Li, Xue Hu, and Lixin Zhang. 2025. "Observer-Based Remote Conductivity Variable-Parameter Sliding Mode Control for Water–Fertilizer Integration Machines Using Recursive Least Squares Adaptive Estimation" Applied Sciences 15, no. 9: 4993. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094993
APA StyleZhang, P., Li, Z., Hu, X., & Zhang, L. (2025). Observer-Based Remote Conductivity Variable-Parameter Sliding Mode Control for Water–Fertilizer Integration Machines Using Recursive Least Squares Adaptive Estimation. Applied Sciences, 15(9), 4993. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094993





