Safety Assessment of Microwave Breast Imaging: Heating Analysis on Digital Breast Phantoms
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Current Breast Cancer Screening Technologies
1.2. Safety Assessment of Microwave Technology
2. Materials and Methods
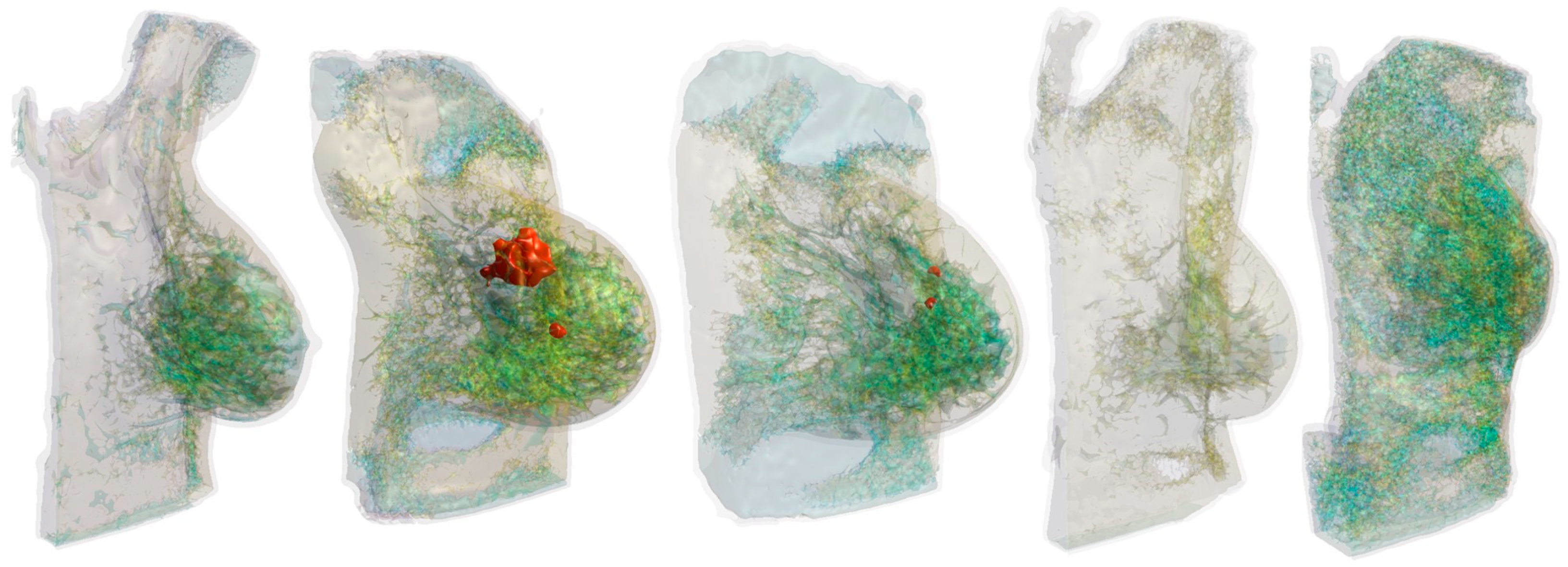
2.1. Anatomical Breast Models
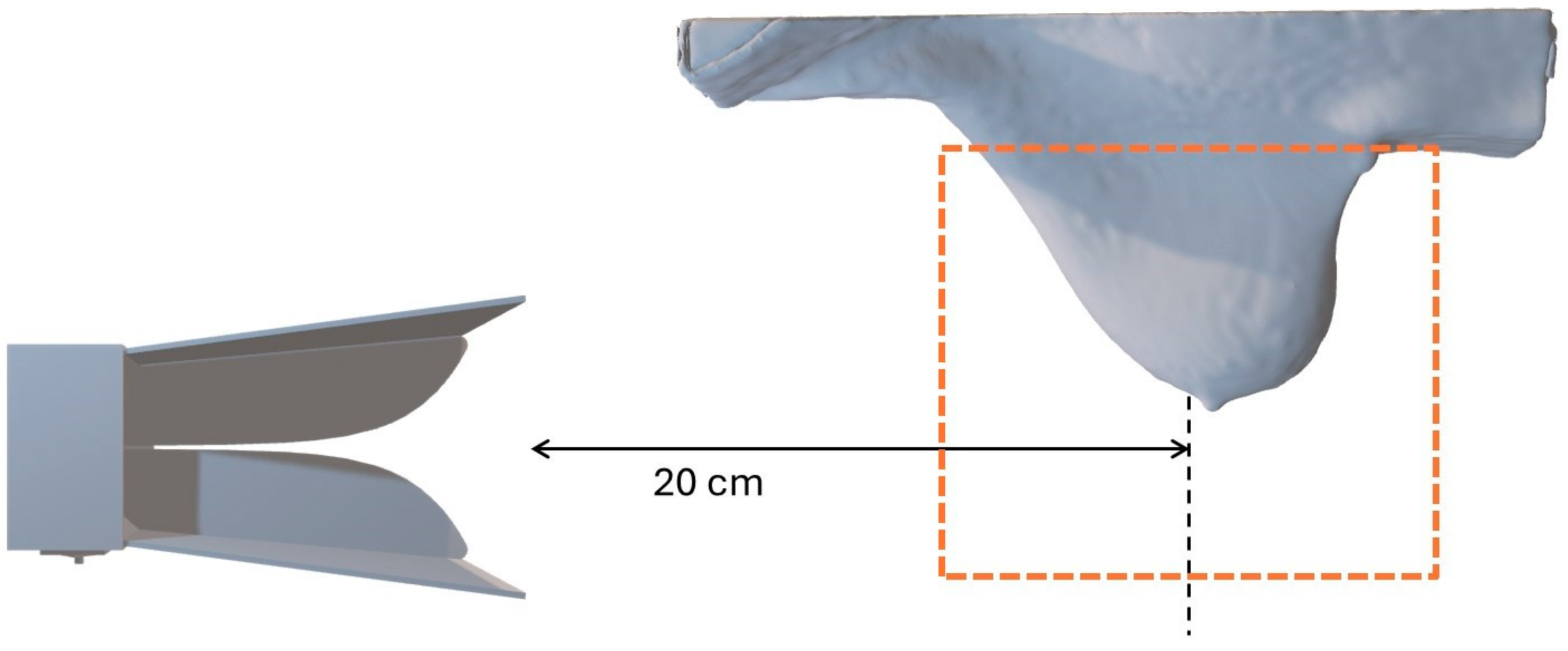
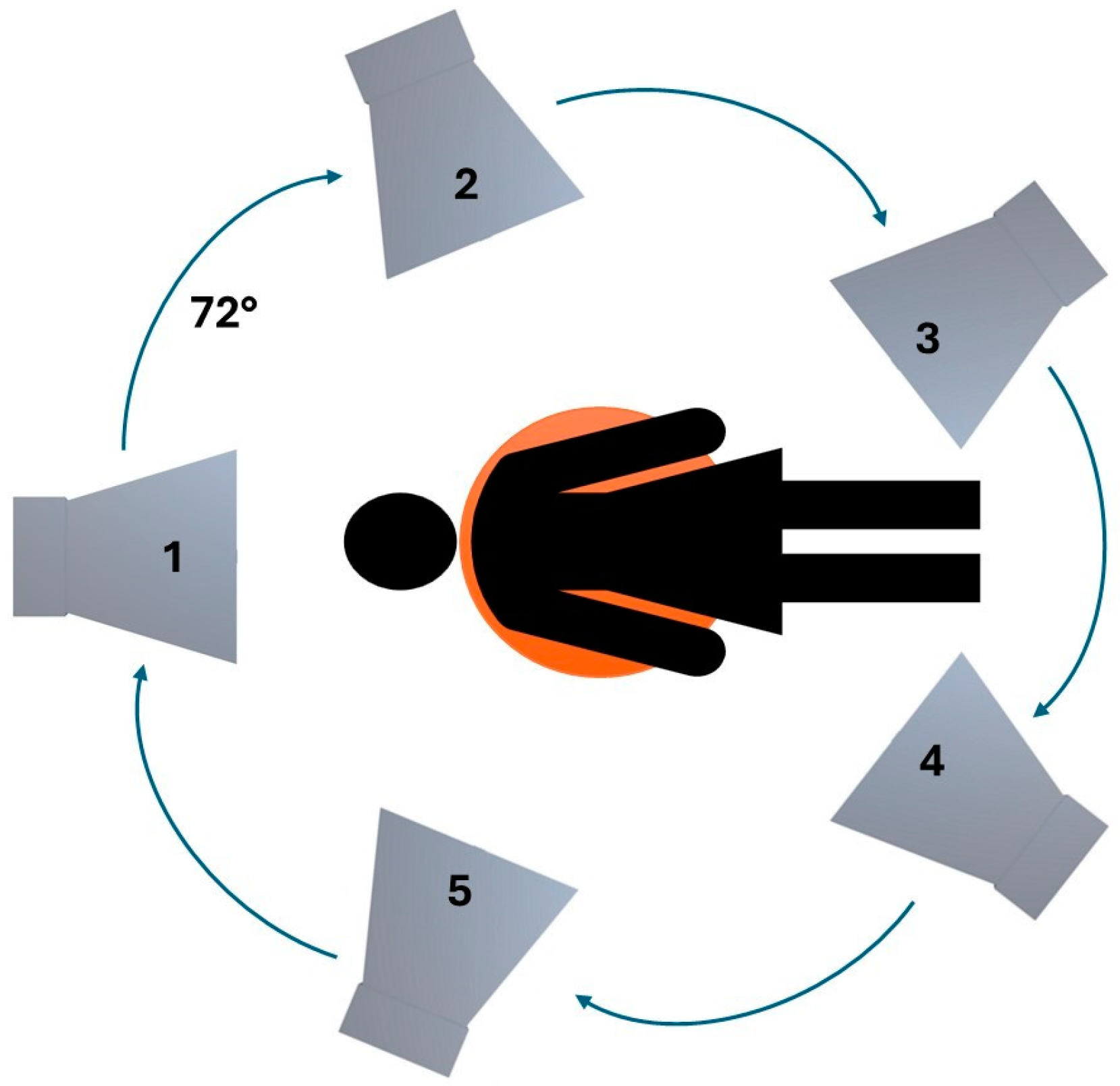
2.2. Hardware Configuration
2.3. Mathematical Modeling
3. Results
4. Discussion
Comparison with Existing Studies About the Safety of MI
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arnold, M.; Morgan, E.; Rumgay, H.; Mafra, A.; Singh, D.; Laversanne, M.; Vignat, J.; Gralow, J.R.; Cardoso, F.; Siesling, S.; et al. Current and future burden of breast cancer: Global statistics for 2020 and 2040. Breast 2022, 66, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliafico, A.S.; Houssami, N. Towards consensus on managing high mammographic density in population breast screening? Breast 2023, 69, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldhaeebi, M.A.; Alzoubi, K.; Almoneef, T.S.; Bamatraf, S.M.; Attia, H.; Ramahi, O.M. Review of Microwaves techniques for breast cancer detection. Sensors 2020, 20, 2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Fu, M. Dielectric properties for non-invasive detection of normal, benign, and malignant breast tissues using microwave theories. Thorac. Cancer 2018, 9, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vispa, A.; Sani, L.; Paoli, M.; Bigotti, A.; Raspa, G.; Ghavami, N.; Caschera, S.; Ghavami, M.; Duranti, M.; Tiberi, G. UWB device for breast microwave imaging: Phantom and clinical validations. Measurement 2019, 146, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solis-Nepote, M.; Reimer, T.; Pistorius, S. An air-operated bistatic system for breast microwave radar imaging: Pre-clinical validation. In Proceedings of the 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1859–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaine, G.; Pistorius, S. Initial characterization of a portable breast microwave detection device. In Proceedings of the 19th International Symposium on Antenna Technology and Applied Electromagnetics (ANTEM), Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 8–11 August 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranold, L.; Taherzadeh, M.; Nabki, F.; Coates, M.; Popović, M. Microwave Breast Screening Prototype: System Miniaturization with IC Pulse Radio. IEEE J. Electromagn. RF Microw. Med. Biol. 2021, 5, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikkawa, T.; Masui, Y.; Toya, A.; Ito, H.; Hirano, T.; Maeda, T.; Ono, M.; Murasaka, Y.; Imamura, T.; Matsumaru, T.; et al. CMOS Gaussian Monocycle Pulse Transceiver for Radar-Based Microwave Imaging. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2022, 14, 1333–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manufacturers MD. Available online: https://health.ec.europa.eu/medical-devices-topics-interest/reprocessing-devices/manufacturers-md_en (accessed on 10 October 2024).
- Sani, L.; Vispa, A.; Loretoni, R.; Duranti, M.; Ghavami, N.; Sánchez-Bayuela, D.A.; Caschera, S.; Paoli, M.; Bigotti, A.; Badia, M.; et al. Breast lesion detection through MammoWave device: Empirical detection capability assessment of microwave images’ parameters. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shere, M.; Lyburn, I.; Sidebottom, R.; Massey, H.; Gillett, C.; Jones, L. MARIA® M5: A multicentre clinical study to evaluate the ability of the Micrima radio-wave radar breast imaging system (MARIA®) to detect lesions in the symptomatic breast. Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 116, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, E.; O’Loughlin, D. Pathway to Demonstrating Clinical Efficacy of Microwave Breast Imaging: Qualitative and Quantitative Performance Assessment. IEEE J. Electromagn. RF Microw. Med. Biol. 2022, 6, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection (ICNIRP). Guidelines for limiting exposure to electromagnetic fields (100 kHz to 300 GHz). Health Phys. 2020, 118, 483–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, D.; Rattanadecho, P. Microwave imaging of breast cancer: Simulation analysis of SAR and temperature in tumors for different age and type. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2022, 31, 101843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santorelli, A.; Vander Schueren, M.; Popovic, M. SAR levels in microwave breast imaging: 3-D safety assessment with plane-wave illumination. Asia Pac. Microw. Conf. 2011, 2011, 481–484. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, V.; Sheoran, G.; Kanumuri, T. SAR analysis of directive antenna on anatomically real breast phantoms for microwave holography. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2020, 62, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Sasada, S.; Kadoya, T.; Okada, M.; Arihiro, K.; Xiao, X.; Kikkawa, T. Detectability of Breast Tumor by a Hand-held Impulse-Radar Detector: Performance Evaluation and Pilot Clinical Study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelicano, A.C.; Gonçalves, M.C.T.; Godinho, D.M.; Castela, T.; Orvalho, M.L.; Araújo, N.A.M.; Porter, E.; Conceição, R.C. Development of 3D MRI-based anatomically realistic models of breast tissues and tumors for microwave imaging diagnosis. Sensors 2021, 21, 8265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmonds, C.E.; O’Brien, S.R.; Conant, E.F. Mammographic breast density: Current assessment methods, clinical implications, and future directions. Semin. Ultrasound CT MR 2023, 44, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Joshi, P.; Singh, D.K.; Shamarendra, N.; Anurag, G. Volumetric breast density evaluation using fully automated Volpara software, its comparison with BIRADS density types and correlation with the risk of malignancy. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2022, 53, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjic, A.; Cayoren, M.; Akduman, I.; Yilmaz, T.; Onemli, E.; Bugdayci, O.; Aribal, M.E. SAFE: A Novel Microwave Imaging System Design for Breast Cancer Screening and Early Detection—Clinical Evaluation. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moloney, B.M.; McAnena, P.F.; Abd Elwahab, S.M.; Fasoula, A.; Duchesne, L.; Gil Cano, J.D.; Glynn, C.; O’Connell, A.; Ennis, R.; Lowery, A.J.; et al. Microwave Imaging in Breast Cancer—Results from the First-In-Human Clinical Investigation of the Wavelia System. Acad. Radiol. 2022, 29, S211–S222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilberti, L.; Arduino, A.; Bottauscio, O.; Chiampi, M. Parametric analysis of transient skin heating induced by terahertz radiation. Bioelectromagnetics 2014, 35, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgartner, C.; Hasgall, P.A.; Di Gennaro, F.; Neufeld, E.; Lloyd, B.; Gosselin, M.C.; Payne, D.; Klingenböck, A.; Kuster, N. IT’IS Database for Thermal and Electromagnetic Parameters of Biological Tissues; v4.2; IT’IS Foundatio: Zurich, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaupel, P.; Piazena, H. Strong correlation between specific heat capacity and water content in human tissues suggests preferred heat deposition in malignant tumors upon electromagnetic irradiation. Int. J. Hyperth. 2022, 39, 987–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottauscio, O.; Zanovello, U.; Arduino, A.; Zilberti, L. Polynomial chaos expansion of SAR and temperature increase variability in 3 T MRI due to stochastic input data. Phys. Med. Biol. 2024, 69, 125005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Health Canada. Limits of Human Exposure to Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields in the Frequency Range from 3 kHz to 300 GHz: Safety Code 6; Health Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Muratoglu, R.; Gerster, D.; Nadobny, J.; Hansch, A.; Krahl, P.; Veltsista, P.D.; Ghadjar, P. Comparisons of computer simulations and experimental data for capacitive hyperthermia using different split-phantoms. Int. J. Hyperth. 2024, 41, 2416999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Tissue | Specific Heat Capacity (J·kg−1·K−1) | Water Content (%) | Mass Density (kg·m−3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fat | 2300 | 50 | 911 |
| Gland | 3000 | 60 | 1041 |
| Skin | 3300 | 60 | 1109 |
| Tumor | 3850 | 80 | 1179 |
| Model #1 | Horn Antenna Position | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| f [GHz] | Breast tissue |  1 1 | 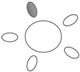 2 2 | 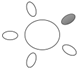 3 3 | 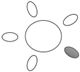 4 4 | 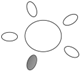 5 5 |
| 2 | Fat | 1.27 | 2.40 | 3.26 | 4.19 | 1.84 |
| Gland | 7.42 | 13.0 | 17.8 | 27.7 | 11.7 | |
| Skin | 2.55 | 2.98 | 6.02 | 9.02 | 2.38 | |
| 4 | Fat | 2.07 | 2.59 | 4.65 | 2.74 | 3.92 |
| Gland | 13.8 | 7.75 | 13.9 | 12.3 | 5.46 | |
| Skin | 5.35 | 4.78 | 8.97 | 8.81 | 5.79 | |
| 6 | Fat | 4.60 | 4.51 | 6.94 | 4.41 | 5.53 |
| Gland | 34.0 | 16.4 | 38.2 | 28.6 | 14.9 | |
| Skin | 11.8 | 9.60 | 11.2 | 17.3 | 12.7 | |
| 8 | Fat | 3.17 | 4.95 | 4.74 | 4.11 | 6.00 |
| Gland | 22.4 | 21.4 | 29.5 | 19.9 | 12.5 | |
| Skin | 11.2 | 15.6 | 19.9 | 23.6 | 15.8 | |
| Model #2 | Horn Antenna Position | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| f [GHz] | Breast tissue | 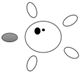 |  |  |  |  |
| 2 | Fat | 1.31 | 3.15 | 3.53 | 2.91 | 3.67 |
| Gland | 5.26 | 14.1 | 12.7 | 18.3 | 13.6 | |
| Skin | 2.27 | 6.21 | 6.17 | 5.49 | 2.95 | |
| Tumor | 1.27 | 3.41 | 0.65 | 0.56 | 0.70 | |
| 4 | Fat | 2.51 | 2.65 | 6.74 | 3.29 | 4.56 |
| Gland | 7.70 | 10.8 | 32.9 | 10.8 | 16.1 | |
| Skin | 3.26 | 5.05 | 9.55 | 5.39 | 4.49 | |
| Tumor | 2.50 | 4.16 | 0.40 | 0.20 | 0.30 | |
| 6 | Fat | 4.08 | 5.15 | 7.20 | 5.64 | 4.08 |
| Gland | 14.0 | 20.7 | 29.6 | 27.7 | 17.1 | |
| Skin | 8.41 | 9.17 | 14.1 | 15.5 | 8.41 | |
| Tumor | 1.58 | 2.10 | 0.46 | 0.04 | 0.38 | |
| 8 | Fat | 3.48 | 3.53 | 9.55 | 3.61 | 3.29 |
| Gland | 8.72 | 17.3 | 23.6 | 13.6 | 11.8 | |
| Skin | 14.8 | 16.1 | 28.0 | 28.2 | 16.2 | |
| Tumor | 0.64 | 0.76 | 0.16 | 0.02 | 0.15 | |
| Model #3 | Horn Antenna Position | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| f [GHz] | Breast tissue |  | 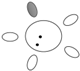 |  |  | 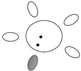 |
| 2 | Fat | 1.27 | 3.52 | 4.86 | 2.08 | 0.574 |
| Gland | 3.45 | 13.5 | 11.3 | 10.9 | 3.20 | |
| Skin | 1.89 | 4.39 | 8.81 | 4.74 | 1.57 | |
| Tumor | 0.59 | 1.19 | 0.43 | 0.63 | 0.39 | |
| 4 | Fat | 1.00 | 3.08 | 7.00 | 2.33 | 1.30 |
| Gland | 3.60 | 7.96 | 24.6 | 6.56 | 4.11 | |
| Skin | 3.64 | 5.11 | 13.1 | 3.91 | 2.19 | |
| Tumor | 0.91 | 0.17 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.40 | |
| 6 | Fat | 3.41 | 4.17 | 11.3 | 3.10 | 2.93 |
| Gland | 14.7 | 15.5 | 23.5 | 13.8 | 7.05 | |
| Skin | 8.12 | 7.89 | 12.6 | 9.39 | 5.52 | |
| Tumor | 0.36 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.17 | |
| 8 | Fat | 2.63 | 3.47 | 5.40 | 3.29 | 2.02 |
| Gland | 10.6 | 15.3 | 15.9 | 18.5 | 9.72 | |
| Skin | 14.9 | 19.6 | 27.7 | 19.7 | 13.3 | |
| Tumor | 0.42 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.06 | |
| Model #4 | Horn Antenna Position | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| f [GHz] | Breast tissue |  |  |  |  |  |
| 2 | Fat | 0.36 | 0.92 | 1.74 | 1.12 | 0.89 |
| Gland | 1.49 | 4.14 | 4.91 | 5.23 | 2.42 | |
| Skin | 1.10 | 1.72 | 3.15 | 5.59 | 2.00 | |
| 4 | Fat | 1.06 | 0.70 | 1.01 | 1.47 | 1.06 |
| Gland | 3.42 | 3.15 | 3.65 | 6.93 | 3.13 | |
| Skin | 2.05 | 2.34 | 2.94 | 4.11 | 3.03 | |
| 6 | Fat | 1.20 | 1.42 | 2.52 | 1.87 | 2.17 |
| Gland | 2.37 | 3.39 | 4.05 | 4.77 | 3.63 | |
| Skin | 4.69 | 5.07 | 9.52 | 8.11 | 4.96 | |
| 8 | Fat | 1.56 | 1.65 | 3.91 | 2.77 | 1.93 |
| Gland | 3.73 | 4.20 | 6.84 | 4.53 | 3.27 | |
| Skin | 10.6 | 11.5 | 15.3 | 15.5 | 10.8 | |
| Model #5 | Horn Antenna Position | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| f [GHz] | Breast tissue |  |  |  |  |  |
| 2 | Fat | 1.77 | 1.89 | 1.27 | 2.46 | 1.07 |
| Gland | 6.48 | 5.70 | 6.99 | 15.7 | 6.41 | |
| Skin | 2.49 | 3.76 | 4.38 | 4.71 | 1.57 | |
| 4 | Fat | 3.07 | 1.87 | 1.62 | 3.39 | 2.56 |
| Gland | 11.9 | 7.91 | 5.92 | 13.9 | 7.93 | |
| Skin | 8.12 | 3.87 | 3.24 | 5.15 | 3.50 | |
| 6 | Fat | 3.10 | 2.02 | 2.71 | 2.42 | 3.05 |
| Gland | 10.5 | 8.54 | 10.7 | 17.5 | 17.1 | |
| Skin | 8.25 | 6.67 | 5.80 | 5.94 | 5.90 | |
| 8 | Fat | 4.97 | 2.12 | 2.41 | 2.60 | 2.36 |
| Gland | 14.1 | 8.28 | 6.63 | 11.6 | 12.3 | |
| Skin | 15.9 | 12.6 | 12.7 | 13.3 | 12.0 | |
| Model #1 | Horn and Vivaldi Antenna Position | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| f [GHz] | Breast tissue | 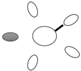 3C 3C |  3D 3D |  3E 3E |
| 6 | Fat | 2.10 | 7.76 | 7.86 |
| Gland | 7.74 | 58.5 | 43.9 | |
| Skin | 6.81 | 11.8 | 10.5 | |
| Model #1 | Horn Antenna Position | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| f [GHz] | Breast tissue |  −10% |  +10% |
| 6 | Fat | 7.80 | 6.25 |
| Gland | 43.7 | 33.7 | |
| Skin | 11.7 | 11.0 | |
| Model #1 | Horn Antenna Position | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| f [GHz] | Breast tissue |  Actual mesh |  Coarser mesh |
| 6 | Fat | 6.94 | 4.91 |
| Gland | 38.2 | 33.9 | |
| Skin | 11.2 | 10.6 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ronca, A.; Zilberti, L.; Bottauscio, O.; Tiberi, G.; Arduino, A. Safety Assessment of Microwave Breast Imaging: Heating Analysis on Digital Breast Phantoms. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4262. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084262
Ronca A, Zilberti L, Bottauscio O, Tiberi G, Arduino A. Safety Assessment of Microwave Breast Imaging: Heating Analysis on Digital Breast Phantoms. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(8):4262. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084262
Chicago/Turabian StyleRonca, Alessandra, Luca Zilberti, Oriano Bottauscio, Gianluigi Tiberi, and Alessandro Arduino. 2025. "Safety Assessment of Microwave Breast Imaging: Heating Analysis on Digital Breast Phantoms" Applied Sciences 15, no. 8: 4262. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084262
APA StyleRonca, A., Zilberti, L., Bottauscio, O., Tiberi, G., & Arduino, A. (2025). Safety Assessment of Microwave Breast Imaging: Heating Analysis on Digital Breast Phantoms. Applied Sciences, 15(8), 4262. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084262









