MEASegNet: 3D U-Net with Multiple Efficient Attention for Segmentation of Brain Tumor Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
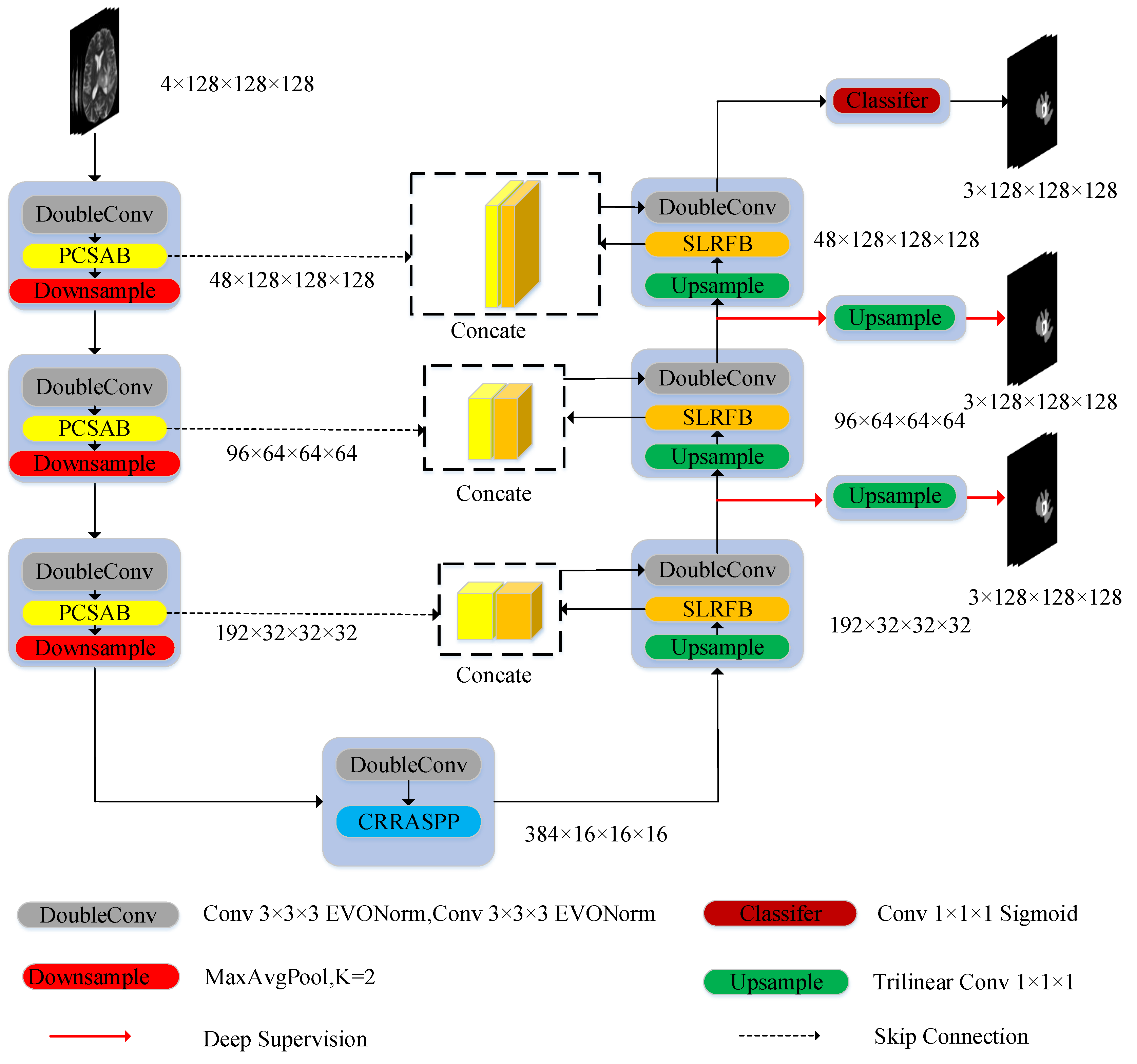
- We propose a PCSAB block for the encoding layer of the 3D U-Net network, such a layer being able to extract more detailed information and integrate global features from the encoding layer, providing more accurate features for the decoding layer.
- (2)
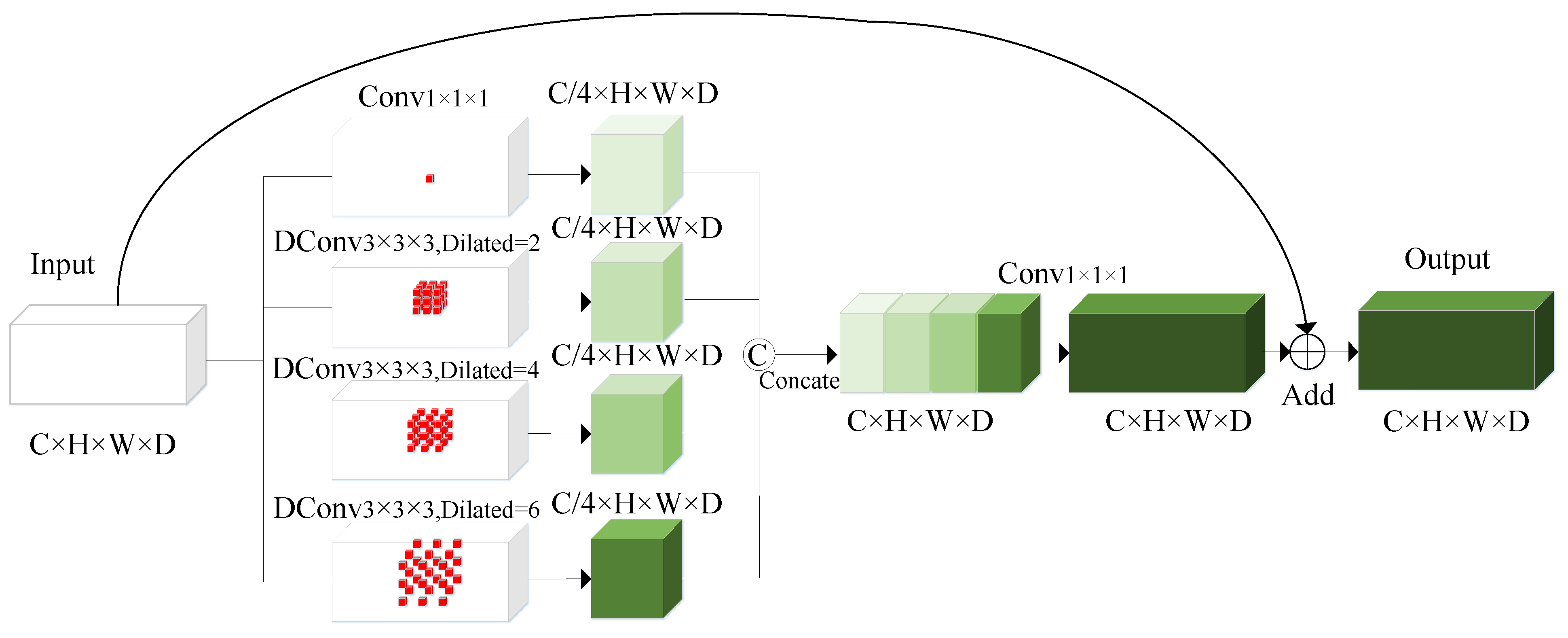
- We design a CRRASPP block for the bottleneck layer which enriches the extraction of detailed features by effectively capturing multiscale features and enhancing the interaction of information between different features.
- (3)
- We develop an SLRFB block for decoder layer that augments the receptive field, significantly boosting the ability to perceive global features. The enhancement ensures a more comprehensive preservation of image details after the upsampling block, leading to an improved segmentation outcome.
- (4)
- We craft an innovative network, MEASegNet, that strategically embeds diverse attention mechanisms within the encoder, bottleneck, and decoder layers of the 3D U-Net architecture. This approach enhances the meaningful feature extraction capabilities of each segment, thereby improving the segmentation accuracy of brain tumor MRI images.
2. Related Work
2.1. Deep-Learning-Based Methods for Medical Image Segmentation
2.2. The Attention-Based Module for Medical Image Segmentation
3. Methodology
3.1. Network Architecture
3.2. Parallel Channel and Spatial Attention Block (PCSAB)
3.3. Channel Reduce Residual Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling Block (CRRASPP)
3.4. Selective Large Receptive Field Block (SLRFB)
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Datasets and Preprocessing
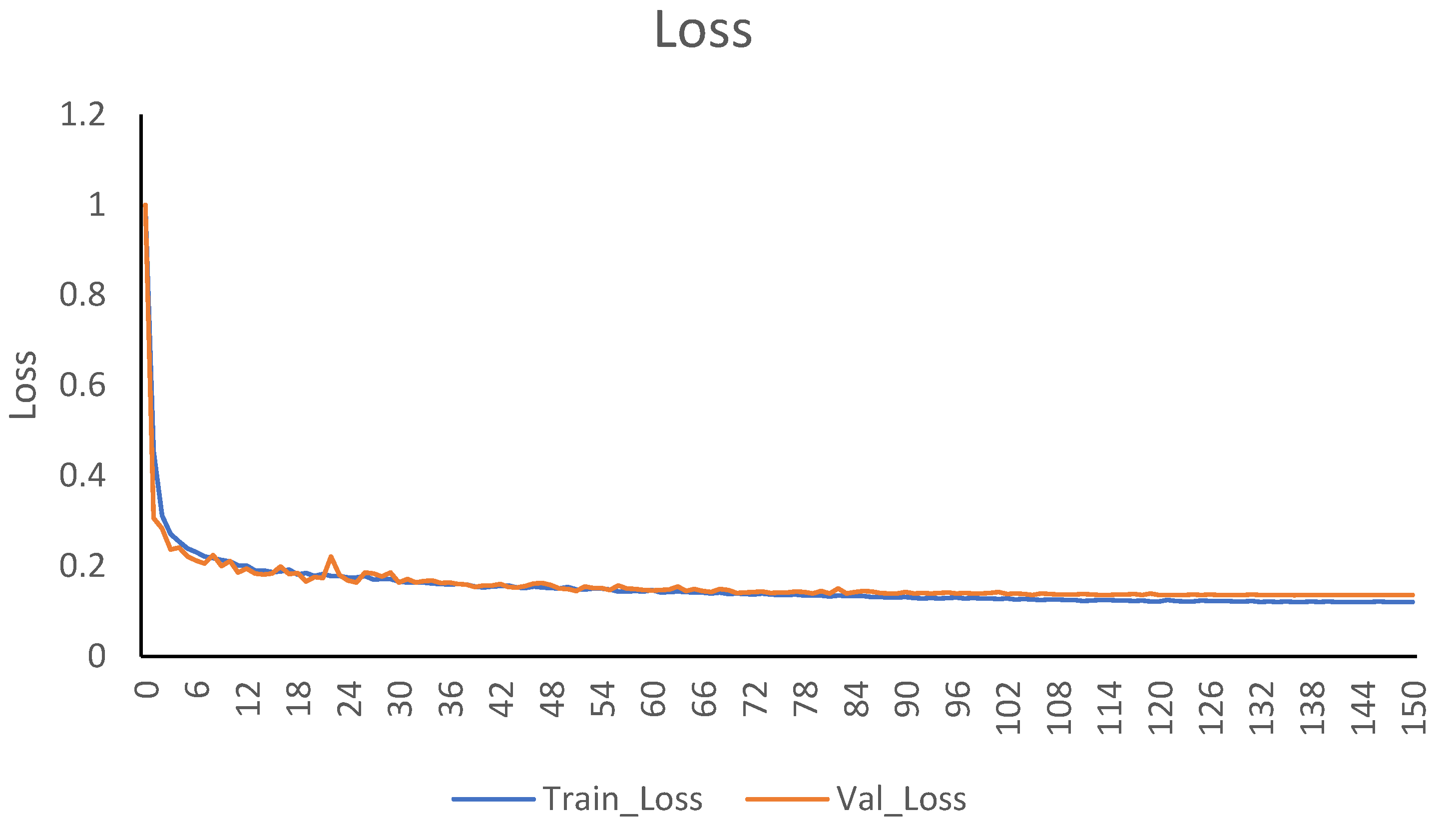
4.2. Implementation Details
4.3. Evaluation Metrics and Loss Function
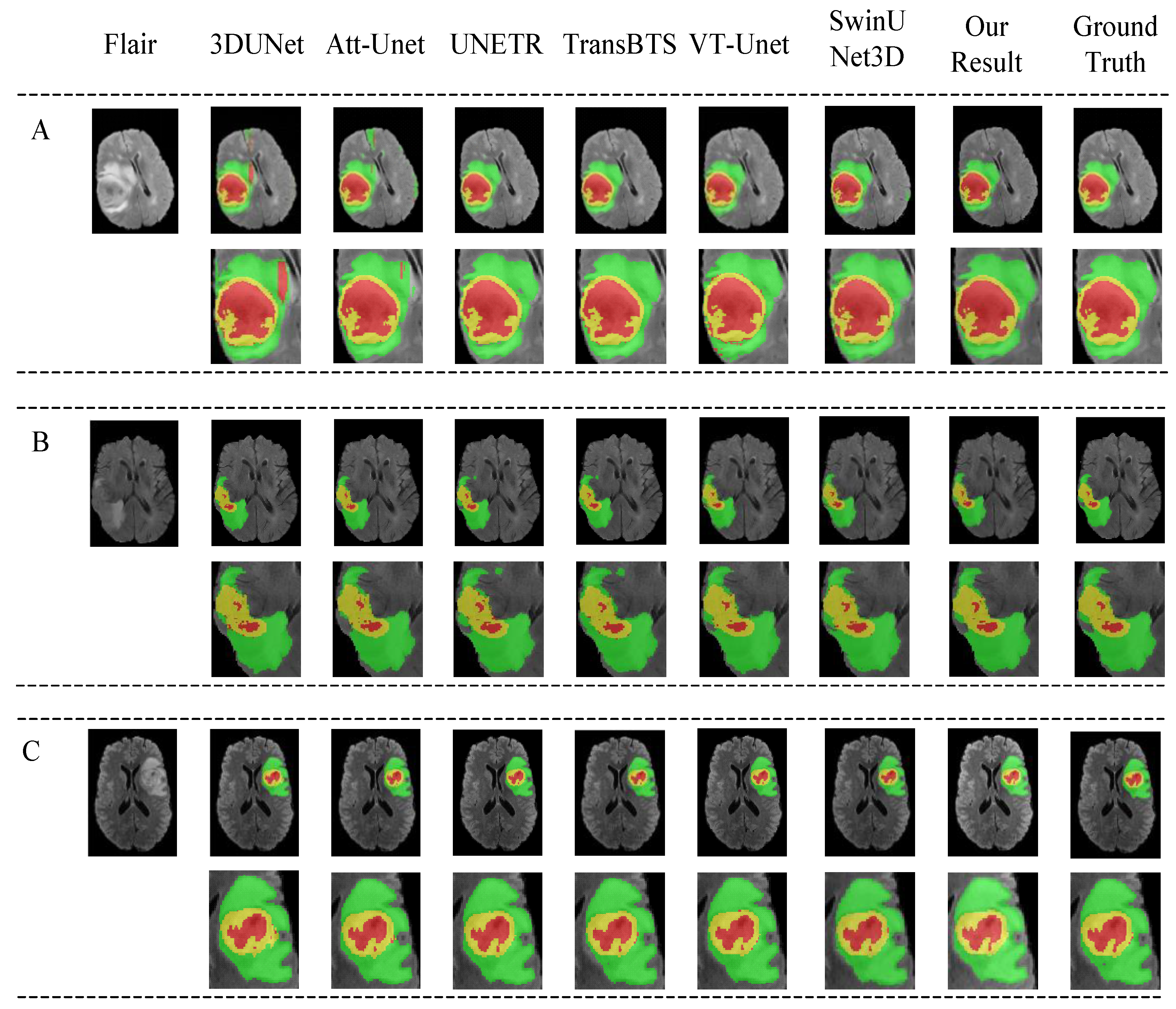
4.4. Comparison with Other Methods
5. Ablation Experiments
5.1. Ablation Study of Each Module in MEASegNet
5.2. The Studies of Different Convolutional Kernels in SLRFB in the Context of Multiscale Feature Extraction
5.3. The Studies of ASPP, CRRASPP, and Deep Supervision
5.4. The Studies of Parameters and Floating-Point Operations in MEASegNet
6. Limitations and Future Perspectives
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Simone, M.; Iaconetta, G.; Palermo, G.; Fiorindi, A.; Schaller, K.; De Maria, L. Clustering functional magnetic resonance imaging time series in glioblastoma characterization: A review of the evolution, applications, and potentials. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owonikoko, T.K.; Arbiser, J.; Zelnak, A.; Shu, H.-K.G.; Shim, H.; Robin, A.M.; Kalkanis, S.N.; Whitsett, T.G.; Salhia, B.; Tran, N.L. Current approaches to the treatment of metastatic brain tumours. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 11, 203–222. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/nrclinonc.2014.25 (accessed on 4 September 2024).
- De Simone, M.; Conti, V.; Palermo, G.; De Maria, L.; Iaconetta, G. Advancements in glioma care: Focus on emerging neurosurgical techniques. Biomedicines 2023, 12, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadhavekar, N.H.; Sabzvari, T.; Laguardia, S.; Sheik, T.; Prakash, V.; Gupta, A.; Umesh, I.D.; Singla, A.; Koradia, I.; Patiño, B.B.R. Advancements in Imaging and Neurosurgical Techniques for Brain Tumor Resection: A Comprehensive Review. Cureus 2024, 16, e72745. Available online: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11607568/ (accessed on 7 November 2024).
- Pulumati, A.; Pulumati, A.; Dwarakanath, B.S.; Verma, A.; Papineni, R.V. Technological advancements in cancer diagnostics: Improvements and limitations. Cancer Rep. 2023, 6, e1764. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, S.; Wiest, R.; Nolte, L.-P.; Reyes, M. A survey of MRI-based medical image analysis for brain tumor studies. Phys. Med. Biol. 2013, 58, R97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Timmerman, R. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy uncertainties: Delineation, setup and motion. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 28, 207–217. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1053429618300183 (accessed on 10 September 2024). [CrossRef]
- Eskandar, K. Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: Explore the Applications of AI in Various Medical Domains, Such as Medical Imaging, Diagnosis, Drug Discovery, and Patient Care. 2023. Available online: https://seriesscience.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/AIHealth.pdf (accessed on 14 September 2024).
- Imtiaz, T.; Rifat, S.; Fattah, S.A.; Wahid, K.A. Automated brain tumor segmentation based on multi-planar superpixel level features extracted from 3D MR images. IEEE Access 2019, 8, 25335–25349. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8939438 (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- Çiçek, Ö.; Abdulkadir, A.; Lienkamp, S.S.; Brox, T.; Ronneberger, O. 3D U-Net: Learning dense volumetric segmentation from sparse annotation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2016: 19th International Conference, Athens, Greece, 17–21 October 2016; Proceedings, Part II 19. pp. 424–432. Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-319-46723-8_49 (accessed on 20 September 2024).
- LeCun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/726791 (accessed on 25 September 2024).
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. Available online: https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_cvpr_2015/html/Long_Fully_Convolutional_Networks_2015_CVPR_paper.html (accessed on 29 September 2024).
- Lu, H.; She, Y.; Tie, J.; Xu, S. Half-UNet: A simplified U-Net architecture for medical image segmentation. Front. Neuroinformatics 2022, 16, 911679. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/neuroinformatics/articles/10.3389/fninf.2022.911679/full (accessed on 4 October 2024). [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.-W.; Yang, Y.-R.; Huang, Z.-H.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Lee, S.-H. Retinal vascular image segmentation using improved UNet based on residual module. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 722. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2306-5354/10/6/722 (accessed on 6 October 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, A.; Yadav, A.K. Residual learning for brain tumor segmentation: Dual residual blocks approach. Neural Comput. Appl. 2024, 36, 22905–22921. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00521-024-10380-2 (accessed on 12 October 2024). [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Singh, Y.; Chinagundi, B. ResUNet++: A comprehensive improved UNet++ framework for volumetric semantic segmentation of brain tumor MR images. Evol. Syst. 2024, 15, 1567–1585. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12530-024-09579-4 (accessed on 19 October 2024).
- Rehman, M.U.; Ryu, J.; Nizami, I.F.; Chong, K.T. Medicine. RAAGR2-Net: A brain tumor segmentation network using parallel processing of multiple spatial frames. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 152, 106426. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0010482522011349 (accessed on 25 October 2024). [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, M.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Control. DPAFNet: A residual dual-path attention-fusion convolutional neural network for multimodal brain tumor segmentation. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 79, 104037. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1746809422005146 (accessed on 4 November 2024).
- Cao, Y.; Zhou, W.; Zang, M.; An, D.; Feng, Y.; Yu, B. Control. MBANet: A 3D convolutional neural network with multi-branch attention for brain tumor segmentation from MRI images. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 80, 104296. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1746809422007509 (accessed on 7 November 2024). [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Tan, T.; Shinichi, T. MimicNet: Mimicking manual delineation of human expert for brain tumor segmentation from multimodal MRIs. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 143, 110394. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S156849462300412X (accessed on 14 November 2024).
- Jiao, C.; Yang, T.; Yan, Y.; Yang, A. RFTNet: Region–Attention Fusion Network Combined with Dual-Branch Vision Transformer for Multimodal Brain Tumor Image Segmentation. Electronics 2023, 13, 77. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2079-9292/13/1/77 (accessed on 17 November 2024). [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, J.; Ma, P. Two-branch network for brain tumor segmentation using attention mechanism and super-resolution reconstruction. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 157, 106751. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0010482523002160 (accessed on 20 November 2024). [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhai, D.-H.; Xia, Y. ERDUnet: An Efficient Residual Double-coding Unet for Medical Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 34, 2083–2096. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/10198487 (accessed on 22 November 2024).
- Liu, Y.; Yao, S.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Li, X. MD-UNet: A medical image segmentation network based on mixed depthwise convolution. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2024, 62, 1201–1212. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11517-023-03005-8 (accessed on 24 November 2024).
- Feng, Y.; Cao, Y.; An, D.; Liu, P.; Liao, X.; Yu, B. DAUnet: A U-shaped network combining deep supervision and attention for brain tumor segmentation. Knowl. Based Syst. 2024, 285, 111348. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0950705123010961 (accessed on 26 November 2024).
- Wang, Z.; Zou, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, P.X.; Chen, J. Multi-scale features and attention guided for brain tumor segmentation. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2024, 100, 104141. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1047320324000968 (accessed on 28 November 2024).
- Li, Y.; Kang, J. TDPC-Net: Multi-scale lightweight and efficient 3D segmentation network with a 3D attention mechanism for brain tumor segmentation. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2025, 99, 106911. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1746809424009698 (accessed on 28 January 2025). [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Brock, A.; Simonyan, K.; Le, Q. Evolving normalization-activation layers. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 13539–13550. Available online: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2020/hash/9d4c03631b8b0c85ae08bf05eda37d0f-Abstract.html (accessed on 31 November 2024).
- Bakas, S.; Akbari, H.; Sotiras, A.; Bilello, M.; Rozycki, M.; Kirby, J.S.; Freymann, J.B.; Farahani, K.; Davatzikos, C. Advancing the cancer genome atlas glioma MRI collections with expert segmentation labels and radiomic features. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 170117. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/sdata2017117 (accessed on 3 December 2024). [CrossRef]
- Baid, U.; Ghodasara, S.; Mohan, S.; Bilello, M.; Calabrese, E.; Colak, E.; Farahani, K.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Kitamura, F.C.; Pati, S. The rsna-asnr-miccai brats 2021 benchmark on brain tumor segmentation and radiogenomic classification. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.02314. [Google Scholar]
- Menze, B.H.; Jakab, A.; Bauer, S.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Farahani, K.; Kirby, J.; Burren, Y.; Porz, N.; Slotboom, J.; Wiest, R. The multimodal brain tumor image segmentation benchmark (BRATS). IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2014, 34, 1993–2024. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/6975210 (accessed on 3 December 2024).
- Liu, L.; Jiang, H.; He, P.; Chen, W.; Liu, X.; Gao, J.; Han, J. On the variance of the adaptive learning rate and beyond. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.03265. [Google Scholar]
- Dice, L.R. Measures of the amount of ecologic association between species. Ecology 1945, 26, 297–302. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/1932409 (accessed on 6 December 2024).
- Kim, I.-S.; McLean, W. Computing the Hausdorff distance between two sets of parametric curves. Commun. Korean Math. Soc. 2013, 28, 833–850. Available online: https://koreascience.kr/article/JAKO201334064306689.page (accessed on 6 December 2024). [CrossRef]
- Aydin, O.U.; Taha, A.A.; Hilbert, A.; Khalil, A.A.; Galinovic, I.; Fiebach, J.B.; Frey, D.; Madai, V.I. On the usage of average Hausdorff distance for segmentation performance assessment: Hidden error when used for ranking. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2021, 5, 4. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s41747-020-00200-2 (accessed on 6 December 2024). [PubMed]
- Oktay, O.; Schlemper, J.; Folgoc, L.L.; Lee, M.; Heinrich, M.; Misawa, K.; Mori, K.; McDonagh, S.; Hammerla, N.Y.; Kainz, B.J.a.p.a. Attention u-net: Learning where to look for the pancreas. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.03999. [Google Scholar]
- Hatamizadeh, A.; Tang, Y.; Nath, V.; Yang, D.; Myronenko, A.; Landman, B.; Roth, H.R.; Xu, D. Unetr: Transformers for 3d medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2022; pp. 574–584. Available online: https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content/WACV2022/html/Hatamizadeh_UNETR_Transformers_for_3D_Medical_Image_Segmentation_WACV_2022_paper.html (accessed on 8 December 2024).
- Wenxuan, W.; Chen, C.; Meng, D.; Hong, Y.; Sen, Z.; Jiangyun, L. Transbts: Multimodal brain tumor segmentation using transformer. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Springer, Strasbourg, France, 27 September–1 October 2021; pp. 109–119. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.04430 (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Peiris, H.; Hayat, M.; Chen, Z.; Egan, G.; Harandi, M. A robust volumetric transformer for accurate 3D tumor segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Singapore, 18–22 September 2022; pp. 162–172. Available online: https://springer.longhoe.net/chapter/10.1007/978-3-031-16443-9_16 (accessed on 11 December 2024).
- Liang, J.; Yang, C.; Zeng, L. 3D PSwinBTS: An efficient transformer-based Unet using 3D parallel shifted windows for brain tumor segmentation. Digit. Signal Process. 2022, 131, 103784. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1051200422004018 (accessed on 14 December 2024).
- Tian, W.; Li, D.; Lv, M.; Huang, P. Axial attention convolutional neural network for brain tumor segmentation with multi-modality MRI scans. Brain Sci. 2022, 13, 12. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3425/13/1/12 (accessed on 16 December 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Pei, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Hu, X.; Wang, C. SDS-Net: A lightweight 3D convolutional neural network with multi-branch attention for multimodal brain tumor accurate segmentation. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2023, 20, 17384–17406. Available online: https://www.aimspress.com/aimspress-data/mbe/2023/9/PDF/mbe-20-09-773.pdf (accessed on 18 December 2024). [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Long, Y.; Han, Z.; Liu, M.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, W.; Chen, L. Swin Unet3D: A three-dimensional medical image segmentation network combining vision transformer and convolution. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2023, 23, 33. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12911-023-02129-z (accessed on 19 December 2024). [CrossRef]
- Håversen, A.H.; Bavirisetti, D.P.; Kiss, G.H.; Lindseth, F. QT-UNet: A self-supervised self-querying all-Transformer U-Net for 3D segmentation. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 62664–62676. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/10510280 (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Akbar, A.S.; Fatichah, C.; Suciati, N.; Za’in, C. Yaru3DFPN: A lightweight modified 3D UNet with feature pyramid network and combine thresholding for brain tumor segmentation. Neural Comput. Appl. 2024, 36, 7529–7544. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00521-024-09475-7 (accessed on 21 December 2024).
- Chen, M.; Wu, Y.; Wu, J. Aggregating multi-scale prediction based on 3D U-Net in brain tumor segmentation. In Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries, Proceedings of the 5th International Workshop, Shenzhen, China, 26–27 September 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 142–152. Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-46640-4_14 (accessed on 23 December 2024).
- Chen, C.; Liu, X.; Ding, M.; Zheng, J.; Li, J. 3D dilated multi-fiber network for real-time brain tumor segmentation in MRI. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2019: 22nd International Conference, Shenzhen, China, 13–17 October 2019; pp. 184–192. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1904.03355 (accessed on 24 December 2024).
- Liu, Z.; Tong, L.; Chen, L.; Zhou, F.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Shan, C.; Li, L.; Zhou, H. Canet: Context aware network for brain glioma segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2021, 40, 1763–1777. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9378564 (accessed on 25 December 2024). [CrossRef]
- Rosas-Gonzalez, S.; Birgui-Sekou, T.; Hidane, M.; Zemmoura, I.; Tauber, C. Asymmetric ensemble of asymmetric u-net models for brain tumor segmentation with uncertainty estimation. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 609646. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/neurology/articles/10.3389/fneur.2021.609646/full (accessed on 26 December 2024).
- Zhou, Z.; Siddiquee, M.M.R.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. Unet++: Redesigning skip connections to exploit multiscale features in image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 39, 1856–1867. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8932614 (accessed on 30 December 2024).
- Ho, N.-V.; Nguyen, T.; Diep, G.-H.; Le, N.; Hua, B.-S. Point-unet: A context-aware point-based neural network for volumetric segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2021: 24th International Conference, Strasbourg, France, 27 September–1 October 2021; pp. 644–655. Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-87193-2_61 (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Ding, Y.; Yu, X.; Yang, Y. RFNet: Region-aware fusion network for incomplete multi-modal brain tumor segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Virtual, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 3975–3984. Available online: https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content/ICCV2021/html/Ding_RFNet_Region-Aware_Fusion_Network_for_Incomplete_Multi-Modal_Brain_Tumor_Segmentation_ICCV_2021_paper.html (accessed on 2 January 2025).
- Chen, L.-C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/7913730 (accessed on 4 January 2025). [PubMed]





| Basic Configuration | Value |
|---|---|
| PyTorch version | 1.11.0 |
| Python | 3.8.10 |
| GPU | NVIDIA RTX A5000 (24 G) |
| Cuda | cu113 |
| Learning rate | 3.00 × 10−4 |
| Optimizer | Ranger |
| Batch size | 1 |
| Loss | Jaccard loss |
| Epoch | 150 |
| Input size | 128 × 128 × 128 |
| Output size | 128 × 128 × 128 |
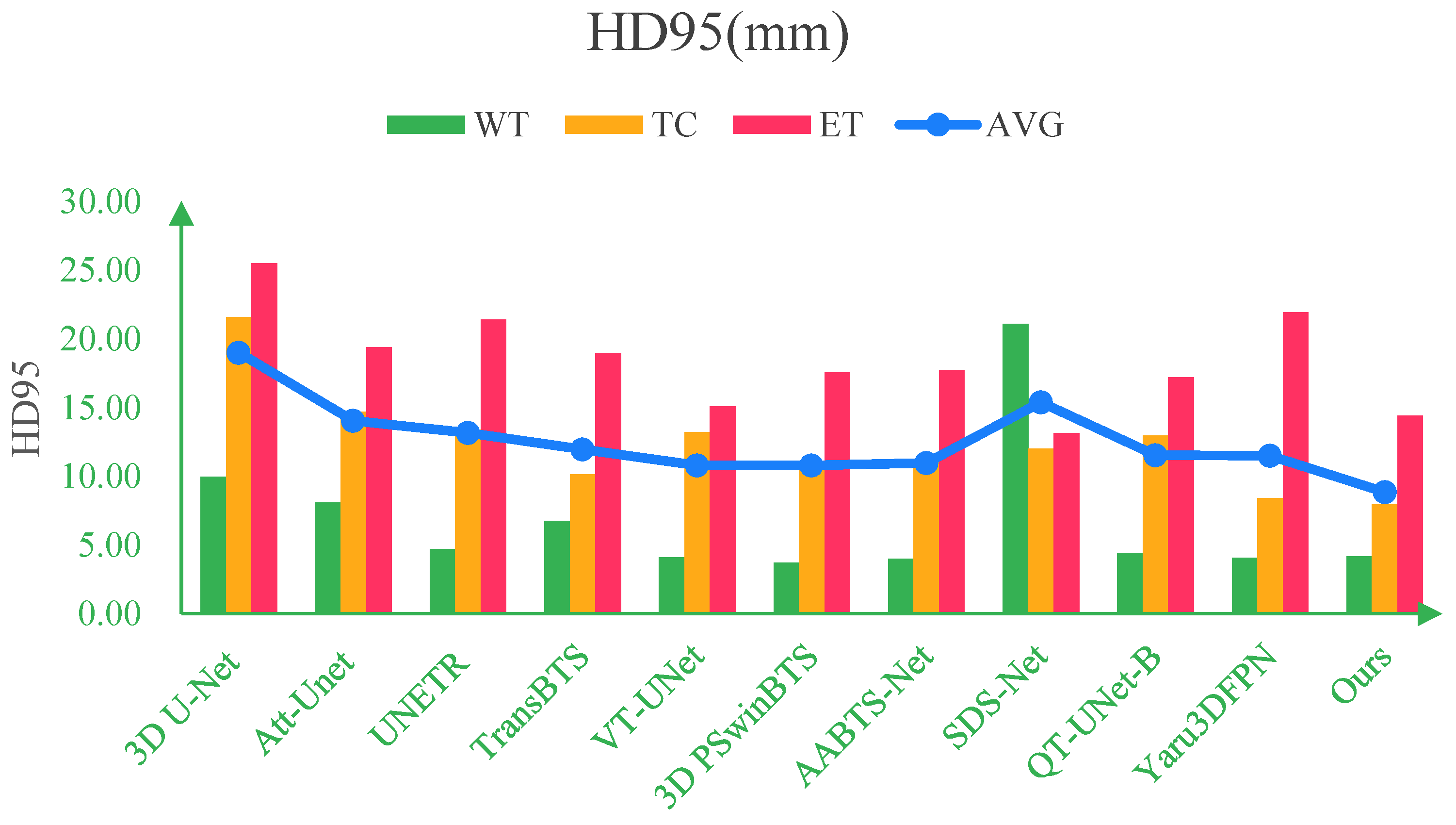
| Methods | Dice (%) | HD95 (mm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | TC | ET | AVG | WT | TC | ET | AVG | |
| 3D U-Net (2016) [10] | 88.02 | 76.17 | 76.20 | 80.13 | 9.97 | 21.57 | 25.48 | 19.00 |
| Att-Unet (2018) [36] | 89.74 | 81.59 | 79.60 | 83.64 | 8.09 | 14.68 | 19.37 | 14.05 |
| UNETR (2021) [37] | 90.89 | 83.73 | 80.93 | 85.18 | 4.71 | 13.38 | 21.39 | 13.16 |
| TransBTS (2021) [38] | 90.45 | 83.49 | 81.17 | 85.03 | 6.77 | 10.14 | 18.94 | 11.95 |
| VT-UNet (2022) [39] | 91.66 | 84.41 | 80.75 | 85.60 | 4.11 | 13.20 | 15.08 | 10.80 |
| 3D PSwinBTS (2022) [40] | 92.64 | 86.72 | 82.62 | 87.32 | 3.73 | 11.08 | 17.53 | 10.78 |
| AABTS-Net (2022) [41] | 92.20 | 86.10 | 83.00 | 87.10 | 4.00 | 11.18 | 17.73 | 10.97 |
| SDS-Net (2023) [42] | 91.80 | 86.80 | 82.50 | 87.00 | 21.07 | 11.99 | 13.13 | 15.40 |
| Swin Unet3D (2023) [43] | 90.50 | 86.60 | 83.40 | 86.83 | - | - | - | - |
| QT-UNet-B (2024) [44] | 91.24 | 83.20 | 79.99 | 84.81 | 4.44 | 12.95 | 17.19 | 11.53 |
| Yaru3DFPN (2024) [45] | 92.02 | 86.27 | 80.90 | 86.40 | 4.09 | 8.43 | 21.91 | 11.48 |
| Our(MEASegNet) | 92.50 | 87.49 | 84.16 | 88.05 | 4.18 | 7.96 | 14.40 | 8.85 |
| Methods | Dice (%) | HD95 (mm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | TC | ET | AVG | WT | TC | ET | AVG | |
| 3D U-Net [10] | 91.29 | 89.13 | 85.78 | 88.73 | 7.50 | 5.47 | 3.82 | 5.59 |
| Att-Unet [36] | 91.43 | 89.51 | 85.71 | 88.88 | 7.30 | 5.39 | 3.81 | 5.50 |
| UNETR [37] | 91.53 | 88.57 | 85.27 | 88.46 | 7.42 | 5.98 | 3.74 | 5.71 |
| TransBTS [38] | 90.61 | 88.78 | 84.29 | 87.89 | 7.64 | 5.56 | 3.90 | 5.70 |
| VT-UNet [39] | 92.39 | 90.12 | 86.07 | 89.53 | 7.14 | 5.17 | 3.97 | 5.42 |
| Swin Unet3D [43] | 92.85 | 90.69 | 86.26 | 89.93 | 7.17 | 4.94 | 3.83 | 5.31 |
| Our (MEASegNet) | 93.29 | 93.16 | 88.19 | 91.55 | 6.87 | 4.57 | 3.59 | 5.01 |
| Methods | WT | TC | ET | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| %Subjects | p | %Subjects | p | %Subjects | p | |
| MEASegNet (ours) vs. 3D U-Net | 78.09 | 7.427 × 10−15 | 84.86 | 2.499 × 10−10 | 79.68 | 0.0007 |
| MEASegNet (ours) vs. Att-Unet | 77.69 | 5.505 × 10−8 | 84.06 | 1.087 × 10−8 | 79.68 | 0.0032 |
| MEASegNet (ours) vs. UNETR | 77.29 | 2.481 × 10−7 | 86.45 | 1.837 × 10−9 | 80.48 | 0.0022 |
| MEASegNet (ours) vs. TransBTS | 82.87 | 1.046 × 10−7 | 85.66 | 1.197 × 10−8 | 82.87 | 5.048 × 10−6 |
| MEASegNet (ours) vs. VT-UNet | 73.71 | 0.0052 | 82.87 | 2.370 × 10−7 | 78.88 | 0.0048 |
| MEASegNet (ours) vs. Swin Unet3D | 71.71 | 0.0047 | 81.27 | 5.619 × 10−6 | 78.49 | 0.0182 |
| Methods | Dice (%) | HD95 (mm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | TC | ET | AVG | WT | TC | ET | AVG | |
| AMPNet [46] | 90.29 | 79.32 | 75.57 | 81.73 | 4.49 | 8.19 | 4.77 | 5.82 |
| 3D U-Net [10] | 88.40 | 79.60 | 77.60 | 81.87 | 9.11 | 8.68 | 4.48 | 7.42 |
| DMFNet [47] | 90.00 | 81.50 | 77.60 | 83.03 | 4.64 | 6.22 | 2.99 | 4.62 |
| CA Net [48] | 88.50 | 85.10 | 75.90 | 83.17 | 7.09 | 8.41 | 4.81 | 6.77 |
| AE AU-Net [49] | 90.20 | 81.50 | 77.30 | 83.00 | 6.15 | 7.54 | 4.65 | 6.11 |
| Our (MEASegNet) | 90.24 | 88.80 | 80.36 | 86.47 | 7.85 | 6.10 | 4.08 | 6.01 |
| Methods | Dice (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | TC | ET | AVG | |
| U-Net++ [50] | 89.77 | 85.57 | 79.83 | 85.06 |
| Point-UNet [51] | 89.67 | 82.97 | 76.43 | 83.02 |
| TransBTS [38] | 90.09 | 81.73 | 78.73 | 83.52 |
| RFNet [52] | 91.11 | 85.21 | 78.00 | 84.77 |
| Our (MEASegNet) | 91.66 | 86.97 | 79.09 | 85.91 |
| NO | Expt | Dice (%) | HD95 (mm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | TC | ET | AVG | WT | TC | ET | AVG | ||
| A | Base | 90.83 | 85.93 | 82.54 | 86.43 | 6.00 | 10.47 | 16.97 | 11.15 |
| B | Base+SLRFB | 92.17 | 86.61 | 82.75 | 87.18 | 5.02 | 8.37 | 19.72 | 11.04 |
| C | Base+CRRASPP | 91.67 | 86.76 | 83.48 | 87.30 | 4.74 | 10.25 | 13.31 | 9.43 |
| D | Base+PCSAB | 92.07 | 86.46 | 82.70 | 87.08 | 4.67 | 10.41 | 18.56 | 11.21 |
| E | Base+SLRFB+CRRASPP | 92.28 | 86.58 | 83.72 | 87.53 | 4.39 | 10.14 | 13.20 | 9.24 |
| F | Base+SLRFB+PCSAB | 92.21 | 87.11 | 83.76 | 87.69 | 5.00 | 9.81 | 17.91 | 10.91 |
| G | Base+PCSAB+CRRASPP | 92.22 | 87.05 | 82.94 | 87.40 | 4.49 | 8.85 | 18.75 | 10.70 |
| H | Base+PCSAB+CRRASPP+SLRFB | 92.50 | 87.49 | 84.16 | 88.05 | 4.18 | 7.96 | 14.40 | 8.85 |
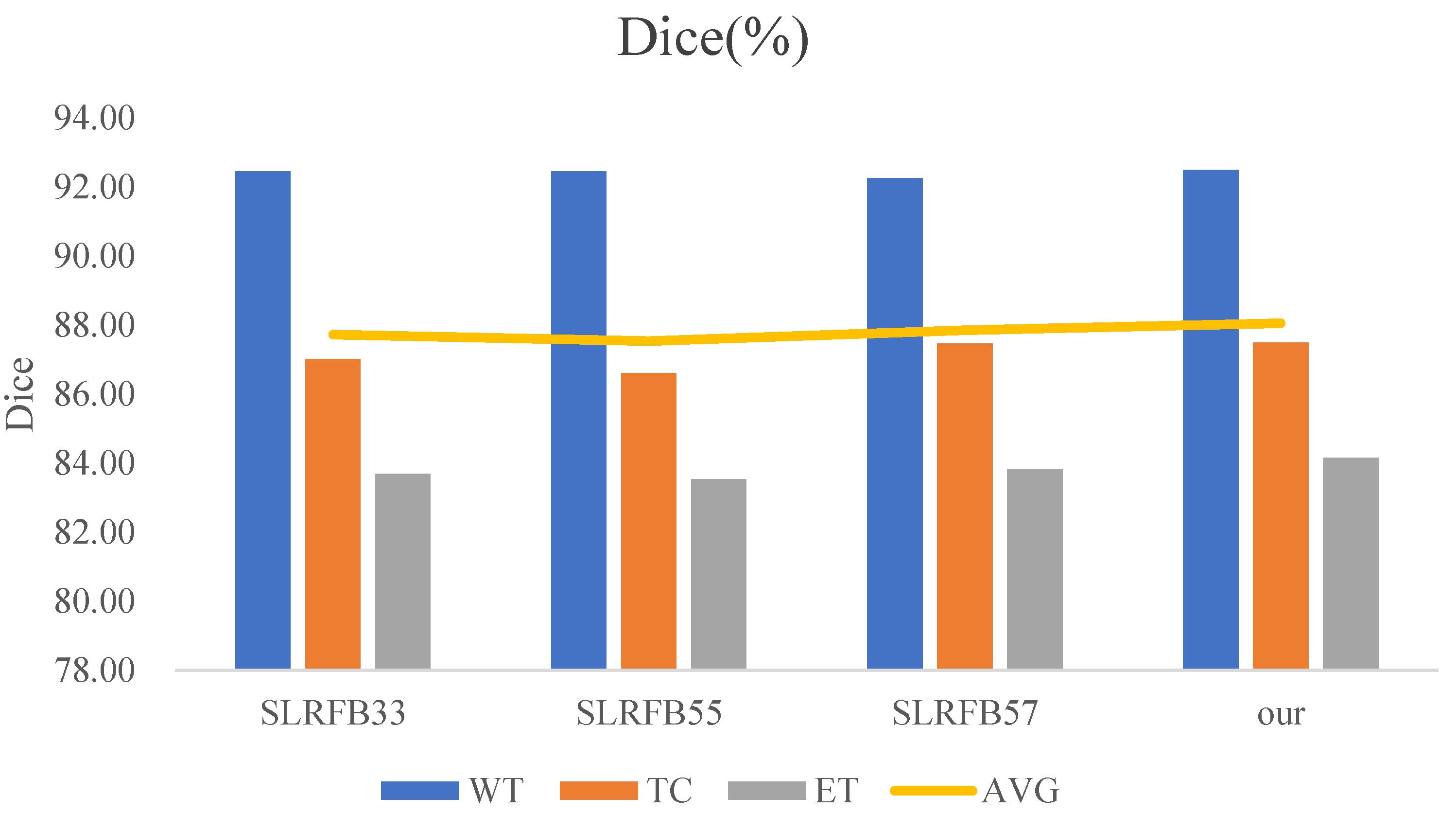
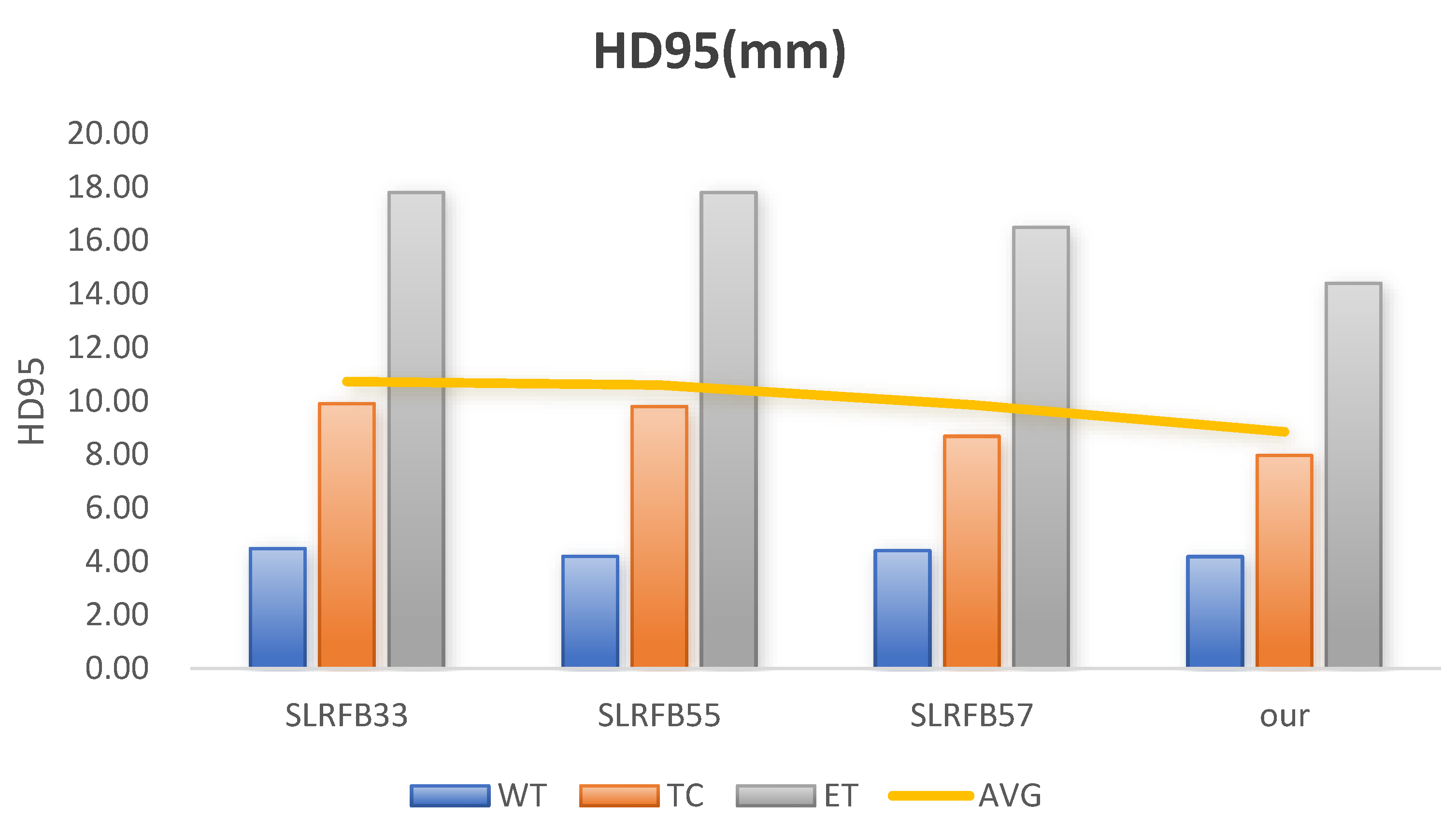
| Methods | Dice (%) | HD95 (mm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | TC | ET | AVG | WT | TC | ET | AVG | |
| SLRFB33 | 92.46 | 87.01 | 83.69 | 87.72 | 4.48 | 9.9 | 17.80 | 10.73 |
| SLRFB55 | 92.46 | 86.61 | 83.53 | 87.53 | 4.19 | 9.79 | 17.80 | 10.59 |
| SLRFB57 | 92.26 | 87.47 | 83.81 | 87.85 | 4.4 | 8.68 | 16.49 | 9.86 |
| SLRFB35 (our) | 92.50 | 87.49 | 84.16 | 88.05 | 4.18 | 7.96 | 14.40 | 8.85 |
| Methods | Dice (%) | HD95 (mm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | TC | ET | AVG | WT | TC | ET | AVG | |
| ASPP | 92.29 | 86.28 | 80.71 | 86.43 | 4.52 | 10.24 | 18.43 | 11.06 |
| CRRASPP (our) | 92.50 | 87.49 | 84.16 | 88.05 | 4.18 | 7.96 | 14.40 | 8.85 |
| Methods | Dice (%) | HD95 (mm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | TC | ET | AVG | WT | TC | ET | AVG | |
| Without deep supervision | 91.63 | 85.03 | 82.43 | 86.36 | 5.64 | 11.36 | 17.37 | 11.46 |
| With deep supervision (our) | 92.50 | 87.49 | 84.16 | 88.05 | 4.18 | 7.96 | 14.40 | 8.85 |
| NO | Expt | Dice (%) | FLOPs (G) | Parameter (M) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | TC | ET | AVG | ||||
| A | Base | 90.83 | 85.93 | 82.54 | 86.43 | 1056.983 | 14.537 |
| B | Base+PCSAB+CRRASPP+SLRFB | 92.50 | 87.49 | 84.16 | 88.05 | 1090.586 | 17.856 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, R.; Yang, P.; Hu, C.; Guo, B. MEASegNet: 3D U-Net with Multiple Efficient Attention for Segmentation of Brain Tumor Images. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3791. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073791
Zhang R, Yang P, Hu C, Guo B. MEASegNet: 3D U-Net with Multiple Efficient Attention for Segmentation of Brain Tumor Images. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(7):3791. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073791
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ruihao, Peng Yang, Can Hu, and Bin Guo. 2025. "MEASegNet: 3D U-Net with Multiple Efficient Attention for Segmentation of Brain Tumor Images" Applied Sciences 15, no. 7: 3791. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073791
APA StyleZhang, R., Yang, P., Hu, C., & Guo, B. (2025). MEASegNet: 3D U-Net with Multiple Efficient Attention for Segmentation of Brain Tumor Images. Applied Sciences, 15(7), 3791. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073791







