The Distribution Characteristics and Genesis Analysis of Overpressure in the Qiongzhusi Formation in the Zizhong Area, Sichuan Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
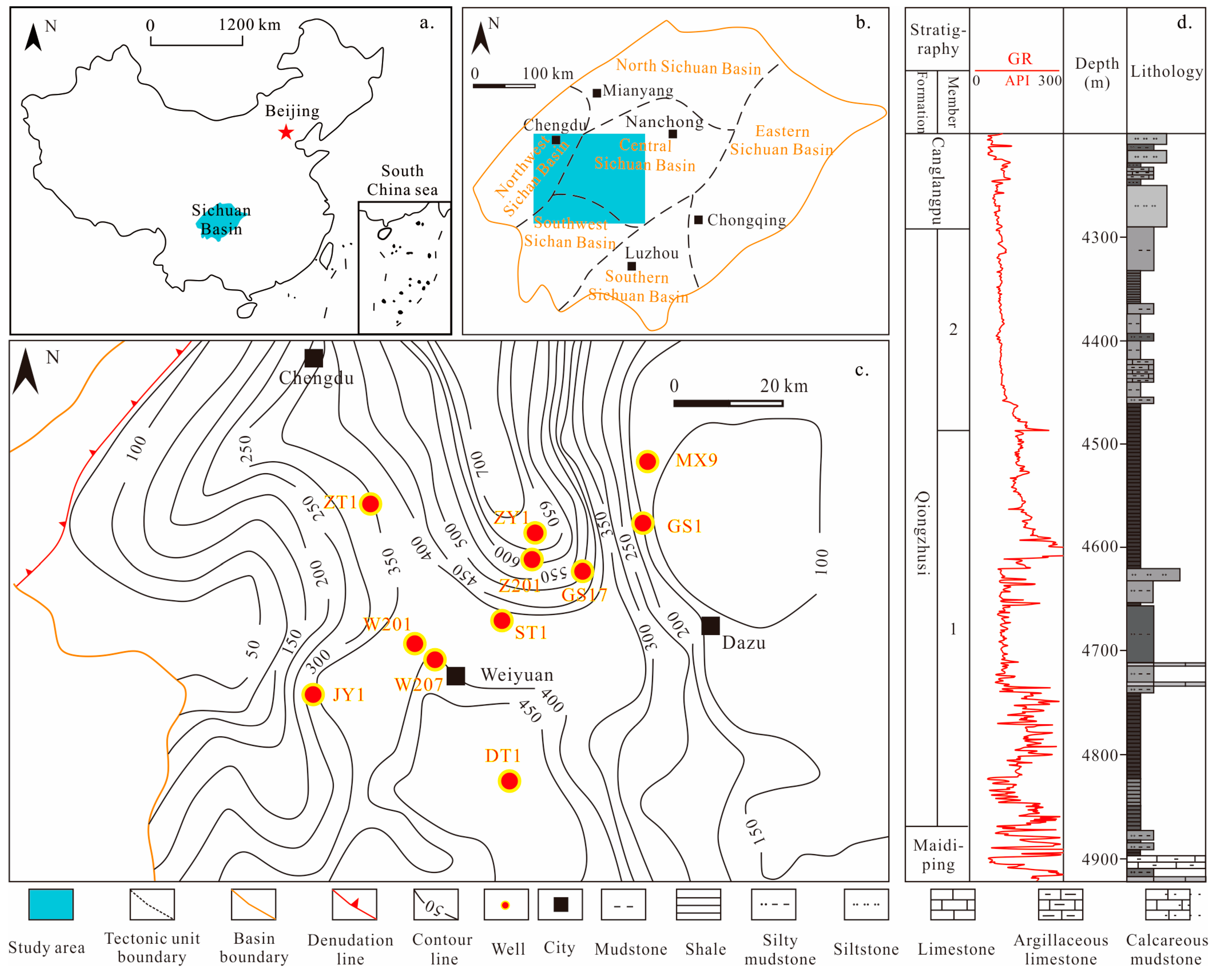
2. Geological Setting
3. Date and Methods
3.1. Date
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Anomalous Pressure Prediction
- (1)
- The equivalent depth method
- (2)
- Eaton method
- (3)
- Bowers method
3.2.2. Evaluation Methods for Overpressure Contribution
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Overpressure Distribution Characteristics
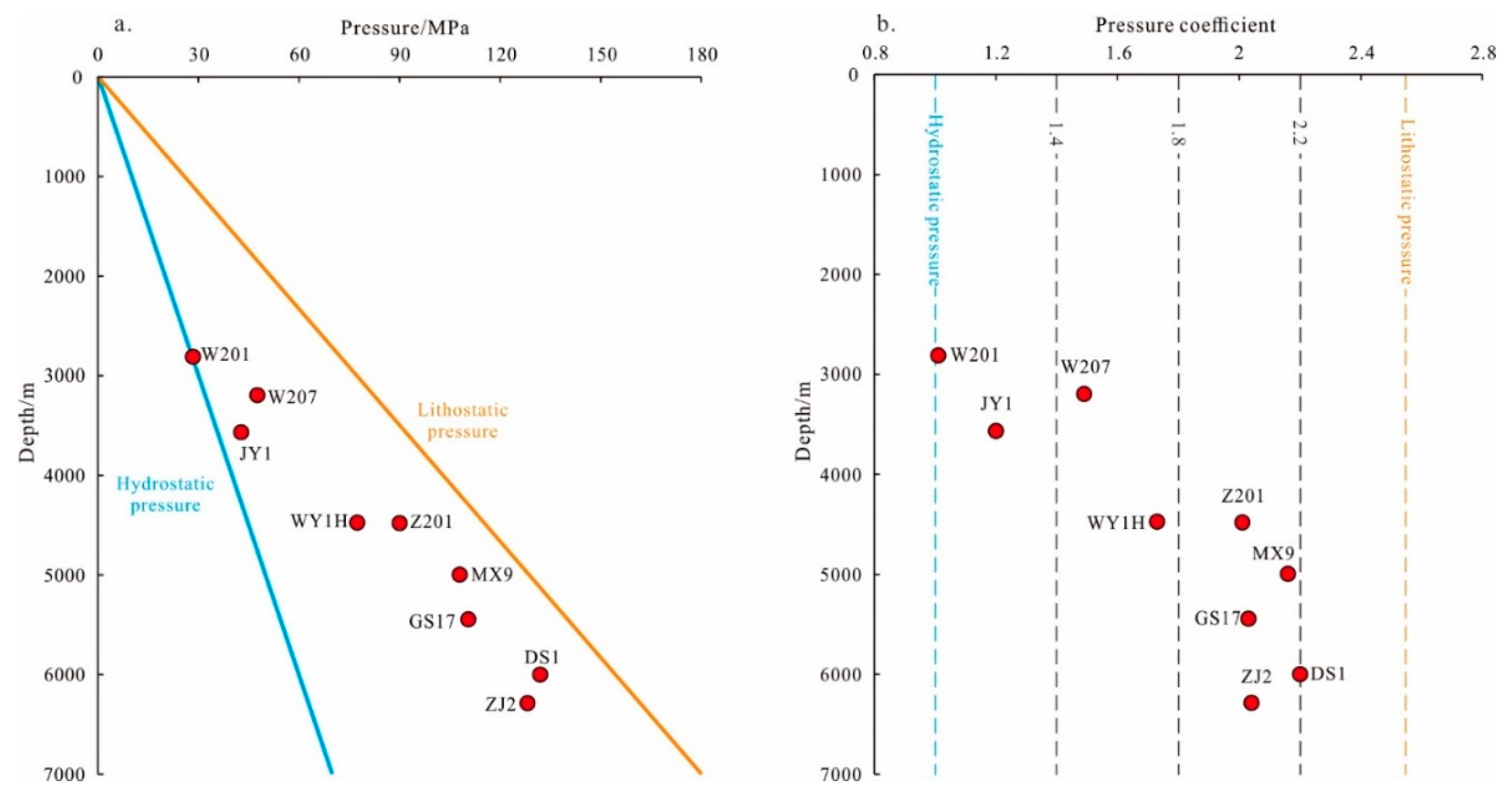
4.1.1. Pressure Characteristics
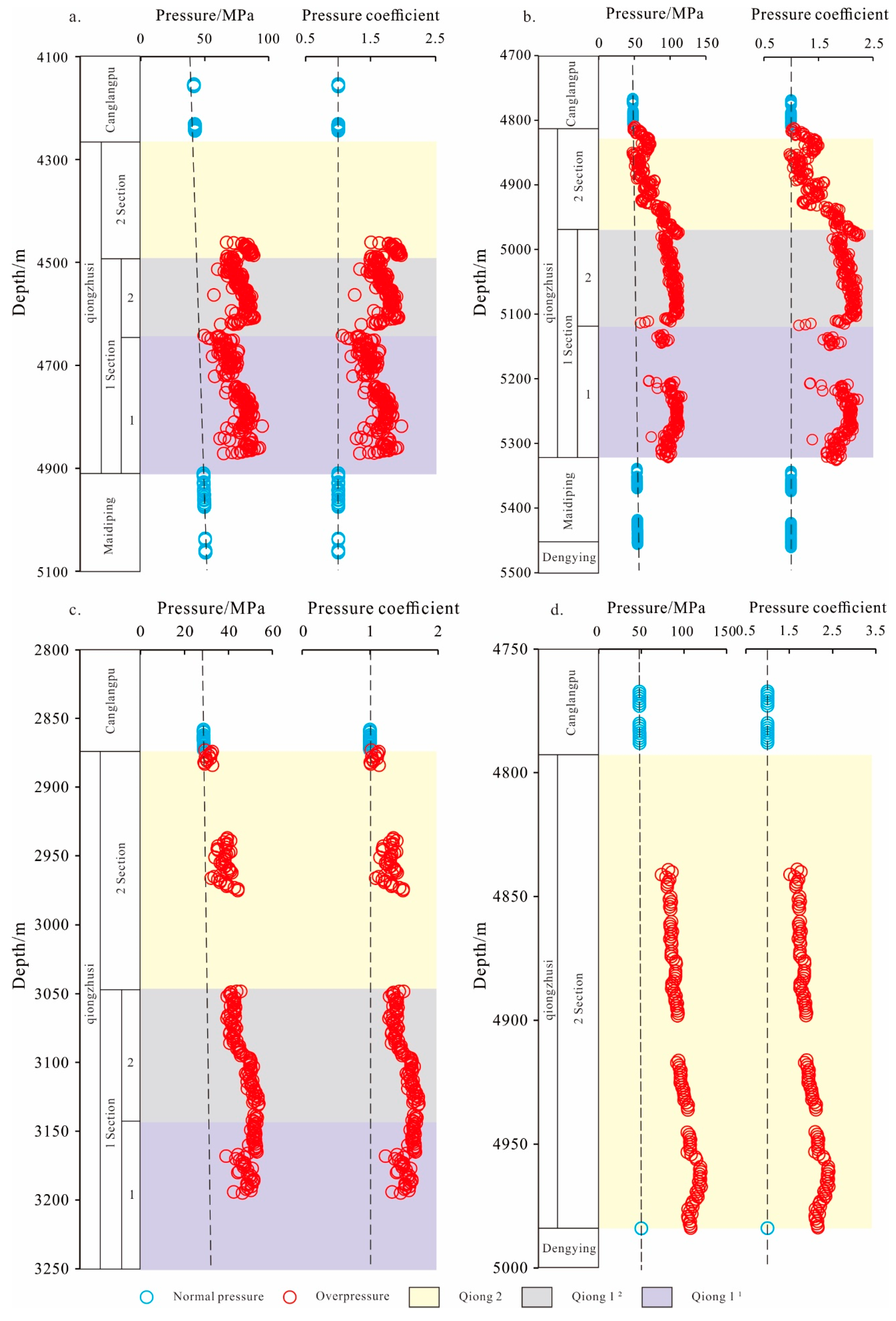
4.1.2. Pressure Prediction Results
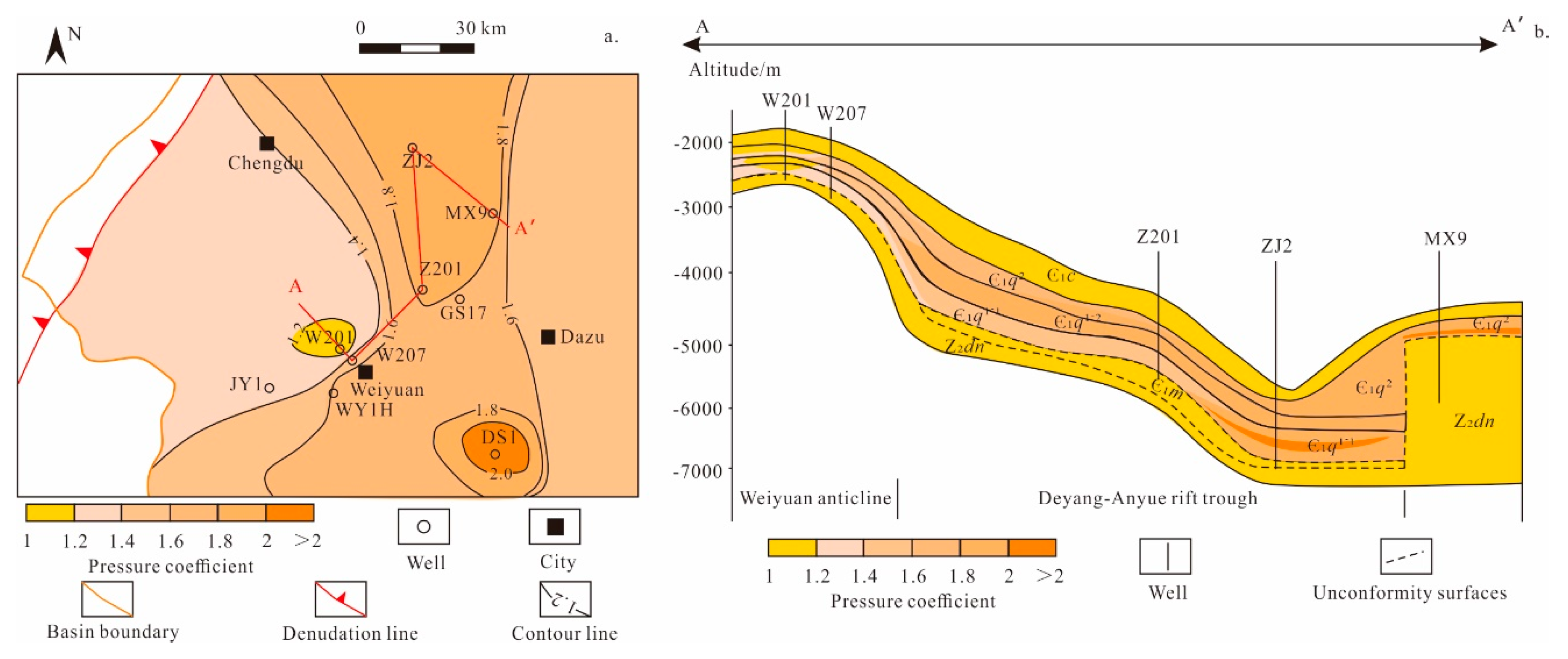
4.1.3. Pressure Distribution Characteristics
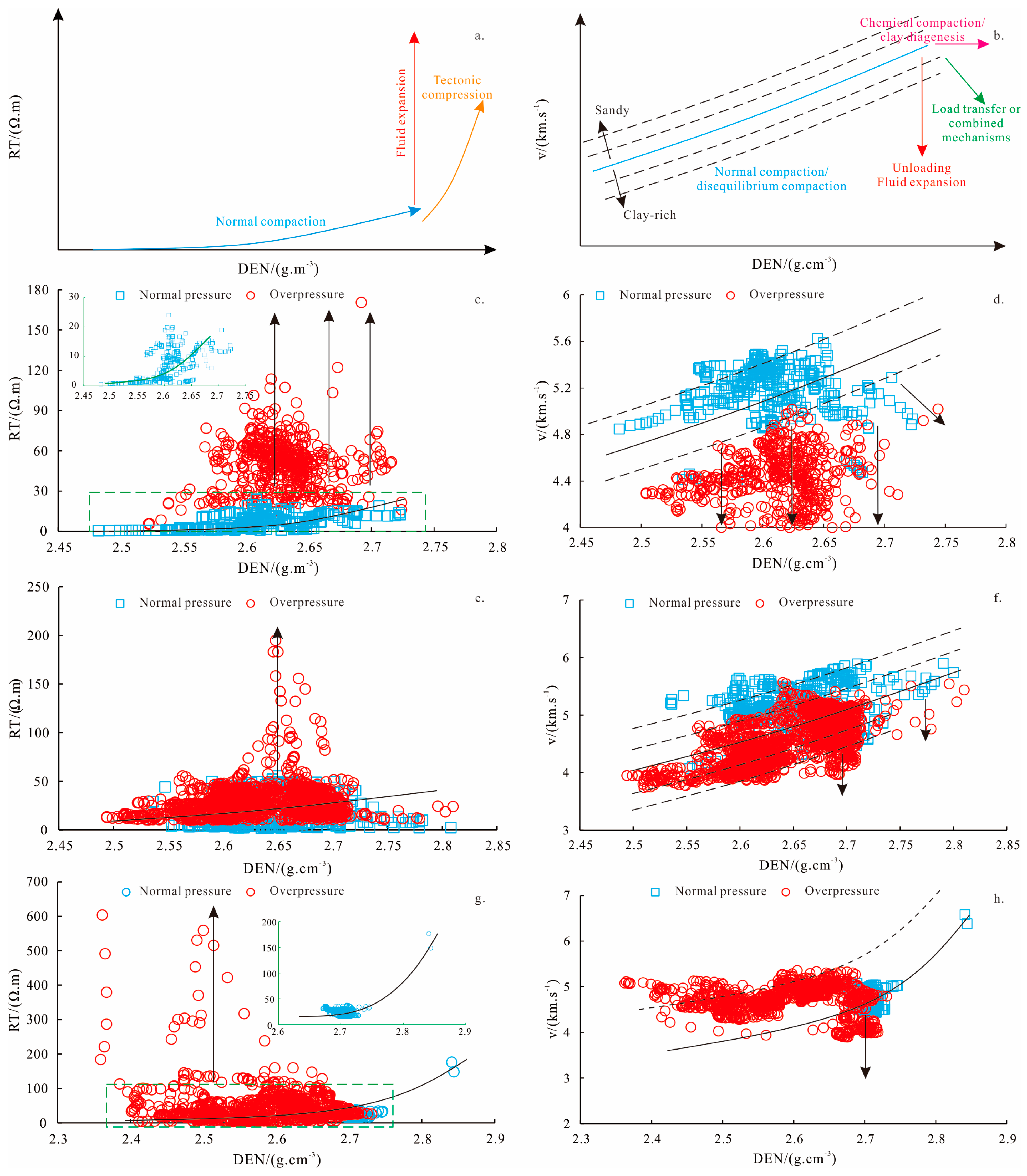
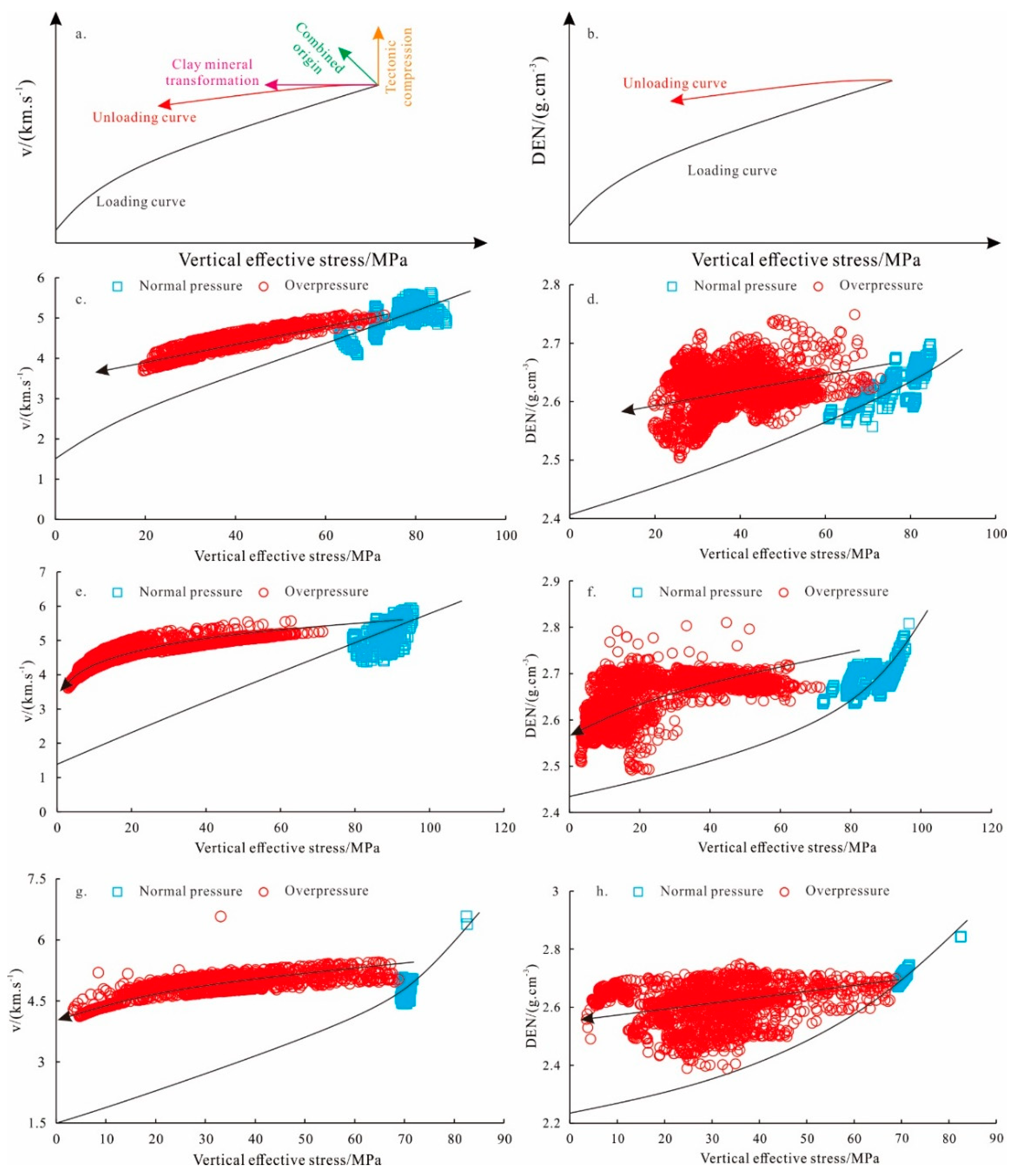
4.2. Origin of Overpressure
4.2.1. Logging Methods
4.2.2. Bowers Method
4.3. Quantitative Evaluation of Overpressure in Different Genesis Types
4.3.1. Disequilibrium Compaction and Pressure Transmission
4.3.2. Uplift Erosion Unloading Effect
4.3.3. Geothermal Decline
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The Qiongzhusi Formation generally exhibits overpressure, with pressure coefficients ranging from 1.0 to 2.5, increasing with depth. The pore pressure in the Deyang–Anyue rift trough is greater than that in the Weiyuan anticline.
- (2)
- The overpressure in the Qiongzhusi Formation is caused by disequilibrium compaction, organic matter maturation, and pressure transmission, with organic matter maturation being the primary contributor to this overpressure.
- (3)
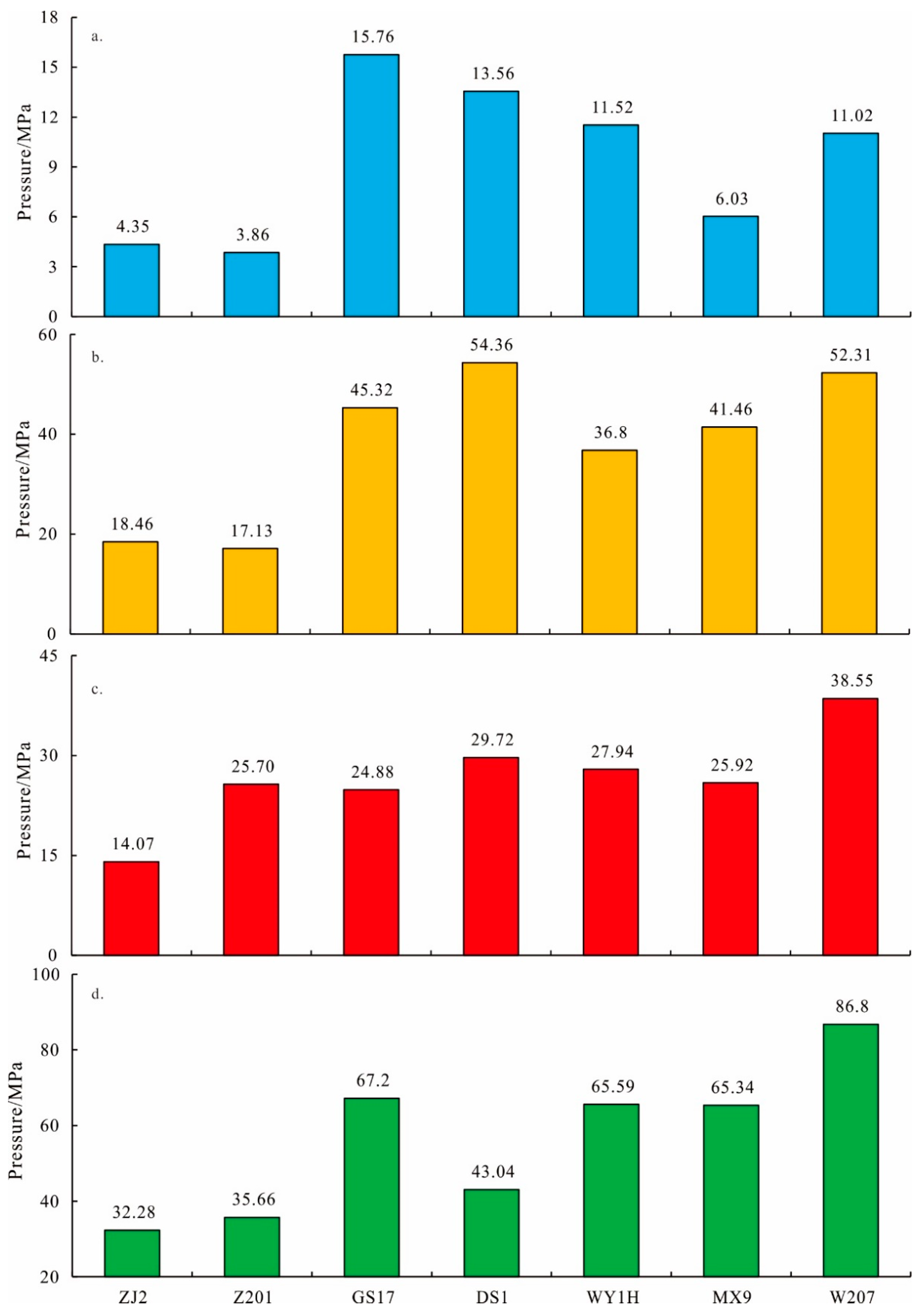
- The evolution of overpressure in the Qiongzhusi Formation has experienced both pressure increase and release, with the amount contributed by disequilibrium compaction being around 9.44 MPa., while OM hydrocarbon generation contributes 82.66 MPa, and pressure transmission contributes 37.98 MPa. Additionally, the uplift erosion unloading effect and geothermal decline led to a reduction in pressure values of approximately 26.68 MPa and 56.56 MPa.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.Z.; Tao, X.W.; Bai, B.; Huang, S.P.; Jiang, Q.C.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Chen, Y.Y.; Ma, D.B.; Zhang, L.P.; Li, N.X.; et al. Geological conditions, reservoir evolution and favorable exploration directions of marine ultra-deep oil and gas in China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2021, 48, 60–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H.; Jiang, Z.X.; Tang, X.L.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, C.J.; Liang, Z.K.; Shi, Y.G. Hydrocarbon generation potential and organic matter accumulation patterns in organic-rich shale during the Mesoproterozoic oxygenation event: Evidence from the Xiamaling formation shale. Geomech. Geophys. GeoEngergy GeoResour. 2023, 9, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H.; Guo, J.Y.; Wang, Y.B.; Jiang, Z.X.; Zhang, C.J.; Li, C.M. Mineralogical and elemental geochemical characteristics of Taodonggou Group mudstone in the Taibei Sag, Turpan-Hami Basin: Implication for its formation mechanism. Solid Earth 2023, 14, 1031–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Ma, X.H.; Liu, Y.Y. Analysis of geological factors affecting propagation behavior of fracture during hydraulic fracturing shale formation. Geomech. Geophys. GeoEngergy GeoResour. 2024, 10, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, J.M. Generation and migration of petroleum from abnormally pressured fluid compartments. AAPG Bull. 1990, 74, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Law, B.E.; Ulmishek, G.F.; Slavin, V.I. Abnormal pressure in hydro-carbon environments. AAPG Mem. 1998, 70, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, X.Q.; Jia, C.Z.; Wang, W.Y. Petroleum geology features and research developments of hydrocarbon accumulation in deep petroliferous basins. Pet. Sci. 2015, 12, 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.Z.; Li, J.; Xu, Z.Y. Advances in the origin of overpressures in sedimentary basins. Acta Pet. Sin. 2017, 38, 973–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H.; Jiang, Z.X.; Lu, J.M.; Zhang, C.J.; Shi, L.D.; Sun, L.D.; Yang, L.; Shang, P. Hydrocarbon Source and Relationship between Hydrocarbon Charging Process and Reservoir Tight Period of the Denglouku Formation Tight Sandstone Gas Reservoirs in the Xujiaweizi Fault Depression, Songliao Basin. Nat. Resour. Res. 2024, 33, 1657–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.J.; Jiang, Z.X.; Lu, J.M.; Shi, L.D.; Bi, Z.Y.; Sun, L.D.; Yang, L.; Li, X.M.; Liu, J.J.; Miao, H. Origin and Evolution Process of Overpressure in the Shahezi Formation of Xujiaweizi Fault Depression in the Northern Songliao Basin, NE China. Acta Geol. Sin. 2025, 99, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tingay, M.R.P.; Hillis, R.R.; Swarbrick, R.E.; Morley, C.K.; Damit, A.R. Origin of overpressure and pore-pressure prediction in the Baram province, Brunei. AAPG Bull. 2009, 93, 51–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.L.; Zhang, Y.M.; Zhao, J. Evolution of formation pressure and accumulation of natural gas in the Upper Palaeozoic, eastern-central Ordos Basin, Central China. Geol. J. 2018, 53, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, T.; Cheng, L.L.; Guo, D.M.; Guan, L.J.; Jiang, Q.T.; Hu, Z.M.; Yin, S.L.; Chen, G.Y. Overpressure characteristics and geological origin of the paleogene in Baiyun Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 11, 1118443. [Google Scholar]
- Eaton, B.A. The Effect of Overburden Stress on Geopressure Prediction from Well Logs. J. Pet. Technol. 1972, 24, 929–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, G.L. Determining an Appropriate Pore-Pressure Estimation Strategy. In Proceedings of the Offshore Technology Conference 2001, Houston, TX, USA, 30 April–3 May 2001; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Tingay, M.R.P.; Morley, C.K.; Laird, A.; Limpornpipat, O.; Krisadasima, K.; Pabchanda, S.; Macintyre, H.R. Evidence for overpressure generation by kerogen-to-gas maturation in the northern Malay Basin. AAPG Bull. 2013, 97, 639–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.Q.; Lu, X.S.; Zhuo, Q.G.; Zhong, H.L.; Zhang, P.; Wei, C.; Liu, W. Genetic mechanism and evolution characteristics of overpressure in the lower play at the southern margin of the Junggar Basin, northwestern China. Oil Gas Geol. 2020, 41, 1004–1016. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, H.; Jiang, Z.X.; Tang, X.L.; Wang, G.Z.; Wu, Q.Z.; Fan, W.L.; Zheng, H.Y. Strata Uplift Controlled Deep Shale Gas Accumulation Modes: A Case Study from the Weiyuan Block, Sichuan Basin. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 12889–12904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.D.; Jiang, Z.X.; Yang, Y.; Shao, X.D.; Feng, X.; Du, W.; Shi, F.L.; Chen, W.Y. Under the Control of Multistage Structure Shallow, Normal-Pressure Shale Gas Accumulation Characteristics in Fuyan Syncline of Northern Guizhou. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 16599–16611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H.; Jiang, Z.X.; Wu, J.F.; Wu, Q.Z.; Shi, X.W.; Deng, Z.; Tang, X.L.; Wu, W.; Tao, C.Q.; Zheng, H.Y. Migration evidence and dynamic enrichment model of shale gas: Take the deep shale gas in the southern Sichuan Basin as an example. Nat. Gas. Ind. 2024, 44, 29–44. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Yu, H.Q.; Deng, H.B. Stratigraphic division and correlation and sedimentary characteristics of the Cambrian in central-southern Sichuan Basin. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2022, 39, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.G.; Deng, B.; Li, Z.W.; Sun, W. The texture of sedimentary basin-orogenic belt system and its influence on oil/gas distribution: A case study from Sichuan basin. Acta Pet. Sin. 2011, 27, 621–635. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.; Liu, S.G.; Wang, S.B.; Deng, B.; Zhou, S.Y.; Ma, W.X. Analysis of the Oldest Carbonate Gas Reservoir in China New Geological Significance of the Dengying Gas Reservoir in the Weiyuan Structure, Sichuan Basin. J. Earth Sci. 2019, 30, 348–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.W.; Wu, W.; Wu, Q.Z.; Zhong, K.S.; Jiang, Z.X.; Miao, H. Controlling Factors and Forming Types of Deep Shale Gas Enrichment in Sichuan Basin, China. Energies 2022, 15, 7023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Liang, F.; Li, H.; Zheng, M.J.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, W.P. Breakthrough and enrichment mode of marine shale gas in the Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation in high-yield wells in Sichuan Basin. China Pet. Exp. 2024, 29, 142–155. [Google Scholar]
- Zachopoulos, F.N.; Nikolaos, C.; Kokkinos, N.C. Detection methodologies on oil and gas kick: A systematic review. Int. J. Oil Gas Coal Technol. 2023, 33, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; He, M.; Xu, M.B.; Wang, S.W.; Dai, B.M. Early gas kick detection-inversion-control integrated system: The significance of applications of managed pressure drilling: A review. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 229, 212134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athy, L.F. Density porosity and compaction of sedimentary rocks. AAPG Bull. 1930, 14, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Yu, F.; Han, K.L.; Zhao, P.; Zheng, L.N.; Wang, T. Method for detecting pore pressure in Carbonate reservoirs. J. Oil Gas Technol. 2011, 33, 111–113. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Gunasekaran, K.; Bhardwaj, N.; Dutta, J.; Banerjee, S. Origin and distribution of abnormally high pressure in the Mahanadi Basin, east coast of India. Interpretation 2016, 4, T303–T311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, B.A. Graphical method predicts geopressures worldwide. World 1976, 183, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Eaton, B.A. The Equation for Geopressure Prediction from Well Logs. In Proceedings of the Fall Meeting of Society of Petroleum Engineers of AIME, Dallas, TX, USA, 28 September–1 October 1975; Volume 5554, pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Bowers, G.L. Pore Pressure Estimation from Velocity Data: Accounting for Overpressure Mechanisms Besides Undercompaction. SPE Drill. Complet. 1995, 10, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, G.L. Detecting high overpressure. Lead. Edge 2002, 21, 174–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.Q.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhong, H.L.; Yang, C.; Wang, J.T. Recognition Model and Contribution Evaluation of Main Overpressure Formation Mechanisms in Sedimentary Basins. Nat Gas Geosci. 2013, 24, 1151–1158. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.Q.; Lu, X.S.; Botterill, S.; Gingras, M.; Zhuo, Q.G.; Zhong, H.L. Horizontal tectonic stress as a cause of overpressure in the southern margin of the Junggar Basin, northwest China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 205, 108861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, J.Z.; Wei, X.S.; Chen, M.N.; Song, P.; Han, Z.H.; Wu, W.T. Origin of abnormal pressure in the Upper Paleozoic shale of the Ordos Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 110, 162–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.C. Pore pressure prediction from well logs: Methods, modifications, and new approaches. Earth Sci. Rev. 2011, 108, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, A.E.; Meng, M.; Zhang, J.J.C. Editorial: Overpressure in sedimentary basins and petroleum geomechanics. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 1062443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, S.H.; Zhao, J.Z.; Meng, Q.A.; Cao, Q.; Wu, W.T.; Zhang, Y.H. The fluid inclusion paleo pressure characteristics and geological implications of gaotaizi tight reservoir in Qijia area of Songliao Basin. J. Geomech. 2018, 24, 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.D.; Zhang, C.J.; Jiang, Y.L.; Wang, L.J.; Zeng, T. Paleo-pressure evolution of reservoir and its main controlling factors in the Third Member of Xujiahe Formation in Yuanba area, Sichuan Basin. J. China Univ. Pet. (Ed. Nat. Sci.) 2021, 45, 31–41. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zhao, J.Z.; Hou, Z.Q.; Zhang, S.P.; Chen, M.N. Origins of overpressure in the central Xihu depression of the East China Sea shelf Basin. AAPG Bull. 2021, 105, 1627–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tingay, M.P.; Hillis, R.R.; Swarbrick, R.E.; Morley, C.K.; Damit, A.R. ‘Vertically transferred’ overpressures in Brunei: Evidence for a new mechanism for the formation of high-magnitude overpressure. Geology 2007, 35, 1023–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qin, D.W.; Yin, W.S.; Wang, X.P.; Dai, Y.; Shi, H.; Fan, C.Y. The Origin of Overpressure in the Pinghu Tectonic Zone of Xihu Depression and Its Relationship with Hydrocarbon Accumulation. Energies 2023, 16, 8055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, N.S.; Liu, Y.F.; Liu, W.; Jia, J.L. Quantitative reconstruction of formation paleo-pressure in sedimentary basins and case studies. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2020, 50, 793–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.B.; Yang, G.; Zeng, Q.; Yu, J.N.; Song, M.W. Burial history analysis of the Sichuan Foreland Basin based on single well data. Nat. Gas Ind. 2012, 32, 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, A.P.; Shen, A.J.; Chen, Y.N.; Zhang, J.Y.; Liang, F.; Wang, Y.S. Reconstruction of tectonic-burial evolution history of Sinian Dengying Formation in Sichuan Basin based on the constraints of in-situ laser ablation U-Pb date and clumped isotopic thermometer(Δ47). Pet. Geol. Exp. 2021, 43, 896–905. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Liu, J.D. Quantitative evaluation on overpressure generated from undercompaction and fluid expansion. Acta Pet. Sin. 2018, 39, 971–979. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Xie, P.Y.; Zhang, F.Q.; Chen, S.G.; Li, Y.X.; Guan, M.; Zhou, R.; Zhang, J. Mechanism and evolution of overpressure in the Linhe Formation of the Xinglong structural belt in the Linhe Depression of the Hetao Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2024, 35, 661–675. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, W.L. Pressure-depth relations in Appalachian region. AAPG Bull. 1972, 56, 528–536. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.X.; Shi, Z.J.; Liu, X.Y.; Yang, S.Y.; Deng, X.Q.; Liu, G.L.; Li, J.H. Quantitative analysis of the Mesozoic abnormal low pressure in Ordos Basin. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2013, 40, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Liu, S.G.; Liu, S.; Li, Z.W.; Zhao, J.C. Restoration of exhumation thickness and its significance in Sichuan Basin, China. J. Chengdu Univ. Technol. Sci. Technol. Ed. 2009, 36, 675–686. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Deng, B.; Wu, J.; Jiang, Q.Q.; Liu, C.J.; Bai, Y.W. Surface exhumation thickness in the southern Sichuan Basin—Based on the date of paleo-temperature indicators and interval transit time method. Geol. Rev. 2023, 69, 90–92. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, J.S. Abnormal formation pressure. AAPG Bull. 1975, 59, 957–973. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, H.Y.; Hao, F.; Cai, Y.X. Summarization of subnormal pressures and accumulation mechanisms of subnormally pressured petroleum reservoirs. Geol. Sci. Technol. Inform. 2003, 2, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.F.; Zheng, L.J.; Qiu, N.S.; Jia, J.K.; Cheng, Q. The effect of temperature on the overpressure distribution and formationin the Central Paleo Uplift of the Sichuan Basin. Chin. J. Geophys. 2015, 58, 2380–2390. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.C. Complex Fluid Pressure Distribution, Evolution and the Its Effects on Hydrocarbon Accumulation in the Third Member of Paleogene Shahejie Formation, Huimin Depression; China University of Petroleum: Beijing, China, 2023; pp. 1–188. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.Q.; Qiu, N.S.; Cao, H.Y.; Jiang, Q.; Branch, E.; SINOPEC. Tectonon-thermal evolution of the eastern Sichuan Basin: Constraints from the vitrinite reflectance and apatite fission track data. Earth Sci. Front. 2017, 24, 94–104. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, L.; Zheng, Z.Y.; Zhang, J.Z.; Luo, Y.; Cai, J.L.; Chen, S.Q.; Li, G.L.; Chen, Y.X.; Zuo, Y.H. Study on the Meso-Cenozoic Thermal History of the Sichuan Basin. Adv. Geosci. 2020, 10, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Methods/Wells | Equivalent Depth Method | Eaton Method | Bowers Method | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Error Rate/% | C | Error Rate/% | A | B | U | Error Rate/% | |
| ZJ2 | 5.33 | 6.85 | 1.84 | 0.122 | 0.723 | 1.19 | 2.99 |
| Z201 | 5.66 | 3.48 | 2.9 | 0.025 | 1.142 | 1.09 | 5.4 |
| GS17 | 6.18 | 4.33 | 2.65 | 0.31 | 0.55 | 1.04 | 2.89 |
| DS1 | 5.54 | 7.7 | 4.77 | 0.26 | 0.963 | 1.22 | 6.31 |
| WY1H | 9.38 | 2.91 | 2.8 | 0.93 | 0.29 | 0.58 | 4.7 |
| MX9 | 6.23 | 4.71 | 0.18 | 1.39 | 0.22 | 1.21 | 0.07 |
| W207 | 4.63 | 2.13 | 2.94 | 2.17 | 0.17 | 0.98 | 3.05 |
| Wells | Pressure Increase Value/MPa | Pressure Decrease Value/MPa | Residual Pressure/MPa | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disequilibrium Compaction | OM Generates Hydrocarbons | Pressure Transmission | Uplift Erosion Unloading Effect | Geothermal Decline | ||
| ZJ2 | 4.35 | 77.6 | 18.46 | 14.07 | 32.28 | 54.06 |
| Z201 | 3.86 | 76.66 | 17.13 | 25.70 | 35.66 | 36.29 |
| GS17 | 15.76 | 90.35 | 45.32 | 24.88 | 67.2 | 39.35 |
| DS1 | 13.56 | 83.51 | 54.36 | 29.72 | 43.04 | 62.78 |
| WY1H | 11.52 | 82 | 36.8 | 27.94 | 65.59 | 37.57 |
| MX9 | 6.03 | 92.1 | 41.46 | 25.92 | 65.34 | 48.33 |
| W207 | 11.02 | 76.4 | 52.31 | 38.55 | 86.8 | 14.38 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, X.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Li, Y.; He, Y.; Tian, H.; Jiang, Z.; Bi, Z.; Miao, H. The Distribution Characteristics and Genesis Analysis of Overpressure in the Qiongzhusi Formation in the Zizhong Area, Sichuan Basin. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2888. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15062888
Shi X, Yang Y, Wu Q, Li Y, He Y, Tian H, Jiang Z, Bi Z, Miao H. The Distribution Characteristics and Genesis Analysis of Overpressure in the Qiongzhusi Formation in the Zizhong Area, Sichuan Basin. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(6):2888. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15062888
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Xuewen, Yuran Yang, Qiuzi Wu, Yanyou Li, Yifan He, He Tian, Zhenxue Jiang, Zhongyu Bi, and Huan Miao. 2025. "The Distribution Characteristics and Genesis Analysis of Overpressure in the Qiongzhusi Formation in the Zizhong Area, Sichuan Basin" Applied Sciences 15, no. 6: 2888. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15062888
APA StyleShi, X., Yang, Y., Wu, Q., Li, Y., He, Y., Tian, H., Jiang, Z., Bi, Z., & Miao, H. (2025). The Distribution Characteristics and Genesis Analysis of Overpressure in the Qiongzhusi Formation in the Zizhong Area, Sichuan Basin. Applied Sciences, 15(6), 2888. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15062888






