Improving the Pharmaceutical Potential of Lycopene Using Hot-Melt Extrusion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of Extrudates
Ultrasound-Assisted Acetone Extraction
Preparation of Extrudates with Polymers Soluplus and PVP/VA64
2.2.2. Extrudate Identity Testing
X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRPD)
ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy
DSC Analysis
2.2.3. In Vitro Dissolution Test
HPLC Method
In Vitro Dissolution Studies
2.2.4. Evaluation of Antioxidant Activity
Preparation of 0.2 mM DPPH Solution
Preparation of Ascorbic Acid Solution
Preparation of Extrudate Solutions
Procedure for the Determination of Antioxidant Activity
3. Results
3.1. Preparation of Extracts and Extrudates
3.2. Extrudate Identity Testing
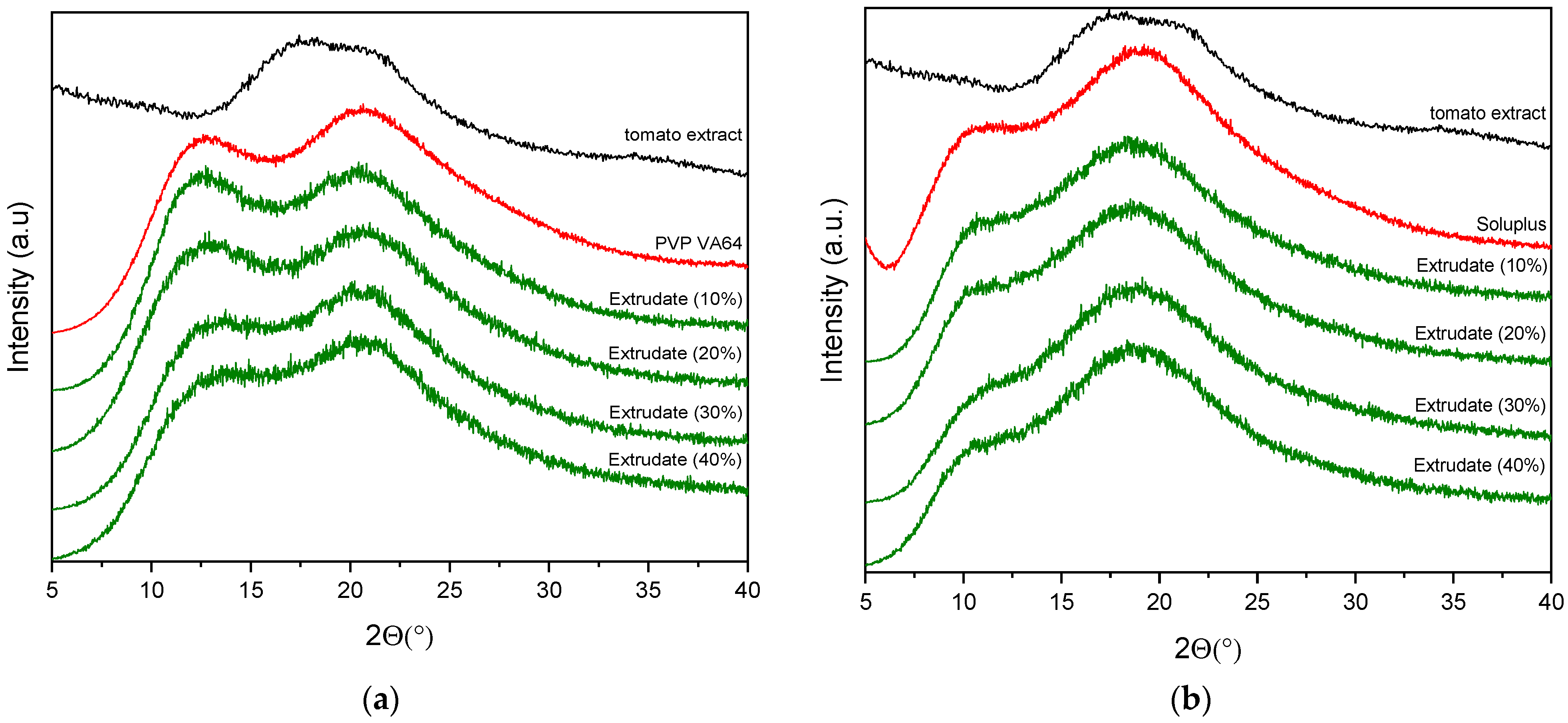
3.2.1. X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRPD)
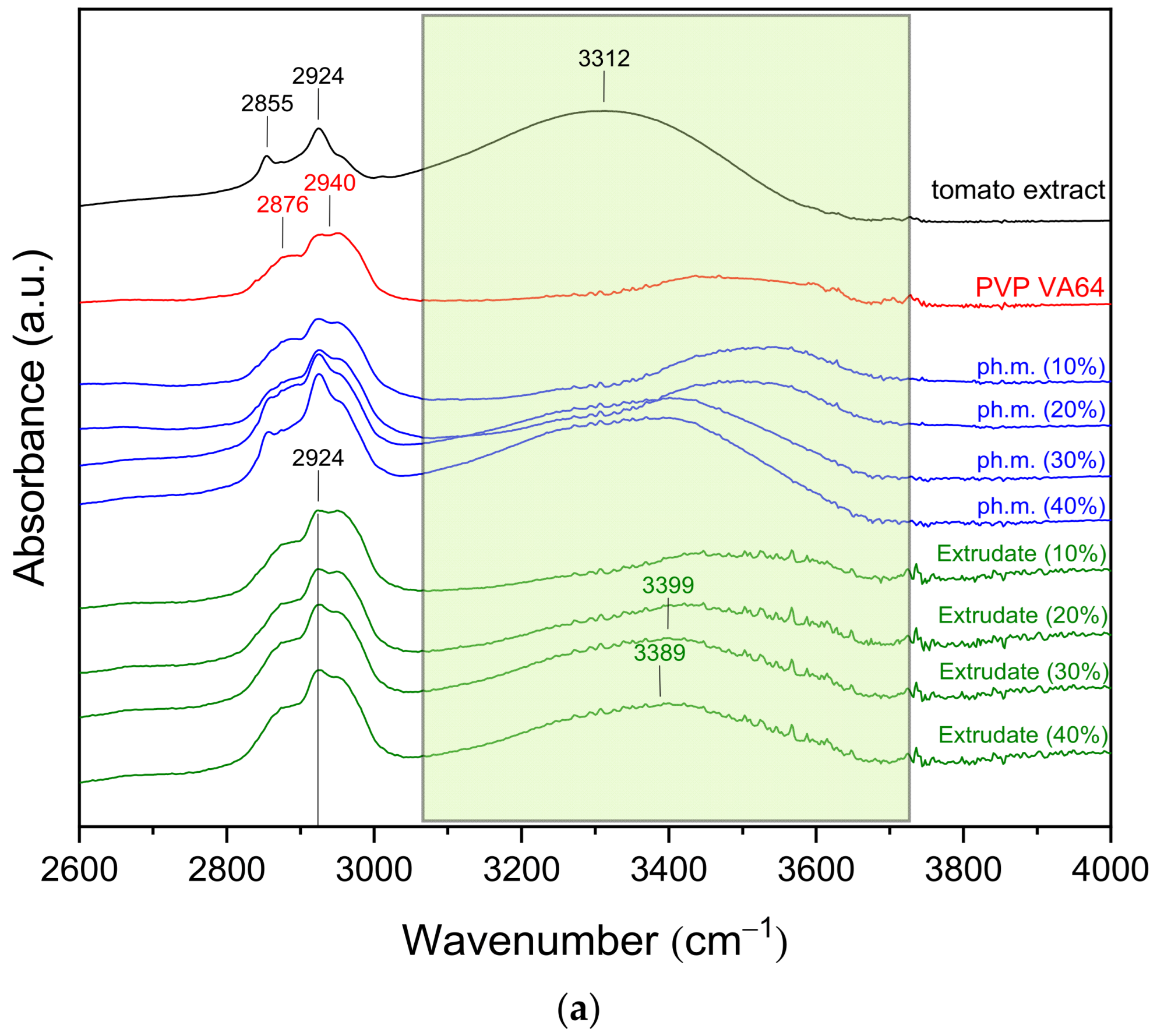
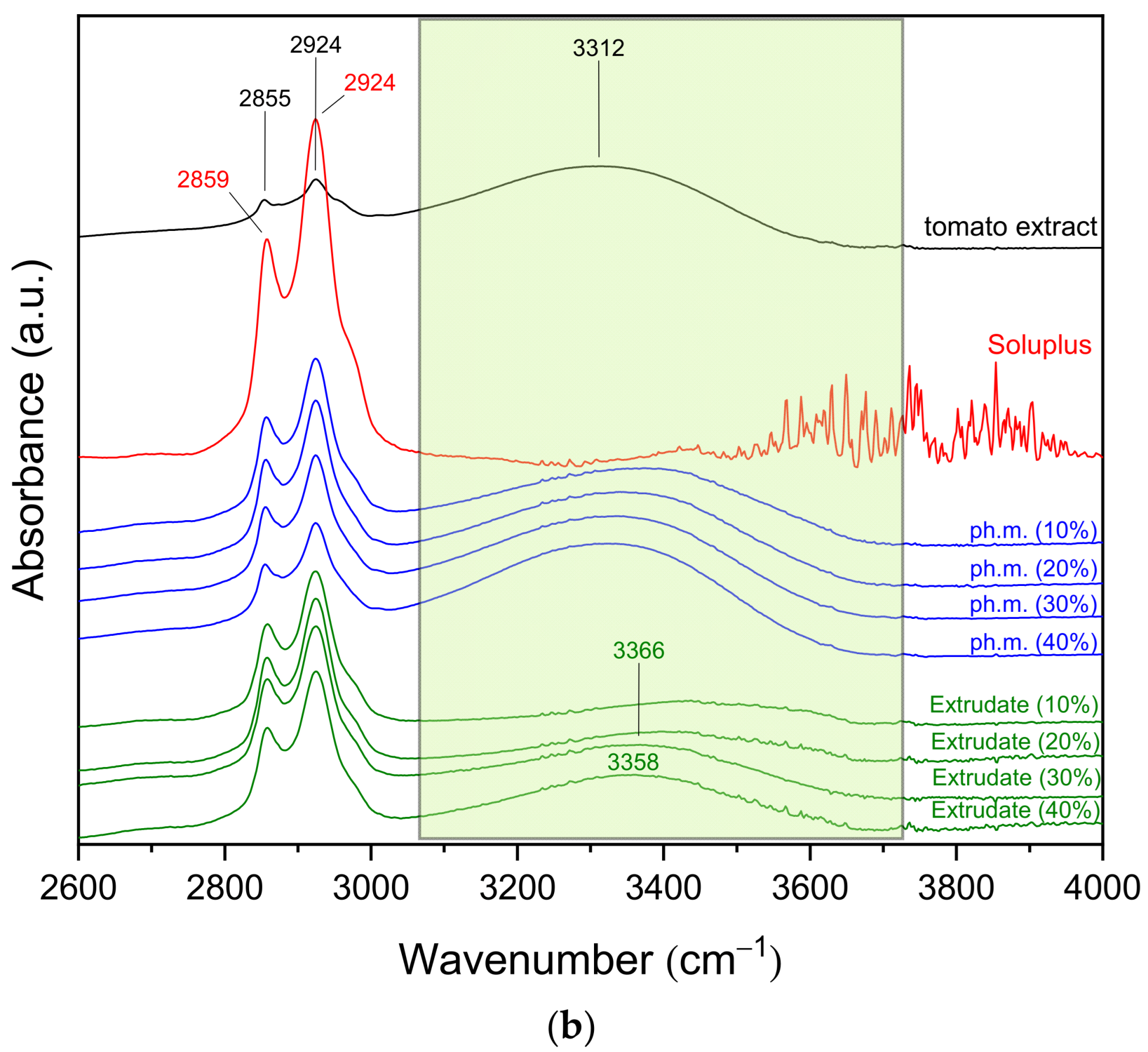
3.2.2. FT-IR Spectroscopy
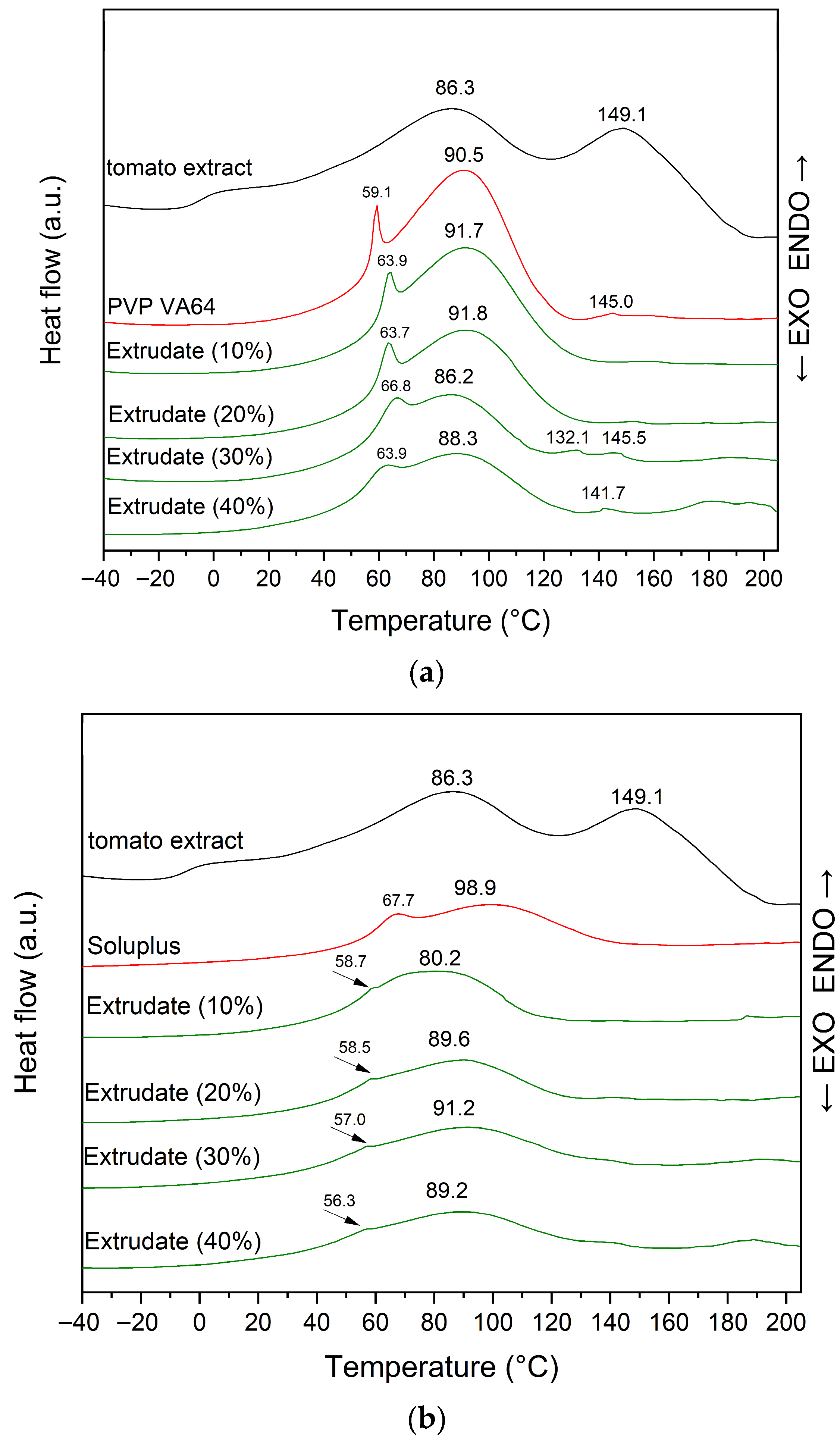
3.2.3. DSC Analysis
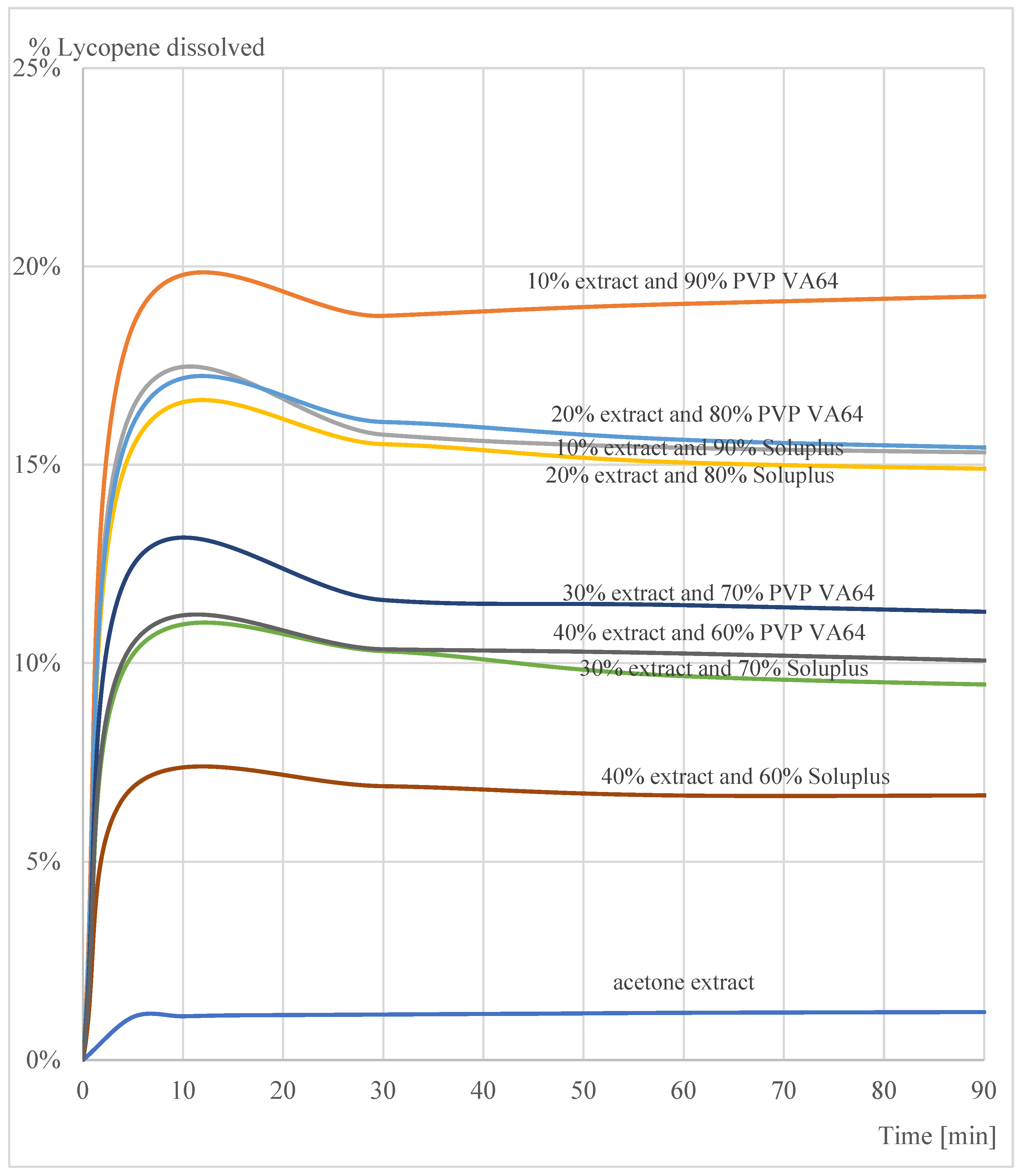
3.3. In Vitro Dissolution Test
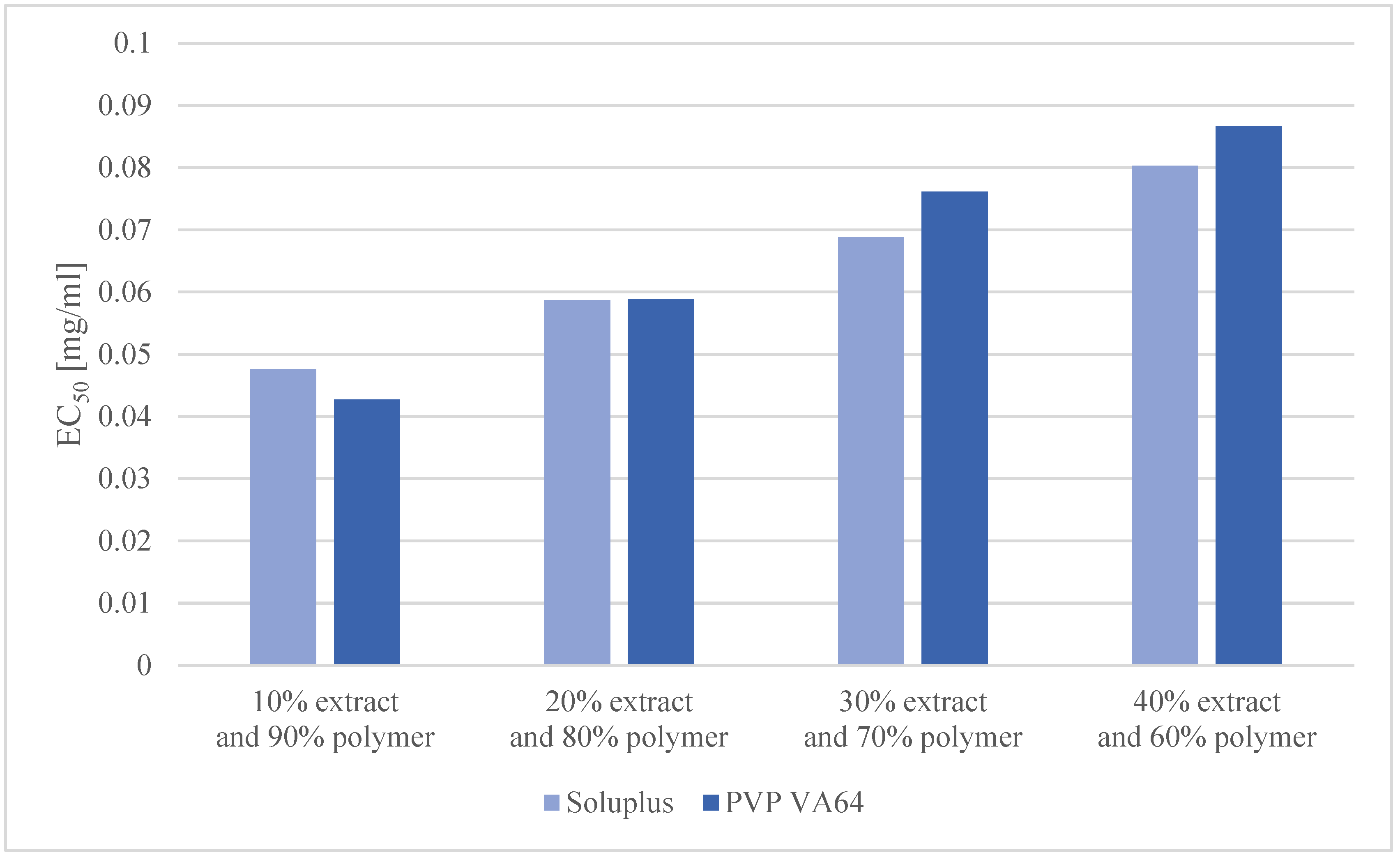
3.4. Determination of Antioxidant Activity Using the DPPH Radical
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Imran, M.; Ghorat, F.; Ul-Haq, I.; Ur-Rehman, H.; Aslam, F.; Heydari, M.; Shariati, M.A.; Okuskhanova, E.; Yessimbekov, Z.; Thiruvengadam, M.; et al. Lycopene as a Natural Antioxidant Used to Prevent Human Health Disorders. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Zhu, H.; Wang, S.; Xing, J. Inclusion Complexes of Lycopene and β-Cyclodextrin: Preparation, Characterization, Stability and Antioxidant Activity. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulawik, A.; Cielecka-Piontek, J.; Zalewski, P. The Importance of Antioxidant Activity for the Health-Promoting Effect of Lycopene. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Kim, Y.-J.; Shin, Y. Estimation of Daily Intake of Lycopene, Antioxidant Contents and Activities from Tomatoes, Watermelons, and Their Processed Products in Korea. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2020, 63, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, G.C.; de Camargo, B.A.F.; de Araújo, J.T.C.; Chorilli, M. Lycopene: From Tomato to Its Nutraceutical Use and Its Association with Nanotechnology. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 118, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin-Jumah, M.N.; Nadeem, M.S.; Gilani, S.J.; Mubeen, B.; Ullah, I.; Alzarea, S.I.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Alshehri, S.; Al-Abbasi, F.A.; Kazmi, I. Lycopene: A Natural Arsenal in the War against Oxidative Stress and Cardiovascular Diseases. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulawik, A.; Rosiak, N.; Miklaszewski, A.; Cielecka-Piontek, J.; Zalewski, P. Investigation of Cyclodextrin as Potential Carrier for Lycopene. Arch. Pharm. 2024, 74, 178–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulawik, A.; Kulawik, M.; Rosiak, N.; Lu, W.; Cielecka-Piontek, J.; Zalewski, P. Amorphous Lycopene–PVP K30 Dispersions Prepared by Ball Milling: Improved Solubility and Antioxidant Activity. Polymers 2025, 17, 2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Wu, Y.; Cui, Z.; Hu, L. Nutraceutical Delivery Systems to Improve the Bioaccessibility and Bioavailability of Lycopene: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 64, 6361–6379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caseiro, M.; Ascenso, A.; Costa, A.; Creagh-Flynn, J.; Johnson, M.; Simões, S. Lycopene in Human Health. LWT 2020, 127, 109323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, U.M.; Sevindik, M.; Zarrabi, A.; Nami, M.; Ozdemir, B.; Kaplan, D.N.; Selamoglu, Z.; Hasan, M.; Kumar, M.; Alshehri, M.M.; et al. Lycopene: Food Sources, Biological Activities, and Human Health Benefits. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 2713511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzocco, S.; Singla, R.K.; Capasso, A. Multifaceted Effects of Lycopene: A Boulevard to the Multitarget-Based Treatment for Cancer. Molecules 2021, 26, 5333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Jia, H.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, C.; Xu, C. Lycopene Alleviates H 2 O 2 -Induced Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Apoptosis in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells via the NFE2L2 Signaling Pathway. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 6276–6285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trejo-Solís, C.; Pedraza-Chaverrí, J.; Torres-Ramos, M.; Jiménez-Farfán, D.; Cruz Salgado, A.; Serrano-García, N.; Osorio-Rico, L.; Sotelo, J. Multiple Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of Action of Lycopene in Cancer Inhibition. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 705121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafe, M.O.; Gumede, N.M.; Nyakudya, T.T.; Chivandi, E. Lycopene: A Potent Antioxidant with Multiple Health Benefits. J. Nutr. Metab. 2024, 2024, 6252426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wu, X.; Zhuang, W.; Xia, L.; Chen, Y.; Wu, C.; Rao, Z.; Du, L.; Zhao, R.; Yi, M.; et al. Tomato and Lycopene and Multiple Health Outcomes: Umbrella Review. Food Chem. 2021, 343, 128396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabowska, M.; Wawrzyniak, D.; Rolle, K.; Chomczyński, P.; Oziewicz, S.; Jurga, S.; Barciszewski, J. Let Food Be Your Medicine: Nutraceutical Properties of Lycopene. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 3090–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, A.d.G.N.; Vasconcelos, A.G.; Souza, J.; Oliveira, A.; Gullón, B.; de Souza de Almeida Leite, J.R.; Pintado, M. Bio-Availability, Anticancer Potential, and Chemical Data of Lycopene: An Overview and Technological Prospecting. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leh, H.E.; Mohd Sopian, M.; Abu Bakar, M.H.; Lee, L.K. The Role of Lycopene for the Amelioration of Glycaemic Status and Peripheral Antioxidant Capacity among the Type II Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Case–Control Study. Ann. Med. 2021, 53, 1060–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulawik, A.; Cielecka-Piontek, J.; Czerny, B.; Kamiński, A.; Zalewski, P. The Relationship Between Lycopene and Metabolic Diseases. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, N.; Patani, P.; Singhvi, I. A Review on Tomato Lycopene. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2018, 9, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, G.C.; Sábio, R.M.; Chorilli, M. An Overview of Properties and Analytical Methods for Lycopene in Organic Nanocarriers. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2021, 51, 674–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leh, H.E.; Lee, L.K. Lycopene: A Potent Antioxidant for the Amelioration of Type II Diabetes Mellitus. Molecules 2022, 27, 2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wdowiak, K.; Pietrzak, R.; Tykarska, E.; Cielecka-Piontek, J. Hot-Melt Extrusion as an Effective Technique for Obtaining an Amorphous System of Curcumin and Piperine with Improved Properties Essential for Their Better Biological Activities. Molecules 2023, 28, 3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, Y.; Tin, Y.-Y.; Soe, M.-T.-P.; Ko, B.; Park, S.; Lee, J. Recent Technologies for Amorphization of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, W.; Löbmann, K.; McCoy, C.P.; Andrews, G.P.; Zhao, M. Microwave-Induced In Situ Amorphization: A New Strategy for Tackling the Stability Issue of Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshahrani, S.M.; Lu, W.; Park, J.-B.; Morott, J.T.; Alsulays, B.B.; Majumdar, S.; Langley, N.; Kolter, K.; Gryczke, A.; Repka, M.A. Stability-Enhanced Hot-Melt Extruded Amorphous Solid Dispersions via Combinations of Soluplus® and HPMCAS-HF. AAPS PharmSciTech 2015, 16, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Censi, R.; Gigliobianco, M.R.; Casadidio, C.; Di Martino, P. Hot Melt Extrusion: Highlighting Physicochemical Factors to Be Investigated While Designing and Optimizing a Hot Melt Extrusion Process. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, R.V.; Patil, H.; Repka, M.A. Contribution of Hot-Melt Extrusion Technology to Advance Drug Delivery in the 21st Century. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, M.F.; Pinto, R.M.A.; Simões, S. Hot-Melt Extrusion in the Pharmaceutical Industry: Toward Filing a New Drug Application. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 1749–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, H.; Tiwari, R.V.; Repka, M.A. Hot-Melt Extrusion: From Theory to Application in Pharmaceutical Formulation. AAPS PharmSciTech 2016, 17, 20–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Repka, M.A.; Bandari, S.; Kallakunta, V.R.; Vo, A.Q.; McFall, H.; Pimparade, M.B.; Bhagurkar, A.M. Melt Extrusion with Poorly Soluble Drugs—An Integrated Review. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 535, 68–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.-Y.; Hsieh, Y.-S.; Ko, H.-H.; Wu, Y.-T. Formulation Approaches to Crystalline Status Modification for Carotenoids: Impacts on Dissolution, Stability, Bioavailability, and Bioactivities. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strojewski, D.; Krupa, A. Kollidon® VA 64 and Soluplus® as Modern Polymeric Carriers for Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Polim. Med. 2022, 52, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guembe-Michel, N.; Nguewa, P.; González-Gaitano, G. Soluplus®-Based Pharmaceutical Formulations: Recent Advances in Drug Delivery and Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba, A.I.O.; Hurtado, M.C.; Mata, M.C.S.; Ruiz, V.F.; Tejada, M.L.S.D. Application of a UV–Vis Detection-HPLC Method for a Rapid Determination of Lycopene and β-Carotene in Vegetables. Food Chem. 2006, 95, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studzińska-Sroka, E.; Paczkowska-Walendowska, M.; Woźna, Z.; Plech, T.; Szulc, P.; Cielecka-Piontek, J. Elderberry Leaves with Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties as a Valuable Plant Material for Wound Healing. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosiak, N.; Tykarska, E.; Cielecka-Piontek, J. Enhanced Antioxidant and Neuroprotective Properties of Pterostilbene (Resveratrol Derivative) in Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosiak, N.; Tykarska, E.; Cielecka-Piontek, J. Amorphous Pterostilbene Delivery Systems Preparation—Innovative Approach to Preparation Optimization. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunghez, I.R.; Raduly, M.; Doncea, S.; Aksahin, I.; Ion, R.M. Lycopene Determination in Tomatoes by Different Spectral Techniques (UV-VIS, FTIR and HPLC). Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2011, 6, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar]
- Yilmaz, T.; Kumcuoglu, S.; Tavman, S. Ultrasound Assisted Extraction of Lycopene and β–Carotene from Tomato Processing Wastes. Ital. J. Food Sci. 2017, 29, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonyali, B.; Sensoy, I.; Karakaya, S. The Effect of Extrusion on the Functional Components and in Vitro Lycopene Bioaccessibility of Tomato Pulp Added Corn Extrudates. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirahmadi, M.; Kamali, H.; Azimi-Hashemi, S.; Lavaee, P.; Gharaei, S.; Sherkatsadi, K.; Pourhossein, T.; Baharara, H.; Nejabat, M.; Ghafourian, T.; et al. Evaluation of Novel Carriers for Enhanced Dissolution of Lycopene. Food Meas. 2024, 18, 4718–4732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhong, L.; Peng, Z.; Liu, X.; Ouyang, D.; Guan, S. Development of a Highly Water-Soluble Lycopene Cyclodextrin Ternary Formulation by the Integrated Experimental and Modeling Techniques. AAPS PharmSciTech 2021, 22, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arballo, J.; Amengual, J.; Erdman, J.W. Lycopene: A Critical Review of Digestion, Absorption, Metabolism, and Excretion. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faisal, W.; Ruane-O’Hora, T.; O’Driscoll, C.M.; Griffin, B.T. A Novel Lipid-Based Solid Dispersion for Enhancing Oral Bioavailability of Lycopene—In Vivo Evaluation Using a Pig Model. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 453, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, G.A.; Fávaro-Trindade, C.S.; Grosso, C.R.F. Microencapsulation of Lycopene by Spray Drying: Characterization, Stability and Application of Microcapsules. Food Bioprod. Process. 2012, 90, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jara, M.O.; Behrend-Keim, B.; Bedogni, G.; Michelena, L.V.; Davis, D.A.; Miller, D.A.; Salomon, C.; Williams, R.O. Comparative Study of Hot-Melt Extrusion, Spray Drying, and KinetiSol® Processing to Formulate a Poorly Water-Soluble and Thermolabile Drug. Int. J. Pharm. 2025, 676, 125582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan-Shoar, Z.; Mandimika, T.; Hardacre, A.K.; Reynolds, G.W.; Brennan, C.S. Lycopene Bioaccessibility and Starch Digestibility for Extruded Snacks Enriched with Tomato Derivatives. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 12047–12053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Gujral, H.S.; Singh, B. Antioxidant Activity of Barley as Affected by Extrusion Cooking. Food Chem. 2012, 131, 1406–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kulawik, A.; Kulawik, M.; Rosiak, N.; Lu, W.; Kryszak, A.; Cielecka-Piontek, J.; Zalewski, P. Improving the Pharmaceutical Potential of Lycopene Using Hot-Melt Extrusion. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 12311. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212311
Kulawik A, Kulawik M, Rosiak N, Lu W, Kryszak A, Cielecka-Piontek J, Zalewski P. Improving the Pharmaceutical Potential of Lycopene Using Hot-Melt Extrusion. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(22):12311. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212311
Chicago/Turabian StyleKulawik, Anna, Maciej Kulawik, Natalia Rosiak, Wei Lu, Aleksandra Kryszak, Judyta Cielecka-Piontek, and Przemysław Zalewski. 2025. "Improving the Pharmaceutical Potential of Lycopene Using Hot-Melt Extrusion" Applied Sciences 15, no. 22: 12311. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212311
APA StyleKulawik, A., Kulawik, M., Rosiak, N., Lu, W., Kryszak, A., Cielecka-Piontek, J., & Zalewski, P. (2025). Improving the Pharmaceutical Potential of Lycopene Using Hot-Melt Extrusion. Applied Sciences, 15(22), 12311. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212311









