Predicting Surface Subsidence in Northern Huainan Based on a Hybrid LSTM–Transformer Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Overview of the Study Area and Research Data
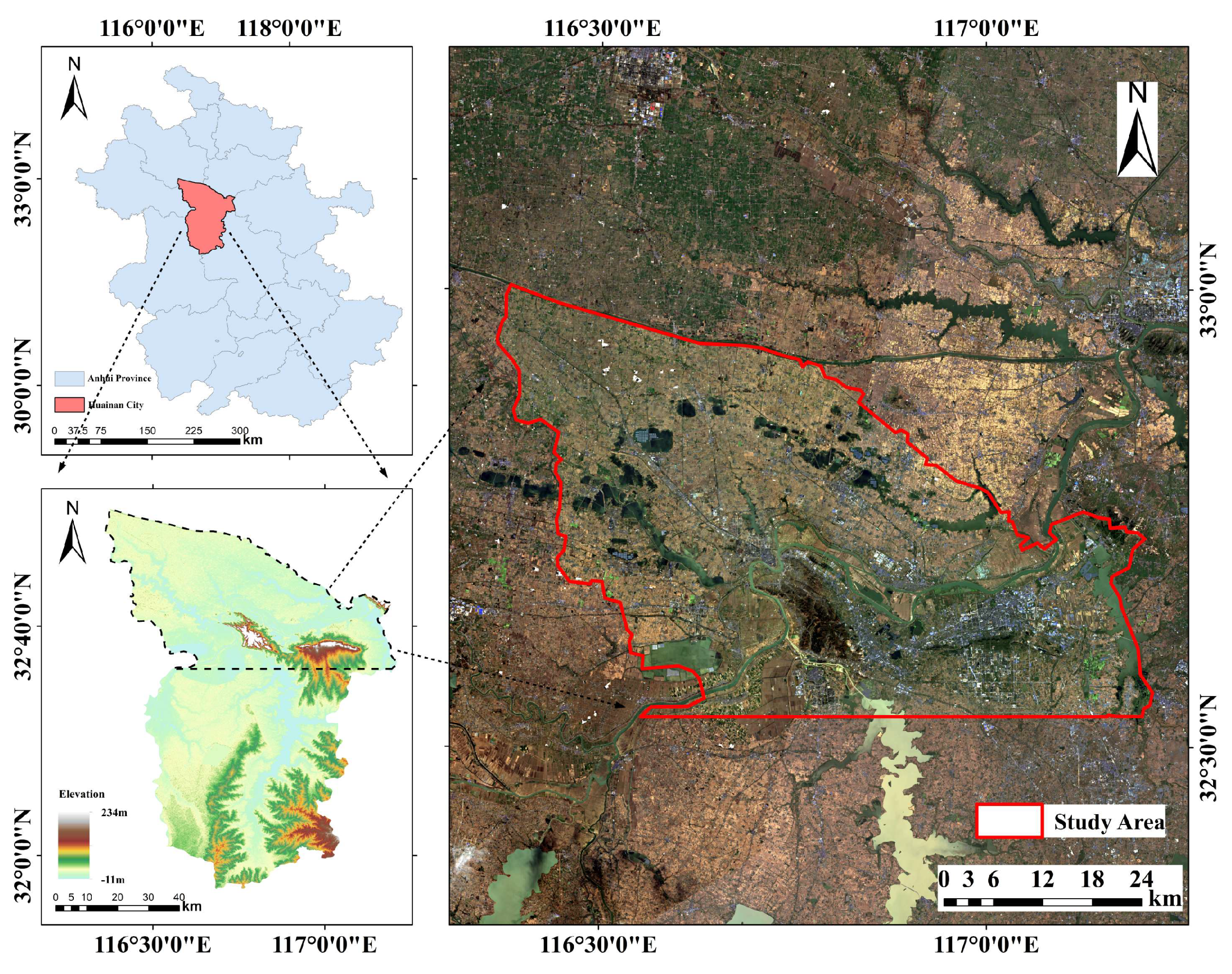
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Research Data
3. Methodology
3.1. SBAS-InSAR Processing
3.2. Model Architecture Choice
3.3. LSTM Long Short-Term Memory Network
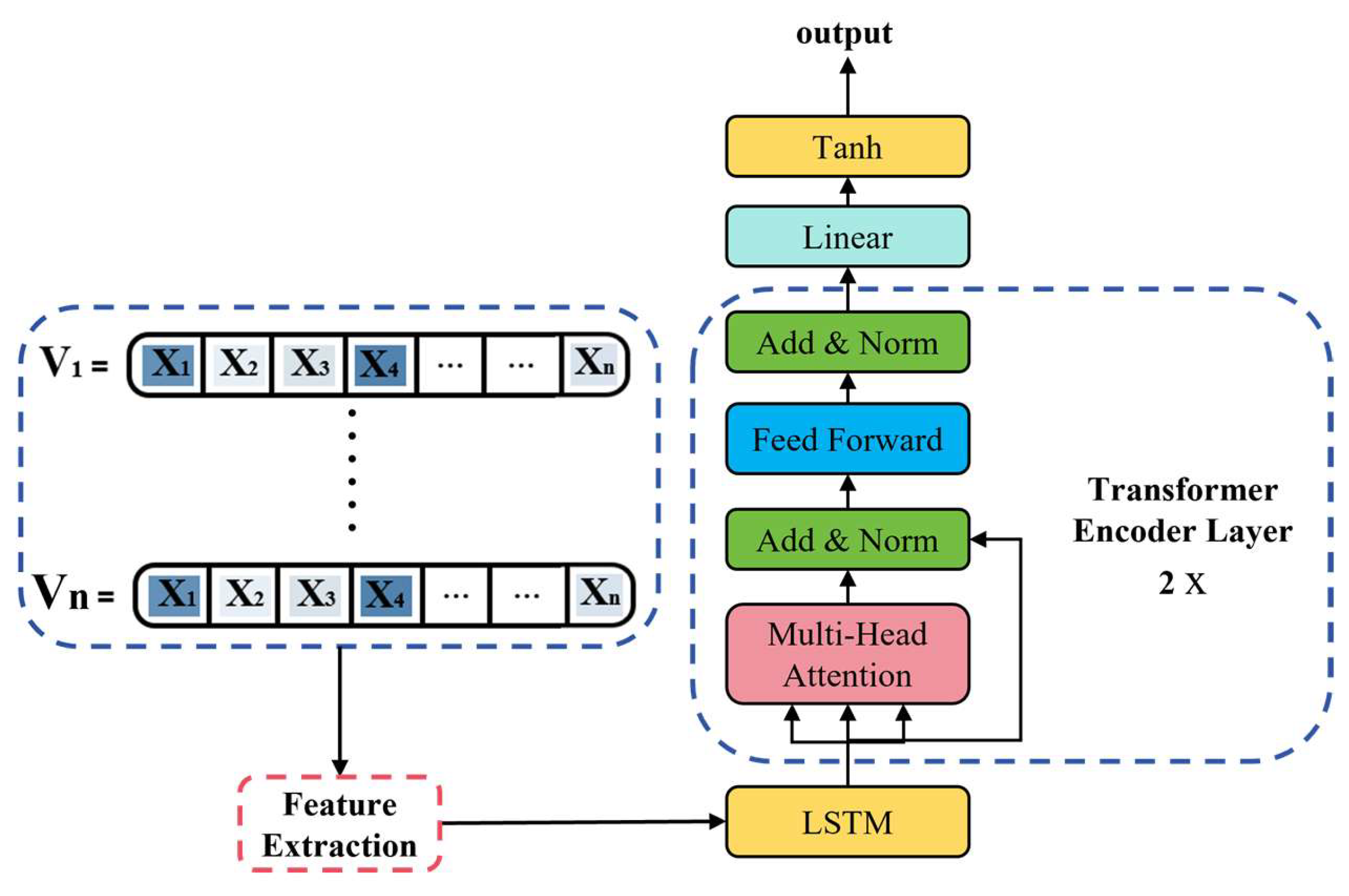
3.4. LSTM–Transformer Model
3.5. Module Ablation Test
3.6. Prediction Accuracy Evaluation Metrics
4. Results
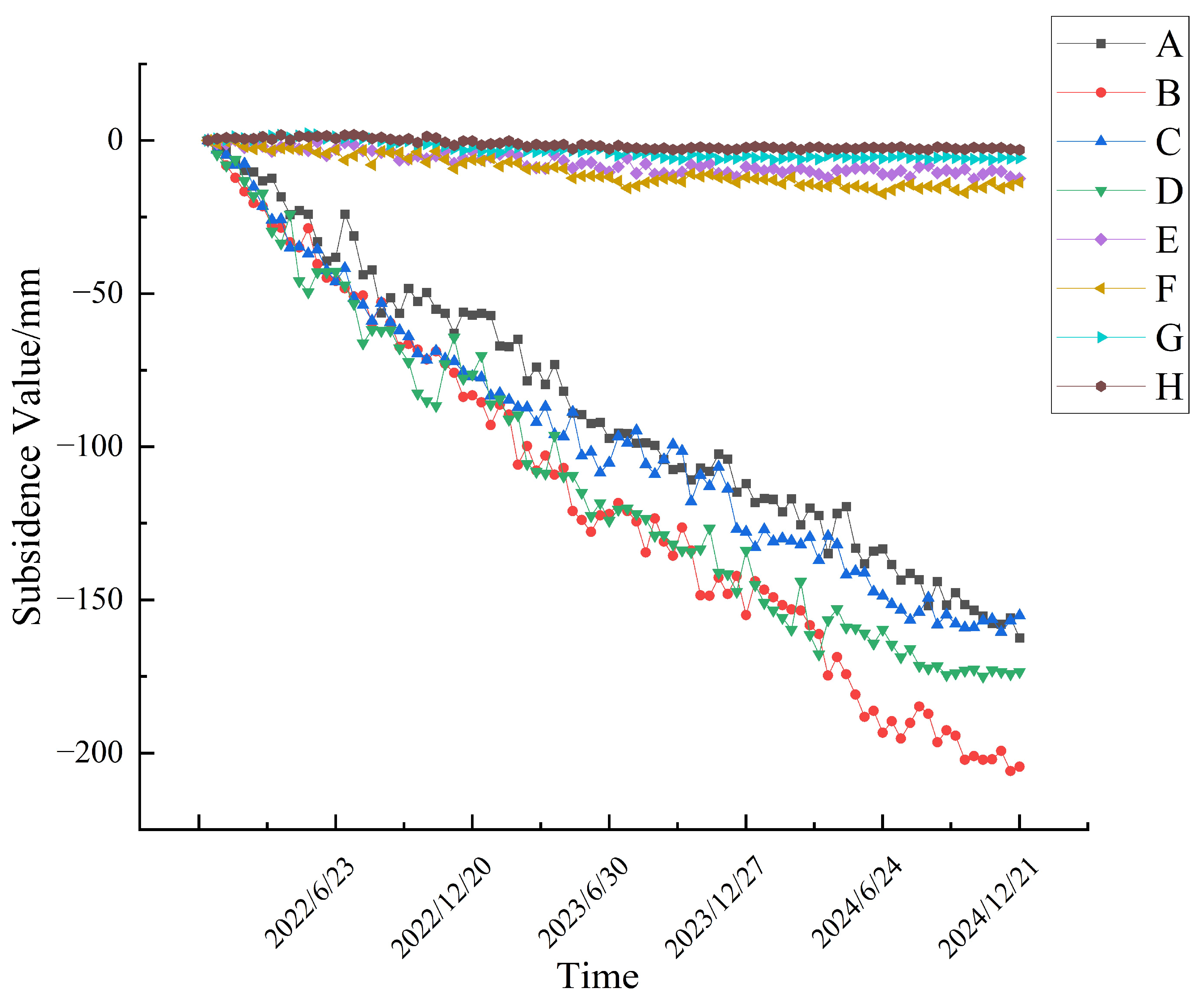
4.1. Subsidence Rate Analysis
4.2. Accuracy Validation
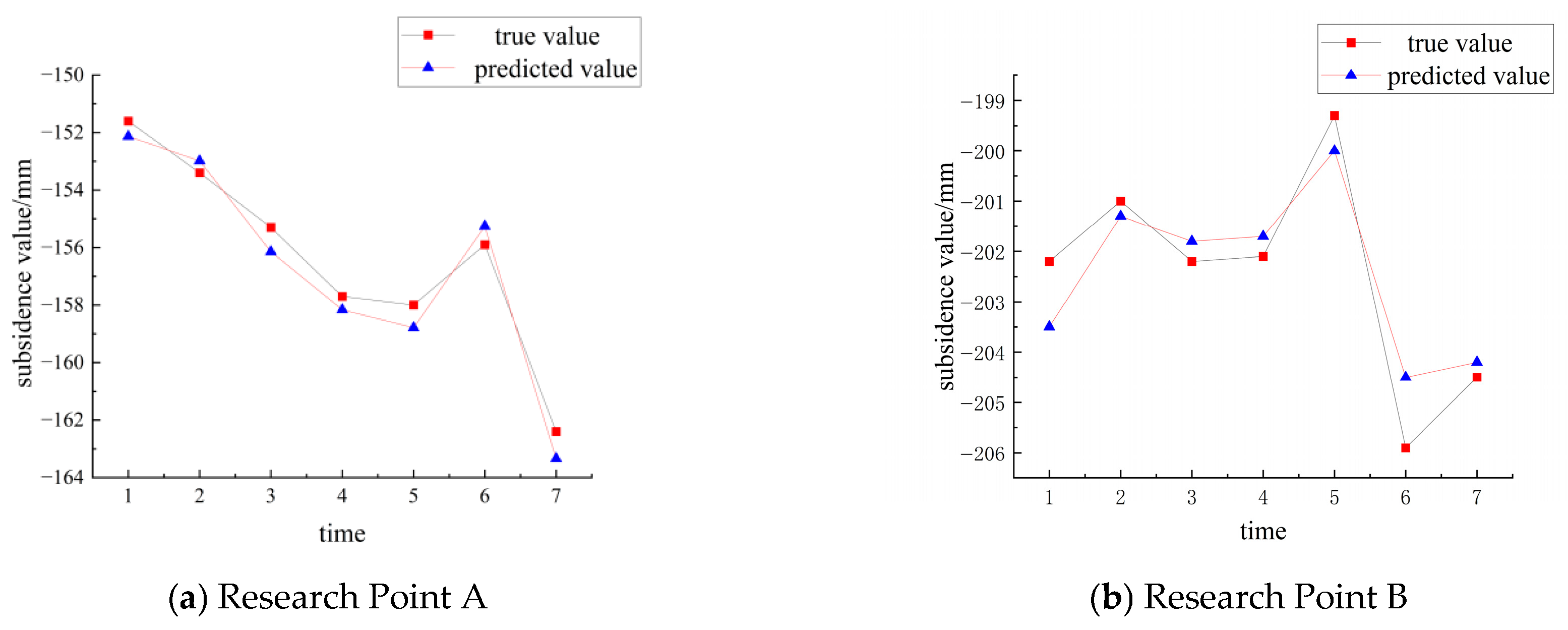
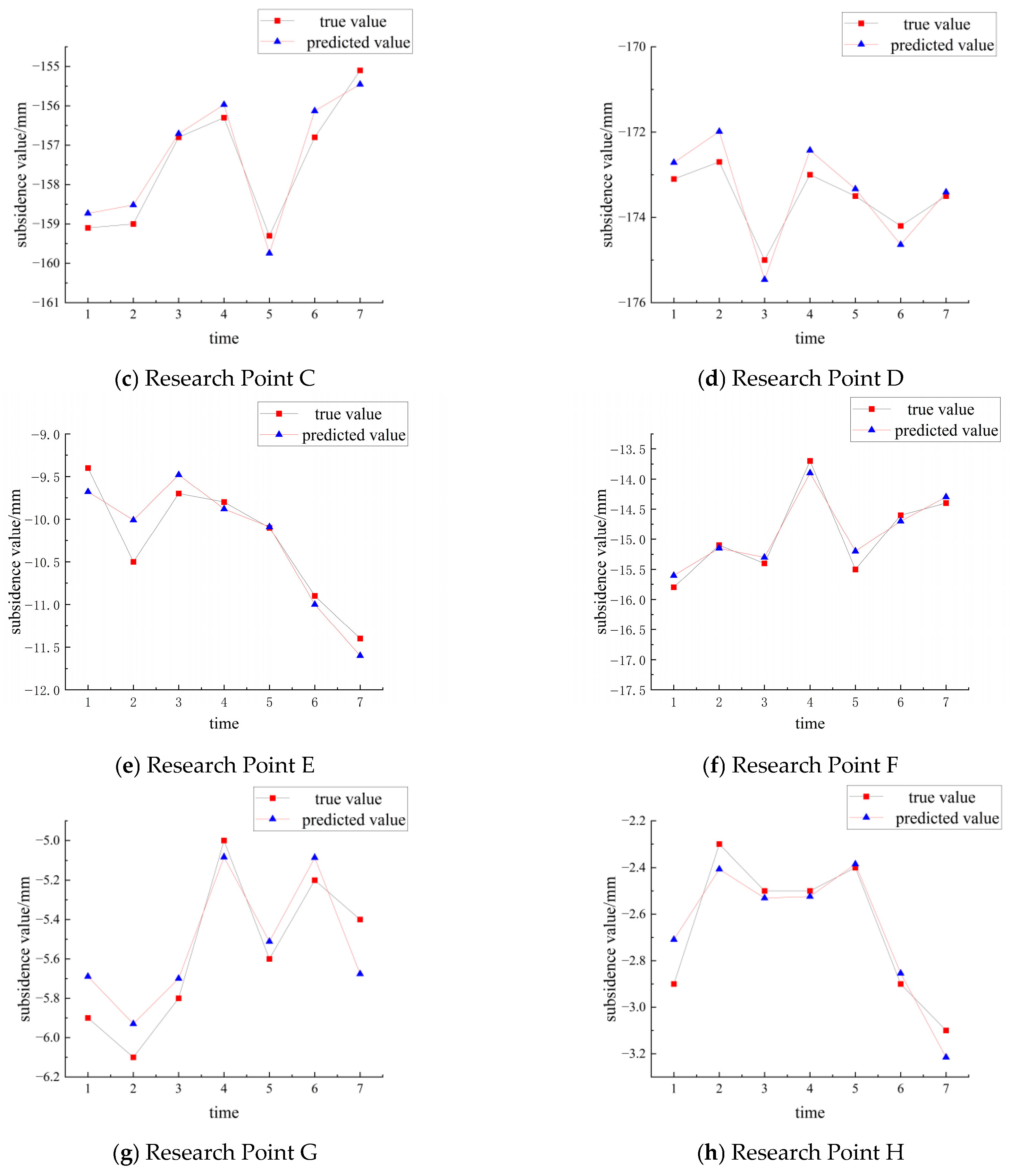
4.3. Prediction Results and Analysis
5. Conclusions and Discussion
- By utilizing time-series settlement data obtained through SBAS-InSAR technology, effective classification and management of the mining area, urban area, and decommissioned mining sites were achieved, providing a solid data foundation for differentiated modeling. The LSTM–Transformer model demonstrated high accuracy in predicting settlement across all three areas, with the RMSE consistently maintained between 1 and 2 mm. These results underscore the feasibility and practical application of this method in the fine monitoring and prediction of surface settlement.
- A comparison of the LSTM–Transformer model’s predictions with the actual data demonstrates a high degree of consistency, highlighting the model’s strong predictive performance and reliability. The integration of SBAS-InSAR technology with the LSTM–Transformer model not only enhances the accuracy of surface settlement monitoring and prediction but also provides a solid scientific foundation and technical support for early warning and mitigation of settlement-related disasters.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.X.; Yuan, X.P.; Gan, S.; Peng, X.; Wang, S. Application of time series lnSAR technology in surface subsidence monitoring and spatio-temporal evolution analysis in mining area. Bull. Surv. Mapp. 2025, 3, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.X.; Pan, J.P.; Zhao, R.Q.; Cai, Z.Y.; Li, P.X. Monitoring Urban Surface Subsidence in the Main Urban Area of Chongqing Using Time-Series InSAR Technology. J. Geomat. 2024, 49, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, A.E.E.; Ingalls, R.P. Venus: Mapping the surface reflectivity by radar interferometry. Science 1969, 165, 797–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.H.; Cai, G.L.; Gan, Q.; Shen, D. Early identification of the jiangdingya landslide of zhouqu based on SBAS-InSAR technology. Earthq. Res. China 2020, 34, 510–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aymar, P.; Luis, M. Seismic risk regularization for urban changes due to earthquakes: A case of study of the 2023 turkey earthquake sequence. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Li, T.; Xia, Y. Study on Urban Area Subsidence Monitoring Based on InSAR Technique. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2008, 33, 850–853. [Google Scholar]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, J.; Babaee, F.; Mahmoudnia, P.; Kia, M.S. Integrated spatiotemporal data mining and DInSAR for improved understanding of subsidence related to groundwater depletion impacts. J. Geogr. Sci. 2025, 35, 598–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.M.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, H.W.; Liu, J.; Jing, Z.H. Land subsidence monitoring and building risk assessment using InSAR and machine learning in a loess plateau city—A case study of Lanzhou, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2851. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-4292/15/11/2851 (accessed on 5 May 2025). [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Sui, L.C.; Lian, W. Prediction of mine subsidence based on insar technology and the LSTM algorithm: A case study of the Shigouyi coalfield, Ningxia (China). Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2755. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-4292/15/11/2755 (accessed on 5 May 2025). [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yu, S.W.; Tao, Q.X.; Liu, G.L.; Wang, L.Y.; Wang, F.Y. Accuracy verification and correction of D-InSAR andSBAS-InSAR in monitoring mining surface subsidence. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4365. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-4292/13/21/4365 (accessed on 5 May 2025). [CrossRef]
- He, Y.F.; Zhang, G.G.; Kaufmann, H.; Xu, G.C. Automatic interferogram selection for sbas-insar based on deep convolutional neural networks. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4468. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-4292/13/21/4468 (accessed on 5 May 2025). [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Deng, K.Z.; Gao, X.X.; Niu, H.P. Monitoring and analysis of surface subsidence in Mining areas based on SBAS-InSAR. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2018, 43, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, C.; Tian, X.J.; Zhao, Y. Monitoring and analysis of ground subsidence in Weishan County based on SBAS-InSAR technology. Coal Sci. Technol. Mag. 2024, 45, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.J.; Shi, M.Y. Monitoring and analysis of land subsidence in Wuhan based on SBAS-InSAR technology. Sci. Technol. Innov. 2022, 33, 42–45. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, W.; Chen, Z.P.; Xu, B.; Feng, Z.X. Long time-series of surface deformation monitoring and cause analysis in Balyun district, Guangzhou base on SBAS-InSAR technology. Bull. Surv. Mapp. 2023, 4, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.J.; Zhu, J.J.; Li, Z.W.; Ding, X.L.; Wang, C.C. A study on deformation monitoring in Mining areas based on SBAS. J. Geod. Geoinf. Sci. 2011, 40, 52–58. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Feng, Y.J.; Tong, X.H.; Li, P.S.; Wang, J.F.; Tang, P.L.; Tang, X.Y.; Xi, M.G.; Zhou, Y. Large-scale surface deformation monitoring using sbas-insar and intelligent prediction in typical cities of yangtze river delta. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.L.; Lu, Y.Y.; Li, M.C.; Zhou, Z. Land subsidence characteristics of cpec as revealed by SBAS-InSAR—A case of gwadar port pakistan. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2022, 31, 1550–1560. [Google Scholar]
- Harintaka, H.; Suhadha, A.G.; Syetiawan, A.; Ardha, M.; Rarasati, A. Current land subsidence in jakarta: A multi-track SBAS-InSAR analysis during 2017–2022 using C-band SAR data. Geocarto Int. 2024, 39, 2364726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Pan, B.; Afzal, Z.; Sajjad, M.M.; Kakar, N.; Ahmed, N.; Hussain, W.; Ali, M. SBAS-InSAR analysis of tectonic derived ground deformation and subsidence susceptibility mapping via machine learning in quetta city, pakistan. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2025, 18, 2441926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhe, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.X.; Wang, K.; Zhang, K.; Wu, R. Monitoring and predicting mining subsidence in mining areas through SBAS-InSAR and CNN-LSTM. J. Saf. Environ. 2024, 24, 3429–3438. [Google Scholar]
- Majeed, M.A.; Shafri, H.Z.M.S.; Zulkafli, Z.; Wayayok, A. A deep learning approach for dengue fever prediction in malaysia using lstm with spatial attention. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.J.; Lei, D.X.; Yuan, J.; Le, H.J.; Shan, W.F.; Li, L.C.; Wang, H.R.; Li, Z.; Yuan, G.M. Lonospheric TEC prediction based on Attention-LSTM. Chin. J. Geophys. 2024, 67, 439–451. [Google Scholar]
- Sang, S.; Li, L. A novel variant of lstm stock prediction method incorporating attention mechanism. Mathematics 2024, 12, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayad, A.; Amrani, M.; Bakkali, S. Quantification of the disturbances of phosphate series using the box-counting method on geoelectrical images (sidi chennane, morocco). Int. J. Geophys. 2019, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayad, A.; Tagma, T. Lithostratigraphic and seismic investigation of the weathered zone in the exploration of deep petroleum structures (Boujdour area, Morocco). Egypt. J. Pet. 2024, 33, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sensor | Orbit Direction | Revisit Period | Polarization Mode | Operating Mode | Number of Images/Scenes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sentinel-1A | Ascending | 12d | VV | IW | 90 |
| Parameters | Settings |
|---|---|
| Number of LSTM Layers | 64 |
| Number of Transformer Layers | 64 |
| Number of Transformer Encoder Layers | 2 |
| Number of Attention Heads | 4 |
| Input Windows | 32 |
| Output Length | 7 |
| Learning Rate | 0.001 |
| Optimizer | Adam |
| Batch Size | 16 |
| Dropout Rate | 0.1 |
| Activation Function | Tanh |
| Loss Function | MSE |
| Epochs | 200 |
| Research Point | Subsidence Rate mm/yr | LSTM | Transformer | LSTM–Transformer | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE/mm | MAE/mm | RMSE/mm | MAE/mm | RMSE/mm | MAE/mm | ||
| A | −52.52 | 2.39 | 2.02 | 2.25 | 1.98 | 2.20 | 1.71 |
| B | −68.14 | 3.73 | 3.35 | 3.59 | 3.36 | 3.52 | 3.08 |
| C | −51.28 | 2.94 | 2.48 | 2.87 | 2.37 | 2.84 | 2.34 |
| D | −58.38 | 2.61 | 2.10 | 2.59 | 2.01 | 2.16 | 1.67 |
| E | −3.60 | 1.43 | 1.21 | 1.25 | 1.08 | 1.03 | 0.81 |
| F | −5.38 | 1.74 | 1.15 | 1.53 | 1.41 | 1.39 | 1.12 |
| G | −2.62 | 1.13 | 1.24 | 0.88 | 0.79 | 0.31 | 0.26 |
| H | −1.25 | 0.87 | 0.79 | 0.74 | 0.63 | 0.22 | 0.17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, J.; Tan, H.; Liu, R.; Duan, J.; Zhu, M. Predicting Surface Subsidence in Northern Huainan Based on a Hybrid LSTM–Transformer Model. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 11780. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111780
Xu J, Tan H, Liu R, Duan J, Zhu M. Predicting Surface Subsidence in Northern Huainan Based on a Hybrid LSTM–Transformer Model. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(21):11780. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111780
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Jia, Hao Tan, Roucen Liu, Jinling Duan, and Mingfei Zhu. 2025. "Predicting Surface Subsidence in Northern Huainan Based on a Hybrid LSTM–Transformer Model" Applied Sciences 15, no. 21: 11780. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111780
APA StyleXu, J., Tan, H., Liu, R., Duan, J., & Zhu, M. (2025). Predicting Surface Subsidence in Northern Huainan Based on a Hybrid LSTM–Transformer Model. Applied Sciences, 15(21), 11780. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111780





