A Bayesian Grid-Free Framework with Global Optimization for Three-Dimensional Acoustic Source Imaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
- a.
- Based on a Bayesian inference model, the negative log-posterior of the source positions is established as the fitness function, replacing the conventional CSM energy function and improving the accuracy of source localization.
- b.
- A global optimization algorithm is introduced to estimate source positions, replacing the HMC sampling procedure and enhancing the computational efficiency of source localization.
2. Problem Statement
3. The Theoretical Description of BGG Method
3.1. 3D Grid-Free Bayesian Inference Model
3.2. Derivation of the Fitness Function
3.3. Source Position Estimation Based on the Global Optimization Algorithm
3.4. Updating Source Strength, Noise, and Position Hyperparameters
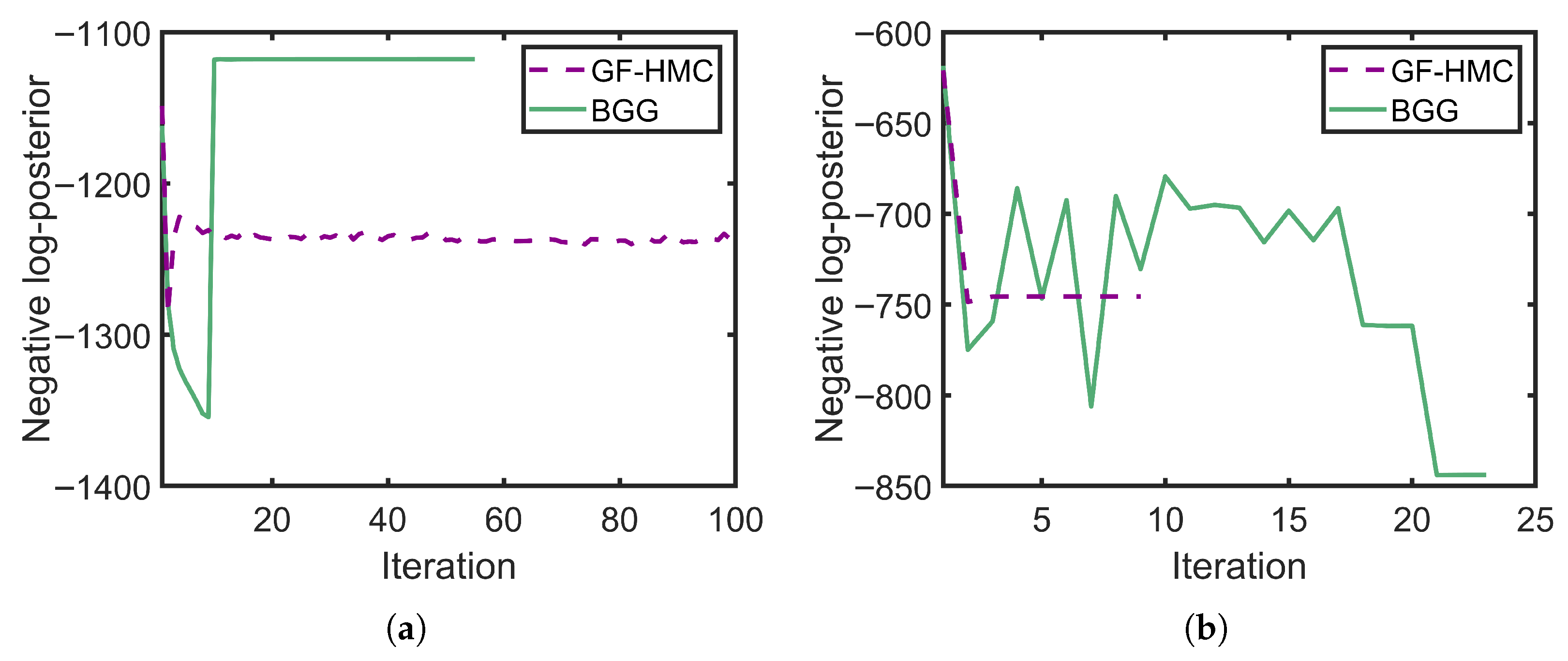
3.5. Termination Criteria and Algorithm Procedure
| Algorithm 1: Bayesian grid-free framework with global optimization for three-dimensional acoustic source imaging (BGG) |
| Input: Initial source positions , initial covariance matrix ,, , measured data , iteration steps K, number of Equivalent Sources N, convergence threshold Output: Final source positions r, final covariance matrix  |
4. Simulations and Experiments on Spatially Distributed Acoustic Source Localization
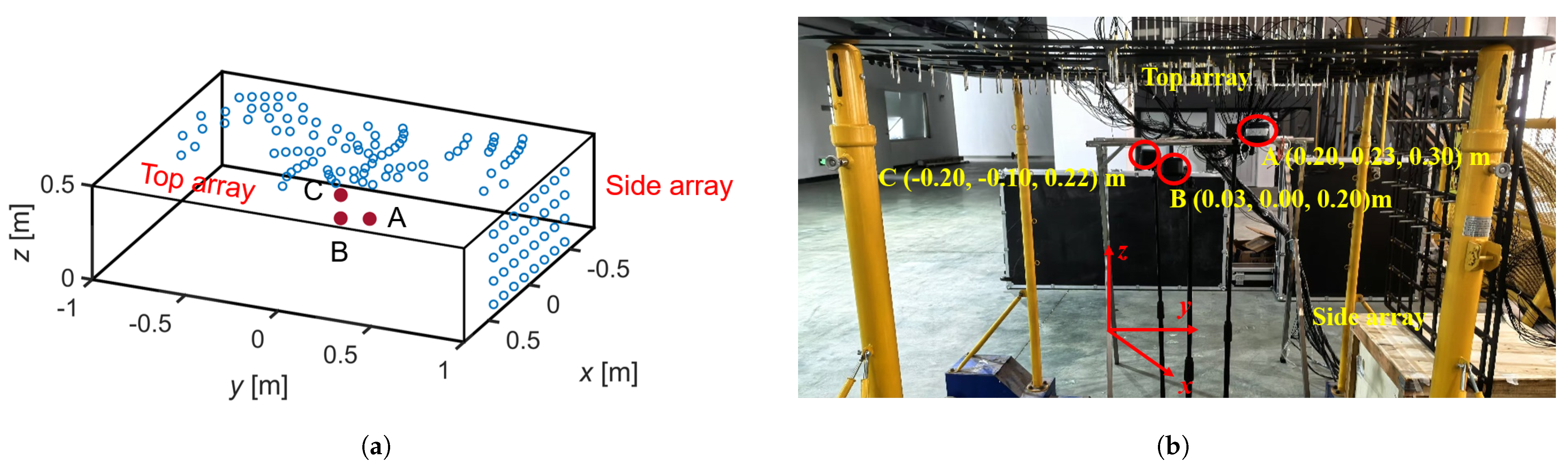
4.1. Simulation and Experiment Setup
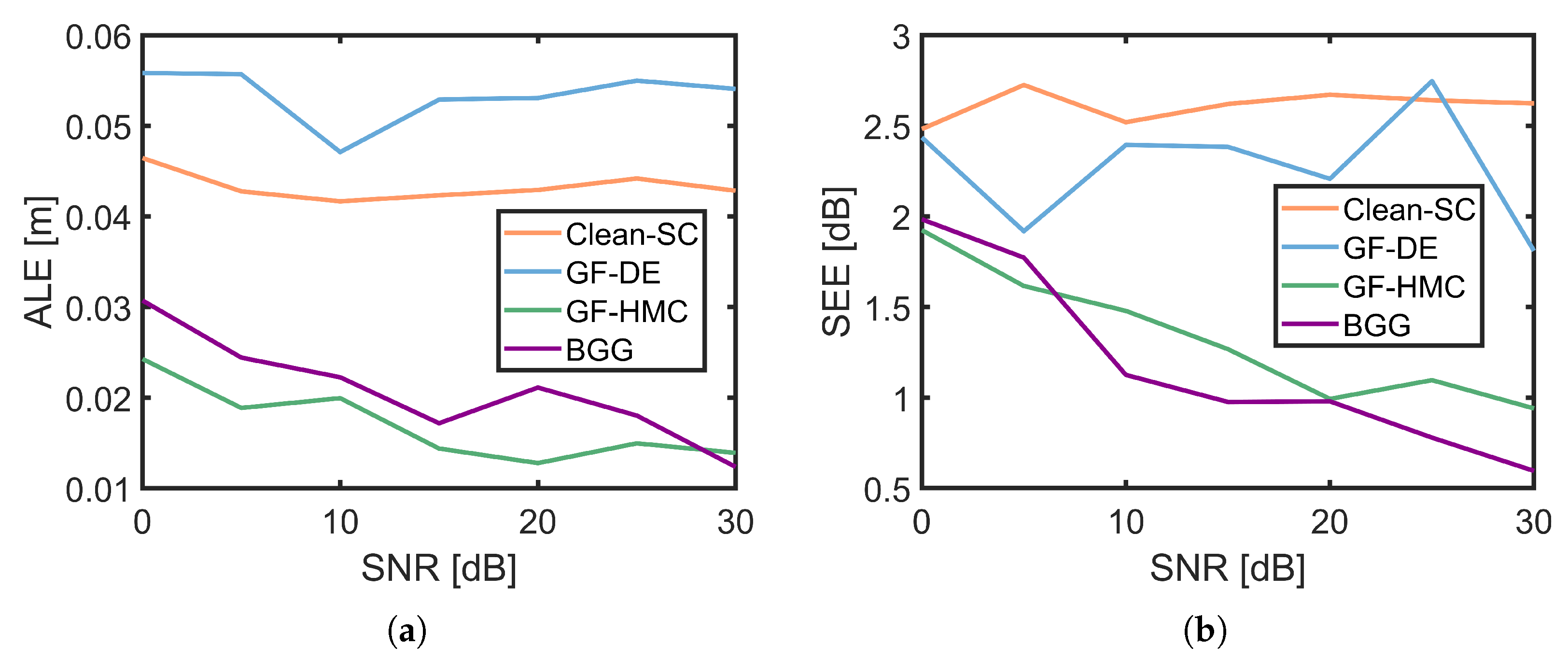
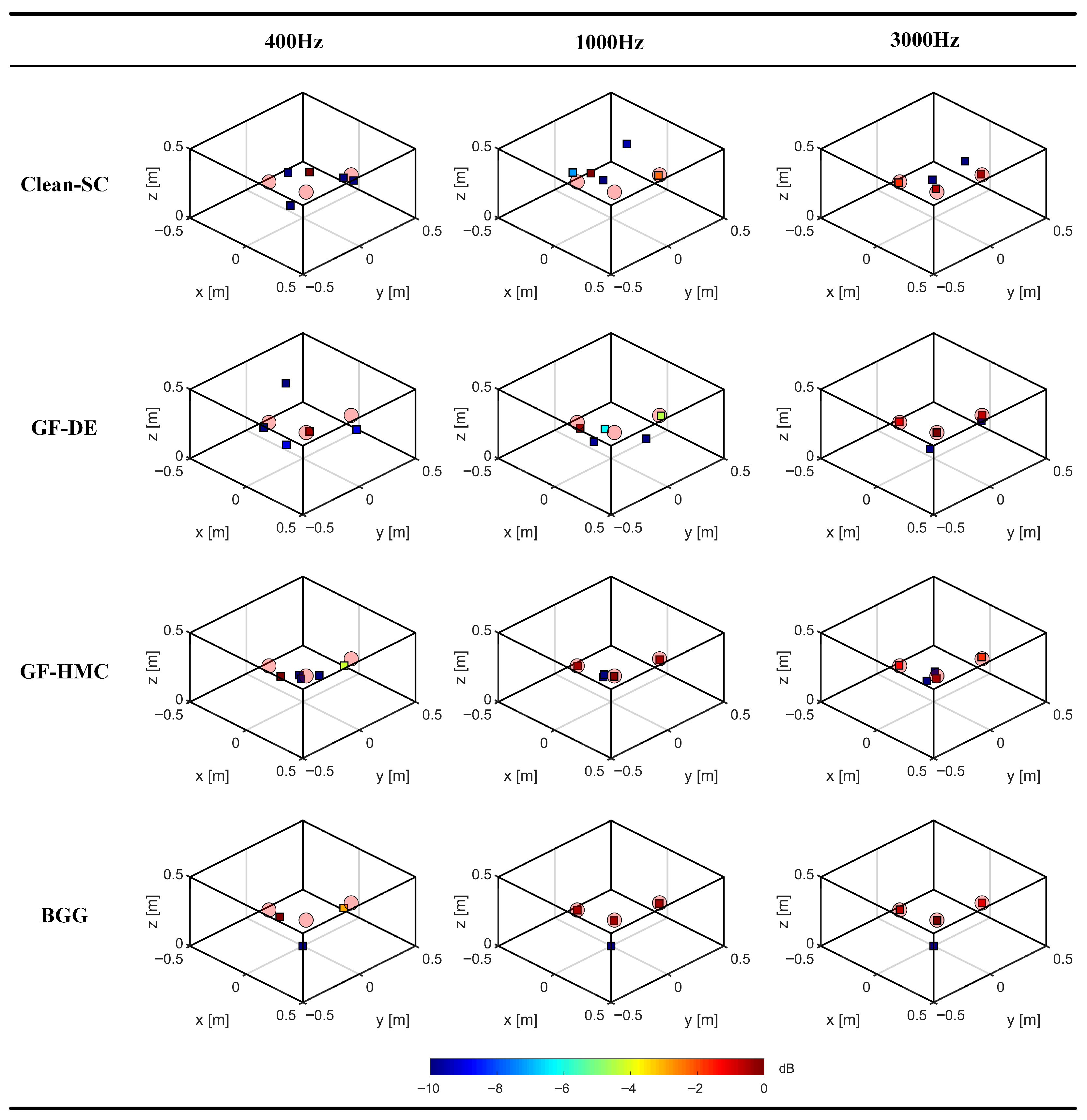
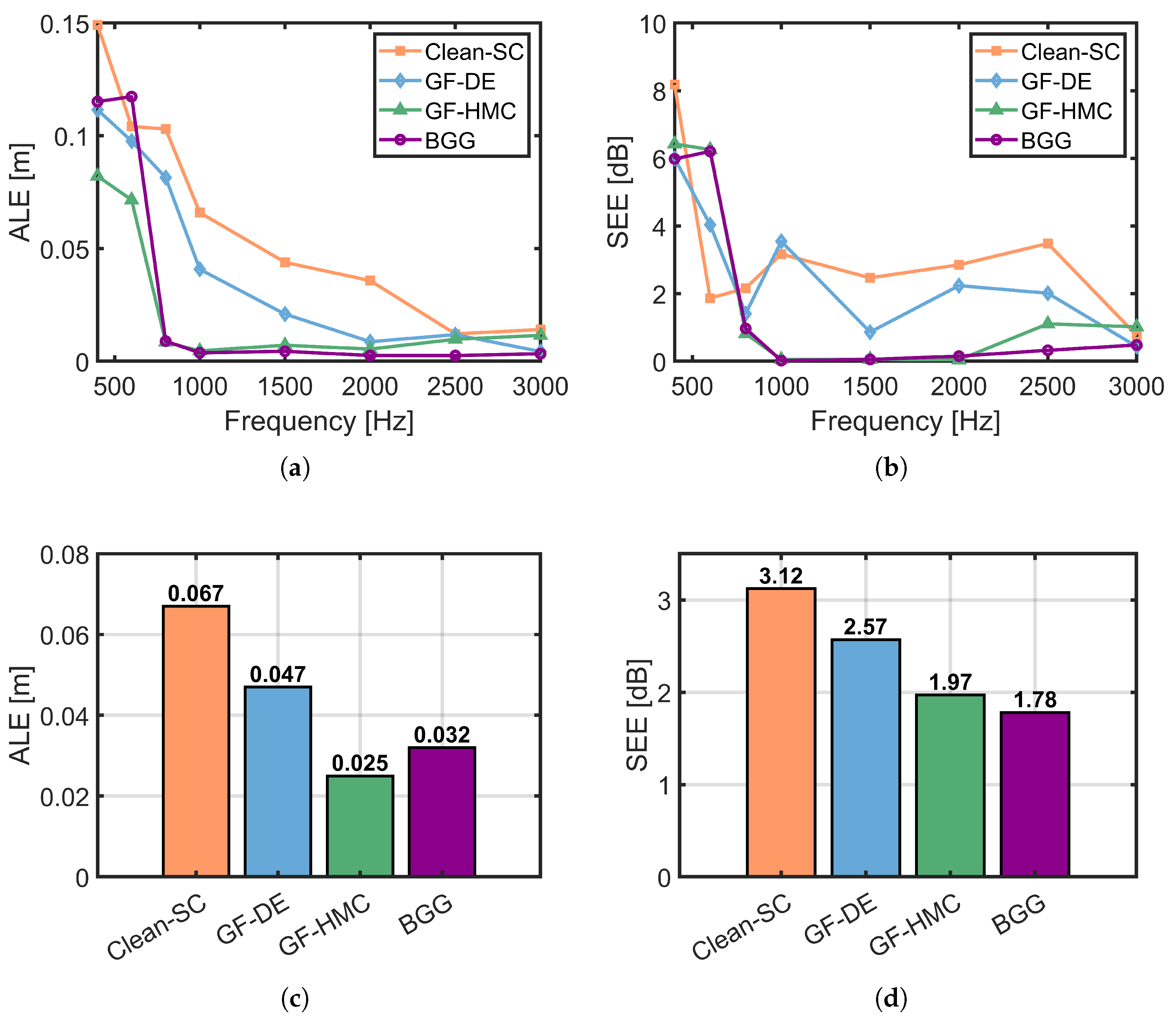
4.2. Simulation Results and Analysis
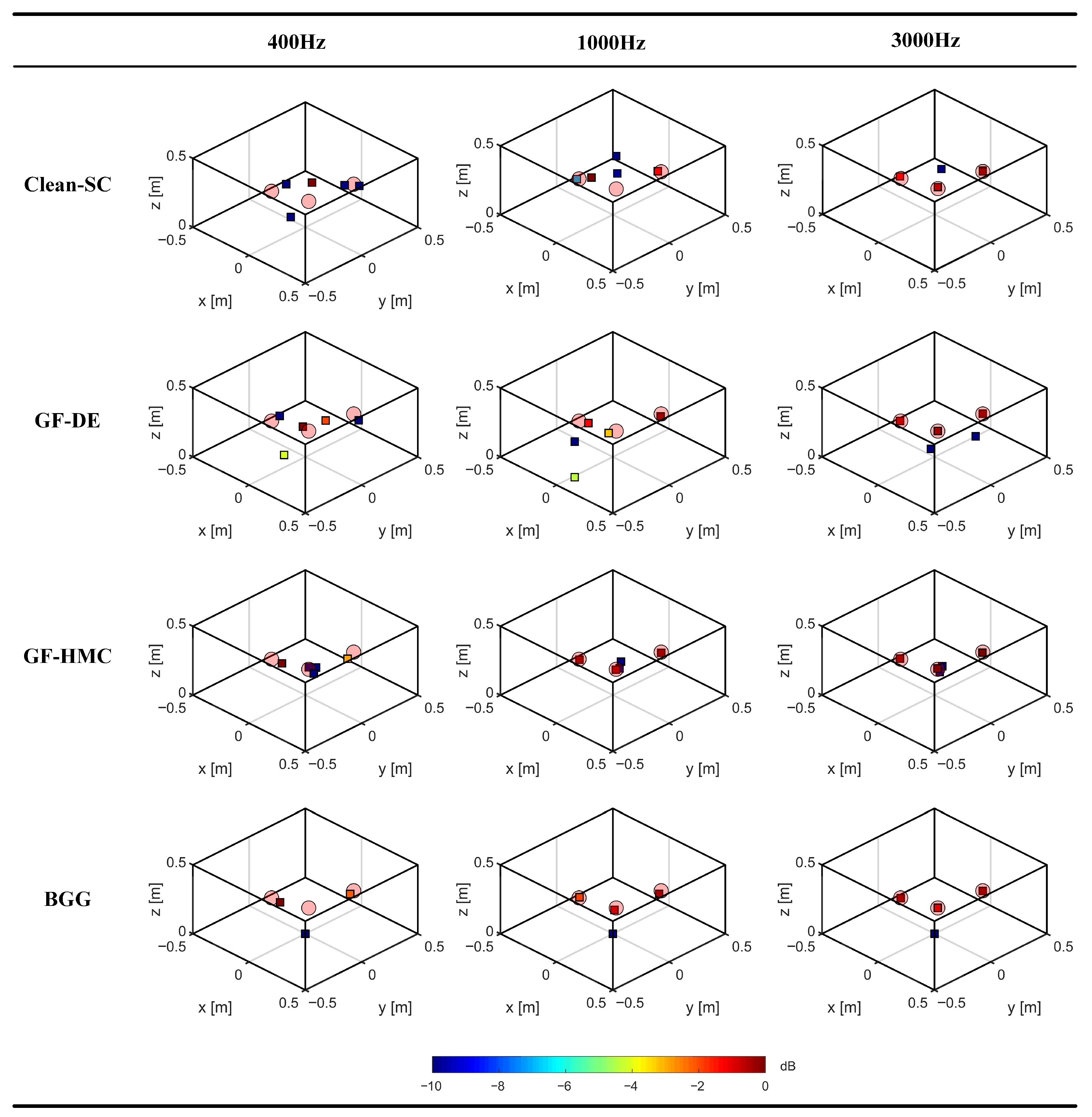
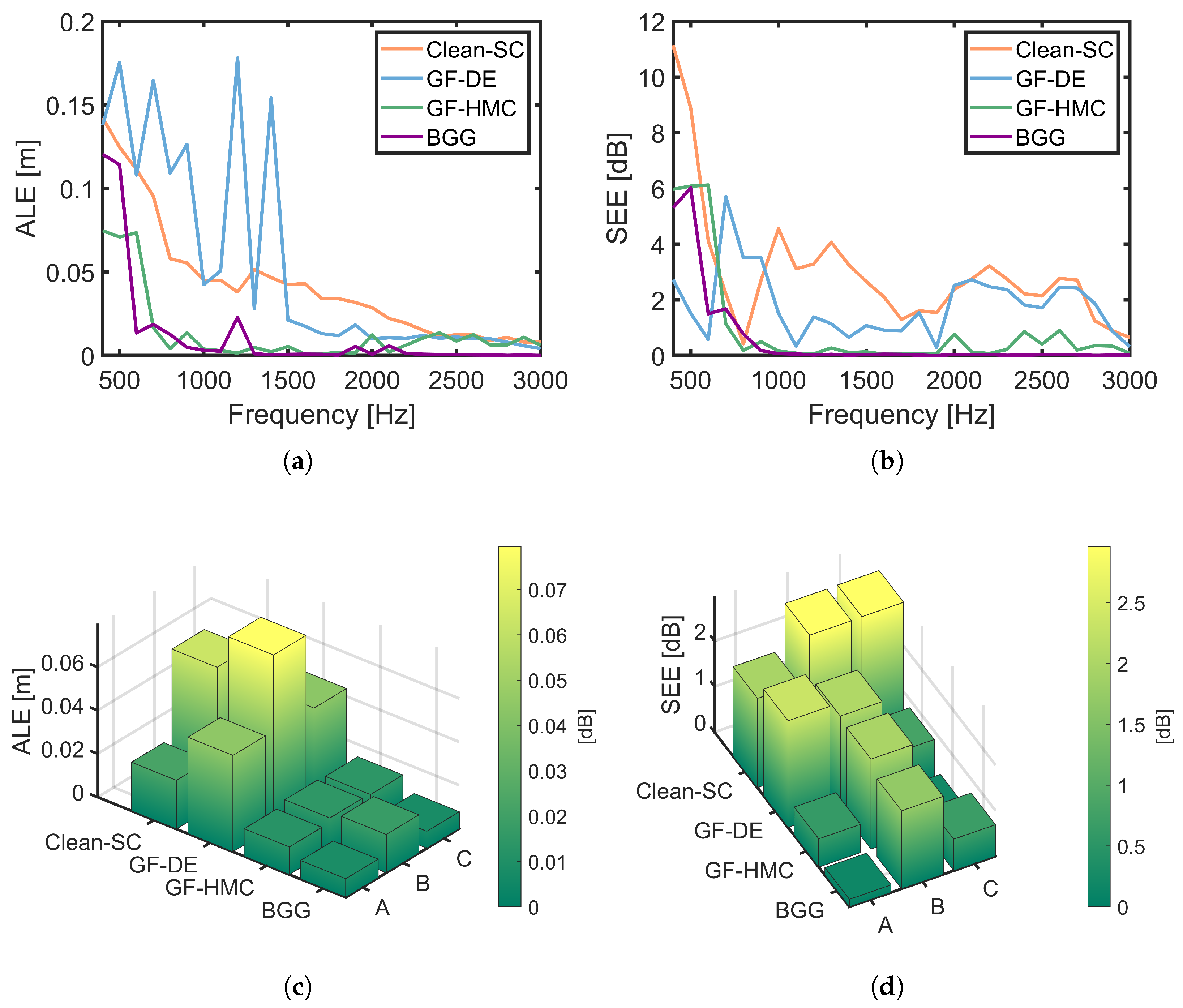
4.3. Experiment Results and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amoiridis, O.; Zarri, A.; Zamponi, R.; Pasco, Y.; Yakhina, G.; Christophe, J.; Moreau, S.; Schram, C. Sound Localization and Quantification Analysis of an Automotive Engine Cooling Module. J. Sound Vib. 2022, 517, 116534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, J.A.; Sarradj, E.; Fernández, M.D.; Geyer, T.; Ballesteros, M.J. Noise Source Identification with Beamforming in the Pass-by of a Car. Appl. Acoust. 2015, 93, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.; Rahman, M.M.; Hickey, J.-P. Recent Advances in Passive Acoustic Localization Methods via Aircraft and Wake Vortex Aeroacoustics. Fluids 2022, 7, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, H.; Huang, X.; Zhang, X. An Overview of Testing Methods for Aeroengine Fan Noise. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2021, 124, 100722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Wang, T.; Yang, H.; Chu, F. Damage Identification of Wind Turbine Blades Using an Adaptive Method for Compressive Beamforming Based on the Generalized Minimax-Concave Penalty Function. Renew. Energ. 2021, 181, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xue, Y.; He, C.; Zhao, Y. Review of the Typical Damage and Damage-Detection Methods of Large Wind Turbine Blades. Energies 2022, 15, 5672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Antoni, J.; Wu, H.; Leclère, Q.; Jiang, W. Fast Iteration Algorithms for Implementing the Acoustic Beamforming of Non-Synchronous Measurements. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 134, 106309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, C.; Yu, L.; Li, J. Sparsity-Enhanced Equivalent Source Method for Acoustic Source Reconstruction via the Generalized Minimax-Concave Penalty. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 167, 108508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Yu, L.; Wei, L.; Shi, Y.; Pan, W.; Li, M. Acoustic Inversion Method Based on the Shear Flow Green’s Function for Sound Source Localization in Open-Jet Wind Tunnels. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2024, 220, 111650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Yin, S. Two-Dimensional Newtonized Orthogonal Matching Pursuit Compressive Beamforming. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2020, 148, 1337–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Wang, T.; Chu, F.; Tan, J. Acoustic Source Identification Using an Off-Grid and Sparsity-Based Method for Sound Field Reconstruction. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 170, 108869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Memon, S.A.; Kim, G.; Choo, Y. 3D Off-Grid Localization for Adjacent Cavitation Noise Sources Using Bayesian Inference. Sensors 2023, 23, 2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xenaki, A.; Gerstoft, P. Grid-Free Compressive Beamforming. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2015, 137, 1923–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chardon, G. Gridless Covariance Matrix Fitting Methods for Three Dimensional Acoustical Source Localization. J. Sound Vib. 2023, 551, 117608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malgoezar, A.; Snellen, M.; Merino-Martinez, R.; Simons, D.G.; Sijtsma, P. On the Use of Global Optimization Methods for Acoustic Source Mapping. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2017, 141, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Z.; Antoni, J.; Bouley, S. Gridless Three-Dimensional Acoustic Imaging Based on the Concept of Sonons: Reconstruction of Source Directivity and Equivalent Spatial Distribution. J. Sound Vib. 2024, 575, 118266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellini, P.; Giulietti, N.; Falcionelli, N.; Dragoni, A.F.; Chiariotti, P. A Neural Network Based Microphone Array Approach to Grid-Less Noise Source Localization. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 177, 107947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chu, Z.; Xu, Z.; Ping, G. Two-Dimensional Grid-Free Compressive Beamforming. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2017, 142, 618–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chu, Z.; Ping, G.; Xu, Z. Resolution Enhancement of Two-Dimensional Grid-Free Compressive Beamforming. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2018, 143, 3860–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chu, Z.; Yin, S. Two-Dimensional Grid-Free Compressive Beamforming with Spherical Microphone Arrays. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 169, 108642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Q.; Ning, F.; Deng, Z.; Hou, H.; Li, J.; Wei, J.; Li, B. A Grid-Free Global Optimization Algorithm for Sound Sources Localization in Three-Dimensional Reverberant Environments. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 188, 109999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Quost, B.; Chazot, J.-D.; Antoni, J. Iterative Beamforming for Identification of Multiple Broadband Sound Sources. J. Sound Vib. 2016, 365, 260–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoni, J.; Vanwynsberghe, C.; Le Magueresse, T.; Bouley, S.; Gilquin, L. Mapping Uncertainties Involved in Sound Source Reconstruction with a Cross-Spectral-Matrix-Based Gibbs Sampler. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2019, 146, 4947–4961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, X. Super-Resolution Localization and Orientation Estimation of Multiple Dipole Sound Sources: From a Maximum Likelihood Framework to Wind Tunnel Validation. J. Sound Vib. 2025, 595, 118764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujawski, A.; Sarradj, E. Fast Grid-Free Strength Mapping of Multiple Sound Sources from Microphone Array Data Using a Transformer Architecture. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2022, 152, 2543–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; He, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Z. Three-Dimensional Grid-Free Sound Source Localization Method Based on Deep Learning. Appl. Acoust. 2025, 227, 110261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Grande, E.; Xenaki, A.; Gerstoft, P. A Sparse Equivalent Source Method for Near-Field Acoustic Holography. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2017, 141, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Ji, G. A Comprehensive Survey on Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm and Its Applications. Math. Probl. Eng. 2015, 2015, 931256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Saihjpal, V.; Singh, N.; Singh, S.B. An Overview of Variants and Advancements of PSO Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarradj, E. Three-Dimensional Acoustic Source Mapping with Different Beamforming Steering Vector Formulations. Adv. Acous. Vib. 2012, 2012, 292695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


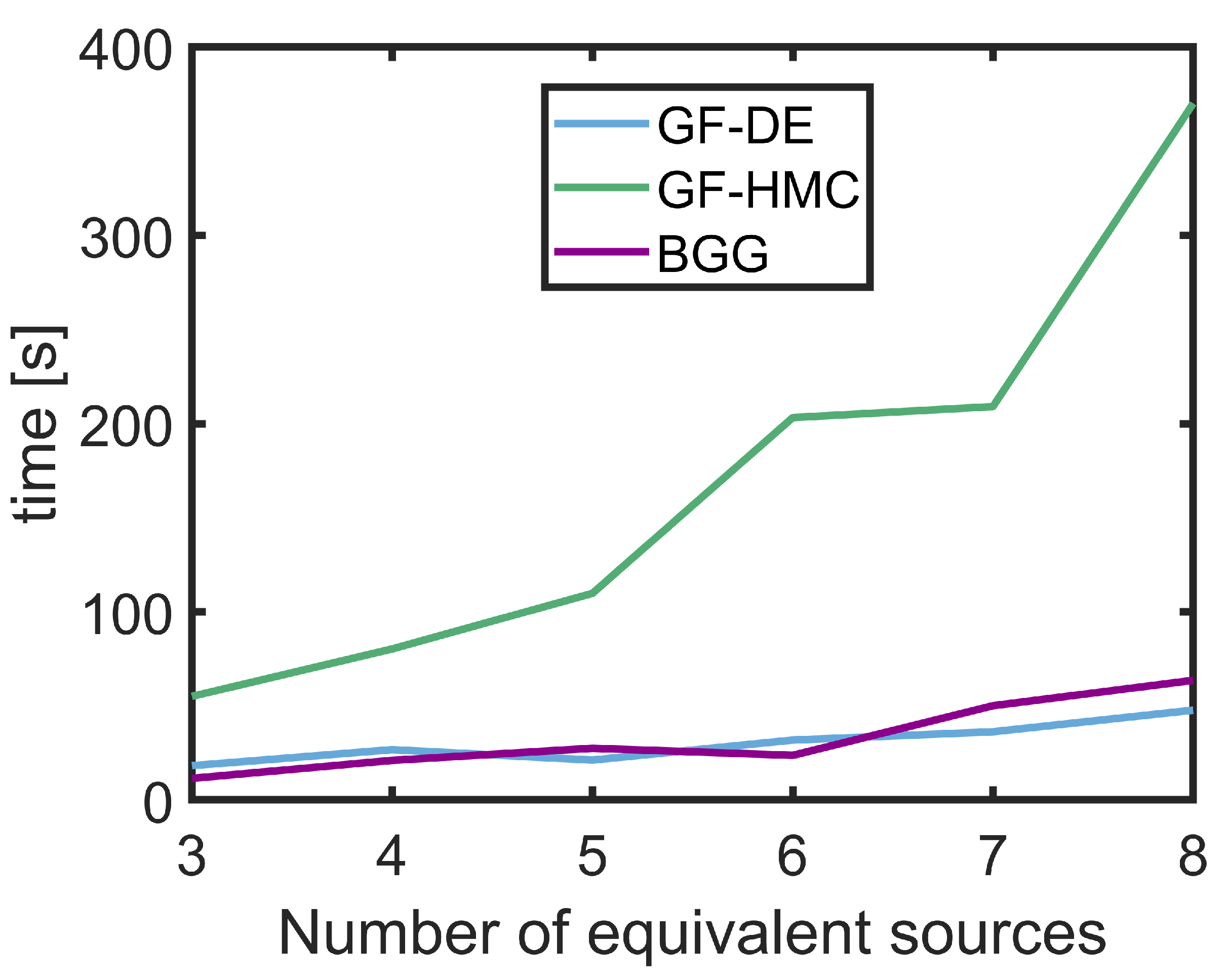
| Clean-SC | GF-DE | GF-HMC | BGG |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3.30 | 21.27 | 109.85 | 27.58 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, D.; Wang, K.; Shi, Y.; Yu, L.; Li, M. A Bayesian Grid-Free Framework with Global Optimization for Three-Dimensional Acoustic Source Imaging. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 11028. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011028
Feng D, Wang K, Shi Y, Yu L, Li M. A Bayesian Grid-Free Framework with Global Optimization for Three-Dimensional Acoustic Source Imaging. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(20):11028. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011028
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Daofang, Kuncheng Wang, Youtai Shi, Liang Yu, and Min Li. 2025. "A Bayesian Grid-Free Framework with Global Optimization for Three-Dimensional Acoustic Source Imaging" Applied Sciences 15, no. 20: 11028. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011028
APA StyleFeng, D., Wang, K., Shi, Y., Yu, L., & Li, M. (2025). A Bayesian Grid-Free Framework with Global Optimization for Three-Dimensional Acoustic Source Imaging. Applied Sciences, 15(20), 11028. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011028





