Analysis of Changes in the Microbial Biodiversity of Soil Contaminated with Cr(III) and Cr(VI)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Experimental Design
- nitrogen (N)—140 mg (CO(NH2)2),
- phosphorus (P)—60 mg (KH2PO4),
- potassium (K)—120 mg (KH2PO4 + KCl),
- magnesium (Mg)—20 mg (MgSO4·7H2O).
2.3. Determination of the Microbial Colony Development Index and Ecophysiological Diversity Index
2.4. Genomic DNA Extraction and Sequence Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
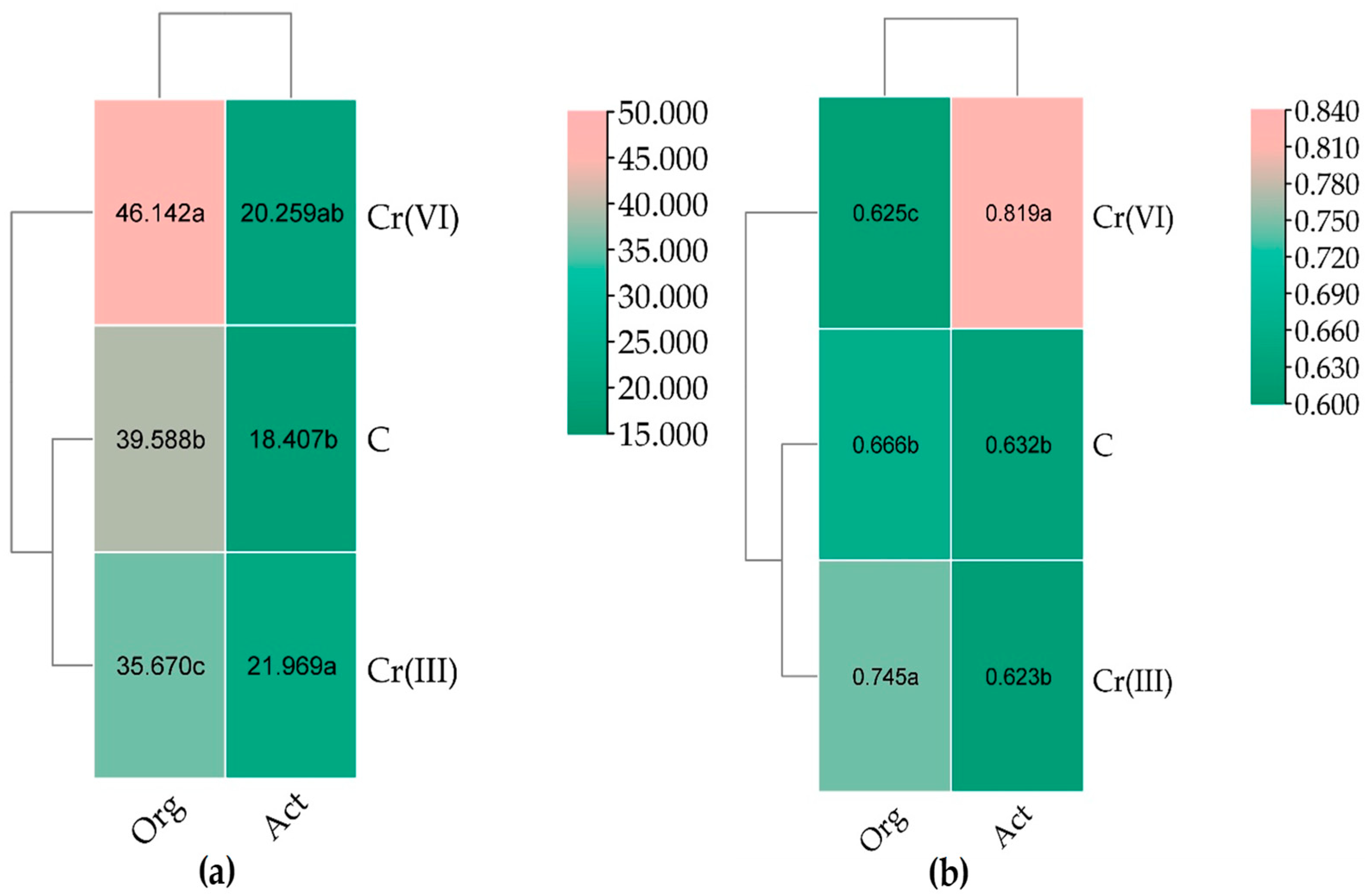
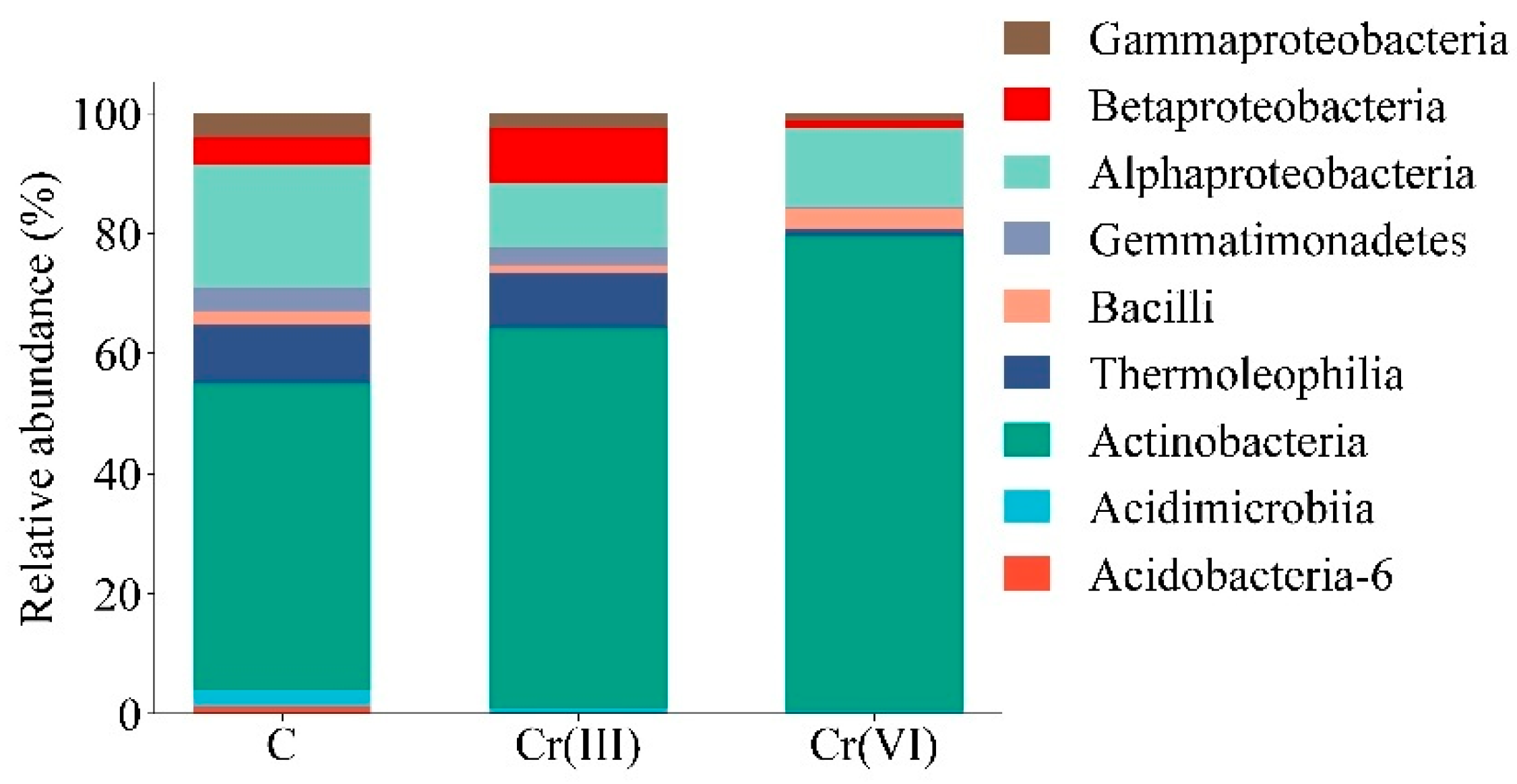
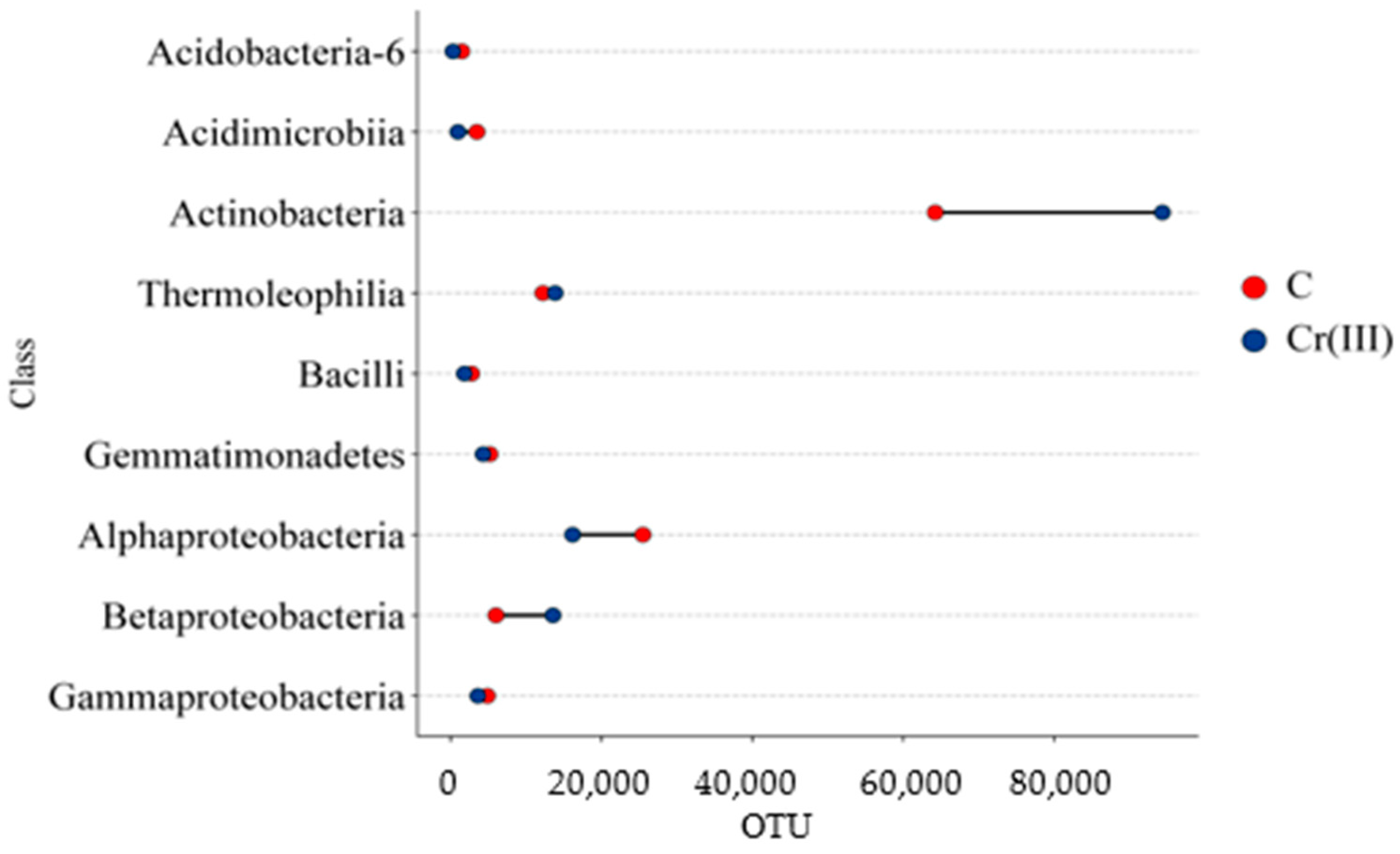
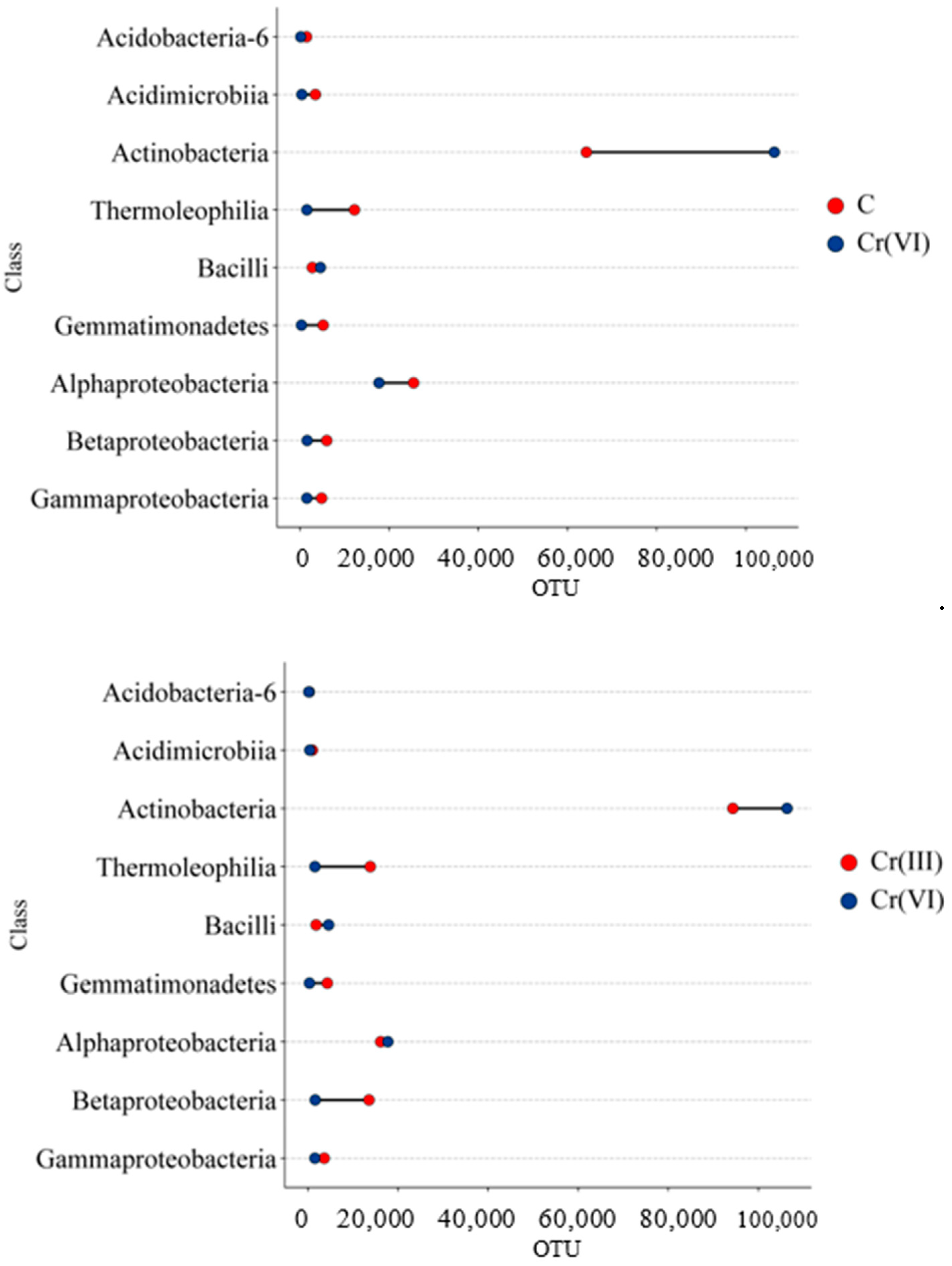
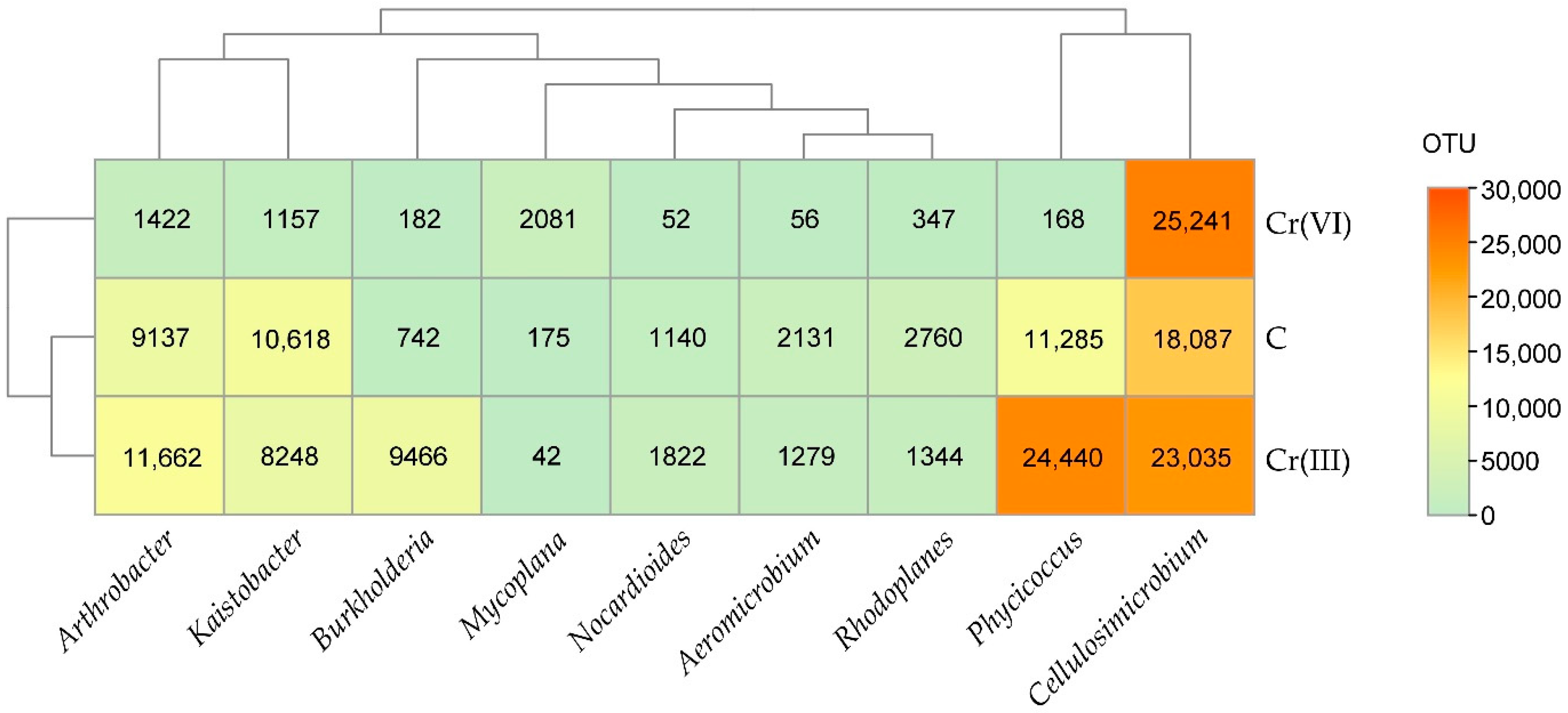
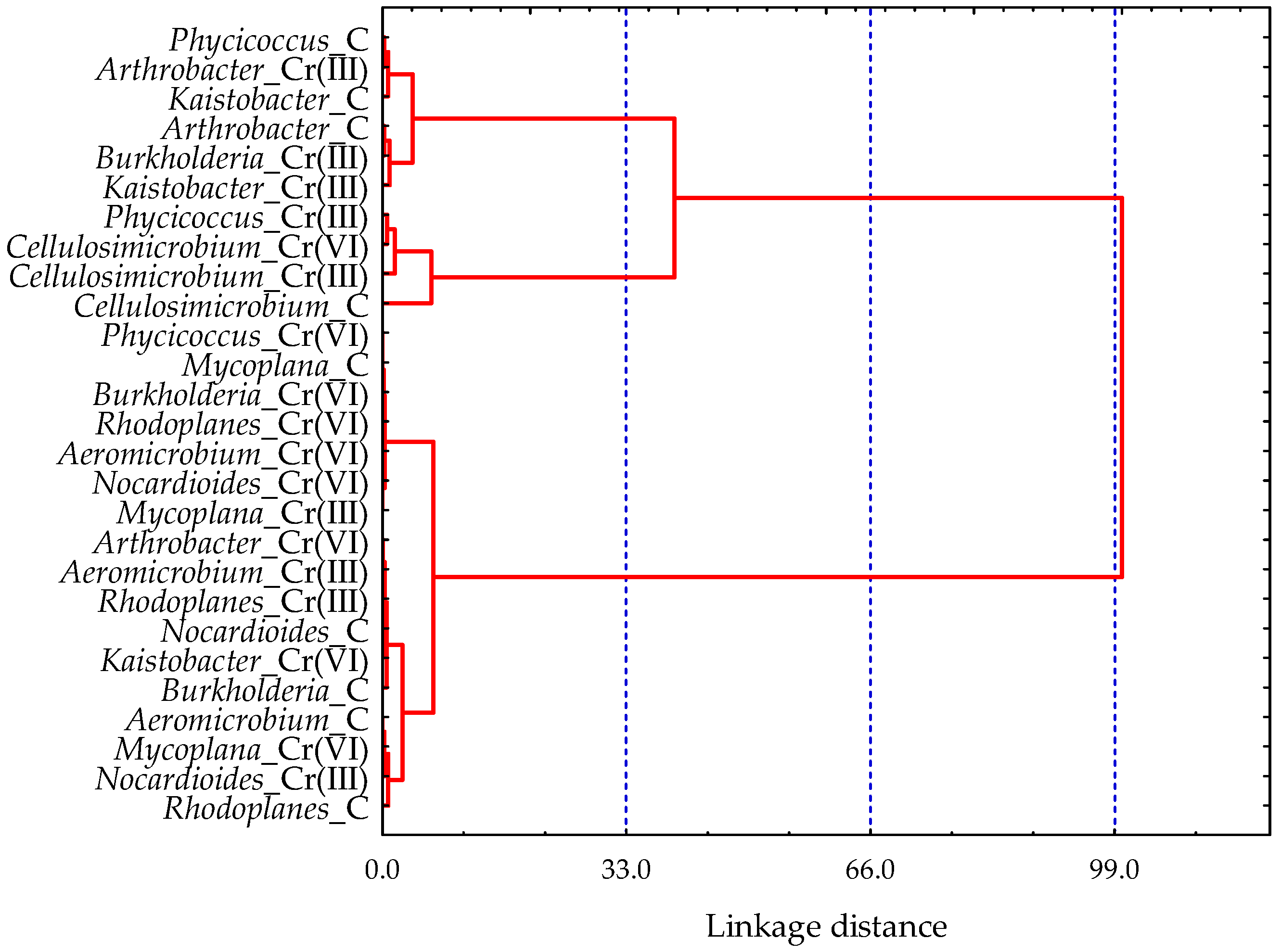
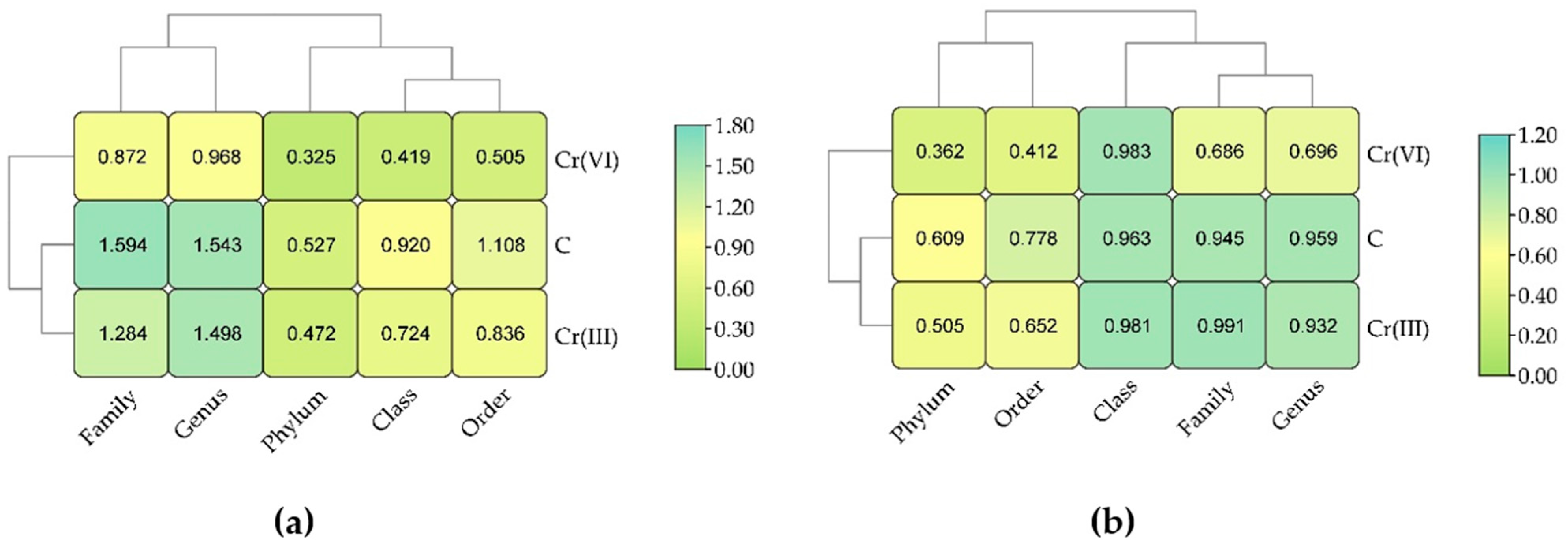
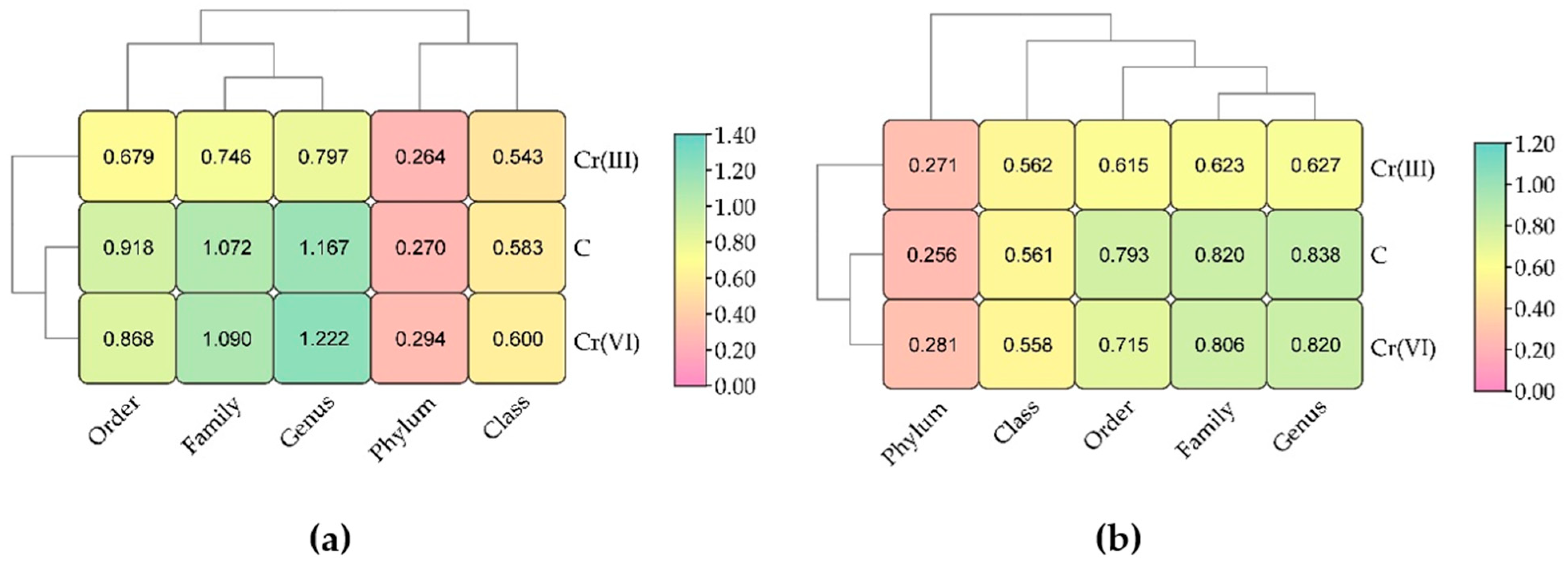
3.1. Effect of Cr(III) and Cr(VI) on the Structure of Bacterial Communities in Soil
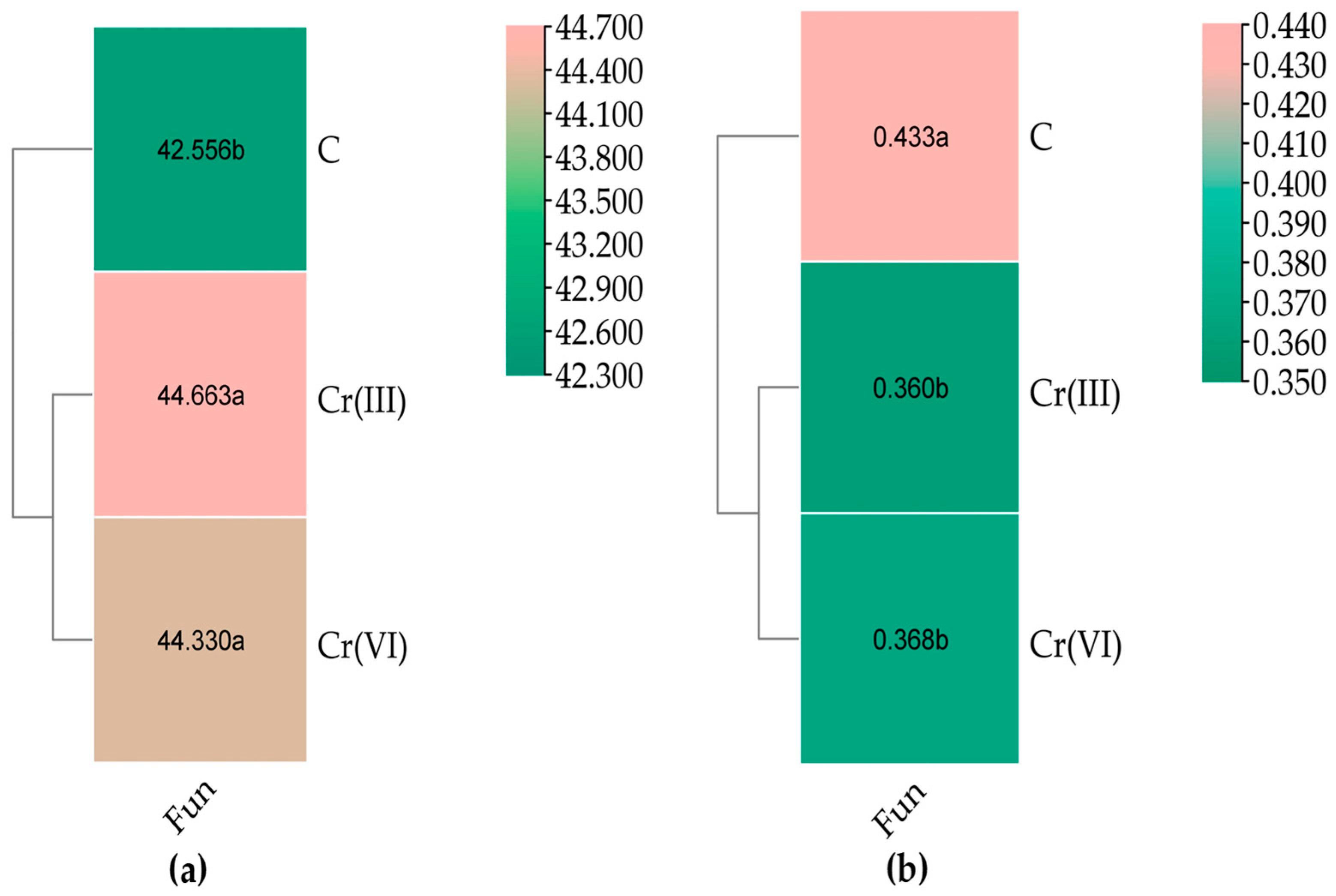
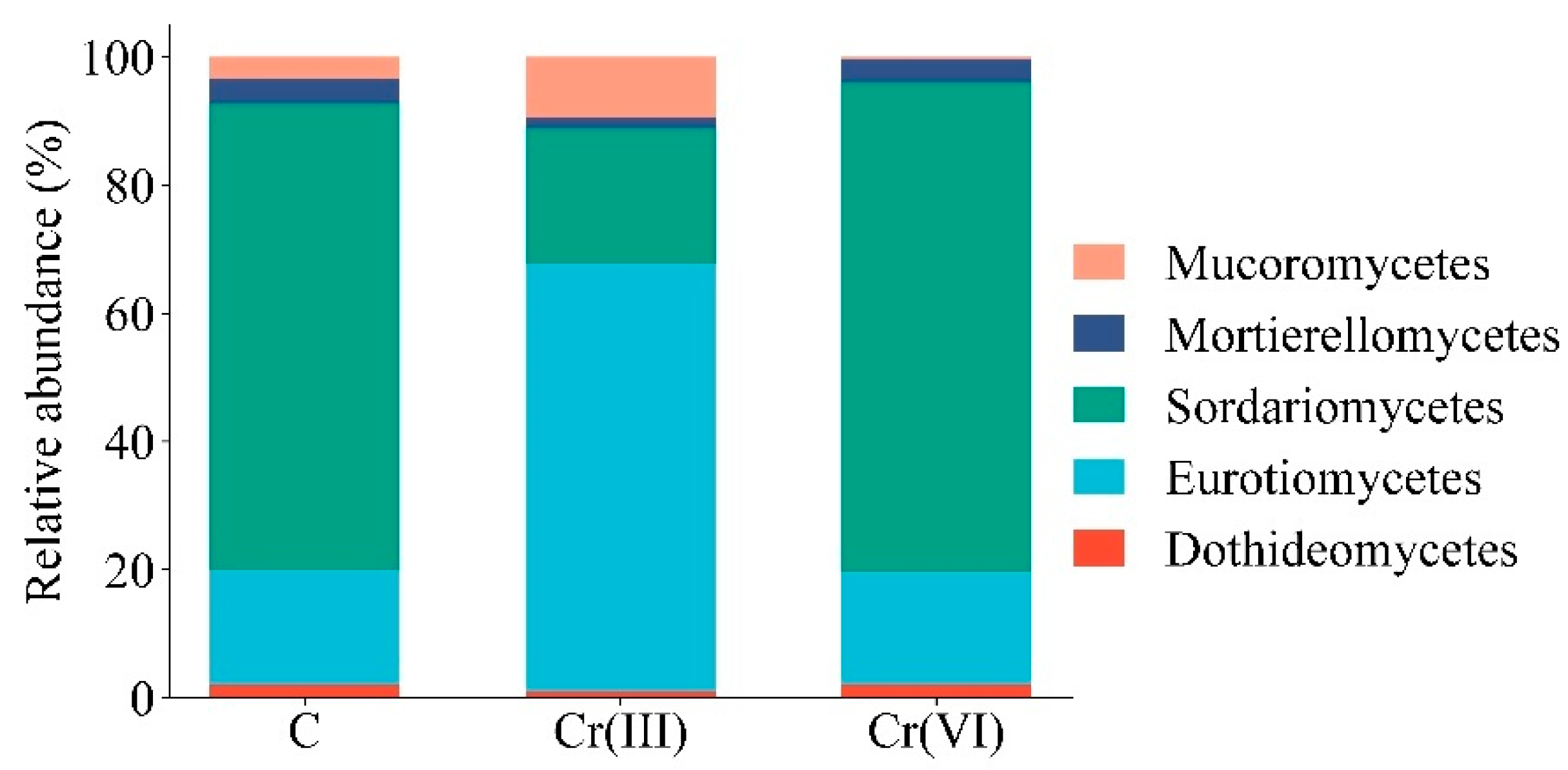
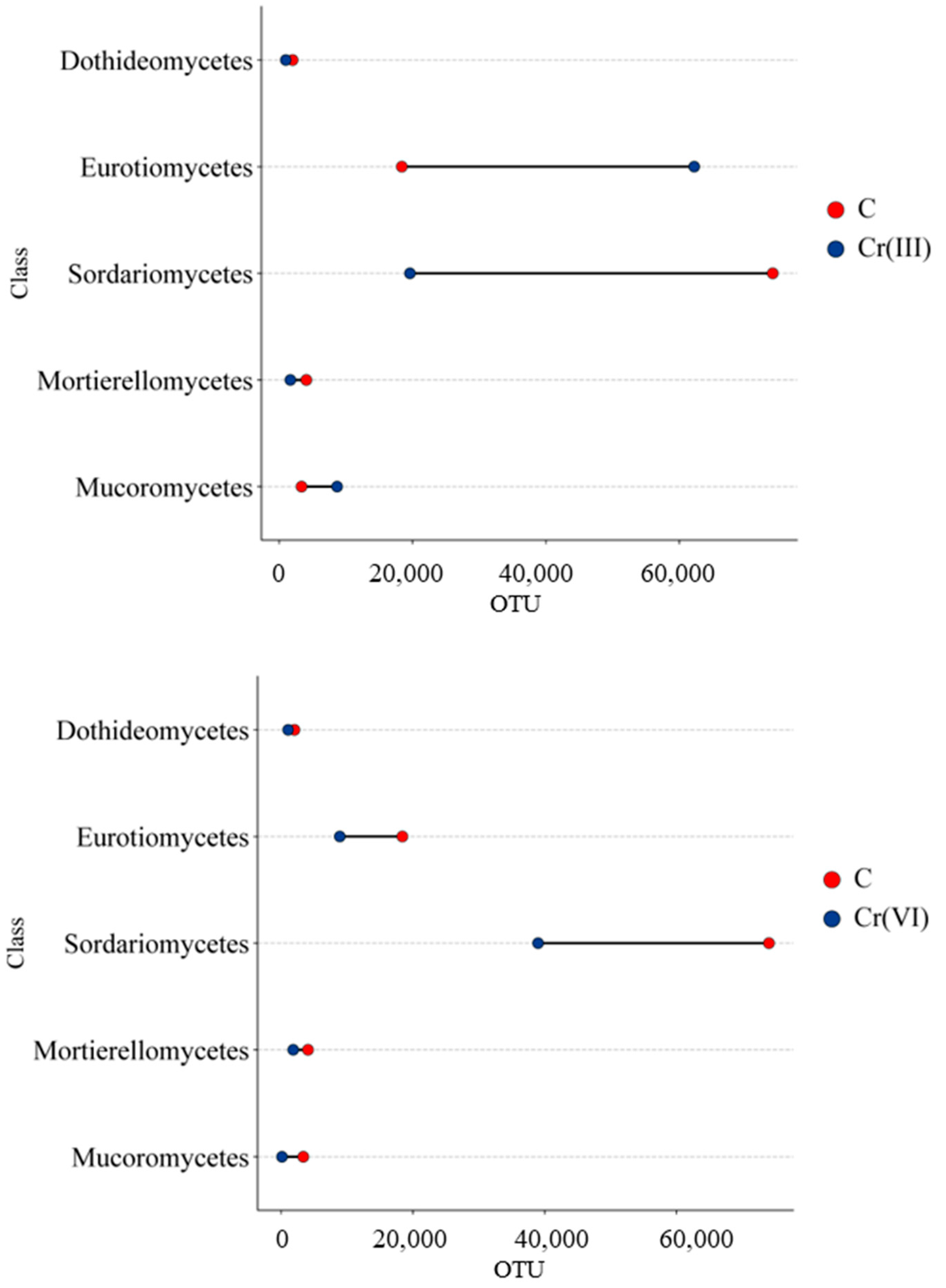
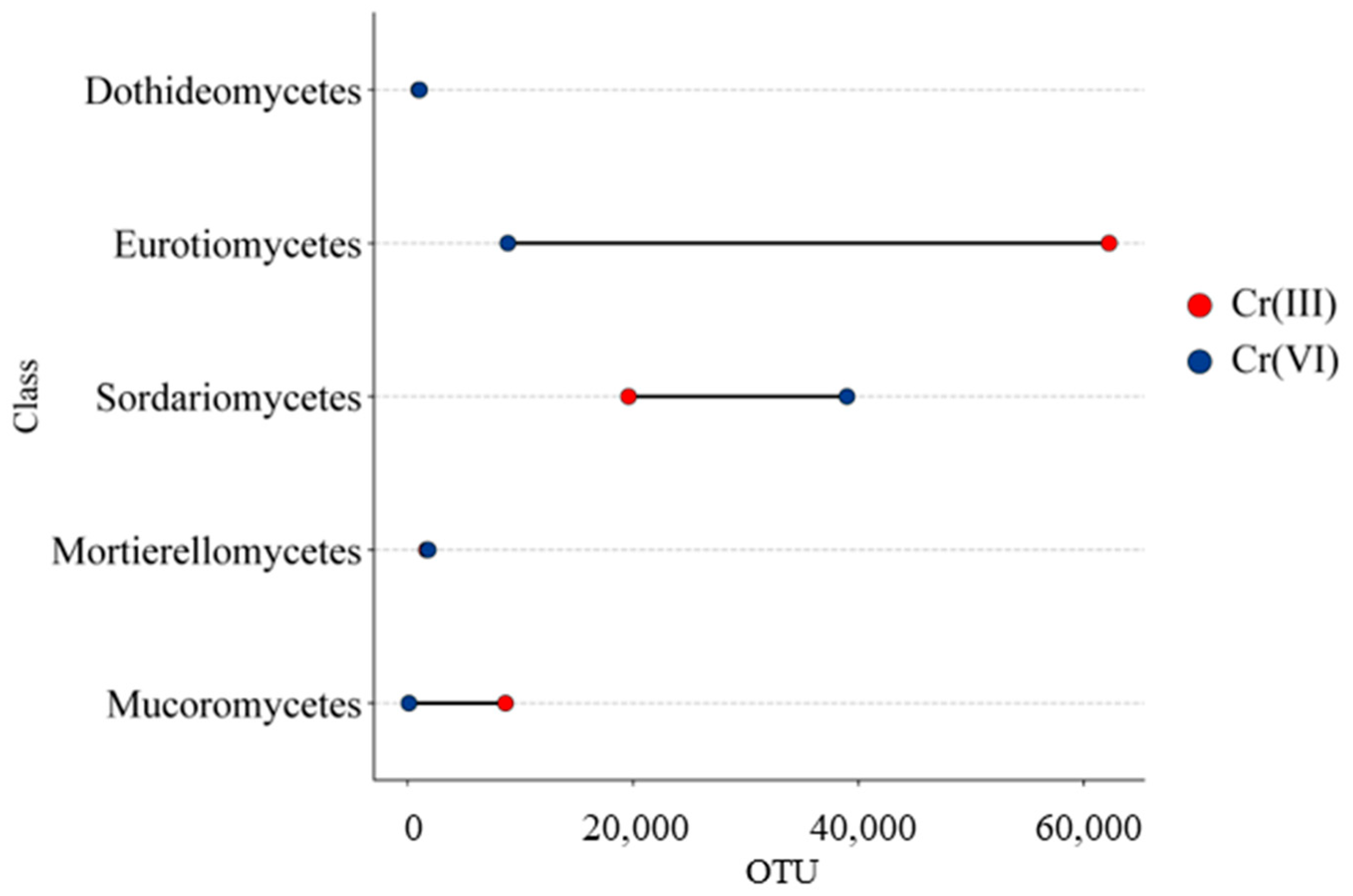
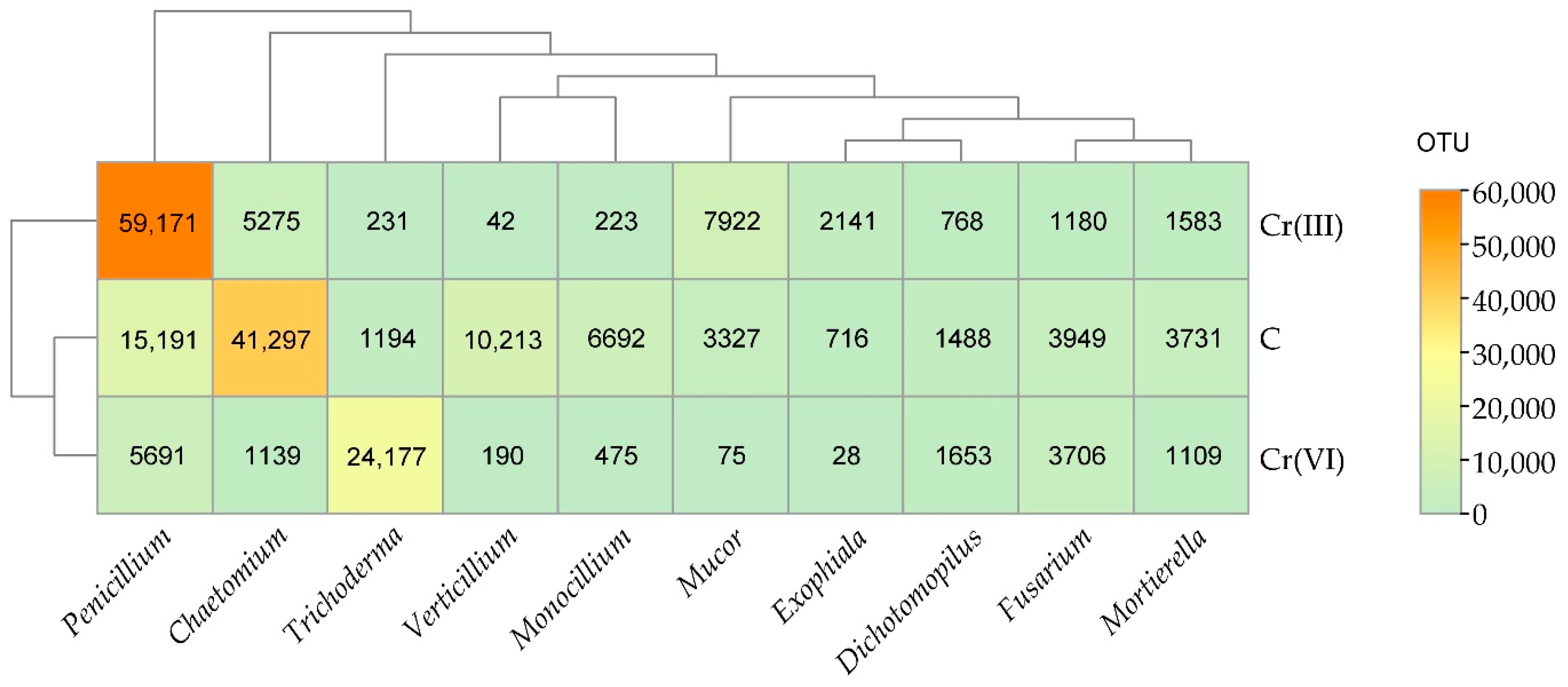
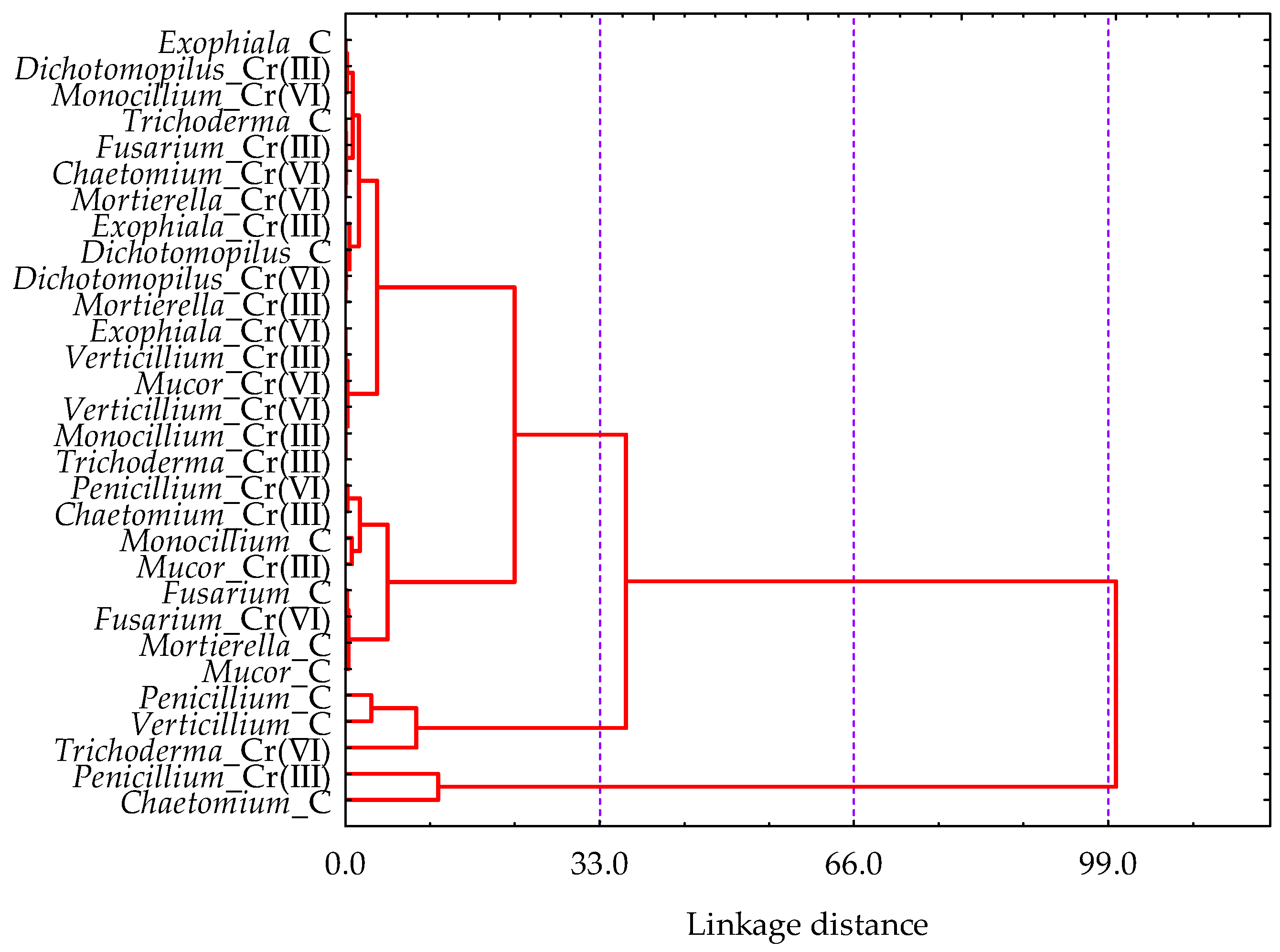
3.2. Effect of Cr(III) and Cr(VI) on the Structure of Soil Fungal Communities
4. Discussion
4.1. Structure of Soil Bacterial Communities Under Exposure to Cr(III) and Cr(VI)
4.2. Structure of Soil Fungal Communities Under Exposure to Cr(III) and Cr(VI)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- López-Bucio, J.S.; Ravelo-Ortega, G.; López-Bucio, J. Chromium in plant growth and development: Toxicity, tolerance and hormesis. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 312, 120084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumolo, M.; Ancona, V.; De Paola, D.; Losacco, D.; Campanale, C.; Massarelli, C.; Uricchio, V.F. Chromium pollution in european water, sources, health risk, and remediation strategies: An Overview. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Feng, A.; Xiao, J.; Wu, Q.; Ye, Q.; Peng, S. Remediation of soil contaminated with high levels of hexavalent chromium by combined chemical-microbial reduction and stabilization. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 404, 123847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfiqar, U.; Jiang, W.; Wang, X.; Hussain, S.; Ahmad, M.; Maqsood, M.F. Insights into the plant-microbe interaction, soil amendments and advanced genetic approaches for cadmium remediation: A review. insights into the plant-microbe interaction, soil amendments and advanced genetic approaches for cadmium remediation: A review. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyszkowska, J.; Borowik, A.; Zaborowska, M.; Kucharski, J. Calorific value of Zea mays biomass derived from soil contaminated with chromium (VI). Energies 2023, 16, 3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; McGill, W.B.; Chen, N.; Rutherford, P.M.; Whitcombe, T.W.; Zhang, W. Formation and immobilization of Cr(VI) species in long-term tannery waste contaminated soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 7226–7235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oloruntoba, A.; Omoniyi, A.O.; Shittu, Z.A.; Ajala, O.R.; Kolawole, S.A. Heavy Metal Contamination in Soils, Water, and Food in Nigeria from 2000–2019: A Systematic Review on Methods, Pollution Level and Policy Implications. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2024, 235, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.statista.com (accessed on 10 September 2025).
- Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/lrtap-1990-2022 (accessed on 10 September 2025).
- Wyszkowska, J.; Kucharski, J.; Jastrzębska, E.; Hłasko, A. The biological properties of the soil as influenced by chromium contamination. Polish J. Environ. Stud. 2001, 10, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Ma, J.; Akhtar, S.; Khan, Z.I.; Ahmad, K.; Ashfaq, A.; Nawaz, H.; Nadeem, M. Assessment of chromium toxicity and potential health implications of agriculturally diversely irrigated food crops in the semi-arid regions of South Asia. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 272, 107833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Hao, X.; Tang, J.; Hu, J.; Deng, Y.; Xu, M.; Zhu, P.; Tao, J.; Liang, Y.; Yin, H.; et al. Assessing chromium contamination in red soil: Monitoring the migration of fractions and the change of related microorganisms. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Singh, J.; Mishra, V. Sorption kinetics of an eco-friendly and sustainable Cr(VI) ion scavenger in a batch reactor. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Guo, B.; Yang, Y. Responses of bacterial communities along vertical soil profile to the chromium-contamination stress. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2023, 179, 105584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyszkowska, J. Soil contamination with chromium and its enzymatic activity and yielding. Polish J. Environ. Stud. 2002, 11, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Boros-Lajszner, E.; Wyszkowska, J.; Kucharski, J. Evaluation and assessment of trivalent and hexavalent chromium on Avena sativa and soil enzymes. Molecules 2023, 28, 4693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Huang, Q.; Men, J.; Wang, J.; Xiao, J.; Jin, D.; Deng, Y. Chromium contamination affects the fungal community and increases the complexity and stability of the network in long-term contaminated soils. Environ. Res. 2024, 262, 119946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, C.; Huang, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, G.; Xing, S.; Fu, W.; Hao, Z.; Chen, B.; Zhang, X. Response of soil fungal community to chromium contamination in agricultural soils with different physicochemical properties. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 879, 163244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manuel, D.-B.; Peter, B.R.; Chanda, T.; David, J.E.; Brajesh, K.S. Multiple elements of soil biodiversity drive ecosystem functions across biomes. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 4, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-R.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Bi, L.; Zhu, J.; He, J.-Z. Consistent responses of soil microbial taxonomic and functional attributes to mercury pollution across China. Microbiome 2018, 6, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, H.; Xiao, C.; Xiao, Y.; Yan, W.; Bai, R.; Ding, R.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, F. Proteomic analysis of the reduction and resistance mechanisms of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 under long-term hexavalent chromium stress. Environ. Int. 2019, 127, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, Z.; Singh, V.P. Bioremediation of toxic heavy metals (THMs) contaminated sites: Concepts, applications and challenges. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 27563–27581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, S.; Piutti, S.; Vallance, J.; Morel, J.-L.; Echevarria, G.; Benizri, E. Nickel drives bacterial community diversity in the rhizosphere of the hyperaccumulator Alyssum murale. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 114, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichorst, S.A.; Trojan, D.; Roux, S.; Herbold, C.; Rattei, T.; Woebken, D. Genomic insights into the Acidobacteria reveal strategies for their success in terrestrial environments. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 1041–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Yan, J.; Xia, L.; Zhang, X.; Luo, L. Mechanisms of Cr(VI) reduction by Bacillus sp. CRB-1, a novel Cr(VI)-reducing bacterium isolated from tannery activated sludge. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 186, 109792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurshid, S.; Shoaib, A.; Javaid, A.; Abid, K. Bioaccumulation of chromium by Fusarium oxysporum. ScienceAsia 2016, 42, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, S.; Hussain, A.; Hamayun, M.; Rahman, H.; Iqbal, A.; Shah, M.; Irshad, M.; Qasim, M.; Islam, B. Bioremediation of hexavalent chromium by endophytic fungi; safe and improved production of Lactuca sativa L. Chemosphere 2018, 211, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canonica, L.; Cecchi, G.; Capra, V.; Di Piazza, S.; Girelli, A.; Zappatore, S.; Zotti, M. Fungal arsenic tolerance and bioaccumulation: Local strains from polluted water vs. allochthonous strains. Environments 2024, 11, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viti, C.; Marchi, E.; Decorosi, F.; Giovannetti, L. Molecular mechanisms of Cr (VI) resistance in bacteria and fungi. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 38, 633–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, Z.; Thomas, L.; Chetri, S.P.K.; Bodhankar, S.; Kumar, V.; Naidu, R. A comprehensive review on chromium (Cr) contamination and Cr(VI)-resistant extremophiles in diverse extreme environments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 59163–59193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.J.; Xia, L.; Chen, W.L.; Huang, Q.Y. Detoxification of hexavalent chromate by growing Paecilomyces lilacinus XLA. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 225, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Hao, R.X.; Xu, X.Y.; Ding, Y.; Lu, A.H.; Li, Y.H. Removal of hexavalent chromium by Aspergillus niger through reduction and accumulation. Geomicrobiol. J. 2020, 38, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, P.; Farooqui, A.; Patel, A.; Srivastava, P.K. Microbial innovations in chromium remediation: Mechanistic insights and diverse applications. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 40, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasir, M.W.; Siddique, M.B.A.; Shabbir, Z.; Ullah, H.; Riaz, L.; Nisa, W.U.; Shafeequr, R.; Shah, A.A. Biotreatment potential of co-contaminants hexavalent chromium and polychlorinated biphenyls in industrial wastewater: Individual and simultaneous prospects. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 779, 146345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohand, T.; Ben El Ayouchia, H.; Achtak, H.; Ghaleb, A.; Derin, Y.; Tutar, A.; Tanemura, K. Design, synthesis, DFT calculations, molecular docking and antimicrobial activities of novel cobalt, chromium metal complexes of heterocyclic moiety-based 1,3,4-oxadiazole derivatives. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 40, 11837–11850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfiqar, U.; Haider, F.U.; Ahmad, M.; Hussain, S.; Maqsood, M.F.; Ishfaq, M.; Shahzad, B.; Waqas, M.M.; Ali, B.; Tayyab, M.N.; et al. Chromium toxicity, speciation, and remediation strategies in soil-plant interface: A critical review. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 13, 1081624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Singh, S.P.; Parakh, S.K.; Tong, Y.W. Health hazards of hexavalent chromium (Cr (VI)) and its microbial reduction. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 4923–4938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq, Z.; Liaquat, M.; Nazir, A.; Liaquat, R.; Iftikhai, H.; Anwar, W.; Itrat, N. Potential of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria to mitigate chromium contamination. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 28, 102826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://zpe.gov.pl/a/soils-in-poland (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Wyszkowska, J.; Boros-Lajszner, E.; Kucharski, J. The impact of soil contamination with lead on the biomass of maize intended for energy purposes, and the biochemical and physicochemical properties of the soil. Energies 2024, 17, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Guo, W.; Dang, Z.; Hu, Q.; Wu, F.; Feng, C.; Zhao, X.; Meng, W.; Xing, B.; Giesy, J.P. Refocusing on nonpriority toxic metals in the aquatic environment in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 3117–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E.; Ilahi, I. Environmental chemistry and ecotoxicology of hazardous heavy metals: Environmental persistence, toxicity, and tioaccumulation. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 6730305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World’s Worst Pollution Problems 2015. The New Top Six Toxic Threats: A Priority List for Remediation. Available online: http://www.worstpolluted.org/docs/WWPP_2015_Final.pdf (accessed on 21 November 2018).
- Regulation of the Minister of the Environment of 1 September 2016 Applicable in Poland (Journal of Laws 2016 item 1395). ISAP—Internet System of Legal Acts. Available online: http://https://isap.sejm.gov.pl/isap.nsf/DocDetails.xsp?id=wdu20160001395 (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Abideen, S.N.U.; Abideen, A.A. Protein level and heavy metals (Pb, Cr, and Cd) concentrations in wheat (Triticum aestivum) and in oat (Avena sativa) plants. IJIAS 2013, 3, 284–289. [Google Scholar]
- Tobiasz-Salach, R.; Pyrek-Bajcar, E.; Bobrecka-Jamro, D. Assessing the possible use of hulled and naked oat grains as energy source. Econtechmod Int. Q. J. Econ. Technol. Model. Process. 2016, 5, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Proszak-Miąsik, D.; Jarecki, W.; Nowak, K. Selected parameters of oat straw as an alternative energy raw material. Energies 2022, 15, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarathchandra, S.U.; Burch, G.; Cox, N.R. Growth patterns of bacterial communities in the rhizoplane and rhizosphere of with clover (Trifolium repens L.) and perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) in long-term pasture. Appl. Soil Ecol. 1997, 6, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leij, F.A.; Whipps, J.M.; Lynch, J.M. The use of colony development for the characterization of bacterial communities in soil and on roots. Microb. Ecol. 1993, 27, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baćmaga, M.; Wyszkowska, J.; Kucharski, J. Influence of prosulfocarb and polymer supplementation on soil bacterial diversity in Triticum aestivum L. cultivation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baćmaga, M.; Wyszkowska, J.; Kucharski, J. Response of soil microbiota, enzymes, and plants to the fungicide azoxystrobin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowik, A.; Wyszkowska, J.; Zaborowska, M.; Kucharski, J. Regulation of the microbiome in soil contaminated with diesel oil and gasoline. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Qu, Y.; Zeng, H.; Yang, J.; Liu, L.; Deng, D.; Ma, Y.; Chen, D.; Jian, B.; Guan, L.; et al. Long-term ecological restoration increased plant diversity and soil total phosphorus content of the alpine flowing sand land in Northwest Sichuan, China. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Turmuhan, R.-G.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Wan, L. Five years of natural vegetation recovery in three forests of karst graben area and its effects on plant diversity and soil properties. Forests 2025, 16, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitikidou, K.; Milios, E.; Stampoulidis, A.; Pipinis, E.; Radoglou, K. Using biodiversity indices effectively: Considerations for forest management. Ecologies 2024, 5, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TIBCO Software Inc Statistica (Data Analysis Software System), Version 13. 2017. Available online: https://www.statistica.com (accessed on 23 April 2024).
- Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Chen, H.; He, Y.; et al. TBtools-II: A “one for all, all for one” bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining. Mol. Plant. 2023, 16, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Chen, M.; Huang, X.; Zhang, G.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, G.; Wu, S.; Wang, Y. SRplot: A free online platform for data visualization and graphing. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0294236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhu, S.; Li, W.; Tang, Q.; Luo, H. Effects of chromium stress on the rhizosphere microbial community composition of Cyperus alternifolius. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 218, 112253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Li, X.; He, F.; Guo, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zong, W.; Liu, R. Molecular toxicity of Cr (III) and Cr (VI) to defensive protein lysozyme and their differential mechanisms. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 390, 123151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyszkowska, J.; Borowik, A.; Zaborowska, M.; Kucharski, J. Sensitivity of Zea mays and soil microorganisms to the toxic effect of chromium (VI). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Sixi, Z.; Baojing, G.; Xiuqing, Y.; Guodong, X.; Baichun, W. Effects of Cr stress on bacterial community structure and composition in rhizosphere soil of iris tectorum under different cultivation modes. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 14, 243–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Tian, Y. Hexavalent chromium reducing bacteria: Mechanism of reduction and characteristics. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 20981–20997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, Z.; Thomas, L. Chemical-assisted microbially mediated chromium (Cr) (vi) reduction under the influence of various electron donors, redox mediators, and other additives: An outlook on enhanced Cr(vi) removal. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 619766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawicka, E.; Jurkowska, K.; Piwowar, A. Chromium (III) and chromium (VI) as important players in the induction of genotoxicity-current view. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2021, 28, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.; Ma, X.; Luan, F.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Y.; Xiao, X.; Thandar, S.M. Sustainable enhancement of Cr (VI) bioreduction by the isolated Cr (VI)-resistant bacteria. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 812, 152433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Li, Y.; Jing, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, P. Response mechanisms of bacterial communities and nitrogen cycle functional genes in millet rhizosphere soil to chromium stress. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1116535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Huang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhao, L.; Qiu, H.; Cao, X. Enhanced microbial reduction of Cr(VI) in soil with biochar acting as an electron shuttle: Crucial role of redox-active moieties. Chemosphere 2023, 328, 138601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobby, R.; Jha, P.; Yadav, A.K.; Desai, N. Biosorption and biotransformation of hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)]: A comprehensive review. Chemosphere 2018, 207, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, G.; Gao, Y.; Xue, K.; Qi, Y.; Fan, Y.; Tian, X.; Wang, J.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Y.; et al. Toxicity mechanisms and remediation strategies for chromium exposure in the environment. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1131204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.W.; Gu, L.P.; Xu, Z.X.; He, H.; Fu, G.; Han, F.X.; Huang, B.; Pan, X.J. Cleaning chromium pollution in aquatic environments by bioremediation, photocatalytic remediation, electrochemical remediation and coupled remediation systems. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 561–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, F.Z.; Kanwal, W.; Faisal, M. Chromate-reducing profile of bacterial strains isolated from industrial effluents. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2016, 25, 2121–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, C.; Barathi, S.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Ramkumar, V.S.; Thi, N.B.D.; Arulselvi, P.I. Evaluation of Cr (VI) reduction mechanism and removal by Cellulosimicrobium funkei strain AR8, a novel haloalkaliphilic bacterium. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 333, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Dong, L.; Zhou, S.; Jia, Y.; Gu, R.; Bai, Q.; Xiao, H. Chromium resistance characteristics of Cr (VI) resistance genes ChrA and ChrB in Serratia sp. S2. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 157, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Chen, N.; Feng, C.; Li, M.; Gao, Y.; Hu, Y. Coupling enhancement of chromium (VI) bioreduction in groundwater by phosphorus minerals. Chemosphere 2020, 240, 124896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, S.; Yu, A.; Wang, Z.; Shi, Q.; Cheng, X.; Liu, C.; Zhou, L. Microbial strategies for effective hexavalent chromium removal: A comprehensive review. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 489, 151457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Huang, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, G.; Ma, Y.; Hao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Chen, B. Deciphering the impacts of chromium contamination on soil bacterial communities: A comparative analysis across various soil types. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 348, 119335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Hao, R.; Shan, B.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Lu, A. Mechanism of Cr(VI) removal by efficient Cr(VI)-resistant Bacillus mobilis CR3. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 40, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Song, K.; Cheng, G.; Xu, H.; Wang, X.; Qi, C.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J. Changes in the bacterial communities in chromium contaminated soils. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 9, 1066048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sharkawy, G.; Alotaibi, M.O.; Zuhair, R.; Mahmoud, E.; El Baroudy, A.; Omara, A.E.-D.; El-Sharkawy, M. Ecological assessment of polluted soils: Linking ecological risks, soil quality, and biota diversity in contaminated soils. Sustainability 2025, 17, 1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzi, W.; Abou Fayad, A.G.; Nasser, A.; Haraoui, L.-P.; Dewachi, O.; Abou-Sitta, G.; Nguyen, V.-K.; Abara, A.; Karah, N.; Landecker, H.; et al. Heavy metal toxicity in armed conflicts potentiates AMR in A. baumannii by selecting for antibiotic and heavy metal co-resistance mechanisms. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, D.; Zhang, R.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, L.; Lei, L.; Xu, H.; Feng, S. Effects of secondary release of chromium and vanadium on soil properties, nutrient cycling and bacterial communities in contaminated acidic paddy soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 326, 116725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Gao, B.; Wang, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, M. Insights into remediation effects and bacterial diversity of different remediation measures in rare earth mine soil with SO42− and heavy metals. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1050635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Ye, Y.; Hu, Y.; Shi, H. The variation in microbial community structure under different heavy metal contamination levels in paddy soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 180, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Dwivedi, S.K. Hexavalent chromium reduction ability and bioremediation potential of Aspergillus flavus CR500 isolated from electroplating wastewater. Chemosphere 2019, 237, 124567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkuna, R.; Matambo, T.S. Insights into metal tolerance and resistance mechanisms in Trichoderma asperellum unveiled by de novo transcriptome analysis during bioleaching. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 356, 120734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Type of Soil | Granulometric Composition (%) | pHKCl | Corg | Ntotal | C:N | HAC | EBC | CEC | BS % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sand | Silt | Clay | g kg−1 d.m. soil | mmol (+) kg−1 d.m. soil | |||||||
| Sandy loam | 69.41 | 27.71 | 2.88 | 5.80 | 7.80 | 1.20 | 6.50 | 13.50 | 31.00 | 44.50 | 69.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boros-Lajszner, E.; Wyszkowska, J.; Baćmaga, M.; Kucharski, J. Analysis of Changes in the Microbial Biodiversity of Soil Contaminated with Cr(III) and Cr(VI). Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 10951. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152010951
Boros-Lajszner E, Wyszkowska J, Baćmaga M, Kucharski J. Analysis of Changes in the Microbial Biodiversity of Soil Contaminated with Cr(III) and Cr(VI). Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(20):10951. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152010951
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoros-Lajszner, Edyta, Jadwiga Wyszkowska, Małgorzata Baćmaga, and Jan Kucharski. 2025. "Analysis of Changes in the Microbial Biodiversity of Soil Contaminated with Cr(III) and Cr(VI)" Applied Sciences 15, no. 20: 10951. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152010951
APA StyleBoros-Lajszner, E., Wyszkowska, J., Baćmaga, M., & Kucharski, J. (2025). Analysis of Changes in the Microbial Biodiversity of Soil Contaminated with Cr(III) and Cr(VI). Applied Sciences, 15(20), 10951. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152010951






