Human Neural Stem Cells Are More Vulnerable to Damage from Pesticide-Induced Oxidative Stress After Differentiation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. MTT Assay
2.4. Lactate Dehydrogenase Assay
2.5. Intracellular ATP Quantification
2.6. Assessment of Acetylcholinesterase Activity
2.7. Measurement of Reactive Oxygen Species
2.8. Cell Lysis and Fractionation
2.9. Protein Quantification
2.10. Quantitation of Protein Carbonyl Content and Characterisation of Oxidatively Damaged Proteins
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
Assessment of the Neurotoxicity of Chlorpyrifos-Oxon, Azamethiphos, and Aldicarb to Human Neural Progenitor Cells
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilson, C.; Tisdell, C. Why farmers continue to use pesticides despite environmental, health and sustainability costs. Ecol. Economics 2001, 39, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popp, J.; Pető, K.; Nagy, J. Pesticide productivity and food security. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2013, 33, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariyanna, B.; Senthil-Nathan, S.; Vasantha-Srinivasan, P.; Reddy, B.V.S.; Krishnaiah, A.; Meenakshi, N.H.; Han, Y.S.; Karthi, S.; Chakravarthy, A.K.; Park, K.B. Comprehensive insights into pesticide residue dynamics: Unraveling impact and management. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2024, 11, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, J.; Chung, H. New and emerging mechanisms of insecticide resistance. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2024, 63, 101184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mew, E.J.; Padmanathan, P.; Konradsen, F.; Eddleston, M.; Chang, S.S.; Phillips, M.R.; Gunnell, D. The global burden of fatal self-poisoning with pesticides 2006-15: Systematic review. J Affect. Disord. 2017, 219, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moebus, S.; Boedeker, W. Case Fatality as an Indicator for the Human Toxicity of Pesticides-A Systematic Scoping Review on the Availability and Variability of Severity Indicators of Pesticide Poisoning. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayaraj, R.; Megha, P.; Sreedev, P. Organochlorine pesticides, their toxic effects on living organisms and their fate in the environment. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2016, 9, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colovic, M.B.; Krstic, D.Z.; Lazarevic-Pasti, T.D.; Bondzic, A.M.; Vasic, V.M. Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors: Pharmacology and Toxicology. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2013, 11, 315–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, L.G. Organophosphorus Compounds at 80: Some Old and New Issues. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 162, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, W.G.; Tarhoni, M.; Rathbone, A.J.; Ray, D.E. Differential protein adduction by seven organophosphorus pesticides in both brain and thymus. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2007, 26, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, W.G.; Tarhoni, M.H.; Ray, D.E. Analytical approaches to investigate protein-pesticide adducts. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2010, 878, 1312–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terry, A.V., Jr. Functional consequences of repeated organophosphate exposure: Potential non-cholinergic mechanisms. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 134, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sule, R.O.; Condon, L.; Gomes, A.V. A Common Feature of Pesticides: Oxidative Stress-The Role of Oxidative Stress in Pesticide-Induced Toxicity. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2022, 5563759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, Z.; Nian, B.; Yu, C.; Maimaiti, D.; Chai, M.; Yang, X.; Zang, X.; Xu, D. Mechanisms of Neurotoxicity of Organophosphate Pesticides and Their Relation to Neurological Disorders. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2024, 20, 2237–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Arshad, M.; Gacem, A.; Soni, S.; Singh, S.; Kumar, M.; Yadav, V.K.; Tariq, M.; Kumar, R.; Shah, D.; et al. Insight into the environmental fate, hazard, detection, and sustainable degradation technologies of chlorpyrifos-an organophosphorus pesticide. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 108347–108369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, H.U.U.; Asghar, W.; Nazir, W.; Sandhu, M.A.; Ahmed, A.; Khalid, N. A comprehensive review on chlorpyrifos toxicity with special reference to endocrine disruption: Evidence of mechanisms, exposures and mitigation strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barisic, J.; Cannon, S.; Quinn, B. Cumulative impact of anti-sea lice treatment (azamethiphos) on health status of Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss, Walbaum 1792) in aquaculture. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couillard, C.M.; Burridge, L.E. Sublethal exposure to azamethiphos causes neurotoxicity, altered energy allocation and high mortality during simulated live transport in American lobster. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 115, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montory, J.A.; Cubillos, V.M.; Chaparro, O.R.; Gebauer, P.; Lee, M.R.; Ramírez-Kuschel, E.; Paredes-Molina, F.; Lara-Sandoval, V.; Cumillaf, J.P.; Salas-Yanquin, L.P.; et al. The Interactive Effects of the Anti-Sea Lice Pesticide Azamethiphos and Temperature on Oxidative Damage and Antioxidant Responses in the Oyster Ostrea chilensis. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mdeni, N.L.; Adeniji, A.O.; Okoh, A.I.; Okoh, O.O. Analytical Evaluation of Carbamate and Organophosphate Pesticides in Human and Environmental Matrices: A Review. Molecules 2022, 27, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risher, J.F.; Mink, F.L.; Stara, J.F. The toxicologic effects of the carbamate insecticide aldicarb in mammals: A review. Environ. Health Perspect. 1987, 72, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, S.M.; McManus, I.C.; Harrison, V.; Mason, O. Neurobehavioral problems following low-level exposure to organophosphate pesticides: A systematic and meta-analytic review. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2013, 43, 21–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roldan-Tapia, L.; Nieto-Escamez, F.A.; del Aguila, E.M.; Laynez, F.; Parron, T.; Sanchez-Santed, F. Neuropsychological sequelae from acute poisoning and long-term exposure to carbamate and organophosphate pesticides. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2006, 28, 694–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandjean, P.; Landrigan, P.J. Neurobehavioural effects of developmental toxicity. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, R.D.; Todd, S.W.; Lumsden, E.; Mullins, R.J.; Mamczarz, J.; Fawcett, W.P.; Gullapalli, R.P.; Randall, W.R.; Pereira, E.F.R.; Albuquerque, E.X. Developmental neurotoxicity of the organophosphorus insecticide chlorpyrifos: From clinical findings to preclinical models and potential mechanism. J. Neurochem. 2017, 142, 162–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, M.F.; Chevrier, J.; Harley, K.G.; Kogut, K.; Vedar, M.; Calderon, N.; Trujillo, C.; Johnson, C.; Bradman, A.; Barr, D.B.; et al. Prenatal exposure to organophosphate pesticides and IQ in 7-year-old children. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1189–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauh, V.A.; Perera, F.P.; Horton, M.K.; Whyatt, R.M.; Bansal, R.; Hao, X.; Liu, J.; Barr, D.B.; Slotkin, T.A.; Peterson, B.S. Brain anomalies in children exposed prenatally to a common organophosphate pesticide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 7871–7876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauh, V.; Arunajadai, S.; Horton, M.; Perera, F.; Hoepner, L.; Barr, D.B.; Whyatt, R. Seven-year neurodevelopmental scores and prenatal exposure to chlorpyrifos, a common agricultural pesticide. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1196–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, C.; Gunier, R.; Bradman, A.; Harley, K.G.; Kogut, K.; Parra, K.; Eskenazi, B. Residential proximity to organophosphate and carbamate pesticide use during pregnancy, poverty during childhood, and cognitive functioning in 10-year-old children. Environ. Res. 2016, 150, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudyanselage, A.W.; Wijamunige, B.C.; Kocon, A.; Carter, W.G. Differentiated Neurons Are More Vulnerable to Organophosphate and Carbamate Neurotoxicity than Undifferentiated Neurons Due to the Induction of Redox Stress and Accumulate Oxidatively-Damaged Proteins. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, R.; Miljan, E.A.; Hines, S.J.; Aouabdi, S.; Pollock, K.; Patel, S.; Edwards, F.A.; Sinden, J.D. Differential development of neuronal physiological responsiveness in two human neural stem cell lines. BMC Neurosci. 2007, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Cruz, B.M.; Markus, R.; Malla, S.; Haig, M.I.; Gell, C.; Sang, F.; Bellows, E.; Sherif, M.A.; McLean, D.; Lourdusamy, A.; et al. Modifying the m6A brain methylome by ALKBH5-mediated demethylation: A new contender for synaptic tagging. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 7141–7153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breier, J.M.; Radio, N.M.; Mundy, W.R.; Shafer, T.J. Development of a high-throughput screening assay for chemical effects on proliferation and viability of immortalized human neural progenitor cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 105, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherif, M.A.; Carter, W.G.; Mellor, I.R. Chlorpyrifos Acts as a Positive Modulator and an Agonist of N-Methyl-D-Aspartate (NMDA) Receptors: A Novel Mechanism of Chlorpyrifos-Induced Neurotoxicity. J. Xenobiot. 2025, 15, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.H.; Jung, C.R.; Lee, M.O.; Kim, J.; Son, M.Y. Comparative analysis of human embryonic stem cell-derived neural stem cells as an in vitro human model. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V., Jr.; Featherstone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdozain, A.M.; Morentin, B.; Bedford, L.; King, E.; Tooth, D.; Brewer, C.; Wayne, D.; Johnson, L.; Gerdes, H.K.; Wigmore, P.; et al. Alcohol-Related Brain Damage in Humans. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Suarez, L.; Awabdh, S.A.; Coumoul, X.; Chauvet, C. The SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cell line, a relevant in vitro cell model for investigating neurotoxicology in human: Focus on organic pollutants. Neurotoxicology 2022, 92, 131–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riss, T.L.; Moravec, R.A.; Niles, A.L.; Duellman, S.; Benink, H.A.; Worzella, T.J.; Minor, L. Cell Viability Assays. In Assay Guidance Manual; Markossian, S., Grossman, A., Baskir, H., et al., Eds.; Eli Lilly & Company and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2004. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK144065/ (accessed on 18 September 2025).
- Kamiloglu, S.; Sari, G.; Ozdal, T.; Capanoglu, E. Guidelines for cell viability assays. Food Front. 2020, 1, 332–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljadaan, A.M.; AlSaadi, A.M.; Shaikh, I.A.; Whitby, A.; Ray, A.; Kim, D.-H.; Carter, W.G. Characterization of the Anticholinesterase and Antioxidant Properties of Phytochemicals from Moringa oleifera as a Potential Treatment for Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, K.D.; Fosso, M.Y.; Garneau-Tsodikova, S. Multifunctional Donepezil Analogues as Cholinesterase and BACE1 Inhibitors. Molecules 2018, 23, 3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Huang, X.; Liu, X.; Li, W. Inhibition of cytoskeletal protein carbonylation may protect against oxidative damage in traumatic brain injury. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 12, 4107–4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigoryan, H.; Schopfer, L.M.; Peeples, E.S.; Duysen, E.G.; Grigoryan, M.; Thompson, C.M.; Lockridge, O. Mass spectrometry identifies multiple organophosphorylated sites on tubulin. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 240, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hernandez-Toledano, D.; Vega, L. The cytoskeleton as a non-cholinergic target of organophosphate compounds. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2021, 346, 109578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudyanselage, A.W.; Wijamunige, B.C.; Kocoń, A.; Turner, R.; McLean, D.; Morentin, B.; Callado, L.F.; Carter, W.G. Alcohol Triggers the Accumulation of Oxidatively Damaged Proteins in Neuronal Cells and Tissues. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prendergast, M.A.; Self, R.L.; Smith, K.J.; Ghayoumi, L.; Mullins, M.M.; Butler, T.R.; Buccafusco, J.J.; Gearhart, D.A.; Terry, A.V., Jr. Microtubule-associated targets in chlorpyrifos oxon hippocampal neurotoxicity. Neuroscience 2007, 146, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huen, K.; Bradman, A.; Harley, K.; Yousefi, P.; Boyd Barr, D.; Eskenazi, B.; Holland, N. Organophosphate pesticide levels in blood and urine of women and newborns living in an agricultural community. Environ. Res. 2012, 117, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thépaut, E.; Tebby, C.; Bisson, M.; Brochot, C.; Ratier, A.; Zaros, C.; Personne, S.; Chardon, K.; Zeman, F. Prenatal exposure to chlorpyrifos of French children from the Elfe cohort. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2025, 263, 114480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wołejko, E.; Łozowicka, B.; Jabłońska-Trypuć, A.; Pietruszyńska, M.; Wydro, U. Chlorpyrifos Occurrence and Toxicological Risk Assessment: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjorling-Poulsen, M.; Andersen, H.R.; Grandjean, P. Potential developmental neurotoxicity of pesticides used in Europe. Environ. Health 2008, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachana, M.; Shafer, T.J.; Terron, A. Toward a Better Testing Paradigm for Developmental Neurotoxicity: OECD Efforts and Regulatory Considerations. Biology 2021, 10, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mie, A.; Rudén, C. Non-disclosure of developmental neurotoxicity studies obstructs the safety assessment of pesticides in the European Union. Environ. Health 2023, 22, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulkrabkova, L.; Muckova, L.; Hrabinova, M.; Sorf, A.; Kobrlova, T.; Jost, P.; Bezdekova, D.; Korabecny, J.; Jun, D.; Soukup, O. Differentiated SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells as a model for evaluation of nerve agent-associated neurotoxicity. Arch. Toxicol. 2023, 97, 2209–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.P.; Wang, T.T.; Wu, X.Z.; Wang, D.W.; Chao, Y.S. An in vivo study in mice: Mother’s gestational exposure to organophosphorus pesticide retards the division and migration process of neural progenitors in the fetal developing brain. Toxicol. Res. 2016, 5, 1359–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmorsy, E.; Al-Ghafari, A.; Al Doghaither, H.; Salama, M.; Carter, W.G. An Investigation of the Neurotoxic Effects of Malathion, Chlorpyrifos, and Paraquat to Different Brain Regions. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkhondeh, T.; Mehrpour, O.; Forouzanfar, F.; Roshanravan, B.; Samarghandian, S. Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in organophosphate pesticide-induced neurotoxicity and its amelioration: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 24799–24814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, B.D.; Seth, V.; Ahmed, R.S. Pesticide-induced oxidative stress: Perspectives and trends. Rev. Environ. Health 2021, 16, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes-Ferreira, M.; Farinha, L.R.L.; Costa, Y.S.O.; Pinto, F.J.; Disner, G.R.; Rosa, J.G.D.S.; Lima, C. Pesticide-Induced Inflammation at a Glance. Toxics 2023, 11, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, M.A.; Ballesteros, S.; Sánchez de la Torre, C.; Sanchiz, A.; Almarza, E.; García-Aguilera, A. Attempted suicide by ingestion of chlorpyrifos: Identification in serum and gastric content by GC-FID/GC-MS. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2004, 28, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.J.; In, S.W.; Lee, S.K.; Choi, W.K.; Park, Y.S.; Chung, H.S. Postmortem blood concentrations of organophosphorus pesticides. Forensic Sci. Int. 2009, 184, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
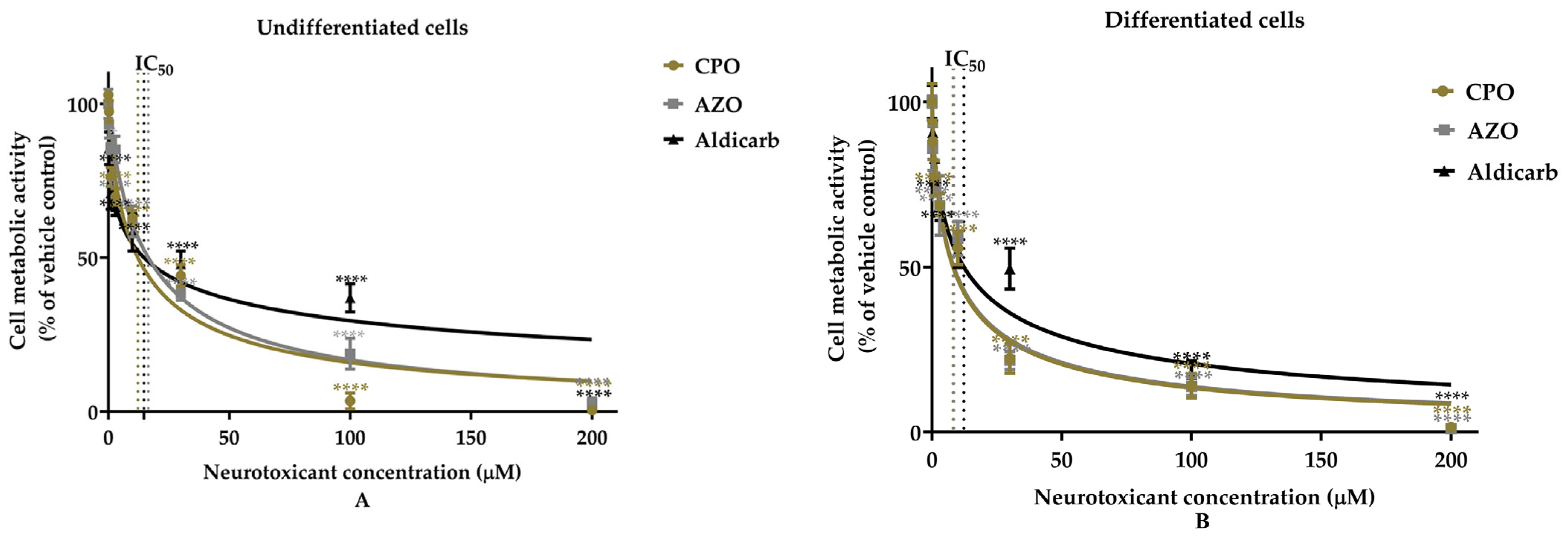
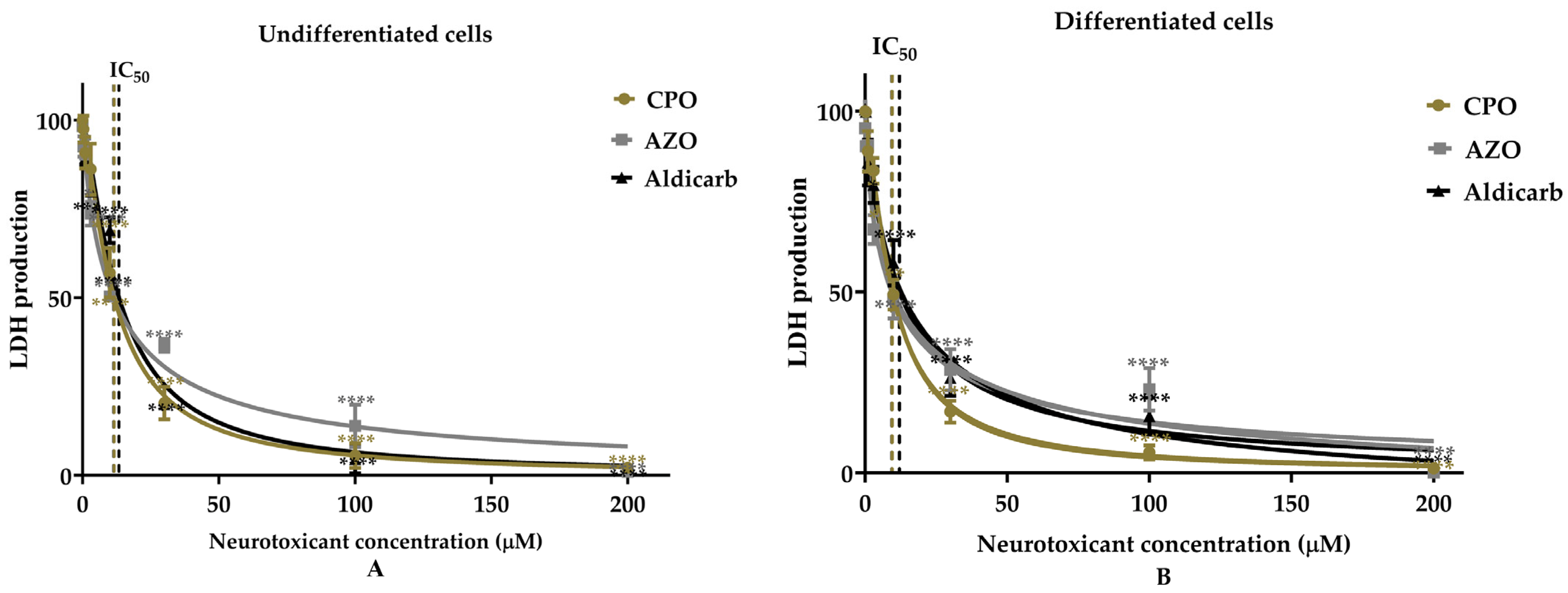

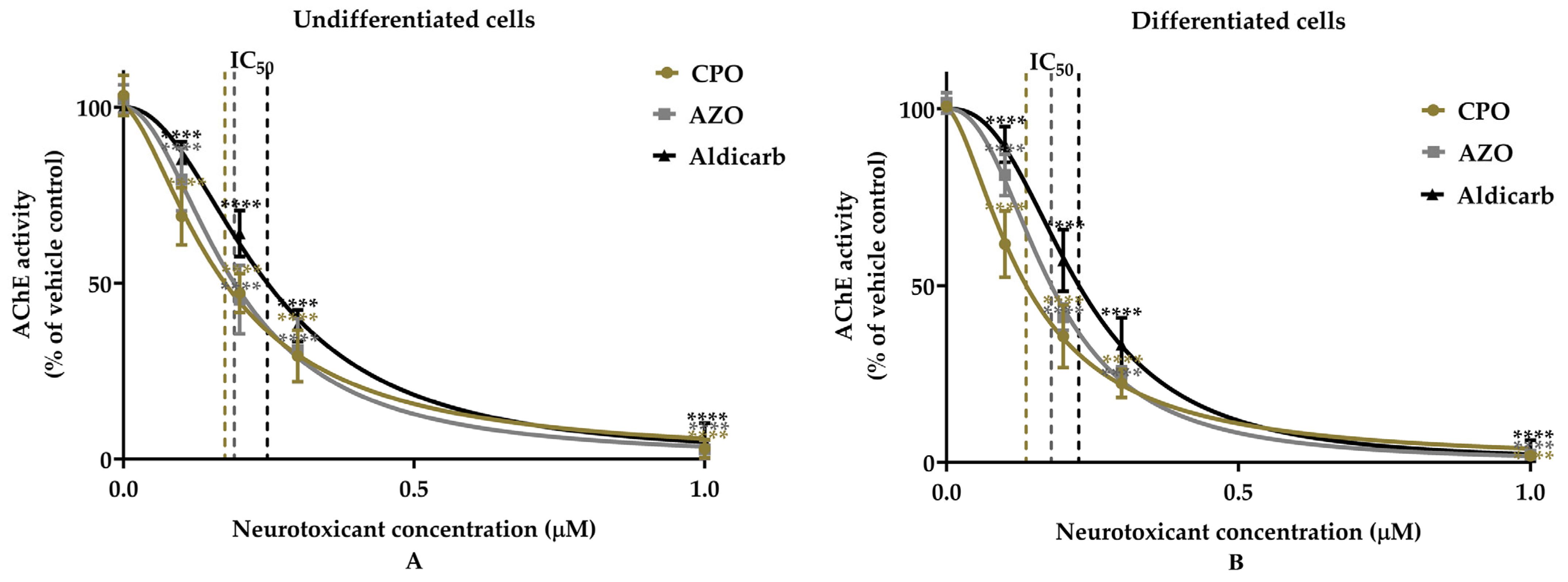
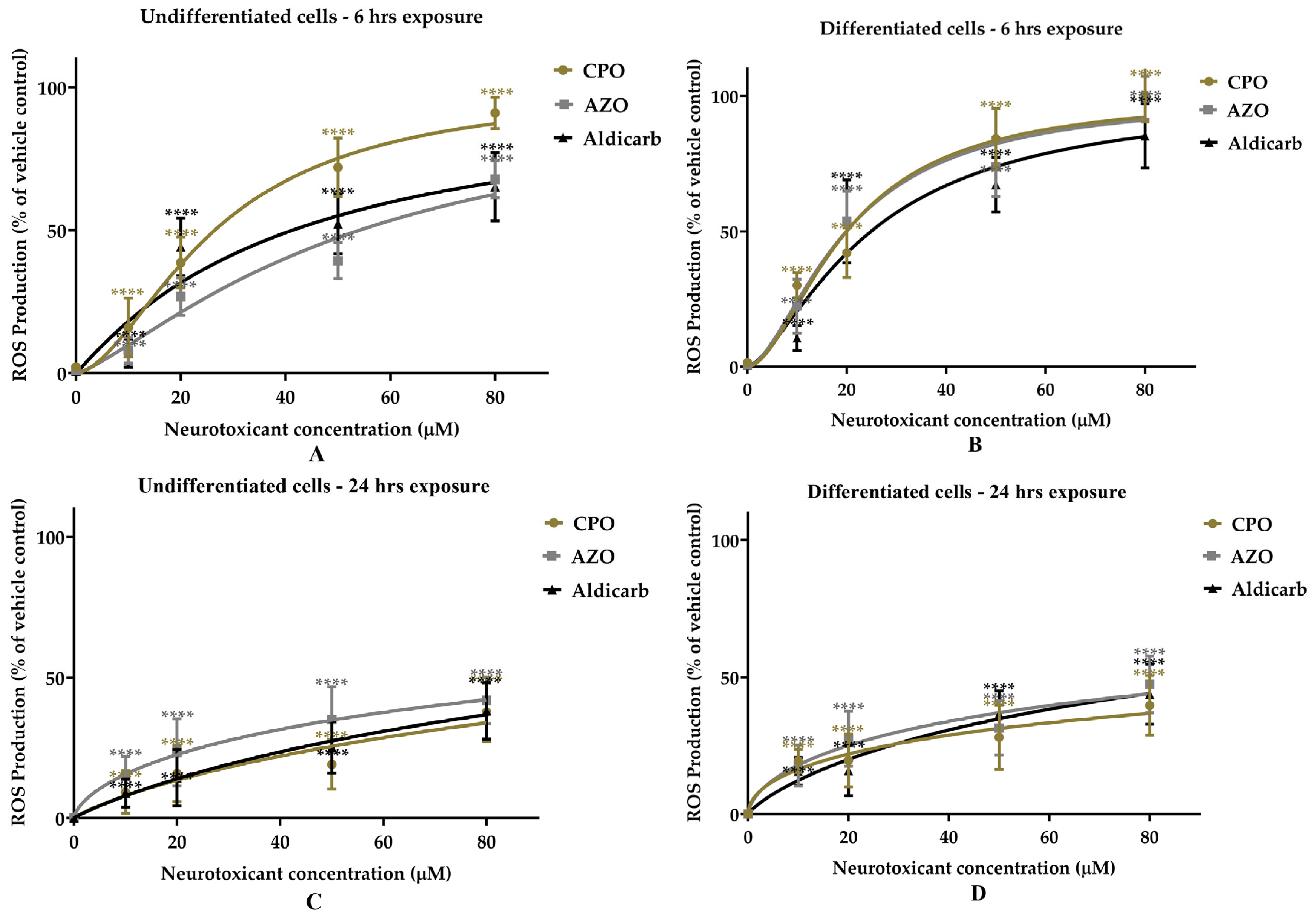
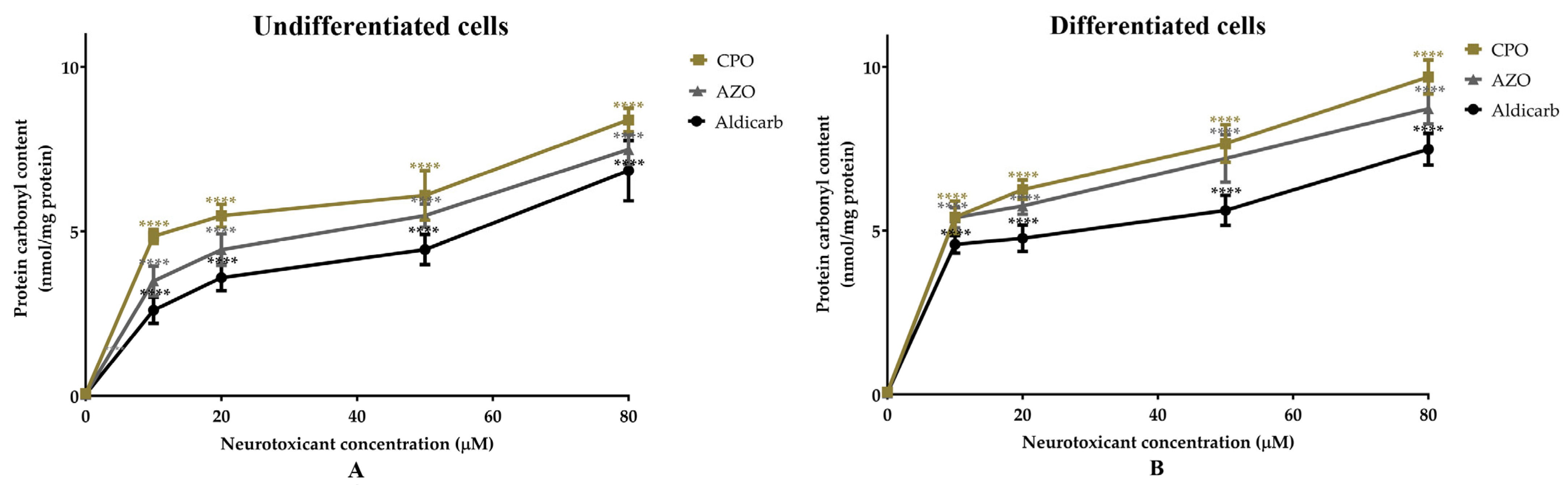
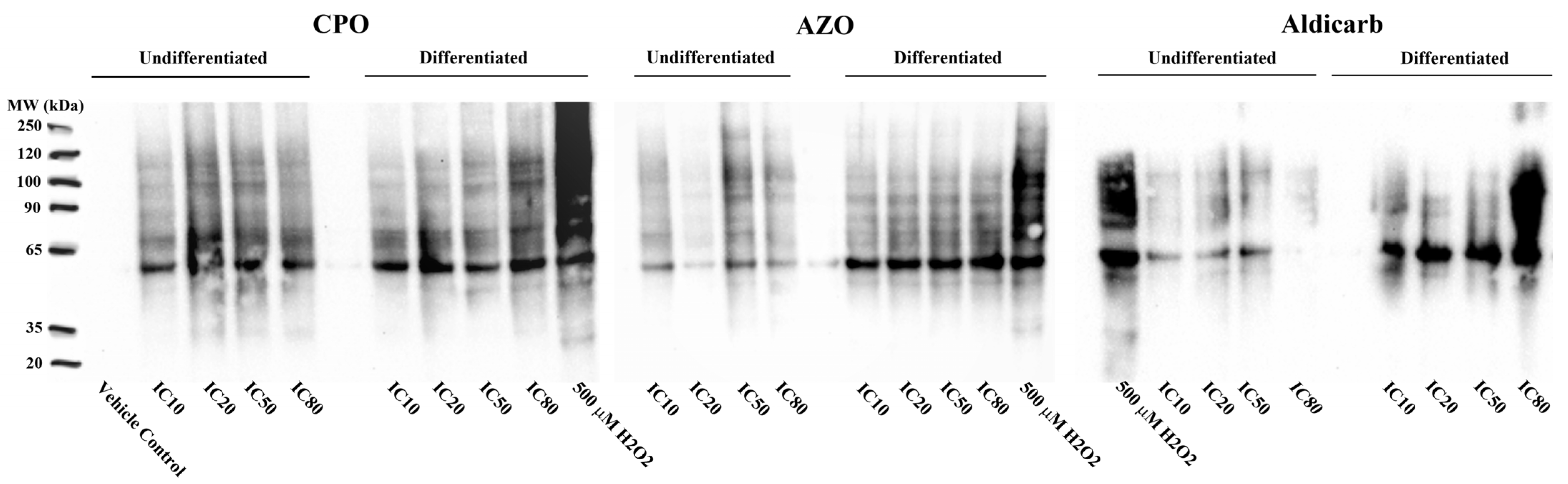
| Cell Type | Pesticides | MTT Assay | LDH Assay | ATP Assay | AChE Inhibition | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 (µM) | R2 | IC50 (µM) | R2 | IC50 (µM) | R2 | IC50 (µM) | R2 | ||
| Undifferentiated | CPO | 12.0 ± 1.9 | 0.937 | 12.2 ± 0.6 | 0.995 | 12.5 ± 1.4 | 0.961 | 0.23 ± 0.02 | 0.949 |
| Differentiated | 8.2 ± 0.8 | 0.971 | 9.8 ± 0.3 | 0.990 | 9.18 ± 0.9 | 0.978 | 0.13 ± 0.01 | 0.949 | |
| Undifferentiated | AZO | 16.5 ± 1.4 | 0.977 | 12.2 ± 1.2 | 0.973 | 12.8 ± 0.2 | 0.997 | 0.21 ± 0.02 | 0.925 |
| Differentiated | 8.6 ± 1.0 | 0.962 | 11.4 ± 1.0 | 0.974 | 11.0 ± 0.3 | 0.995 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | 0.964 | |
| Undifferentiated | Aldicarb | 14.8 ± 2.9 | 0.910 | 14.2 ± 1.0 | 0.979 | 14.8 ± 1.2 | 0.970 | 0.22 ± 0.01 | 0.993 |
| Differentiated | 12.3 ± 1.7 | 0.949 | 13.5 ± 0.7 | 0.990 | 13.8 ± 1.4 | 0.961 | 0.21 ± 0.01 | 0.997 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wijesekara, A.; Wijamunige, B.; Kocon, A.; Mellor, I.R.; Carter, W.G. Human Neural Stem Cells Are More Vulnerable to Damage from Pesticide-Induced Oxidative Stress After Differentiation. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 10800. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910800
Wijesekara A, Wijamunige B, Kocon A, Mellor IR, Carter WG. Human Neural Stem Cells Are More Vulnerable to Damage from Pesticide-Induced Oxidative Stress After Differentiation. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(19):10800. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910800
Chicago/Turabian StyleWijesekara, Anusha, Buddhika Wijamunige, Artur Kocon, Ian R. Mellor, and Wayne G. Carter. 2025. "Human Neural Stem Cells Are More Vulnerable to Damage from Pesticide-Induced Oxidative Stress After Differentiation" Applied Sciences 15, no. 19: 10800. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910800
APA StyleWijesekara, A., Wijamunige, B., Kocon, A., Mellor, I. R., & Carter, W. G. (2025). Human Neural Stem Cells Are More Vulnerable to Damage from Pesticide-Induced Oxidative Stress After Differentiation. Applied Sciences, 15(19), 10800. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910800







