Statistical Modeling and Analysis of Similar Compound Interaction in Scientific Research
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Nonlinear Assessment of Interaction: The Finney Model and Extensions
2.1. Example 1
2.2. Example 2
2.3. Example 3
3. Nonlinear Assessment of Interaction: The Separate Ray Model and Extensions
3.1. Example 4
3.2. Example 5
3.3. Example 6
4. Additional Applications and Extensions of Interaction Assessment
4.1. Example 7
4.2. Example 8
4.3. Example 9
4.4. Example 10
5. Discussion
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CI | Confidence interval |
| LA | Lower asymptote |
| LSE | Least-squares estimate |
| MLE | Maximum likelihood estimate |
| MSE | Mean squares estimate (of variance) |
| NES | Not-equal slope (model) |
| PLCI | Profile likelihood confidence interval |
| REML | Restricted maximum likelihood (estimate) |
| SR(M) | Separate ray (model) |
| UA | Upper asymptote |
References
- Heggestad, H.E.; Bennett, J.H. Photochemical Oxidants Potentiate Yield Losses in Snap Beans Attributable to Sulfur Dioxide. Science 1981, 213, 1008–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heagle, A.S.; Heck, W.W.; Rawlings, J.O.; Philbeck, R.B. Effects of Chronic Doses of Ozone and Sulfur Dioxide on Injury and Yield of Soybeans in Open-Top Field Chambers. Crop Sci. 1983, 23, 1184–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, M.E.; Kappel, Q.E.; Fenical, W. Synergisms in Plant Defenses Against Herbivores: Interactions of Chemistry, Calcification, and Plant Quality. Ecology 1994, 75, 1714–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauderly, J.L.; Samet, J.M. Is There Evidence for Synergy Among Air Pollutants in Causing Health Effects? Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Box, G.E.P.; Draper, N.R. Response Surfaces, Mixtures, and Ridge Analysis, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, R.H.; Montgomery, D.C.; Anderson-Cook, C.M. Response Surface Methodology: Process and Product Optimization Using Designed Experiments, 4th ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Goldin, A.; Venditti, J.M.; Humphreys, S.R.; Dennis, D.; Mantel, N.; Greenhouse, S.W. An Investigation into the Synergistic Antileukemic Action of Amethopterin and 6-Mercaptopurine in Mice. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1955, 16, 129–138. [Google Scholar]
- Gerig, T.M.; Blum, U.; Meier, K. Statistical Analysis of the Joint Inhibitory Action of Similar Compounds. J. Chem. Ecol. 1989, 15, 2403–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, S.G.; Robinson, G.A. A Direct, General Approach Based on Isobolograms for Assessing the Joint Action of Drugs in Pre-Clinical Experiments. Stat. Med. 1994, 13, 2289–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindarajulu, Z. Statistical Techniques in Bioassay, 2nd ed.; Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Sims, S.R.; O’Brien, T.E. Mineral Oil and Aliphatic Alcohols: Toxicity and Analysis of Synergistic Effects on German Cockroaches (Dictyoptera: Blattellidac). J. Econ. Entomol. 2011, 104, 1680–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, N.; Hoang, T.; O’Brien, T.E. Acute Toxicity of Binary-Metal Mixtures of Copper, Zinc, and Nickel to Pimephales Promelas: Evidence of More-Than-Additive Effect. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 5, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, J.; Lee, Y.-S.; Kim, Y.; Shin, K.-I.; Hyun, S.; Cho, K. Joint Toxic Action of Binary Metal Mixtures of Copper, Manganese and Nickel to Paronychiurus kimi (Collembola). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 132, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, S.; Wolff, C.; Sures, B. Toxicity of Platinum, Palladium and Rhodium to Daphnia magna in Single and Binary Metal Exposure Experiments. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 224, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, U. Simple Phenolic Acids in Solution Culture I: pH and pKa. In Plant-Plant Allelopathic Interactions III; Blum, U., Ed.; Springer Nature Switzerland AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 71–113. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, N.; Goel, N. Phenolic Acids: Natural Versatile Molecules with Promising Therapeutic Applications. Biotech. Rep. 2019, 24, e00370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makariadou, E.; Wang, X.; Hein, N.; Deresa, N.W.; Mutambanengwe, K.; Verbist, B.; Thas, O. Synergy Detection: A Practical Guide to Statistical Assessment of Potential Drug Combinations. Pharm. Stat. 2024, 24, e2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muriel, J.; Escorial, M.; Carratalá, C.; Margarit, C.; Barrachina, J.; López, A.; Gallardo, E.; Kringen, M.K.; Peiró, A.M. Use of CYP2D6 Substrates and Inhibitors During Pain Management with Analgesic Opioids: Drug-Drug Interactions That Lead to Lack of Analgesic Effectiveness. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 176, 116882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, A.C.; Donev, A.N.; Tobias, R.D. Optimum Experimental Designs, with SAS; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, N.; Ye, R.; He, Q.; Guo, P.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Q. Capsaicin and Sorafenib Combination Treatment Exerts Synergist Anti-hepatocellular Carcinoma Activity by Suppressing EGFR and PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 3235–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, M.; Mandal, N.K. Optimum Mixture Designs for the Log-logistic Dose-response Model with Mixture of Two Similar Compounds. Commun. Stat. Simul. Comput. 2018, 47, 800–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, A.S.; Marques, C.R.; Encamação, J.C.; Abrantes, A.M.; Marques, I.A.; Laranjo, M.; Olivera, R.; Casalta-Lopes, J.E.; Gonçalves, A.C.; Sarmento-Ribeiro, A.B.; et al. Ascorbic Acid Chemosensitizes Colorectal Cancer Cells and Synergistically Inhibits Tumor Growth. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, Z.B.; Kuru, N.; Kiriakov, S.; Palmer, A.C.; Khalil, A.S.; Clemons, P.A.; Zaman, M.H.; Roth, F.P.; Cokoi, M. Modeling the Impact of Drug Interactions on Therapeutic Selectivity. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amzallag, A.; Ramaswamy, S.; Benes, C.H. Statistical Assessment and Visualization of Synergies for Large-scale Sparse Drug Combination Datasets. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, I.-H.; Kim, Y.; Baik, S.; Kim, J. Investigation of the Synergistic Toxicity of Binary Mixtures of Pesticides and Pharmaceuticals on Aliivibrio fischeri in Major River Basins in South Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blangiardo, M.; Pirani, M.; Kanapka, L.; Hansell, A.; Fuller, G. A Hierarchical Modelling Approach to Assess Multi Pollutant Effects in Time-series Studies. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demidenko, E.; Miller, T.W. Statistical Determination of Synergy Based on Bliss Definition of Drugs Independence. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regan-Fendt, K.E.; Xu, J.; DiVincenzo, M.; Duggan, M.C.; Shakya, R.; Na, R.; Carson, W.E.; Payne, P.R.O.; Li, F. Synergy from Gene Expression and Network Mining (SynGeNet) Method Predicts Synergistic Drug Combinations for Diverse Melanoma Genomic Subtypes. NPJ Syst. Biol. Appl. 2019, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robichaud, A.; Comtois, P. Environmental Factors and Asthma Hospitalization in Montreal, Canada, During Spring 2006–2008: A Synergy Perspective. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2019, 12, 1495–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidorov, P.; Naulaerts, S.; Ariey-Bonnet, J.; Pasquier, E.; Ballester, P.J. Predicting Synergism of Cancer Drug Combinations Using NCI-ALMANAC Data. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Wang, L.; Xu, H. Application of Kriging Models for a Drug Combination Experiment on Lung Cancer. Stat. Med. 2019, 38, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Yan, G. Synergistic Drug Combinations Prediction by Integrating Pharmacological Data. Synth. Syst. Biotechnol. 2019, 4, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonelli, J.; Mazumdar, M.; Bellinger, D.; Christiani, D.; Wright, R.; Coull, B. Estimating the Health Effects of Environmental Mixtures Using Bayesian Semiparametric Regression and Sparsity Inducing Priors. Ann. Appl. Stat. 2020, 14, 257–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, O.; Moeltner, K.; Yang, W. Respiratory Illness, Hospital Visits, and Health Costs: Is it Air Pollution or Pollen? Environ. Res. 2020, 187, 109572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, W.; Zou, B.; Wang, J.; Deng, Y.; Deng, L. DrugCombDB: A Comprehensive Database of Drug Combinations Toward the Discovery of Combinatorial Therapy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D871–D881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, S.K.; Eeles, C.; Ho, C.; Beri, G.; Yoo, E.; Tkachuk, D.; Tang, A.; Nijrabi, P.; Smirnov, P.; Seo, H.; et al. ToxicoDB: An Integrated Database to Mine and Visualize Large-Scale Toxicogenomic Datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W455–W462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wambaugh, M.A.; Denham, S.T.; Ayala, M.; Brammer, B.; Stonhill, M.A.; Brown, J.C.S. Synergistic and Antagonistic Drug Interactions in the Treatment of Systemic Fungal Infections. eLife 2020, 9, e54160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Jaaks, P.; Dry, J.; Garnett, M.; Menden, M.P.; Saez-Rodriguez, J. Stratification and Prediction of Drug Synergy Based on Target Functional Similarity. NPJ Syst. Biol. Appl. 2020, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wooten, D.J.; Meyer, C.T.; Lubbock, A.L.R.; Quaranta, V.; Lopez, C.F. MuSyC is a Consensus Framework that Unifies Multi-Drug Synergy Metrics for Combinatorial Drug Discovery. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeuner, S.; Vollmer, J.; Sigaud, R.; Oppermann, S.; Peterziel, H.; ElHarouni, D.; Oehme, I.; Witt, O.; Milde, T.; Ecker, J. Combination Drug Screen Identifies Synergistic Drug Interaction of BCL-XL and Class I Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors in MYC-Amplified Medulloblastoma Cells. J. Neuro. Oncol. 2024, 166, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finney, D.J. Probit Analysis; Cambridge University Press: London, UK, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Finney, D.J. Statistical Method in Biological Assay; Charles Griffin & Co.: London, UK, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Ratkowsky, D.A. Nonlinear Regression Modeling: A Unified Practical Approach; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Seber, G.A.F.; Wild, C.J. Nonlinear Regression; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Ratkowsky, D.A. Handbook of Nonlinear Regression Models; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, D.M.; Watts, D.G. Nonlinear Regression Analysis and Its Applications; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Archontoulis, S.V.; Miguez, F.E. Nonlinear Regression Models and Applications in Agricultural Research. Agron. J. 2015, 107, 786–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarantow, S.W.; Pisors, E.D.; Chiu, M.L. Introduction to the Use of Linear and Nonlinear Regression Analysis in Quantitative Biological Assays. Curr. Protoc. 2023, 3, e801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, T.E.; Silcox, J. Nonlinear Modelling: A Primer, Illustrations and Caveats. Bull. Math. Biol. 2024, 86, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, J.J. Bioassay; Kendall/Hunt Publishing: Dubuque, IA, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Brunden, M.N.; Vidmar, T.J.; McKean, J.W. Drug Interaction and Lethality Analysis; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Berenbaum, M.C. What is Synergy? Pharmacol. Rev. 1989, 41, 93–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, C.N.; Braunberg, R.C.; Friedman, L. Nonlinear Statistical Models for the Joint Action of Toxins. Biometrics 1993, 49, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouws, E. Drug Resistance in Malaria Research—The Statistical Approach; Univ. Natal Pietermaritzburg Press: Scottsville, Africa, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Greco, W.R.; Bravo, G.; Parsons, J.C. The Search for Synergy: A Critical Review from a Response Surface Perspective. Pharmacol. Rev. 1995, 47, 331–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, K.S.; Carter, W.H., Jr.; Gennings, C. A Statistical Test for Detecting and Characterizing Departures from Additivity in Drug/Chemical Combinations. J. Agric. Biol. Environ. Stat. 2000, 5, 342–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallarida, R.J. Drug Synergism and Dose-Effect Data Analysis; Chapman & Hall/CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bliss, C.I. The Toxicity of Poisons Applied Jointly. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1939, 26, 585–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loewe, S. The Problem of Synergism and Antagonism of Combined Drugs. Arzneimittelforschung 1953, 3, 285–290. [Google Scholar]
- Fraser, T.R. Lecture on the Antagonism Between the Actions of Active Substances. Br. Med. J. 1872, 2, 485–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tang, J.; Wennerberg, K.; Aittokallio, T. What is Synergy? The Saariselkä Agreement Revisited. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedergreen, N.; Christensen, A.M.; Kamper, A.; Kudsk, P.; Mathiassen, S.K.; Streibig, J.C.; Sørensen, H. A Review of Independent Action Compared to Concentration Addition as Reference Models for Mixtures of Compounds with Different Molecular Target Sites. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2008, 27, 1621–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuels, M.L.; Witmer, J.A.; Schaffner, A.A. Statistics for the Life Sciences, 5th ed.; Pearson: Boston, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzmaurice, G.M.; Laird, N.M.; Ware, J.H. Applied Longitudinal Analysis, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Giltinan, D.M.; Capizzi, T.P.; Malani, H. Diagnostic Tests for Similar Action of Two Compounds. Appl. Stat. 1988, 37, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straetemans, R.; O’Brien, T.; Wouters, L.; van Dun, J.; Janicot, M.; Bijnens, L.; Burzykowski, T.; Aerts, M. Design and Analysis of Drug Combination Experiments. Biom. J. 2005, 47, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.T. The Problem of the Evaluation of Rotenone-Containing Plants. VI. The Toxicity of l-Elliptone and of Poisons Applied Jointly, with Further Observations of the Rotenone Equivalent Method of Assessing the Toxicity of Derris Root. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1942, 29, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornfield, J. Comparative Bioassays and the Role of Parallelism. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1964, 144, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streibig, J.C.; Rudemo, M.; Jensen, J.E. Dose-Response Curves and Statistical Models. In Herbicide Bioassays; Streibig, J.C., Kudsk, P., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993; pp. 29–55. [Google Scholar]
- Gessner, P.K.; Cabana, B.E. A Study of the Interaction of the Hypnotic Effects and of the Toxic Effects of Chloral Hydrate and Ethanol. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1970, 174, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilder, C.R.; Loughin, T.M. Analysis of Categorical Data with R, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Darby, S.C.; Ellis, M.J. A Test for Synergism Between Two Drugs. Appl. Stat. 1976, 25, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, T.E.; Chooprateep, S.; Homkham, N. Efficient Geometric and Uniform Design Strategies for Sigmoidal Regression Models. S. Afr. Stat. J. 2009, 43, 49–83. [Google Scholar]
- Short, T.G.; Plummer, J.L.; Chui, P.T. Hypnotic and Anaesthetic Interactions Between Midazolam, Propofol and Alfentanil. Br. J. Anaesth. 1992, 69, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozanne, G.; Mathieu, L.G. Analysis of Interactions Between Treatments Applied Concurrently Onto Biological Systems. Comput. Biol. Med. 1983, 13, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, J.; Overvad, K. The Concept of Multifactorial Etiology of Cancer. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1993, 72, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, T.E. Designing for Parameter Subsets in Gaussian Nonlinear Regression Models. J. Data Sci. 2005, 3, 179–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.J.; Kong, M.; Ayers, G.D.; Lotan, R. Interaction Index and Different Methods for Determining Drug Interaction in Combination Therapy. J. Biopharm. Stat. 2007, 17, 461–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almohaimeed, B.; Donev, A.N. Experimental Designs for Drug Combination Studies. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2014, 71, 1077–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland-Letz, T.; Gunkel, N.; Amtmann, E.; Kopp-Schneider, A. Parametric Modeling and Optimal Experimental Designs for Estimating Isobolograms for Drug Interactions in Toxicology. J. Biopharm. Stat. 2018, 28, 763–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, T.E. Contemporary Robust Optimal Design Strategies. In Trends and Perspectives in Linear Statistical Inference; Tez, M., von Rosen, D., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, T.E.; Silcox, J. Practical Design Approaches for Assessing Parallelism in Dose Response Modelling. In Contemporary Biostatistics with Biopharmaceutical Applications; Zhang, L., Chen, D., Jiang, H., Li, G., Quan, H., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 167–181. [Google Scholar]
- O’Brien, T.E.; Silcox, J. Efficient Experimental Design for Dose Response Modelling. J. Appl. Stat. 2021, 48, 2864–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, D.C. Design and Analysis of Experiments, 10th ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
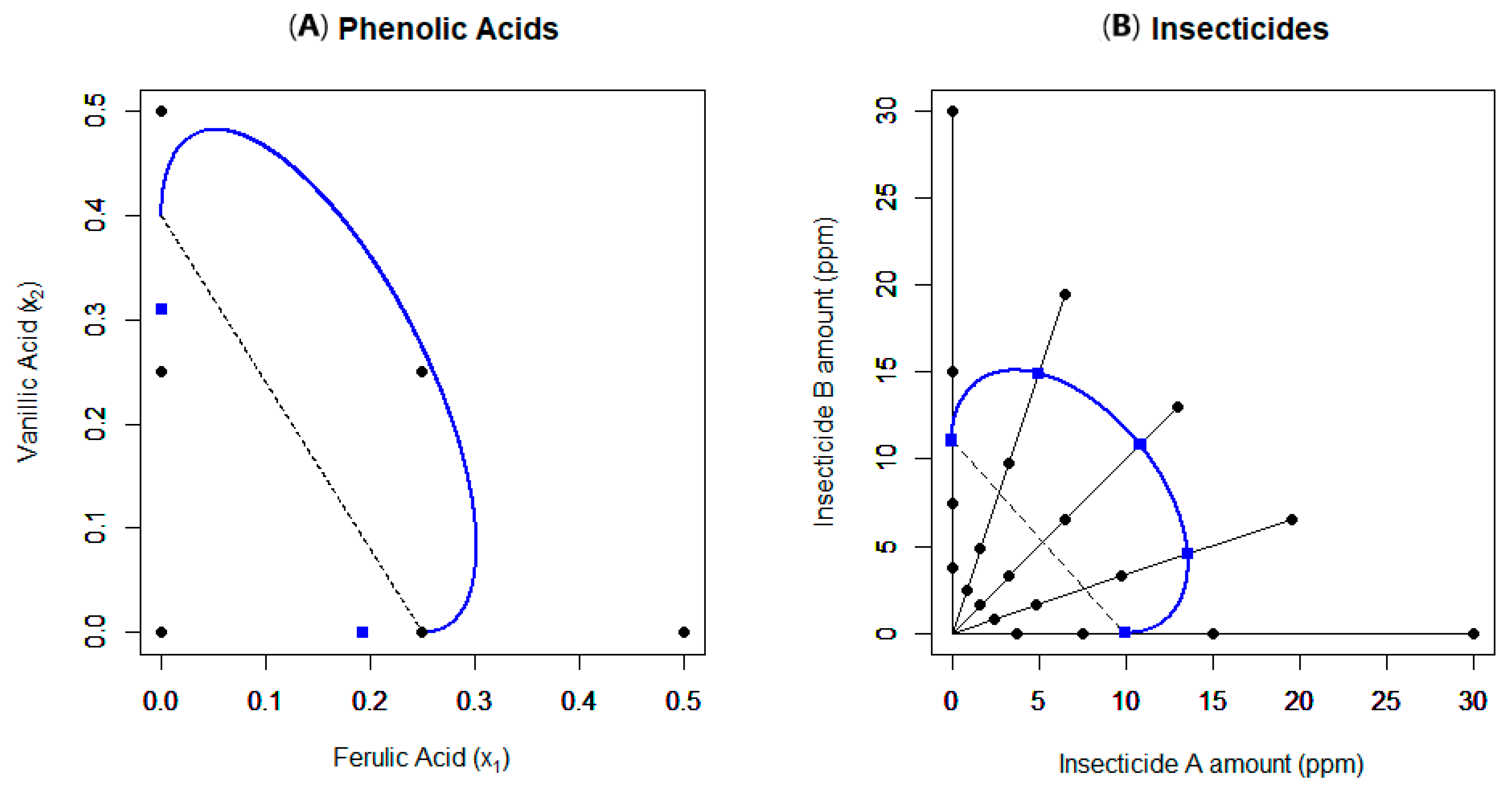
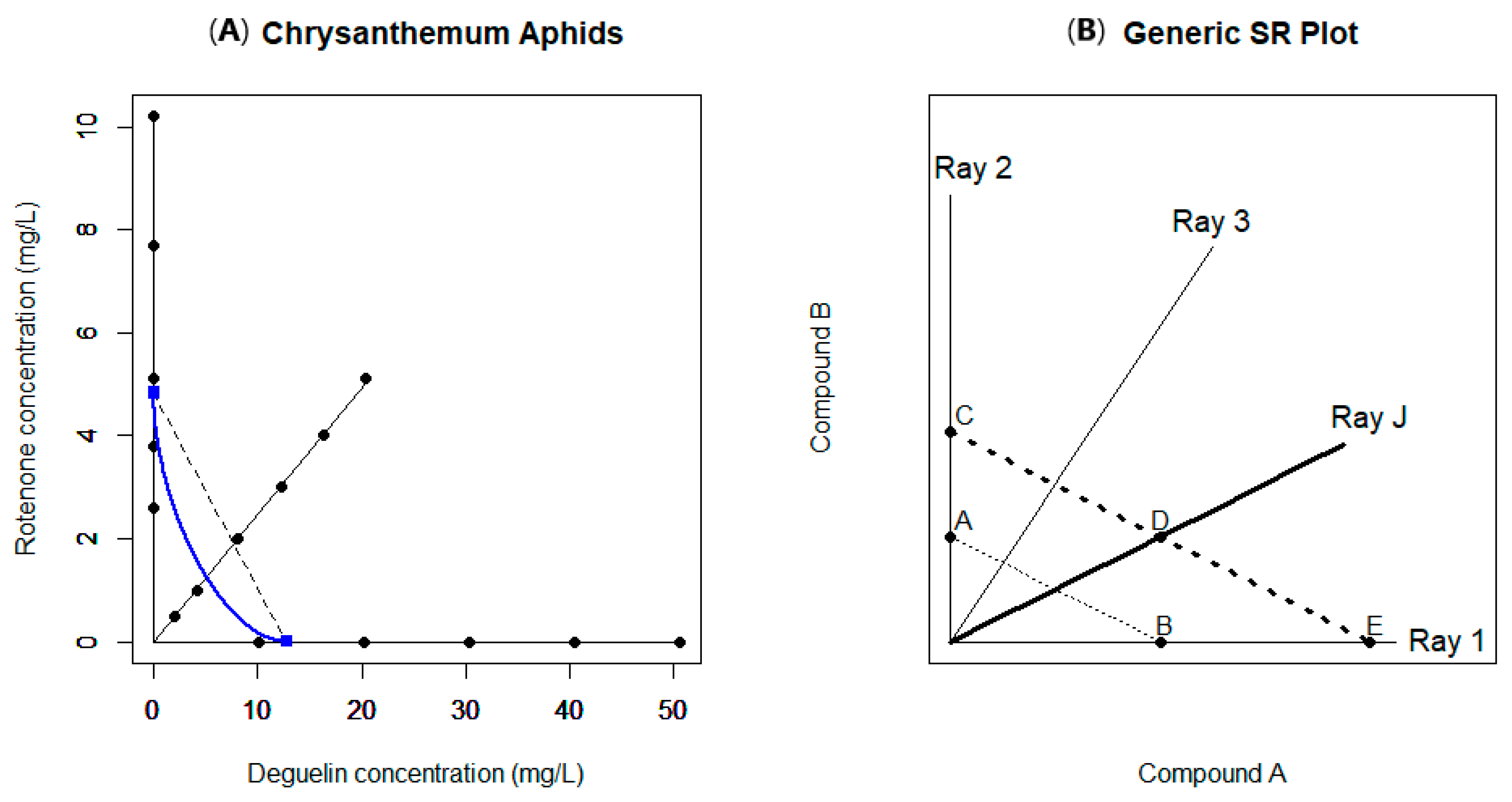
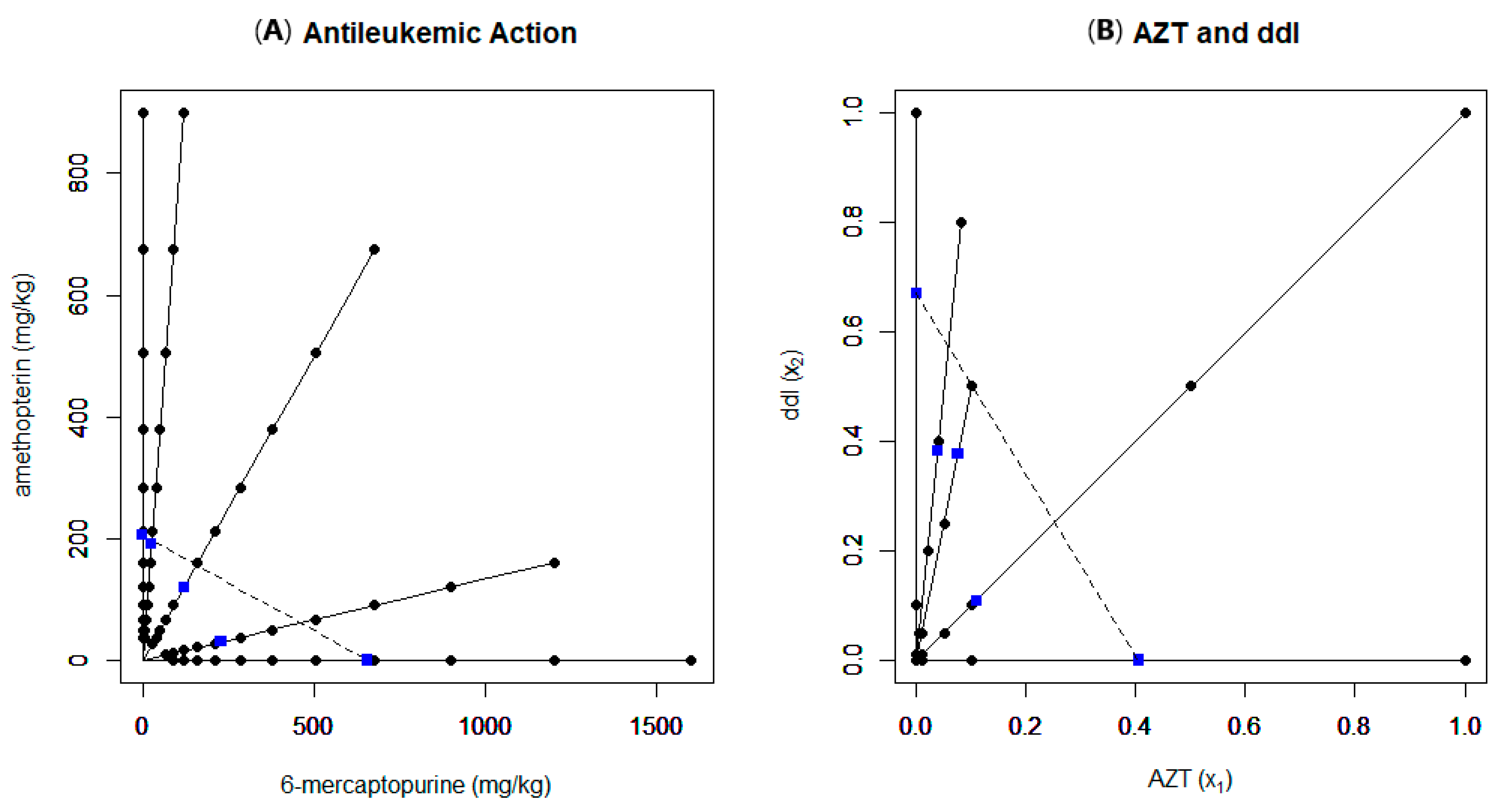
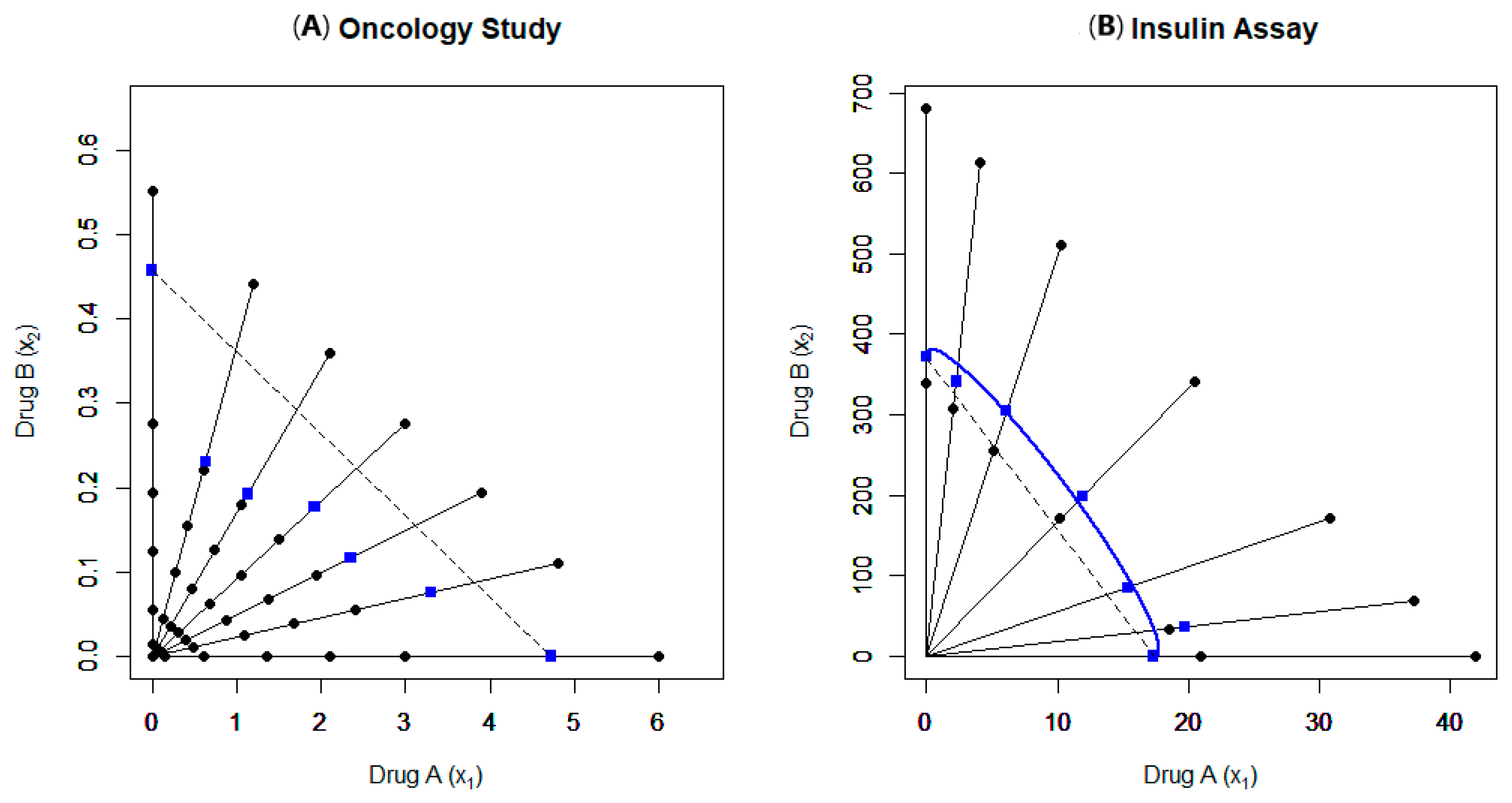
| Example Number | Data Source Reference | Experimental Setup | Model(s) Used | Findings | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [8] | Six support points; only one interior point | Finney 5 (normal); fixed & random chamber effects | Antagonism | Consider adding more interior points and ray(s) |
| 2 | [65] | Ray design; 3 interior rays | Finney 4b (binomial dist.) | Antagonism | Good design and spread of rays |
| 3 | [67] | Ray design; 1 interior ray | Finney 4b (binomial dist.), separate slopes | Synergy | Consider adding more interior ray(s) |
| 4 | [7] | Ray design; 3 interior rays | SR model; binomial distribution | Mixed; synergy for some rays | Acceptable design; change ray slopes; use fewer support points per ray and increase |
| 5 | [9] | Ray design; 3 interior rays | SR model; NB distribution (count data) | Mixed; synergy for some rays | Good design; change ray slopes for better spread |
| 6 | [11] | Ray design; 3 interior rays (two studies) | SR model; binomial distribution | Mixed; both synergy and antagonism | Good design; use fewer support points per ray to increase |
| 7 | [66] | Ray design; 5 interior rays; nine 96-well plates | SR model; normal with random effects; model variance | Synergy | Good design and spread of rays; reduce no. support points per ray |
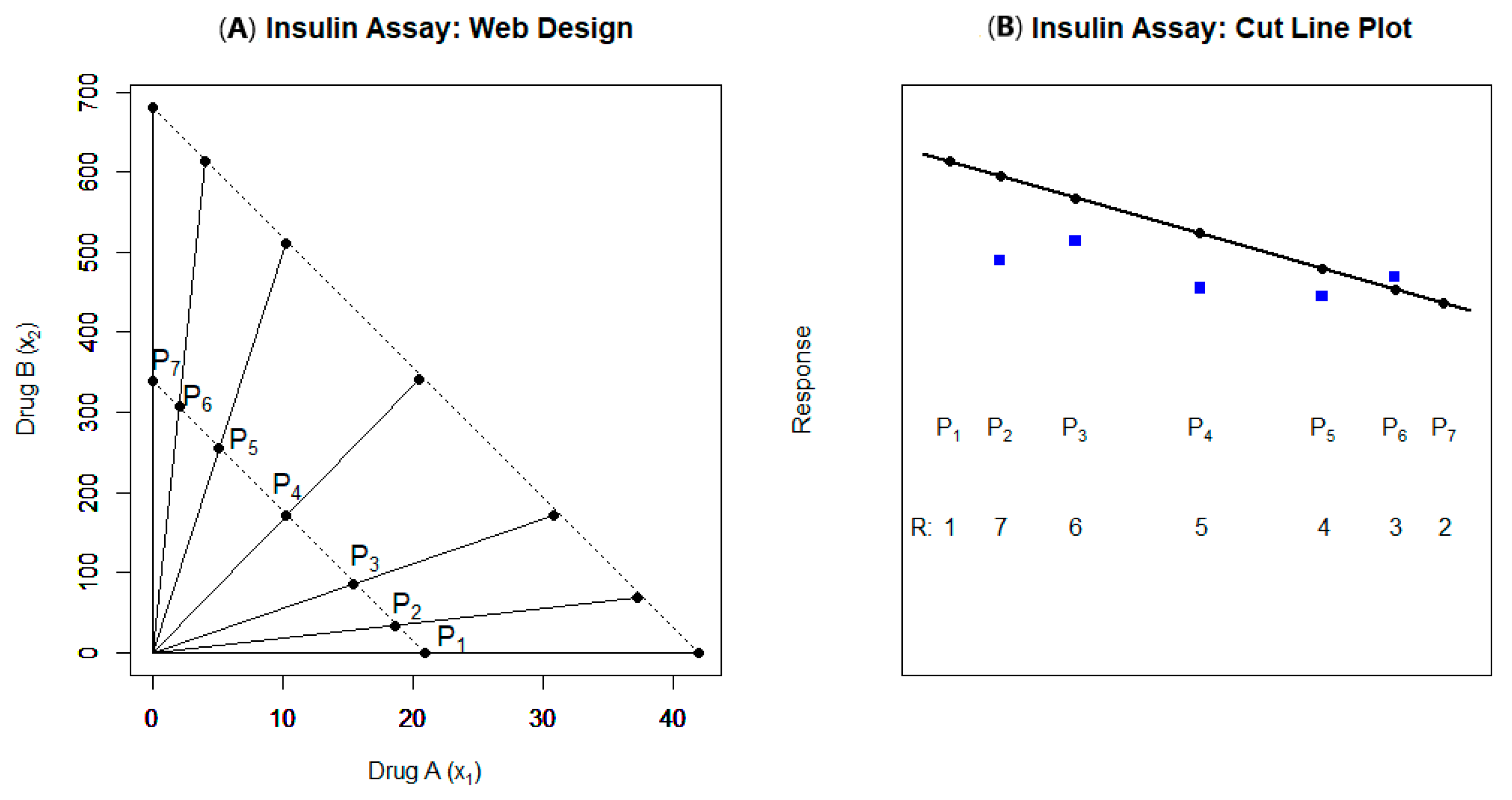
| 8 | [72] | Web design; 5 interior rays; only 2 cut lines | Finney and SR model with normal dist. | (Marginal) antagonism | Reasonable design; consider using 4 cut lines (not two) |
| 9 | [12] | 3 factors, non-ray design used due to practical limitations | Extended Finney model; binomial distribution | Pairwise synergy between all metal pairs | Three-way combination (7th ray) should be added |
| 10 | [74] | 3 factors, ray design with one interior ray per pair and the variable triple | Extended Finney and SR models; binomial distribution | (Marginal) three-way antagonism | Consider a larger study to increase power (i.e., increase chosen ) |
| Model | Potential Advantages | Potential Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Finney |
|
|
| SR |
|
|
| CLCI |
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
O’Brien, T.E. Statistical Modeling and Analysis of Similar Compound Interaction in Scientific Research. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9971. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189971
O’Brien TE. Statistical Modeling and Analysis of Similar Compound Interaction in Scientific Research. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(18):9971. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189971
Chicago/Turabian StyleO’Brien, Timothy E. 2025. "Statistical Modeling and Analysis of Similar Compound Interaction in Scientific Research" Applied Sciences 15, no. 18: 9971. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189971
APA StyleO’Brien, T. E. (2025). Statistical Modeling and Analysis of Similar Compound Interaction in Scientific Research. Applied Sciences, 15(18), 9971. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189971




