Analysis of Hemodynamic Markers in Atrial Fibrillation Using Advanced Imaging Techniques
Abstract
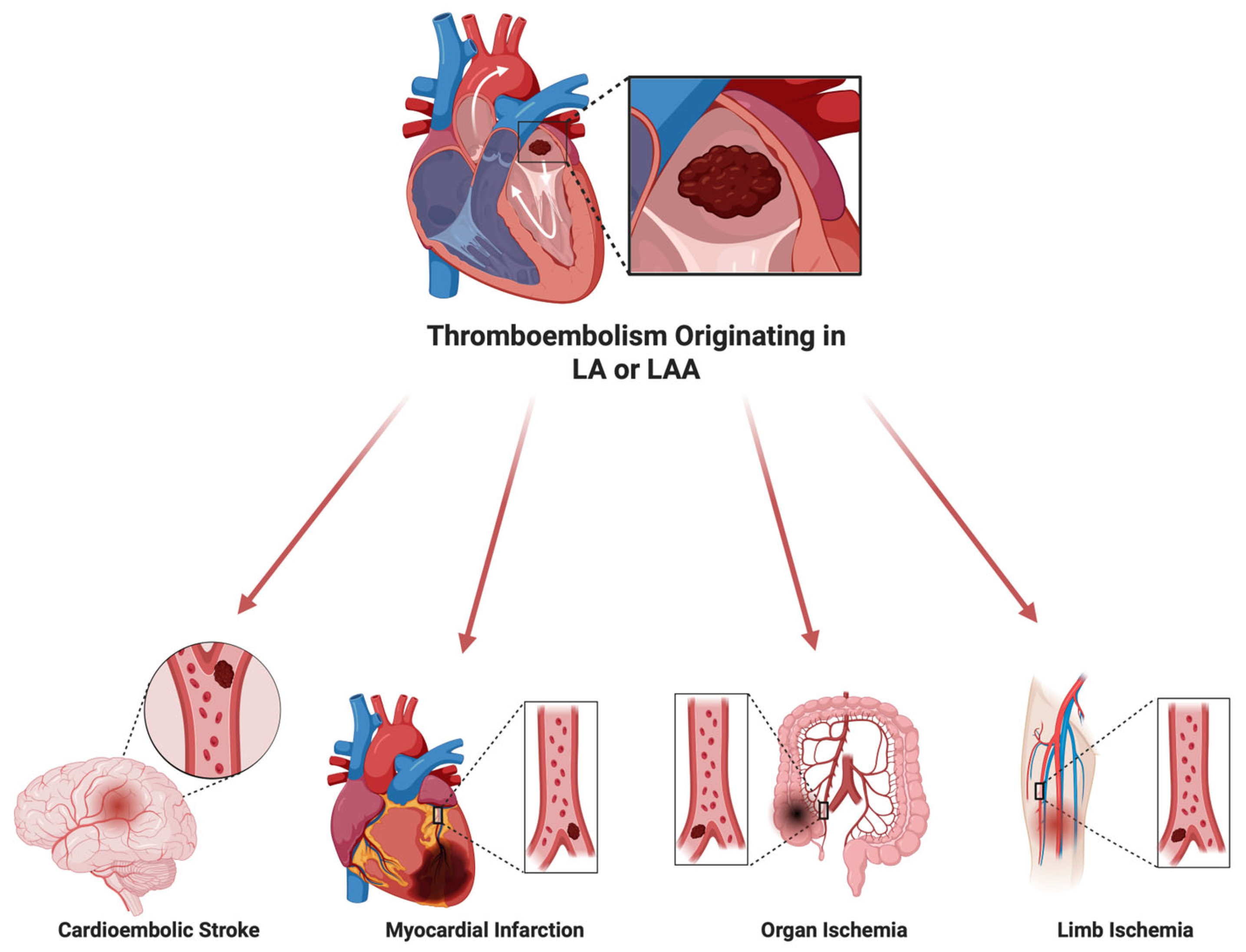
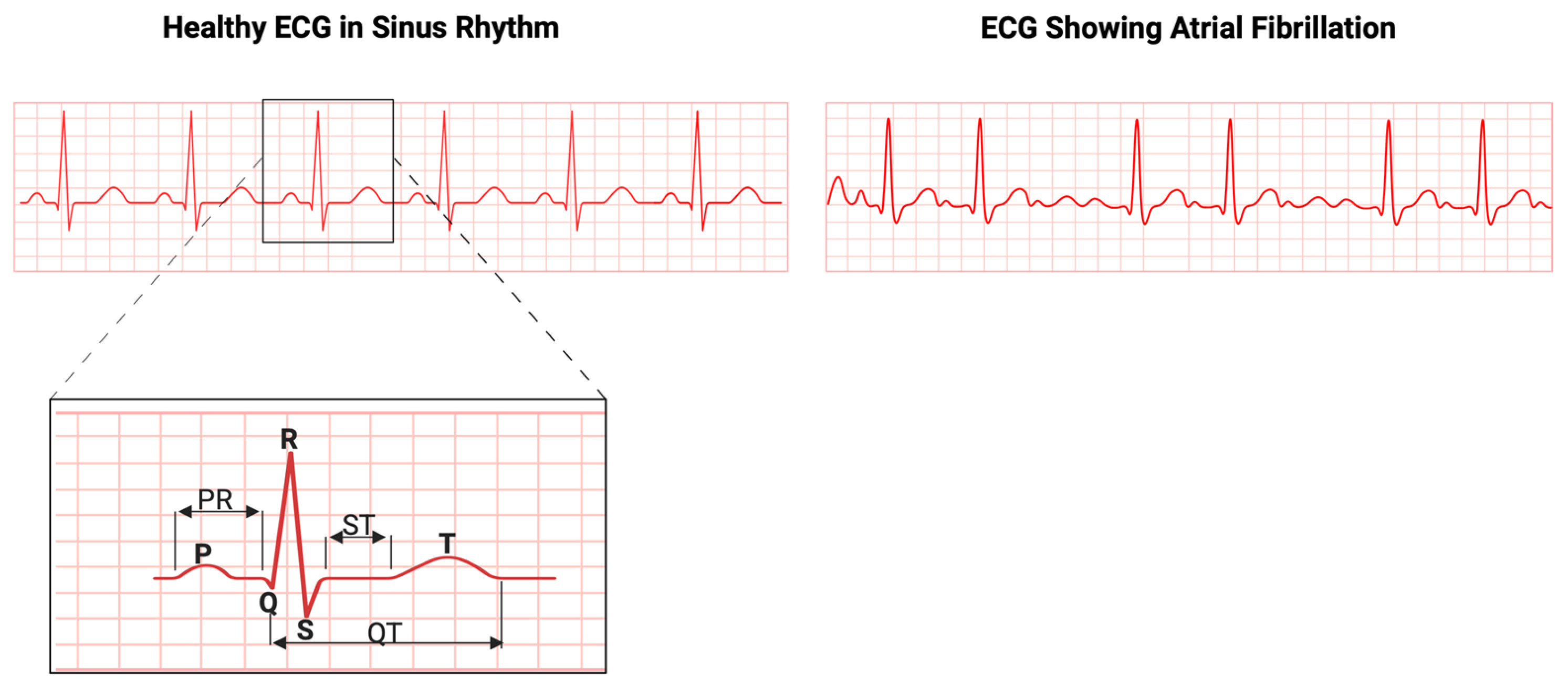
1. Introduction
2. Standard of Care
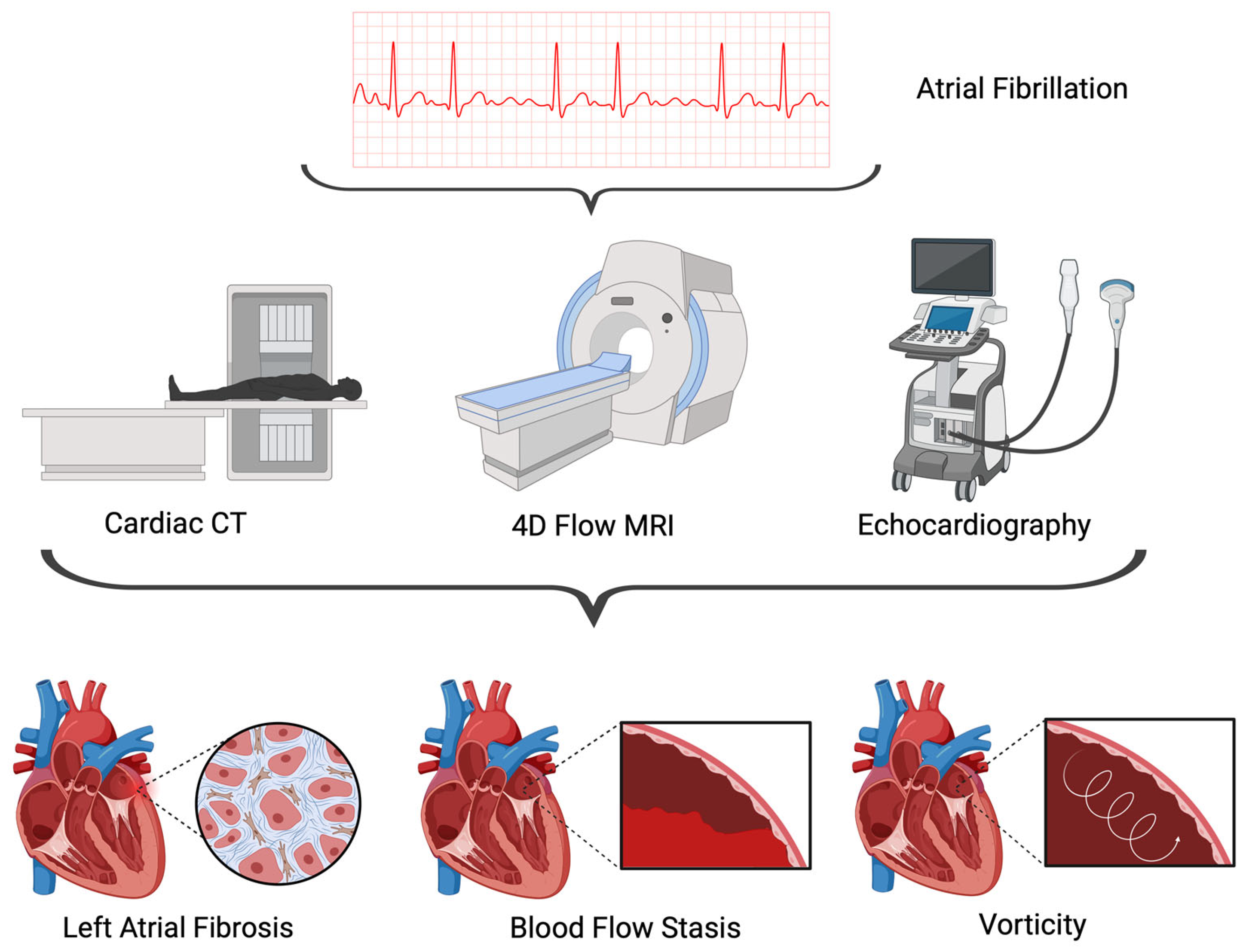
3. Imaging Modalities
3.1. Echocardiography
3.2. Cardiac CT
3.3. Cardiac MRI
4. Hemodynamic Markers of Atrial Fibrillation
4.1. Blood Flow Stasis
4.2. LA Strain
4.3. Vorticity
4.4. Wall Shear Stress
4.5. Oscillatory Shear Index
5. Discussion
5.1. Gaps in the Literature and Future Directions
5.2. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Linz, D.; Gawalko, M.; Betz, K.; Hendriks, J.M.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Vinter, N.; Guo, Y.; Johnsen, S. Atrial Fibrillation: Epidemiology, Screening and Digital Health. Lancet Reg. Health-Eur. 2024, 37, 100786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.C.; Hobbs, F.D.R.; Kenkre, J.E.; Roalfe, A.K.; Iles, R.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Davies, M.K. Prevalence of Atrial Fibrillation in the General Population and in High-Risk Groups: The ECHOES Study. Europace 2012, 14, 1553–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, P.G.; Healey, J.S.; Raina, P.; Connolly, S.J.; Ibrahim, Q.; Gupta, R.; Avezum, A.; Dans, A.L.; Lopez-Jaramillo, P.; Yeates, K.; et al. Global Variations in the Prevalence, Treatment, and Impact of Atrial Fibrillation in a Multi-National Cohort of 153 152 Middle-Aged Individuals. Cardiovasc. Res. 2021, 117, 1523–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shantsila, E.; Choi, E.-K.; Lane, D.A.; Joung, B.; Lip, G.Y.H. Atrial Fibrillation: Comorbidities, Lifestyle, and Patient Factors. Lancet Reg. Health–Eur. 2024, 37, 100784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurkas, E.; Akpınar, C.K.; Ozdemir, A.O.; Aykac, O.; Önalan, A. Is Cardioembolic Stroke More Frequent than Expected in Acute Ischemic Stroke Due to Large Vessel Occlusion? Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 27, 4046–4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellman, J.; Sheikh, F. Atrial Fibrillation: Mechanisms, Therapeutics, and Future Directions. In Comprehensive Physiology; Prakash, Y.S., Ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 649–665. ISBN 978-0-470-65071-4. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.; Scherlag, B.J.; Lin, J.; Niu, G.; Fung, K.-M.; Zhao, L.; Ghias, M.; Jackman, W.M.; Lazzara, R.; Jiang, H.; et al. Atrial Fibrillation Begets Atrial Fibrillation: Autonomic Mechanism for Atrial Electrical Remodeling Induced by Short-Term Rapid Atrial Pacing. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2008, 1, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchhof, P.; Benussi, S.; Kotecha, D.; Ahlsson, A.; Atar, D.; Casadei, B.; Castella, M.; Diener, H.-C.; Heidbuchel, H.; Hendriks, J.; et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the Management of Atrial Fibrillation Developed in Collaboration with EACTS. Eur Heart J 2016, 37, 2893–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gelder, I.C.; Rienstra, M.; Bunting, K.V.; Casado-Arroyo, R.; Caso, V.; Crijns, H.J.G.M.; De Potter, T.J.R.; Dwight, J.; Guasti, L.; Hanke, T.; et al. 2024 ESC Guidelines for the Management of Atrial Fibrillation Developed in Collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 3314–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Galvez, R.; Rivera-Caravaca, J.M.; Roldán, V.; Orenes-Piñero, E.; Esteve-Pastor, M.A.; López-García, C.; Saura, D.; González, J.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Marín, F. Imaging in Atrial Fibrillation: A Way to Assess Atrial Fibrosis and Remodeling to Assist Decision-Making. Am. Heart J. 2023, 258, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, J.G.; Aguilar, M.; Atzema, C.; Bell, A.; Cairns, J.A.; Cheung, C.C.; Cox, J.L.; Dorian, P.; Gladstone, D.J.; Healey, J.S.; et al. The 2020 Canadian Cardiovascular Society/Canadian Heart Rhythm Society Comprehensive Guidelines for the Management of Atrial Fibrillation. Can. J. Cardiol. 2020, 36, 1847–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joglar, J.A.; Chung, M.K.; Armbruster, A.L.; Benjamin, E.J.; Chyou, J.Y.; Cronin, E.M.; Deswal, A.; Eckhardt, L.L.; Goldberger, Z.D.; Gopinathannair, R.; et al. 2023 ACC/AHA/ACCP/HRS Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Atrial Fibrillation: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2024, 149, e1–e156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, B.; Camm, J.; Calkins, H.; Healey, J.S.; Rosenqvist, M.; Wang, J.; Albert, C.M.; Anderson, C.S.; Antoniou, S.; Benjamin, E.J.; et al. Screening for Atrial Fibrillation: A Report of the AF-SCREEN International Collaboration. Circulation 2017, 135, 1851–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, J.; Sheitt, H.; Bristow, M.S.; Lydell, C.; Howarth, A.G.; Heydari, B.; Prato, F.S.; Drangova, M.; Thornhill, R.E.; Nery, P.; et al. Left Atrial Vortex Size and Velocity Distributions by 4D Flow MRI in Patients with Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation: Associations with Age and CHA2 DS2–VASc Risk Score. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 51, 871–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, D.P.; Delgado, V.; Bax, J.J. Imaging for Atrial Fibrillation. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2012, 37, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tops, L.F.; Schalij, M.J.; Bax, J.J. Imaging and Atrial Fibrillation: The Role of Multimodality Imaging in Patient Evaluation and Management of Atrial Fibrillation. Eur. Heart J. 2010, 31, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troughton, R.W. The Role of Echocardiography in Atrial Fibrillation and Cardioversion. Heart 2003, 89, 1447–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marincheva, G.; Iakobishvili, Z.; Valdman, A.; Laish-Farkash, A. Left Atrial Strain: Clinical Use and Future Applications—A Focused Review Article. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 23, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eren, H.; Acar, R.D.; Demir, S.; Omar, M.B.; Öcal, L.; Kalkan, M.E.; Cerşit, S.; Akçakoyun, M. Speckle–tracking Echocardiography Can Predict Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Supraventricular Tachycardia. Pacing Clin. Electrophis 2021, 44, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-S.; Youn, H.-J. Role of Echocardiography in Atrial Fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Ultrasound 2011, 19, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.D.; Edvardsen, T.; Abraham, T.; Appadurai, V.; Badano, L.; Banchs, J.; Cho, G.-Y.; Cosyns, B.; Delgado, V.; Donal, E.; et al. Clinical Applications of Strain Echocardiography: A Clinical Consensus Statement From the American Society of Echocardiography Developed in Collaboration With the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging of the European Society of Cardiology. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2025, S0894731725003955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, F.J.; Diederichsen, S.Z.; Jørgensen, P.G.; Jensen, M.T.; Dahl, A.; Landler, N.E.; Graff, C.; Brandes, A.; Krieger, D.; Haugan, K.; et al. Left Atrial Strain Predicts Subclinical Atrial Fibrillation Detected by Long-Term Continuous Monitoring in Elderly High-Risk Individuals. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2024, 17, e016197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Fei, H.; Yu, Y.; Ren, S.; Lin, Q.; Li, H.; Tang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Li, M. Left Atrial Strain Reproducibility Using Vendor-Dependent and Vendor-Independent Software. Cardiovasc. Ultrasound 2019, 17, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodagh, N.; Williams, M.C.; Vickneson, K.; Gharaviri, A.; Niederer, S.; Williams, S.E. State of the Art Paper: Cardiac Computed Tomography of the Left Atrium in Atrial Fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2023, 17, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, K.; Brinker, J.A.; Henrikson, C.A. Computed Tomography Imaging in Atrial Fibrillation Ablation. J. Atr. Fibrillation 2011, 4, 319. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Veillet-Chowdhury, M.; Dabbagh, G.S.; Benton, S.M.; Hill, A.M.; Lee, J.H.; Singleton, M.J.; Fazio, G.P.; Harvey, J.E.; Samady, H.; Singh, D.; et al. CT-Guided Direct Current Cardioversion for Atrial Arrhythmias During the COVID-19 Pandemic. JACC: Cardiovasc. Imaging 2023, 16, 135–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aimo, A.; Kollia, E.; Ntritsos, G.; Barison, A.; Masci, P.-G.; Figliozzi, S.; Klettas, D.; Stamatelopoulos, K.; Delialis, D.; Emdin, M.; et al. Echocardiography versus Computed Tomography and Cardiac Magnetic Resonance for the Detection of Left Heart Thrombosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2021, 110, 1697–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tore, D.; Faletti, R.; Palmisano, A.; Salto, S.; Rocco, K.; Santonocito, A.; Gaetani, C.; Biondo, A.; Bozzo, E.; Giorgino, F.; et al. Cardiac Computed Tomography with Late Contrast Enhancement: A Review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e32436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, D.; Schoepf, U.-J.; Zhao, P.; Goller, M.; Li, J.; Tian, J.; Shen, M.; Cao, K.; et al. The Role of Epicardial Fat Radiomic Profiles for Atrial Fibrillation Identification and Recurrence Risk with Coronary CT Angiography. Br. J. Radiol. 2024, 97, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Dagher, L.; Huang, C.; Miller, P.; Marrouche, N.F. Cardiac MRI to Manage Atrial Fibrillation. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. Rev. 2020, 9, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, A.; Shetty, R.; Hodis, B.; Chowdhury, Y.S. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Physics. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Daccarett, M.; McGann, C.J.; Akoum, N.W.; MacLeod, R.S.; Marrouche, N.F. MRI of the Left Atrium: Predicting Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Expert. Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2011, 9, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisbal, F.; Gómez-Pulido, F.; Cabanas-Grandío, P.; Akoum, N.; Calvo, M.; Andreu, D.; Prat-González, S.; Perea, R.J.; Villuendas, R.; Berruezo, A.; et al. Left Atrial Geometry Improves Risk Prediction of Thromboembolic Events in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2016, 27, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Biase, L.; Natale, A.; Romero, J. Thrombogenic and Arrhythmogenic Roles of the Left Atrial Appendage in Atrial Fibrillation: Clinical Implications. Circulation 2018, 138, 2036–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alinezhad, L.; Ghalichi, F.; Ahmadlouydarab, M.; Chenaghlou, M. Left Atrial Appendage Shape Impacts on the Left Atrial Flow Hemodynamics: A Numerical Hypothesis Generating Study on Two Cases. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 213, 106506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, M.C.P.; Handschumacher, M.D.; Levine, R.A.; Barbosa, M.M.; Carvalho, V.T.; Esteves, W.A.; Zeng, X.; Guerrero, J.L.; Zheng, H.; Tan, T.C.; et al. Role of LA Shape in Predicting Embolic Cerebrovascular Events in Mitral Stenosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2014, 7, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, B.; Sirajuddin, A.; Zhao, S.; Lu, M. The Role of 4D Flow MRI for Clinical Applications in Cardiovascular Disease: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2021, 11, 4193–4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markl, M.; Carr, M.; Ng, J.; Lee, D.C.; Jarvis, K.; Carr, J.; Goldberger, J.J. Assessment of Left and Right Atrial 3D Hemodynamics in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: A 4D Flow MRI Study. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 32, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markl, M.; Lee, D.C.; Furiasse, N.; Carr, M.; Foucar, C.; Ng, J.; Carr, J.; Goldberger, J.J. Left Atrial and Left Atrial Appendage 4D Blood Flow Dynamics in Atrial Fibrillation. Circ Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markl, M.; Lee, D.C.; Ng, J.; Carr, M.; Carr, J.; Goldberger, J.J. Left Atrial 4-Dimensional Flow Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Stasis and Velocity Mapping in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation. Investig. Radiol. 2016, 51, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankovic, Z.; Allen, B.D.; Garcia, J.; Jarvis, K.B.; Markl, M. 4D Flow Imaging with MRI. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2014, 4, 173–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Sun, H.; Chen, X.; Jiang, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Xiao, Y. Advance in the Application of 4-Dimensional Flow MRI in Atrial Fibrillation. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2025, 115, 110254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, L.-W.; Chen, S.-A. Cardiac Remodeling After Atrial Fibrillation Ablation. J. Atr. Fibrillation 2013, 6, 877. [Google Scholar]
- Nattel, S.; Burstein, B.; Dobrev, D. Atrial Remodeling and Atrial Fibrillation: Mechanisms and Implications. Circ: Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2008, 1, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Shim, J.; Choi, E.-K.; Oh, I.-Y.; Kim, J.; Lee, Y.S.; Park, J.; Ko, J.-S.; Park, K.-M.; Sung, J.-H.; et al. Long-Term Anticoagulation Discontinuation After Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation: The ALONE-AF Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costello, B.T.; Voskoboinik, A.; Qadri, A.M.; Rudman, M.; Thompson, M.C.; Touma, F.; La Gerche, A.; Hare, J.L.; Papapostolou, S.; Kalman, J.M.; et al. Measuring Atrial Stasis during Sinus Rhythm in Patients with Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation Using 4 Dimensional Flow Imaging. Int. J. Cardiol. 2020, 315, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirkiran, A.; Amier, R.P.; Hofman, M.B.M.; Van Der Geest, R.J.; Robbers, L.F.H.J.; Hopman, L.H.G.A.; Mulder, M.J.; Van De Ven, P.; Allaart, C.P.; Van Rossum, A.C.; et al. Altered Left Atrial 4D Flow Characteristics in Patients with Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation in the Absence of Apparent Remodeling. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spartera, M.; Pessoa-Amorim, G.; Stracquadanio, A.; Von Ende, A.; Fletcher, A.; Manley, P.; Neubauer, S.; Ferreira, V.M.; Casadei, B.; Hess, A.T.; et al. Left Atrial 4D Flow Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance: A Reproducibility Study in Sinus Rhythm and Atrial Fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2021, 23, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Yerly, J.; Di Sopra, L.; Piccini, D.; Lee, J.; DiCarlo, A.; Passman, R.; Greenland, P.; Kim, D.; Stuber, M.; et al. Using 5D Flow MRI to Decode the Effects of Rhythm on Left Atrial 3D Flow Dynamics in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Magn. Reson. Med. 2021, 85, 3125–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekine, T.; Nakaza, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Ando, T.; Inoue, T.; Sakamoto, S.-I.; Maruyama, M.; Obara, M.; Leonowicz, O.; Usuda, J.; et al. 4D Flow MR Imaging of the Left Atrium: What Is Non-Physiological Blood Flow in the Cardiac System? MRMS 2022, 21, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiCarlo, A.L.; Haji-Valizadeh, H.; Passman, R.; Greenland, P.; McCarthy, P.; Lee, D.C.; Kim, D.; Markl, M. Assessment of Beat–To–Beat Variability in Left Atrial Hemodynamics Using Real Time Phase Contrast MRI in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2023, 58, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, M.J.; An, D.-G.; Kang, M.; Kim, H.M.; Kim, S.-W.; Cho, I.; Hong, J.; Choi, H.; Cho, J.-H.; Shin, S.Y.; et al. Correct Closure of the Left Atrial Appendage Reduces Stagnant Blood Flow and the Risk of Thrombus Formation: A Proof-of-Concept Experimental Study Using 4D Flow Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Korean J. Radiol. 2023, 24, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fluckiger, J.U.; Goldberger, J.J.; Lee, D.C.; Ng, J.; Lee, R.; Goyal, A.; Markl, M. Left Atrial Flow Velocity Distribution and Flow Coherence Using Four–dimensional FLOW MRI: A Pilot Study Investigating the Impact of Age and Pre– and Postintervention Atrial Fibrillation on Atrial Hemodynamics. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2013, 38, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.C.; Markl, M.; Ng, J.; Carr, M.; Benefield, B.; Carr, J.C.; Goldberger, J.J. Three-Dimensional Left Atrial Blood Flow Characteristics in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation Assessed by 4D Flow CMR. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 17, 1259–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spartera, M.; Stracquadanio, A.; Pessoa-Amorim, G.; Von Ende, A.; Fletcher, A.; Manley, P.; Ferreira, V.M.; Hess, A.T.; Hopewell, J.C.; Neubauer, S.; et al. The Impact of Atrial Fibrillation and Stroke Risk Factors on Left Atrial Blood Flow Characteristics. Eur. Heart J.-Cardiovasc. Imaging 2021, 23, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamopoulos, D.; Rovas, G.; Johner, N.; Müller, H.; Deux, J.-F.; Crowe, L.A.; Vallée, J.-P.; Mach, F.; Stergiopulos, N.; Shah, D. Left Atrial Wall Shear Stress Correlates with Fibrosis in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Nat. Cardiovasc. Res. 2025, 4, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, L.; Bollache, E.; Soulez, S.; Bouazizi, K.; Badenco, N.; Giese, D.; Gandjbakhch, E.; Redheuil, A.; Laredo, M.; Kachenoura, N. A Multi-Modal Computational Fluid Dynamics Model of Left Atrial Fibrillation Haemodynamics Validated with 4D Flow MRI. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2025, 24, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjeldsberg, H.A.; Albors, C.; Mill, J.; Medel, D.V.; Camara, O.; Sundnes, J.; Valen-Sendstad, K. Impact of Left Atrial Wall Motion Assumptions in Fluid Simulations on Proposed Predictors of Thrombus Formation. Numer. Methods Biomed. Eng. 2024, 40, e3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Sheitt, H.; Wilton, S.B.; White, J.A.; Garcia, J. Left Ventricular Flow Distribution as a Novel Flow Biomarker in Atrial Fibrillation. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 725121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasaki, Y.; Nishida, K.; Kato, T.; Nattel, S. Atrial Fibrillation Pathophysiology: Implications for Management. Circulation 2011, 124, 2264–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaaf, M.; Andre, P.; Altman, M.; Maucort-Boulch, D.; Placide, J.; Chevalier, P.; Bergerot, C.; Thibault, H. Left Atrial Remodelling Assessed by 2D and 3D Echocardiography Identifies Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2017, 18, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paliwal, N.; Ali, R.L.; Salvador, M.; O’Hara, R.; Yu, R.; Daimee, U.A.; Akhtar, T.; Pandey, P.; Spragg, D.D.; Calkins, H.; et al. Presence of Left Atrial Fibrosis May Contribute to Aberrant Hemodynamics and Increased Risk of Stroke in Atrial Fibrillation Patients. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 657452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paliwal, N.; Park, H.-C.; Mao, Y.; Hong, S.J.; Lee, Y.; Spragg, D.D.; Calkins, H.; Trayanova, N.A. Slow Blood-Flow in the Left Atrial Appendage Is Associated with Stroke in Atrial Fibrillation Patients. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamori, S.; Nezafat, M.; Ngo, L.H.; Manning, W.J.; Nezafat, R. Left Atrial Epicardial Fat Volume Is Associated With Atrial Fibrillation: A Prospective Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance 3D Dixon Study. JAHA 2018, 7, e008232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Author | Sample Size and Controls (N) | Methods | Hemodynamic Markers | Major Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [53] | 29 age-matched participants; 19 healthy controls, 10 with AF (4 with persistent AF, 6 post intervention) |
|
| Persistent AF patients exhibited reduced blood flow velocities and impaired flow coherence compared to post-intervention AF patients and healthy controls. |
| [38] | 70 subjects; 62 AF patients (33 in sinus rhythm, 29 with persistent AF), 8 healthy controls |
|
| AF patients showed no left-right atrial flow velocity differences but had significantly lower velocities and higher stasis than controls. |
| [39] | 75 subjects; 60 AF patients (30 in sinus rhythm, 30 in AF), 15 healthy controls) |
|
| AF patients had reduced LAA velocities, higher stasis, and more disorganized flow compared to controls, with worsening flow dynamics linked to higher CHA2DS2-VASc scores. |
| [54] | 70 subjects; 40 AF patients in sinus rhythm, 20 age-appropriate controls, 10 young healthy volunteers |
|
| AF patients exhibited significantly lower LA velocities than controls, with greater reductions linked to higher CHA2DS2-VASc scores. |
| [14] | 60 subjects; 45 PAF patients, 15 healthy controls |
|
| PAF patients had larger LA vortices than controls, which correlated with slower pulmonary vein flow, enlarged LA volume, and higher CHA2DS2-VASc scores. |
| [46] | 109 subjects; 91 PAF patients and 18 healthy controls |
|
| PAF patients showed greater atrial stasis (higher RTD Time Constant) than controls, with even more pronounced stasis in those with elevated CHA2DS2-VASc scores. |
| [47] | 15 subjects; 10 PAF patients and 5 age/gender-matched controls |
|
| PAF patients exhibited significantly reduced LA flow velocities, higher stasis, and lower kinetic energy compared to controls, indicating impaired atrial hemodynamics. |
| [48] | 86 subjects; 64 in sinus rhythm and 22 in AF |
|
| AF patients had greater LA stasis, lower peak velocity, and altered vortical flow, while LA peak velocity and vorticity were stable across heart rate, blood pressure, and rhythm changes. |
| [49] | 25 patients with a history of AF |
|
| High AF burden correlated with increased LA stasis and reduced peak velocity and mean velocity. |
| [59] | 80 subjects; 50 PAF patients and 30 healthy controls |
|
| PAF patients had reduced direct flow and increased delayed ejection with occult LV hemodynamic inefficiencies despite normal systolic function. |
| [55] | 95 participants: Group 1 (37 patients with persistent AF), Group 2 (35 individuals with no AF but similar stroke risk), Group 3 (23 low-risk individuals). |
|
| Patients with persistent AF (Group 1) had impaired LA flow velocities and vorticity, while Groups 1 and 2 (moderate-to-high stroke risk) showed altered LA flow in sinus rhythm, linked to LA and LV diastolic dysfunction. |
| [50] | N/A as this was a literature review |
|
| AF patients exhibit reduced vortex flow and increased stasis, with vortex flow preservation correlating to lower thrombotic risk. |
| [52] | 3 3D-printed LA phantoms from 86 year old male patient with AF |
|
| Correct occlusion reduced stasis volume and had the lowest ECAP and highest WSS, while the incorrect occlusion model showed high stasis and longer PRT compared to the corrected occlusion rate. |
| [51] | 45 subjects; 35 AF patients, 10 healthy controls |
|
| High HRV patients showed greater variability in flow metrics, lower mean velocity, higher stasis, and a correlation between longer RR intervals and increased stasis was observed. |
| [58] | 1 AF patient with 4 wall motion control models: rigid, generic, semi-generic, patient-specific |
|
| There were minimal LA hemodynamic differences between the models; the rigid model underestimated WSS and overestimated RRT/ECAP in the LAA, while generic/semi-generic models matched patient-specific motion. |
| [42] | 12 studies with mixed cohorts (AF patients vs. healthy controls) |
|
| AF impacts velocity, stasis, ECAP, and vortices, with flow changes linked to thrombosis risk, CHA2DS2-VASc scores, LAA closure, ablation, and remodeling. |
| [57] | 5 AF patients in sinus rhythm |
|
| Morphing model improved TAWSS, OSI, and mitral flow accuracy; LAA had lower TAWSS and higher OSI than LA. |
| [56] | 15 AF patients (10 paroxysmal AF, 5 persistent AF, 3 atrial flutter) |
|
| Fibrosis and electrical scarring were more prevalent in high-TAWSS regions, while low-TAWSS areas were associated with blood stagnation but not fibrosis, with left pulmonary veins exhibiting higher TAWSS than right pulmonary veins. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hassan, H.; Prasai, S.; Hassan, O.; Rajput, F.; Garcia, J. Analysis of Hemodynamic Markers in Atrial Fibrillation Using Advanced Imaging Techniques. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 10679. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910679
Hassan H, Prasai S, Hassan O, Rajput F, Garcia J. Analysis of Hemodynamic Markers in Atrial Fibrillation Using Advanced Imaging Techniques. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(19):10679. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910679
Chicago/Turabian StyleHassan, Hadi, Shuvam Prasai, Omar Hassan, Fiza Rajput, and Julio Garcia. 2025. "Analysis of Hemodynamic Markers in Atrial Fibrillation Using Advanced Imaging Techniques" Applied Sciences 15, no. 19: 10679. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910679
APA StyleHassan, H., Prasai, S., Hassan, O., Rajput, F., & Garcia, J. (2025). Analysis of Hemodynamic Markers in Atrial Fibrillation Using Advanced Imaging Techniques. Applied Sciences, 15(19), 10679. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910679






