Cold Plasma Treatment on Titanium Implants and Osseointegration: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
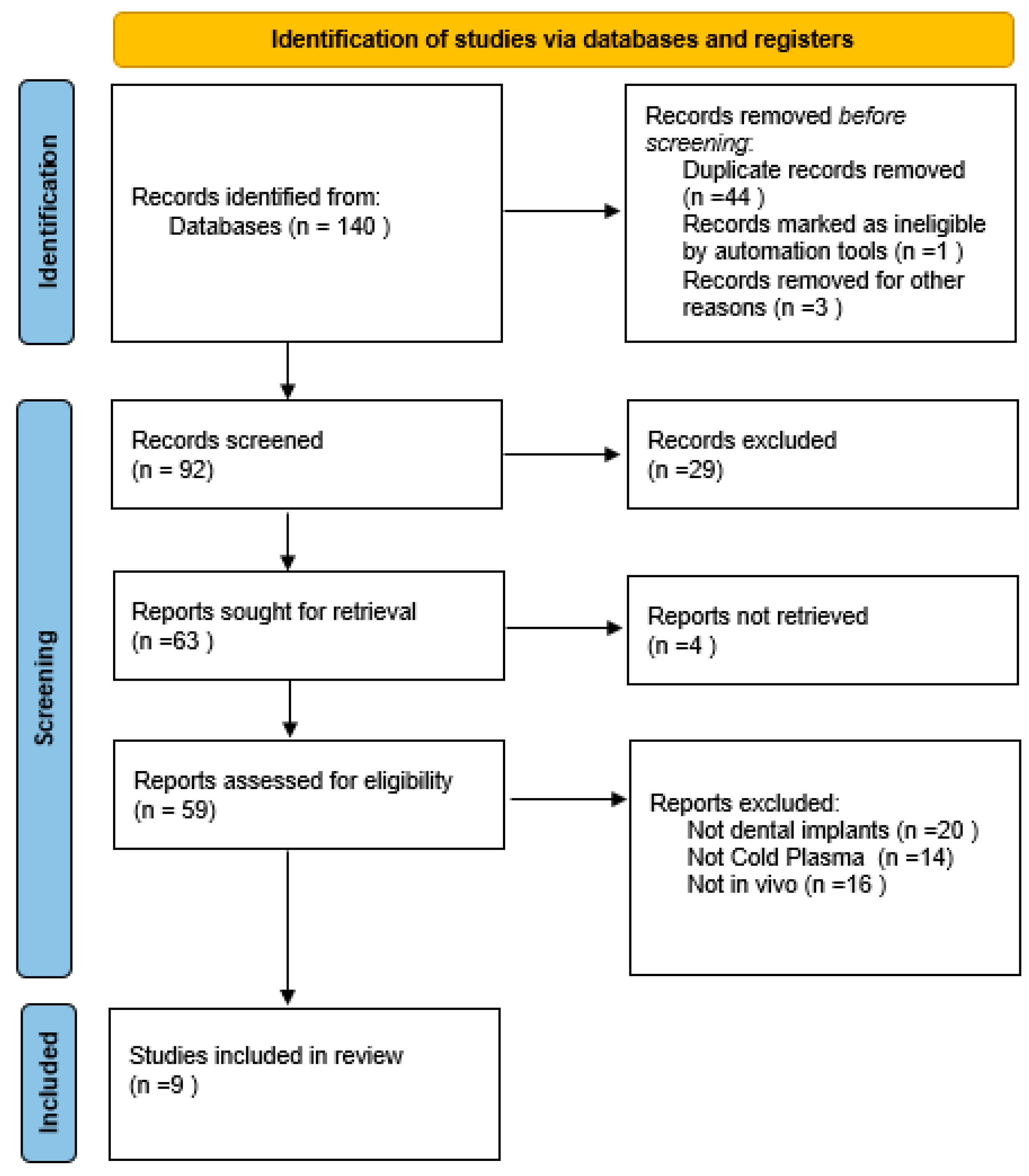
2.3. Article Selection Process
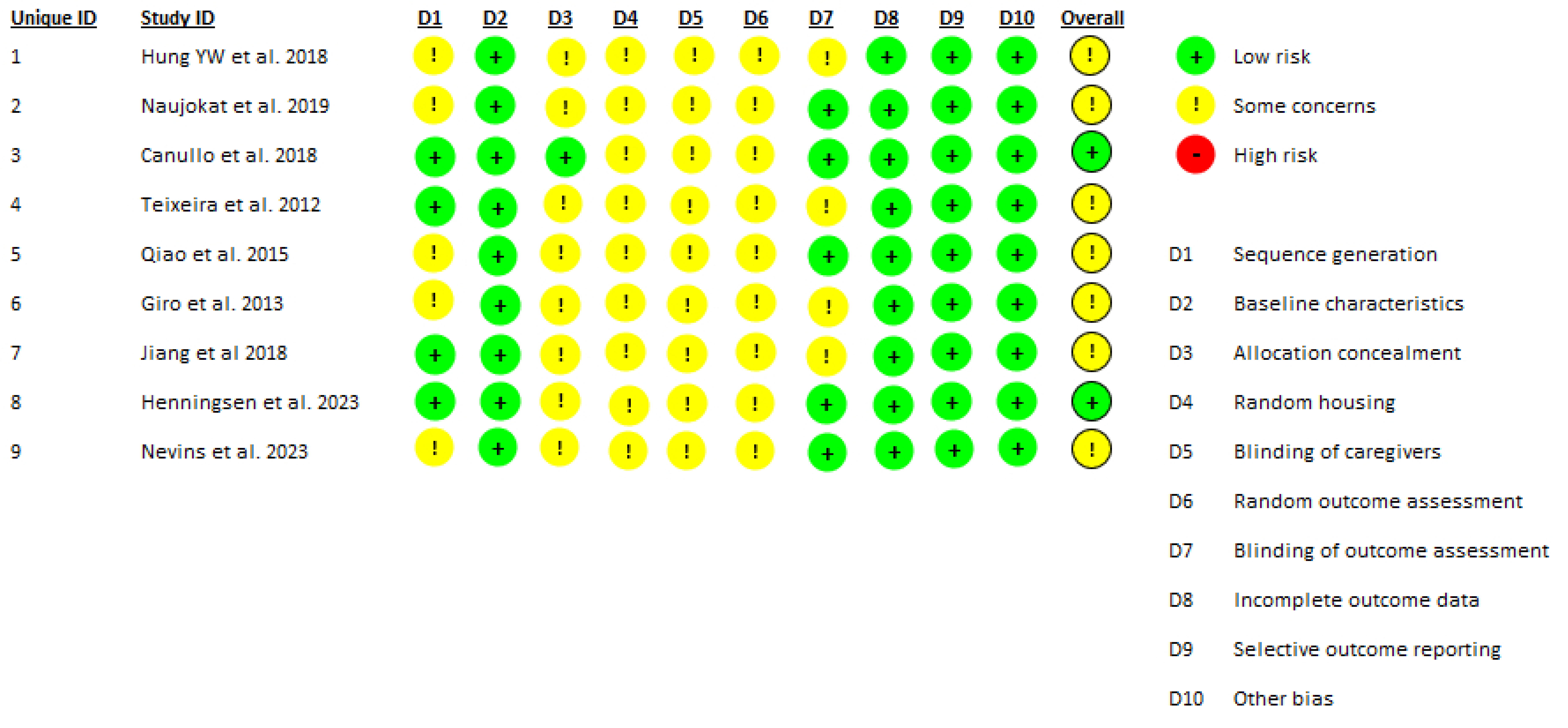
2.4. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
3. Results
3.1. Histomorphometric Bone Response
3.2. Biomechanical Fixation and Implant Stability
3.3. Bone Quality and Radiographic Outcomes
3.4. Safety and Adverse Events
3.5. Limitations
4. Discussion
4.1. Biological Effects of CAP on Osseointegration
4.2. Biomechanical and Radiographic Outcomes
4.3. The Current Vision of CAP in the Literature
4.4. Limitations of Current Preclinical Evidence
4.5. Translational Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CAP | Cold Atmospheric Plasma |
| BIC | Bone-to-implant-contact |
| BAFO | Bone Area Fraction Occupancy |
| ISQ | Implant Stability Quotient |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| NTAPP | Non-thermal Atmospheric Pressure Plasma |
| ROS/RNS | Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species |
| ALP | Alkaline Phosphatase |
| Runx2 | Runt-related transcription factor 2 |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| Ag-PIII | Silver-ion plasma immersion ion implantation |
| BDWT | Bone density within threads |
| SLA | Sandblasted Large-grit Acid-etcher |
| PBID | Peri Implant Bone Density |
| IBD | Interthread Bone Density |
References
- Albrektsson, T.; Brånemark, P.I.; Hansson, H.A.; Lindström, J. Osseointegrated titanium implants. Requirements for ensuring a long-lasting, direct bone-to-implant anchorage in man. Acta Orthop. Scand. 1981, 52, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javed, F.; Ahmed, H.B.; Crespi, R.; Romanos, G.E. Role of primary stability for successful osseointegration of dental implants: Factors of influence and evaluation. Interv. Med. Appl. Sci. 2013, 5, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Schimmel, M.; Srinivasan, M.; McKenna, G.; Müller, F. Effect of advanced age and/or systemic medical conditions on dental implant survival: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Oral. Implants Res. 2018, 29 (Suppl. 16), 311–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sbricoli, L.; Bazzi, E.; Stellini, E.; Bacci, C. Systemic Diseases and Biological Dental Implant Complications: A Narrative Review. Dent. J. 2022, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pavel, K.; Seydlova, M.; Dostalova, T.; Zdenek, V.; Chleborad, K.; Jana, Z.; Feberova, J.; Radek, H. Dental implants and improvement of oral health-related quality of life. Community Dent. Oral. Epidemiol. 2012, 40 (Suppl. 1), 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqutaibi, A.Y.; Aboalrejal, A.N. Microgap and Micromotion at the Implant Abutment Interface Cause Marginal Bone Loss Around Dental Implant but More Evidence is Needed. J. Evid. Based Dent. Pract. 2018, 18, 171–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakitian, F.A. A Comprehensive Review of the Contemporary Methods for Enhancing Osseointegration and the Antimicrobial Properties of Titanium Dental Implants. Cureus 2024, 16, e68720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Stich, T.; Alagboso, F.; Křenek, T.; Kovářík, T.; Alt, V.; Docheva, D. Implant-bone-interface: Reviewing the impact of titanium surface modifications on osteogenic processes in vitro and in vivo. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2021, 7, e10239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rupp, F.; Liang, L.; Geis-Gerstorfer, J.; Scheideler, L.; Hüttig, F. Surface characteristics of dental implants: A review. Dent. Mater. 2018, 34, 40–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimes, D.; Becker, P.; Pabst, A.; Smeets, R.; Kraus, A.; Hartmann, A.; Sagheb, K.; Kämmerer, P.W. How does dental implant macrogeometry affect primary implant stability? A narrative review. Int. J. Implant. Dent. 2023, 9, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shayeb, M.A.; Elfadil, S.; Abutayyem, H.; Shqaidef, A.; Marrapodi, M.M.; Cicciù, M.; Minervini, G. Bioactive surface modifications on dental implants: A systematic review and meta-analysis of osseointegration and longevity. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2024, 28, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Karthik, K.S.; Sreevidya, B.; Ramya, T.K.; Divya, B.M.; Dedeepya, N.R.; Badiyani, B.K.; Kumar, A. Comparative Analysis of Surface Modification Techniques for Assessing Oral Implant Osseointegration: An Animal Study. Cureus 2024, 16, e54014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lata, S.; Chakravorty, S.; Mitra, T.; Pradhan, P.K.; Mohanty, S.; Patel, P.; Jha, E.; Panda, P.K.; Verma, S.K.; Suar, M. Aurora Borealis in dentistry: The applications of cold plasma in biomedicine. Mater. Today Bio 2021, 13, 100200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rehman, M.U.; Jawaid, P.; Uchiyama, H.; Kondo, T. Comparison of free radicals formation induced by cold atmospheric plasma, ultrasound, and ionizing radiation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 605, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tominami, K.; Kanetaka, H.; Sasaki, S.; Mokudai, T.; Kaneko, T.; Niwano, Y. Cold atmospheric plasma enhances osteoblast differentiation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Campos-Bijit, V.; Inostroza, N.C.; Orellana, R.; Rivera, A.; Von Marttens, A.; Cortez, C.; Covarrubias, C. Influence of Topography and Composition of Commercial Titanium Dental Implants on Cell Adhesion of Human Gingiva-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells: An In Vitro Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gund, M.P.; Naim, J.; Lehmann, A.; Hannig, M.; Lange, M.; Schindler, A.; Rupf, S. Cold Atmospheric Plasma Improves the Colonization of Titanium with Primary Human Osteoblasts: An In Vitro Study. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Matthes, R.; Duske, K.; Kebede, T.G.; Pink, C.; Schlüter, R.; von Woedtke, T.; Weltmann, K.D.; Kocher, T.; Jablonowski, L. Osteoblast growth, after cleaning of biofilm-covered titanium discs with air-polishing and cold plasma. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niedźwiedź, I.; Waśko, A.; Pawłat, J.; Polak-Berecka, M. The State of Research on Antimicrobial Activity of Cold Plasma. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Scholtz, V.; Pazlarova, J.; Souskova, H.; Khun, J.; Julak, J. Nonthermal plasma--A tool for decontamination and disinfection. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33 Pt 2, 1108–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkawareek, M.Y.; Algwari, Q.T.; Gorman, S.P.; Graham, W.G.; O’Connell, D.; Gilmore, B.F. Application of atmospheric pressure nonthermal plasma for the in vitro eradication of bacterial biofilms. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 65, 381–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brun, P.; Bernabè, G.; Marchiori, C.; Scarpa, M.; Zuin, M.; Cavazzana, R.; Zaniol, B.; Martines, E. Antibacterial efficacy and mechanisms of action of low power atmospheric pressure cold plasma: Membrane permeability, biofilm penetration and antimicrobial sensitization. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 125, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Kim, K.H.; Park, S.Y.; Yoon, S.Y.; Kim, G.H.; Lee, Y.M.; Rhyu, I.C.; Seol, Y.J. The bactericidal effect of an atmospheric-pressure plasma jet on Porphyromonas gingivalis biofilms on sandblasted and acid-etched titanium discs. J. Periodontal Implant. Sci. 2019, 49, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jungbauer, G.; Moser, D.; Müller, S.; Pfister, W.; Sculean, A.; Eick, S. The Antimicrobial Effect of Cold Atmospheric Plasma against Dental Pathogens-A Systematic Review of In-Vitro Studies. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Idlibi, A.N.; Al-Marrawi, F.; Hannig, M.; Lehmann, A.; Rueppell, A.; Schindler, A.; Jentsch, H.; Rupf, S. Destruction of oral biofilms formed in situ on machined titanium (Ti) surfaces by cold atmospheric plasma. Biofouling 2013, 29, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakudo, A.; Yagyu, Y.; Onodera, T. Disinfection and Sterilization Using Plasma Technology: Fundamentals and Future Perspectives for Biological Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zheng, Z.; Ao, X.; Xie, P.; Wu, J.; Dong, Y.; Yu, D.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Xu, H.H.K.; Chen, W. Effects of novel non-thermal atmospheric plasma treatment of titanium on physical and biological improvements and in vivo osseointegration in rats. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, J.; Jansen, J.A.; Walboomers, X.F.; van den Beucken, J.J. Mechanical aspects of dental implants and osseointegration: A narrative review. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 103, 103574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggers, B.; Marciniak, J.; Deschner, J.; Stope, M.B.; Mustea, A.; Kramer, F.J.; Nokhbehsaim, M. Cold Atmospheric Plasma Promotes Regeneration-Associated Cell Functions of Murine Cementoblasts In Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Moraschini, V.; Barboza, E.S.; Peixoto, G.A. The impact of diabetes on dental implant failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 45, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dioguardi, M.; Cantore, S.; Quarta, C.; Sovereto, D.; Zerman, N.; Pettini, F.; Muzio, L.L.; Cosola, M.D.; Santacroce, L.; Ballini, A. Correlation between Diabetes Mellitus and Peri-implantitis: A Systematic Review. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets. 2023, 23, 596–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlos, A.; Ziada, H.; Abubakr, N.H. Correlation between marginal bone loss around dental implants and various systemic diseases: A cross-sectional study. Int. J. Implant. Dent. 2024, 10, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Corcuera-Flores, J.R.; López-Giménez, J.; López-Jiménez, J.; López-Giménez, A.; Silvestre-Rangil, J.; Machuca-Portillo, G. Four years survival and marginal bone loss of implants in patients with Down syndrome and cerebral palsy. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2017, 21, 1667–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bredberg, C.; Vu, C.; Häggman-Henrikson, B.; Chrcanovic, B.R. Marginal bone loss around dental implants: Comparison between matched groups of bruxer and non-bruxer patients: A retrospective case-control study. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2023, 25, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Aghaloo, T.; Pi-Anfruns, J.; Moshaverinia, A.; Sim, D.; Grogan, T.; Hadaya, D. The Effects of Systemic Diseases and Medications on Implant Osseointegration: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Implants. 2019, 34, s35–s49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henningsen, A.; Smeets, R.; Hartjen, P.; Heinrich, O.; Heuberger, R.; Heiland, M.; Precht, C.; Cacaci, C. Photofunctionalization and non-thermal plasma activation of titanium surfaces. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2018, 22, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, G.; Eggers, B.; Duddeck, D.; Kramer, F.J.; Bourauel, C.; Jepsen, S.; Deschner, J.; Nokhbehsaim, M. Influence of cold atmospheric plasma on dental implant materials-an in vitro analysis. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2022, 26, 2949–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kamionka, J.; Matthes, R.; Holtfreter, B.; Pink, C.; Schlüter, R.; von Woedtke, T.; Kocher, T.; Jablonowski, L. Efficiency of cold atmospheric plasma, cleaning powders and their combination for biofilm removal on two different titanium implant surfaces. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2022, 26, 3179–3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Bai, N. Bioactive Effects of Low-Temperature Argon-Oxygen Plasma on a Titanium Implant Surface. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 3996–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Duske, K.; Jablonowski, L.; Koban, I.; Matthes, R.; Holtfreter, B.; Sckell, A.; Nebe, J.B.; von Woedtke, T.; Weltmann, K.D.; Kocher, T. Cold atmospheric plasma in combination with mechanical treatment improves osteoblast growth on biofilm covered titanium discs. Biomaterials 2015, 52, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komasa, S.; Kusumoto, T.; Hayashi, R.; Takao, S.; Li, M.; Yan, S.; Zeng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hu, H.; Kobayashi, Y.; et al. Effect of Argon-Based Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Treatment on Hard Tissue Formation on Titanium Surface. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hooijmans, C.R.; Rovers, M.M.; de Vries, R.B.; Leenaars, M.; Ritskes-Hoitinga, M.; Langendam, M.W. SYRCLE’s risk of bias tool for animal studies. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2014, 14, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hung, Y.W.; Chen, H.L.; Lee, L.T.; Tung, K.C.; Bau, D.T.; Wong, Y.K. Effects of non-thermal plasma on sandblasted titanium dental implants in beagle dogs. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2018, 81, 920–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naujokat, H.; Harder, S.; Schulz, L.Y.; Wiltfang, J.; Flörke, C.; Açil, Y. Surface conditioning with cold argon plasma and its effect on the osseointegration of dental implants in miniature pigs. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 47, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canullo, L.; Tallarico, M.; Botticelli, D.; Alccayhuaman, K.A.A.; Martins Neto, E.C.; Xavier, S.P. Hard and soft tissue changes around implants activated using plasma of argon: A histomorphometric study in dog. Clin. Oral. Implants Res. 2018, 29, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, H.S.; Marin, C.; Witek, L.; Freitas, A., Jr.; Silva, N.R.; Lilin, T.; Tovar, N.; Janal, M.N.; Coelho, P.G. Assessment of a chair-side argon-based non-thermal plasma treatment on the surface characteristics and integration of dental implants with textured surfaces. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2012, 9, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, S.; Cao, H.; Zhao, X.; Lo, H.; Zhuang, L.; Gu, Y.; Shi, J.; Liu, X.; Lai, H. Ag-plasma modification enhances bone apposition around titanium dental implants: An animal study in Labrador dogs. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giro, G.; Tovar, N.; Witek, L.; Marin, C.; Silva, N.R.; Bonfante, E.A.; Coelho, P.G. Osseointegration assessment of chairside argon-based nonthermal plasma-treated Ca-P coated dental implants. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2013, 101, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, W.; Lin, Z.; Liu, Z. Effect of Plasma Oxidation-Treated TiOx Film on Early Osseointegration. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Implants. 2018, 33, 1011–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henningsen, A.; Precht, C.; Karnatz, N.; Bibiza, E.; Yan, M.; Guo, L.; Gosau, M.; Smeets, R. Osseointegration of titanium implants after surface treatment with ultraviolet light or cold atmospheric plasma in vivo. Int. J. Oral. Implantol. 2023, 16, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nevins, M.; Chen, C.Y.; Parma-Benfenati, S.; Kim, D.M. Gas Plasma Treatment Improves Titanium Dental Implant Osseointegration-A Preclinical In Vivo Experimental Study. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pesce, P.; Menini, M.; Santori, G.; Giovanni, E.; Bagnasco, F.; Canullo, L. Photo and Plasma Activation of Dental Implant Titanium Surfaces. A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis of Pre-Clinical Studies. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Alqutaibi, A.Y.; Aljohani, A.; Alduri, A.; Masoudi, A.; Alsaedi, A.M.; Al-Sharani, H.M.; Farghal, A.E.; Alnazzawi, A.A.; Aboalrejal, A.N.; Mohamed, A.H.; et al. The Effectiveness of Cold Atmospheric Plasma (CAP) on Bacterial Reduction in Dental Implants: A Systematic Review. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Najeeb, S.; Khurshid, Z.; Matinlinna, J.P.; Siddiqui, F.; Nassani, M.Z.; Baroudi, K. Nanomodified Peek Dental Implants: Bioactive Composites and Surface Modification-A Review. Int. J. Dent. 2015, 2015, 381759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
| Title | Authors + Year | Study Design | Animal Model | Number of Implants | Type of Plasma Treatment | Follow-Up | Comparison | BIC (%) | ISQ | BAFO % | Removal Torque | PIBD (Peri Implant Bone Density)% | IBD (Interthread Bone Density) % | BDWT (Bone-to-Implant Distance Within Threads) % | Bone Loss (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effects of non-thermal plasma on sandblasted titanium dental implants in beagle dogs | Hung et al., 2018 [44] | Preclinical in vivo | 9 Beagle dogs | 36 implants (18 treated, 18 untreated), 4 implants per dog | Argon NTAPP | T0: placement T1: 4 weeks T2: 8 weeks T3: 12 weeks | Argon NTAPP treated VS Non treated implants | CONTROL GROUP (T1): 65.27% ± 3.62 (T2): 82.10% ± 0.23 (T3): 90.20% ± 3.49 STUDY GROUP (T1): 66.40% ± 3.71 (T2): 80.30% ± 0.66 (T3): 87.38% ± 1.98 (p = non significant) | CONTROL GROUP (T0): 68.04 ± 3.37 (T1): 66.53 ± 7.40 (T2): 69.20 ± 2.55 (T3): 74.20 ± 2.68 STUDY GROUP (T0): 67.36 ± 0.52 (T1): 70.17 ± 0.76 (T2): 71.50 ± 1.41 (T3): 77.00 ± 5.87 (p = non significant) | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported |
| Surface conditioning with cold argon plasma and its effect on the osseointegration of dental implants in miniature pigs | Naujokat et al., 2019 [45] | Preclinical in vivo | 4 mini pigs | 16 implants (8 treated,8 not treated), 4 implants per pig | Argon NTAPP | 8 weeks | Argon NTAPP treated VS Non treated implants | CONTROL GROUP 86.5 ± 1.23 STUDY GROUP 90.4 ± 1.24 (p = non significant) | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | CONTROL GROUP 61.14 ± 6.10 STUDY GROUP 60.48 ± 5.03 (p = non significant) | CONTROL GROUP 63.36 ± 6.21 STUDY GROUP 72.47 ± 5.21 (p = 0.002) | Not reported | Not reported |
| Hard and soft tissue changes around implants activated using plasma of argon: A histomorphometric study in dog | Canullo et al., 2018 [46] | Preclinical in vivo | 8 Beagle dogs | 32 implants (16 treated,16 untreated), 4 implants per dog | Argon NTAPP | T1:1 month T2: 2 months | Argon NTAPP treated VS Non treated implants | CONTROL GROUP (T1): 57.2 ± 13.1 (T2): 64.7 ± 17.3 STUDY GROUP (T1): 60.1 ± 15.6 (T2): 72.5 ± 12.4 p = 0.012 (T2) | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported |
| Assessment of a chair-side argon-based non-thermal plasma treatment on the surface characteristics and integration of dental implants with textured surfaces | Teixeira et al., 2012 [47] | Preclinical in vivo | 6 Beagle dogs | 36 implants (24 treated, 12 untreated), 6 per dog (2 plasma 20’, 2 plasma 60’, 2 untreated) | Argon NTAPP | T1: 2 weeks T2: 4 weeks | Implants treated with NTAPP for 20’ VS Implants treated for 60’ VS Non treated | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | CONTROL(mean rank) (T1): 8.48 ± 2.08 (T2): 9.50 ± 1.96 PLASMA 20’ (m.r) 9.75 ± 2.40 PLASMA 60’ (m.r) 12.33 ± 2.40 (p = 0–001) | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported |
| Ag-plasma modification enhances bone apposition around titanium dental implants: an animal study in Labrador dogs | Qiao et al., 2015 [48] | Preclinical in vivo | 6 Labrador dogs | 48 implants (4 types: Control, Ag-PIII 30 min,60 min,90 min) | Silver-ion plasma immersion (Ag-PIII) | T0: placement T1:4 weeks T2: 8 weeks T3: 12 weeks | Ag-PIII 30 min VS Ag-PIII 60 min VS Ag-PIII 90 min VS Control Group | CONTROL GROUP (T2): 61.99 ± 4.66 Ag-PIII 30 MIN (T2): 73.18 ± 5.23 Ag-PIII 60 MIN (T2): 69.92 ± 4.10 Ag-PIII 90 MIN (T2): 66.05 ± 3.97 | CONTROL GROUP (T0): >65 (T1): <59 (T2): ~65 (T3): ~70 STUDY GROUPS (T0): >65 (T1): <59 (T2): significant increase (p = 0.01) (T3):~ 70–72 | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | CONTROL GROUP (T2): 66.52 ± 3.46 Ag-PIII 30 MIN (T2): 77.58 ± 4.3 Ag-PIII 60 MIN (T2): 77.97 ± 3.34 Ag-PIII 90 MIN (T2): 69.69 ± 3.68 | Not reported |
| Osseointegration assessment of chairside argon-based nonthermal plasma-treated Ca-P coated dental implants | Giro et al., 2013 [49] | Preclinical in vivo | 6 Beagle dogs | 12 implants (6 treated,6 untreated), 2 implants per dog (1 treated, 1 untreated) | NTAPP on CaP | T1: 1 week T2: 3 weeks | CaP coating (control group) VS CaP+ NTP coating (study group) | T1: no differences T3: increase of 100% Vs Control Group | Not reported | T1: no differences T3: increase of 82% Vs Control Group | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported |
| Effect of Plasma Oxidation-Treated TiOx Film on Early Osseointegration | Jiang et al., 2018 [50] | Preclinical in vivo | 20 rats | 40 implants (20 treated,20 untreated) | Anodic oxidation plasma (PO-SLA) | 4 weeks | SLA surface VS PO-SLA surface | CONTROL GROUP 39.41 ± 9.00 STUDY GROUP 47.79 ± 9.59 (p < 0.05) | Not reported | CONTROL GROUP 29.01 ± 7.24 STUDY GROUP: 39.10 ± 10.01 (p <0.05) | CONTROL GROUP 9.05 ± 1.42 STUDY GROUP 12.68 ± 1.07 (p <0.05) | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported |
| Osseointegration of titanium implants after surface treatment with ultraviolet light or cold atmospheric plasma in vivo | Henningsen et al., 2023 [51] | Preclinical in vivo | 6 pigs | 54 implants (18 untreated,18 UV treated, 18 plasma treated), 9 implants per pig | CAP | T0: placement T1: 2 weeks T2: 4 weeks T3: 8 weeks | UV treated VS CAP treated VS untreated | CONTROL GROUP (T1): >69% (T3): 73.0 ± 2.8 STUDY GROUP (T1): (p < 0.05) (T3): 80.6 ± 5.0 | CONTROL GROUP (T0): 90.4 ± 7.2 (T3): 93.1 ± 5.4 STUDY GROUP (T0): 92.4 ± 5.9 (T3): 89.2 ± 8.3 | CONTROL GROUP (T3): 73.9 ± 12.2 STUDY GROUP (T3): 80.4 ± 7.0 (p = 0.027) | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported |
| Gas Plasma Treatment Improves Titanium Dental Implant Osseointegration—A Preclinical In Vivo Experimental Study | Nevins et al., 2023 [52] | Preclinical in vivo | 6 Foxhounds dogs | 36 implants (18 treated,18 untreated) | Argon NTAPP | T0: placement T1: 2 weeks T2: 4 weeks T3: 6 weeks | Argon NTAPP treated VS non treated implants | CONTROL GROUP (T2): 88.3 ± 4.8 STUDY GROUP (T2): 93.7 ±3.3 (p = 0.046) | CONTROL GROUP (T0): 79.39 ± 2.95 STUDY GROUP (T0): 79.53 ± 4.05 (p = 0.6, non significant) | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | CONTROL GROUP (T3): 0.79 ± 0.20 STUDY GROUP (T3): 0.56 ± 0.24 (p = 0.016) |
| Title | Authors | Type of Plasma Treatment | Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Effects of non-thermal plasma on sandblasted titanium dental implants in beagle dogs | Hung et al., 2018 [44] | Argon NTAPP | Device: Yih Dar Technology, Hsinchu County, Taiwan (ISO 9001 certified) Electrodes: Aluminum tape electrodes on quartz tube (4 mm inner diameter, 10 mm spacer) Argon flow rate: 1.8 L/min Oxygen flow rate: 0.01 L/min Voltage: High-voltage mono-polar square pulses Repetition rate: 0.5–4 kHz Duration: 60 s per implant |
| Surface conditioning with cold argon plasma and its effect on the osseointegration of dental implants in miniature pigs | Naujokat et al., 2019 [45] | Argon NTAPP | Pressure: 2 bar Flow rate: 4.3–4.4 L/min Frequency: 20 kHz Voltage: 115–230 V Temperature: <40 °C at the point of application Distance: 7 mm Duration: 240 s total (60 s per quadrant, from the neck to the tip of the implant) |
| Hard and soft tissue changes around implants activated using plasma of argon: A histomorphometric study in dog | Canullo et al., 2018 [46] | Argon NTAPP | Power: 75 W Pressure: −10 mbar Temperature: room temperature Duration: 12 min |
| Assessment of a chair-side argon-based non-thermal plasma treatment on the surface characteristics and integration of dental implants with textured surfaces | Teixeira et al., 2012 [47] | Argon NTAPP | Pressure: atmospheric Temperature: room temperature Duration: 20 or 60 s per quadrant (KinPen™ device, Neoplas tool GmbH, Greifswald, Germany) |
| Ag-plasma modification enhances bone apposition around titanium dental implants: an animal study in Labrador dogs | Qiao et al., 2015 [48] | Silver-ion plasma immersion (Ag-PIII) | Cathode rod: Pure silver (99.99% purity, 10 mm diameter) Temperature during silver release test: 37 °C Duration of silver release test: 3 months (samples in 10 mL water) Analysis: Silver release quantified by Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES) |
| Osseointegration assessment of chairside argon-based nonthermal plasma-treated Ca-P coated dental implants | Giro et al., 2013 [49] | NTAPP on CaP | Pressure: atmospheric Temperature: Room temperature Duration: 20 s per quadrant (KinPen™ device, portable, length 155 mm, diameter 20 mm, weight 170 g) |
| Effect of Plasma Oxidation-Treated TiOx Film on Early Osseointegration | Jiang et al., 2018 [50] | Anodic oxidation plasma (PO-SLA) | Plasma oxidation treatment technical parameters not specified in detail |
| Osseointegration of titanium implants after surface treatment with ultraviolet light or cold atmospheric plasma in vivo | Henningsen et al., 2023 [51] | CAP | Device: Yocto III CAP reactor (Diener electronic GmbH, Ebhausen, Germany) Power: 24 W Pressure: vacuum of –0.5 mbar Duration: 12 min |
| Gas Plasma Treatment Improves Titanium Dental Implant Osseointegration—A Preclinical In Vivo Experimental Study | Nevins et al., 2023 [52] | Argon NTAPP | Device: ACTILINK Reborn (Plasmapp Co., Ltd., Daejon, Republic of Korea) Vacuum base pressure: ~5 torr reached within 30 s Operating pressure: 5–10 torr (optimal range for hydrocarbon removal) Electrical input: sinusoidal power, frequency 100 kHz, voltage 3 kV Treatment time: 8 s plasma exposure Additional cycle: Vacuum generation: 30 s, Plasma treatment: 8 s, Purification/by-product elimination: 17 s, Venting: 5 s Total cycle: ~60 s Gas management: chamber vented via HEPA filter to prevent reattachment of impurities |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barausse, C.; Tayeb, S.; Pellegrino, G.; Sansavini, M.; Mancuso, E.; Mazzitelli, C.; Felice, P. Cold Plasma Treatment on Titanium Implants and Osseointegration: A Systematic Review. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 10302. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910302
Barausse C, Tayeb S, Pellegrino G, Sansavini M, Mancuso E, Mazzitelli C, Felice P. Cold Plasma Treatment on Titanium Implants and Osseointegration: A Systematic Review. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(19):10302. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910302
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarausse, Carlo, Subhi Tayeb, Gerardo Pellegrino, Martina Sansavini, Edoardo Mancuso, Claudia Mazzitelli, and Pietro Felice. 2025. "Cold Plasma Treatment on Titanium Implants and Osseointegration: A Systematic Review" Applied Sciences 15, no. 19: 10302. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910302
APA StyleBarausse, C., Tayeb, S., Pellegrino, G., Sansavini, M., Mancuso, E., Mazzitelli, C., & Felice, P. (2025). Cold Plasma Treatment on Titanium Implants and Osseointegration: A Systematic Review. Applied Sciences, 15(19), 10302. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910302










