Evaluation of the Inclusion of the Seaweed Ulva lactuca Produced in an Integrated System with Biofloc in the Diet of Juvenile Tilapia Oreochromis niloticus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Location and Origin of the Animals and Macroalgae
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Water Quality and Fish Performance
- 1.
- Initial body weight (g): initial biomass of live animals (g)/total number of animals;
- 2.
- Average final weight (g): final biomass of live animals (g)/total number of animals;
- 3.
- Weight gain (g): final weight (g) − initial weight (g);
- 4.
- Specific growth rate (% d−1): 100 × [ln (final weight (g) − initial weight (g))/(cultivation time)];
- 5.
- Feed conversion rate (FCR) = ∑ration offered (g)/(final biomass (g) − initial biomass (g));
- 6.
- Survival (%) = (final number of animals/initial number of animals) × 100.
2.4. Proximal Composition and Hematology
2.5. Biochemical Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Water Quality and Fish Performance
3.2. Fish Proximal Composition and Hematology
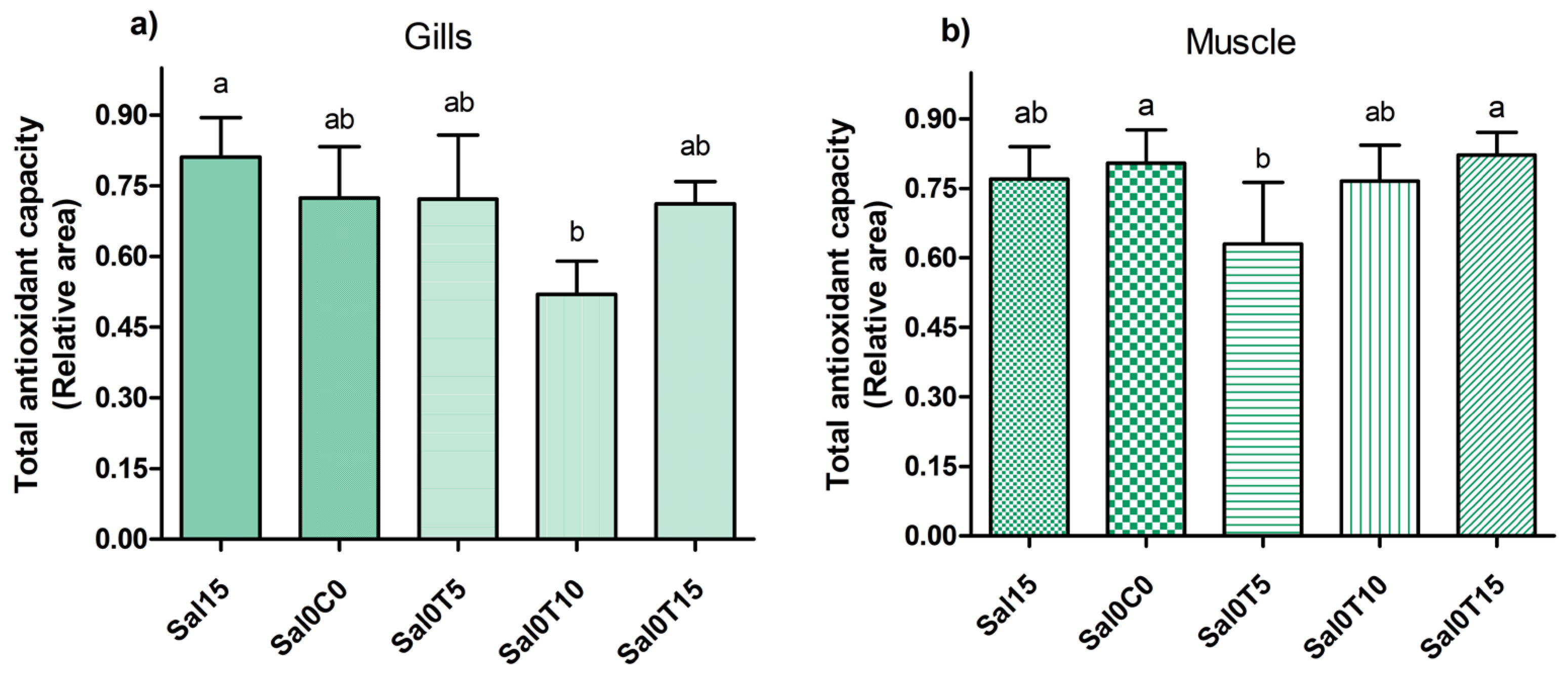
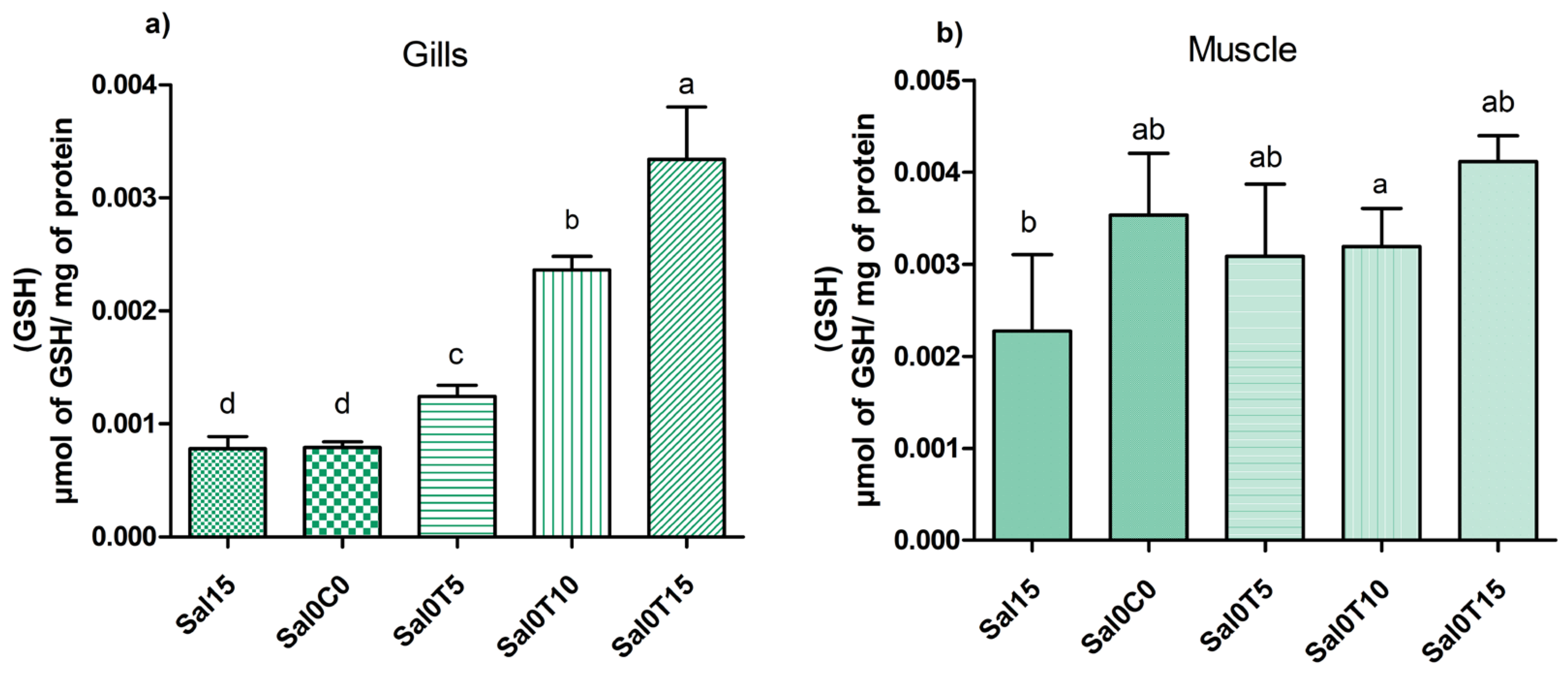
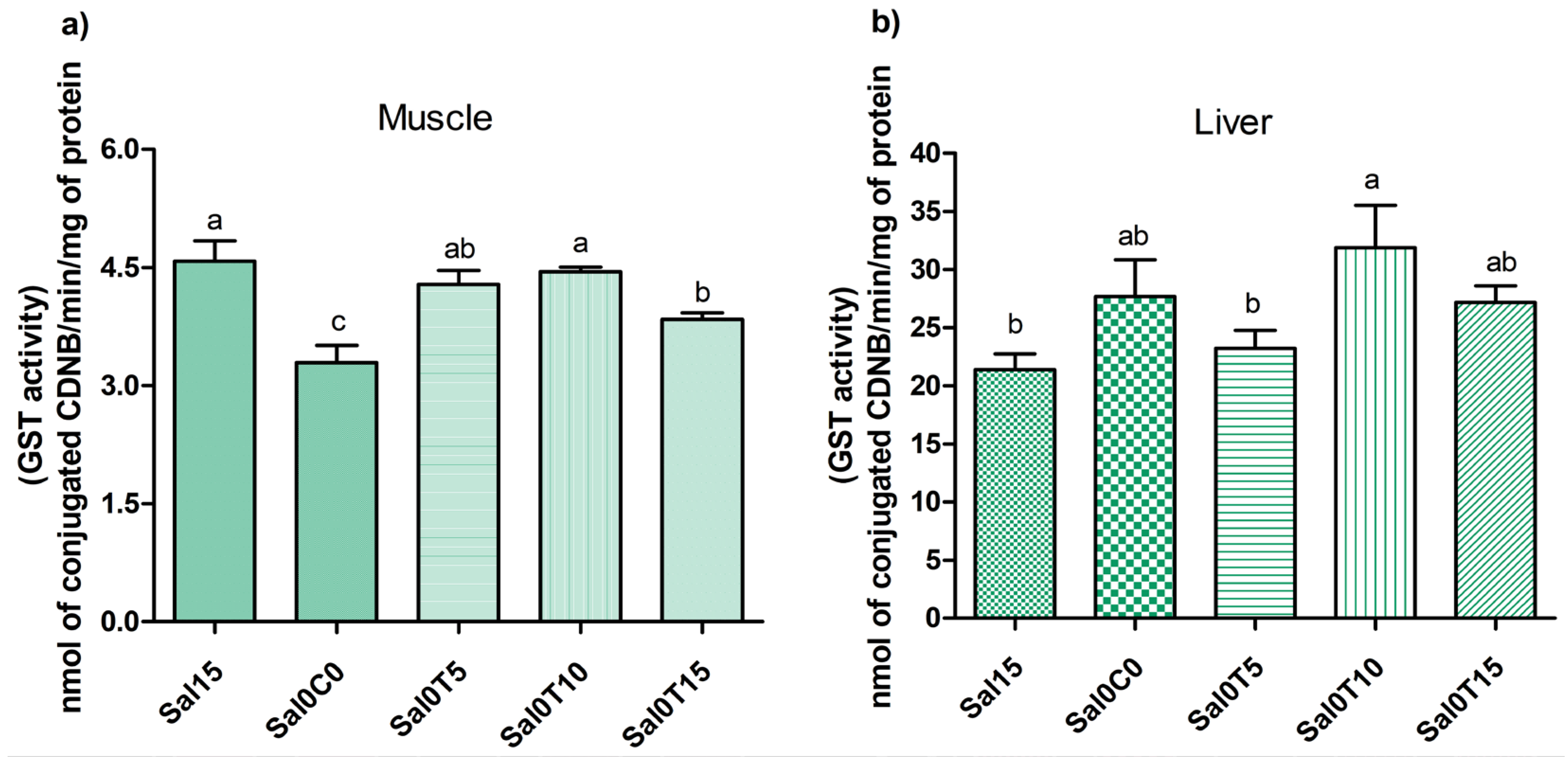
3.3. Biochemical Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ben-Ari, T.; Neori, A.; Ben-Ezra, D.; Shauli, L.; Odintsov, V.; Shpigel, M. Management of Ulva lactuca as a Biofilter of Mariculture Effluents in IMTA System. Aquaculture 2014, 434, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queirós, A.S.; Circuncisão, A.R.; Pereira, E.; Válega, M.; Abreu, M.H.; Silva, A.M.S.; Cardoso, S.M. Valuable Nutrients from Ulva rigida: Modulation by Seasonal and Cultivation Factors. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resende, L.; Flores, J.; Moreira, C.; Pacheco, D.; Baeta, A.; Garcia, A.C.; Rocha, A.C.S. Effective and Low-Maintenance IMTA System as Effluent Treatment Unit for Promoting Sustainability in Coastal Aquaculture. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopin, T. Marine Aquaculture in Canada: Well-Established Monocultures of Finfish and Shellfish and an Emerging Integrated Multi-Trophic Aquaculture (IMTA) Approach Including Seaweeds, Other Invertebrates, and Microbial Communities. Fisheries 2015, 40, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Alencar, J.R.; Junior, P.A.H.; Celino, J.J. Cultivo de Camarão Branco Litopenaeus Vannamei (Boone, 1931) Com a Macro- Alga Ulva lactuca Linneaus (Chlorophyta) No Tratamento de Efluentes Em Sistema Fechado de Recirculação. Rev. Biol. Ciências Terra 2010, 10, 117–137. [Google Scholar]
- Khanjani, M.H.; Mozanzadeh, M.T.; Sharifinia, M.; Emerenciano, M.G.C. Biofloc: A Sustainable Dietary Supplement, Nutritional Value and Functional Properties. Aquaculture 2023, 562, 738757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebeling, J.M.; Timmons, M.B.; Bisogni, J.J. Engineering Analysis of the Stoichiometry of Photoautotrophic, Autotrophic, and Heterotrophic Removal of Ammonia-Nitrogen in Aquaculture Systems. Aquaculture 2006, 257, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, K.R.; Wasielesky, W.; Abreu, P.C. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Dynamics in the Biofloc Production of the Pacific White Shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2013, 44, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, W.G.; Wasielesky, W.; Abreu, P.C.; Brandão, H.; Krummenauer, D. Rearing of the Pacific White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone, 1931)in BFT System with Different Photoperiods: Effects on the Microbial Community, Water Quality and Zootechnical Performance. Aquaculture 2019, 508, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.; Braga, Í.; Chaar, F.; Cardozo, A.P.; Monserrat, J.M.; Ramírez, J.R.B.; Wasielesky, W.; Poersch, L.H. Production of the Macroalgae Ulva lactuca Integrated with the Shrimp Penaeus Vannamei in a Biofloc System: Effect of Total Suspended Solids and Nutrient Concentrations. Phycology 2024, 4, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levavasseur, G. Analyse Comparée Des Complexes Pigment-Protéines de Chlorophycophytes Marines Benthiques. Phycologia 1989, 28, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.; Costa, L.C.d.O.; Holanda, M.; Poersch, L.H.; Turan, G. Influence of Total Suspended Solids on the Growth of the Sea Lettuce Ulva lactuca Integrated with the Pacific White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei in a Biofloc System. Fishes 2023, 8, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Tan, H.; Jin, W.; Li, Y.; Santhoshkumar, C.; Li, P.; Liu, W. Antioxidative and Antimicrobial Activities of Intertidal Seaweeds and Possible Effects of Abiotic Factors on These Bioactivities. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2018, 36, 2243–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, W.L.; Gerking, S.D. Marine Macroalgae as Foods for Fishes: An Evaluation of Potential Food Quality. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1980, 5, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchherr, J.; Reike, D.; Hekkert, M. Conceptualizing the Circular Economy: An Analysis of 114 Definitions. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 127, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornejo-Ponce, L.; Vilca-Salinas, P.; Lienqueo-Aburto, H.; Arenas, M.J.; Pepe-Victoriano, R.; Carpio, E.; Rodríguez, J. Integrated Aquaculture Recirculation System (Iars) Supported by Solar Energy as a Circular Economy Alternative for Resilient Communities in Arid/Semi-Arid Zones in Southern South America: A Case Study in the Camarones Town. Water 2020, 12, 3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooney, R.; de Sousa, D.B.; Fernández-Ríos, A.; Mellett, S.; Rowan, N.; Morse, A.P.; Hayes, M.; Laso, J.; Regueiro, L.; Wan, A.H.; et al. A Circular Economy Framework for Seafood Waste Valorisation to Meet Challenges and Opportunities for Intensive Production and Sustainability. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 392, 136283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanati, C.; Willer, D.; Schubert, J.; Aldridge, D.C. Sustainable Intensification of Aquaculture through Nutrient Recycling and Circular Economies: More Fish, Less Waste, Blue Growth. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2021, 30, 143–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwendwa, R.; Wawire, M.; Kahenya, P. Potential for Use of Seaweed as a Fish Feed Ingredient: A Review. J. Agric. Sci. 2023, 15, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, N.E.; Shalaby, S.M.; Sakr, E.M.; Elmonem, A.I.A.; Michael, F.R. Effect of Dietary Inclusion of Ulva fasciata on Red Hybrid Tilapia Growth and Carcass Composition. J. Appl. Aquac. 2014, 26, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinho, G.; Nunes, C.; Sousa-Pinto, I.; Pereira, R.; Rema, P.; Valente, L.M.P. The IMTA-Cultivated Chlorophyta Ulva Spp. as a Sustainable Ingredient in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Diets. J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 25, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, G.; Celikler, S.; Vatan, O.; Dere, S. Determination of the Anti-Oxidative Capacity and Bioactive Compounds in Green Seaweed Ulva rigida C. Agardh. Int. J. Food Prop. 2012, 15, 1182–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Xu, Y.; Chen, H.; Sun, P. Extraction, Structural Characterization, and Potential Antioxidant Activity of the Polysaccharides from Four Seaweeds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidgell, J.T.; Magnusson, M.; de Nys, R.; Glasson, C.R.K. Ulvan: A Systematic Review of Extraction, Composition and Function. Algal Res. 2019, 39, 101422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, I.L.M.; Melatti, E.; de Souza Correia, E.; Ferreira, D.A.; da Silva, L.O.B. Economic Viability of Tilapia Cultivation (Oreochromis niloticus) in Net Tanks Located in the Municipality of Glória-BA. Custos Agronegócios Online 2020, 16, 900. [Google Scholar]
- Oliva-Teles, A. Nutrition and Health of Aquaculture Fish. J. Fish Dis. 2012, 35, 83–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W.; Wei, Y.; Yuan, H.; Tan, Y. Seaweed Polysaccharide Fibers: Solution Properties, Processing and Applications. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 140, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhlongo, G.; Mnisi, C.M. Effect of Seaweed (Ecklonia maxima) on Apparent Nutrient Digestibility, Growth Performance, and Physiological and Meat Quality Parameters in Boschveld Cockerels. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Huang, K.; Ma, Y.; Qin, X.; Wen, Y.; Sun, L.; Tang, L. Feeding Frequency and Rate Effects on Growth and Physiology of Juvenile Genetically Improved Farmed Nile Tilapia. N. Am. J. Aquac. 2015, 77, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gontijo, Á.M.D.M.C.; Barreto, R.E.; Speit, G.; Valenzuela Reyes, V.A.; Volpato, G.L.; Favero Salvadori, D.M. Anesthesia of Fish with Benzocaine Does Not Interfere with Comet Assay Results. Mutat. Res.-Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2003, 534, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO. Chemical Methods for Use in Marine Environmental Monitoring; Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission: Paris, France, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Bendschneider, K.; Robinson, R.J. New Spectrophotometric Method for the Determination of Nitrite in Water. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 1952, 10, 781–784. [Google Scholar]
- Aminot, A.; Chaussepied, M. Manuel des Analyses Chimiques en Milieu Marin; Centre National Pour L’exploitation des Océans: Brest, France, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Association of Official Analytical Chemists (A.O.A.C). Official Methods of Analysis of the AOAC; AOAC: New Orleans, LA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Baethgen, W.E.; Alley, M. A Manual Colorimetric Procedure for Measuring Ammonium Nitrogen in Soil and Plant Kjeldahl Digests. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1989, 20, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, G. Corante Pancrômico Para Hematologia e Citologia Clínica, 20th ed.; Inst. Butantan: São Paulo, Brazil, 1947. [Google Scholar]
- Amado, L.L.; Garcia, M.L.; Ramos, P.B.; Freitas, R.F.; Zafalon, B.; Ferreira, J.L.R.; Yunes, J.S.; Monserrat, J.M. A Method to Measure Total Antioxidant Capacity against Peroxyl Radicals in Aquatic Organisms: Application to Evaluate Microcystins Toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 2115–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakes, K.D.; Van Der Kraak, G.J. Utility of the TBARS Assay in Detecting Oxidative Stress in White Sucker (Catostomus commersoni) Populations Exposed to Pulp Mill Effluent. Aquat. Toxicol. 2003, 63, 447–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryther, J.H.; DeBusk, T.A.; Peterson, J.E. Studies of Marine Macroalgae: Saline Desert Water Cultivation and Effects of Environmental Stress on Proximate Composition. Sol. Energy 1985, 6456763. [Google Scholar]
- Sedlak, J.; Lindsay, R.H. Estimation of Total, Protein-Bound, and Nonprotein Sulfhydryl Groups in Tissue with Ellman’s Reagent. Anal. Biochem. 1968, 25, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcos Limiñana, V.; Benoist, T.; Anton Sempere, S.; Maestre Pérez, S.E.; Prats Moya, M.S. Chemical Composition of Sustainable Mediterranean Macroalgae Obtained from Land-Based and Sea-Based Aquaculture Systems. Food Biosci. 2023, 54, 102902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angell, A.R.; Pirozzi, I.; de Nys, R.; Paul, N.A. Feeding Preferences and the Nutritional Value of Tropical Algae for the Abalone Haliotis asinina. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legarda, E.C.; da Silva, D.; Miranda, C.S.; Pereira, P.K.M.; Martins, M.A.; Machado, C.; de Lorenzo, M.A.; Hayashi, L.; do Nascimento Vieira, F. Sea Lettuce Integrated with Pacific White Shrimp and Mullet Cultivation in Biofloc Impact System Performance and the Sea Lettuce Nutritional Composition. Aquaculture 2021, 534, 736265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Neori, A.; Kim, J.K.; Yarish, C.; Shpigel, M.; Guttman, L.; Ben Ezra, D.; Odintsov, V.; Davis, D.A. Evaluation of Green Seaweed Ulva Sp. as a Replacement of Fish Meal in Plant-Based Practical Diets for Pacific White Shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 1305–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergün, S.; Soyutürk, M.; Güroy, B.; Güroy, D.; Merrifield, D. Influence of Ulva Meal on Growth, Feed Utilization, and Body Composition of Juvenile Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) at Two Levels of Dietary Lipid. Aquac. Int. 2009, 17, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassef, E.A.; El-Sayed, A.F.M.; Sakr, E.M. Pterocladia (Rhodophyta) and Ulva (Chlorophyta) as Feed Supplements for European Seabass, Dicentrarchus labrax L.; Fry. J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 25, 1369–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryaningrum, L.H.; Samsudin, R. Nutrient Digestibility of Green Seaweed Ulva Meal and the Influence on Growth Performance of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Emir. J. Food Agric. 2020, 32, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.M.; Valente, L.M.P.; Pereira, R.; Pires, M.A.; Seixas, F.; Rema, P. Evaluation of IMTA-Produced Seaweeds (Gracilaria, Porphyra, and Ulva) as Dietary Ingredients in Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus L., Juveniles. Effects on Growth Performance and Gut Histology. J. Appl. Phycol. 2015, 27, 1671–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azaza, B.M.S.; Mensi, F.; Ksouri, J.; Dhraief, M.N.; Brini, B.; Abdelmouleh, A.; Kraı, M.M. Growth of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.) Fed with Diets Containing Graded Levels of Green Algae Ulva Meal (Ulva rigida) Reared in Geothermal Waters of Southern Tunisia. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2008, 24, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, J.; Romero, N.; Robert, P.; Araya, J.; Lopez-Hernández, J.; Bozzo, C.; Navarrete, E.; Osorio, A.; Rios, A. Dietary Fiber, Amino Acid, Fatty Acid and Tocopherol Contents of the Edible Seaweeds Ulva lactuca and Durvillaea antarctica. Food Chem. 2006, 99, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, H. Effect of Dietary Algae on Improvement of Lipid Metabolism in Fish. Biomed. Pharmacother. 1997, 51, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satheeshkumar, P.; Ananthan, G.; Kumar, D.S.; Jagadeesan, L. Haematology and Biochemical Parameters of Different Feeding Behaviour of Teleost Fishes from Vellar Estuary, India. Comp. Clin. Path. 2012, 21, 1187–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerônimo, G.; Laffitte, L.; Speck, G.; Martins, M. Seasonal Influence on the Hematological Parameters in Cultured Nile Tilapia from Southern Brazil. Braz. J. Biol. 2011, 71, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlie-Silva, I.; Klein, A.; Gomes, J.M.M.; Prado, E.J.R.; Moraes, A.C.; Eto, S.F.; Fernandes, D.C.; Fagliari, J.J.; Junior, J.D.C.; Lima, C.; et al. Acute-Phase Proteins during Inflammatory Reaction by Bacterial Infection: Fish-Model. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amar, E.C.; Kiron, V.; Satoh, S.; Watanabe, T. Enhancement of Innate Immunity in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum) Associated with Dietary Intake of Carotenoids from Natural Products. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2004, 16, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendonça, A.J.C.; Rosas, V.T.; Monserrat, J.M.; Romano, L.A.; Tesser, M.B. The Inclusion of Algae Gracilaria domingensis in the Diet of Mullet Juveniles (Mugil liza) Improves the Immune Response. J. Appl. Aquac. 2019, 31, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrhman, A.M.; Ashour, M.; Al-Zahaby, M.A.; Sharawy, Z.Z.; Nazmi, H.; Zaki, M.A.A.; Ahmed, N.H.; Ahmed, S.R.; El-Haroun, E.; Van Doan, H.; et al. Effect of Polysaccharides Derived from Brown Macroalgae Sargassum dentifolium on Growth Performance, Serum Biochemical, Digestive Histology and Enzyme Activity of Hybrid Red Tilapia. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 25, 101212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, B.A.; Iwama, G.K. Physiological Changes in Fish from Stress in Aquaculture with Emphasis on the Response and Effects of Corticosteroids. Annu. Rev. Fish Dis. 1991, 1, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, B.; Gutteridge, J.M.C. Fee Radicals in Biology and Medicine Carcinogenesis. J. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1985, 1, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernet, D.; Schmidt, H.; Meier, W.; Burkhardt-Holm, P.; Wahli, T. Histopathology in Fish: Proposal for a Protocol to Assess Aquatic Pollution. J. Fish Dis. 1999, 22, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poljsak, B.; Šuput, D.; Milisav, I. Achieving the Balance between ROS and Antioxidants: When to Use the Synthetic Antioxidants. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 956792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, R.L.; de Lima, E.C.R.; de Melo, F.P.; Ferreira, M.G.P.; de Souza Correia, E. The Culture of Nile Tilapia at Different Salinities Using a Biofloc System. Rev. Cienc. Agron. 2019, 50, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caxico Vieira, C.A.S.; Vieira, J.S.; Bastos, M.S.; Zancanela, V.; Barbosa, L.T.; Gasparino, E.; Del Vesco, A.P. Expression of Genes Related to Antioxidant Activity in Nile Tilapia Kept under Salinity Stress and Fed Diets Containing Different Levels of Vitamin C. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health-Part A Curr. Issues 2018, 81, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura-Lima, J.; de Castro, M.R.; Acosta, D.; Fattorini, D.; Regoli, F.; de Carvalho, L.M.; Bohrer, D.; Geracitano, L.A.; Barros, D.M.; Marins, L.F.F.; et al. Effects of Arsenic (As) Exposure on the Antioxidant Status of Gills of the Zebrafish Danio rerio (Cyprinidae). Comp. Biochem. Physiol.-Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2009, 149, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Wu, X.Y.; Zhou, X.Q.; Feng, L.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, W.D.; Wu, P.; Zhao, Y. Effects of Dietary Curcumin Supplementation on Growth Performance, Intestinal Digestive Enzyme Activities and Antioxidant Capacity of Crucian Carp Carassius auratus. Aquaculture 2016, 463, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tziveleka, L.A.; Tammam, M.A.; Tzakou, O.; Roussis, V.; Ioannou, E. Metabolites with Antioxidant Activity from Marine Macroalgae. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srikanth, K.; Pereira, E.; Duarte, A.C.; Ahmad, I. Glutathione and Its Dependent Enzymes’ Modulatory Responses to Toxic Metals and Metalloids in Fish-a Review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 2133–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-gálvez, A.; Viera, I.; Roca, M. Carotenoids and Chlorophylls as Antioxidants. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikker, P.; Stokvis, L.; van Krimpen, M.M.; van Wikselaar, P.G.; Cone, J.W. Evaluation of Seaweeds from Marine Waters in Northwestern Europe for Application in Animal Nutrition. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2020, 263, 114460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, S.; Kawakatsu, M.; Izumi, S.i.; Urata, Y.; Kageyama, K.; Ihara, Y.; Koji, T.; Kondo, T. Glutathione S-Transferase π Localizes in Mitochondria and Protects against Oxidative Stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 46, 1392–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.D.; Liu, W.B.; Zhang, C.Y.; Xu, C.Y.; Zheng, X.C.; Zhang, D.D.; Chi, C. Dietary Glutathione Supplementation Enhances Antioxidant Activity and Protects against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Hepatopancreatic Injury and Cell Apoptosis in Chinese Mitten Crab, Eriocheir Sinensis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 97, 440–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, A.H.L.; Davies, S.J.; Soler-Vila, A.; Fitzgerald, R.; Johnson, M.P. Macroalgae as a Sustainable Aquafeed Ingredient. Rev. Aquac. 2019, 11, 458–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardjani, D.K.; Suantika, G.; Aditiawati, P. Nutritional Profile of Red Seaweed Kappaphycus alvarezii after Fermentation Using Saccharomyces Cerevisiae as a Feed Supplement for White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei Nutritional Profile of Fermented Red Seaweed. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 11, 1637–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, S.M.; Roy, K.; Mraz, J.; Wan, A.H.L.; Davies, S.J.; Tibbetts, S.M.; Overland, M.; Francis, D.S.; Rocker, M.M.; Gasco, L.; et al. Towards Achieving Circularity and Sustainability in Feeds for Farmed Blue Foods. Rev. Aquac. 2023, 15, 1115–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Protein (%) | Lipid (%) | Fiber (%) | Ash (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ulva meal | 19.31 ± 0.30 | 0.46 ± 0.04 | 10.34 ± 0.72 | 29.05 ± 0.63 |
| Ingredients | Experimental Diets | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | T5 | T10 | T15 | |
| Fish meal | 40.00 | 40.00 | 40.00 | 40.00 |
| Soybean meal | 33.00 | 32.00 | 31.00 | 30.00 |
| Wheat bran | 12.00 | 8.00 | 4.00 | 0.00 |
| Gelatin | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 |
| Soy oil | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 |
| Fish oil | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 |
| Cellulose | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 |
| Vitamin/mineral mix | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 |
| Ulva meal | 0.00 | 5.00 | 10.00 | 15.00 |
| Proximal composition (%) | ||||
| Protein | 42.44 | 41.82 | 41.37 | 39.98 |
| Lipids | 8.23 | 8.07 | 8.05 | 8.64 |
| Ash | 16.28 | 17.45 | 19.01 | 20.02 |
| Gross energy | 17.63 | 17.34 | 17.32 | 17.42 |
| Treatments | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Control | T5 | T10 | T15 |
| Average initial weight (g) | 0.93 ± 0.01 | 0.93 ± 0.01 | 0.94 ± 0.01 | 0.94 ± 0.00 |
| Average final weight (g) | 10.78 ± 0.51 | 11.44 ± 0.84 | 10.35 ± 0.92 | 10.33 ± 0.15 |
| Weight gain (g) | 9.85 ± 051 | 10.50 ± 0.83 | 9.41 ± 0.92 | 9.39 ± 0.15 |
| SGR (% day−1) | 5.82 ± 0.11 | 5.95 ± 0.15 | 5.71 ± 0.20 | 5.70 ± 0.40 |
| FCR | 1.00 ± 0.07 | 0.96 ± 0.09 | 0.99 ± 0.06 | 1.02 ± 0.02 |
| Survival (%) | 87.50 ± 15.00 | 85.00 ± 5.77 | 95.00 ± 5.77 | 90.0 ± 0.00 |
| Treatments | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters (%) | Control | T5 | T10 | T15 |
| Moisture | 77.31 ± 1.23 | 77.95 ± 0.30 | 77.68 ± 0.18 | 77.58 ± 0.27 |
| Protein | 14.23 ± 0.63 | 13.73 ± 0.74 | 13.67 ± 0.79 | 13.81 ± 0.96 |
| Lipid | 3.72 ± 0.53 | 3.33 ± 0.30 | 3.74 ± 0.35 | 3.55 ± 0.28 |
| Ash | 4.04 ± 0.17 | 4.08 ± 0.21 | 4.01 ± 0.11 | 4.09 ± 0.18 |
| Treatments | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters (×10−4 cel mL−1) | Control | T5 | T10 | T15 |
| Lymphocytes | 273.50 ± 97.65 | 240.00 ± 78.50 | 209.60 ± 78.54 | 278.50 ± 186.76 |
| Granulocytes | 10.50 ± 9.20 b | 26.17 ± 20.73 ab | 36.60 ± 36.84 a | 23.17 ± 13.98 ab |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carvalho, A.; Müller, L.; Rosas, V.; Tesser, M.B.; Ventura-Lima, J.; Turan, G.; Pias, M.; Poersch, L.H. Evaluation of the Inclusion of the Seaweed Ulva lactuca Produced in an Integrated System with Biofloc in the Diet of Juvenile Tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6410. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126410
Carvalho A, Müller L, Rosas V, Tesser MB, Ventura-Lima J, Turan G, Pias M, Poersch LH. Evaluation of the Inclusion of the Seaweed Ulva lactuca Produced in an Integrated System with Biofloc in the Diet of Juvenile Tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(12):6410. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126410
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarvalho, Andrezza, Larissa Müller, Victor Rosas, Marcelo Borges Tesser, Juliane Ventura-Lima, Gamze Turan, Marcelo Pias, and Luís H. Poersch. 2025. "Evaluation of the Inclusion of the Seaweed Ulva lactuca Produced in an Integrated System with Biofloc in the Diet of Juvenile Tilapia Oreochromis niloticus" Applied Sciences 15, no. 12: 6410. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126410
APA StyleCarvalho, A., Müller, L., Rosas, V., Tesser, M. B., Ventura-Lima, J., Turan, G., Pias, M., & Poersch, L. H. (2025). Evaluation of the Inclusion of the Seaweed Ulva lactuca Produced in an Integrated System with Biofloc in the Diet of Juvenile Tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Applied Sciences, 15(12), 6410. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126410









