Research on the Single-Leg Compliance Control Strategy of the Hexapod Robot for Collapsible Terrains
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Single-Leg Kinematics and Dynamics Modelling
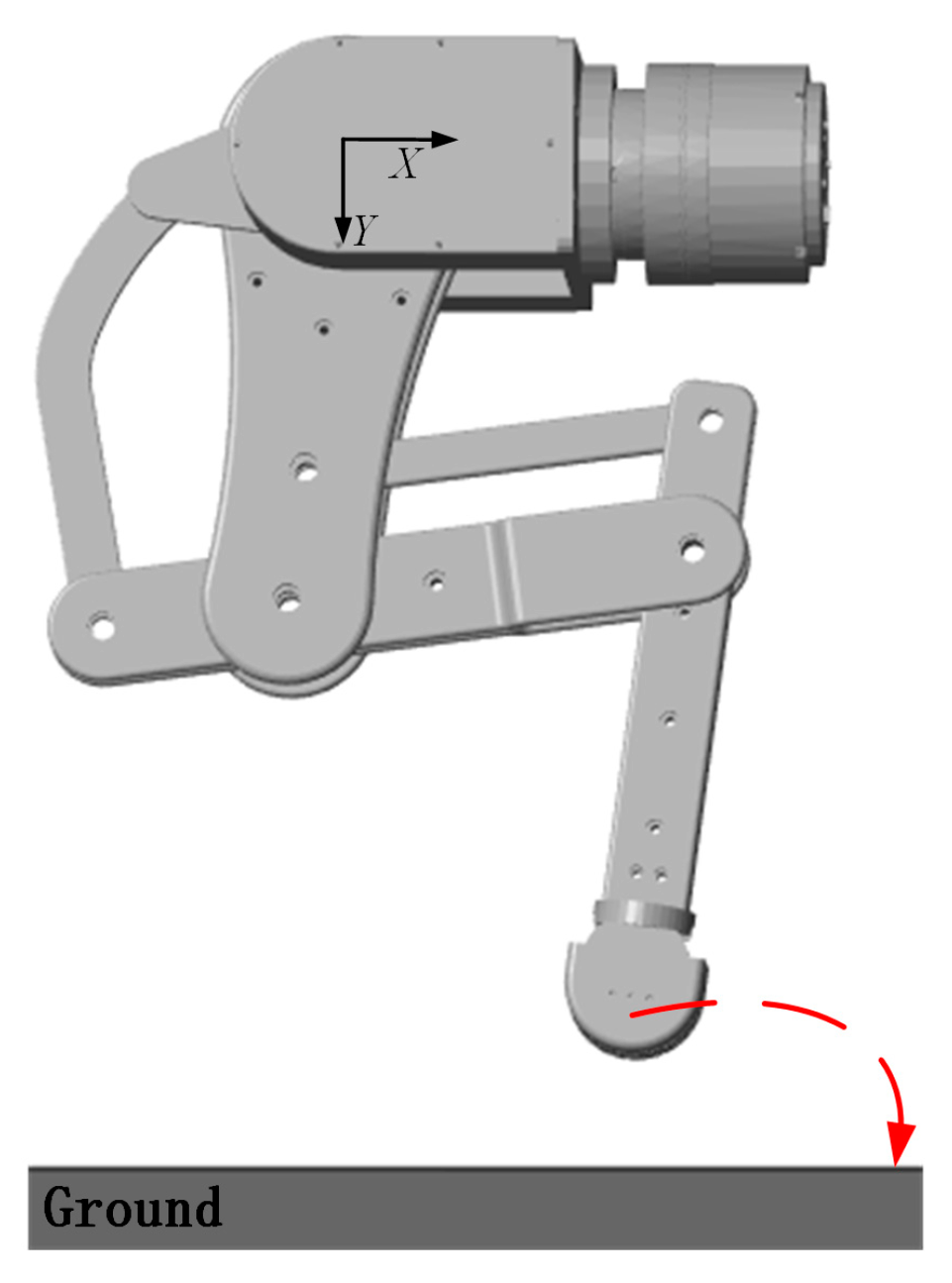
2.1. Single-Leg Structural Analysis
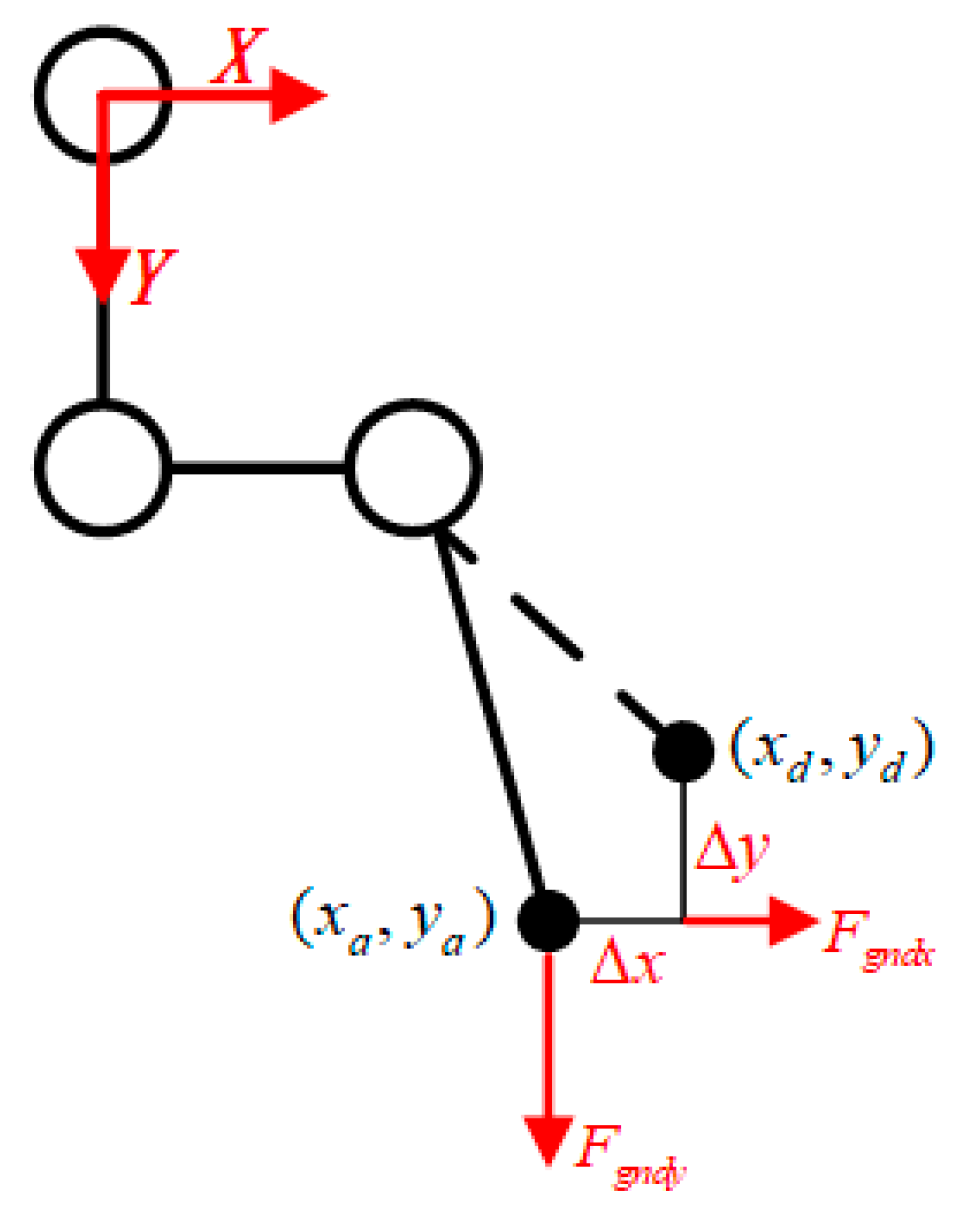
2.2. Single-Leg Kinetic Modeling
2.3. Single-Leg Dynamic Modeling
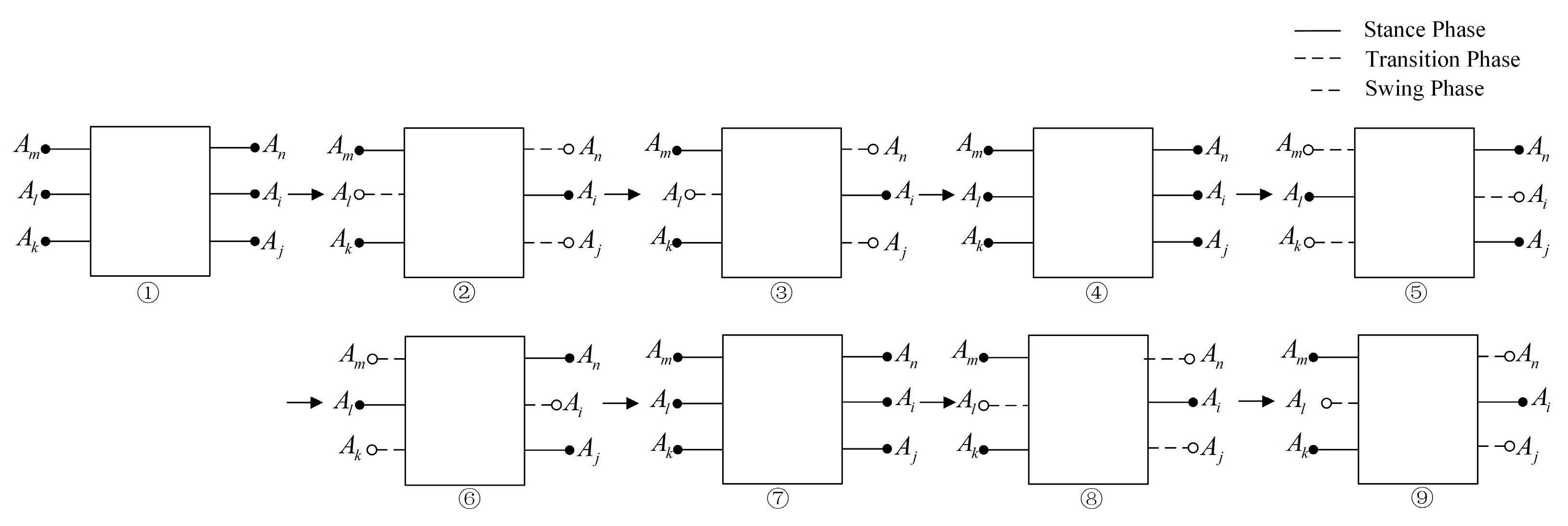
3. State Machine Strategy Based on FASM Stabilization Criterion
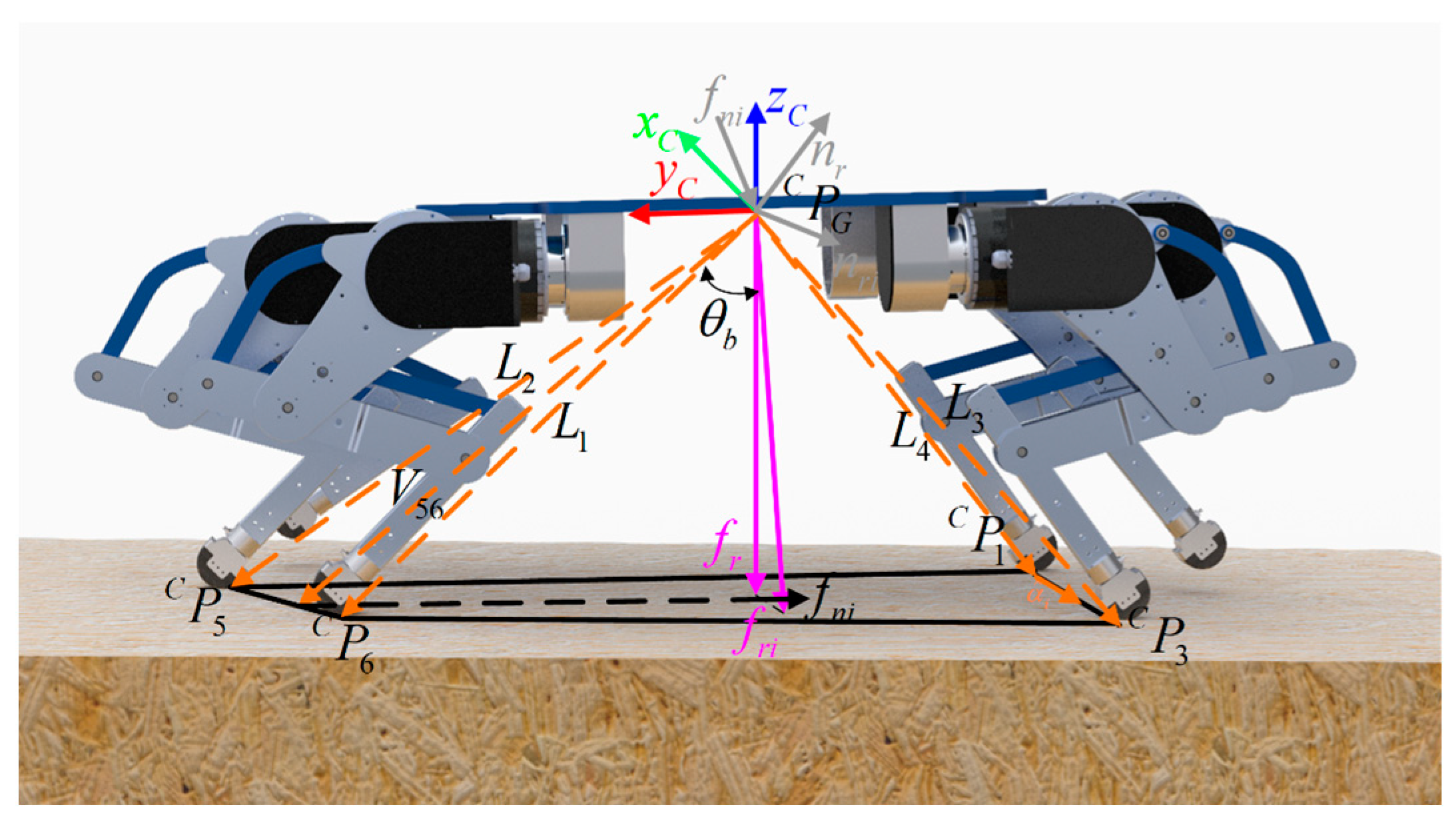
3.1. Robot Tipping and Instability Determination
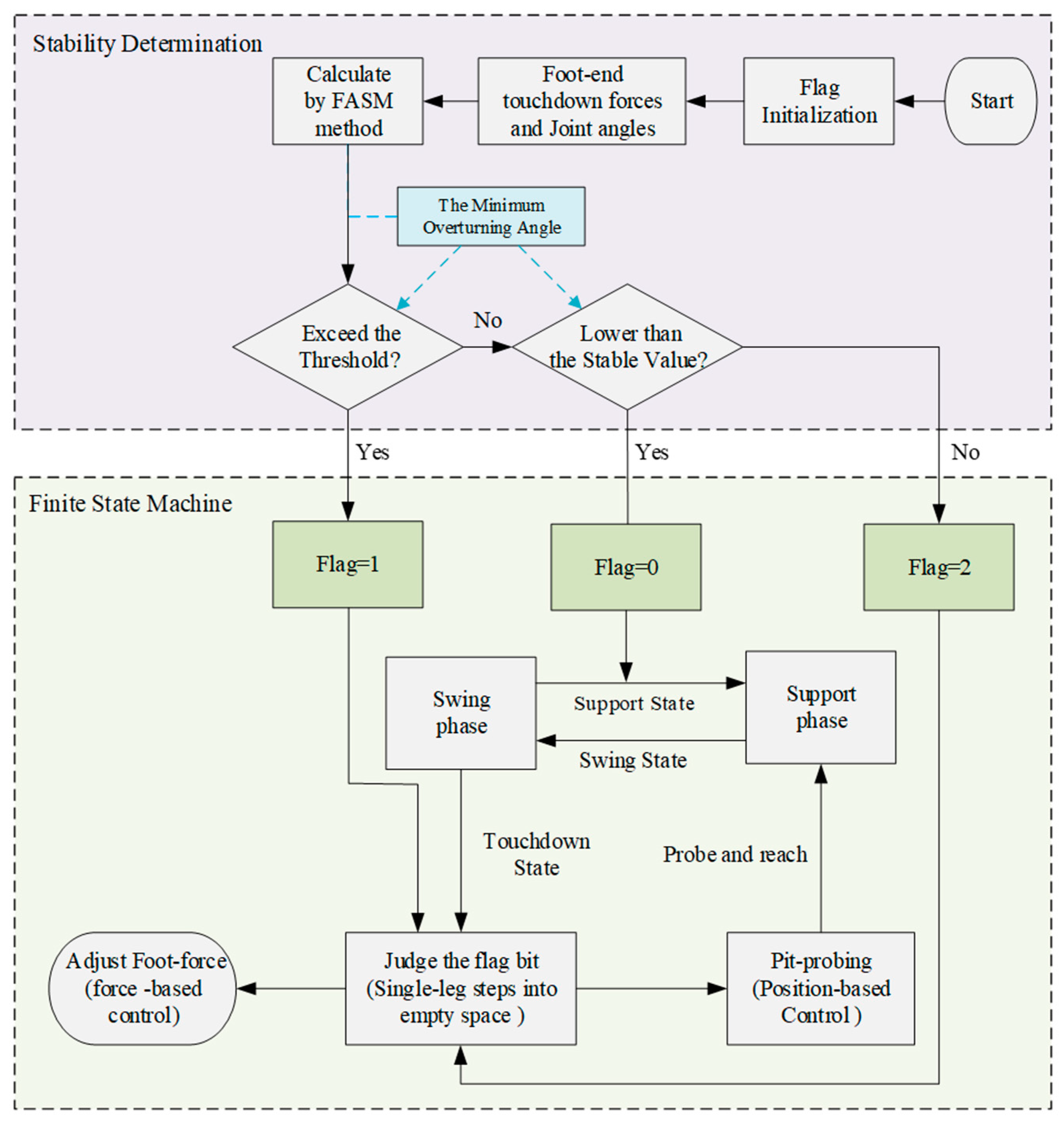
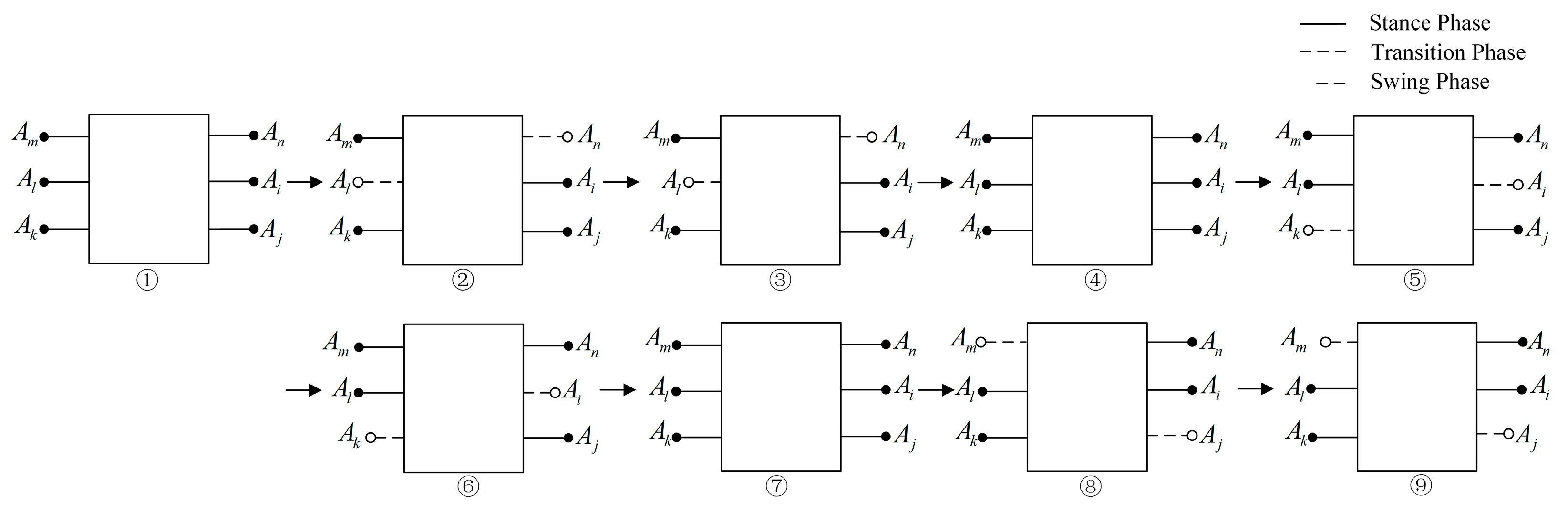
3.2. Finite State Machine Design
- (1)
- Swing state: When the foot end enters the swing phase, execute the desired trajectory tracking.
- (2)
- Support state: When the foot end enters the support phase, if the value measured by the force sensor is greater than the set value and Flag = 0, it is determined to be in a stable support state.
- (3)
- Empty-stepping state: When the foot end enters the support phase, if the force feedback suddenly changes and is lower than the set value, it is determined as empty-stepping, and corresponding decisions are triggered according to the flag bit.
- (4)
- Pit-probing state: In the empty-stepping state, if the finite state machine flag bit Flag = 2, the leg adopts admittance control to make the foot end probe the bottom of the pit along the preset trajectory and land on the ground.
- (5)
- Foot-force adjustment state: In the empty-stepping state, if the flag bit Flag = 1, the leg adopts force-based impedance control to adjust the force exerted by the foot end to reduce the impact.
4. Design of Pit-Probing Control Based on Admittance Control Method
4.1. Admittance Control Method
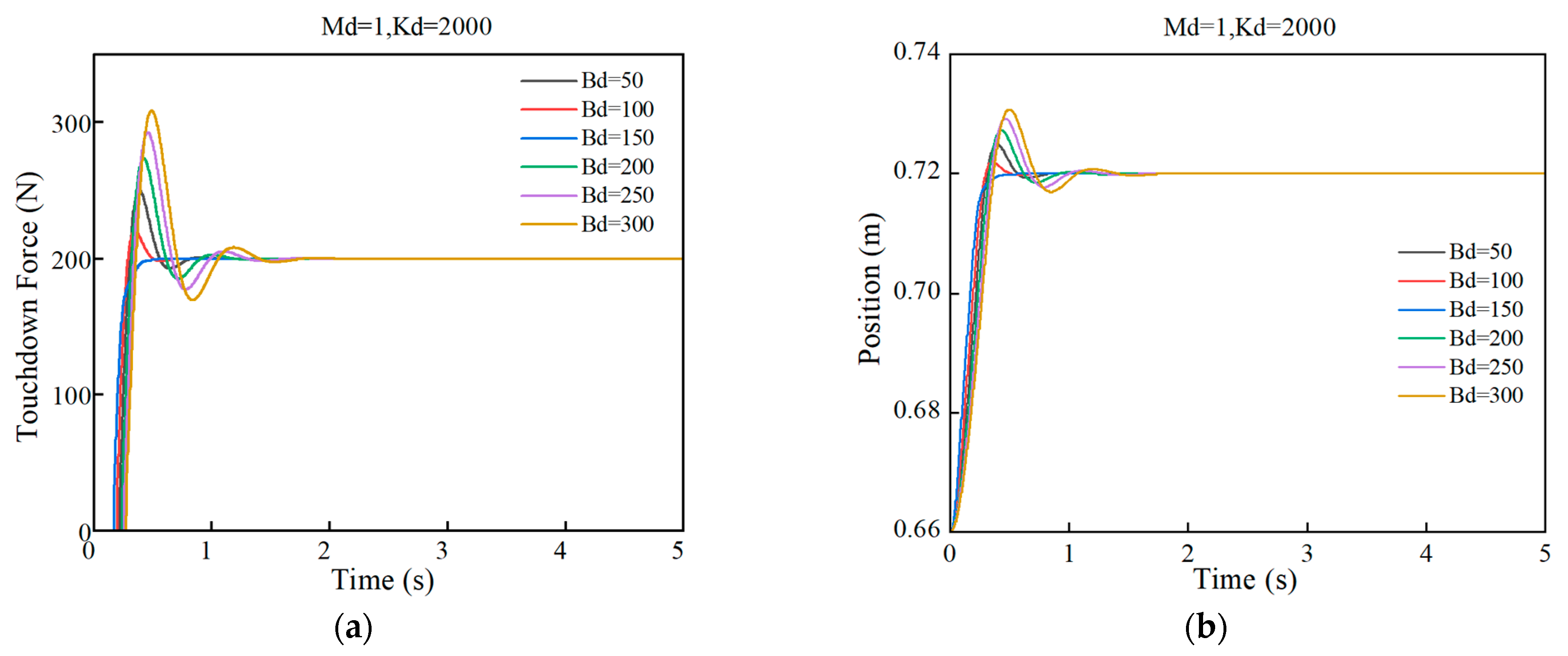
4.2. Comparison of Control Effects of Impedance Optimization Parameters
4.3. Simulation Based on Admittance Control
5. Design of Force-Based Impedance Control for Foot Cushioning
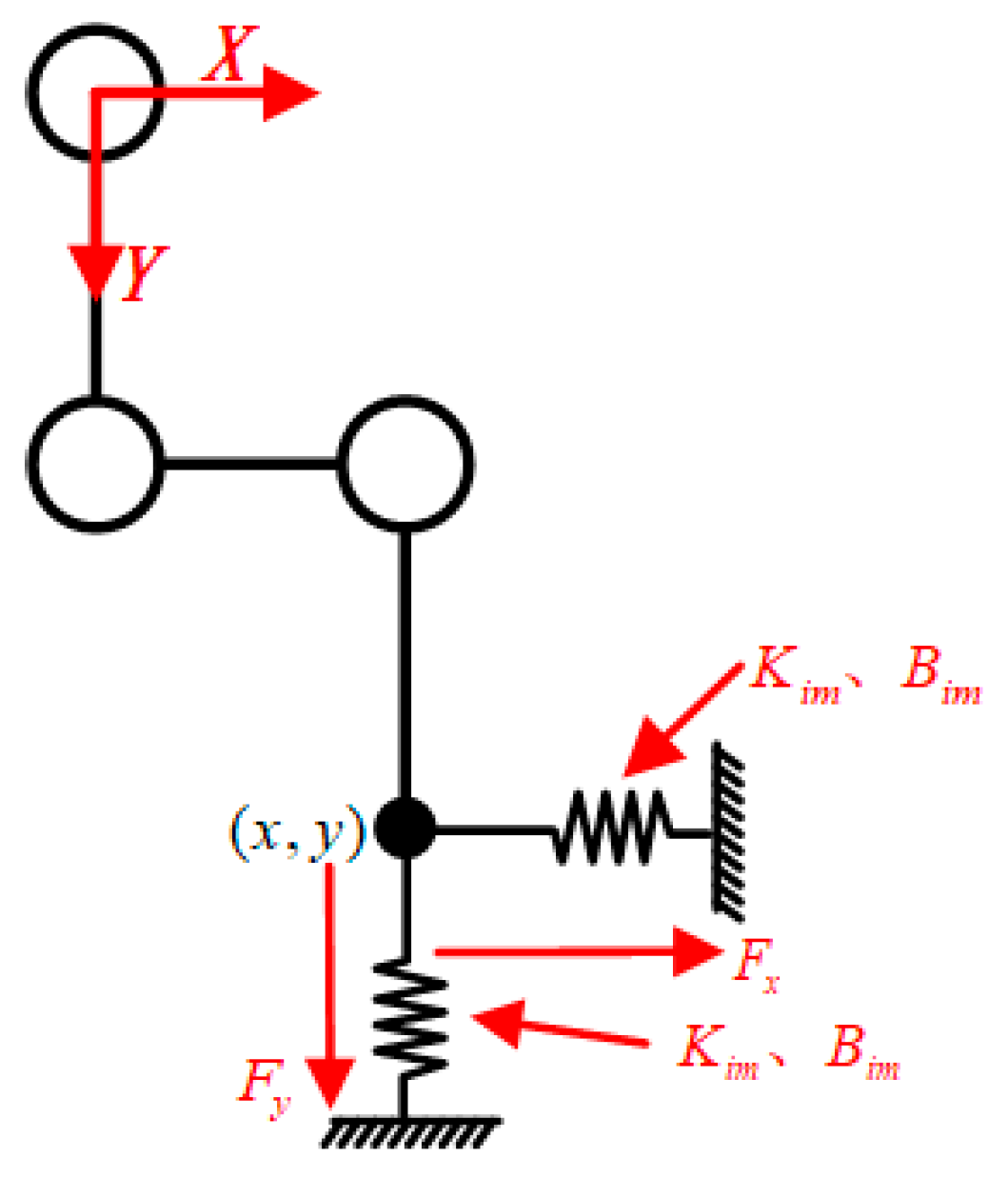
5.1. Force-Based Impedance Control Design
5.2. Stability Analysis of the Control System
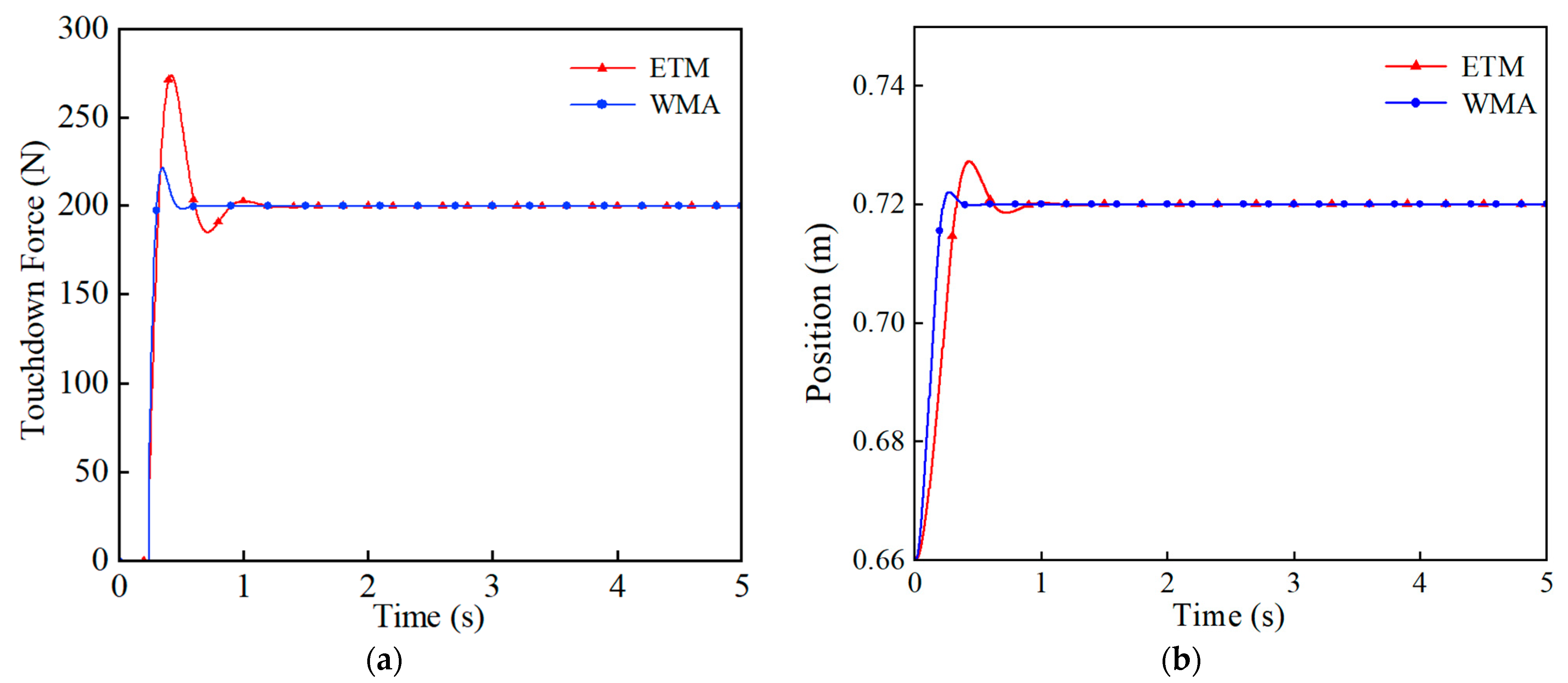
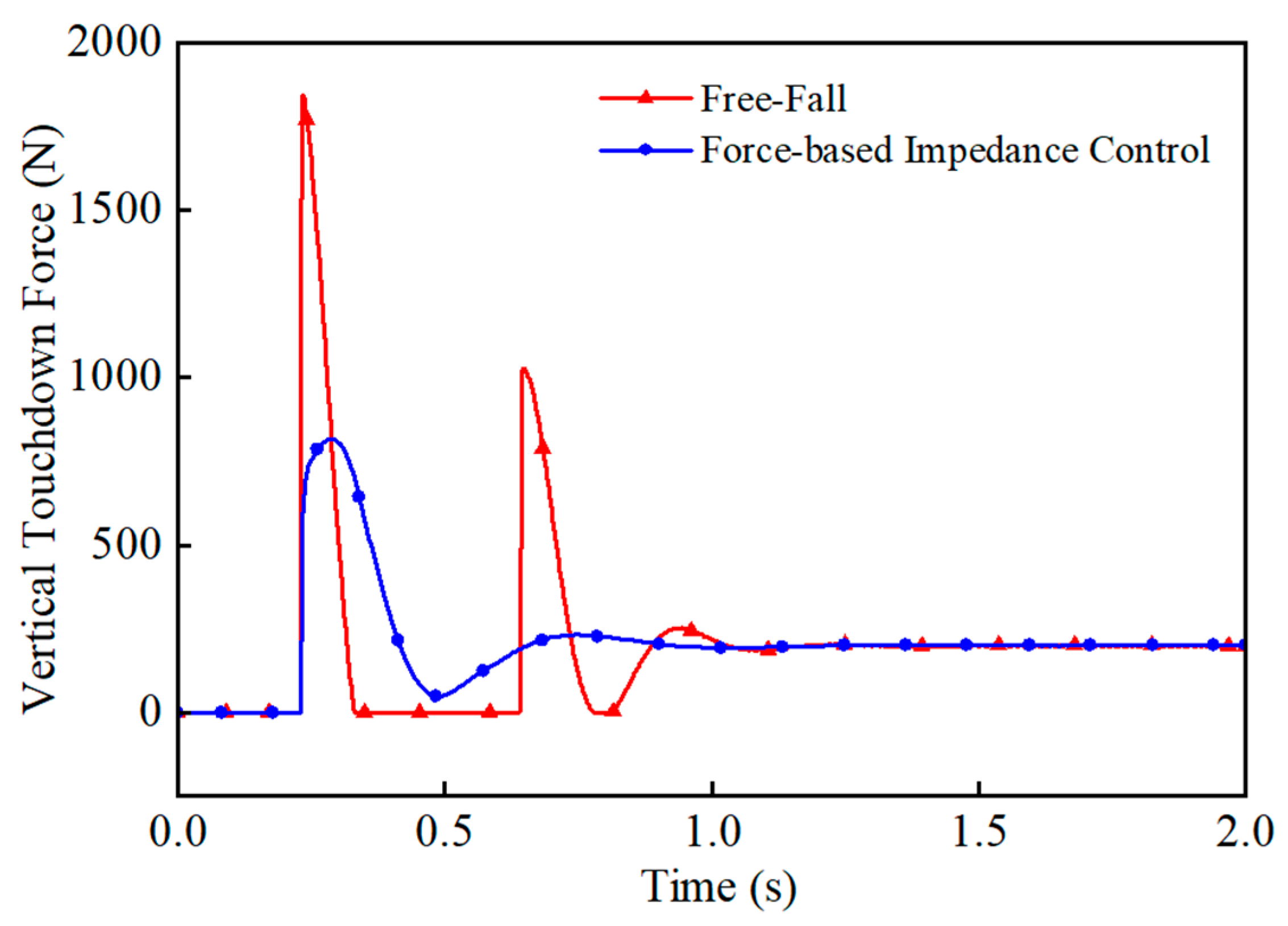
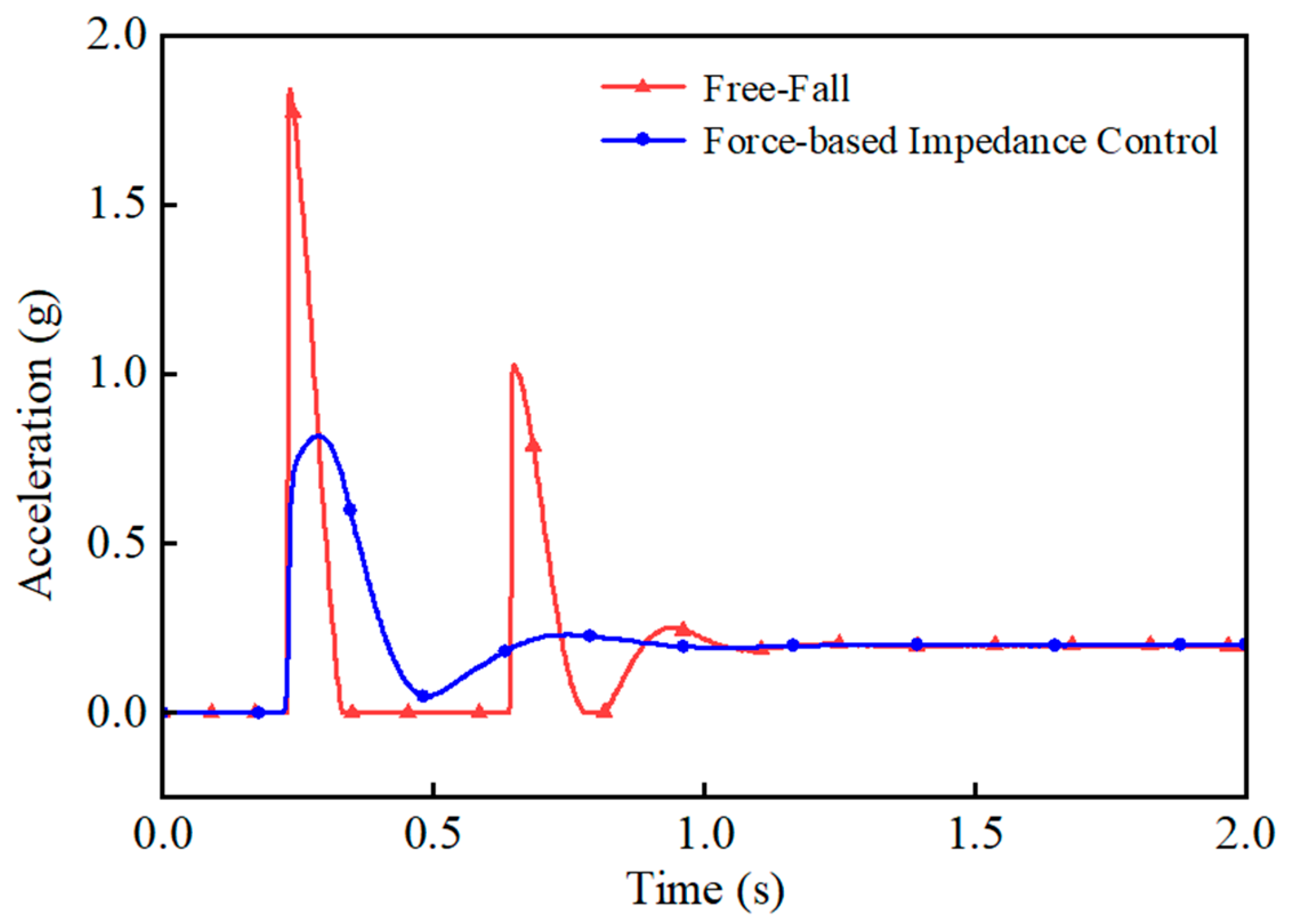
5.3. Force-Based Impedance Control Simulation
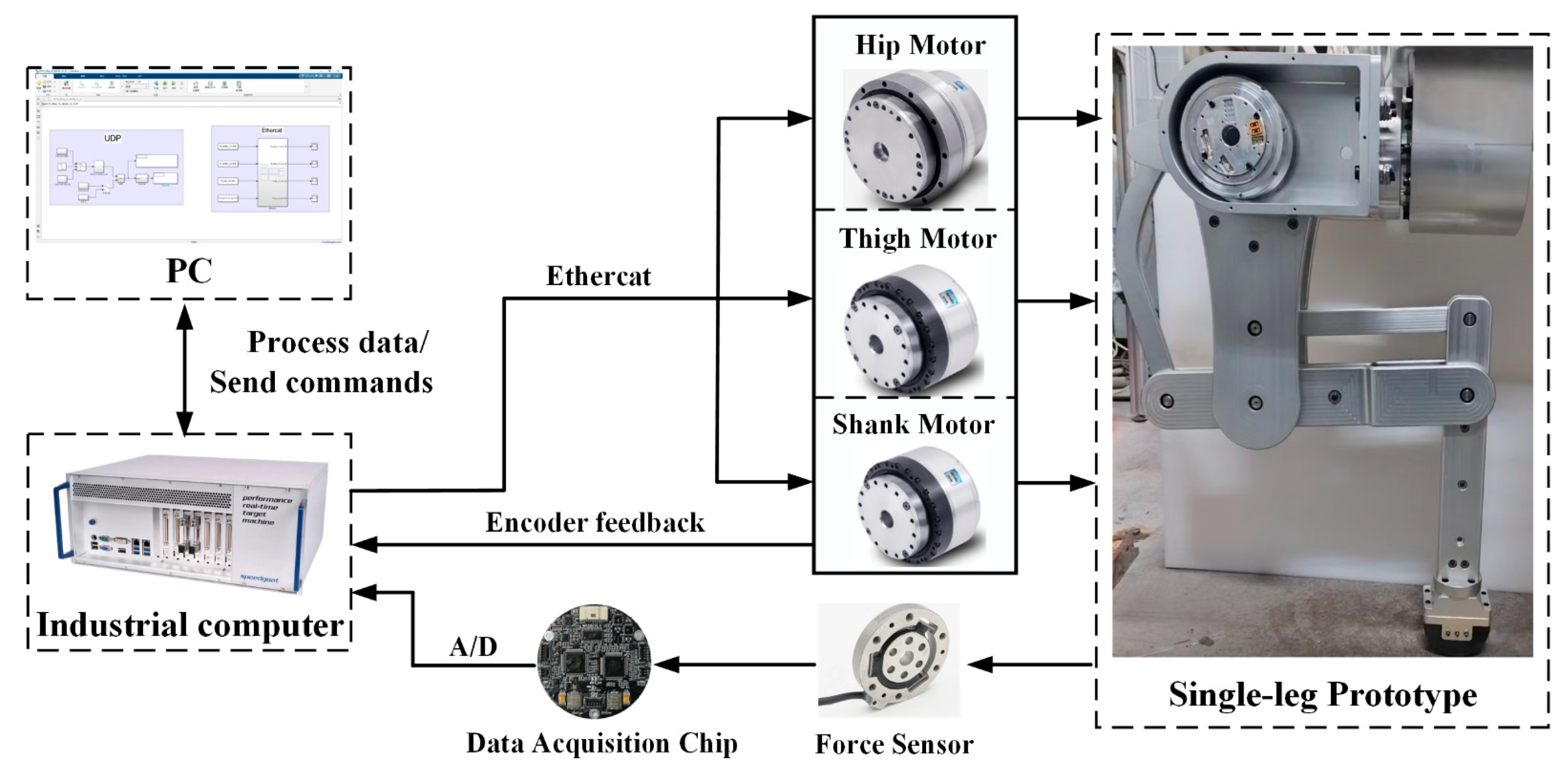
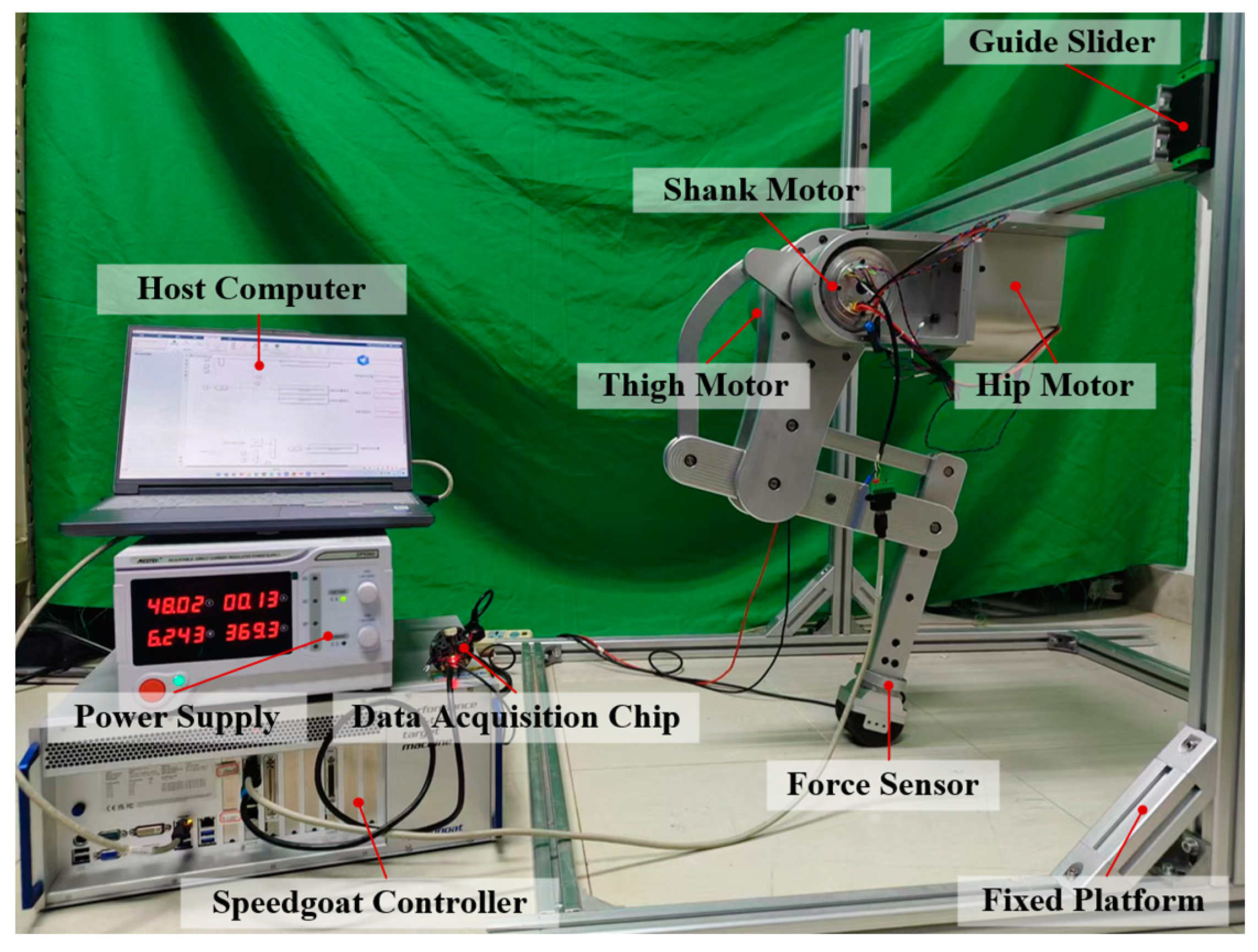
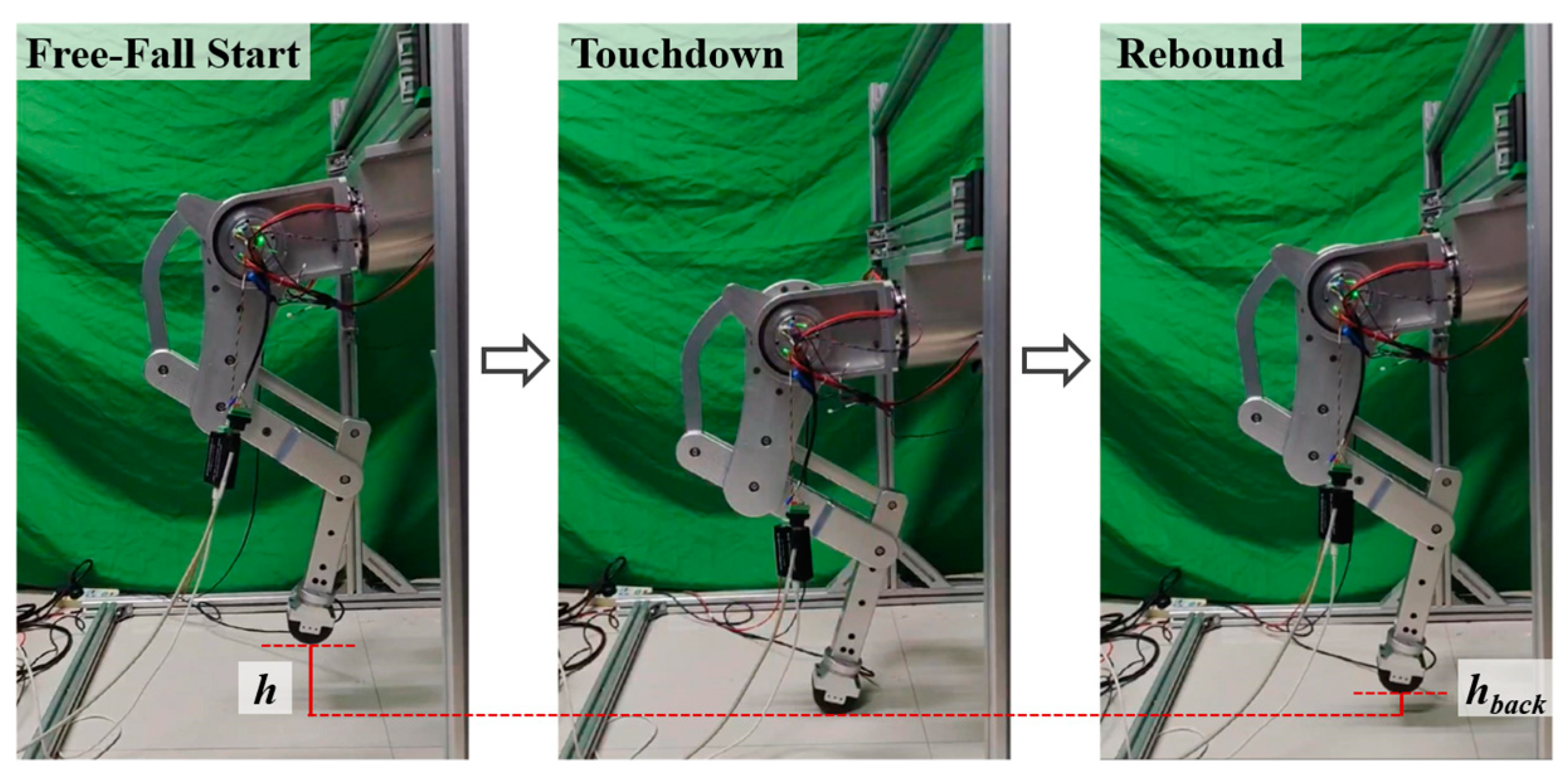
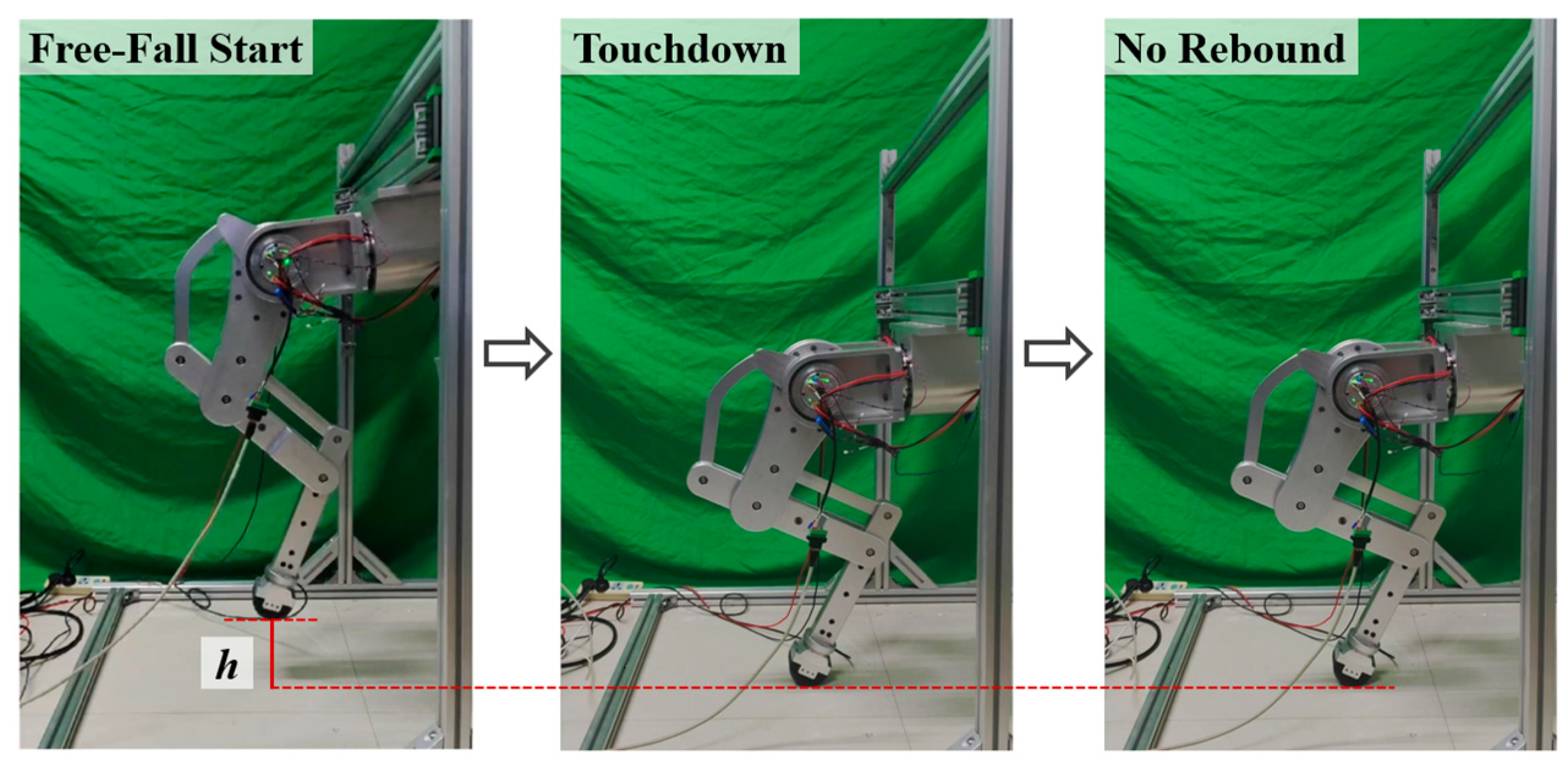
6. Prototype Experiment
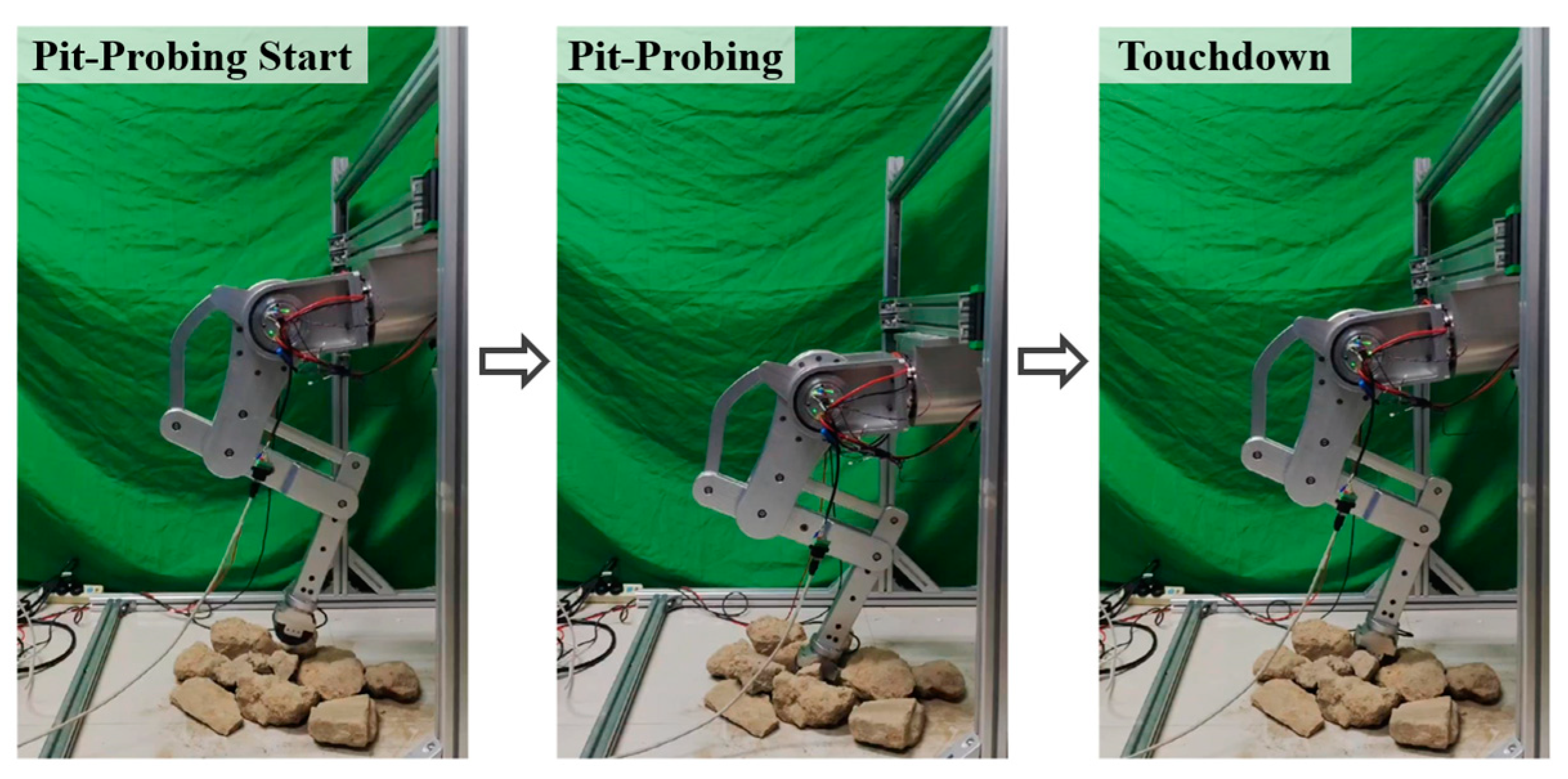
6.1. Experimental Scenario
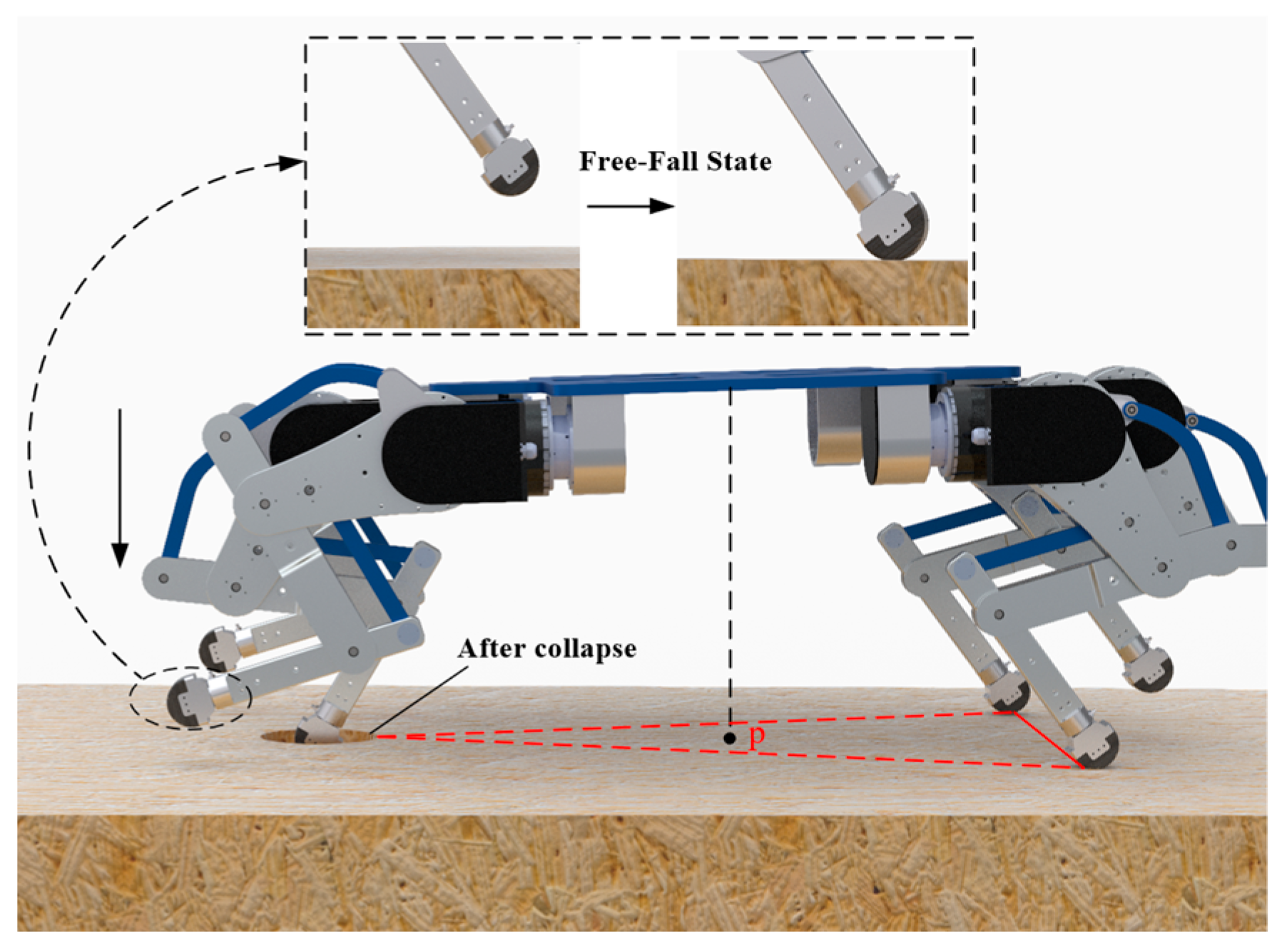
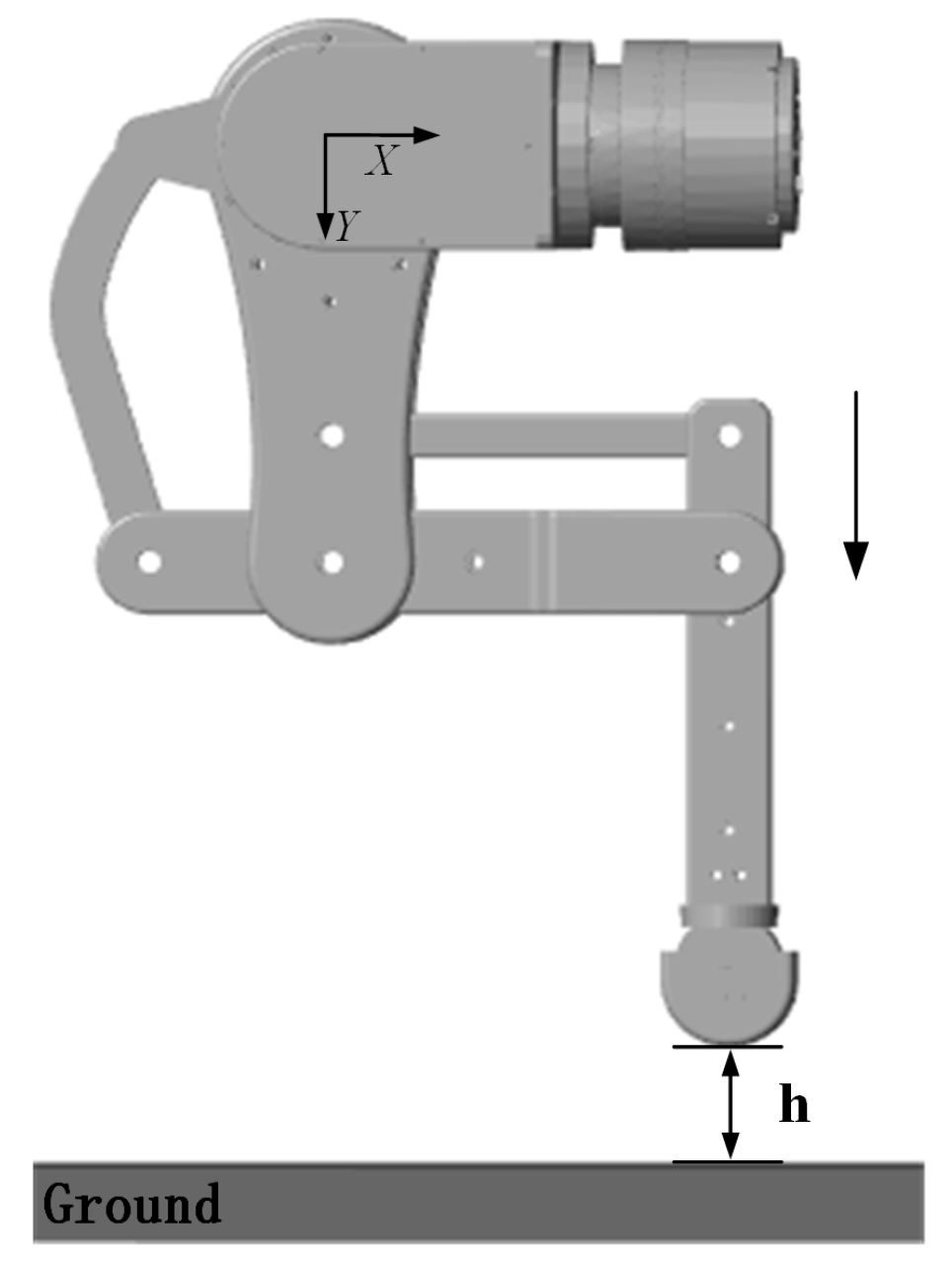
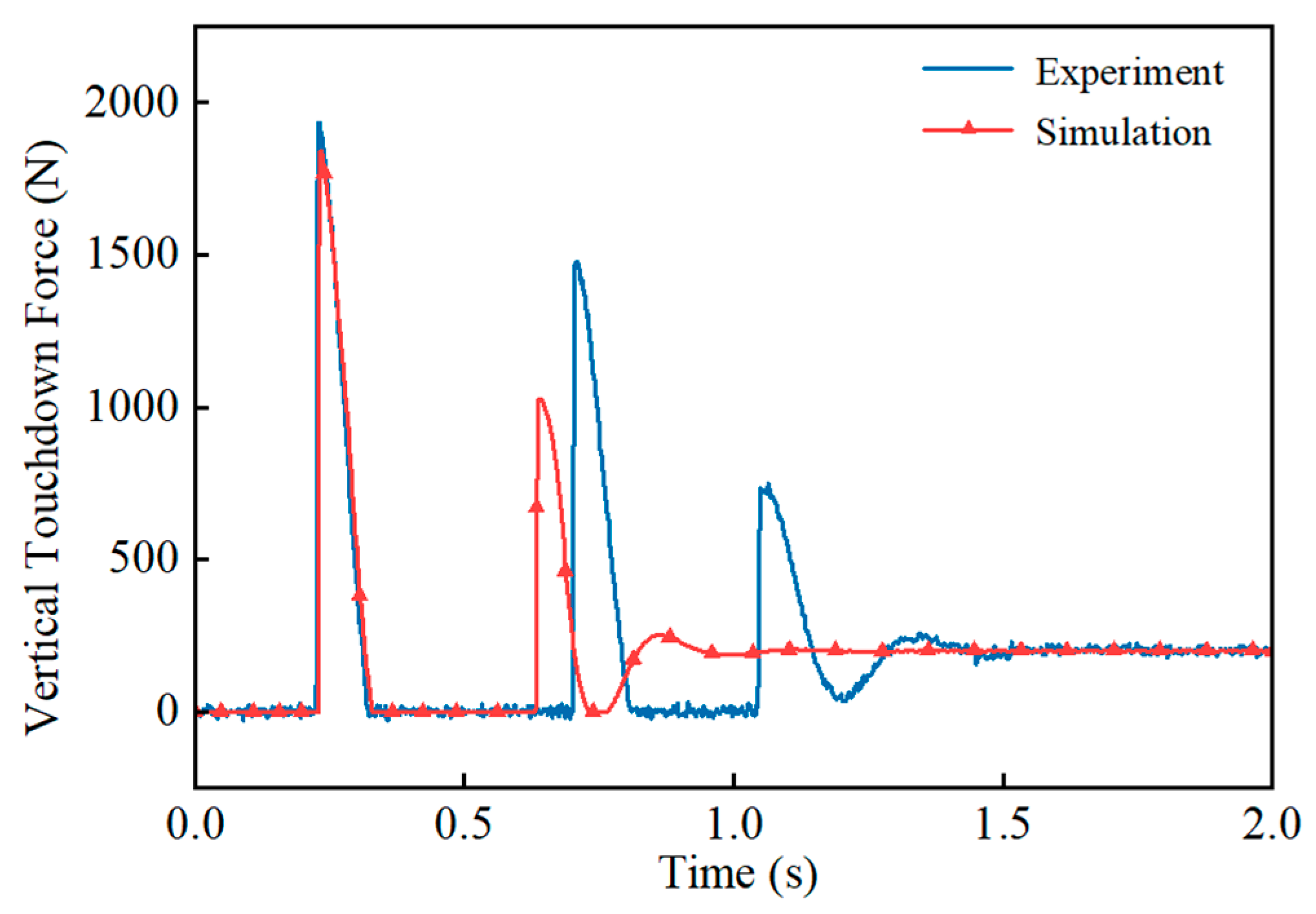
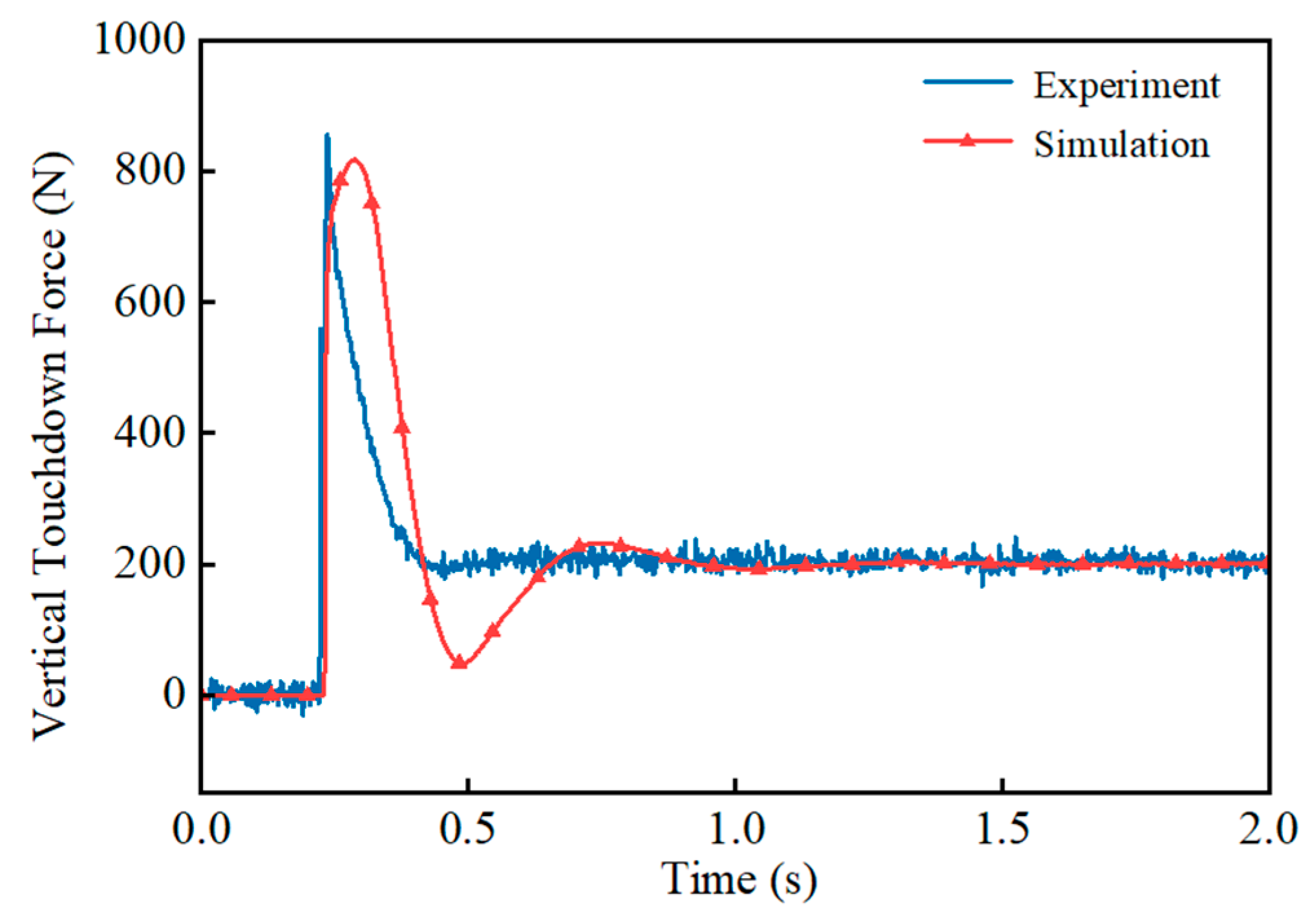
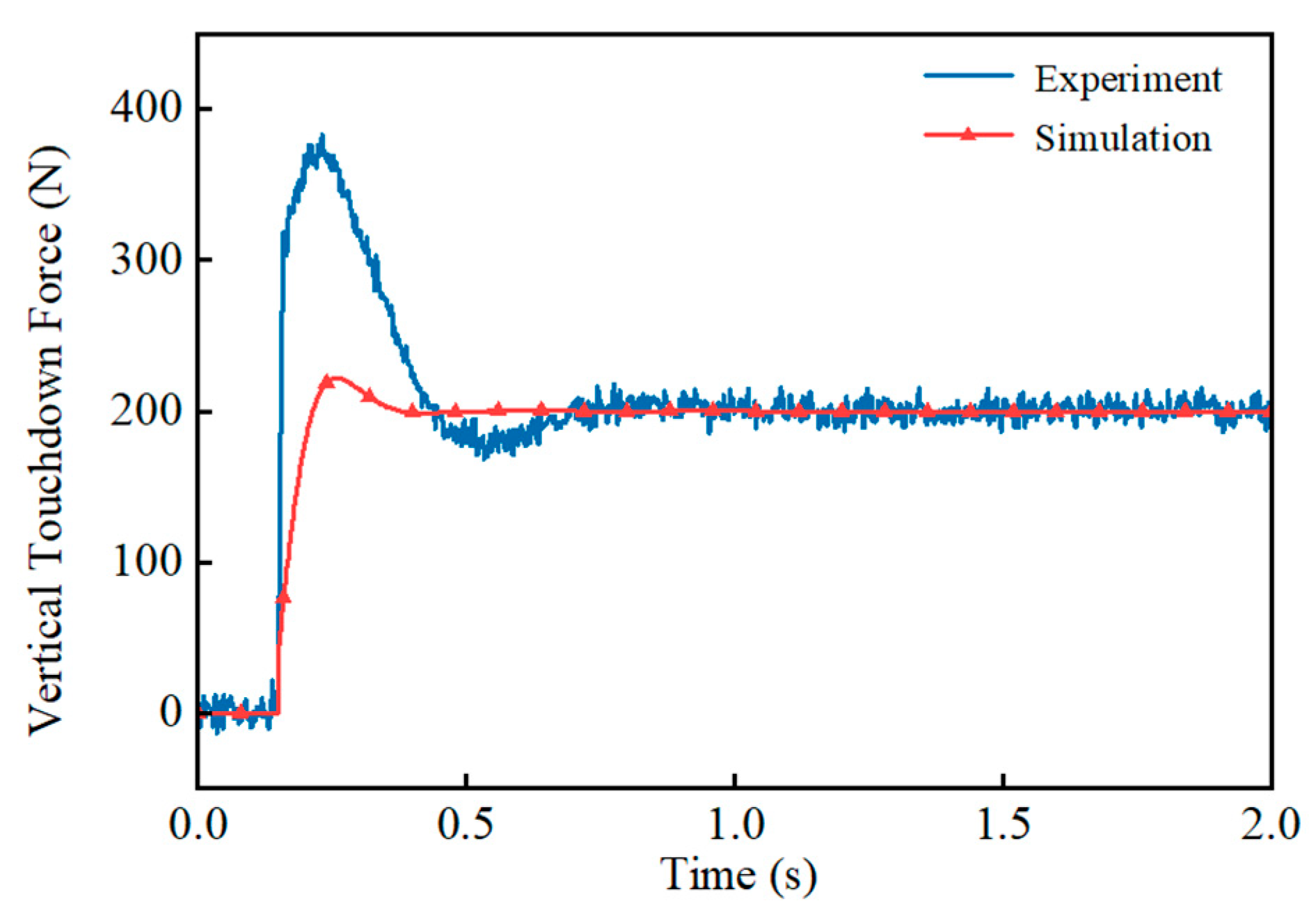
6.2. Single-Leg Free-Falling Experiment
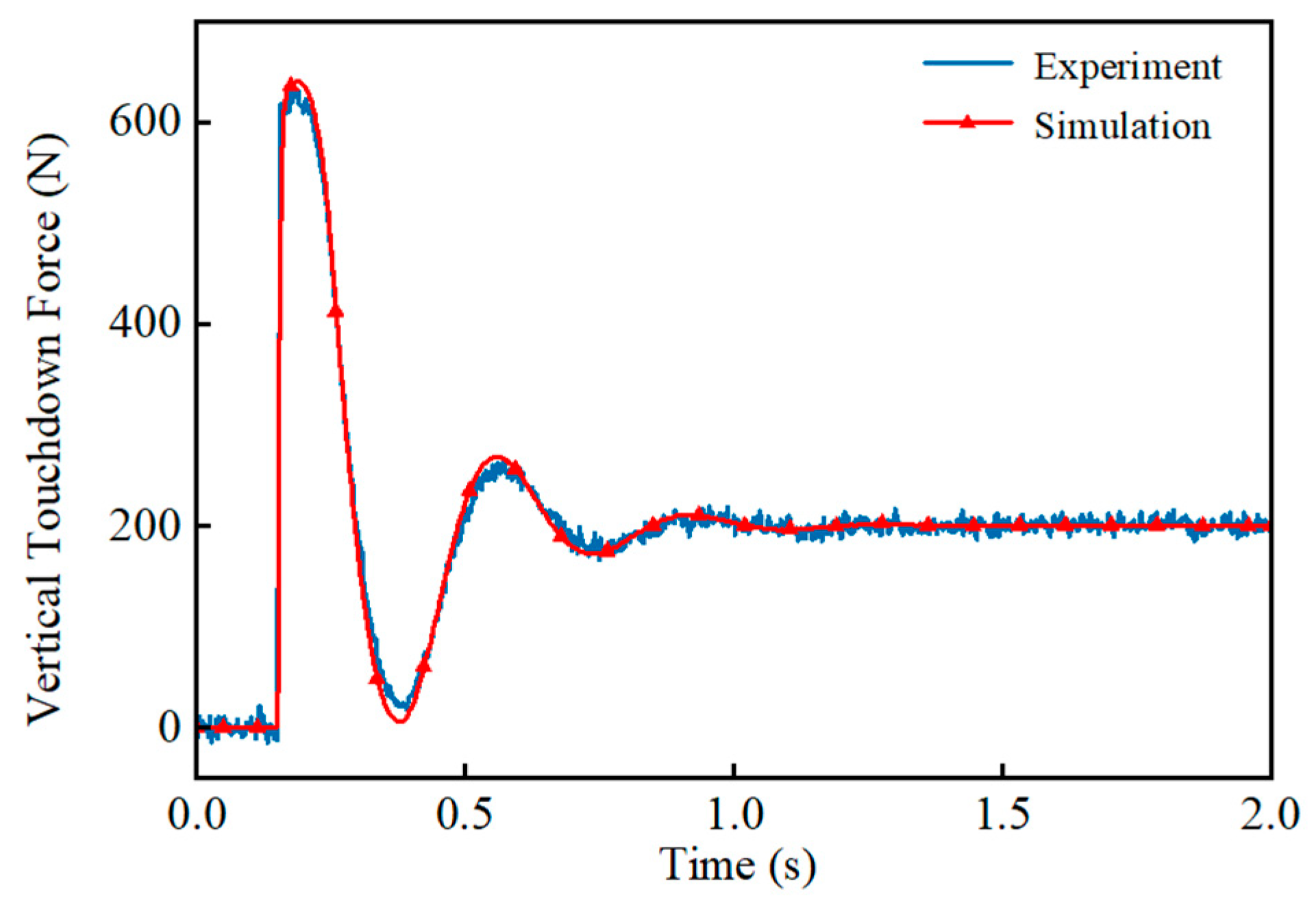
6.3. Single-Leg Pit-Probing Exploration Experiment
7. Conclusions
- (1)
- Aiming at the characteristics of the hybrid single leg, this paper constructs a kinematic model of the single leg based on the geometric method, establishes a dynamic model based on the product of the exponential formula and the principle of virtual work, and calculates the joint torques. Meanwhile, we adopt the FASM method as a stability criterion and combine it with state machine decision making to improve the stability of the hexapod robot during walking.
- (2)
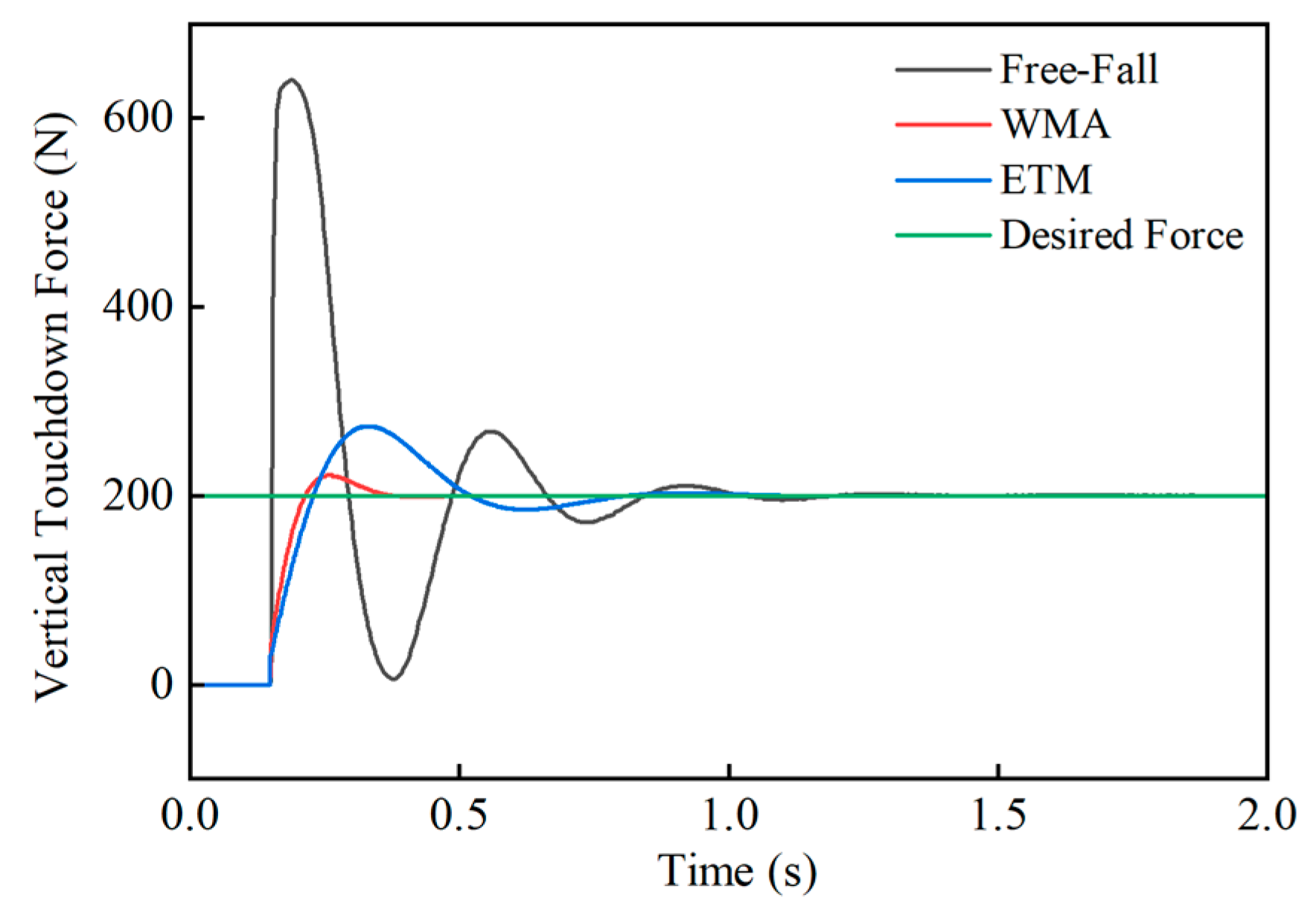
- The force-based impedance control significantly reduces the touchdown force during the free-fall state of the single leg. Experimental results show that the maximum touchdown force is reduced to 45% without control, and there is no rebound phenomenon, which verifies the effectiveness of the method.
- (3)
- Admittance control indirectly controls the single-leg touchdown force by adjusting the end displacement to make it approach the desired value, thus effectively reducing the touchdown force. Experimental results show that this method reduces the maximum touchdown force to 61% of that without control, which proves its effectiveness and practicality.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FASM | Force-angle stability margin |
| WMA | Whale migrating algorithm |
| SEAs | Series elastic actuators |
| ETM | Empirical tuning method |
References
- Sheng, J.; Chen, Y.; Fang, X.; Zhang, W.; Song, R.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Y. Bio-inspired rhythmic locomotion for quadruped robots. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 6782–6789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, P.; Mohanty, P.K. Development of quadruped walking robots: A review. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021, 12, 2017–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedeschi, F.; Carbone, G. Design issues for hexapod walking robots. Robotics 2014, 3, 181–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chai, X.; Gao, F.; Qi, C. Obstacle avoidance and motion planning scheme for a hexapod robot Octopus-III. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2018, 103, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayyaadi, H.; Sharifi, M. Adaptive Impedance Control of UAVs Interacting with Environment Using a Robot Manipulator. In Proceedings of the Second RSI/ISM International Conference on Robotics and Mechatronics (ICRoM), Tehran, Iran, 15–17 October 2014; pp. 636–641. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; He, J.; Feng, H.; Zhou, H.; Fu, Y. Research on Compliance Control for the Single Joint of a Hydraulic Legged Robot. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 12–15 December 2018; pp. 1720–1726. [Google Scholar]
- Vukobratovic, M.; Surdilovic, D.; Ekalo, Y.; Katic, D. Dynamics and Robust Control of Robot-Environment Interaction; World Scientific: Singapore, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa, R.; Kobayashi, H.; Ishibashi, R. Adaptive impedance control of a variable stiffness actuator. Adv. Robot. 2015, 29, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neville, H. Impedance control: An approach to manipulation: Part I-III. Trans. ASME J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 1985, 107, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Hogan, N. Impedance control: An approach to manipulation: Part II—Implementation. J. Dyn. Sys. Meas. Control. 1985, 107, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boaventura, T.; Semini, C.; Buchli, J.; Frigerio, M.; Focchi, M.; Caldwell, D.G. Dynamic Torque Control of a Hydraulic Quadruped Robot. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, St Paul, MN, USA, 14–18 May 2012; pp. 1889–1894. [Google Scholar]
- Grimminger, F.; Meduri, A.; Khadiv, M.; Viereck, J.; Wüthrich, M.; Naveau, M.; Berenz, V.; Heim, S.; Widmaier, F.; Flayols, T.; et al. An open torque-controlled modular robot architecture for legged locomotion research. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 3650–3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, J. Flexible motion framework of the six wheel-legged robot: Experimental results. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2021, 27, 2246–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hörger, M.; Kottege, N.; Bandyopadhyay, T.; Elfes, A.; Moghadam, P. Real-Time Stabilisation for Hexapod Robots. In Experimental Robotics: The 14th International Symposium on Experimental Robotics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 729–744. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.L.; Wang, Z.Y.; Rovetta, A. Typical gaits and motion analysis of a hexagonal symmetrical hexapod robot. Robot 2010, 32, 759–765. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zha, F.; Guo, W.; Chen, C.; Sun, L.; Wang, P. Heavy-duty hexapod robot sideline tipping judgment and recovery. Robotica 2024, 42, 1403–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roan, P.R.; Burmeister, A.; Rahimi, A.; Holz, K.; Hooper, D. Real-World Validation of Three Tipover Algorithms for Mobile Robot. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Anchorage, AK, USA, 3–8 May 2010; pp. 4431–4436. [Google Scholar]
- Hutter, M.; Gehring, C.; Jud, D.; Lauber, A.; Bellicoso, C.D.; Tsounis, V.; Hwangbo, J.; Bodie, K.; Fankhauser, P.; Bloesch, M.; et al. Anymal-a Highly Mobile and Dynamic Quadrupedal Robot. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 9–14 October 2016; pp. 38–44. [Google Scholar]
- Sokolov, A.; Xirouchakis, P. Kinematics of a 3-DOF parallel manipulator with an RPS joint structure. Robotica 2005, 23, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hervé, J.M. The Lie group of rigid body displacements, a fundamental tool for mechanism design. Mech. Mach. Theory 1999, 34, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.M.; Waldron, K.J. Machines that Walk: The Adaptive Suspension Vehicle; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F.X.; Liu, X.H.; Chen, W.; Zhou, C.; Cao, B.W. Improving handling stability performance of four-wheel steering vehicle based on the H2/H∞ robust control. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, M.; Deriche, M.; Trojovský, P.; Mansor, Z.; Zare, M.; Trojovská, E.; Abualigah, L.; Ezugwu, A.E.; kadkhoda Mohammadi, S. An efficient bio-inspired algorithm based on humpback whale migration for constrained engineering optimization. Results Eng. 2025, 25, 104215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, C.; Yuan, P.; Li, D. Active impedance control based adaptive locomotion for a bionic hexapod robot. J. Field Robot. 2025, 42, 327–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Optimization Method | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| ETM | 1 | 200 | 2000 |
| WMA | 0.5 | 60 | 1500 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, P.; He, Y.; Feng, S.; Dai, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y. Research on the Single-Leg Compliance Control Strategy of the Hexapod Robot for Collapsible Terrains. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5312. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105312
Sun P, He Y, Feng S, Dai X, Zhang H, Li Y. Research on the Single-Leg Compliance Control Strategy of the Hexapod Robot for Collapsible Terrains. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(10):5312. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105312
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Peng, Yinwei He, Shaojiang Feng, Xianyong Dai, Hanqi Zhang, and Yanbiao Li. 2025. "Research on the Single-Leg Compliance Control Strategy of the Hexapod Robot for Collapsible Terrains" Applied Sciences 15, no. 10: 5312. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105312
APA StyleSun, P., He, Y., Feng, S., Dai, X., Zhang, H., & Li, Y. (2025). Research on the Single-Leg Compliance Control Strategy of the Hexapod Robot for Collapsible Terrains. Applied Sciences, 15(10), 5312. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105312






