Experimental Evaluation of a Lignocellulosic Biomass Downdraft Gasifier on a Small-Scale Basis: A Thermodynamic Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Background
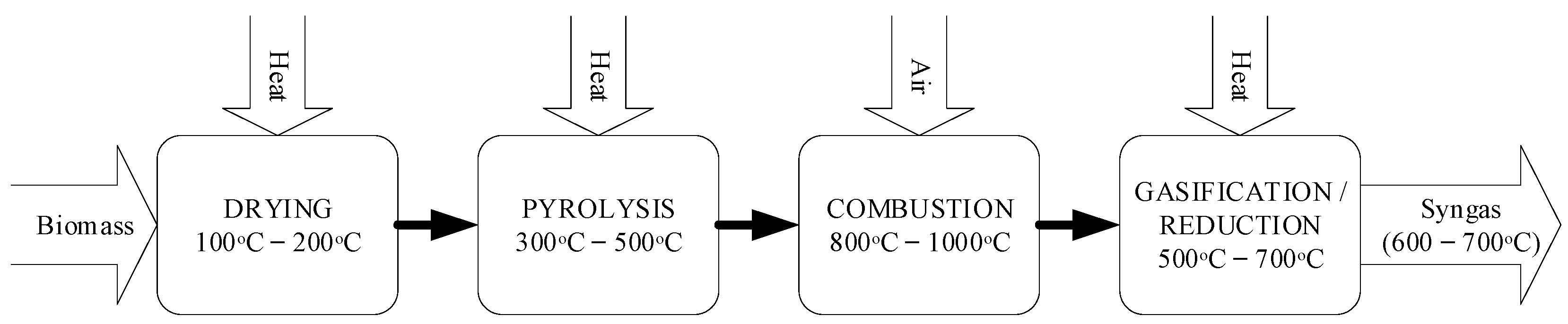
2.1. Fixed-Bed Downdraft Gasifiers
2.2. Biomass Resources
2.3. Power Production from Biomass
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Characterization of Biomass Waste: Pellet
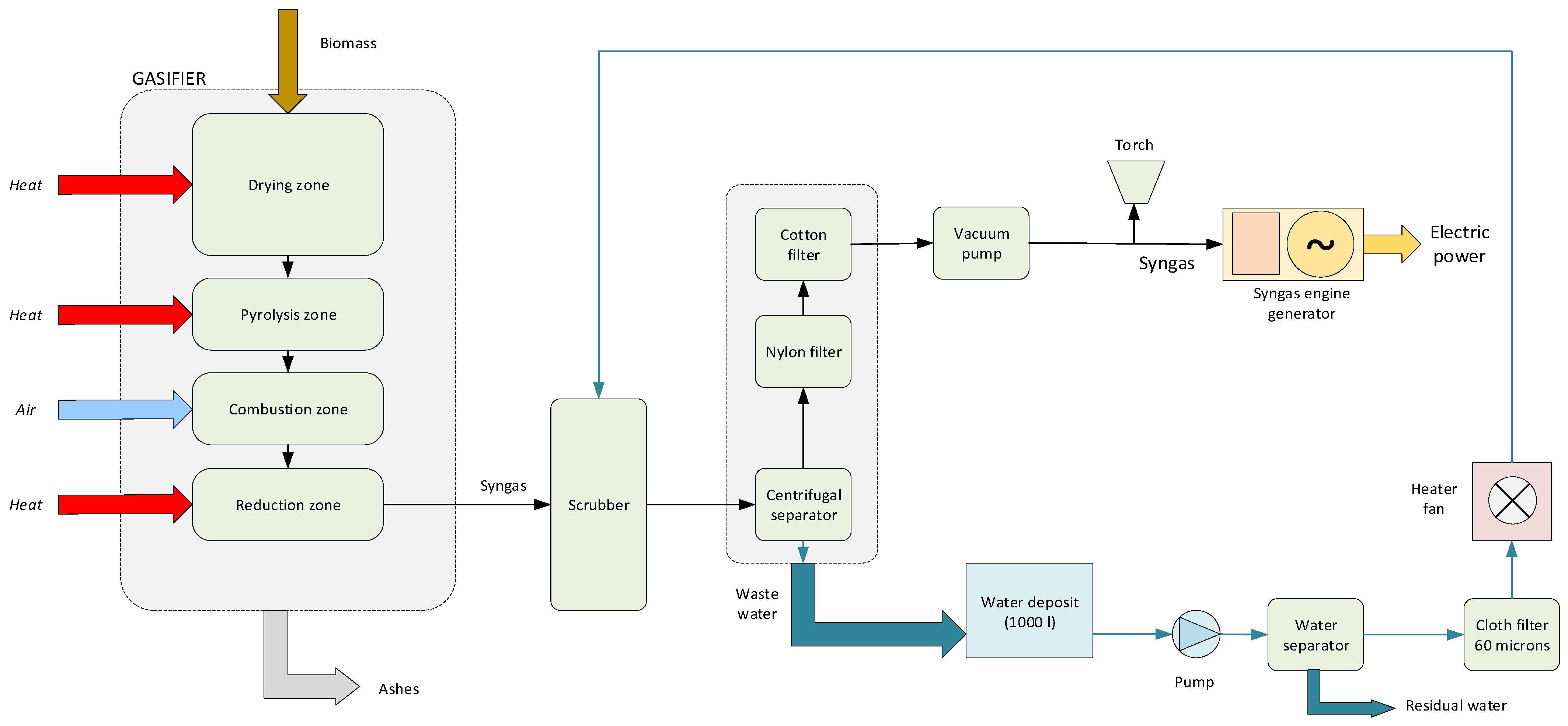
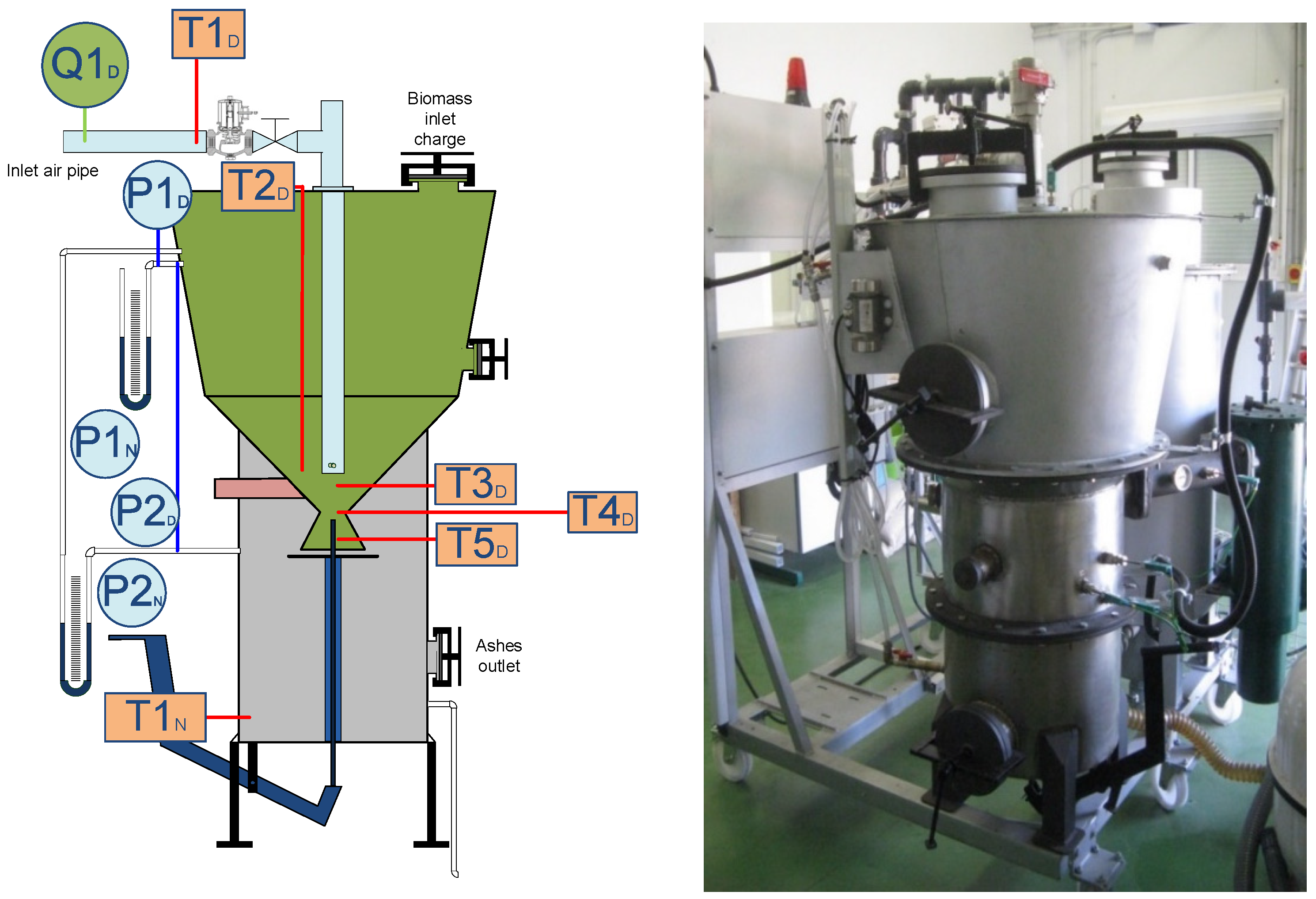
3.2. Pilot Facility Description
- Increase in the diameter of the throat reactor from 7 cm to 10 cm (see Figure 2);
- Increase in the diameter of the grid from 220 mm up to 280 mm by adding an additional ring;
- Reduction in the height of the grid underneath the reducer cone by 1.5 cm (see Figure 2). The distance between the grid and the cone of the reactor influences the pressure drop in the bed, in this case reducing it. To vary this parameter, an auxiliary piece to support the grid was mounted;
- Installation of two automatic solenoid valves at the beginning of the air inlet pipe and the exhaust outlet pipe of the gasifier and at the beginning of the pipes of the torch and the motor.
- Reduces the total amount of biomass unburnt in the ashes deposit;
- Avoids the formation of holes;
- Reduces the ingress of unburnt air that could result in undesired combustion in the ash deposit.
- Turning on the gasification facility;
- Operating the facility at different loads, increasing the load from 8 to 15 m3/h;
- For each load, measuring temperatures, pressures, flow rates, and electrical variables;
- According to the results obtained, the most significant operating parameters of the facility are determined:
- Temperature at the reduction and combustion zones;
- Air–fuel ratio;
- Gas flow generated per kg of biomass consumed (m3/h·kg);
- Percentage of intake air to total gas produced;
- Gas velocity in the throat (fixed bed) (m/s);
- Biomass processing capacity (kg/m2·h);
- Electric power generated by the biomass;
- Gas conversion efficiency;
- Composition and calorific value of the produced gas;
- After each test, improvements to the gasification facility are considered and implemented;
- Repeating the same procedure to assess the effect on the operation of the gasification facility;
- Evaluating the results obtained through the comparison of the two configurations of the gasification facility.
3.3. Instrumentation
- Hot wire anemometers:
- Pressure transducers:
- K-type thermocouples:
- Gas analyzer:
3.4. Experiments
- (1)
- The system is in a steady state condition, the ambient conditions during all tests are the same, and the properties of all used biomass and air are uniform;
- (2)
- There is no pressure drop (defined as the difference between the atmospheric pressure and the pressure at the syngas bed);
- (3)
- The mass flow rate of the produced gas and air are approximately the same;
- (4)
- No occurrence of gas leakage. In order to verify this assumption, a preliminary test was conducted and, with no load, the produced gas volume flow rate measured was equal to the inlet air flow rate.
4. Definition of the Theoretical Process Parameters
4.1. Lower Heating Value (LHV)
4.2. Gasifier Efficiency (ηcon) and Motor–Generator Efficiency (ηmot-gen)
4.3. Combustion and Reduction Temperature
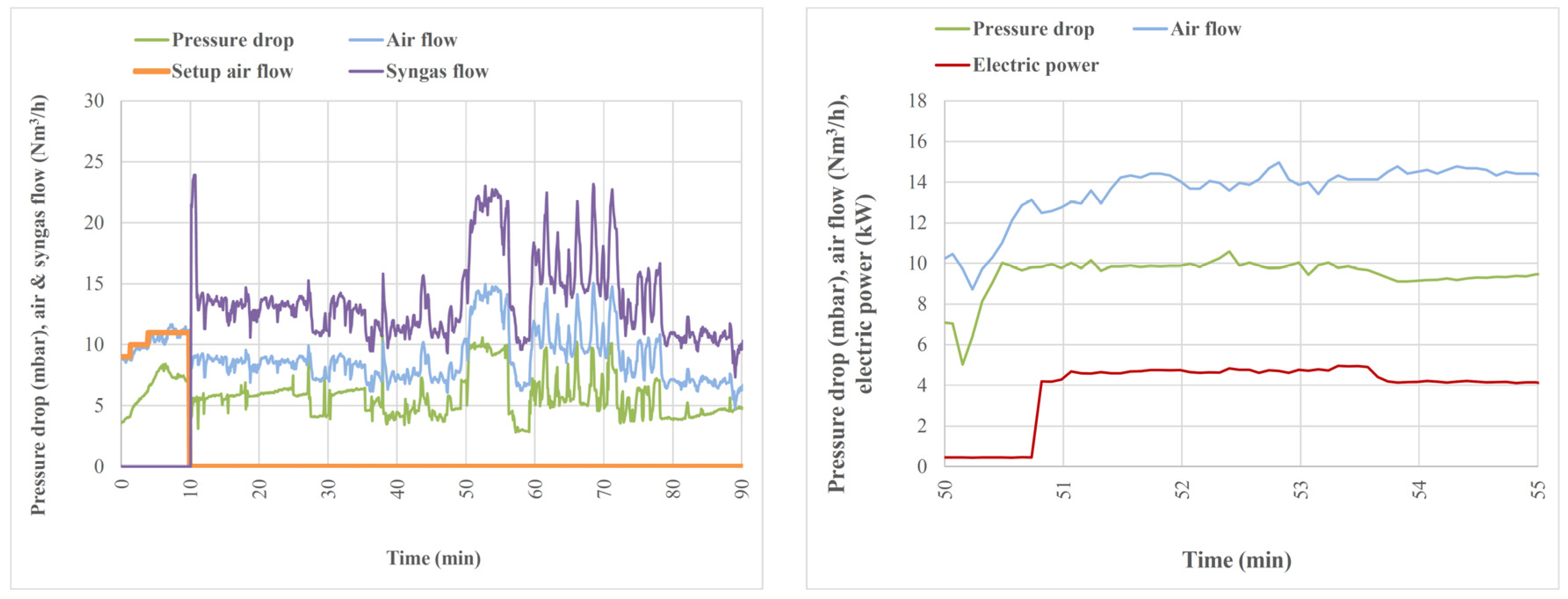
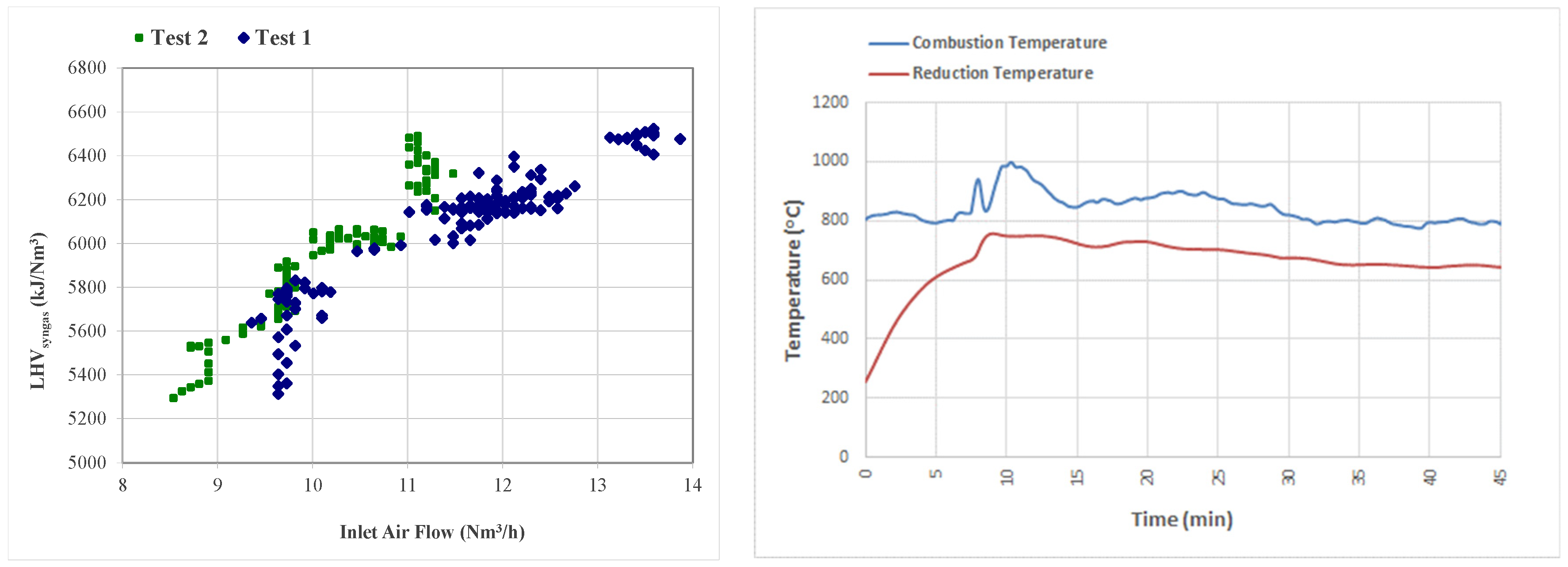
5. Discussion and Results
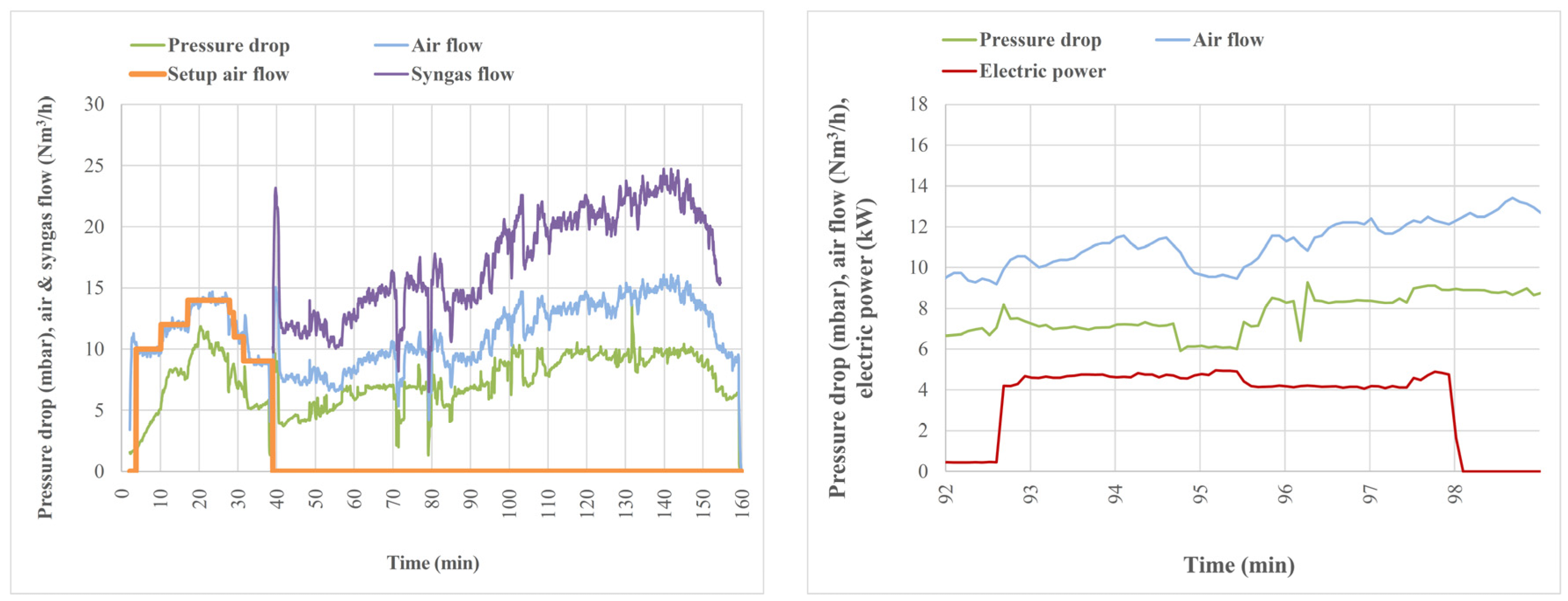
5.1. Electrical Power and Syngas Production
5.2. LHV of Syngas, Global Efficiency, and Temperatures Inside the Gasifier
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bórawski, P.; Bełdycka-Bórawska, A.; Szymańska, E.J.; Jankowski, K.J.; Dubis, B.; Dunn, J.W. Development of renewable energy sources market and biofuels in The European Union. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 467–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Salgado, C.; Borras, I.M.; Alcazar-Ortega, M.; Montuori, L. Floating PV Solar-Powered Systems: Design Applied to an Irrigators Community in the Valencia Region—Spain. In Proceedings of the 2020 Global Congress on Electrical Engineering (GC-ElecEng), Valencia, Spain, 4–6 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Monir, M.U.; Aziz, A.A.; Kristanti, R.A.; Yousuf, A. Gasification of lignocellulosic biomass to produce syngas in a 50 kW downdraft reactor. Biomass-Bioenergy 2019, 119, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Chang, J.; Guan, Y.; Chen, H.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, J. Lignocellulosic biomass gasification technology in China. Renew. Energy 2013, 49, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, D.; Roberts, D.G. Coal gasification and conversion. In The Coal Handbook; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 665–691. [Google Scholar]
- Hoo, P.Y.; Hashim, H.; Ho, W.S.; Tan, S.T. Successful biogas implementation—A mini-review on biogas utilization, energy policies and economic incentives. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2017, 61, 1495–1500. [Google Scholar]
- Situmorang, Y.A.; Zhao, Z.; Yoshida, A.; Abudula, A.; Guan, G. Small-scale biomass gasification systems for power generation (<200 kW class): A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 117, 109486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwood, J. The significance of biomass in a circular economy. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 300, 122755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, J.; Juárez, M.; Morales, M.; Muñoz, P.; Mendívil, M. Biomass gasification for electricity generation: Review of current technology barriers. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 18, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Salgado, C.; Montuori, L.; Alcázar-Ortega, M. Experimental Analysis of a Bubbling Fluidized Bed Gasification Plant Fed by Biomass: Design, Implementation and Validation of the Control System. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Renewable Energy (ICREN 2020), Online, 25–27 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Samadi, S.H.; Ghobadian, B.; Nosrati, M.; Rezaei, M. Investigation of factors affecting performance of a downdraft fixed bed gasifier using optimized MLP neural networks approach. Fuel 2023, 333, 126249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grauwin, O.; Hrbek, J.; Alberts, K.; Artemis, L.; Alphen, M.; Vreugdenhil, B.; Held, J.; Pfeifer, C.; Böcker-Riese, B.; Hofmann, A.; et al. Gasification: A Sustainable Technology for Circular Economies; EBA: Brussels, Belgium, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Belgiorno, V.; De Feo, G.; Della Rocca, C.; Napoli, D.R. Energy from gasification of solid wastes. Waste Manag. 2003, 23, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molino, A.; Migliori, M.; Larocca, V.; Marino, T.; Figoli, A.; Casella, P.; Iovane, P.; Cerbone, A.; Rimauro, J.; Donatelli, A. Power Production by Biomass Gasification Technologies. In Current Trends and Future Developments on Bio-Membranes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 293–318. [Google Scholar]
- Mahinpey, N.; Abdalla, A.; Farooqui, A. Chapter 9—Biomass gasification for hydrogen production: A pathway to cleaner energy transition. In Biomass to Bioenergy. Modern Technological Strategies for Biorefineries; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2024; pp. 205–235. ISBN 9780443153778. [Google Scholar]
- Magalhães, M.A.; Carneiro, A.D.C.O.; da Silva Guimarães, D.P.; de Deus Ribeiro, G.B.; Martins, M.A.; Carvalho, A.M.M.L.; de Jesus Jorge, F. Gasification of different biomasses in a concurrent fixed bed reactor: Thermodynamics assessment towards its bioenergy potential. Biomass Bioenergy 2025, 193, 107530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, N.; Rouboa, A.; Silva, V.; Monteiro, E.; Bouziane, K. Influence of the Biomass Gasification Processes on the Final Composition of Syngas. Energy Procedia 2013, 36, 596–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgwater, A. Renewable fuels and chemicals by thermal processing of biomass. Chem. Eng. J. 2003, 91, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainal, Z.; Rifau, A.; Quadir, G.; Seetharamu, K. Experimental investigation of a downdraft biomass gasifier. Biomass-Bioenergy 2002, 23, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montuori, L.; Vargas-Salgado, C.; Alcázar-Ortega, M. Impact of the throat sizing on the operating parameters in an experimental fixed bed gasifier: Analysis, evaluation and testing. Renew. Energy 2015, 83, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susastriawan, A.; Saptoadi, H. Purnomo Small-scale downdraft gasifiers for biomass gasification: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 76, 989–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izydorczyk, G.; Skrzypczak, D.; Mironiuk, M.; Mikula, K.; Samoraj, M.; Gil, F.; Taf, R.; Moustakas, K.; Chojnacka, K. Lignocellulosic biomass fertilizers: Production, characterization, and agri-applications. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 923, 171343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, L.; Subbarao, P.; Subrahmanyam, J. Experimental investigation on gasification characteristic of high lignin biomass (Pongamia shells). Renew. Energy 2015, 80, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlNouss, A.; McKay, G.; Al-Ansari, T. Production of syngas via gasification using optimum blends of biomass. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 242, 118499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachl, A.; Urbancl, D.; Buchmayr, M.; Gruber, J.; Anca-Couce, A.; Scharler, R.; Hochenauer, C. Investigation of the utilization of forest woodchips in a commercial small-scale open-top gasifier. J. Energy Inst. 2024, 116, 101746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deore, S.P.; Kumar, S.; Mahajani, S.M.; De Blasio, C. Co-gasification of sanitary napkin with sawdust biomass in downdraft gasifier for thermal applications: An experimental approach. Energy 2023, 276, 127562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Ling, C.; Chia, Y.; Sun, Z.; Xu, X.; Li, S.F.Y.; Wang, X.; Tan, H.T.W.; Yusof, M.L.M.; Ghosh, S.; et al. Sustainable management of water hyacinth via gasification: Economic, environmental, and toxicity assessments. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 20, 133725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njogu, P.; Kinyua, R.; Muthoni, P.; Nemoto, Y. Biogas Production Using Water Hyacinth (Eicchornia crassipes) for Electricity Generation in Kenya. Energy Power Eng. 2015, 7, 56389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Subbarao, P.; Kala, L.; Vijay, V. Experimental assessment of producer gas generation using agricultural and forestry residues in a fixed bed downdraft gasifier. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2023, 13, 100431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, G.; Karmee, S.K. Chapter 22—Thermochemical routes applying biomass: A critical assessment. In Handbook of Biofuels; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 435–451. ISBN 9780128228104. [Google Scholar]
- Fiore, M.; Magi, V.; Viggiano, A. Internal combustion engines powered by syngas: A review. Appl. Energy 2020, 276, 115415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banapurmath, N.R.; Yaliwal, V.S.; Kambalimath, S.; Hunashyal, A.M.; Tewari, P.G. Effect of wood type and carburetor on the performance of producer gas-biodiesel operated dual fuel engines. Waste Biomass-Valorization 2011, 2, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, J.; Leitner, A.; Tinschmann, G.; Trapp, C. Concept for High-performance Direct Ignition Gas Engines. MTZ Worldw. 2013, 74, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paykani, A.; Chehrmonavari, H.; Tsolakis, A.; Alger, T.; Northrop, W.F.; Reitz, R.D. Synthesis gas as a fuel for internal combustion engines in transportation. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2022, 90, 100995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, P.; Xiong, Z.; Chang, J.; Wu, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, J. An experimental study on biomass air–steam gasification in a fluidized bed. Bioresour. Technol. 2004, 95, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldheim, L.; Nilsson, T. Heating Value of Gases from Biomass Gasification. IEA Bioenergy Agreement, Task 20—Thermal Gasification of Biomass, Nyköping. 2001. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/authors/references (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Abouemara, K.; Shahbaz, M.; Mckay, G.; Al-Ansari, T. The review of power generation from integrated biomass gasification and solid oxide fuel cells: Current status and future directions. Fuel 2023, 360, 130511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, P.; Kaushal, P. Design of biomass gasifiers. In Biomass Gasification, Pyrolysis, and Torrefaction; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 259–328. [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyay, D.S.; Chaudhary, A.; Trada, A.; Patel, D.; Patel, R.N. Improvement Of Syngas Quality In Fixed Bed Gasifier Using Camg(CO3)2 Catalyst. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Fluid Flow, Heat and Mass Transfer, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 7–9 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Akhator, P.; Obanor, A.; Sadjere, G. Experimental Studies on Synthesis Gas Production from Wood Wastes in a Pilot Downdraft Gasifier. Int. J. Eng. Res. Afr. 2022, 61, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, R.; Kwong, P.; Ahmad, E.; Nigam, K. Clean syngas from small commercial biomass gasifiers; a review of gasifier development, recent advances and performance evaluation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 21087–21111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Chemical Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ultimate analysis | Proximate analysis | ||
| Carbon (C) | 47% | Fixed carbon | 15% |
| Hydrogen (H) | 7% | Volatile matter | 76% |
| Oxygen (O) | 45% | Ash | 2% |
| Nitrogen (N) | 2% | Moisture | 6% |
| Sulfur (S) | 0% | HHV (kJ/kg) | 17.89 |
| H/C | 15% | LHV (kJ/kg) | 16.22 |
| O/C | 96% | LHV/HHV | 91% |
| Component Analysis | |||
| Cellulose (wt.% dry) | 54.6 | ||
| Lignin (wt.% dry) | 16.2 | ||
| Hemicellulose (wt.% dry) | 27.0 | ||
| Extractives (wt.% dry) | 2.2 | ||
| Fuel | Pellets |
|---|---|
| Biomass diameter | 0.5–5 cm |
| Biomass length | 2–5 cm |
| Fuel consumption | 5–10 kg/h (depending on size, moisture properties of the biomass, and the air/fuel relation) |
| Biomass deposit volume | 0.23 m3 |
| Storage capacity | 40–90 kg (depending on biomass apparent density) |
| Autonomy | 5–10 h |
| Motor–generator | PRAMAC Honda GX630 two-cylinder engine |
| Gas cooling medium | Water and wet scrubber. |
| Gas cleaning | Scrubber, tar separator pump, filter chips, filter fabric, and filter cotton |
| Water flow | 1 m3/h |
| TEST 1 (150 min) | TEST 2 (117 min) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | Final | Difference | Initial | Final | Difference | |
| Pellets (kg) | 39.60 | 19.50 | 20.10 | 42.05 | 29.05 | 13.00 |
| Char pellets (kg) | 3.15 | 4.35 | −1.20 | 2.40 | 3.60 | −1.20 |
| Total Biomass (kg) | 42.75 | 23.85 | 18.90 | 44.45 | 32.65 | 11.80 |
| Average | Min | Max | Average | Min | Max | |
| Air flow (Nm3/h) | 11.17 | 8.00 | 16.07 | 10.50 | 8.00 | 15.06 |
| Biomass consumption (kg/h) | 7.56 | 6.05 | ||||
| Air/Biomass (Nm3/kg) | 1.48 | 1.74 | ||||
| Air intro/Stoich. Rate (%) | 31.80 | 37.3 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Montuori, L.; Alcázar-Ortega, M.; Vargas-Salgado, C.; Adinolfi, E.A. Experimental Evaluation of a Lignocellulosic Biomass Downdraft Gasifier on a Small-Scale Basis: A Thermodynamic Approach. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15010177
Montuori L, Alcázar-Ortega M, Vargas-Salgado C, Adinolfi EA. Experimental Evaluation of a Lignocellulosic Biomass Downdraft Gasifier on a Small-Scale Basis: A Thermodynamic Approach. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(1):177. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15010177
Chicago/Turabian StyleMontuori, Lina, Manuel Alcázar-Ortega, Carlos Vargas-Salgado, and Ennio Andrea Adinolfi. 2025. "Experimental Evaluation of a Lignocellulosic Biomass Downdraft Gasifier on a Small-Scale Basis: A Thermodynamic Approach" Applied Sciences 15, no. 1: 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15010177
APA StyleMontuori, L., Alcázar-Ortega, M., Vargas-Salgado, C., & Adinolfi, E. A. (2025). Experimental Evaluation of a Lignocellulosic Biomass Downdraft Gasifier on a Small-Scale Basis: A Thermodynamic Approach. Applied Sciences, 15(1), 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15010177









