The Effects of Vermicompost and Steel Slag Amendments on the Physicochemical Properties and Bacterial Community Structure of Acidic Soil Containing Copper Sulfide Mines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tested Soil and Amendments
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Plant Sampling and Analysis
2.4. Soil Chemical Analysis
2.5. Soil Bacterial Community Diversity Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Amendments
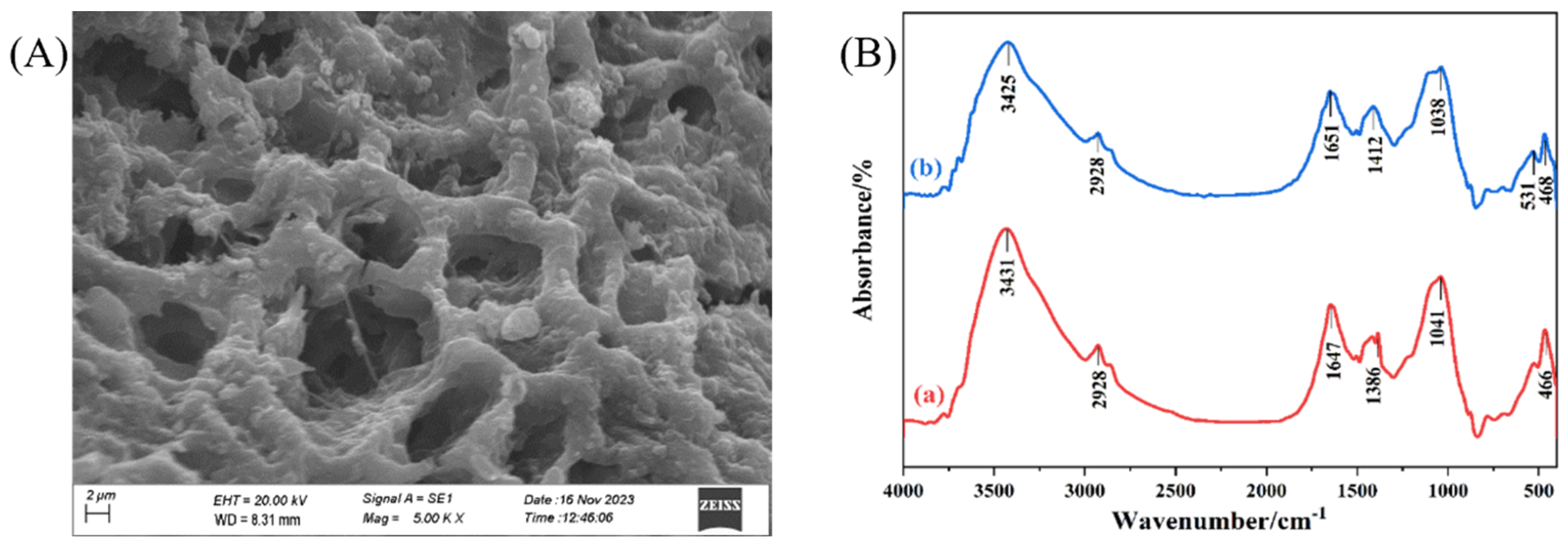
3.1.1. SEM and FTIR Analysis of Vermicompost
3.1.2. SEM and XRD Analysis of Steel Slag
3.2. The Impact of Amendments on Soil Physicochemical Properties and the Bioavailability of Cu
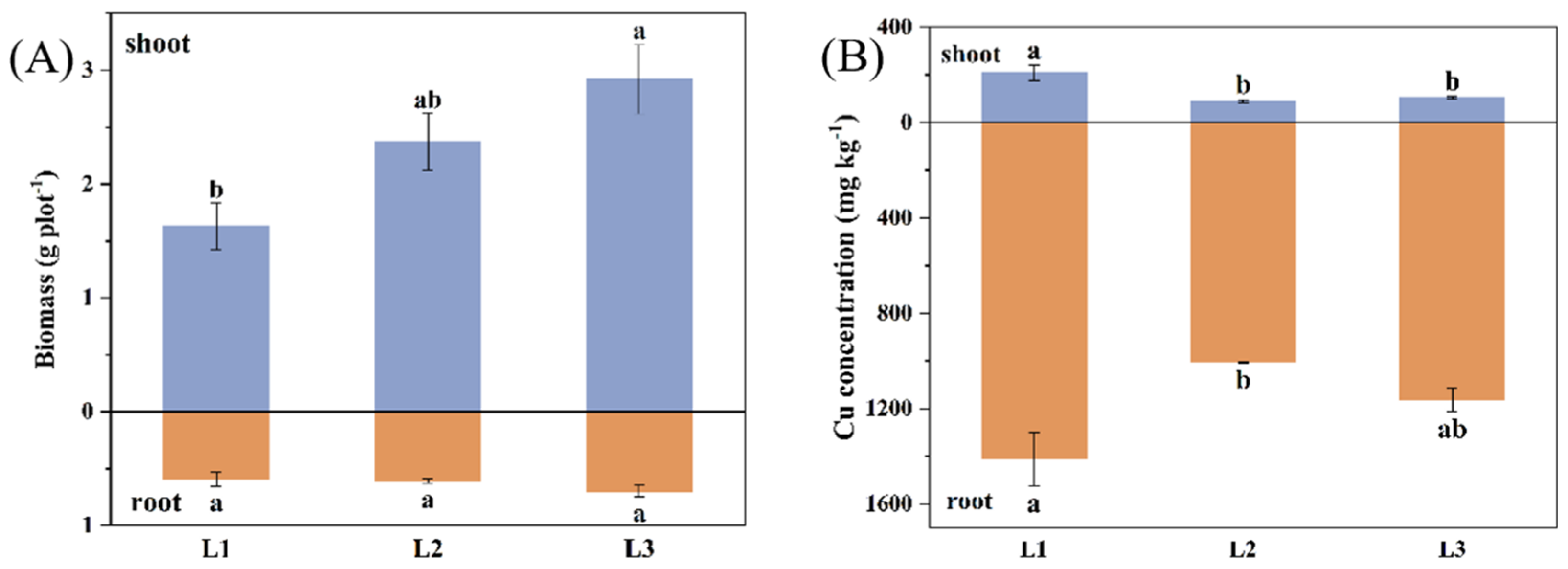
3.3. Effects of Amendments on Biomass and Cu Bioaccumulation in L. perenne
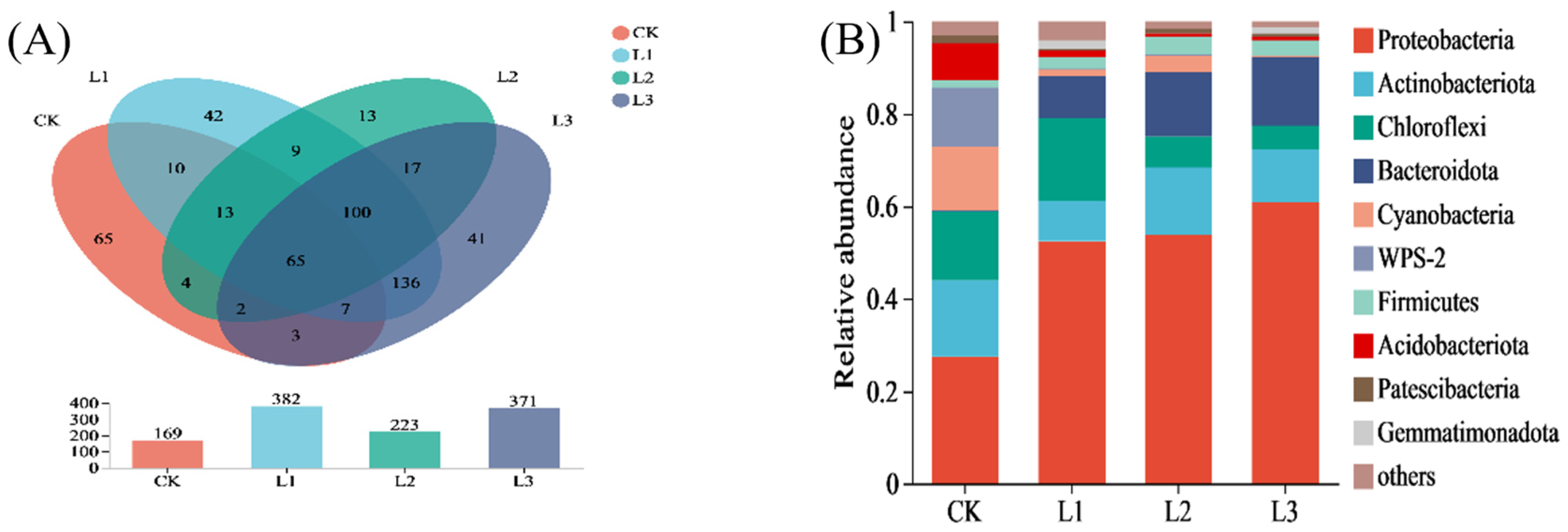
3.4. Impact of Amendments on the Composition of Soil Bacterial Communities
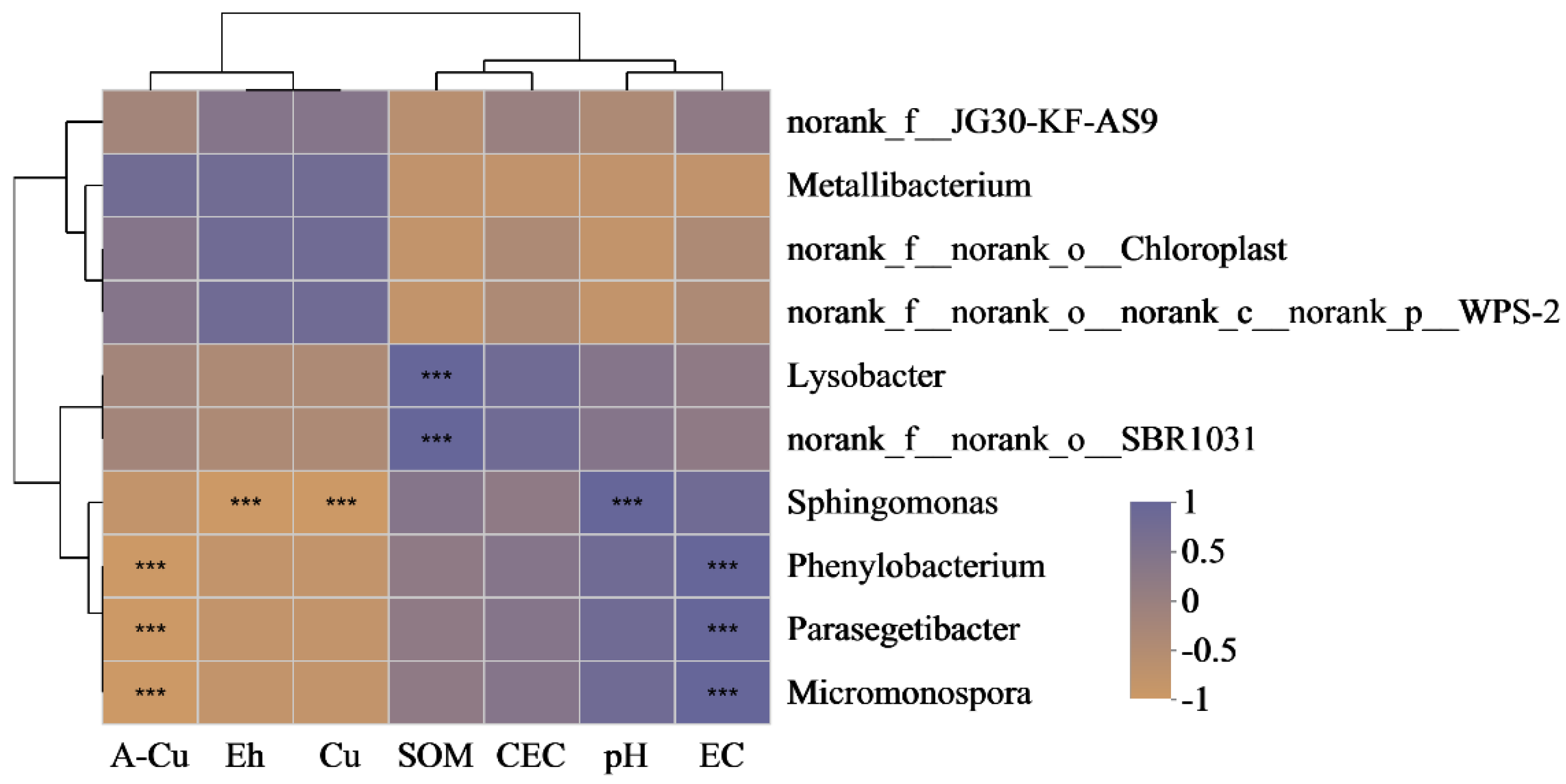
3.5. The Relationship between Soil Physicochemical Properties and Bacterial Community
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, P.; Chen, J.; Liu, T.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Liang, S. Heavy metal pollution and risk assessment of tailings in one low-grade copper sulfide mine. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1132268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-Conti, L.; Ceretta, C.A.; Melo, G.W.B.; Tiecher, T.L.; Silva, L.O.S.; Garlet, L.P.; Mimmo, T.; Cesco, S.; Brunetto, G. Intercropping of young grapevines with native grasses for phytoremediation of Cu-contaminated soils. Chemosphere 2019, 216, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Fu, R.; Wang, J.; Shi, Y.; Guo, X. Chemical stabilization remediation for heavy metals in contaminated soils on the latest decade: Available stabilizing materials and associated evaluation methods—A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 321, 128730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.; Yu, H. Rethinking biochar: Black gold or not? Nat. Rev. Mater. 2023, 9, 4–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Carswell, A.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, F.; De-Vries, W. Modelling long-term impacts of fertilization and liming on soil acidification at Rothamsted experimental station. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swati, A.; Hait, S. Fate and bioavailability of heavy metals during vermicomposting of various organic wastes—A review. Process Saf. Environ. 2017, 109, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Tam, N.F.Y.; Yao, A.; Qiu, R.; Li, W.; Ye, Z. Growth and Cd uptake by rice (Oryza sativa) in acidic and Cd-contaminated paddy soils amended with steel slag. Chemosphere 2017, 189, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutillas-Barreiro, L.; Fernandez-Calvino, D.; Nunez-Delgado, A.; Fernandez-Sanjurjo, M.J.; Alvarez-Rodriguez, E.; Carlos-Novoa-Munoz, J.; Arias-Estevez, M. Pine Bark Amendment to Promote Sustainability in Cu-Polluted Acid Soils: Effects on Lolium perenne Growth and Cu Uptake. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Xie, L.; Jin, D.; Mi, B.; Wang, D.; Li, X.; Dai, X.; Zou, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, Y. Bacterial community response to cadmium contamination of agricultural paddy soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 139, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvendu, D.; Gwon, H.S.; Muhammad, I.K.; Jeong, S.K.; Kim, P.J. Steel slag amendment impacts on soil microbial communities and activities of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaoui, H.I.; Zibilske, L.M.; Ohno, T. Effects of earthworm casts and compost on soil microbial activity and plant nutrient availability. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R. Analytical Methods for Soil Agrochemistry; Chinese Agricultural Science and Technology Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 205–226. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S. Soil and Agrochemistry Analysis; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 25–38. [Google Scholar]
- Kahr, G.; Madsen, F.T. Determination of the cation exchange capacity and the surface area of bentonite, illite and kaolinite by methylene blue adsorption. Appl. Clay Sci. 1995, 9, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottes, J.; Saquet, A.; Palayret, L.; Husson, O.; Beghin, R.; Allen, D.; Guiresse, M. Effects of soil redox potential (Eh) and pH on growth of sunflower and wheat. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2020, 66, 473–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. Fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaac, R.; Siddiqui, S.; Aldosari, O.F.; Uddin, M.K. Magnetic biochar derived from Juglans regia for the adsorption of Cu2+ and Ni2+: Characterization, Modelling, Optimization, and Cost analysis. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2023, 27, 101749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anamika, S.; Savita, S.; Sonali, S.; Nitika, S.; Satveer, S.; Rahil, D.; Adarsh, P.V.; Avinash, K.N. Bio-conversion of Jamun leaf litter and kitchen waste into vermicompost: Implications for Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal in vitro conservation. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2023, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok-Kumar, K.; Subalakshmi, R.; Jayanthi, M.; Abirami, G.; Vijayan, D.S.; Venkatesa-Prabhu, S.; Baskaran, L. Production and characterization of enriched vermicompost from banana leaf biomass waste activated by biochar integration. Environ. Res. 2023, 219, 115090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soobhany, N.; Gunasee, S.; Rago, Y.P.; Joyram, H.; Raghoo, P.; Mohee, R.; Garg, V.K. Spectroscopic, thermogravimetric and structural characterization analyses for comparing Municipal Solid Waste composts and vermicomposts stability and maturity. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 236, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da-Silva, M.D.; Schnorr, C.; Lütke, S.F.; Silva, L.F.O.; Manera, C.; Perondi, D.; Godinho, M.; Collazzo, C.C.; Dotto, G.L. Citrus fruit residues as alternative precursors to developing H2O and CO2 activated carbons and its application for Cu(II) adsorption. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 63661–63677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, X.; Xie, R.; Han, L. Characteristics, adsorption behaviors, Cu(II) adsorption mechanisms by cow manure biochar derived at various pyrolysis temperatures. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 331, 125013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchisi, J.; Matinde, E.; Rowson, N.A.; Simmons, M.J.H.; Simate, G.S.; Ndlovu, S.; Mwewa, B. Ironmaking and Steelmaking Slags as Sustainable Adsorbents for Industrial Effluents and Wastewater Treatment: A Critical Review of Properties, Performance, Challenges and Opportunities. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Lu, C.; Quan, X.; Cao, D. Mechanism of Acid Mine Drainage Remediation with Steel Slag: A Review. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 30205–30213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Tam, N.F.Y.; Yao, A.; Qiu, R.; Li, W.; Ye, Z. Effects of alkaline and bioorganic amendments on cadmium, lead, zinc, and nutrient accumulation in brown rice and grain yield in acidic paddy fields contaminated with a mixture of heavy metals. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 23551–23560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Fu, P.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X. Steel slag as a cost-effective adsorbent for synergic removal of collectors, Cu(II) and Pb(II) ions from flotation wastewaters. Miner. Eng. 2022, 183, 107593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, J.; Nguyen, T.B.T.; Honeyands, T.; Monaghan, B.; O’Dea, D.; Rinklebe, J.; Vinu, A.; Hoang, S.A.; Singh, G.; Kirkham, M.B.; et al. Production, characterisation, utilisation, and beneficial soil application of steel slag: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nur-Sa’adah, A.H.; Rosazlin, A.; Karsani, S.A.; Osman, N.; Qurban, A.P.; Ishak, C.F. Influence of Soil Amendments on the Growth and Yield of Rice in Acidic Soil. Agronomy 2018, 8, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Shah, K.J.; Shi, L.; Chiang, P.; You, Z. Red soil amelioration and heavy metal immobilization by a multi-element mineral amendment: Performance and mechanisms. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 112964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Xia, H.; Wu, J.; Yang, G.; Zhang, X.; Peng, H.; Yu, X.; Li, L.; Xiao, H.; Qi, H. Shifts in the relative abundance of bacteria after wine-lees-derived biochar intervention in multi metal-contaminated paddy soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 1297–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Jin, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, X.; Shen, S.; Ding, L. Feasibility of Pb phytoextraction using nano-materials assisted ryegrass: Results of a one-year field-scale experiment. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 190, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, F.; Chen, C.; Chen, X.; Liu, W.; Wen, X.; Hu, S. Cadmium transport in red paddy soils amended with wheat straw biochar. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Shen, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ding, Y.; Zhu, W. Evaluation of the effectiveness of amendments derived from vermicompost combined with modified shell powder on Cd immobilization in Cd-contaminated soil by multiscale experiments. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 262, 115166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, D.; Liang, Y.; Song, A.; Duan, A.; Liu, Z. In situ stabilization of heavy metals in multiple-metal contaminated paddy soil using different steel slag-based silicon fertilizer. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 23638–23647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, T.; Tong, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Huang, D.; Zeng, X. Effect of humic and calcareous substance amendments on the availability of cadmium in paddy soil and its accumulation in rice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 231, 113186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.; Bardos, R.P.; Kidd, P.S.; Mench, M.; De-Leij, F.; Hutchings, T.; Cundy, A.; Joyce, C.; Soja, G.; Friesl-Hanl, W.; et al. Biochar and compost amendments enhance copper immobilisation and support plant growth in contaminated soils. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 171, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, S.; Steve, P.; Fernando, P.; Frédéric, P.; Jacques, M.; Noureddine, M.; Olivier, F. Aided-phytostabilization of steel slag dumps: The key-role of pH adjustment in decreasing chromium toxicity and improving manganese, phosphorus and zinc phytoavailability. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 124225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadia, K.; Rafael, C.; Eduardo, M.; Nicholas, W.L.; Luke, B. Efficiency of green waste compost and biochar soil amendments for reducing lead and copper mobility and uptake to ryegrass. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 191, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarathchandra, S.S.; Rengel, Z.; Solaiman, Z.M. Remediation of heavy metal-contaminated iron ore tailings by applying compost and growing perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.; Adebayo, A.; Jia, J.; Xing, Y.; Deng, S.; Guo, L.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, D. Impacts of heavy metals and soil properties at a Nigerian e-waste site on soil microbial community. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 362, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drzewiecka, D. Significance and Roles of Proteus spp. Bacteria in Natural Environments. Microb. Ecol. Int. J. 2016, 72, 741–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altimira, F.; Yáñez, C.; Bravo, G.; González, M.; Rojas, L.A.; Seeger, M. Characterization of copper-resistant bacteria and bacterial communities from copper-polluted agricultural soils of central Chile. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadaf, K.; Anirban, B.; Iqbal, A.; Sayyed, R.Z.; Hesham, A.E.; Daniel, J.D.; Ni, L.S. Recent Understanding of Soil Acidobacteria and Their Ecological Significance: A Critical Review. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 580024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriy, S.; Gareth, M.J.; Jessica, J.; Robert, M.B.; Isaac, B.; Cassandra, C.; Emiley, A.E.; Natalia, I.; Rex, R.M.; Stephen, E.G.; et al. Ecological and genomic analyses of candidate phylum WPS-2 bacteria in an unvegetated soil. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 3143–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, W.; Miao, L.; Ji, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ding, Y.; Zhu, W. The effects of vermicompost and shell powder addition on Cd bioavailability, enzyme activity and bacterial community in Cd-contaminated soil: A field study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 215, 112163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Yang, B.; Zhang, M.; Song, D.; Xu, X.; Ai, C.; Liang, G.; Zhou, W. Investigating the effects of organic amendments on soil microbial composition and its linkage to soil organic carbon: A global meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 894, 164899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Shao, T.; Gao, X.; Long, X.; Rengel, Z. Effects of planting quinoa on soil properties and microbiome in saline soil. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 2689–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahm, M.; Son, J.; Kim, B.; Ghim, S. Comparative study of rhizobacterial communities in pepper greenhouses and examination of the effects of salt accumulation under different cropping systems. Arch. Microbiol. 2017, 199, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mujakic, I.; Piwosz, K.; Koblízek, M. Phylum Gemmatimonadota and Its Role in the Environment. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortúzar, M.; Trujillo, M.E.; Román-Ponce, B.; Carro, L. Micromonospora metallophores: A plant growth promotion trait useful for bacterial-assisted phytoremediation? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Wang, J.; Lv, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhong, J.; Cui, X.; Zhang, M.; Ma, D.; Yan, X.; Zhu, X. Effects of Heavy Metals/Metalloids and Soil Properties on Microbial Communities in Farmland in the Vicinity of a Metals Smelter. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 707786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Properties | Tested Soil | V | S |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 3.78 | 6.4 | 12.52 |
| cation exchange capacity (CEC, cmol·kg−1) | 17 | na | na |
| soil organic matter (SOM, g·kg−1) | 5.93 | 470.6 | na |
| Total N (TN, g·kg−1) | 0.98 | 16.94 | na |
| Total P (TP, g·kg−1) | 0.45 | 16.73 | na |
| Total K (TK, g·kg−1) | 5.61 | 12.88 | na |
| Total Cu (g·kg−1) | 2.41 | na | 0.02 |
| Treatments | pH | EC | SOM | CEC | Eh |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mS cm−1) | (g kg−1) | (cmol kg−1) | (mv) | ||
| CK | 3.78 ± 0.45 c | 858 ± 36.1 c | 5.85 ± 0.05 d | 17.2 ± 0.45 d | 509 ± 6.06 a |
| L1 | 5.17 ± 0.17 b | 1005 ± 73.4 bc | 14.5 ± 0.27 a | 30.6 ± 0.82 a | 492 ± 3.38 b |
| L2 | 6.76 ± 0.04 a | 1241 ± 47.2 a | 9.90 ± 0.01 c | 28.2 ± 0.26 b | 417 ± 1.70 c |
| L3 | 6.86 ± 0.05 a | 1150 ± 34.9 ab | 12.5 ± 0.45 b | 23.2 ± 0.51 c | 403 ± 2.80 d |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Xue, J.; He, M.; Qi, H.; Wang, S. The Effects of Vermicompost and Steel Slag Amendments on the Physicochemical Properties and Bacterial Community Structure of Acidic Soil Containing Copper Sulfide Mines. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14031289
Wang X, Xue J, He M, Qi H, Wang S. The Effects of Vermicompost and Steel Slag Amendments on the Physicochemical Properties and Bacterial Community Structure of Acidic Soil Containing Copper Sulfide Mines. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(3):1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14031289
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaojuan, Jinchun Xue, Min He, Hui Qi, and Shuting Wang. 2024. "The Effects of Vermicompost and Steel Slag Amendments on the Physicochemical Properties and Bacterial Community Structure of Acidic Soil Containing Copper Sulfide Mines" Applied Sciences 14, no. 3: 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14031289
APA StyleWang, X., Xue, J., He, M., Qi, H., & Wang, S. (2024). The Effects of Vermicompost and Steel Slag Amendments on the Physicochemical Properties and Bacterial Community Structure of Acidic Soil Containing Copper Sulfide Mines. Applied Sciences, 14(3), 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14031289





