A Systematic Review on Earthworms in Soil Bioremediation
Abstract
1. Introduction
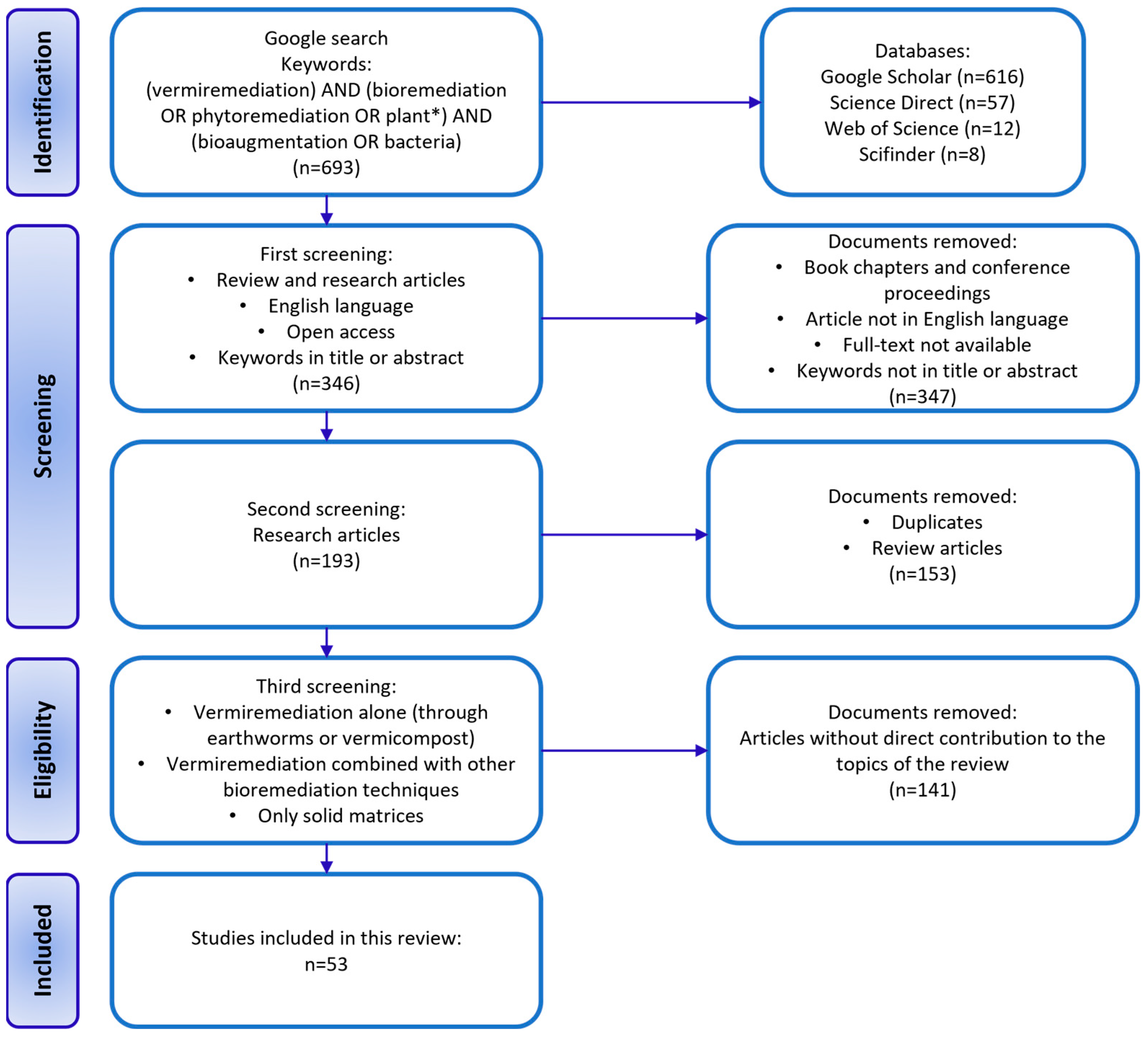
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources and Search Strategies
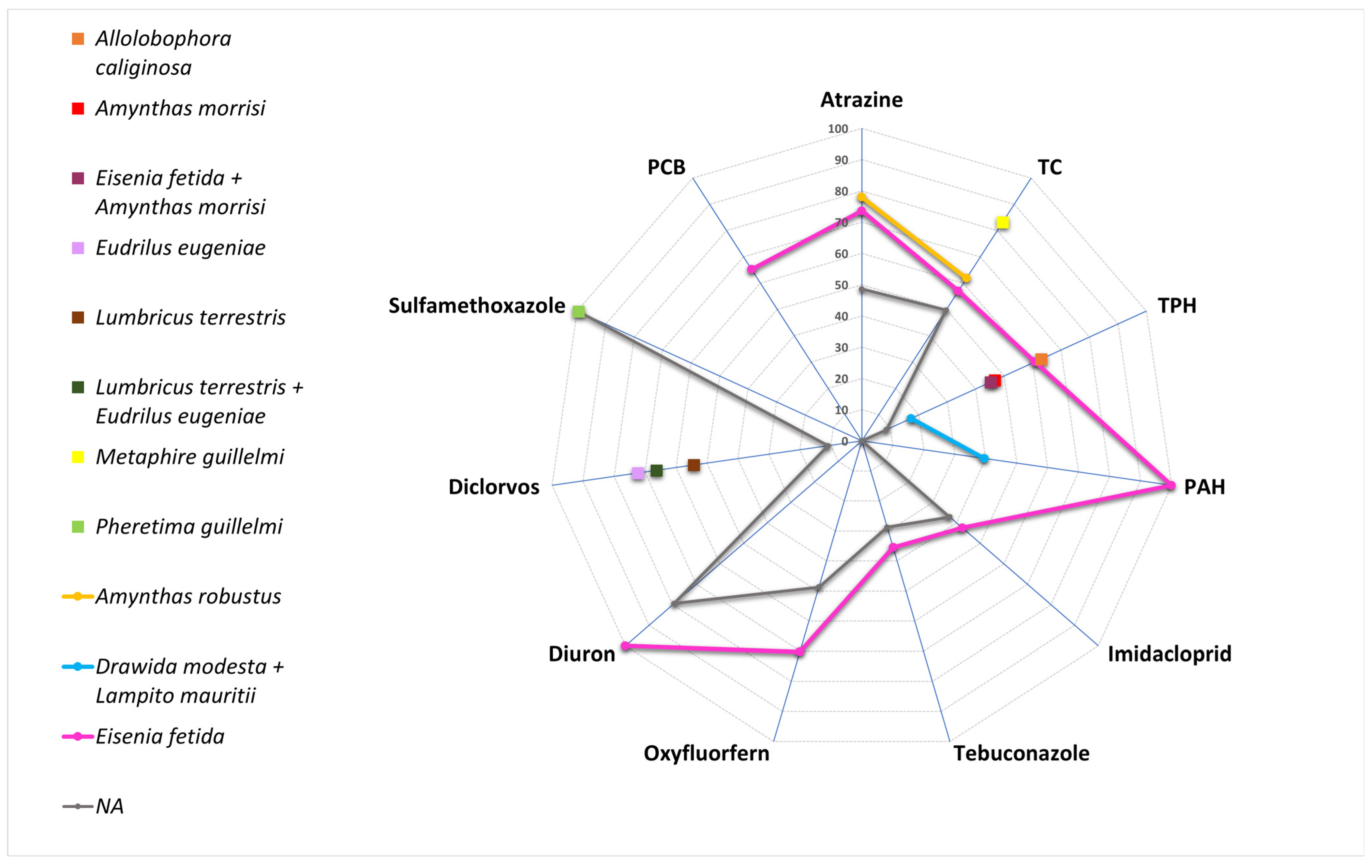
2.2. Graphical Construction
- -
- S refers to the substrate;
- -
- E indicates the presence of earthworms for the application of vermiremediation;
- -
- P indicates the presence of plants for the application of phytoremediation;
- -
- M indicates the presence of microorganisms for the application of bioaugmentation;
- -
- O indicates the presence of other remediation strategies.
3. Results
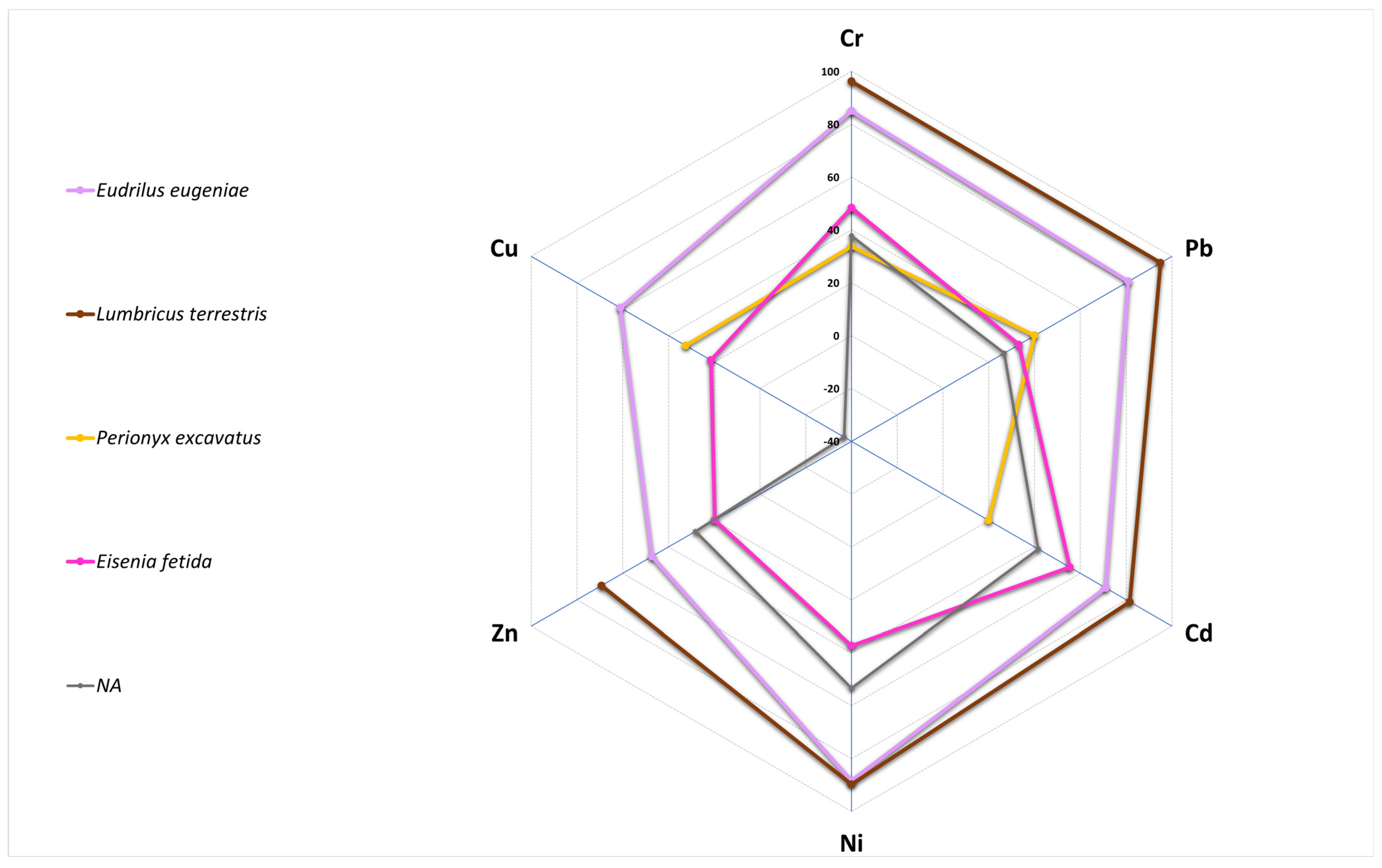
3.1. Alone Inorganic Vermiremediation
3.2. Alone Organic Vermiremediation
3.3. Combined Vermiremediation for Inorganic Pollution
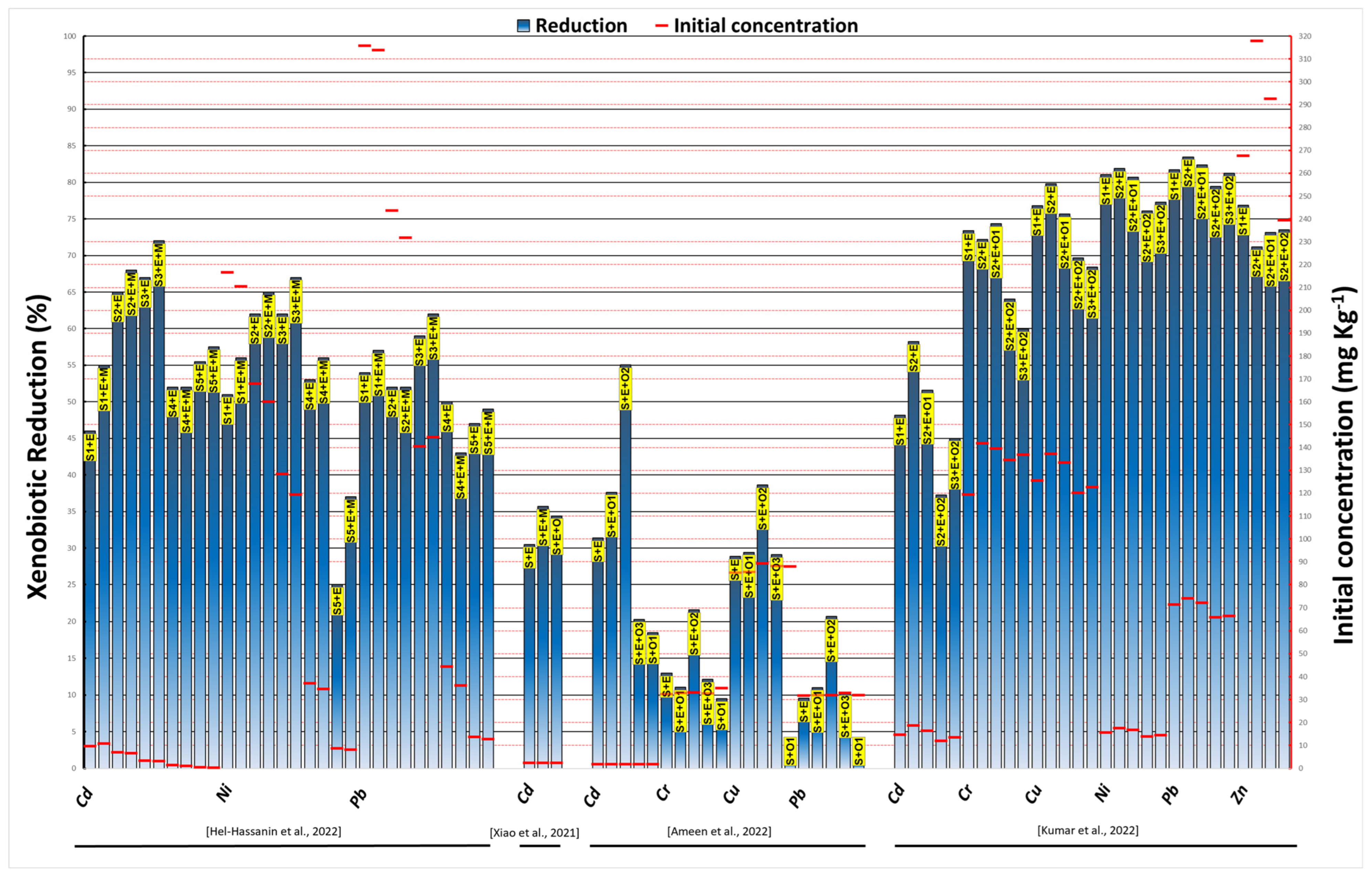
3.4. Combined Vermiremediation for Organic Pollution
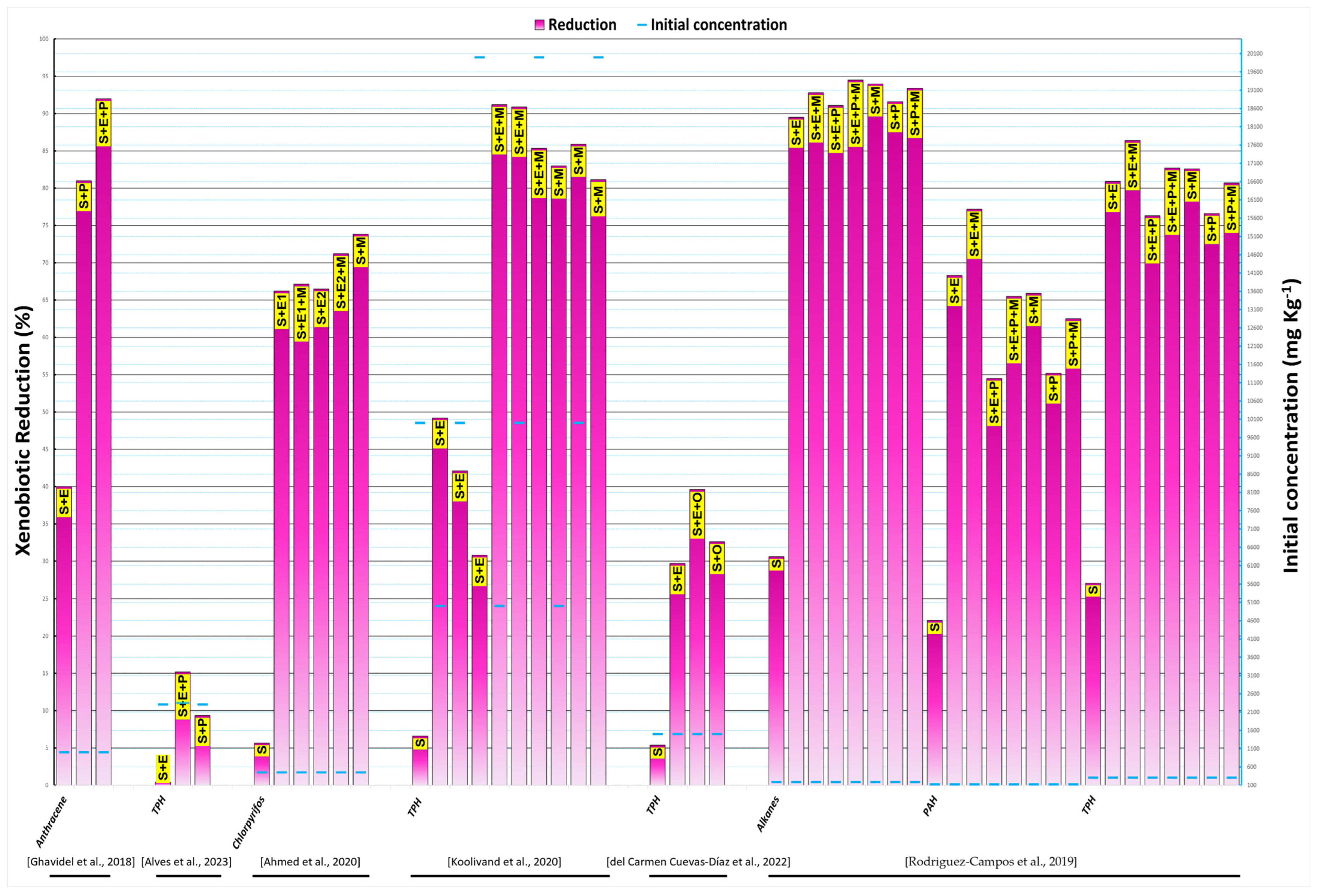
3.5. Combined Vermiremediation for Co-Contamination Pollution
4. Conclusions
- -
- Vermiremediation alone should be considered, especially in conditions of limited contamination, which allows the survival of earthworms regardless of the species and type of contaminant.
- -
- In the case of vermiremediation to restore PTEs pollution, the solutions in which manure is added to the substrate as an organic amendment gave better remediation results.
- -
- When vermiremediation is applied for organic pollutants, the results are highly variable and extremely dependent on the contaminant and the species studied.
- -
- The combination of several strategies improves the effectiveness of remediation and allows working with high contamination. Despite the contaminant, plants, earthworms and microbes stimulate each other and establish symbiotic relationships even in decontamination processes.
- -
- The use of native species (earthworms, plants and microorganisms) adapted to the contamination of the study site should be increased.
- -
- To understand and identify the most promising combinations, experimental designs should consider comparisons between different species and levels of contamination.
- -
- Few works deal with substrates affected by simultaneous contamination of organic and inorganic pollutants, a very frequent situation; therefore, implementing these studies is hoped for.
- -
- The addition of amendments as a nutrient supply must be carefully evaluated in the case of contamination by organic xenobiotics, seeking the proper dosage to favour earthworm activity but, at the same time, not affect the biodegradation capacity.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Sousa, C. Contaminated Sites: The Canadian Situation in an International Context. J. Environ. Manage. 2001, 62, 131–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L.; Liu, W.; Sun, Y.; Huo, X.; Li, S.; Zhou, Q. Phytoremediation of Heavy Metal Contaminated Saline Soils Using Halophytes: Current Progress and Future Perspectives. Environ. Rev. 2017, 25, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, A.; Li, S.; Wu, J.; Lian, J.; Liu, W.; Sun, Y. Insights into the Mechanisms Underlying the Remediation Potential of Earthworms in Contaminated Soil: A Critical Review of Research Progress and Prospects. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uwizeyimana, H.; Wang, M.; Chen, W.; Khan, K. The Eco-Toxic Effects of Pesticide and Heavy Metal Mixtures towards Earthworms in Soil. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 55, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, J. Pollution: Causes, Effects and Control. Environ. Pollut. 1997, 96, 276–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan Al-Taai, S.H. Soil Pollution-Causes and Effects. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 790, 012009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Han, Y.; Peng, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhan, L.; Li, J. Human Health Risk Assessment for Contaminated Sites: A Retrospective Review. Environ. Int. 2023, 171, 107700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alengebawy, A.; Abdelkhalek, S.T.; Rana Qureshi, S.; Wang, M.-Q. Plants: Ecological Risks and Human Health Implications. Toxics 2021, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Shukla, A.; Attri, K.; Kumar, M.; Kumar, P.; Suttee, A.; Singh, G.; Barnwal, R.P.; Singla, N. Global Trends in Pesticides: A Looming Threat and Viable Alternatives. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 201, 110812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kole, R.K.; Banerjee, H.; Bhattacharyya, A. Monitoring of Market Fish Samples for Endosulfan and Hexachlorocyclohexane Residues in and Around Calcutta. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2001, 67, 0554–0559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization. FAO Pesticides Use, Pesticides Trade and Pesticides Indicators 1990–2019; FAOSTAT. 29; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2021; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Cara, I.G.; Țopa, D.; Puiu, I.; Jităreanu, G. Biochar a Promising Strategy for Pesticide-Contaminated Soils. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffa, C.M.; Chiampo, F. Bioremediation of Agricultural Soils Polluted with Pesticides: A Review. Bioengineering 2021, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarfeen, N.; Nisa, K.U.; Hamid, B.; Bashir, Z.; Yatoo, A.M.; Dar, M.A.; Mohiddin, F.A.; Amin, Z.; Ahmad, R.A.; Sayyed, R.Z. Microbial Remediation: A Promising Tool for Reclamation of Contaminated Sites with Special Emphasis on Heavy Metal and Pesticide Pollution: A Review. Processes 2022, 10, 1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.J.; Zia, M.S.; Qasim, M. Use of Pesticides and Their Role in Environmental Pollution. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2010, 72, 122–128. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.; Kumar, V.; Shahzad, B.; Tanveer, M.; Sidhu, G.P.S.; Handa, N.; Kohli, S.K.; Yadav, P.; Bali, A.S.; Parihar, R.D.; et al. Worldwide Pesticide Usage and Its Impacts on Ecosystem. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzano, R.; Rascio, I.; Allegretta, I.; Porfido, C.; Spagnuolo, M.; Khanghahi, M.Y.; Crecchio, C.; Sakellariadou, F.; Gattullo, C.E. Fire Effects on the Distribution and Bioavailability of Potentially Toxic Elements (PTEs) in Agricultural Soils. Chemosphere 2021, 281, 130752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabata-Pendias, A. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000; ISBN 042919112X. [Google Scholar]
- Akram, R.; Turan, V.; Hammad, H.M.; Ahmad, S.; Hussain, S.; Hasnain, A.; Maqbool, M.M.; Rehmani, M.I.A.; Rasool, A.; Masood, N.; et al. Fate of Organic and Inorganic Pollutants in Paddy Soils. Environ. Pollut. Paddy Soils 2018, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suman, J.; Uhlik, O.; Viktorova, J.; Macek, T. Phytoextraction of Heavy Metals: A Promising Tool for Clean-up of Polluted Environment? Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Shentu, J.; Yang, X.; Baligar, V.C.; Zhang, T.; Stoffella, P.J. Heavy Metal Contamination of Soils: Sources, Indicators, and Assessment. J. Environ. Indic. 2015, 9, 17–18. [Google Scholar]
- Raffa, C.M.; Chiampo, F.; Shanthakumar, S. Remediation of Metal/Metalloid-Polluted Soils: A Short Review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwolak, A.; Sarzyńska, M.; Szpyrka, E.; Stawarczyk, K. Sources of Soil Pollution by Heavy Metals and Their Accumulation in Vegetables: A Review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafique, N.; Tariq, S.R. Distribution and Source Apportionment Studies of Heavy Metals in Soil of Cotton/Wheat Fields. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.A.Z.; De Queiroz, M.E.L.R.; De Oliveira, A.F.; Neves, A.A.; Heleno, F.F.; Zambolim, L.; Freitas, J.F.; Morais, E.H.C. Pesticide Residue Removal in Classic Domestic Processing of Tomato and Its Effects on Product Quality. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2017, 52, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiseman, C.L.S.; Zereini, F.; Püttmann, W. Metal and Metalloid Accumulation in Cultivated Urban Soils: A Medium-Term Study of Trends in Toronto, Canada. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 538, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuppusamy, S.; Maddela, N.R.; Megharaj, M.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Kuppusamy, S.; Maddela, N.R.; Megharaj, M.; Venkateswarlu, K. An Overview of Total Petroleum Hydrocarbons. In Total Petroleum Hydrocarbons–Environmental Fate, Toxicity, and Remediation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Patowary, R.; Patowary, K.; Devi, A.; Kalita, M.C.; Deka, S. Uptake of Total Petroleum Hydrocarbon (TPH) and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) by Oryza sativa L. Grown in Soil Contaminated with Crude Oil. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 98, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnaik, P. Health Hazard, Which Includes Toxic, Corrosive, Carcinogenic, and Teratogenic Properties, Exposure Limits. In A Comprehensive Guide to the Hazardous Properties of Chemical Substances; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1992; pp. 425–445. [Google Scholar]
- Blumer, M.; Blumer, W.; Reich, T. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Soils of a Mountain Valley: Correlation with Highway Traffic and Cancer Incidence. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1977, 11, 1082–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, A.T. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons. A Review. Cogent Environ. Sci. 2017, 3, 1339841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Wu, X.; Song, X.; Shi, C.; Zhang, Z. Sorption and Desorption of Petroleum Hydrocarbons on Biodegradable and Nondegradable Microplastics. Chemosphere 2021, 273, 128553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuppusamy, S.; Thavamani, P.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Lee, Y.B.; Naidu, R.; Megharaj, M. Remediation Approaches for Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) Contaminated Soils: Technological Constraints, Emerging Trends and Future Directions. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 944–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, F.U.; Ejaz, M.; Cheema, S.A.; Khan, M.I.; Zhao, B.; Liqun, C.; Salim, M.A.; Naveed, M.; Khan, N.; Núñez-Delgado, A.; et al. Phytotoxicity of Petroleum Hydrocarbons: Sources, Impacts and Remediation Strategies. Environ. Res. 2021, 197, 111031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grifoni, M.; Rosellini, I.; Angelini, P.; Petruzzelli, G.; Pezzarossa, B. The Effect of Residual Hydrocarbons in Soil Following Oil Spillages on the Growth of Zea Mays Plants. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.B.; Shaikh, S.; Jain, K.R.; Desai, C.; Madamwar, D. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Sources, Toxicity, and Remediation Approaches. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 562813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeniji, A.O.; Okoh, O.O.; Okoh, A.I. Levels of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Water and Sediment of Buffalo River Estuary, South Africa and Their Health Risk Assessment. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 76, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Shafy, H.I.; Mansour, M.S.M. A Review on Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Source, Environmental Impact, Effect on Human Health and Remediation. Egypt. J. Pet. 2016, 25, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Jahan, S.A.; Kabir, E.; Brown, R.J.C. A Review of Airborne Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) and Their Human Health Effects. Environ. Int. 2013, 60, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, G.R.; Guizellini, G.M.; da Silva, S.A.; de Almeida, A.P.; Pinaffi-Langley, A.C.C.; Rogero, M.M.; de Camargo, A.C.; Torres, E.A.F.S. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Foods: Biological Effects, Legislation, Occurrence, Analytical Methods, and Strategies to Reduce Their Formation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Zhang, J.; Krebs, P. Global Trade Drives Transboundary Transfer of the Health Impacts of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Emissions. Commun. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.; Huang, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhu, D.; Li, W.; Shen, G.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lu, Y.; et al. From 1960 to 2008 and Future Predictions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6415–6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, I.G.S.; de Almeida, F.C.G.; da Rocha e Silva, N.M.P.; Casazza, A.A.; Converti, A.; Sarubbo, L.A. Soil Bioremediation: Overview of Technologies and Trends. Energies 2020, 13, 4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Dai, M.; Yang, J.; Sun, L.; Tan, X.; Peng, C.; Ali, I.; Naz, I. A Critical Review on the Phytoremediation of Heavy Metals from Environment: Performance and Challenges. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vischetti, C.; Marini, E.; Casucci, C.; De Bernardi, A. Nickel in the Environment: Bioremediation Techniques for Soils with Low or Moderate Contamination in European Union. Environments 2022, 9, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berti, W.R.; Cunningham, S.D. Phytostabilization of Metals. In Phytoremediation Toxic Metals: Using Plants to Clean Up Environ; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 71–88. [Google Scholar]
- Sarwar, N.; Imran, M.; Shaheen, M.R.; Ishaque, W.; Kamran, M.A.; Matloob, A.; Rehim, A.; Hussain, S. Phytoremediation Strategies for Soils Contaminated with Heavy Metals: Modifications and Future Perspectives. Chemosphere 2017, 171, 710–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagnano, M.; Agrelli, D.; Pascale, A.; Adamo, P.; Fiorentino, N.; Rocco, C.; Pepe, O.; Ventorino, V. Copper Accumulation in Agricultural Soils: Risks for the Food Chain and Soil Microbial Populations. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 734, 139434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Beiyuan, J.; Hu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Duan, C.; Cui, Q.; Zhu, X.; He, H.; Huang, X.; Fang, L. Phytoremediation of Potentially Toxic Elements (PTEs) Contaminated Soils Using Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.): A Comprehensive Review. Chemosphere 2022, 293, 133577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, S.; Singh, V.K.; Srivastava, P.; Singh, R.; Devi, R.S.; Kumar, A.; Bhadouria, R. Phytoremediation of Organic Pollutants: Current Status and Future Directions. Abat. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 81–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salt, D.E.; Smith, R.D.; Raskin, I. Phytoremediation. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 1998, 49, 643–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, J.M.; Karthik, C.; Saratale, R.G.; Kumar, S.S.; Prabakar, D.; Kadirvelu, K.; Pugazhendhi, A. Biological Approaches to Tackle Heavy Metal Pollution: A Survey of Literature. J. Environ. Manage. 2018, 217, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhashini, V.; Swamy, A.V.V.S. Open Access Phytoremediation of Pb and Ni Contaminated Soils Using Catharanthus roseus (L.). Univers. J. Environ. Res. Technol. 2013, 3, 465–472. [Google Scholar]
- Susarla, S.; Medina, V.F.; McCutcheon, S.C. Phytoremediation: An Ecological Solution to Organic Chemical Contamination. Ecol. Eng. 2002, 18, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awa, S.H.; Hadibarata, T. Removal of Heavy Metals in Contaminated Soil by Phytoremediation Mechanism: A Review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limmer, M.; Burken, J. Phytovolatilization of Organic Contaminants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 6632–6643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, A.; Wang, Y.; Tan, S.N.; Mohd Yusof, M.L.; Ghosh, S.; Chen, Z. Phytoremediation: A Promising Approach for Revegetation of Heavy Metal-Polluted Land. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olguìn, E.J.; Sànchez-Galvàn, G. Heavy Metal Removal in Phytofiltration and Phycoremediation: The Need to Differentiate between Bioadsorption and Bioaccumulation. New Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cycoń, M.; Mrozik, A.; Piotrowska-Seget, Z. Bioaugmentation as a Strategy for the Remediation of Pesticide-Polluted Soil: A Review. Chemosphere 2017, 172, 52–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwankwegu, A.S.; Zhang, L.; Xie, D.; Onwosi, C.O.; Muhammad, W.I.; Odoh, C.K.; Sam, K.; Idenyi, J.N. Bioaugmentation as a Green Technology for Hydrocarbon Pollution Remediation. Problems and Prospects. J. Environ. Manage. 2022, 304, 114313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, I.P.; Van Der Gast, C.J.; Ciric, L.; Singer, A.C. Bioaugmentation for Bioremediation: The Challenge of Strain Selection. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taccari, M.; Milanovic, V.; Comitini, F.; Casucci, C.; Ciani, M. Effects of Biostimulation and Bioaugmentation on Diesel Removal and Bacterial Community. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2012, 66, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semrany, S.; Favier, L.; Djelal, H.; Taha, S.; Amrane, A. Bioaugmentation: Possible Solution in the Treatment of Bio-Refractory Organic Compounds (Bio-ROCs). Biochem. Eng. J. 2012, 69, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Liu, J.; Tang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, C. Vermiremediation of Organically Contaminated Soils: Concepts, Current Status, and Future Perspectives. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 147, 103377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Campos, J.; Dendooven, L.; Alvarez-Bernal, D.; Contreras-Ramos, S.M. Potential of Earthworms to Accelerate Removal of Organic Contaminants from Soil: A Review. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2014, 79, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dada, E.O.; Akinola, M.O.; Owa, S.O.; Dedeke, G.A.; Aladesida, A.A.; Owagboriaye, F.O.; Oludipe, E.O. Efficacy of Vermiremediation to Remove Contaminants from Soil. J. Heal. Pollut. 2021, 11, 210302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yatoo, A.M.; Ali, N.; Zaheen, Z.; Ahmad, Z.; Shafat, B.; Saiema, A.; Ahmad, T.; Mika, S.; Kumar, P.; Burhan, G.; et al. Assessment of Pesticide Toxicity on Earthworms Using Multiple Biomarkers: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 2573–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelosi, C.; Barot, S.; Capowiez, Y.; Hedde, M.; Vandenbulcke, F. Pesticides and Earthworms. A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 34, 199–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaswamy, V.G.; Jaffar, M.F.; Sridharan, R.; Ganesh, S.; Kalidas, S.; Palanisamy, V.; Mani, K. Effect of Chlorpyrifos on the Earthworm Eudrilus Euginae and Their Gut Microbiome by Toxicological and Metagenomic Analysis. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 37, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, M.F.; Poch, R.M.; Olarieta, J.R.; Wiedner, K. Charcoal and Biological Activity in Formiguer Soils of Catalonia (Spain): Application of a Micromorphological Approach. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 234, 105810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurgeon, D.J.; Weeks, J.M.; Van Gestel, C.A.M. A Summary of Eleven Years Progress in Earthworm Ecotoxicology. Pedobiologia 2003, 47, 588–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, M. Assessing 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene (TNT)-Contaminated Soil Using Three Different Earthworm Test Methods. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2004, 57, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svobodovà, M.; Smídovà, K.; Hvezdovà, M.; Hofman, J. Uptake Kinetics of Pesticides Chlorpyrifos and Tebuconazole in the Earthworm Eisenia Andrei in Two Different Soils. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Ji, D.; Wang, C. Interaction between Earthworms and Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi on the Degradation of Oxytetracycline in Soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 90, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.M.; Xu, L.; Hu, F. A Hierarchic Method for Studying the Distribution of Phenanthrene in Eisenia Fetida. Pedosphere 2014, 24, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlatter, D.C.; Reardon, C.L.; Johnson-Maynard, J.; Brooks, E.; Kahl, K.; Norby, J.; Huggins, D.; Paulitz, T.C. Mining the Drilosphere: Bacterial Communities and Denitrifier Abundance in a No-till Wheat Cropping System. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzyakov, Y.; Blagodatskaya, E. Microbial Hotspots and Hot Moments in Soil: Concept & Review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 83, 184–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, S.S.; Lone, A.R.; Singh, K.; Bhattacharyya, S.S.; Ratnasari, A.; Yadav, A.N.; Jain, S.K.; Yadav, S. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon (PAH)–Contaminated Soil Decontamination Through Vermiremediation. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Test 222: Earthworms Reproduction Test (Eisenia Fetida/Eisenia Andrei) Guidel; Testing Chemical; Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development: Paris, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Guideline for Testing of Chemicals “Earthworm, Acute Toxicity Tests” 207; Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development: Paris, France, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karwal, M.; Kaushik, A. Co-Composting and Vermicomposting of Coal Fly-Ash with Press Mud: Changes in Nutrients, Micro-Nutrients and Enzyme Activities. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 18, 100708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Choudhury, M.; Deb, U.; Pegu, R.; Das, S.; Bhattacharya, S.S. Assessing the Ecological Impacts of Ageing on Hazard Potential of Solid Waste Landfills: A Green Approach through Vermitechnology. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 236, 117643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Goswami, L.; Pegu, R.; Kumar Chatterjee, S.; Sundar Bhattacharya, S. Epigenetic Regulations Enhance Adaptability and Valorization Efficiency in Eisenia Fetida and Eudrilus Eugeniae during Vermicomposting of Textile Sludge: Insights on Repair Mechanisms of Metal-Induced Genetic Damage and Oxidative Stress. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 345, 126493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohal, B.; Singh, S.; Indra, S.; Singh, K.; Bhat, S.A.; Kaur, J. Comparing the Nutrient Changes, Heavy Metals, and Genotoxicity Assessment before and after Vermicomposting of Thermal Fly Ash Using Eisenia Fetida. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 48154–48170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Das, S.; Raul, P.; Bhattacharya, S.S. Vermi-Sanitization of Toxic Silk Industry Waste Employing Eisenia Fetida and Eudrilus Eugeniae: Substrate Compatibility, Nutrient Enrichment and Metal Accumulation Dynamics. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 266, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.I.; Singh, W.R.; Bhat, S.A.; Sohal, B.; Khanna, N.; Vig, A.P.; Ameen, F.; Jones, S. Vermiremediation of Allopathic Pharmaceutical Industry Sludge Amended with Cattle Dung Employing Eisenia Fetida. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mupondi, L.T.; Mnkeni, P.N.S.; Muchaonyerwa, P.; Mupambwa, H.A. Vermicomposting Manure-Paper Mixture with Igneous Rock Phosphate Enhances Biodegradation, Phosphorus Bioavailability and Reduces Heavy Metal Concentrations. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mago, M.; Yadav, A.; Gupta, R.; Garg, V.K. Management of Banana Crop Waste Biomass Using Vermicomposting Technology. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 326, 124742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suthar, S. Metal Remediation from Partially Composted Distillery Sludge Using Composting Earthworm Eisenia Fetida. J. Environ. Monit. 2008, 10, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, P.; Sarkar, S.; Mondal, S.; Agarwal, B.K.; Kumar, A.; Bhattacharya, S.; Bhattacharya, S.S.; Bhattacharyya, P. Eisenia Fetida Mediated Vermi-Transformation of Tannery Waste Sludge into Value Added Eco-Friendly Product: An Insight on Microbial Diversity, Enzyme Activation, and Metal Detoxification. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 348, 131368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.B.; Cui, X.; Jilani, G.; Ting, Y.; Zehra, A.; Hamid, Y.; Hussain, B.; Tang, L.; Yang, X.; He, Z. Preincubation and Vermicomposting of Divergent Biosolids Exhibit Vice Versa Multielements Stoichiometry and Earthworm Physiology. J. Environ. Manage. 2019, 243, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žaltauskaitė, J.; Kniuipytė, I.; Praspaliauskas, M. Earthworm Eisenia Fetida Potential for Sewage Sludge Amended Soil Valorization by Heavy Metal Remediation and Soil Quality Improvement. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sugir, M.E.; Li, Y.; Yuan, L.; Zhou, M.; Lv, P.; Yu, Z.; Wang, L. Effects of Vermicomposting on the Main Chemical Properties and Bioavailability of Cd/Zn in Pure Sludge. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 20949–20960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iheme, P.O.; Ajayi, A.T.; Njoku, K.L. Vermiremediation Potentials of Lumbricus Terrestris and Eudrilus Euginae in Heavy Metal Contaminated Soil from Mechanic, Welder Workshop and Metallic Dumpsite. Niger. J. Biotechnol. 2021, 38, 118–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Goswami, L.; Pegu, R.; Sundar Bhattacharya, S. Vermiremediation of Cotton Textile Sludge by Eudrilus Eugeniae: Insight into Metal Budgeting, Chromium Speciation, and Humic Substance Interactions. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 314, 123753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnhart, J. Occurrences, Uses, and Properties of Chromium. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 1997, 26, S3–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, L.; Mukhopadhyay, R.; Sundar, S.; Das, P. Bioresource Technology Detoxi Fi Cation of Chromium-Rich Tannery Industry Sludge by Eudrillus Eugeniae: Insight on Compost Quality Forti Fi Cation and Microbial Enrichment. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 266, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuvaraj, A.; Karmegam, N.; Thangaraj, R. Vermistabilization of Paper Mill Sludge by an Epigeic Earthworm Perionyx Excavatus: Mitigation Strategies for Sustainable Environmental Management. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 120, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescano, M.R.; Masin, C.E.; Rodríguez, A.R.; Godoy, J.L.; Zalazar, C.S. Earthworms to Improve Glyphosate Degradation in Biobeds. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 27023–27031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Cao, J.; Wang, C. Bioremediation by Earthworms on Soil Microbial Diversity and Partial Nitrification Processes in Oxytetracycline-Contaminated Soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 189, 109996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubiyatno; Teh, Z.C.; Lestari, D.V.; Yulisa, A.; Musa, M.; Chen, T.-W.; Darwish, N.M.; AlMunqedhi, B.M.; Hadibarata, T. Tolerance of Earthworms in Soil Contaminated with Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon. Ind. Domest. Waste Manag. 2022, 2, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenteno-Rojas, A.; Martinez-Romero, E.; Rincón-Molina, C.I.; Ruíz-Valdiviezo, V.M.; Meza-Gordillo, R.; Villalobos-Maldonado, J.J.; Rincón-Rosales, R. Removal of High Concentrations Decachlorobiphenyl of Earthworm Eisenia Fetida and Its Symbiotic Bacteria in a Vermicomposting System. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owagboriaye, F.; Dedeke, G.; Bamidele, J.; Aladesida, A.; Isibor, P.; Feyisola, R.; Adeleke, M. Biochemical Response and Vermiremediation Assessment of Three Earthworm Species (Alma millsoni, Eudrilus eugeniae and Libyodrilus violaceus) in Soil Contaminated with a Glyphosate-Based Herbicide. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 108, 105678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi-Moghadam, F.; Khodadadi, R.; Sedehi, M.; Arbabi, M. Bioremediation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Contaminated Soils Using Vermicompost. Int. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 2022, 5294170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, S.E. Bioremediation Assessment, Hematological, and Biochemical Responses of the Earthworm (Allolobophora caliginosa) in Soil Contaminated with Crude Oil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 54565–54574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawole, C.; Salami, S.J.; Dashak, D.A.; Chimezie-Nwosu, H.A. Bioengineered Approach for Ex Situ Vermiextraction of Acenaphthylene, Benzo (E)Pyrene and Benzo (Ghi) Perylene Soil Contamination. Curr. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2021, 40, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Immerzeel, J.; Bodt, J. Earthworm and Food Interaction on Bioaccumulation and Disappearance in Soil of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Studies on Phenanthrene and Fluoranthene. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1995, 32, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobili, S.; Elisabet, C.; Susana, C.; Raquel, M. Bioremediation of Hydrocarbon Contaminated Soil Using Local Organic Materials and Earthworms. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 314, 120169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajadurai, M.; Karmegam, N.; Kannan, S.; Yuvaraj, A.; Thangaraj, R. Vermiremediation of Engine Oil Contaminated Soil Employing Indigenous Earthworms, Drawida Modesta and Lampito Mauritii. J. Environ. Manage. 2022, 301, 113849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njoku, K.L.; Ogwara, C.A.; Adesuyi, A.A.; Akinola, M.O. Vermiremediation of Pesticide Contaminated Soil Using Eudrilus Euginae and Lumbricus Terrestris. EnvironmentAsia 2018, 11, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Moreno, L.; Nogales, R.; Romero, E. Vermiremediation of Biomixtures from Biobed Systems Contaminated with Pesticides. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Zhen, Z.; Liang, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Zhong, L.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; Luo, C.; Ren, L.; et al. Changes in Atrazine Speciation and the Degradation Pathway in Red Soil during the Vermiremediation Process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 364, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baran, W.; Adamek, E.; Ziemiańska, J.; Sobczak, A. Effects of the Presence of Sulfonamides in the Environment and Their Influence on Human Health. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 196, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, T.; Domingues, S.; Silva, G.J. Da Manure as a Potential Hotspot for Antibiotic Resistance Dissemination by Horizontal Gene Transfer Events. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, H.; Xiong, P.; Zhu, Q.; Liao, C.; Jiang, G. Occurrence, Fate, and Risk Assessment of Typical Tetracycline Antibiotics in the Aquatic Environment: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 753, 141975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundström, S.V.; Östman, M.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Rutgersson, C.; Thoudal, M.; Sircar, T.; Blanck, H.; Eriksson, K.M.; Tysklind, M.; Flach, C.F.; et al. Minimal Selective Concentrations of Tetracycline in Complex Aquatic Bacterial Biofilms. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 553, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ECDC. Antimicrobial Consumption in the EU/EEA (ESAC-Net); European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control: Solna, Sweden, 2021.
- Lin, Z.; Zhen, Z.; Luo, S.; Ren, L.; Chen, Y.; Wu, W.; Zhang, W.; Liang, Y.Q.; Song, Z.; Li, Y.; et al. Effects of Two Ecological Earthworm Species on Tetracycline Degradation Performance, Pathway and Bacterial Community Structure in Laterite Soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 412, 125212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.; Zhang, M.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, H.; Fan, T.; Wu, Z.; Cao, L.; Zhao, Q. The Changes of Antioxidant System and Intestinal Bacteria in Earthworms (Metaphire guillelmi) on the Enhanced Degradation of Tetracycline. Chemosphere 2021, 265, 129097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; He, N.; Chang, D.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Sun, J.; Li, W.; Li, H.; et al. Does Ecotype Matter? The Influence of Ecophysiology on Benzo[a]Pyrene and Cadmium Accumulation and Distribution in Earthworms. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 121, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, K.; Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Ye, G.; Cao, H.; Chen, M.; Cai, S.; Cao, X.; Zheng, X.; et al. Removal of Sulfamethoxazole and Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Paddy Soil by Earthworms (Pheretima guillelmi): Intestinal Detoxification and Stimulation of Indigenous Soil Bacteria. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, G. The Public Health Implications of Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) in the Environment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2004, 59, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EPA. PCBs: Cancer Dose-Response Assessment and Application to Environmental Mixtures; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1996; p. 74.
- Luo, S.; Ren, L.; Wu, W.; Chen, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, W.; Wei, T.; Liang, Y.Q.; Zhang, D.; Wang, X.; et al. Impacts of Earthworm Casts on Atrazine Catabolism and Bacterial Community Structure in Laterite Soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 425, 127778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniadis, V.; Levizou, E.; Shaheen, S.M.; Ok, Y.S.; Sebastian, A.; Baum, C.; Prasad, M.N.V.; Wenzel, W.W.; Rinklebe, J. Trace Elements in the Soil-Plant Interface: Phytoavailability, Translocation, and Phytoremediation–A Review. Earth-Science Rev. 2017, 171, 621–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sizmur, T.; Hodson, M.E. Do Earthworms Impact Metal Mobility and Availability in Soil?–A Review. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1981–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, S.A.; Bhatti, S.S.; Singh, J.; Sambyal, V.; Nagpal, A.; Vig, A.P. Vermiremediation and Phytoremediation: Eco Approaches for Soil Stabilization. Austin Envronmental Sci. 2016, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, B.; Hu, X.Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.S.; Feng, M.H.; Shan, X.Q. The Role of Earthworms (Eisenia fetida) in Influencing Bioavailability of Heavy Metals in Soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2004, 40, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibihenda, C.; Zhang, M.; Zhong, H.; Xiao, L.; Wu, L.; Dai, J.; Liu, K.; Zhang, C. Growth and Pb Uptake of Brassica Campestris Enhanced by Two Ecological Earthworm Species in Relation to Soil Physicochemical Properties. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseer, A.; Andleeb, S.; Basit, A.; Ali, S.; ud-Din, M.S.; Ali, N.M.; Liaqat, I.; Nazir, A. Efficacy of Cow and Buffalo Dung on Vermiremediation and Phytoremediation of Heavy Metals via Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy and Comet Assay. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 37912–37928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruley, J.A.; Amoding, A.; Tumuhairwe, J.B.; Basamba, T.A.; Opolot, E.; Oryem-Origa, H. Enhancing the Phytoremediation of Hydrocarbon-Contaminated Soils in the Sudd Wetlands, South Sudan, Using Organic Manure. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2020, 2020, 4614286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Proctor, G.; Larson, S.L.; Ballard, J.H.; Zan, S.; Yang, R.; Wang, X.; Han, F.X. Earthworm Enhanced Phytoremediation of U in Army Test Range Soil with Indian Mustard and Sun Fl Ower. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2022, 6, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Kuila, A. Bioremediation of Heavy Metals by Microbial Process. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2019, 14, 100369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munnoli, P.M.; Jaime, M.; Teixeira, A.; Saroj, S. Dynamics of the Soil-Earthworm-Plant Relationship: A Review. Dyn. Soils Dyn. Plant 2010, 4, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Lemtiri, A.; Colinet, G.; Alabi, T.; Cluzeau, D.; Zirbes, L.; Haubruge, É.; Francis, F. Impacts of Earthworms on Soil Components and Dynamics. A Review. Biotechnol. Agron. Soc. Environ. 2014, 18, 121–133. [Google Scholar]
- Nechitaylo, T.Y.; Yakimov, M.M.; Godinho, M.; Timmis, K.N.; Belogolova, E.; Byzov, B.A.; Kurakov, A.V.; Jones, D.L.; Golyshin, P.N. Effect of the Earthworms Lumbricus Terrestris and Aporrectodea Caliginosa on Bacterial Diversity in Soil. Microb. Ecol. 2010, 59, 574–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šrut, M.; Menke, S.; Höckner, M.; Sommer, S. Earthworms and Cadmium–Heavy Metal Resistant Gut Bacteria as Indicators for Heavy Metal Pollution in Soils? Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 171, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hassanin, A.S.; Samak, M.R.; Ahmed, S.M.; Afifi, M.M.I.; El-satar, M.A. Bioaccumulation of Heavy Metals during Composting and Vermicomposting Processes of Sewage Sludge. Egypt. J. Chem. 2022, 65, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Liu, X.; Ali, A.; Chen, A.; Zhang, M.; Li, R.; Chang, H.; Zhang, Z. Bioremediation of Cd-Spiked Soil Using Earthworms (Eisenia fetida): Enhancement with Biochar and Bacillus Megatherium Application. Chemosphere 2021, 264, 128517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tara, N.; Arslan, M.; Hussain, Z.; Iqbal, M.; Khan, Q.M.; Afzal, M. On-Site Performance of Floating Treatment Wetland Macrocosms Augmented with Dye-Degrading Bacteria for the Remediation of Textile Industry Wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 217, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, L.; Ma, F.; You, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, D. Integration of Earthworms and Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi into Phytoremediation of Cadmium-Contaminated Soil by Solanum nigrum L. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 121873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, J.; Joseph, S. Biochar for Environmental Management: An Introduction. In Biochar for Environmental Management; Routledge: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 1–13. ISBN 0203762266. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, M.; Upamali, A.; Eun, J.; Zhang, M.; Bolan, N.; Mohan, D.; Vithanage, M.; Soo, S.; Sik, Y. Chemosphere Biochar as a Sorbent for Contaminant Management in Soil and Water: A Review. Chemosphere 2014, 99, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameen, F.; Al-Homaidan, A.A. Treatment of Heavy Metal–Polluted Sewage Sludge Using Biochar Amendments and Vermistabilization. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blenis, N.; Hue, N.; Maaz, T.M.C.; Kantar, M. Biochar Production, Modification, and Its Uses in Soil Remediation: A Review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.B.; Cui, X.; Jilani, G.; Lazzat, U.; Zehra, A.; Hamid, Y.; Hussain, B.; Tang, L.; Yang, X.; He, Z. Eisenia Fetida and Biochar Synergistically Alleviate the Heavy Metals Content during Valorization of Biosolids via Enhancing Vermicompost Quality. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 684, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Badhwar, V.; Singh, S.; Singh, B. Vermiremediation of Paper Mill Sludge with Cow Dung and Tea Waste Amendments Using Epigeic Earthworm Eisenia Fetida (Savigny). Res. Sq. 2022, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghavidel, A.; Rad, S.N.; Alikhani, H.A.; Yakhchali, B.; Pourbabai, A.A. Presence of Eisenia fetida enhanced phytoremediation of anthracene by Lolium perenne. Biosci. J. 2018, 34, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, D.; Villar, I.; Mato, S. Joint Application of Biological Techniques for the Remediation of Waste Contaminated with Hydrocarbons. Waste Biomass Valorization 2023, 14, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, F.; Gao, D.; Xing, B. Remediation of Petroleum Contaminated Soils through Composting and Rhizosphere Degradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remelli, S.; Scibona, A.; Nizzoli, D.; Mantovani, L.; Tribaudino, M.; Celico, F.; Menta, C. Vermiremediation Applied to PCB and PCDD/F Contaminated Soils and Its Implications for Percolating Water. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, N.A.M.; Sulieman, H.N.A.; Ahmed, M.A.H.; Abd, E.S.A.I.; Azhari, O.A. Bacterial and Vermi-Remediation of Soil Contaminated with Chlorpyrifos Insecticide. African J. Biotechnol. 2020, 19, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koolivand, A.; Saeedi, R.; Coulon, F.; Kumar, V.; Villaseñor, J.; Asghari, F.; Hesampoor, F. Bioremediation of Petroleum Hydrocarbons by Vermicomposting Process Bioaugmentated with Indigenous Bacterial Consortium Isolated from Petroleum Oily Sludge. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 198, 110645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Núñez, E.; Molina-Guerrero, C.E.; Peña-Castro, J.M.; Fernández-Luqueño, F.; de la Rosa-Álvarez, M.G. Use of Nanotechnology for the Bioremediation of Contaminants: A Review. Processes 2020, 8, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharagava, R.N.; Saxena, G.; Mulla, S.I. Introduction to Industrial Wastes Containing Organic and Inorganic Pollutants and Bioremediation Approaches for Environmental Management. In Bioremediation of Industrial Waste for Environmental Safety; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; He, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Lin, D. Bioresponses of Earthworm-Microbiota Symbionts to Polychlorinated Biphenyls in the Presence of Nano Zero Valent Iron in Soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 159226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissenfels, W.D.; Klewer, H.-J.; Langhoff, J. Adsorption of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) by Soil Particles: Influence on Biodegradability and Biotoxicity. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1992, 36, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzetti, A.; Di Gennaro, P.; Bestetti, G.; Lasagni, M.; Pitea, D.; Collina, E. Selection of Surfactants for Enhancing Diesel Hydrocarbons-Contaminated Media Bioremediation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, E.; Ron, E.Z. High- and Low-Molecular-Mass Microbial Surfactants. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1999, 52, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Y. Effects of Surfactants on the Fractionation, Vermiaccumulation, and Removal of Fluoranthene by Earthworms in Soil. Chemosphere 2020, 250, 126332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, Z.; Luo, S.; Chen, Y.; Li, G.; Li, H.; Wei, T.; Huang, F.; Ren, L.; Liang, Y.Q.; Lin, Z.; et al. Performance and Mechanisms of Biochar-Assisted Vermicomposting in Accelerating Di-(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate Biodegradation in Farmland Soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443, 130330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Carmen Cuevas-Díaz, M.; Ramos-Morales, F.R.; Castro-Luna, A.; Vázquez-Luna, D.; Martínez-Hernández, S.; Guzmán-López, O.; Zavala-Cruz, J.; Ortiz-Ceballos, Á.I. Synergy of the Tropical Earthworm Pontoscolex Corethrurus and Oil Palm Bagasse in the Removal of Heavy Crude Oil. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 108, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topoliantz, S.; Ponge, J.F. Burrowing Activity of the Geophagous Earthworm Pontoscolex Corethrurus (Oligochaeta: Glossoscolecidae) in the Presence of Charcoal. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2003, 23, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Campos, J.; Perales-Garcia, A.; Hernandez-Carballo, J.; Martinez-Rabelo, F.; Hernández-Castellanos, B.; Barois, I.; Contreras-Ramos, S.M. Bioremediation of Soil Contaminated by Hydrocarbons with the Combination of Three Technologies: Bioaugmentation, Phytoremediation, and Vermiremediation. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 1981–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Castellanos, B.; Zavala-Cru, J.; Martinez-H, S.; Dendooven, L.; Contreras-, S.M.; Noa-Carraz, J.C.; Fragoso, C.; Ortiz-Ceba, A.I. Earthworm Populations in an Aged Hydrocarbon Contaminated Soil. Res. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 7, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Urionabarrenetxea, E.; Garcia-Velasco, N.; Anza, M.; Artetxe, U.; Lacalle, R.; Garbisu, C.; Becerril, T.; Soto, M. Application of in Situ Bioremediation Strategies in Soils Amended with Sewage Sludges. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 766, 144099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacalle, R.G.; Aparicio, J.D.; Artetxe, U.; Urionabarrenetxea, E.; Polti, M.A.; Soto, M.; Garbisu, C.; Becerril, J.M. Gentle Remediation Options for Soil with Mixed Chromium (VI) and Lindane Pollution: Biostimulation, Bioaugmentation, Phytoremediation and Vermiremediation. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aparicio, J.D.; Lacalle, R.G.; Artetxe, U.; Urionabarrenetxea, E.; Becerril, J.M.; Polti, M.A.; Garbisu, C.; Soto, M. Successful Remediation of Soils with Mixed Contamination of Chromium and Lindane: Integration of Biological and Physico-Chemical Strategies. Environ. Res. 2021, 194, 110666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tagliabue, F.; Marini, E.; De Bernardi, A.; Vischetti, C.; Casucci, C. A Systematic Review on Earthworms in Soil Bioremediation. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10239. https://doi.org/10.3390/app131810239
Tagliabue F, Marini E, De Bernardi A, Vischetti C, Casucci C. A Systematic Review on Earthworms in Soil Bioremediation. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(18):10239. https://doi.org/10.3390/app131810239
Chicago/Turabian StyleTagliabue, Francesca, Enrica Marini, Arianna De Bernardi, Costantino Vischetti, and Cristiano Casucci. 2023. "A Systematic Review on Earthworms in Soil Bioremediation" Applied Sciences 13, no. 18: 10239. https://doi.org/10.3390/app131810239
APA StyleTagliabue, F., Marini, E., De Bernardi, A., Vischetti, C., & Casucci, C. (2023). A Systematic Review on Earthworms in Soil Bioremediation. Applied Sciences, 13(18), 10239. https://doi.org/10.3390/app131810239





