Complementary Strategies for Deciphering the Information Contained in Ancient Parchment Documentary Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
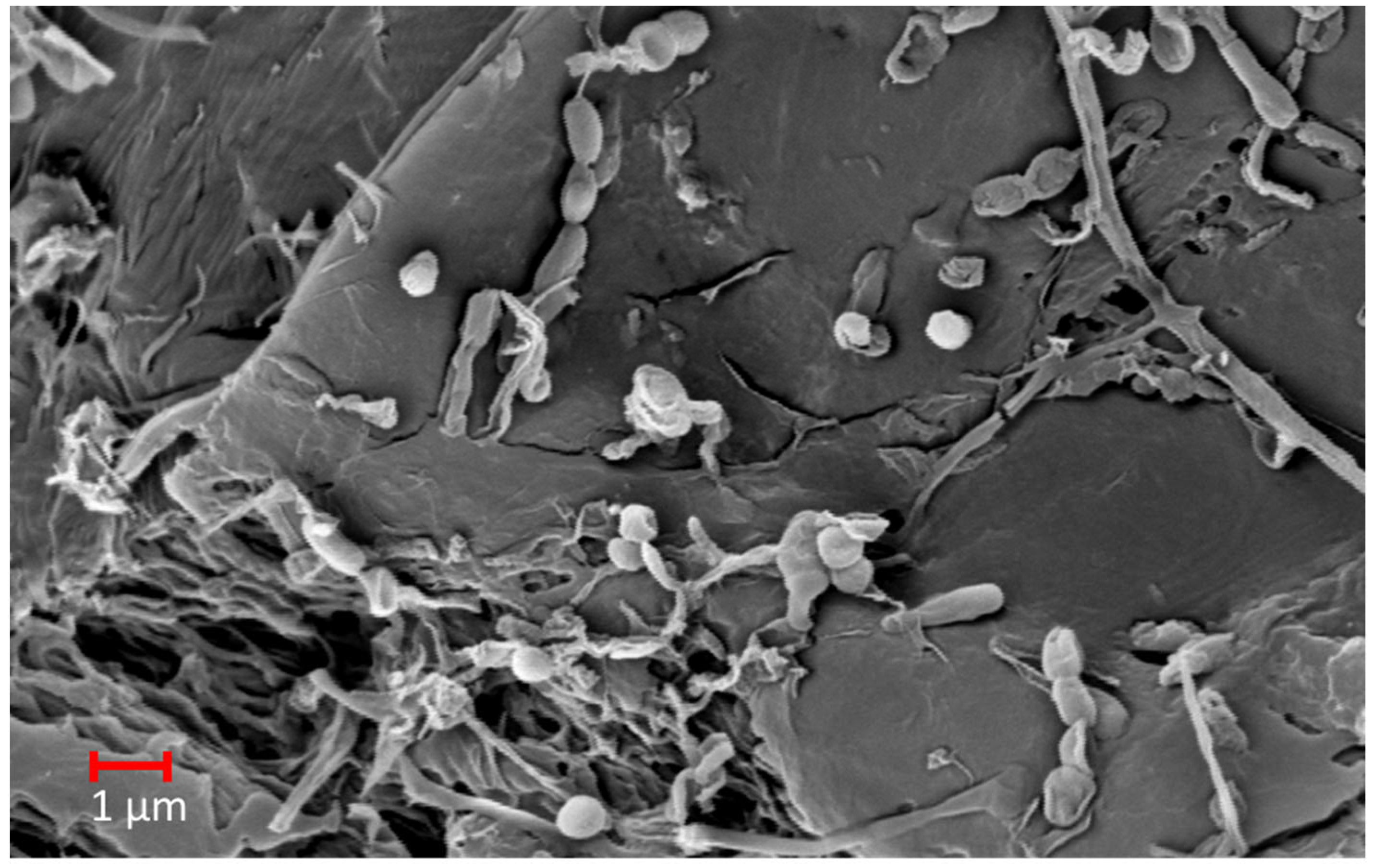
2. Visual and Microscopical Analyses
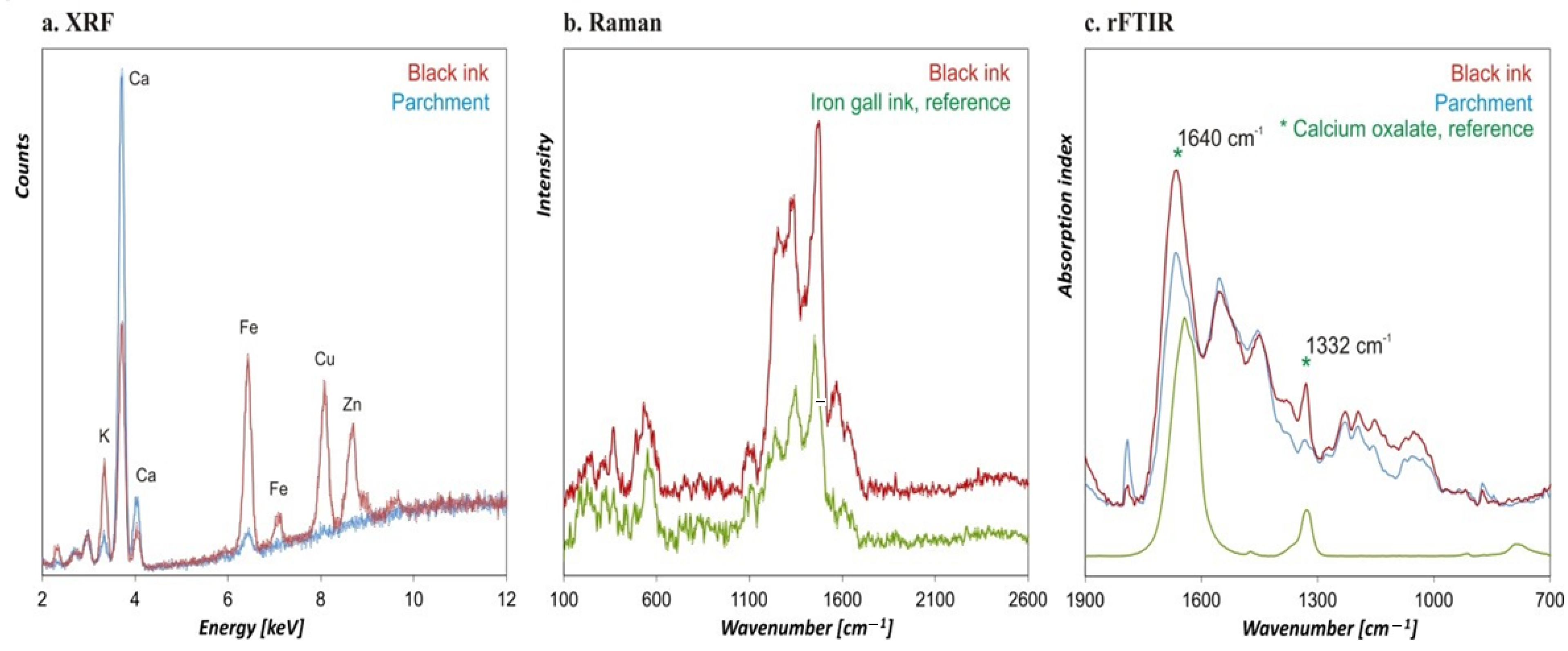
3. Physico-Chemical Analyses
4. Molecular Analyses
4.1. Protein Analysis and Applications
4.2. DNA Analysis
4.2.1. Identification of Animal Skins via DNA Analyses
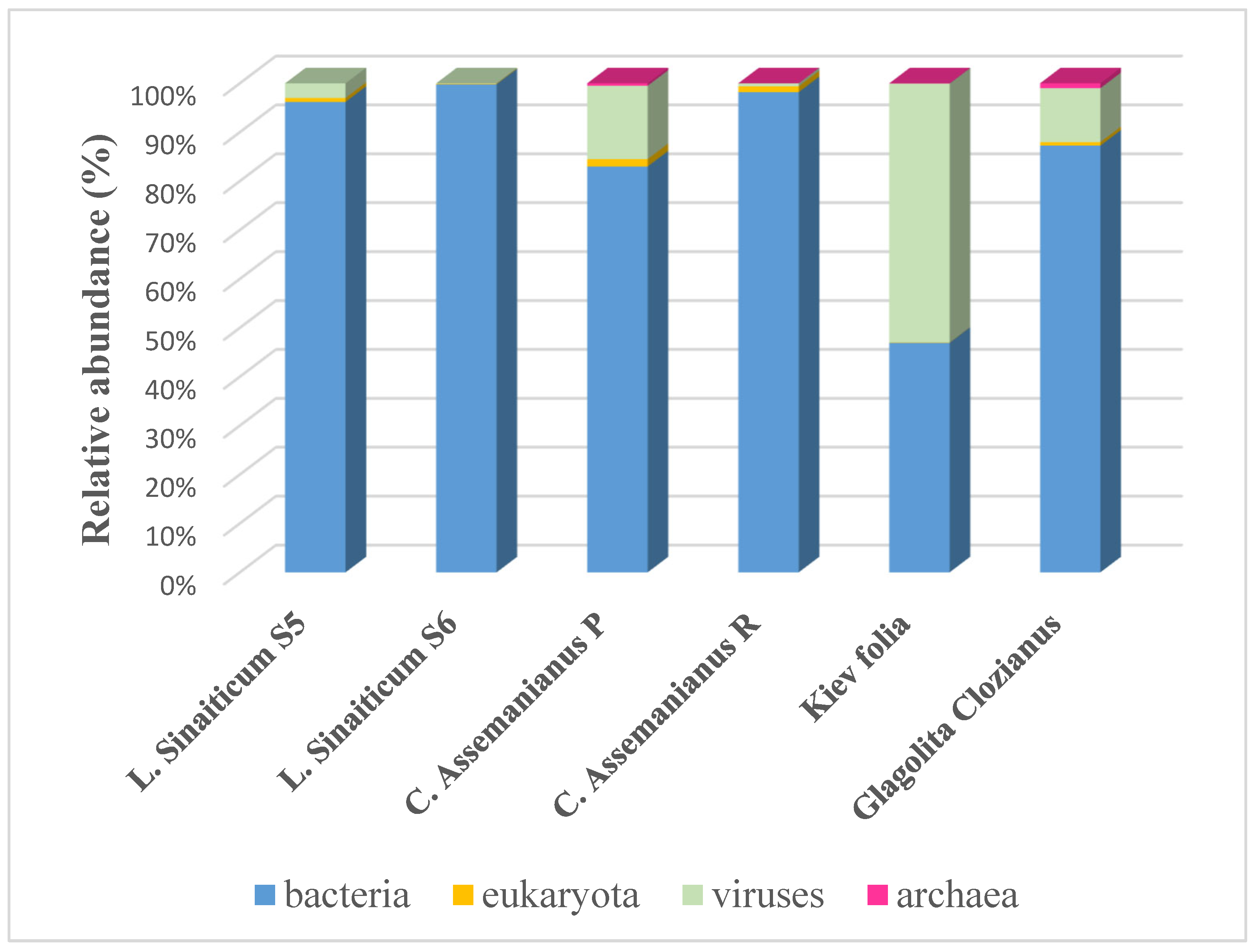
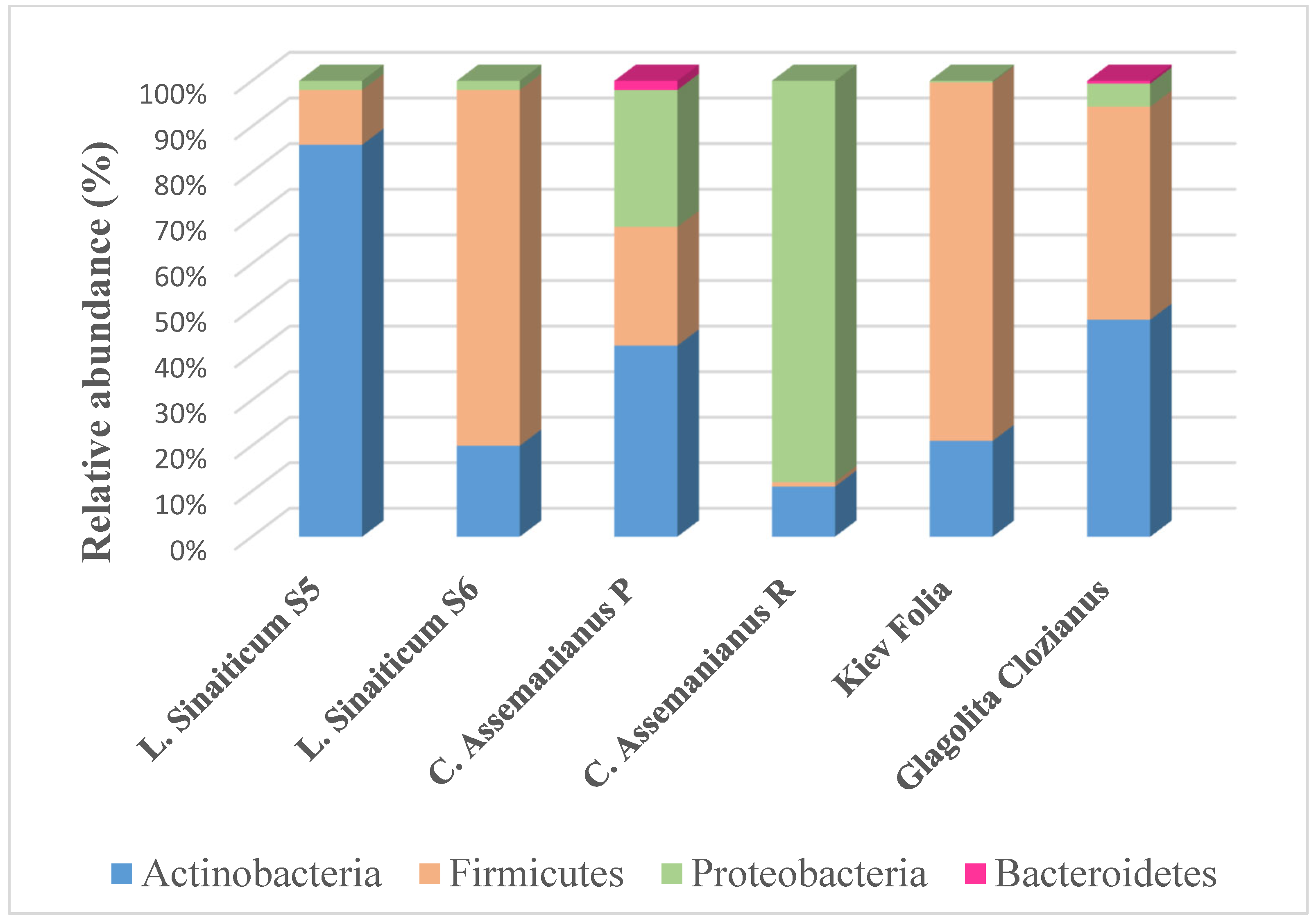
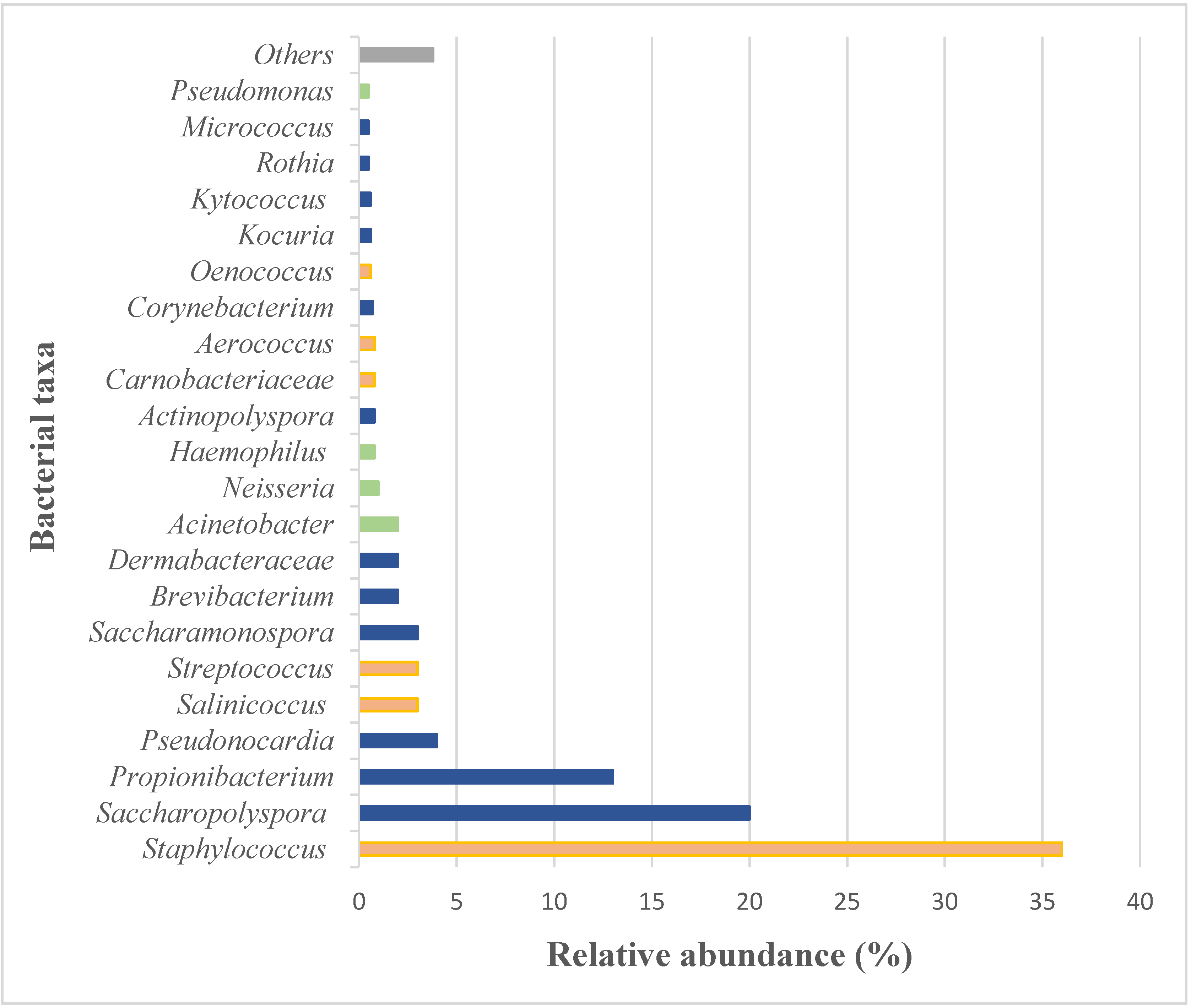
4.2.2. Microbiome Analyses and Applications
Prokaryotic Community in the Microbiome
Eukaryotic Community in the Microbiome
Viruses in Parchments
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Teasdale, M.D.; van Doorn, N.L.; Fiddyment, S.; Webb, C.C.; O’Connor, T.; Hofreiter, M.; Collins, M.J.; Bradley, D.G. Paging through history: Parchment as a reservoir of ancient DNA for next generation sequencing. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 370, 20130379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teasdale, M.D.; Fiddyment, S.; Vnouček, J.; Mattiangeli, V.; Speller, C.; Binois, A.; Carver, M.; Dand, C.; Newfield, T.P.; Webb, C.C.; et al. The york gospels: A 1000-year biological palimpsest. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 4, 170988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piñar, G.; Tafer, H.; Schreiner, M.; Miklas, H.; Sterflinger, K. Decoding the biological information contained in two ancient Slavonic parchment codices: An added historical value. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 3218–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinzari, F.; Gutarowska, B. Extreme Colonizers and Rapid Profiteers: The Challenging World of Microorganisms That Attack Paper and Parchment. In Microorganisms in the Deterioration and Preservation of Cultural Heritage; Joseph, E., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliore, L.; Thaller, M.C.; Vendittozzi, G.; Mejia, A.Y.; Mercuri, F.; Orlanducci, S.; Rubechini, A. Purple spot damage dynamics investigated by an integrated approach on a 1244 A.D. parchment roll from the Secret Vatican Archive. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiddyment, S.; Teasdale, M.D.; Vnouček, J.; Lévêque, É.; Binois, A.; Collins, M.J. So you want to do biocodicology? A field guide to the biological analysis of parchment. Herit. Sci. 2019, 7, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiddyment, S.; Holsinger, B.; Ruzzier, C.; Devine, A.; Binois, A.; Albarella, U.; Fischer, R.; Nichols, E.; Curtis, A.; Cheese, E.; et al. Animal origin of 13th-century uterine vellum revealed using noninvasive peptide fingerprinting. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 15066–15071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappa, F.; Piñar, G.; Brenner, S.; Frühmann, B.; Wetter, W.; Schreiner, M.; Engel, P.; Miklas, H.; Sterflinger, K. The Kiev Folia: An interdisciplinary approach to unravelling the past of an ancient Slavonic manuscript. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2022, 167, 105342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, R. Des Widerspenstigen Zähmung-Pergament in Geschichte und Struktur. In Pergament–Geschichte, Struktur, Restaurierung, Herstellung; Rück, P., Ed.; J. Thorbecke: Sigmaringen, Germany, 1991; ISBN 3799542027. [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff, F.M. Pergamentdicke und Lagenordnung. Beobachtung zur Herstellungstechnik Helmarshausener Evangeliare des 11. und 12. Jahrhunderts. In Pergament–Geschichte, Struktur, Restaurierung, Herstellung; J. Thorbecke: Sigmaringen, Germany, 1991; pp. 97–144. [Google Scholar]
- Ryder, M.L. Parchment—its history, manufacture and composition. J. Soc. Arch. 1960, 2, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, A.M.F.; Bouhy, J.; Dieu, M.; Charles, C.; Deparis, O. Animal species identification in parchments by light. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, R.; Poulsen, D.V.; Odlyha, M.; De Groot, J.; Wang, Q.; Wess, T.; Hiller, J.; Kennedy, C. Damage assessment of parchment: Complexity and relations at different structural levels Giuseppe Della Gatta, Elena Badea and Admir Mas Soghomon Boghosian. In Proceedings of the ICOM-CC 14th Triennial Meeting, The Hague, The Netherlands, 12–16 September 2005; pp. 199–208. [Google Scholar]
- Vilde, V.; Fourneau, M.; Charles, C.; Van Vlaender, D.; Bouhy, J.; Poumay, Y.; Deparis, O. Use of Polarised Light Microscopy to Improve Conservation of Parchment. Stud. Conserv. 2019, 64, 284–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinzari, F.; Colaizzi, P.; Maggi, O.; Persiani, A.M.; Schütz, R.; Rabin, I. Fungal bioleaching of mineral components in a twentieth-century illuminated parchment. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 1541–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, J.; Odlyha, M.; Bozec, L.; Horotn, M.; Masic, A.; Coluccia, S. Damage assessment of parchment by micro-thermal analysis and scanning electron miscroscopy. In Proceedings of the ICOM-CC 14th Triennial Meeting, Hague Volume II, The Hague, The Netherlands, 12–16 September 2005; pp. 759–765. Available online: http://www.bcin.ca/Interface/openbcin.cgi?submit=submit&Chinkey=238589 (accessed on 10 July 2022).
- Sterflinger, K.; Pinzari, F. The revenge of time: Fungal deterioration of cultural heritage with particular reference to books, paper and parchment. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñar, G.; Sterflinger, K.; Ettenauer, J.; Quandt, A.; Pinzari, F. A Combined Approach to Assess the Microbial Contamination of the Archimedes Palimpsest. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 69, 118–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicero, C.; Mercuri, F.; Paoloni, S.; Orazi, N.; Zammit, U.; Glorieux, C.; Thoen, J. Integrated adiabatic scanning calorimetry, light transmission and imaging analysis of collagen deterioration in parchment. Thermochim. Acta 2019, 676, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliore, L.; Perini, N.; Mercuri, F.; Orlanducci, S.; Rubechini, A.; Thaller, M.C. Three ancient documents solve the jigsaw of the parchment purple spot deterioration and validate the microbial succession model. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perini, N.; Mercuri, F.; Thaller, M.C.; Orlanducci, S.; Castiello, D.; Talarico, V.; Migliore, L. The stain of the original salt: Red heats on chrome tanned leathers and Purple spots on ancient parchments are two sides of the same ecological coin. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perini, N.; Mercuri, F.; Orlanducci, S.; Thaller, M.C.; Migliore, L. The Integration of Metagenomics and Chemical Physical Techniques Biodecoded the Buried Traces of the Biodeteriogens of Parchment Purple Spots. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 598945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappa, F.; Fruehmann, B.; Schreiner, M. Raman Spectroscopy for the Material Analysis of Medieval Manuscripts. In Nanotechnologies and Nanomaterials for Diagnostic, Conservation, and Restoration of Cultural Heritage; Lazzara, G., Fakhrullin, R., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 127–147. ISBN 9780128139103. [Google Scholar]
- Frühmann, B.; Cappa, F.; Vetter, W.; Schreiner, M. Father Petrus Multianalytical approach for the analysis of the Codices Millenarius Maior and Millenarius Minor in Kremsmuenster Abbey, Upper Austria. Herit. Sci. 2018, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetter, W.; Frühmann, B.; Cappa, F.; Schreiner, M. Materials and techniques used for the “Vienna Moamin”: Multianalytical investigation of a book about hunting with falcons from the thirteenth century. Herit. Sci. 2021, 9, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappa, F.; Schreiner, M.; Zoleo, A. Preliminary Studies of Parchment and Ink Degradation in Medieval Manuscripts promoted by Light and Heat. In Ink Corrosion–the Missing Links; Berger, Ferdinand Verlag: Horn, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Vetter, W.; Schreiner, M.; Frühmann, B.; Cappa, F. Three complementary non-invasive methods applied to historical manuscripts. In Manuscript cultures 11, Proceedings of the ‘Second International Conference on Natural Sciences and Technology in Manuscript Analysis’ at the University of Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany, 13–14 June 2018; University of Hamburg: Hamburg, Germany; pp. 97–108. Available online: https://www.csmc.uni-hamburg.de/publications/mc/mc11.html (accessed on 6 July 2022).
- Cappa, F.; Sterflinger, K. Non-Invasive Physico-Chemical and Biological Analysis of Parchment Manuscripts–An Overview. Restaur. Int. J. Preserv. Libr. Arch. Mater. 2022, 43, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, B.; Daveri, A.; Clementi, C.; Romani, A.; Bioletti, S.; Brunetti, B.; Sgamellotti, A.; Miliani, C. The Book of Kells: A non-invasive MOLAB investigation by complementary spectroscopic techniques. Spectrochim. Acta-Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2013, 115, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badillo-Sanchez, D.; Chelazzi, D.; Giorgi, R.; Cincinelli, A.; Baglioni, P. Characterization of the secondary structure of degummed Bombyx mori silk in modern and historical samples. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 157, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magistro, F.; Majolino, D.; Migliardo, P.; Ponterio, R.; Rodriquez, M.T. Confocal Raman spectroscopic study of painted medieval manuscripts. J. Cult. Herit. 2001, 2, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastaugh, N.; Walsh, V.; Chaplin, T. Pigment Compendium: A Dictionary of Historical Pigments; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, D.V. The Materials and Techniques of Medieval Paintings; Dover Publ.: New York, NY, USA, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Bicchieri, M.; Biocca, P.; Colaizzi, P.; Pinzari, F. Microscopic observations of paper and parchment: The archaeology of small objects. Herit. Sci. 2019, 7, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marvasi, M.; Cavalieri, D.; Mastromei, G.; Casaccia, A.; Perito, B. Omics technologies for an in-depth investigation of biodeterioration of cultural heritage. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2019, 144, 104736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutarowska, B. The use of -omics tools for assessing biodeterioration of cultural heritage: A review. J. Cult. Herit. 2020, 45, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñar, G.; Sterflinger, K. Natural sciences at the service of art and cultural heritage: An interdisciplinary area in development and important challenges. Microb. Biotechnol. 2021, 14, 806–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, D.P.; Buckley, M.; Promise, E.; Trauger, S.A.; Holdcraft, T.R. Identification of collagen-based materials in cultural heritage. Analyst 2013, 138, 4849–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toniolo, L.; D’Amato, A.; Saccenti, R.; Gulotta, D.; Righetti, P.G. The Silk Road, Marco Polo, a bible and its proteome: A detective story. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 3365–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, S.P.; Henderson, S.; Fiddyment, S.; Finch, J.; Collins, M.J. Scratching the surface: The use of sheepskin parchment to deter textual erasure in early modern legal deeds. Herit. Sci. 2021, 9, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, G. Labour productivity in English agriculture, 1300–1860. In Land, Labour and livestock: Historical Studies in European Agricultural Productivity; Manchester University Press: Manchester, UK, 1991; pp. 211–235. [Google Scholar]
- Koppenhoefer, R.M. The lipids of sheepskins. I. Lipid of fresh sheepskin. J. Am. Leather. Chem. As. 1938, 15, 33–203. [Google Scholar]
- Palop, R. Sheepskin and Cattle Hide Degreasing; Cromogenia Linits: Barcelona, Spain, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bower, M.A.; Campana, M.G.; Checkley-Scott, C.; Knight, B.; Howe, C.J. The potential for extraction and exploitation of DNA from parchment: A review of the opportunities and hurdles. J. Inst. Conserv. 2010, 33, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J.; Hummel, S.; Herrmann, B. Palaeogenetics and cultural heritage. Species determination and STR-genotyping from ancient DNA in art and artefacts. Thermochim. Acta 2000, 365, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulakakis, N.; Tselikas, A.; Bitsakis, I.; Mylonas, M.; Lymberakis, P. Ancient DNA and the genetic signature of ancient Greek manuscripts. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2007, 34, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campana, M.G.; Bower, M.A.; Bailey, M.J.; Stock, F.; O’Connell, T.C.; Edwards, C.J.; Checkley-Scott, C.; Knight, B.; Spencer, M.; Howe, C.J. A flock of sheep, goats and cattle: Ancient DNA analysis reveals complexities of historical parchment manufacture. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2010, 37, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangallo, D.; Chovanova, K.; Makova, A. Identification of animal skin of historical parchments by polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based methods. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2010, 37, 1202–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lech, T. Ancient DNA in historical parchments-Identifying a procedure for extraction and amplification of genetic material. Genet. Mol. Res. 2016, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuissoz, A.; Worobey, M.; Odegaard, N.; Bunce, M.; Machado, C.A.; Lynnerup, N.; Peacock, E.E.; Gilbert, M.T.P. The survival of PCR-amplifiable DNA in cow leather. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2007, 34, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñar, G.; Sterflinger, K.; Pinzari, F. Unmasking the measles-like parchment discoloration: Molecular and microanalytical approach. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 427–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lech, T. Evaluation of a parchment document, the 13th century incorporation charter for the city of Krakow, Poland, for microbial hazards. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 2620–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadrucci, M.; Borgognoni, F.; Cicero, C.; Perini, N.; Migliore, L.; Mercuri, F.; Orazi, N.; Rubechini, A. Parchment processing and analysis: Ionizing radiation treatment by the REX source and multidisciplinary approach characterization. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2019, 149, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñar, G.; Sclocchi, M.C.; Pinzari, F.; Colaizzi, P.; Graf, A.; Sebastiani, M.L.; Sterflinger, K. The Microbiome of Leonardo da Vinci’s Drawings: A Bio-Archive of Their History. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, J.; Briggs, A.W.; Kircher, M.; Maricic, T.; Zwyns, N.; Derevianko, A.; Pääbo, S. A Complete mtDNA Genome of an Early Modern Human from Kostenki, Russia. Curr. Biol. 2010, 20, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, L.D.; Whitehead, P.; Whitehead, A. Genetic analysis identifies the missing parchment of New Zealand’s founding document, the Treaty of Waitangi. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paabo, S. Ancient DNA: Extraction, characterization, molecular cloning, and enzymatic amplification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 1939–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pääbo, S.; Poinar, H.; Serre, D.; Jaenicke-Després, V.; Hebler, J.; Rohland, N.; Kuch, M.; Krause, J.; Vigilant, L.; Hofreiter, M. Genetic analyses from ancient DNA. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2004, 38, 645–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofreiter, M.; Serre, D.; Poinar, H.N.; Kuch, M.; Pääbo, S. Hofreiter_Ancient_NatRevGen_2001_1556040. Nat. Commun. 2001, 2, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Green, E.J.; Speller, C.F. Novel substrates as sources of ancient DNA: Prospects and hurdles. Genes 2017, 8, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campana, M.G.; Robinson, T.; Campos, P.F.; Tuross, N. Independent confirmation of a diagnostic sheep/goat peptide sequence through DNA analysis and further exploration of its taxonomic utility within the Bovidae. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2013, 40, 1421–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anava, S.; Neuhof, M.; Gingold, H.; Sagy, O.; Munters, A.; Svensson, E.M.; Afshinnekoo, E.; Danko, D.; Foox, J.; Shor, P.; et al. Illuminating Genetic Mysteries of the Dead Sea Scrolls. Cell 2020, 181, 1218–1231.e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliore, L.; Perini, N.; Alabiso, A. May metagenomics disclose the hidden secrets of the ancient damaged parchments? In Proceedings of the IMEKO TC4 International Conference on Metrology for Archaeology and Cultural Heritage, Online, 22–24 October 2020; pp. 590–593. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, R. The Nature and Making of Parchment; The Elemen: Leeds, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, D.G. The preservation of hides and skins. J. Am. Leath. Chem. Ass 2003, 98, 308–319. [Google Scholar]
- Hernàndez, E.; Marmer, W.; Kolomazník, K.; Cooke, P.; Dudley, R. Mathematical model of raw hide curing with brine. J. Am. Leath. Chem. Ass 2008, 103, 167–173. [Google Scholar]
- Chun, J.; Bae, K.S.; Moon, E.Y.; Jung, S.O.; Lee, H.K.; Kim, S.J. Nocardiopsis kunsanensis sp. nov., a moderately halophilic actinomycete isolated from a saltern. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2000, 50, 1909–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.G.; Li, W.J.; Xu, P.; Cui, X.L.; Xu, L.H.; Jiang, C.L. Nocardiopsis xinjiangensis sp. nov., a halophilic actinomycete isolated from a saline soil sample in China. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraková, L.; Chovanová, K.; Selim, S.A.; Šimonovičová, A.; Puškarová, A.; Maková, A.; Pangallo, D. A multiphasic approach for investigation of the microbial diversity and its biodegradative abilities in historical paper and parchment documents. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2012, 70, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennur, T.; Kumar, A.R.; Zinjarde, S.; Javdekar, V. Nocardiopsis species: Incidence, ecological roles and adaptations. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 174, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waino, M. Gracilibacillus gen. nov., with description of Gracilibacillus halotolerans gen. nov., sp. nov.; transfer of Bacillus dipsosauri to Gracilibacillus dipsosauri comb, nov., and Bacillus salexigens to the genus Salibacillus gen. nov., as Salibacillus salexig. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1999, 49, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirota, K.; Hanaoka, Y.; Nodasaka, Y.; Yumoto, I. Gracilibacillus alcaliphilus sp. nov., a facultative alkaliphile isolated from indigo fermentation liquor for dyeing. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 3174–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varbanets, L.D.; Matseliukh, O.V.; Avdiiuk, K.V.; Hudzenko, O.V.; Nidialkova, N.A.; Romanovs’ka, V.O.; Tashirev, O.B. Hydrolytic activity of microorganisms of the Dead Sea coastal ecosystems. Mikrobiol. Z 2014, 76, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, D.W.; Heo, S.; Ryu, S.; Blom, J.; Lee, J.H. Genomic insights into the virulence and salt tolerance of Staphylococcus equorum. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Heo, S.; Jeong, D.W. Genomic insights into Staphylococcus equorum KS1039 as a potential starter culture for the fermentation of high-salt foods. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, V.; Oren, A. Metabolism of chloride in halophilic prokaryotes. Extremophiles 2003, 7, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.J.; Chen, H.H.; Xu, P.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Schumann, P.; Tang, S.K.; Xu, L.H.; Jiang, C.L. Yania halotolerans gen nov., sp. nov., a novel member of the suborder Micrococcineae from saline soil in China. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, B. What Have We Learned about the Microbiomes of Indoor Environments? mSystems 2016, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattray, F.P.; Fox, P.F. Aspects of Enzymology and Biochemical Properties of Brevibacterium linens Relevant to Cheese Ripening: A Review. J. Dairy Sci. 1999, 82, 891–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siński, E.; Behnke, J.M. Apicomplexan parasites: Environmental contamination and transmission. Polish J. Microbiol. 2004, 53, 67–73. [Google Scholar]
- Chartier, C.; Paraud, C. Coccidiosis due to Eimeria in sheep and goats, a review. Small Rumin. Res. 2012, 103, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polacheck, I.; Salkin, I.F.; Schenhav, D.; Ofer, L.; Maggen, M.; Haines, J.H. Aspergillus. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1989, 8, 413–437. [Google Scholar]
- Troiano, F.; Polo, A.; Villa, F.; Cappitelli, F. Assessing the microbiological risk to stored sixteenth century parchment manuscripts: A holistic approach based on molecular and environmental studies. Biofouling 2014, 30, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva de Carvalho, H.; Mesquita, N.; Trovão, J.; Peixoto da Silva, J.; Rosa, B.; Martins, R.; Bandeira, A.M.L.; Portugal, A. Diversity of fungal species in ancient parchments collections of the Archive of the University of Coimbra. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 108, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinzari, F. Microbial processes involved in the deterioration of paper and parchment. In Biodeterioration and Preservation in Art, Archaeology and Architecture; Mitchell, R., Clifford, J., Eds.; Archetype Publications: London, UK, 2018; pp. 33–56. [Google Scholar]
- Vijaya Chandra, S.H.; Srinivas, R.; Dawson, T.L.; Common, J.E. Cutaneous Malassezia: Commensal, Pathogen, or Protector? Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemmer, C.M.; DeAngelis, Y.M.; Theelen, B.; Boekhout, T.; Dawson, T.L. Fast, noninvasive method for molecular detection and differentiation of Malassezia yeast species on human skin and application of the method to dandruff microbiology. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 3350–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triana, S.; de Cock, H.; Ohm, R.A.; Danies, G.; Wösten, H.A.B.; Restrepo, S.; González Barrios, A.F.; Celis, A. Lipid metabolic versatility in Malassezia spp. yeasts studied through metabolic modeling. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duerkop, B.A.; Hooper, L.V. Resident viruses and their interactions with the immune system. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotondo, J.C.; Bononi, I.; Puozzo, A.; Govoni, M.; Foschi, V.; Lanza, G.; Gafa, R.; Gaboriaud, P.; Touzé, F.A.; Selvatici, R.; et al. Merkel cell carcinomas arising in autoimmune disease affected patients treated with biologic drugs including anti-TNF. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 3929–3934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schowalter, R.M.; Pastrana, D.V.; Pumphrey, K.A.; Moyer, A.L.; Buck, C.B. Merkel cell polyomavirus and two previously unknown polyomaviruses are chronically shed from human skin. Cell Host Microbe 2010, 7, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, D.F.; Querat, G. A history of ovine pulmonary adenocarcinoma (jaagsiekte) and experiments leading to the deduction of the JSRV nucleotide sequence. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2003, 275, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Arnaud, F.; Varela, M.; Spencer, T.E.; Palmarini, M. Coevolution of endogenous betaretroviruses of sheep and their host. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 3422–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chessa, B.; Pereira, F.; Arnaud, F.; Amorim, A.; Goyache, F.; Mainland, I. Revealing the history of sheep domestication using retrovirus integrations. Science 2009, 324, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusop, M.S.M.; Saad, M.F.M.; Talip, N.; Baharum, S.N.; Bunawan, H. A Review on Viruses Infecting Taro. Pathogens 2019, 8, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Fukuhara, T.; Kitazawa, H.; Kormelink, R. Virus Latency and the Impact on Plants. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimaldi, I.M.; Muthukumaran, S.; Tozzi, G.; Nastasi, A.; Boivin, N.; Matthews, P.J.; Van Andel, T. Literary evidence for taro in the ancient Mediterranean: A chronology of names and uses in a multilingual world. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghan, H.T.; Kao-Jao, H.C.; Nakayama, T.O.M. Anthocyanin Composition of Taro. J. Food Sci. 1977, 42, 19–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicchieri, M. The purple Codex Rossanensis: Spectroscopic characterisation and first evidence of the use of the elderberry lake in a sixth century manuscript. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 14146–14157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiner, M.; Hammerschmid, E.G.; Melcher, M. Materialanalytische Untersuchungen mittels portabler Röntgenfluoreszenzanalyse (RFA) an Sinaitischen glagolitischen Sakramentarfragmenten im Katharinen-Kloster, Sinai/Ägypten; Institute of Science and Technology in Art, Academy of Fine Arts Vienna: Vienna, Austria, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Miklas, H. Zur editorischen Vorbereitung des sog. Missale Sinaiticum (Sin. slav. 5/N). In Glagolitica–Zum Ursprung der slavischen Schriftkultur; Österreichische Akademie der Wissenschaften: Wien, Austria, 2000; pp. 117–129. [Google Scholar]
- Babiuk, S.; Bowden, T.R.; Boyle, D.B.; Wallace, D.B.; Kitching, R.P. Capripoxviruses: An emerging worldwide threat to sheep, goats and cattle. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2008, 55, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIver, L.J.; Abu-Ali, G.; Franzosa, E.A.; Schwager, R.; Morgan, X.C.; Waldron, L.; Segata, N.; Huttenhower, C. bioBakery: A metageomic analysis environment. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 1235–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, D.T.; Franzosa, E.; Tickle, T.L.; Scholz, M.; Weingart, G.; Pasolli, E. MetaPhlAn2 for enhanced metagenomic taxonomic profiling. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 902–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asnicar, F.; Weingart, G.; Tickle, T.L.; Huttenhower, C.; Segata, N. Compact graphical representation of phylogenetic data and metadata with GraPhlAn. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondov, B.D.; Bergman, N.H.; Phillippy, A.M. Interactive metagenomic visualization in a Web browser. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingett, S.W.; Andrews, S. FastQ Screen: A tool for multi-genome mapping and quality control. F1000Research 2018, 7, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Codex | Homo sapiens | Bos taurus | Ovis aries | Capra hircus |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liturgiarium Sinaiticum S5 | 208,416 | 15,204 | 49,223 | 8803 |
| Liturgiarium Sinaiticum S6 | 64,370 | 4630 | 483 | 174 |
| Codex Assemanianus P | 7,852,951 | 13,544 | 55,146 | 11,576 |
| Codex Assemanianus R | 143,268 | 19,958 | 24,465 | 3972 |
| Kiev Folia | 5,903,087 | 356,967 | 289,404 | 347,337 |
| Glagolita Clozianus | 243,594 | 180,518 | 224,188 | 59,737 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piñar, G.; Cappa, F.; Vetter, W.; Schreiner, M.; Miklas, H.; Sterflinger, K. Complementary Strategies for Deciphering the Information Contained in Ancient Parchment Documentary Materials. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10479. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122010479
Piñar G, Cappa F, Vetter W, Schreiner M, Miklas H, Sterflinger K. Complementary Strategies for Deciphering the Information Contained in Ancient Parchment Documentary Materials. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(20):10479. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122010479
Chicago/Turabian StylePiñar, Guadalupe, Federica Cappa, Wilfried Vetter, Manfred Schreiner, Heinz Miklas, and Katja Sterflinger. 2022. "Complementary Strategies for Deciphering the Information Contained in Ancient Parchment Documentary Materials" Applied Sciences 12, no. 20: 10479. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122010479
APA StylePiñar, G., Cappa, F., Vetter, W., Schreiner, M., Miklas, H., & Sterflinger, K. (2022). Complementary Strategies for Deciphering the Information Contained in Ancient Parchment Documentary Materials. Applied Sciences, 12(20), 10479. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122010479







