Development and Characterization of a Low-Fat Mayonnaise Salad Dressing Based on Arthrospira platensis Protein Concentrate and Sodium Alginate
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Spirulina Conditioning and Protein Extraction
2.2. Protein Concentrates Characterization
2.2.1. Protein Content
2.2.2. Water Holding Capacity (WHC) and Oil Holding Capacity (OHC)
2.3. Mayonnaise Preparation
2.4. Mayonnaise Characterization
2.4.1. Stability Analysis
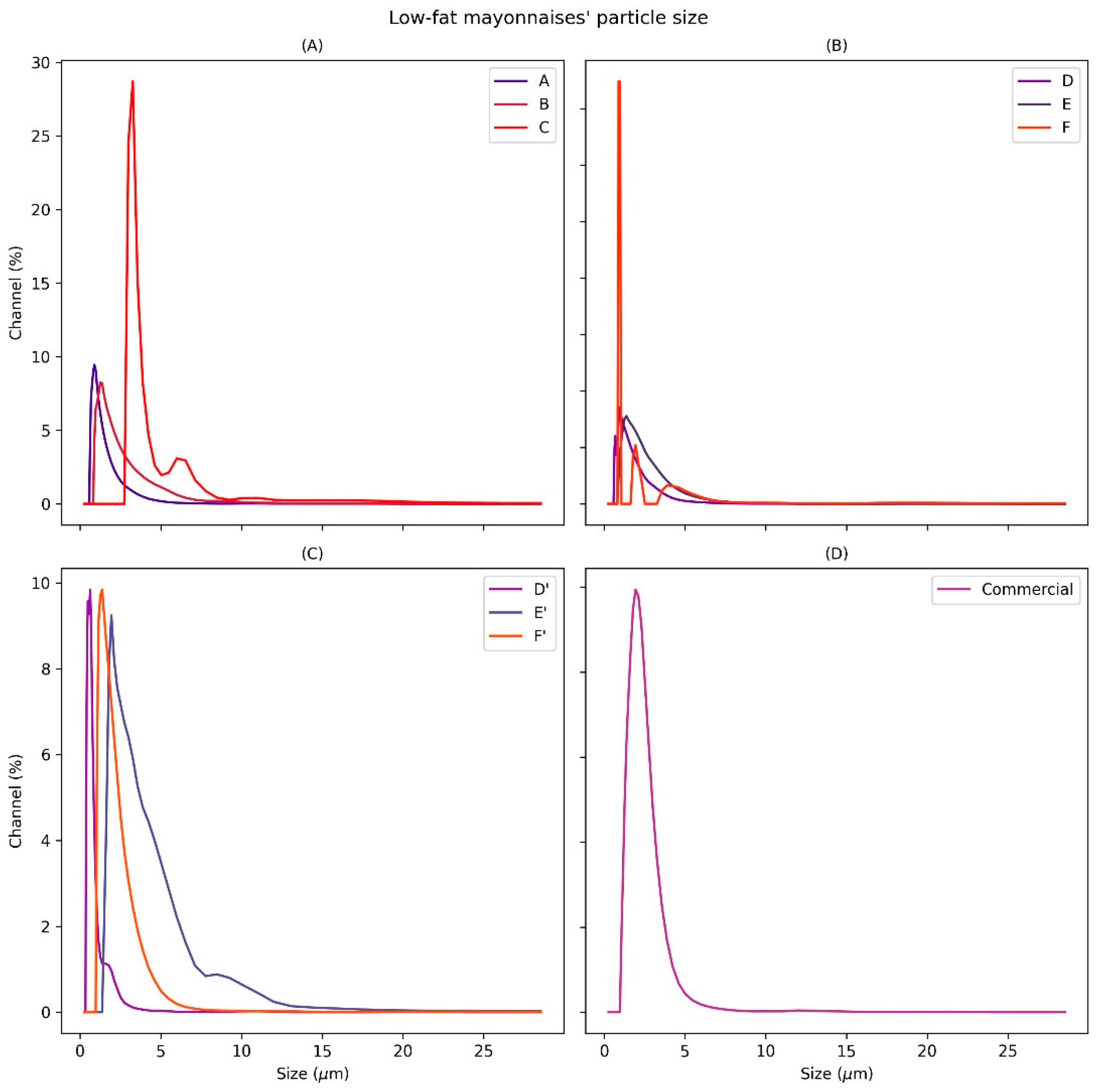
2.4.2. Particle Size Analysis
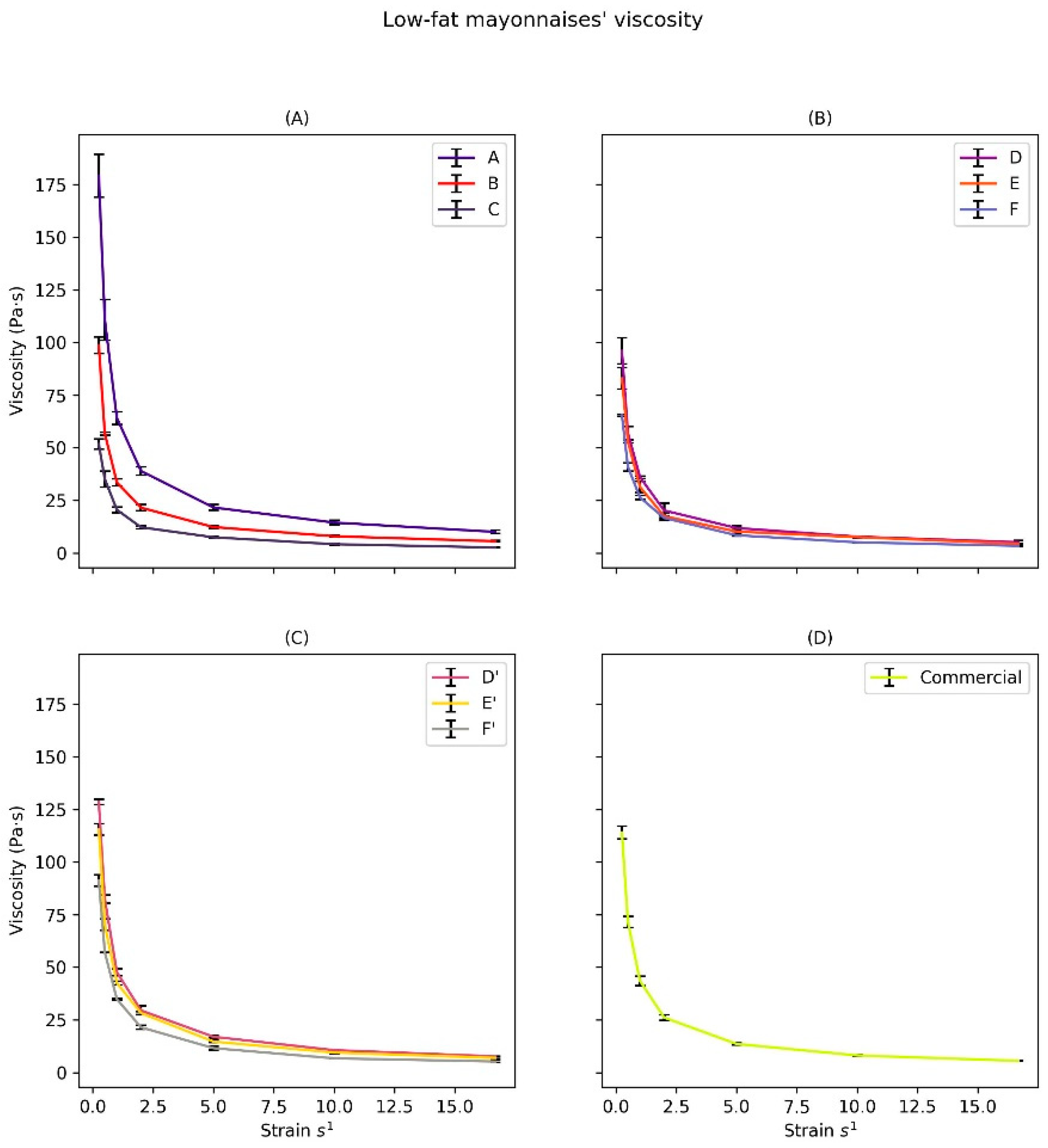
2.4.3. Rheological Characterization
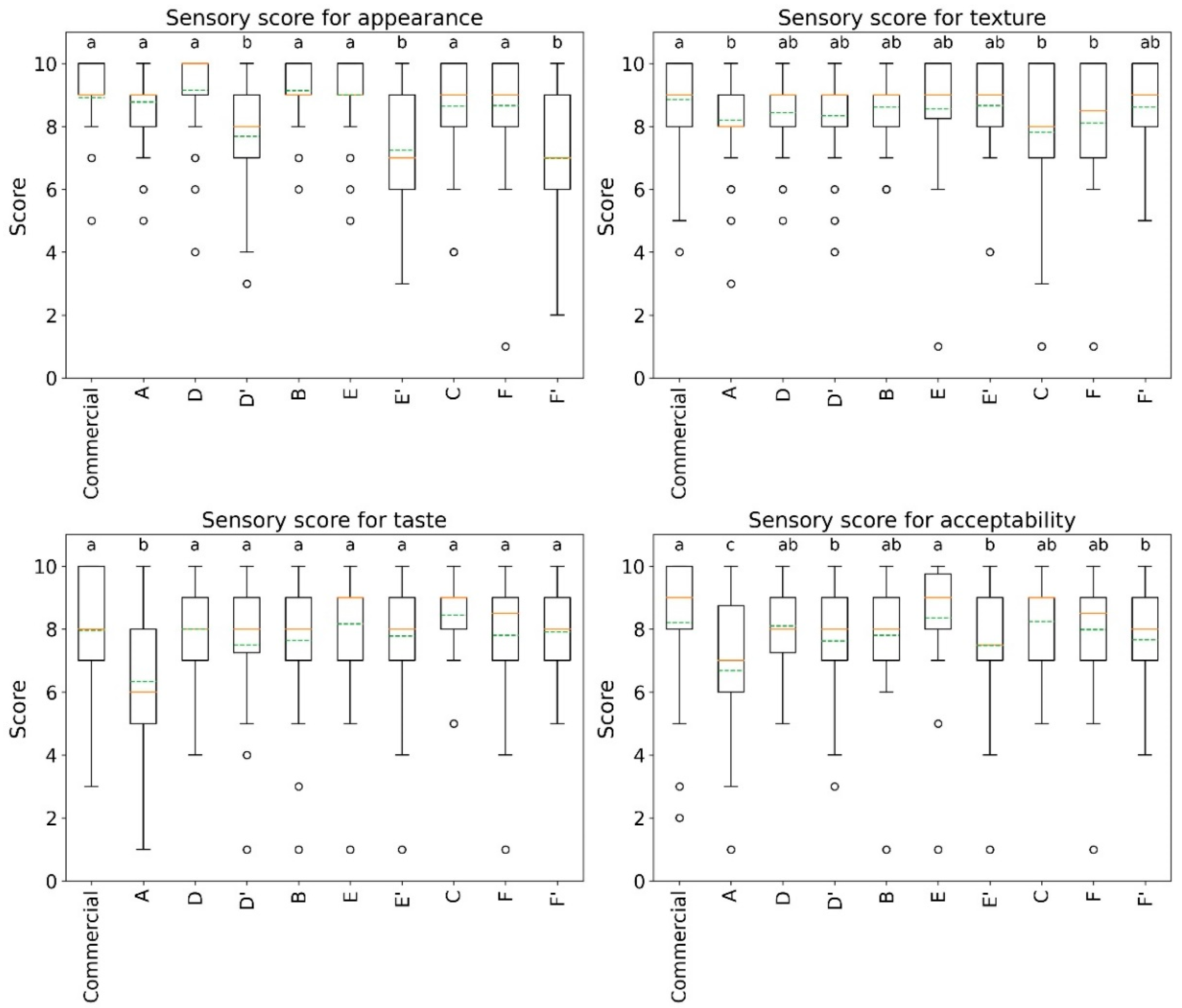
2.4.4. Sensory Analysis
2.4.5. Amino Acid Bioavailability
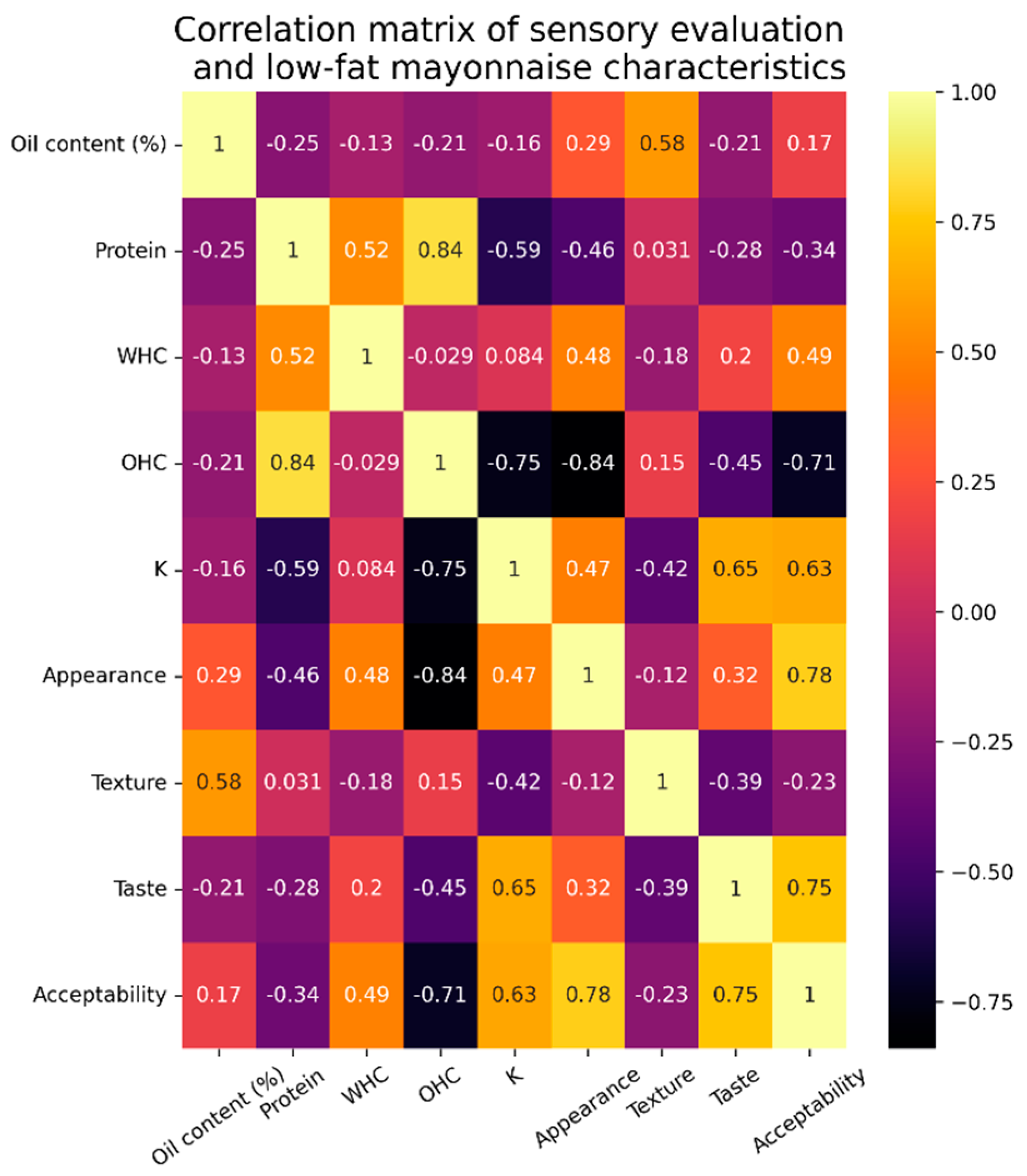
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Protein Concentrates Characterization and Techno-Functional Properties
3.2. Mayonnaise Characterization
3.2.1. Stability Analysis
3.2.2. Particle Size Analysis
3.2.3. Rheological Characterization
3.2.4. Sensory Analysis
3.2.5. Amino Acid Bioavailability
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maruyama, S.; Streletskaya, N.A.; Lim, J. Clean label: Why this ingredient but not that one? Food Qual. Prefer. 2020, 87, 104062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taslikh, M.; Mollakhalili-Meybodi, N.; Alizadeh, A.M.; Mousavi, M.-M.; Nayebzadeh, K.; Mortazavian, A.M. Mayonnaise main ingredients influence on its structure as an emulsion. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 59, 2108–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzanajafi-Zanjani, M.; Yousefi, M.; Ehsani, A. Challenges and approaches for production of a healthy and functional mayonnaise sauce. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 2471–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teklehaimanot, W.H.; Duodu, K.G.; Emmambux, M.N. Maize and teff starches modified with stearic acid as potential fat replacer in low calorie mayonnaise-type emulsions. Starch-Stärke 2013, 65, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agyei-Amponsah, J.; Macakova, L.; DeKock, H.L.; Emmambux, M.N. Effect of Substituting Sunflower Oil with Starch-Based Fat Replacers on Sensory Profile, Tribology, and Rheology of Reduced-Fat Mayonnaise-Type Emulsions. Starch-Stärke 2021, 73, 2000092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Lien, C.; Lee, T.; Ho, J. Development of Low-fat Mayonnaise Containing Polysaccharide Gums as Functional Ingredi-ents. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, R.; Singh, N.; Kaur, A. Properties of octenyl succinic anhydride (OSA) modified starches and their application in low fat mayonnaise. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.J.; Olawuyi, I.; Lee, W.Y. Characteristics of low-fat mayonnaise using different modified arrowroot starches as fat replacer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 153, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, P.; Fiszman, S. Exploring consumers’ knowledge and perceptions of hydrocolloids used as food additives and ingredients. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 30, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farjami, T.; Madadlou, A. An overview on preparation of emulsion-filled gels and emulsion particulate gels. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 86, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geremias-Andrade, I.M.; Souki, N.P.; Moraes, I.C.; Pinho, S.C. Rheology of Emulsion-Filled Gels Applied to the Development of Food Materials. Gels 2016, 2, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Gong, T.; Hou, Y.; Yang, X.; Guo, Y. Alginate-stabilized thixotropic emulsion gels and their applications in fabrication of low-fat mayonnaise alternatives. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 146, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Gong, T.; Lu, Y.-H.; Li, A.; Sun, L.; Guo, Y. Compatibility of sodium alginate and konjac glucomannan and their applications in fabricating low-fat mayonnaise-like emulsion gels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benslima, A.; Sellimi, S.; Hamdi, M.; Nasri, R.; Jridi, M.; Cot, D.; Li, S.; Nasri, M.; Zouari, N. The brown seaweed Cystoseira schiffneri as a source of sodium alginate: Chemical and structural characterization, and antioxidant activities. Food Biosci. 2020, 40, 100873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Rodrigues, M.; Estrada-Beristain, C.; Metri-Ojeda, J.; Pérez-Alva, A.; Baigts-Allende, D. Spirulina platensis Protein as Sustainable Ingredient for Nutritional Food Products Development. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Tiji, Y.; Fields, F.J.; Mayfield, S.P. Microalgae as a future food source. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 41, 107536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benelhadj, S.; Gharsallaoui, A.; Degraeve, P.; Attia, H.; Ghorbel, D. Effect of pH on the functional properties of Arthrospira (Spirulina) platensis protein isolate. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 1056–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böcker, L.; Bertsch, P.; Wenner, D.; Teixeira, S.; Bergfreund, J.; Eder, S.; Fischer, P.; Mathys, A. Effect of Arthrospira platensis microalgae protein purification on emulsification mechanism and efficiency. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 584, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menegotto, A.L.L.; de Souza, L.E.S.; Colla, L.M.; Costa, J.A.V.; Sehn, E.; Bittencourt, P.R.S.; Flores, L.D.M.; Canan, C.; Colla, E. Investigation of techno-functional and physicochemical properties of Spirulina platensis protein concentrate for food enrichment. LWT 2019, 114, 108267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yücetepe, A.; Saroğlu, Ö.; Özçelik, B. Response surface optimization of ultrasound-assisted protein extraction from Spirulina platensis: Investigation of the effect of extraction conditions on techno-functional properties of protein concentrates. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 3282–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojeda, J.M.; Rodrigues, M.R.; Allende, D.B. Study of the perception and the acceptability of mayonnaise ingredients among Mexican consumers and its global preference. Rev. Española De Nutr. Hum. Y Dietética 2022, 26, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, A.K.; Avarmenko, N.A.; Warkentin, T.D.; Nickerson, M.T. Functional properties of protein isolates from different pea cultivars. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 24, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourbehesht, N.; Shekarchizadeh, H.; Soltanizadeh, N. Investigation of stability, consistency, and oil oxidation of emulsion filled gel prepared by inulin and rice bran oil using ultrasonic radiation. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2018, 42, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Z.; Luo, D.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Shah, B.R. Stability, microstructural and rheological properties of complex prebiotic emulsion stabilized by sodium caseinate with inulin and konjac glucomannan. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 105, 105772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, Y.; Roy, S.; Devra, A.; Dhiman, A.; Prabhakar, P.K. Ultrasonication of mayonnaise formulated with xanthan and guar gums: Rheological modeling, effects on optical properties and emulsion stability. LWT 2021, 149, 111632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukkwai, S.; Chonpracha, P.; Kijroongrojana, K.; Prinyawiwatkul, W. Influences of a natural colourant on colour and salty taste perception, liking, emotion and purchase intent: A case of mayonnaise-based dipping sauces. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 2256–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, X.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, J.; Li, W.; Chen, X.; Jiang, M.; Dong, M. Does lactic fermentation influence soy yogurt protein digestibility: A comparative study between soymilk and soy yogurt at different pH. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 99, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, S.-M.; Choi, M.-H.; Park, S.-H.; Gu, Y.-U.; Oh, J.-M.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.-Y.; Kim, G.-H.; Lee, Y. Assessing the digestibility of genetically modified soybean: Physiologically based in vitro digestion and fermentation model. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, K. Automatic Precolumn Derivatization of Amino Acids and Analysis by Fast LC Using the Agilent 1290 Infinity LC System. Agil. Tech. Note 2010, 5990, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Zaiontz, C. Real Statistics Software. Available online: https://www.real-statistics.com/appendix/citation-real-statistics-software-website/ (accessed on 5 February 2022).
- Safi, C.; Ursu, A.V.; Laroche, C.; Zebib, B.; Merah, O.; Pontalier, P.-Y.; Vaca-Garcia, C. Aqueous extraction of proteins from microalgae: Effect of different cell disruption methods. Algal Res. 2014, 3, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bleakley, S.; Hayes, M. Functional and Bioactive Properties of Protein Extracts Generated from Spirulina platensis and Isochrysis galbana T-Iso. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozober, H.S.; Okun, Z.; Shpigelman, A. The impact of high-pressure homogenization on thermal gelation of Arthrospira platensis (Spirulina) protein concentrate. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 74, 102857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, A.K.; Karalash, A.; Tyler, R.T.; Warkentin, T.D.; Nickerson, M.T. Functional attributes of pea protein isolates prepared using different extraction methods and cultivars. Food Res. Int. 2015, 76, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro-Diaz, A.; Urías-Silvas, J.; Loarca-Piña, G.; Gaytan-Martínez, M.; Prado-Ramirez, R.; Mojica, L. Techno-functional properties of thermally treated black bean protein concentrate generated through ultrafiltration process. LWT 2020, 136, 110296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Zhao, Y.; Li, T.; Li, D.; Chen, S.; Wu, N.; Jiang, L.; Wang, L. Effect of electrochemical modification on the structural characteristics and emulsion storage stability of soy protein isolate. Process. Biochem. 2018, 75, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bühler, J.M.; Dekkers, B.L.; Bruins, M.E.; van der Goot, A.J. Modifying Faba Bean Protein Concentrate Using Dry Heat to Increase Water Holding Capacity. Foods 2020, 9, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe-Wandurraga, Z.N.; Martínez-Sánchez, I.; Savall, C.; García-Segovia, P.; Martínez-Monzó, J. Microalgae fortification of low-fat oil-in-water food emulsions: An evaluation of the physicochemical and rheological properties. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 58, 3701–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Babu, K.S.; Amamcharla, J.; Li, Y. Emulsifying properties of pea protein/guar gum conjugates and mayonnaise application. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 3955–3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carcelli, A.; Crisafulli, G.; Carini, E.; Vittadini, E. Can a Physically Modified Corn Flour Be Used as Fat Replacer in a May-onnaise? Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2020, 246, 2493–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, A.C.; Moraes, K.; Cunha, R. Development of gelled emulsions with improved oxidative and pH stability. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 34, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, A.; Yu, W.; Li, X.; Sun, L.; Xue, J.; Guo, Y. Structuring Oil-in-Water Emulsion by Forming Egg Yolk/Alginate Complexes: Their Potential Application in Fabricating Low-Fat Mayonnaise-like Emulsion Gels and Redispersible Solid Emul-sions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 147, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Jin, W.; Zhou, B.; Li, B. Application of micronized konjac gel for fat analogue in mayonnaise. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 35, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Mao, L.; Hou, Z.; Yuan, F.; Gao, Y. Roles of additional emulsifiers in the structures of emulsion gels and stability of vitamin E. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 99, 105372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Xiang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, M.; Chen, T.; Liu, C. Fabrication and characterization of oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by macadamia protein isolate/chitosan hydrochloride composite polymers. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 103, 105655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Liu, R.; Liang, B.; Wu, T.; Sui, W.; Zhang, M. Microparticulated whey protein-pectin complex: A texture-controllable gel for low-fat mayonnaise. Food Res. Int. 2018, 108, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozłowska, E.; Bartkowiak, A.; Łopusiewicz, Ł. Characterization of Flaxseed Oil Bimodal Emulsions Prepared with Flaxseed Oil Cake Extract Applied as a Natural Emulsifying Agent. Polymers 2020, 12, 2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schädle, C.N.; Bader-Mittermaier, S.; Sanahuja, S. Characterization of Reduced-Fat Mayonnaise and Comparison of Sensory Perception, Rheological, Tribological, and Textural Analyses. Foods 2022, 11, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsaros, G.; Tsoukala, M.; Giannoglou, M.; Taoukis, P. Effect of storage on the rheological and viscoelastic properties of mayonnaise emulsions of different oil droplet size. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León, O.; Soto, D.; López, D.; Muñoz-Bonilla, A.; Fernández-García, M. Fat-Replacer Properties of Oxidized Cassava Starch Using Hydrogen Peroxide/Sodium Bicarbonate Redox System in Mayonnaise Formulation and Its Stability. Starch-Stärke 2019, 71, 1900112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Cai, Y.; Liu, T.; Huang, L.; Deng, X.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, M. Improvements in physicochemical and emulsifying properties of insoluble soybean fiber by physical-chemical treatments. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 93, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Lu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Mata, A.; Fang, Y. Natural polymer-sourced interpenetrating network hydrogels: Fabrication, properties, mechanism and food applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 116, 342–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiao, A.; Qiu, C.; Liu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Bian, S.; Zeng, F.; Jin, Z. A combined enzymatic and ionic cross-linking strategy for pea protein/sodium alginate double-network hydrogel with excellent mechanical properties and freeze-thaw stability. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 131, 107737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Marin, L.; Xiao, Y.; Gillies, E.; Siqueira, W. pH-Sensitive Chitosan Nanoparticles for Salivary Protein Delivery. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, M.; Xiong, S.; Hu, Y.; Yin, T.; You, J. In vitro pepsin digestion of silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) surimi gels after cross-linking by Microbial Transglutaminase (MTGase). Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 95, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketnawa, S.; Ogawa, Y. Evaluation of protein digestibility of fermented soybeans and changes in biochemical characteristics of digested fractions. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 52, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Protein and Amino Acids Requirement in Human Nutrition; WHO Technical Report Series; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002; p. 935. [Google Scholar]


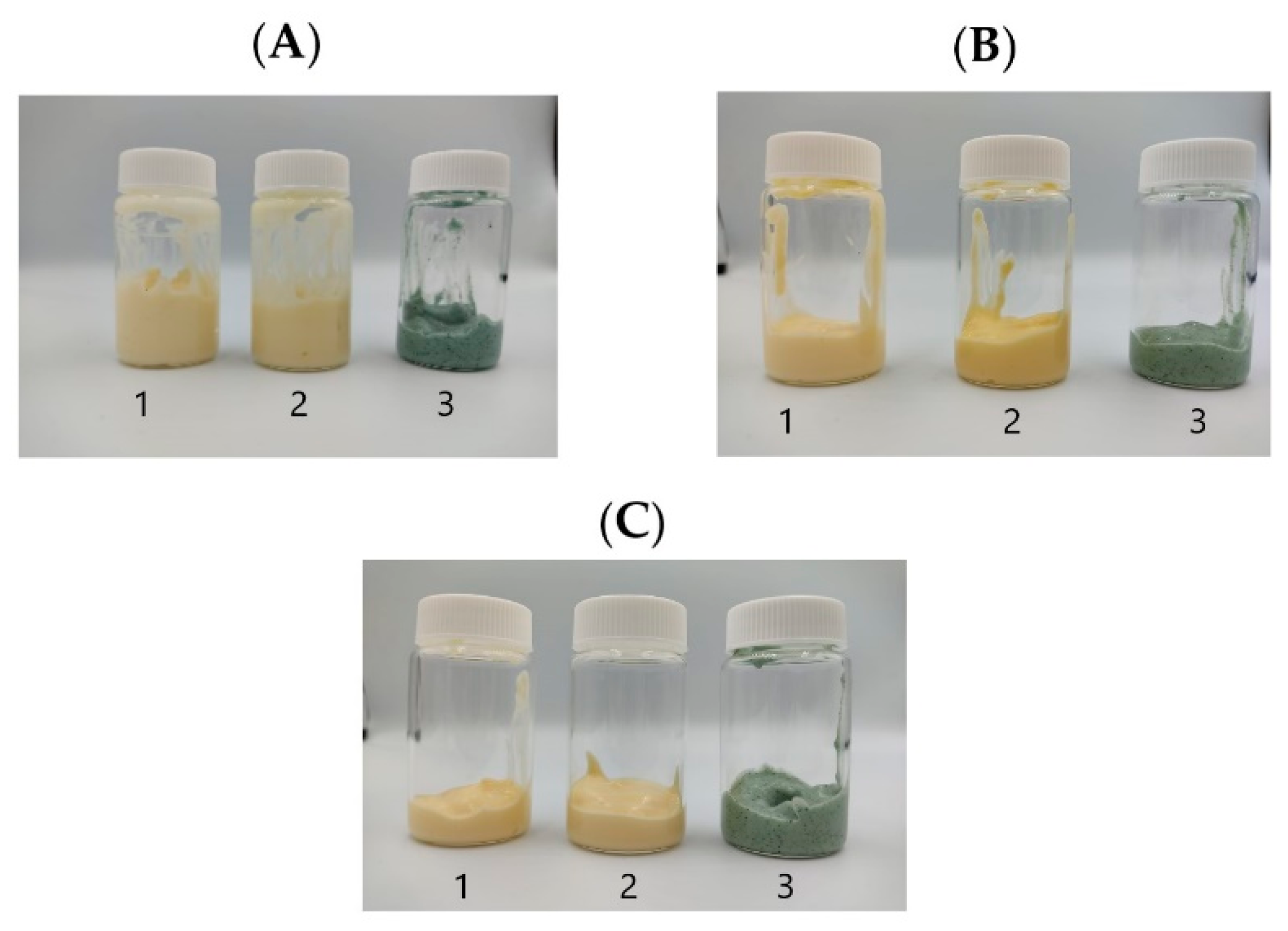
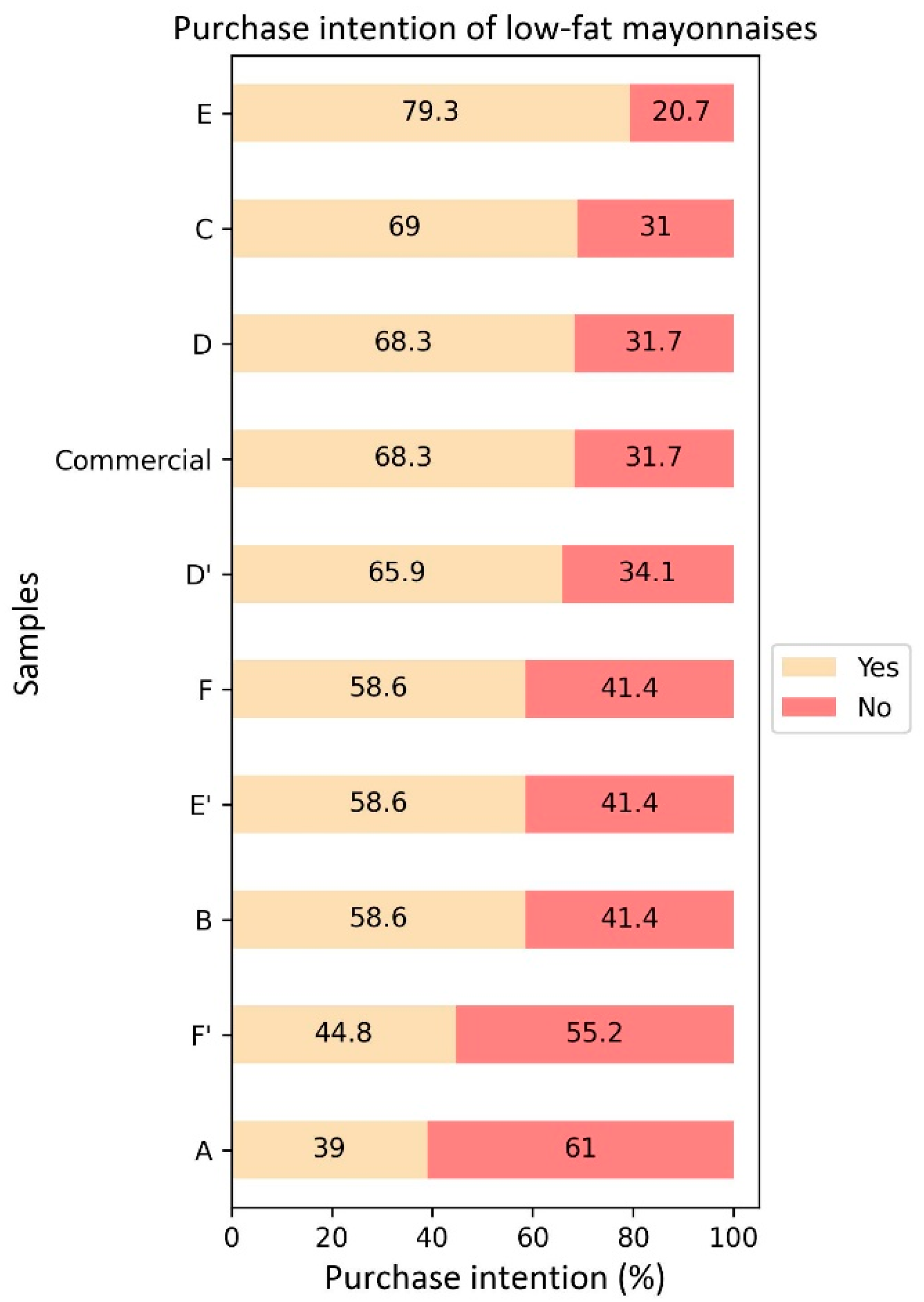
| Aqueous Phase | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Oil (%) | Egg Yolk (%) | Water (%) | Vinegar (%) | Sugar (%) | Salt (%) | Protein (Type; %) | Sodium Alginate (%) |
| A | 30.0 | 10 | 22 | 4.5 | 2 | 1.5 | NA | 30 |
| B | 22.5 | 10 | 26 | 4.5 | 2 | 1.5 | NA | 34 |
| C | 15.0 | 10 | 30 | 4.5 | 2 | 1.5 | NA | 38 |
| D | 30.0 | 10 | 21 | 4.5 | 2 | 1.5 | SPI; 1 | 30 |
| E | 22.5 | 10 | 25 | 4.5 | 2 | 1.5 | SPI; 1 | 34 |
| F | 15.0 | 10 | 29 | 4.5 | 2 | 1.5 | SPI; 1 | 38 |
| D’ | 30.0 | 10 | 21 | 4.5 | 2 | 1.5 | SPC; 1 | 30 |
| E’ | 22.5 | 10 | 25 | 4.5 | 2 | 1.5 | SPC; 1 | 34 |
| F’ | 15.0 | 10 | 29 | 4.5 | 2 | 1.5 | SPC; 1 | 38 |
| Mayonnaise Sample | K (Pa·sn) | ΔK | n | RMSE | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Commercial | 43.284 | ND | 0.297 | 0.583 | 0.999 |
| A | 66.262 | 0.000 | 0.281 | 1.442 | 0.998 |
| B | 35.008 | 31.223 | 0.260 | 1.397 | 0.999 |
| C | 20.922 | 45.291 | 0.335 | 0.915 | 0.999 |
| D | 35.284 | 0.000 | 0.281 | 0.883 | 0.999 |
| E | 31.524 | 3.524 | 0.299 | 1.062 | 0.998 |
| F | 25.876 | 9.408 | 0.329 | 0.380 | 0.999 |
| D’ | 49.552 | 0.000 | 0.308 | 1.324 | 0.998 |
| E’ | 43.879 | 5.673 | 0.305 | 0.839 | 0.999 |
| F’ | 35.013 | 14.539 | 0.308 | 0.284 | 0.999 |
| Amino Acid (mg/25 g Product) | D’ | E | Commercial |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time 0 | |||
| His | ND | 1.740 ± 0.068 a | ND |
| Thr | 2.613 ± 0.096 a | 2.266 ± 0.059 b | 2.191 ± 0.157 b |
| Val | 1.566 ± 0.098 a | 1.102 ± 0.043 b | 0.656 ± 0.076 c |
| Met | 0.774 ± 0.155 a | 0.621 ± 0.131 a | 0.511 ± 0.054 a |
| Trp | 8.149 ± 1.478 ab | 7.533 ± 0.535 b | 9.278 ± 0.106 a |
| Phe | 2.120 ± 0.177 b | 2.537 ± 0.083 a | ND |
| Ile | 1.142 ± 0.300 a | 1.059 ± 0.048 a | ND |
| Leu | 3.400 ± 0.091 a | 2.699 ± 0.187 b | 2.007 ± 0.069 c |
| Lys | 1.729 ± 0.108 a | 1.506 ± 0.170 a | ND |
| ∑ EAA | 21.496 ± 1.203 a | 21.066 ± 1.328 a | 14.645 ± 0.464 b |
| Time 1 | |||
| His | ND | ND | ND |
| Thr | 2.451 ± 0.162 a | 2.217 ± 0.212 a | 1.520 ± 0.033 b |
| Val | 1.302 ± 0.071 a | 1.032 ± 0.077 b | 0.709 ± 0.004 c |
| Met | 0.914 ± 0.149 a | 0.753 ± 0.024 a | 0.628 ± 0.005 b |
| Trp | 10.624 ± 0.095 a | 7.731 ± 0.997 b | 10.966 ± 0.492 a |
| Phe | 3.029 ± 0.190 a | 2.435 ± 0.021 b | ND |
| Ile | 1.331 ± 0.107 a | 1.186 ± 0.038 a | ND |
| Leu | 3.176 ± 0.478 a | 2.825 ± 0.463 a | 1.527 ± 0.064 b |
| Lys | 2.303 ± 0.930 a | 1.501 ± 0.093 a | ND |
| ∑ EAA | 25.132 ± 2.181 a | 19.684 ± 1.929 b | 15.352 ± 0.601 c |
| Time 2 | |||
| His | ND | ND | ND |
| Thr | 3.219 ± 0.164 a | 3.038 ± 0.131 a | 2.481 ± 0.499 a |
| Val | 1.326 ± 0.141 a | 1.274 ± 0.115 a | 0.610 ± 0.166 b |
| Met | 0.850 ± 0.146 a | 0.779 ± 0.024 a | ND |
| Trp | 13.222 ± 0.048 a | 13.354 ± 1.291 a | 2.471 ± 0.301 b |
| Phe | 3.587 ± 0.630 a | 3.113 ± 0.352 a | ND |
| Ile | 1.355 ± 0.140 a | 1.094 ± 0.187 a | ND |
| Leu | 3.714 ± 0.235 a | 3.324 ± 0.065 a | ND |
| Lys | 1.992 ± 0.191 a | 2.076 ± 0.105 a | ND |
| ∑ EAA | 29.265 ± 1.695 a | 28.052 ± 2.270 a | 5.562 ± 0.966 b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Metri-Ojeda, J.; Ramírez-Rodrigues, M.; Rosas-Ordoñez, L.; Baigts-Allende, D. Development and Characterization of a Low-Fat Mayonnaise Salad Dressing Based on Arthrospira platensis Protein Concentrate and Sodium Alginate. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7456. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157456
Metri-Ojeda J, Ramírez-Rodrigues M, Rosas-Ordoñez L, Baigts-Allende D. Development and Characterization of a Low-Fat Mayonnaise Salad Dressing Based on Arthrospira platensis Protein Concentrate and Sodium Alginate. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(15):7456. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157456
Chicago/Turabian StyleMetri-Ojeda, Jorge, Milena Ramírez-Rodrigues, Lizbeth Rosas-Ordoñez, and Diana Baigts-Allende. 2022. "Development and Characterization of a Low-Fat Mayonnaise Salad Dressing Based on Arthrospira platensis Protein Concentrate and Sodium Alginate" Applied Sciences 12, no. 15: 7456. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157456
APA StyleMetri-Ojeda, J., Ramírez-Rodrigues, M., Rosas-Ordoñez, L., & Baigts-Allende, D. (2022). Development and Characterization of a Low-Fat Mayonnaise Salad Dressing Based on Arthrospira platensis Protein Concentrate and Sodium Alginate. Applied Sciences, 12(15), 7456. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157456








