Abstract
Every year, millions of tons of fish waste are generated from fishing activities, and a similar amount is discarded and returned to the sea as unwanted catches. This material can be used as a biological source for many potential new added-value products, such asobtaining hyaluronic acid from fish eyeballs or extracting collagen from fish skin, but there are not many utilities for fish bones yet. This work tackles the transformation of fish discards into calcium phosphates. Discards from scorpionfish (Scorpaena scrofa) and Atlantic horse mackerel (Trachurus trachurus), as well as by-products generated from aquaculture activities (heads and trimmings frames) of salmon (Salmon salar), were used to obtain calcium phosphate. Biphasic carbonated hydroxyapatite (HA) /beta-tricalcium phosphate (TCP) material was obtained. The biphasic HA-TCP material has a promising range of applications in the biomedical field based on its similarity to calcium phosphates found in human bones in terms of crystallite size and carbonate content. The presence of Na, Mg, Sr, and K ions in the HA-TCP material is very beneficial, since they contribute to bone metabolism and cell adhesion.
1. Introduction
Fish discarding is the practice of returning unwanted catches, either dead or alive, back to the sea. This could occur due to economic reasons such as market demands or fishermen quota levels, or because the sizes of the species do not meet minimum requirements. This is a serious problem according to data provided by the Food and Agricultural Organisation (FAO), which estimates that nearly 50% of the more than 90 million tons of fish and shellfish caught globally each year are discarded [1]. This is not only harmful for fish species themselves, but can also substantially alter the marine environment and even favour the development of parasites such as anisakis [2].
In order to reduce this practice, the European Union put several landing regulations into action that came into force in 2019. Since then, fish discards of the main species have been completely banned [3]. However, this measure left some issues unclear—mainly the use of fish after landing if it cannot be marketed. Additionally, the degradation of the large amount of fish waste generated by fish processing units in coastal cities can have a very negative effect on the environment [4]. Hence, finding an application for fish waste and discards is becoming a very important issue.
In recent years, a variety of applications for fish waste have been discovered, such as, obtaining hyaluronic acid from fish eyeballs [5], extracting collagen from fish skin [6,7], from swim bladders [8] or from cartilaginous edoskeleton [9], or isolating gelatine from scales [10,11,12]. However, there are not many utilities for fish bones yet. The most widespread application of fish bones today is the production of animal feed, providing only a limited benefit.
In recent years, the possibility of obtaining calcium phosphate from fish bones has been explored [13]. Different species have been used as source of calcium phosphates, including Bigeye tuna (Thunnus obesus) [14], swordfish (Xiphias gladius) [15], Atlantic bluefin tuna (Thunnus thynnus) [15], Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) [16], greater amberjack (Seriola dumerili) [17], European sardines (Sardina pilchardus) [18], sheelavati river fish (Roho labio) [19], and barramundi (Lates calcarifer) [20].
This work tackles the transformation of fish discards, not just fish bones, into calcium phosphates. All these works reported a careful preparation of the fish bones prior to the treatment used to obtain the calcium phosphates. As an example, Venkatesan et al. [14] described that tuna bones were washed with hot water over two days in order to take away the traces of skin and meat. Piccirillo et al. [16,18] also explained that prior to the thermal treatment, bones from cod fish or sardines were manually cleaned with a brush in hot water to remove all fragments of skin, meat, etc. A similar procedure was reported by Goto and Sasaki [17]. They boiled and washed the fish bones to remove the soft tissues, such as cartilage, and dried them at room temperature for 1 week prior to the calcination treatment that leads to calcium phosphates isolation. A similar procedure to assure that all remains from the fish (flesh, skin, etc.), except the bones, were eliminated in order to assure that the precursor material was as pure as possible, was also followed by Sunil and Jagannatham [19] and by Pal et al. [20]. In our prior work [15], we also took extra care to guarantee that bones were extracted directly at the factory ships, frozen immediately in each ship, and that the cold chain was not broken. At the lab, we boiled and cleaned the bones and removed all organic matter prior to the thermal treatment.
These procedures are excellent from a laboratory point of view, but they are far from the capabilities of the factory ships processing fish or the aquaculture facilities for human consumption. Therefore, the objective of this work is to study the transformation of fish discards (not only bones) into calcium phosphates. Fish discards were used as received from the aquaculture facilities and the fishing ships without any extraordinary cleaning process. Discards from scorpionfish (Scorpaena scrofa) and Atlantic horse mackerel (Trachurus trachurus), as well as from by-products generated from aquaculture and canning processes (heads and trimmings frames) of Atlantic salmon (Salmon salar) were used to obtain calcium phosphate.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish Samples
The fish samples belong to three specimens of different fish species previously treated in order to obtain the starting material used as an HA source. This raw material was obtained as co-product from the production of fish protein hydrolysates (FPH) of red scorpionfish (Scorpaena scrofa) and Atlantic horse mackerel (Trachurus trachurus) discards, as well as from by-products generated from aquaculture activities (heads and trimmings frames) of salmon (Salmon salar) that were also digested by a commercial protease. In order to simplify the identification of the different species, throughout the text the designation will be Scorp for Scorpaena scrofa, Trach for Trachurus trachurus and Salmo for Salmon salar.
In all cases, the procedure for fish waste processing and mineral source recovery is shown in Figure 1.
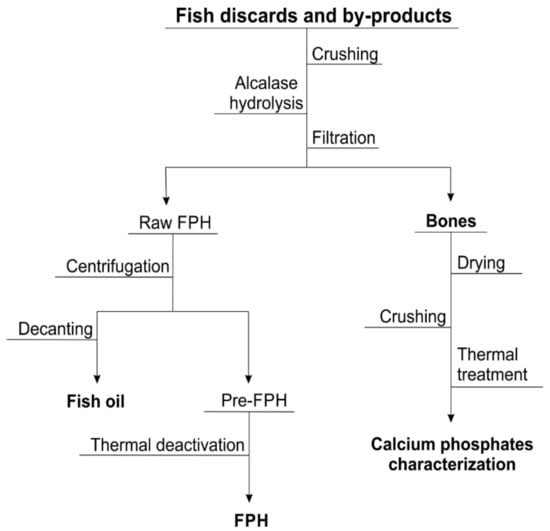
Figure 1.
A flowchart describing the recovery of bones/calcium phosphate as a co-product of fish protein hydrolysates (FPH) production from fish discards and aquaculture by-products.
Briefly, the fish samples (whole individuals of fish discards and heads and trimmings derived from aquaculture processing) were homogenized by crushing and hydrolysed by Alcalase 2.4L (Novozymes, Nordisk, Bagsvaerd, Denmark) under the following conditions: 0.2 or 1% (v/w) of enzyme concentration, 61 or 64.2 °C, pH 8.6 or pH 8.98, agitation of 200 rpm, solid:liquid ratio of (1:1) or (1:2), and 3 or 4 h of hydrolysis. After proteolysis, protein hydrolysates were separated from bones by filtration (500 µm). The liquid fraction was employed for the selective production of fish oils and FPH and the solids were dried in an oven (60 °C/24 h) and finally grinded [21,22]. Proximal composition of these solids was performed by determination of water, ash and organic matter content according to the Official Method of Analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC, 1997) [23].
During the thermal treatment, fish samples were calcined in an industrial furnace at temperatures of 750 °C and 950 °C for 10 h at a heating rate of 10 °C/min. After the calcination temperature was reached, samples remained inside the furnace isothermally for a period of 10 h and cooled down at a cooling rate of 10 °C/min before being extracted from the furnace.
2.2. Characterization Techniques
Morphologies of the structures present within the obtained powder were analysed by field emission scanning electron Microscopy (FESEM) using a JEOL JSM 6700F microscope (JEOL, Akishima, Japan) equipped with an EDAX PV 9760 detector used to perform energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) on the samples, which identified their main chemical composition. High-resolution SEM images were taken in order to observe the resulting morphologies of the powder.
The powder was also analysed by a PANanalytical X’Pert Pro X-ray diffractometer (Almelo, The Netherlands) using monochromated Cu-Kα radiation (wavelength 1.54 Å) over the 20–100° 2θ range with a step size of 0.02° in order to obtain its crystalline structure and phase composition. Identification of phases was achieved by comparing the diffraction patterns of HA with standards from the International Centre for Diffraction Data (ICDD), formerly known as Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards (JCPDS).
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) was applied to obtain the functional groups of the resulting powders by using a Thermo Nicolet 6700 spectrometer. Spectra were acquired between 400 and 4000 cm−1. The typical acquisition conditions were 4 cm−1 of resolution, averaging of 32 scans, an apodization Happ–Genzel, a Mertz phase correction, and zero filling 2.
To obtain a quantitative evaluation of the chemical composition of the materials obtained, as well as the Ca/P ratio, and identify the possible presence of heavy metals, a PerkinElmer Optima 4300 DV spectrometer was used for inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES). Calibration for Ca, P, Na, Mg and K analyses were performed with 10-mg/L standards with RSD values below 2.0%.
The characterization techniques used in this study were performed and repeated for the powders obtained from the three different fish species and after thermal treatment at temperature levels of 750 °C and 950 °C.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Raw Material and Thermal Treatment
The first step in the extraction of calcium phosphate from fish waste was to evaluate the yield values of wet and dry bones recovered from discards and fish waste. These values are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Yields of bones recovered from the initial substrate.
As expected, the main component of the proximal analysis was the ashes (mineral fraction); however, there was still a considerable percentage of organic matter in the samples. The colour and smell of the samples confirm that they kept a significant amount of organic matter, over 30%, as can be seen in Table 1. Therefore, a thermal treatment was applied to all species to eliminate these remaining organic parts from the samples.
After the thermal process, a significant mass reduction was also observed in the samples of every selected fish species. The mass loss in the heat treatment process is listed in Table 2.

Table 2.
Mass loss of fish bones at 750 and 950 °C.
This fact showed that most of the organic compounds that remained in the initial powder were removed from the samples. The change in colour after pyrolysis (see Figure 2) proves the importance of this step to the success of the process. Moreover, the mass loss percentage remains practically constant between both temperature levels. Hence, organic mass is interpreted to be fully eliminated at 750 °C.

Figure 2.
Crushed fish bones before and after thermal treatment.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images reveal porous-shaped structures without significant differences between the three fish species under study and the two temperatures of the thermal treatment. However, an additional porosimetry study is required to measure the pore size distribution, porosity, and the specific surface area, as well as determine the relationship between the calcination temperature and porosity. As shown in Figure 3, granules of irregular morphologies can be found in samples from all three studied species. Furthermore, some granules show a porous structure (Figure 3b–e).

Figure 3.
SEM micrographs of (a) Scorpaena scrofa, (b) Trachurus trachurus, and (c) Salmo salar bones calcined at 750 °C, as well as (d) Scorpaena scrofa, (e) Trachurus trachurus, and (f) Salmo salar bones calcined at 950 °C.
3.2. Chemical Composition
The first approximation of the chemical composition of the different powders was obtained from energy dispersive spectroscopy performed during the scanning microscopy. As can be seen in Figure 4, corresponding to Scorpaena scrofa treated at 950 °C, the main components of the powders were phosphorus, calcium, magnesium, and sodium.
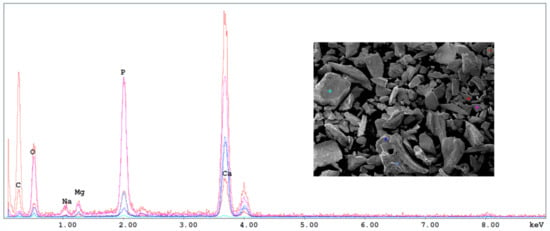
Figure 4.
Energy dispersive spectroscopy spectrum obtained at several points of the sample Scorpaena scrofa at 950 °C.
EDS gives just a qualitative evaluation of the chemical composition, therefore inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES) was carried out in order to perform a quantitative evaluation of the chemical compositions of the powders obtained. This analysis allowed us to determine the amount of heavy metals present in the fish samples, as well as the Ca/P molar ratio. The elementary composition of the given species for the different temperatures and fish powder samples is listed in Table 3. As already pointed out by the EDS analyses, calcium and phosphorus were the two main components in all samples, showing a similar amount of both elements with an average Ca/P molar ratio of around 1.81 ± 0.2. This value is slightly higher than that of stoichiometric hydroxyapatite (1.67), which is due to the fact that what we have here is a type B hydroxyapatite as a result of the substitution of (PO4)−3 groups by (CO3)−2. This type of hydroxyapatite has a higher degree of biocompatibility than that of type A, where the hydroxyl groups (OH)− are substituted by (CO3)−2 groups. Hence, type B hydroxyapatite obtained from natural sources will have a better acceptance from a human body perspective [24,25,26].

Table 3.
Elemental composition of the samples at 750 and 950 °C and their corresponding Ca/P ratio.
In general terms, the results of the EDS analysis agree with those from the ICP-OES. Moreover, EDS and ICP-OES analyses show the important presence of ions, such as Na, Mg, Sr, and K. These elements usually replace Ca ions in biological HA obtained from natural sources while promoting higher biological activity and thus enhance a faster growth of bone structures and cell adhesion [27]. HA presents in a hexagonal structure and features two calcium sites (CaI and CaII). Due to significant differences in ionic radius, some ions may be incorporated into the hydroxyapatite lattice structure. Cations smaller than Ca (radius = 0.99 Å), e.g., Na or Mg, tend to occupy the CaI site, while larger cations (Sr and K) usually replace calcium at the CaII site [28]. Sodium and magnesium play a significant role in bone metabolism and osteoporosis, while strontium reduces bone resorption and increases the formation of new bone structures, which may lead to increased prevention of fractures [29,30,31].
HA is able to store heavy metals by means of ionic substitutions between element cations, which is a matter of big importance according to health and safety regulations. The use of elements like Hg, Cd, and Pb is highly restricted in products intended for use in humans as they can result in harmful effects due to their toxic or carcinogenic behaviour. The ICP-OES composition analysis showed the amount of these elements present in the fish bone powder from all samples was lower than the maximum permitted for organic bone implant material as established by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM F1185—03(2014)) and indicated in Table 4.

Table 4.
Concentration of heavy metals in samples.
From the ICP-OES analysis (see Table 3), a change of phase in the HA samples can be deduced due to a reduction in the Ca/P molar ratio when the processing temperature was changed from 750 °C to 950 °C in all analysed species. Hydroxyapatite suffers a relevant change of phase at a certain temperature threshold to form β-tricalcium phosphate (TCP), which presents with a stoichiometric Ca/P molar ratio of 1.5 [32]. The clear reduction of the Ca/P ratio in all samples when calcination temperature was set to 950 °C, can be interpreted as a partial transformation of the HA within the powder and formation of a biphasic HA-TCP compound phase. In order to confirm these phase changes and to evaluate the functional groups present in the powders, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction were carried out.
3.2.1. Functional Groups Analysis
FTIR analyses were performed on all samples calcined at 950 °C to identify the functional groups. Figure 5 shows the FTIR spectra from all the samples analysed, exhibiting narrow bands that suggest a high crystallinity degree. The presence of phosphate groups (PO4)−3 can be identified for the three species. These groups show bands at ~960 cm−1 and between 1000 and 1200 cm−1 due to the stretching modes of P-O bonds, as well as bands between 540 and 600 cm−1 corresponding to the bending mode of the phosphate groups. Hydroxyl groups (OH)− can be observed in two different regions, with low intensity bands between 3500 and 3600 cm−1, corresponding to its stretching mode, and at ~630 cm−1, corresponding to its bending mode. Carbonate groups (CO3)−2 are also present with bands around 714 cm−1, 875 cm−1, and between 1400 and 1460 cm−1 [33]. In particular, peaks between 1400 and 1460 cm−1 are associated with the bending mode in B-type hydroxyapatite, due to the substitution of (PO4)−3 by the (CO3)−2 group [15,34,35], in accordance to the high Ca/P ratio obtained from ICP-OES analysis. Peaks located in these bands, associated with the carbonate groups, present a very low intensity, especially for the Salmo sample, which can probably be due to the carbonate decomposition into carbon dioxide that takes place at temperatures between 750 and 1100 °C [36].
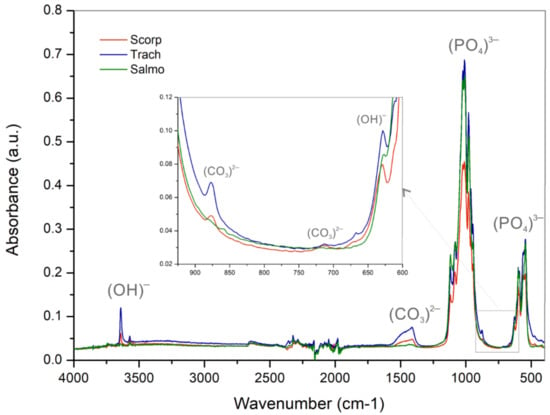
Figure 5.
Fourier transform infrared spectra of fish bone samples thermally treated at 950 °C.
3.2.2. Crystalline Structure
The crystalline structures of the samples were analysed by means of X-ray powder diffraction (XRD). The XRD patterns of the different samples are compared with that of HA and β-TCP in Figure 6 and Figure 7. This comparison reveals that even though HA was the major component of the resultant powders, there was a small amount of β-tricalcium phosphate (β-Ca3(PO4)2: β-TCP) in all of them. Furthermore, the presence of β-TCP was observed with higher frequency for the powders calcined at 950 °C, which explains the decrease in the Ca/P ratio by increasing the calcination temperature, as obtained from ICP-OES analysis. Many authors have observed that this change of phase, from HA to β-TCP, takes place at calcination temperatures between 600 °C and 950 °C [20].
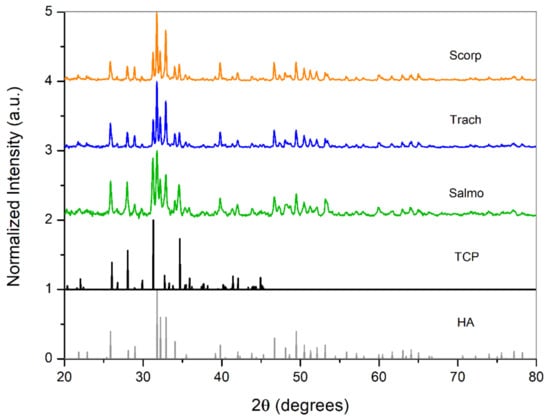
Figure 6.
X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) patterns of material thermally treated at 750 °C compared with stoichiometric HA and TCP.
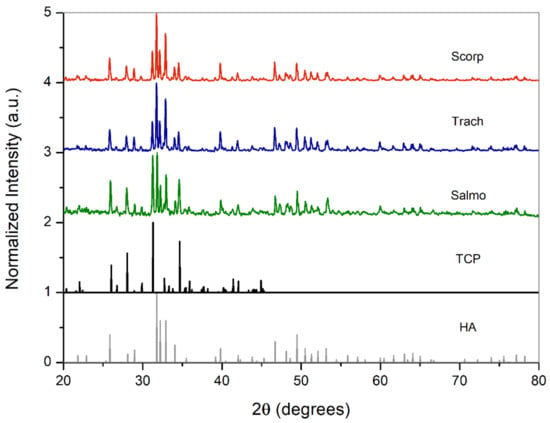
Figure 7.
XRD patterns of material thermally treated at 950 °C compared with stoichiometric HA and TCP.
This biphasic calcium phosphate is a very suitable material for bone substitute applications, because while the HA provides a scaffold for new bone formation via osteoconduction, the reabsorption of β-TCP oversaturates the local environment with calcium and phosphate ions, accelerating the new bone formation [37].
The main peaks identified in the XRD patterns of the samples are slightly shifted with respect to synthetic HA, which indicates a change in the unit cell parameters. This change in lattice is due to the substitutions of Ca ions by Na, Mg, Sr, or K ions observed in the composition analysis. The lattice parameters and the unit cell volume can be calculated from XRD patterns by combining Bragg’s Law equation and the following equation [38]:
where ‘d’ is the interplanar distance, (h k l) are the lattice planes, ‘a’ and ‘c’ are the lattice parameters, and ‘’ is the unit cell volume.
Crystallite size was calculated by using Scherrer’s equation [39]:
where ‘t’ is the average dimension of crystallites in a direction normal to the diffracting plane, β is the full width of the peak at half maximum intensity (in radians) located at 2θ, λ is the wavelength of X-ray radiation (1.5418 Ȧ), and k is the Scherrer constant that is usually assumed to be 1. The cell parameters of the different samples after thermal treatment are compared with those of synthetic HA in Table 5.

Table 5.
Cell parameters, unit cell volume, crystallite size and carbonate content of powders obtained from fish bones at different calcination temperatures.
Additionally, the cell parameter ratio c/a can be used to estimate the carbonate content in B-type HA (Table 5), according to a quantitative method [40] that relates the c/a ratio with the stoichiometric coefficient x that can be replaced in the B-type HA formula.
The crystallite size of the samples calcined at 750 °C, measured from the (211) reflection, was around 50 nm (except for Salmo), which is very similar to the average crystallite size in mature bone [41]. However, the increase in calcination temperature to 950 °C lead to an increase in crystallinity and the growth of the crystallites to values around 60 nm.
The amount of carbonate in the resultant powders was around 2.5% for samples thermally treated at 750 °C and it decreased by increasing the temperature to 950 °C. This loss of carbonate also explains the low intensity peaks associated with carbonate groups obtained from the FTIR analysis of the samples treated at 950 °C. Furthermore, the amount of carbonate in powders treated at 750 °C is closer to the carbonate content in human bones, which is around 5% [42]. Thus, the obtained results demonstrate that, both in terms of crystallite size and carbonate content, a calcination temperature of 750 °C leads to a calcium phosphate with greater resemblance to that of an average human bone.
The poor mechanical properties of calcium phosphates are known to be the main drawback preventing use of these materials for load-bearing bone replacements [43]. Early works in the 1990s described the limited properties of calcium phosphates if a direct replacement of large bones was the objective [44]. Regardless of whether the origin is synthetic or natural, calcium phosphates are brittle and their fatigue resistance is quite limited [45]. Therefore, the main application of this biogenic biphasic material could be as bone defect filler, provided all compulsory in-vitro, in-vivo, and clinical studies were successfully accomplished.
The powder obtained could also be used as precursor material for nanoparticle production [46] that could also be incorporated into sunscreen creams [47], or directly used in filters for the treatment of polluted water [48]. This biphasic material could be converted into coatings for implants by means of the pulsed laser deposition technique [49] that improves the osseointegration of dental and orthopaedic implants.
4. Conclusions
Biogenic calcium phosphate has been obtained from fish discards, giving them an additional application as a cheap raw material that does not have any negative effect on the environment. The powders obtained consisted of a biphasic material whose major component was B-type carbonated hydroxyapatite and a minor amount of beta-tricalcium phosphate.
The amount of β-TCP within the biphasic HA-TCP biphasic material was increased by turning up the temperature of the thermal treatment from 750 °C to 950 °C. Ions of Na, Mg, Sr, and K were also detected, replacing Ca ions and slightly modifying the unit cell parameters with respect to the synthetic hydroxyapatite ones. Additionally, the concentration of heavy metals (Hg, Cd, and Pb) in the obtained powders was below the maximum permitted by the ASTM for organic bone implant materials.
The biphasic HA-TCP material has a promising range of applications in the biomedical field based on its great similarity to calcium phosphates found in human bones in terms of crystallite size and carbonate content. The presence of Na, Mg, Sr, and K ions is usual in biological apatites, and is very beneficial, since they contribute to bone metabolism and cell adhesion.
Author Contributions
M.F.-A.: formal analysis, investigation, writing—original draft preparation; I.Á.-O.: formal analysis, investigation, writing—original draft preparation; P.M.-F.: formal analysis, investigation, writing—original draft preparation; J.A.V.: conceptualization, resources, writing—review and editing, supervision, funding acquisition; M.B.: conceptualization, methodology, data curation, writing—review and editing; R.C.: validation, formal analysis; J.P.: conceptualization, writing—review and editing, supervision, funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was partially supported by the EU research project Bluehuman (EAPA_151/2016 Interreg Atlantic Area), and by Xunta de Galicia (ED431C 2019/23, ED481D 2017/010, ED481B 2016/047-0). REVAL-Lab also wants to thank to GAIN (EU, Horizon 2020 Framework Research and Innovation Programme under GA n. 773330) and Xunta de Galicia (Grupos de Potencial Crecimiento, IN607B 2018/19) for the financial support of this investigation.
Acknowledgments
The technical staff from CACTI (University of Vigo) is gratefully acknowledged.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Roda, M.A.P.; Gilman, E.; Huntington, T.; Kennelly, S.J.; Suuronen, P.; Chaloupka, M.; Medley, P.A. A Third Assessment of Global Marine Fisheries Discards; FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Technical Paper No. 633; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2019; p. 78. [Google Scholar]
- González, A.F.; Gracia, J.; Miniño, I.; Romón, J.; Larsson, C.; Maroto, J.; Requeira, M.; Pascual, S. Approach to reduce the zoonotic parasite load in fish stocks: When science meets technology. Fish. Res. 2018, 202, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda, M.; Ulrich, C.; Le Gallic, B.; Borges, L.; Metz, S.; Prellezo, R.; Santurtún, M. Research for PECH Committee—EU Fisheries Policy–Latest Developments and Future Challenges; European Parliament, Policy Department for Structural and Cohesion Policies: Brussels, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Daouda, A.B.; Ajadi, A.; Tola-Fabunmi, A.S.; Akinwole, A.O. Waste production in aquaculture: Sources, components and managements in different culture systems. Aquac. Fish. 2019, 4, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murado, M.A.; Montemayor, M.I.; Cabo, M.L.; Vázquez, J.A.; González, M.P. Optimization of extraction and purification process of hyaluronic acid from fish eyeball. Food Bioprod. Process. 2012, 90, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, A.; Shaw, N.B.; Murphy, S.C.; van de Vis, J.W.; van Pelt-Heerschap, H.; Kerry, J.P. Extraction of collagen from fish skins and its use in the manufacture of biopolymer films. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2006, 15, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, R.O.; Martins, E.; Carvalho, D.N.; Alves, A.L.; Oliveira, C.; Duarte, A.R.C.; Silva, T.H.; Reis, R.L. Collagen from Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) skins extracted using CO2 acidified water with potential application in healthcare. J. Polym. Res. 2020, 27, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, R.O.; Alves, A.L.; Carvalho, D.N.; Martins, E.; Oliveira, C.; Duarte, A.R.C.; Silva, T.H.; Reis, R.L. Acid and enzymatic extraction of collagen from Atlantic cod (Gadus Morhua) swim bladders envisaging health-related applications. Biomater. Sci. Polym. 2020, 31, 20–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seixas, M.J.; Martins, E.; Oliveira, C.; Duarte, A.R.C.; Silva, T.H.; Reis, R.L. Extraction and characterization of collagen from elasmobranch byproducts for potential biomaterial use. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herpandi, H.; Huda, N.; Adzitey, F. Fish bone and scale as a potential source of halal gelatin. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2011, 6, 379–389. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, L.C.; Huang, Q.Y.; Ding, W.; Xiao, X.H.; Zhang, H.Y.; Xiong, L.X. Fish gelatin: The novel potential applications. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 63, 103581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafael, M.Y.B.; Rafael, R.R.; Landingin, E.P.; Rafael, R.B.; Tayag, G.G.; Santos, J.P.E.; Rafael, M.J.R. Gelatin from Milkfish Scales for Food Application. CLSU Int. J. Sci. Technol. 2021, 5, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Terzioğlu, P.; Öğüt, H.; Kalemtaş, A. Natural calcium phosphates from fish bones and their potential biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 91, 899–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, J.; Qian, Z.J.; Ryu, B.; Thomas, N.V.; Kim, S.K. A comparative study of thermal calcination and an alkaline hydrolysis method in the isolation of hydroxyapatite from Thunnus obesus bone. Biomed. Mater. 2011, 6, 035003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutinguiza, M.; Pou, J.; Comesaña, R.; Lusquiños, F.; De Carlos, A.; León, B. Biological hydroxyapatite obtained from fish bones. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2012, 32, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccirillo, C.; Silva, M.; Pullar, R.; da Cruz, I.B.; Jorge, R.; Pintado, M.; Castro, P.M. Extraction and characterisation of apatite-and tricalcium phosphate-based materials from cod fish bones. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, T.; Sasaki, K. Effects of trace elements in fish bones on crystal characteristics of hydroxyapatite obtained by calcination. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 10777–10785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccirillo, C.; Pullar, R.C.; Tobaldi, D.M.; Castro, P.M.L.; Pintado, M.M.E. Hydroxyapatite and chloroapatite derived from sardine by-products. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 13231–13240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunil, B.R.; Jagannatham, M. Producing hydroxyapatite from fish bones by heat treatment. Mater. Lett. 2016, 185, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A.; Paul, S.; Choudhury, A.R.; Balla, V.K.; Das, M.; Sinha, A. Synthesis of hydroxyapatite from Lates calcarifer fish bone for biomedical applications. Mater. Lett. 2017, 203, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, J.A.; Fernández-Compás, A.; Blanco, M.; Rodríguez-Amado, I.; Moreno, H.; Borderías, J.; Pérez-Martín, R.I. Development of bioprocesses for the integral valorisation of fish discard. Biochem. Eng. J. 2019, 144, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, J.A.; Sotelo, C.G.; Sanz, N.; Pérez-Martín, R.I.; Rodríguez-Amado, I.; Valcarcel, J. Valorization of aquaculture by-products of salmonids to produce enzymatic hydrolysates: Process optimization, chemical characterization and evaluation of bioactives. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Association of Official Analytical Chemistry. Methods of Analysis, 15th ed.; AOAC: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Grossardt, C.; Ewald, A.; Grover, L.M.; Barralet, J.E.; Gbureck, U. Passive and active in vitro resorption of calcium and magnesium phosphate cements by osteoclastic cells. Tissue Eng. A 2010, 16, 3687–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunouchi, K.; Tsuru, K.; Maruta, M.; Kawachi, G.; Matsuya, S.; Terada, Y.; Ishikawa, K. Fabrication of solid and hollow carbonate apatite microspheres as bone substitutes using calcite microspheres as a precursor. Dent. Mater. J. 2012, 31, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosenko, V.; Strutynska, N.; Vorona, I.; Zatovsky, I.; Dzhagan, V.; Lemishko, S.; Epple, M.; Prymak, O.; Baran, N.; Ishchenko, S.; et al. Structure of biocompatible coatings produced from hydroxyapatite nanoparticles by detonation spraying. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu’ad, N.A.S.M.; Koshy, P.; Abdullah, H.Z.; Idris, M.I.; Lee, T.C. Synthesis of hydroxyapatite from natural sources. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01588. [Google Scholar]
- Kannan, S.; Goetz-Neunhoeffer, F.; Neubauer, J.; Ferreira, J.M.F. Ionic substitutions in biphasic hydroxyapatite and β-Tricalcium phosphate mixtures: Structural analysis by Rietveld refinement. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 91, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiglioni, S.; Cazzaniga, A.; Albisetti, W.; Maier, J.A.M. Magnesium and osteoporosis: Current state of knowledge and future research directions. Nutrients 2013, 5, 3022–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dermience, M.; Lognay, G.; Mathieu, F.; Goyens, P. Effects of thirty elements on bone metabolism. Biology 2015, 32, 86–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baier, M.; Staudt, P.; Klein, R.; Sommer, U.; Wenz, R.; Grafe, I.; Meeder, P.J.; Nawroth, P.P.; Kasperk, C. Strontium enhances osseointegration of calcium phosphate cement: A histomorphometric pilot study in ovariectomized rats. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2013, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseinzadeh, E.; Davarpanah, M.; Nemati, N.H.; Tavakoli, S.A. Fabrication of a hard tissue replacement using natural hydroxyapatite derived from bovine bones by thermal decomposition method. Int. J. Organ Transplant. Med. 2014, 5, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Arias, J.L.; Mayor, M.B.; García-Sanz, F.J.; Pou, J.; León, B.; Pérez-Amor, M. Structural analysis of calcium phosphate coatings produced by pulsed laser deposition at different water-vapour pressures. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1997, 8, 873–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barinov, S.M.; Rau, J.V.; Cesaro, S.N.; Durisin, J.; Fadeeva, I.V.; Ferro, D.; Medvecky, L.; Trionfetti, G. Carbonate release from carbonated hydroxyapatite in the wide temperature rage. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2006, 17, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, D.S.R.; Siddharthan, A.; Seshadri, S.K.; Kumar, T.S. A novel route for synthesis of nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite from eggshell waste. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2007, 18, 1735–1743. [Google Scholar]
- Akram, M.; Ahmed, R.; Shakir, I.; Ibrahim, W.A.W.; Hussain, R. Extracting hydroxyapatite and its precursors from natural resources. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 1461–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyenvalle, E.; Aguado, E.; Nguyen, J.M.; Passuit, N.; Le Guenennec, L.; Layrolle, P.; Daculsi, G. Osteointegration of femoral stem prostheses with a bilayered calcium phosphate coating. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullity, B.D.; Stock, S.R. Elements of X-ray Diffraction, 3rd ed.; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bindu, P.; Thomas, S. Estimation of lattice strain in ZnO nanoparticles: X-ray peak profile analysis. J. Theor. Appl. Phys. 2014, 8, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeGeros, R.Z.; Myers, H. (Eds.) Calcium Phosphates in Oral Biology and Medicine. In Monographs in Oral Sciences; Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 1991; Volume 15, pp. 82–107. [Google Scholar]
- Stock, S.R. The Mineral–Collagen Interface in Bone. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2015, 97, 262–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, H.; Kobayashi-Fujioka, M.; Fujisawa, K.; Ohe, G.; Takamaru, N.; Hara, K.; Uchida, D.; Tamatani, T.; Ishikawa, K.; Miyamoto, Y. Effects of low crystalline carbonate apatite on proliferation and osteoblastic differentiation of human bone marrow cells. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2015, 26, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hench, L.L. Bioceramics: From concept to clinic. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1991, 74, 1487–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hench, L.L.; Wilson, J. An Introduction to Bioceramics; World Scientifi: Singapore, 1993; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Dorozhkin, S.V. Bioceramics of calcium orthophosphates. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 1465–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutinguiza, M.; Lusquiños, F.; Riveiro, A.; Comesaña, R.; Pou, J. Hydroxylapatite nanoparticles obtained by fiber laser-induced fracture. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 5382–5385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, E.A.B.; Costa, C.A.E.; Vilar, V.J.P.; Botelho, C.M.S.; Larosi, M.B.; Saracho, J.M.P.; Boaventura, R.A.R. Water remediation using calcium phosphate derived from marine residues. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 989–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccirillo, C.; Fernández-Arias, M.; Boutinguiza, M.; Tobaldi, D.M.; Del Val, J.; Pintado, M.M.; Pou, J. Increased UV absorption properties of natural hydroxyapatite-based sunscreen through laser ablation in liquid. J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 102, 3163–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peraire, C.; Arias, J.L.; Bernal, D.; Pou, J.; Leon, B.; Arano, A.; Roth, W. Biological stability and osteoconductivity in rabbit tibia of pulsed laser deposited hydroxylapatite coatings. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2006, 77, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).