The Influence of Three Different Digital Cement Spacers on the Marginal Gap Adaptation of Zirconia-Reinforced Lithium Silicate Crowns Fabricated by CAD-CAM System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
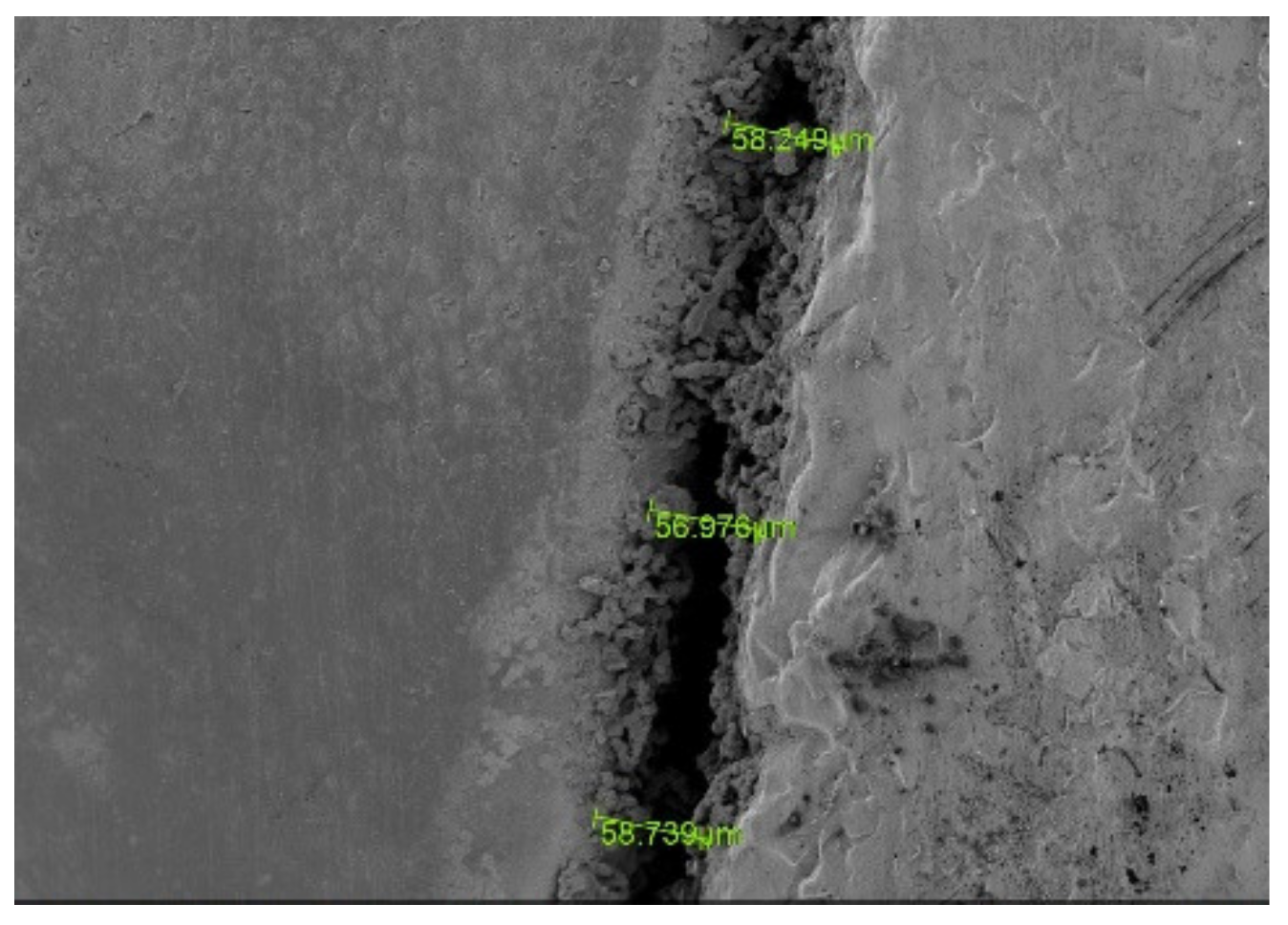
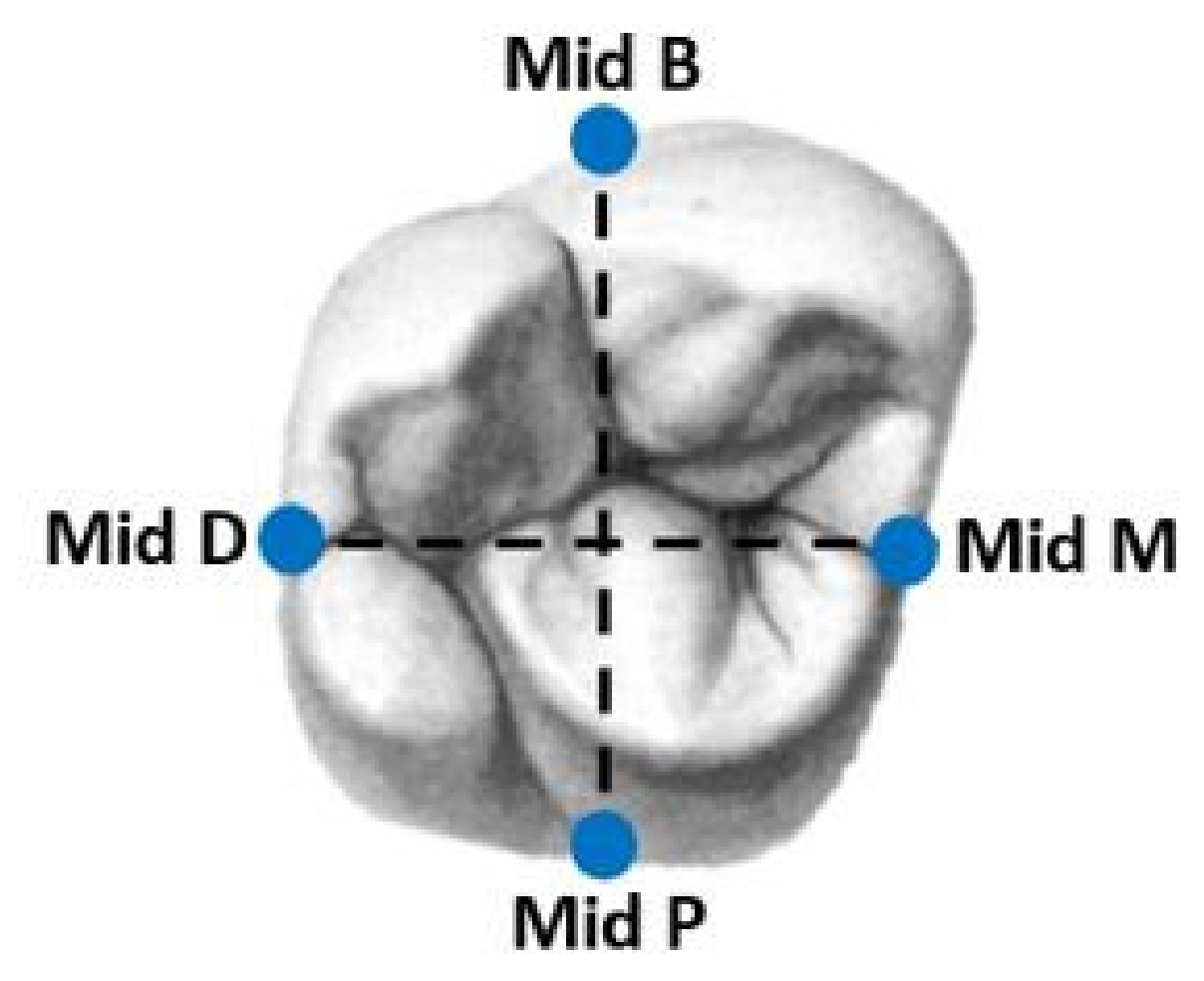
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- 1.
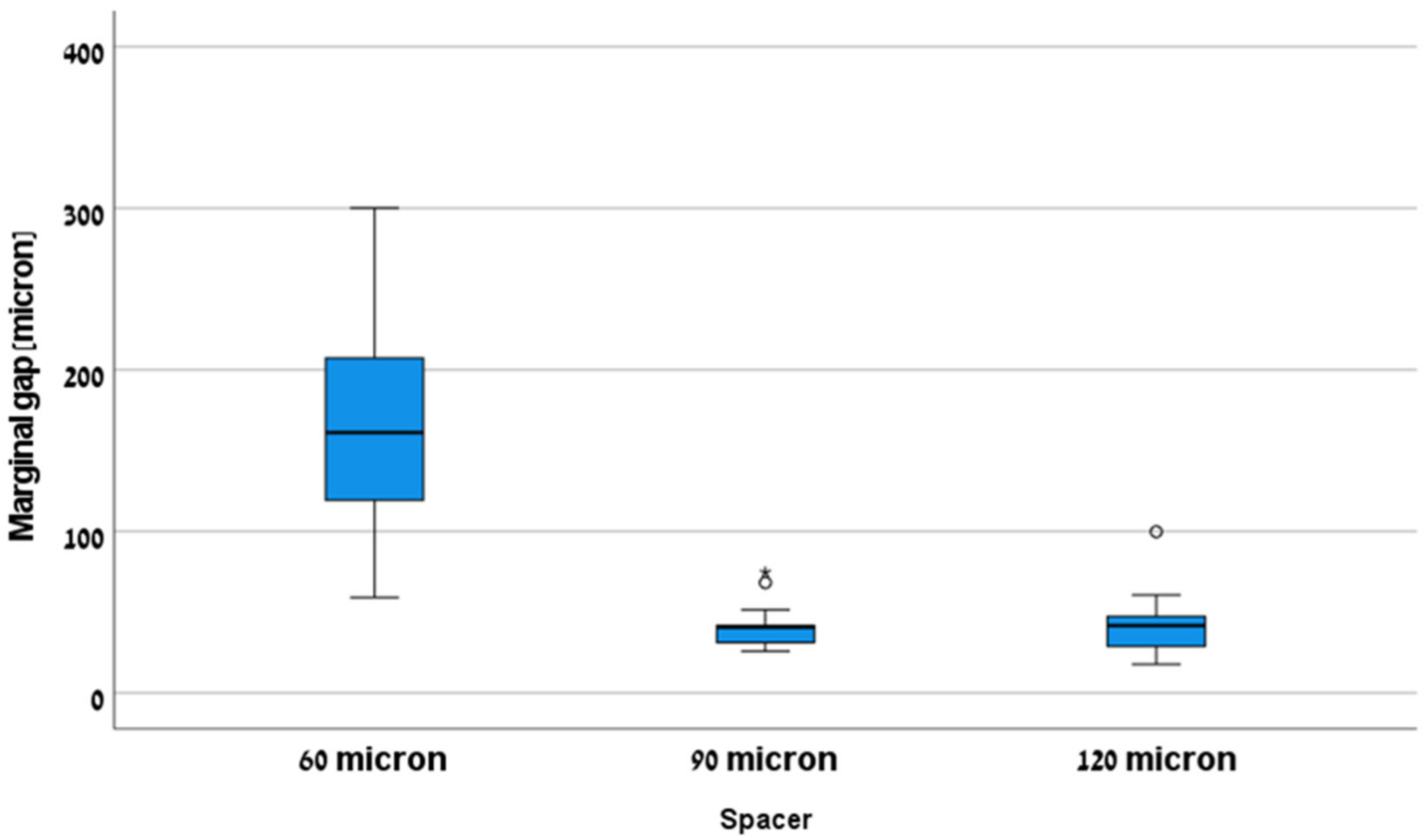
- A radial spacer of 60 microns showed a significantly higher marginal gap compared to 90 and 120 microns and was not clinically accepted (>120 microns).
- 2.
- The radial spacer for both 90 and 120 microns was clinically accepted (<120 microns).
- 3.
- The radial spacer which should be considered optimum for CELTRA® DUO crowns is 90 microns.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raigrodski, A.J.; Hillstead, M.B.; Meng, G.K.; Chung, K.H. Survival and complications of zirconia-based fixed dental prosthesis: A systematic review. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2012, 107, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raigrodski, A.J. Concepts of design for contemporary anterior all-ceramic restorations: Advantages and limitations of new technologies and materials. J. Cosmet. Dent. 2013, 28, 46–58. [Google Scholar]
- Lawson, N.C.; Bansal, R.; Burgess, J.O. Wear, strength, modulus and hardness of CAD/CAM restorative materials. Dent. Mater. 2016, 32, e275–e283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belli, R.; Wendler, M.; de Ligny, D.; Cicconi, M.R.; Petschelt, A.; Peterlik, H.; Lohbauer, U. Chairside CAD/CAM materials. Part 1: Measurement of elastic constants and microstructural characterization. Dent. Mater. 2017, 33, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, J.A. A rationale for comparison of plaque-retaining properties of crown systems. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1989, 62, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüksel, E.; Zaimoğlu, A. Influence of marginal fit and cement types on microleakage of all-ceramic crown systems. Braz. Oral Res. 2011, 25, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, M.J.; De Villaumbrosia, P.G.; Pradíes, G.; Lozano, J.F.L. Comparison of the marginal fit of Procera AllCeram crowns with two finish lines. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2003, 16, 229–232. [Google Scholar]
- Coli, P.; Karlsson, S. Fit of a new pressure-sintered zirconium dioxide coping. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2004, 17, 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- McLean, J.W.; Von Fraunhofer, J. The estimation of cement film thickness by an in vivo technique. Br. Dent. J. 1971, 131, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherberg, J.W.; Nicholls, J.I. Analysis of gold removal by acid etching and electrochemical stripping. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1979, 42, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campagni, W.; Preston, J.; Reisbick, M. Measurement of paint-on die spacers used for casting relief. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1982, 47, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccitiello, F.; Amato, M.; Leone, R.; Spagnuolo, G.; Sorrentino, R. In vitro Evaluation of the Marginal Fit and Internal Adaptation of Zirconia and Lithium Disilicate Single Crowns: Micro-CT Comparison Between Different Manufacturing Procedures. Open Dent. J. 2018, 12, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, N.; Ozturk, A.N.; Malkoc, M.A. Evaluation of the marginal fit of full ceramic crowns by the microcomputed tomography (micro-CT) technique. Eur. J. Dent. 2014, 08, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuer, F.; Aggstaller, H.; Edelhoff, D.; Gernet, W.; Sorensen, J. Marginal and internal fits of fixed dental prostheses zirconia retainers. Dent. Mater. 2009, 25, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, F.; Chai, J.; Jameson, L.M.; Wozniak, W.T. A comparison of the marginal fit of In-Ceram, IPS Empress, and Procera crowns. Int. J. Prosthodont. 1998, 10, 478–484. [Google Scholar]
- Worley, J.; Hamm, R.; Von Fraunhofer, J. Effects of cement on crown retention. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1982, 48, 289–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grajower, R.; Lewinstein, I.; Zeltser, C. The effective minimum cement thickness of zinc phosphate cement for luted non-precious crowns. J. Oral Rehabil. 1985, 12, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, E.; Seker, E.; Yilmaz, B.; Özcelik, T.B. Effect of cement space on the marginal fit of CAD-CAM-fabricated monolithic zirconia crowns. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2016, 116, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dudley, J. The influence of different cement spaces on the marginal gap of CAD/CAM all-ceramic crowns. Aust. Dent. J. 2019, 64, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özçelik, T.; Yilmaz, B.; Şeker, E.; Shah, K. Marginal Adaptation of Provisional CAD/CAM Restorations Fabricated Using Various Simulated Digital Cement Space Settings. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2018, 33, 1064–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passon, C.; Lambert, R.H.; Lambert, R.L.; Newman, S. The effect of multiple layers of die-spacer on crown retention. Oper. Dent. 1992, 17, 42–49. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, P.R. Effect of increasing cement space on cementation of artificial crowns. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1994, 71, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grajower, R.; Zuberi, Y.; Lewinstein, I. Improving the fit of crowns with die spacers. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1989, 61, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuntiprawon, M.; Wilson, P.R. The effect of cement thickness on the fracture strength of all-ceramic crowns. Aust. Dent. J. 1995, 40, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| 95% Confidence Interval | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spacer | Mean | SE | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | Min | Max |
| 60 (µm) | 162.99 (µm) | 16.25 (µm) | 128.13 (µm) | 197.85 (µm) | 59.22 | 300.18 |
| 90 (µm) | 41.85 (µm) | 3.57 (µm) | 34.20 (µm) | 49.50 (µm) | 25.83 | 74.73 |
| 120 (µm) | 41.85 (µm) | 5.30 (µm) | 30.48 (µm) | 53.23 (µm) | 17.85 | 99.87 |
| 95% Confidence Interval | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (I) Spacer | (J) Spacer | (I–J) | Std. Error | Sig. | Lower Limit | Upper Limit |
| 60 microns | 90 microns | 121.14 | 14.26 | 0.00 | 85.58 | 156.69 |
| 120 microns | 121.13 | 14.26 | 0.00 | 85.58 | 156.69 | |
| 90 microns | 60 microns | −121.14 | 14.26 | 0.00 | −156.69 | −85.58 |
| 120 microns | 0.00 | 14.26 | 1.00 | −35.56 | 35.56 | |
| 120 microns | 60 microns | −121.13 | 14.26 | 0.00 | −156.69 | −85.58 |
| 90 microns | 0.00 | 14.26 | 1.00 | −35.56 | 35.56 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ben-Izhack, G.; Shely, A.; Naishlos, S.; Glikman, A.; Frishman, L.; Meirowitz, A.; Dolev, E. The Influence of Three Different Digital Cement Spacers on the Marginal Gap Adaptation of Zirconia-Reinforced Lithium Silicate Crowns Fabricated by CAD-CAM System. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10709. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210709
Ben-Izhack G, Shely A, Naishlos S, Glikman A, Frishman L, Meirowitz A, Dolev E. The Influence of Three Different Digital Cement Spacers on the Marginal Gap Adaptation of Zirconia-Reinforced Lithium Silicate Crowns Fabricated by CAD-CAM System. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(22):10709. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210709
Chicago/Turabian StyleBen-Izhack, Gil, Asaf Shely, Sarit Naishlos, Ari Glikman, Liad Frishman, Avi Meirowitz, and Eran Dolev. 2021. "The Influence of Three Different Digital Cement Spacers on the Marginal Gap Adaptation of Zirconia-Reinforced Lithium Silicate Crowns Fabricated by CAD-CAM System" Applied Sciences 11, no. 22: 10709. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210709
APA StyleBen-Izhack, G., Shely, A., Naishlos, S., Glikman, A., Frishman, L., Meirowitz, A., & Dolev, E. (2021). The Influence of Three Different Digital Cement Spacers on the Marginal Gap Adaptation of Zirconia-Reinforced Lithium Silicate Crowns Fabricated by CAD-CAM System. Applied Sciences, 11(22), 10709. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210709






