Effective Design of Cr-Co-Ni-Ta Eutectic Medium Entropy Alloys with High Compressive Properties Using Combined CALPHAD and Experimental Approaches
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Design Principle and Experimental Scheme
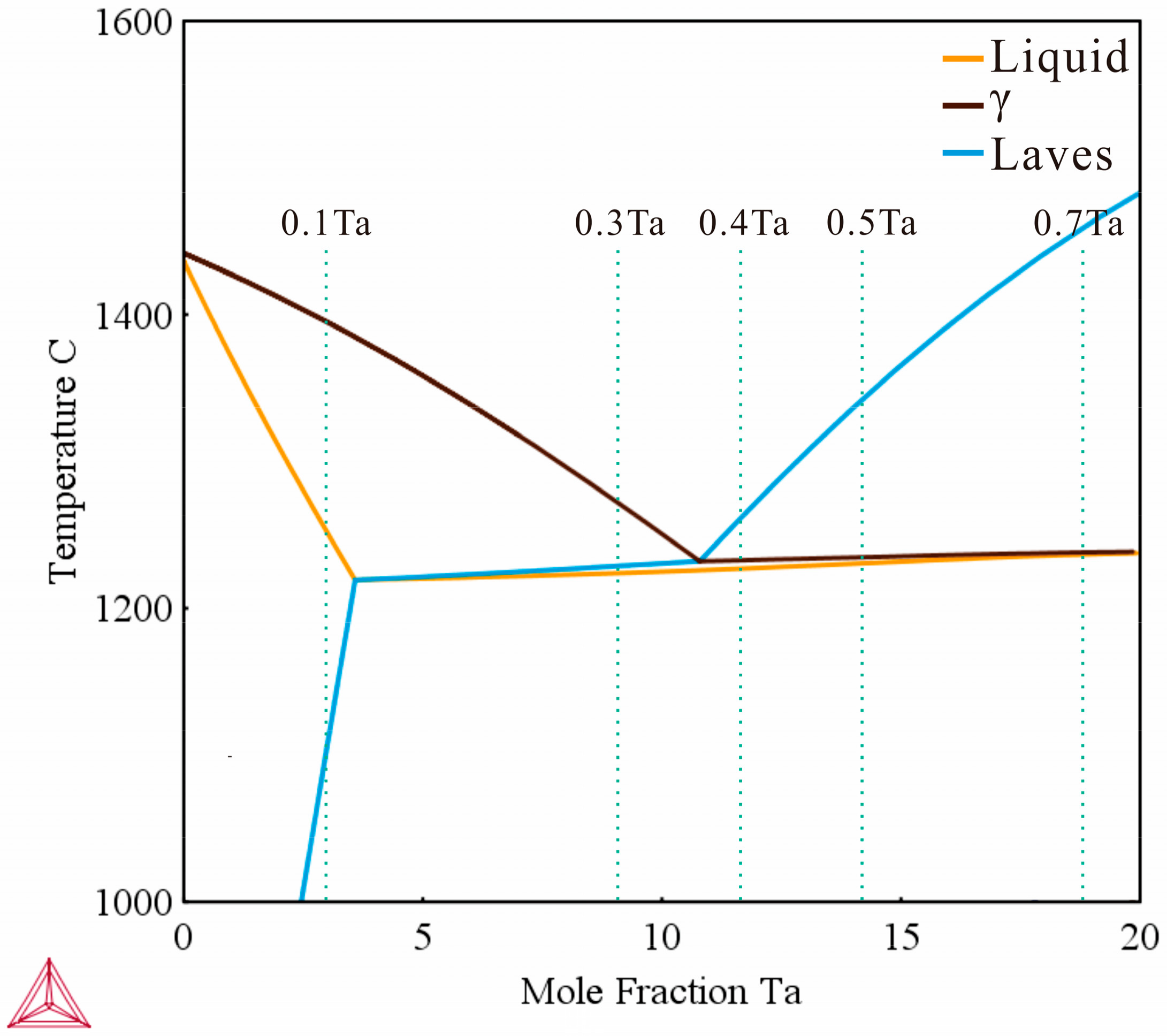
2.1. CALPHAD Modeling
2.2. Experimental Scheme
3. Results and Discussion
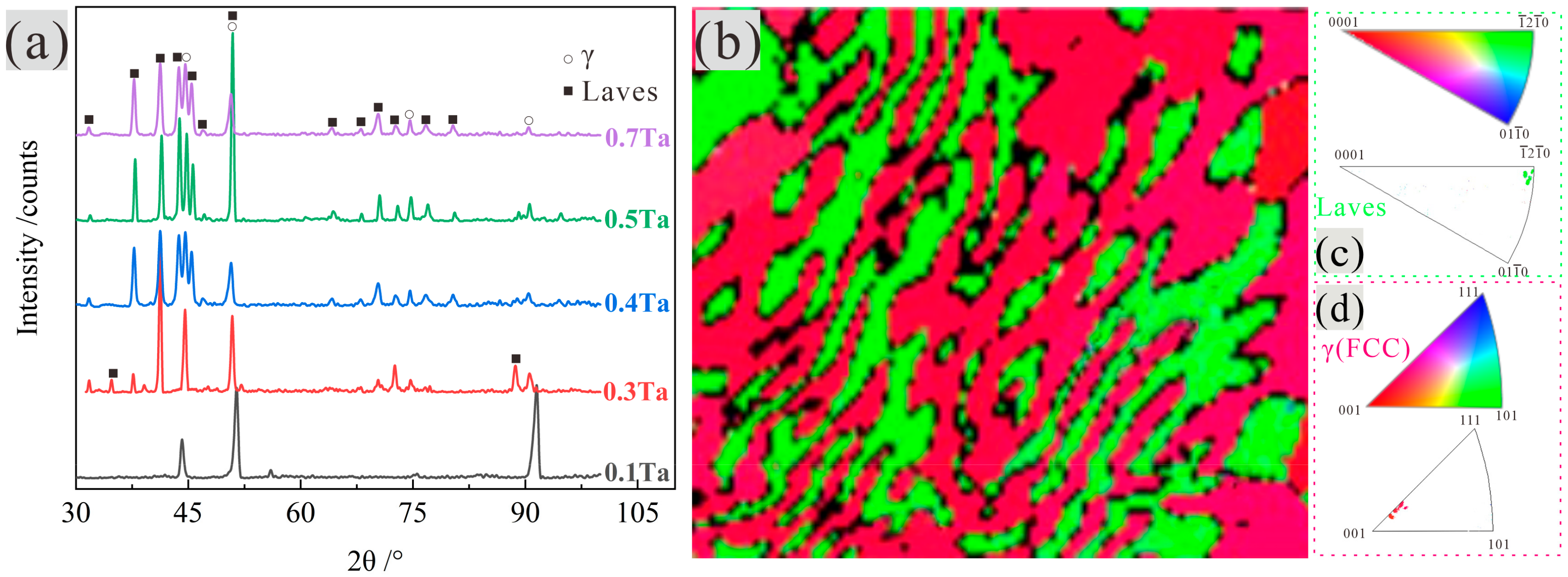
3.1. Microstructural Features
3.2. Phase Characterization
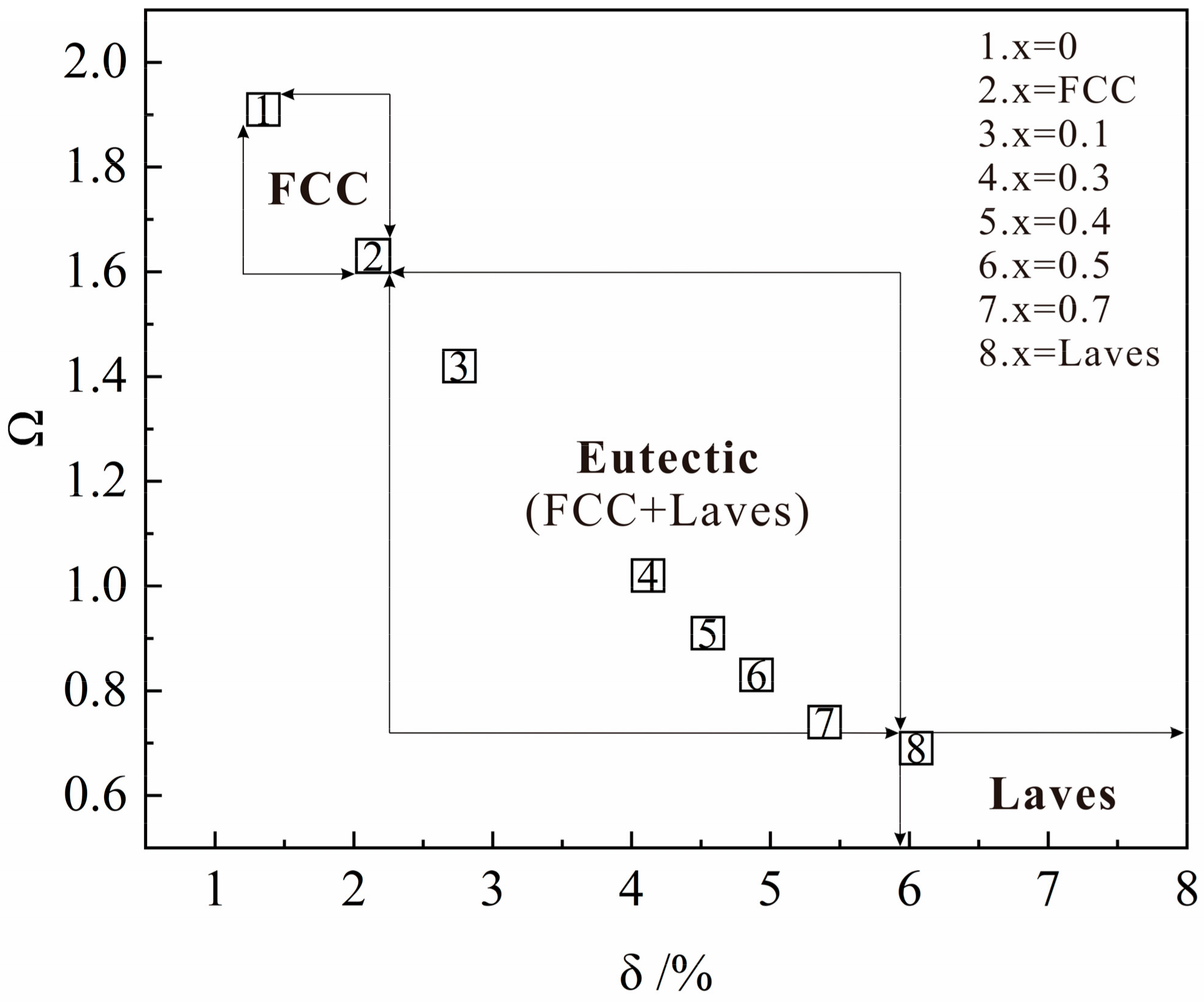
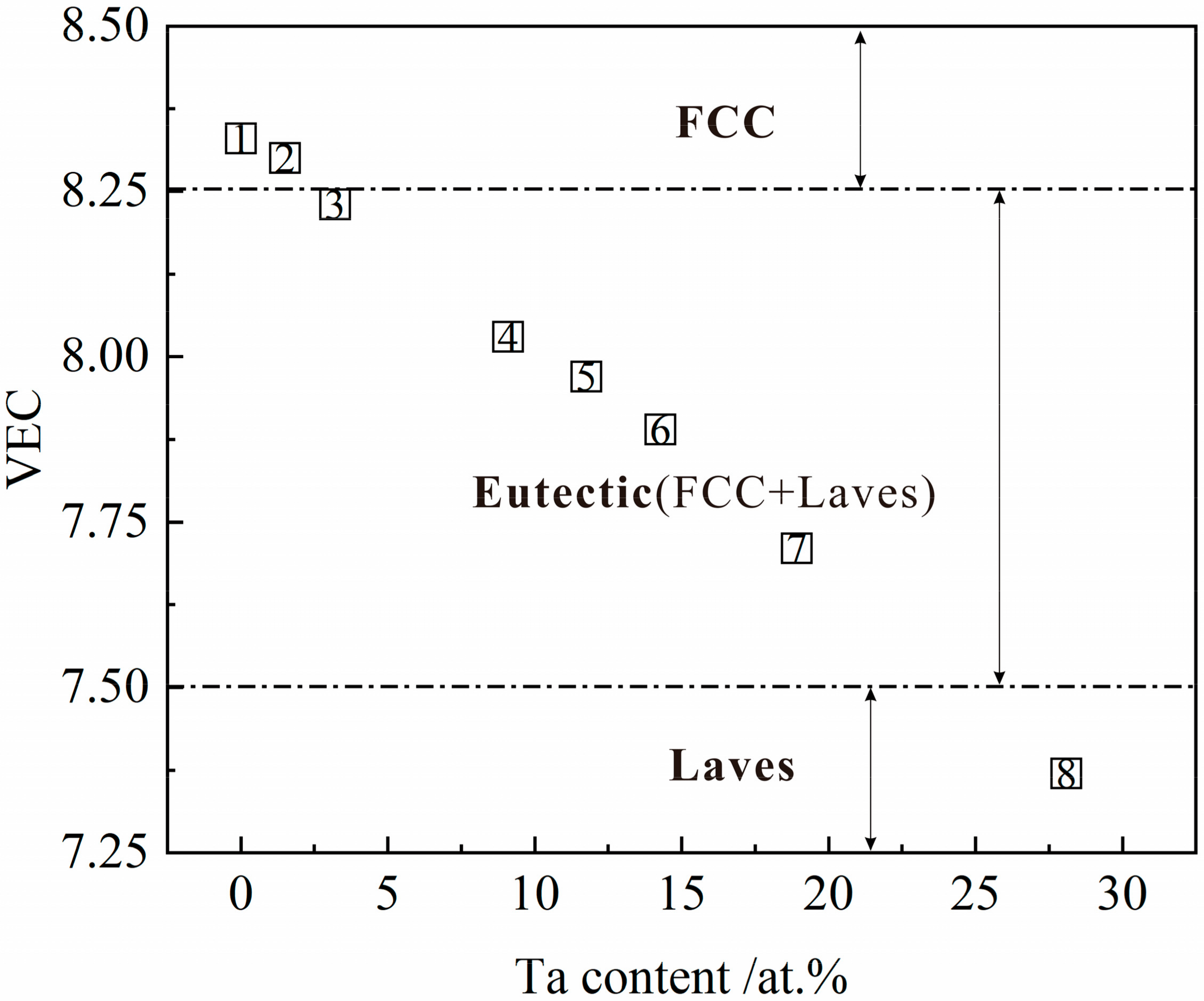
3.3. Assessment on the Phase Formation
3.4. Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- CrCoNiTax alloys contain γ phase with FCC structure and Laves phase with C14 HCP structure. With increasing Ta content, it can be seen a complete transformation from hypoeutectic (Ta0.1 and Ta0.3) to hypereutectic (Ta0.5 and Ta0.7). As for Ta0.4 alloy, the Ta0.4 alloy exhibits a lamellar eutectic composition.
- (2)
- Assessment on the phase evolution is established on thermodynamic parameters (Ω), atomic size differences (δ), valence electron concentration (VEC) which are useful parameters to determine the formation of eutectic microstructure with FCC and Laves phase. The Laves phase evolves when δ 2.2 and VEC 8.25.
- 3)
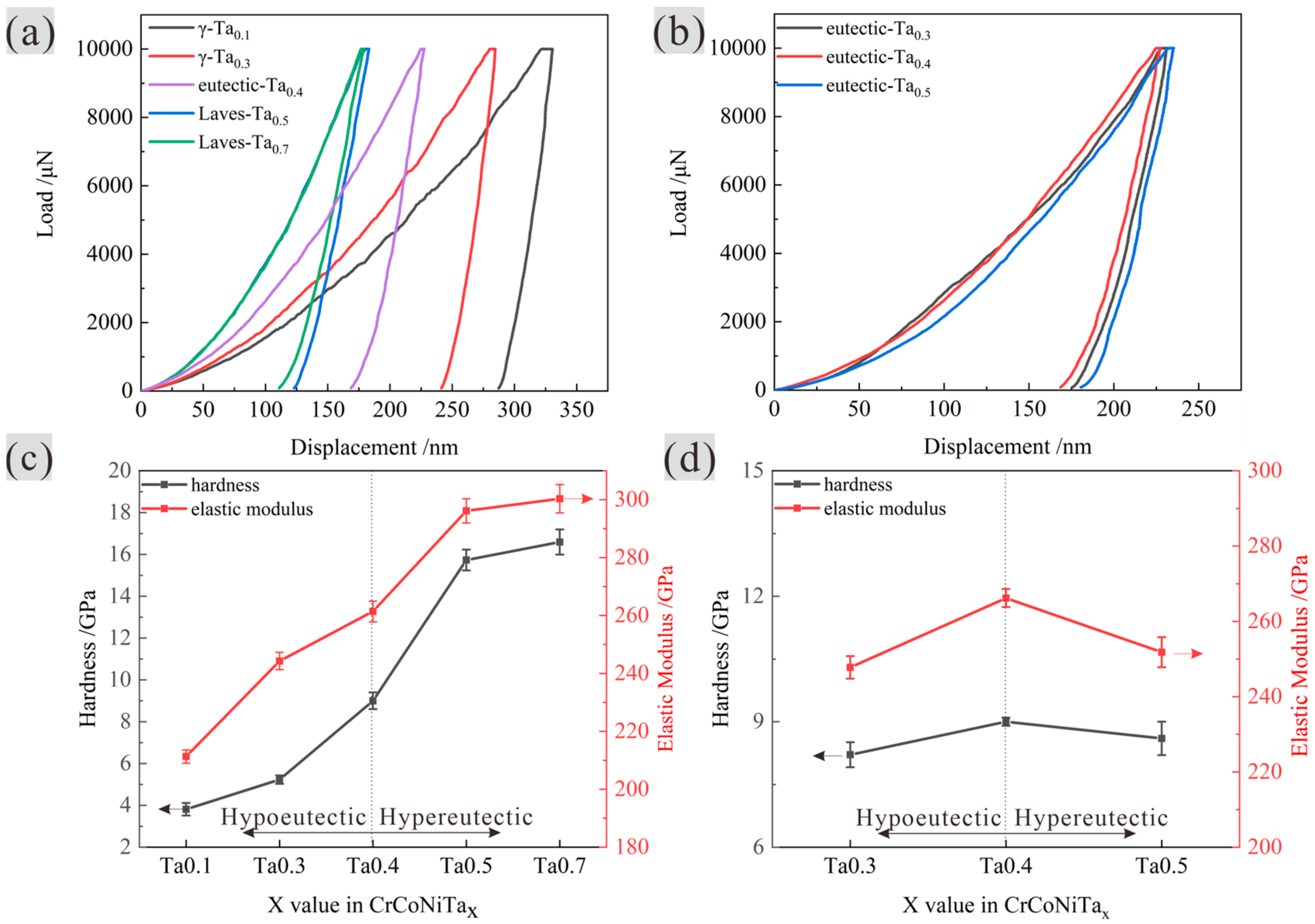
- With increasing Ta addition, the microhardness of the alloys increased and the hardness of the γ phase increased. While the Laves phase hardness stayed unchanged. Ta0.4 alloy has the highest nano-hardness and elastic modulus due to the full complete eutectic structure with small lamellar spacing and enhanced solid solution strengthening.
- (4)
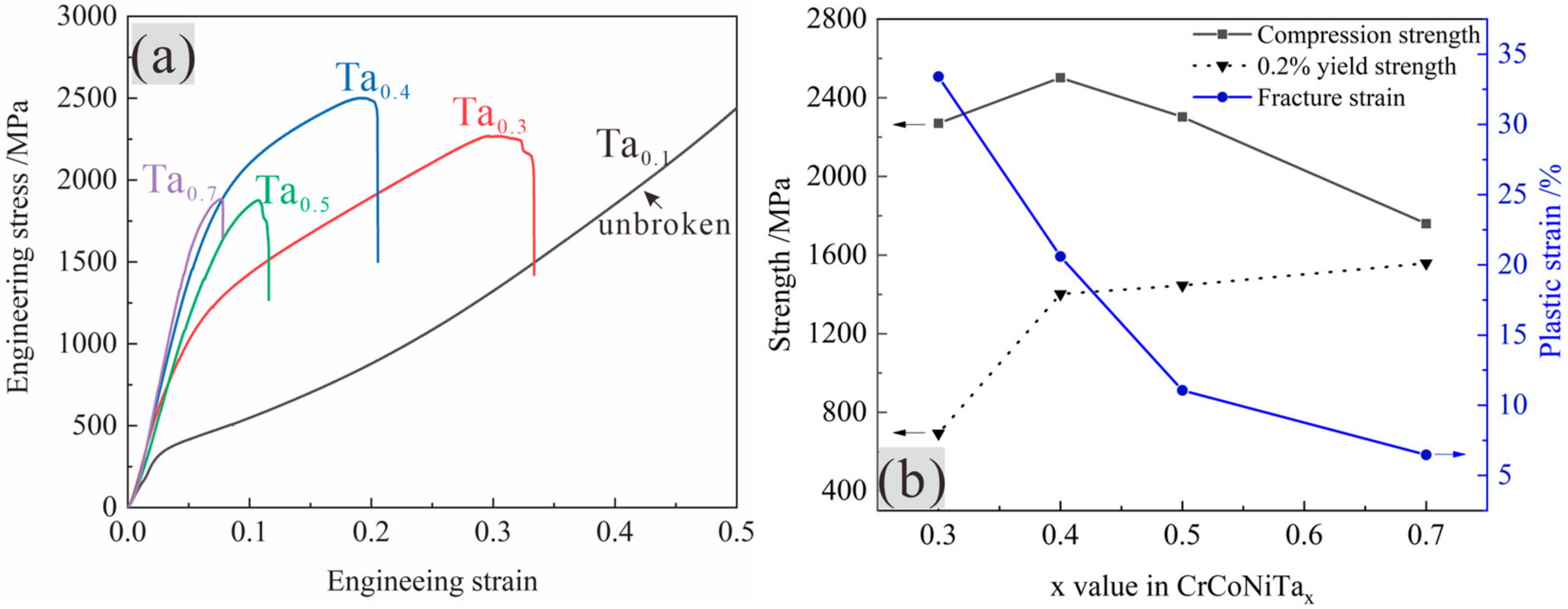
- With Ta addition increasing, the hard and brittle Laves phase is increasing, the plasticity of the alloy is decreasing, the compressive strength is increasing and then decreasing, The CrCoNiTa0.4 EMEA with complete eutectic has the best balance of microstructure and properties, highest compressive strength (2502 MPa) and plastic strain (20.6%).
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cantor, B.; Chang, I.; Knight, P.; Vincent, A. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 375–377, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.-W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.-J.; Gan, J.-Y.; Chin, T.-S.; Shun, T.-T.; Tsau, C.-H.; Chang, S.-Y. Nanostructured High-Entropy Alloys with Multiple Principal Elements: Novel Alloy Design Concepts and Outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zuo, T.T.; Tang, Z.; Gao, M.C.; Dahmen, K.A.; Liaw, P.K.; Lu, Z.P. Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2014, 61, 1–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miracle, D.; Senkov, O. A critical review of high entropy alloys and related concepts. Acta Mater. 2017, 122, 448–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, M.-H.; Yeh, J.-W. High-Entropy Alloys: A Critical Review. Mater. Res. Lett. 2014, 2, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Wang, H.; Chen, M.; Baker, I.; Yeh, J.; Liu, C.; Nieh, T. An assessment on the future development of high-entropy alloys: Summary from a recent workshop. Intermetallics 2015, 66, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hemphill, M.; Yuan, T.; Wang, G.; Yeh, J.; Tsai, C.; Chuang, A.; Liaw, P. Fatigue behavior of Al0.5CoCrCuFeNi high entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 5723–5734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Gao, X.; Jiang, L.; Chen, Z.; Wang, T.; Jie, J.; Kang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, S.; Ruan, H.; et al. Directly cast bulk eutectic and near-eutectic high entropy alloys with balanced strength and ductility in a wide temperature range. Acta Mater. 2017, 124, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Guo, S.; Jiang, L.; Kang, H.; Wang, T.; Wen, B.; Wang, Z.; Jie, J.; Cao, Z.; et al. A Promising New Class of High-Temperature Alloys: Eutectic High-Entropy Alloys. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, srep06200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liang, N.; Wu, G.; Sha, G.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Y. Microstructural origins of high strength and high ductility in an AlCoCrFeNi2.1 eutectic high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 2017, 141, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, P.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Dang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, C. Designing eutectic high entropy alloys of CoCrFeNiNb x. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 656, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, C.; He, F.; Guo, M.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L. Alloy design, micromechanical and macromechanical properties of CoCrFeNiTax eutectic high entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 735, 2653–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laplanche, G.; Kostka, A.; Reinhart, C.; Hunfeld, J.; Eggeler, G.; George, E. Reasons for the superior mechanical properties of medium-entropy CrCoNi compared to high-entropy CrMnFeCoNi. Acta Mater. 2017, 128, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Sheng, H.; Wang, Z.; Gludovatz, B.; Zhang, Z.; George, E.P.; Yu, Q.; Mao, S.X.; Ritchie, R.O. Dislocation mechanisms and 3D twin architectures generate exceptional strength-ductility-toughness combination in CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gludovatz, B.; Hohenwarter, A.; Thurston, K.V.S.; Bei, H.; Wu, Z.; George, Z.W.E.P.; Ritchie, B.G.K.V.S.T.R.O. Exceptional damage-tolerance of a medium-entropy alloy CrCoNi at cryogenic temperatures. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, H. Cr-Ta (chromium-tantalum). J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 1996, 17, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, H. Co-Ta (Cobalt-Tantalum). J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 2004, 25, 571–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, H. Ni-Ta (Nickel-Tantalum). J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 2000, 21, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, T.; Cao, K.; Chen, J.; Zong, H.; Wang, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L. A correlative multidimensional study of γ′ precipitates with Ta addition in Re-containing Ni-based single crystal superalloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 75, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, J.; Omori, T.; Oikawa, K.; Ohnuma, I.; Kainuma, R.; Ishida, K. Cobalt-Base High-Temperature Alloys. Science 2006, 312, 90–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santodonato, L.J.; Zhang, Y.; Feygenson, M.; Parish, C.; Gao, M.C.; Weber, R.J.; Neuefeind, J.C.; Tang, Z.; Liaw, P.K. Deviation from high-entropy configurations in the atomic distributions of a multi-principal-element alloy. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 5964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takeuchi, A.; Amiya, K.; Wada, T.; Yubuta, K.; Zhang, W.; Makino, A. Entropies in Alloy Design for High-Entropy and Bulk Glassy Alloys. Entropy 2013, 15, 3810–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.-H.; Fan, A.-C.; Wang, H.-A. Effect of atomic size difference on the type of major intermetallic phase in arc-melted CoCrFeNiX high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 695, 1479–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinagawa, K.; Chinen, H.; Omori, T.; Oikawa, K.; Ohnuma, I.; Ishida, K.; Kainuma, R. Phase equilibria and thermodynamic calculation of the Co–Ta binary system. Intermetallics 2014, 49, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.J.; Lin, J.P.; Chen, G.L.; Liaw, P.K. Solid-Solution Phase Formation Rules for Multi-component Alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2008, 10, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; He, J.; Huang, H.; Wang, H.; Lu, Z.; Liu, C. Effects of Nb additions on the microstructure and mechanical property of CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2015, 60, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Ng, C.; Lu, J.; Liu, C.T. Effect of valence electron concentration on stability of fcc or bcc phase in high entropy alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 103505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otto, F.; Yang, Y.; Bei, H.; George, E. Relative effects of enthalpy and entropy on the phase stability of equiatomic high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 2628–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- King, D.; Middleburgh, S.; McGregor, A.; Cortie, M. Predicting the formation and stability of single phase high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2016, 104, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Lu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Wang, T.; Cao, Z.; Li, T. Effects of Nb addition on structural evolution and properties of the CoFeNi2V0.5 high-entropy alloy. Appl. Phys. A 2015, 119, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, W.; Zhou, H.; Fang, F.; Zhou, X.; Xie, Z.; Jiang, J. Microstructure and properties of novel CoCrFeNiTax eutectic high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 735, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, H.; Huang, T.; Lu, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, T. Microstructures and mechanical properties of Co2MoxNi2VWx eutectic high entropy alloys. Mater. Des. 2016, 109, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Cao, Z.; Jie, J.; Zhang, J.; Lu, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, T. Effect of Mo and Ni elements on microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of the CoFeNixVMoy high entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 649, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Alloy | Region | Cr | Co | Ni | Ta |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ta0.1 | Primary γ phase | 32.6 | 32.8 | 33.1 | 1.5 |
| Eutectic | 29.1 | 27.6 | 28.8 | 14.5 | |
| Ta0.3 | Primary γ phase | 30.3 | 33.3 | 30.5 | 5.9 |
| Eutectic | 28.4 | 29.1 | 27.8 | 13.7 | |
| Ta0.4 | Eutectic | 29.4 | 30.1 | 28.9 | 11.6 |
| Ta0.5 | Eutectic | 30.3 | 29.3 | 29.7 | 10.7 |
| Primary Laves phase | 23.3 | 29.1 | 20.8 | 26.8 | |
| Ta0.7 | Eutectic | 32.1 | 27.3 | 29.5 | 11.1 |
| Primary Laves phase | 23.8 | 27.5 | 20.6 | 28.1 |
| Composition | Phase | ΔSmix/J mol−1 K−1 | ΔHmix/kj mol−1 | Ω | δ/% | VEC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CrCoNi | FCC | 9.13 | −4.79 | 1.91 | 1.35 | 8.33 |
| X = FCC | FCC | 9.64 | −5.92 | 1.63 | 2.14 | 8.30 |
| Ta0.1 | FCC+Laves | 10.02 | −7.06 | 1.42 | 2.76 | 8.24 |
| Ta0.3 | FCC+Laves | 10.84 | −10.66 | 1.02 | 4.12 | 8.03 |
| Ta0.4 | FCC+Laves | 11.07 | −12.13 | 0.91 | 4.55 | 7.97 |
| Ta0.5 | FCC+Laves | 11.24 | −13.47 | 0.83 | 4.90 | 7.89 |
| Ta0.7 | FCC+Laves | 11.44 | −15.52 | 0.74 | 5.39 | 7.71 |
| X = Laves | Laves | 11.46 | −16.56 | 0.69 | 6.05 | 7.37 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, T.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L. Effective Design of Cr-Co-Ni-Ta Eutectic Medium Entropy Alloys with High Compressive Properties Using Combined CALPHAD and Experimental Approaches. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6102. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11136102
Huang T, Zhang J, Zhang J, Liu L. Effective Design of Cr-Co-Ni-Ta Eutectic Medium Entropy Alloys with High Compressive Properties Using Combined CALPHAD and Experimental Approaches. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(13):6102. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11136102
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Taiwen, Jiachen Zhang, Jun Zhang, and Lin Liu. 2021. "Effective Design of Cr-Co-Ni-Ta Eutectic Medium Entropy Alloys with High Compressive Properties Using Combined CALPHAD and Experimental Approaches" Applied Sciences 11, no. 13: 6102. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11136102
APA StyleHuang, T., Zhang, J., Zhang, J., & Liu, L. (2021). Effective Design of Cr-Co-Ni-Ta Eutectic Medium Entropy Alloys with High Compressive Properties Using Combined CALPHAD and Experimental Approaches. Applied Sciences, 11(13), 6102. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11136102





