Dynamic Characteristics of the Bouc–Wen Nonlinear Isolation System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
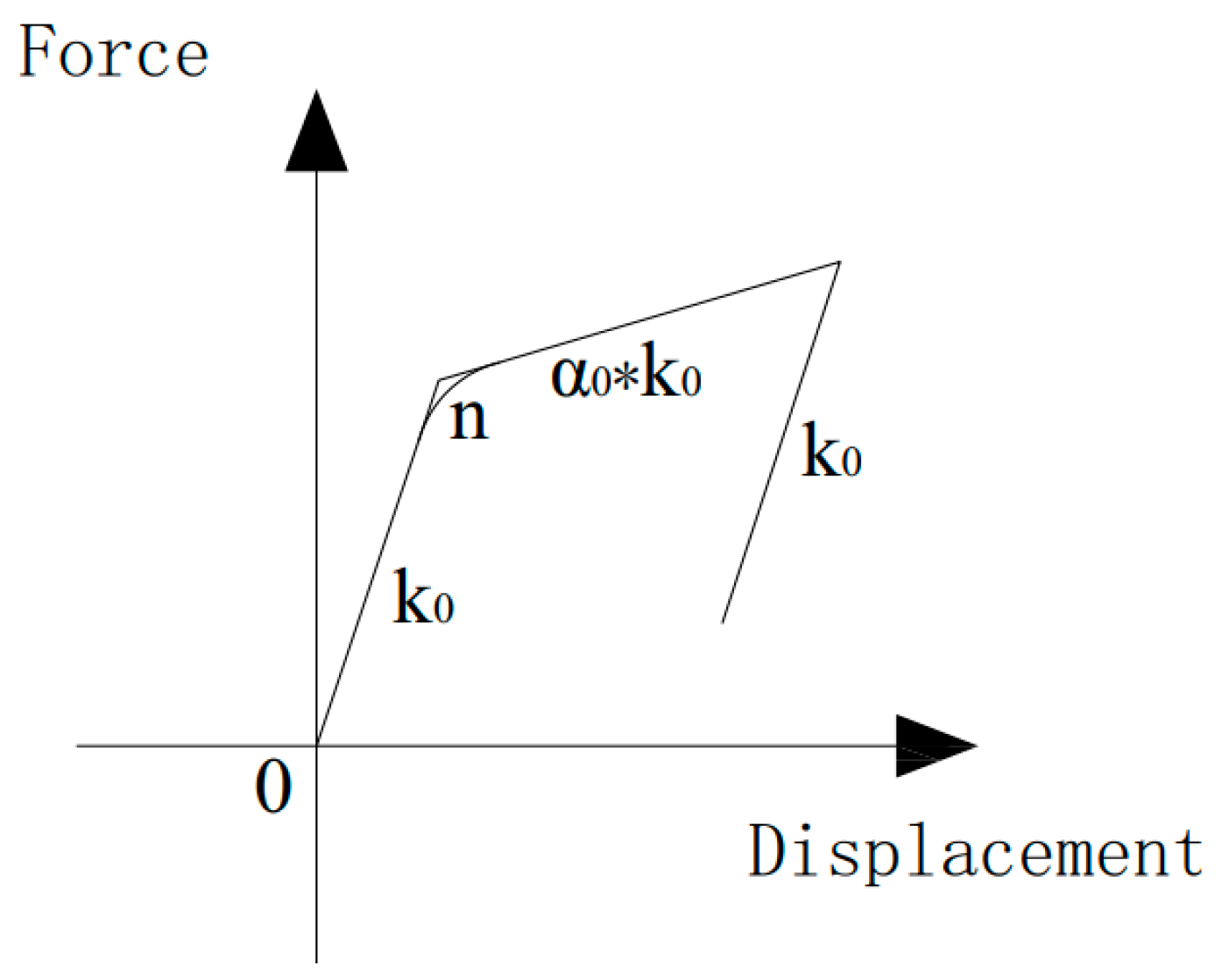
2. Mechanical Properties of the Bouc–Wen Model
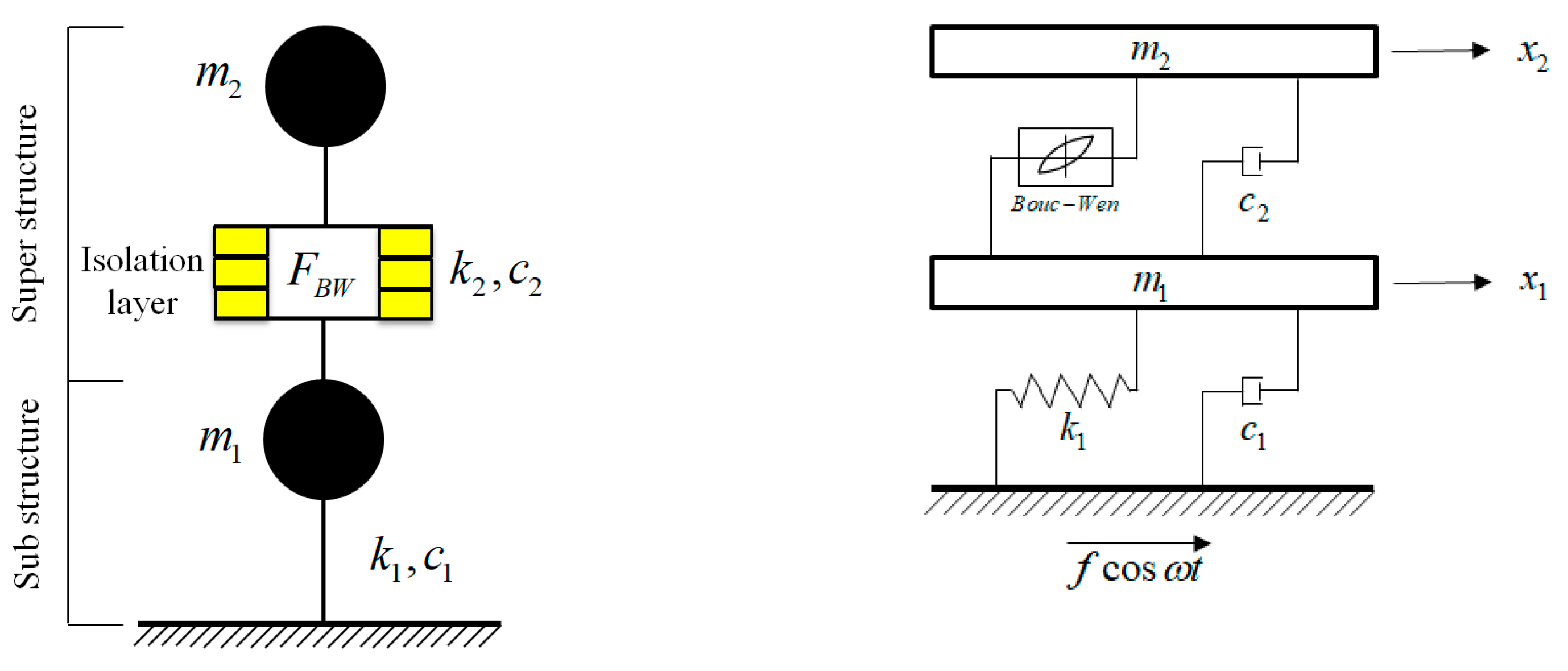
3. Theoretical Analysis of the Nonlinear Isolation System
4. Analysis of the Influence Factors of the Nonlinear Isolation System
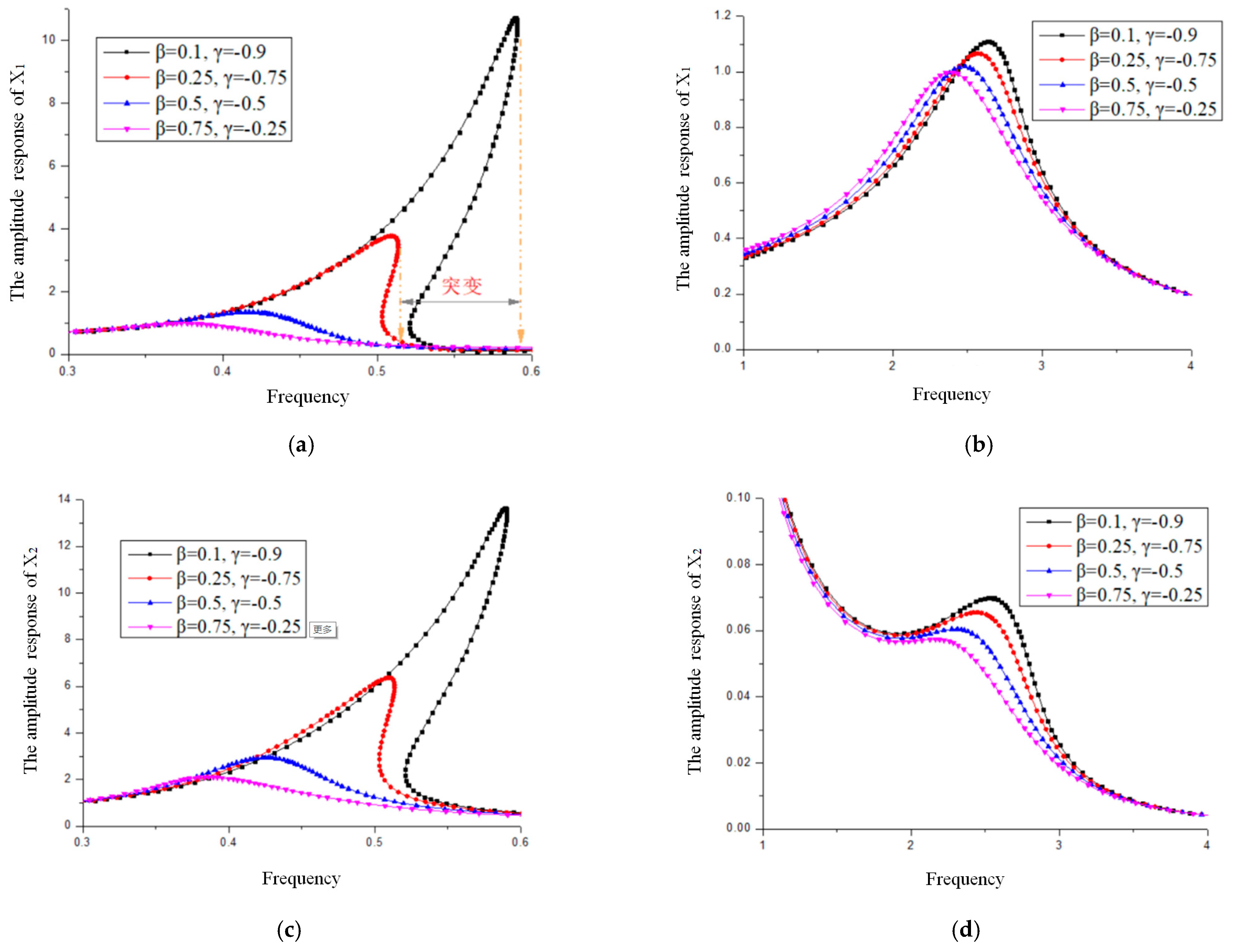
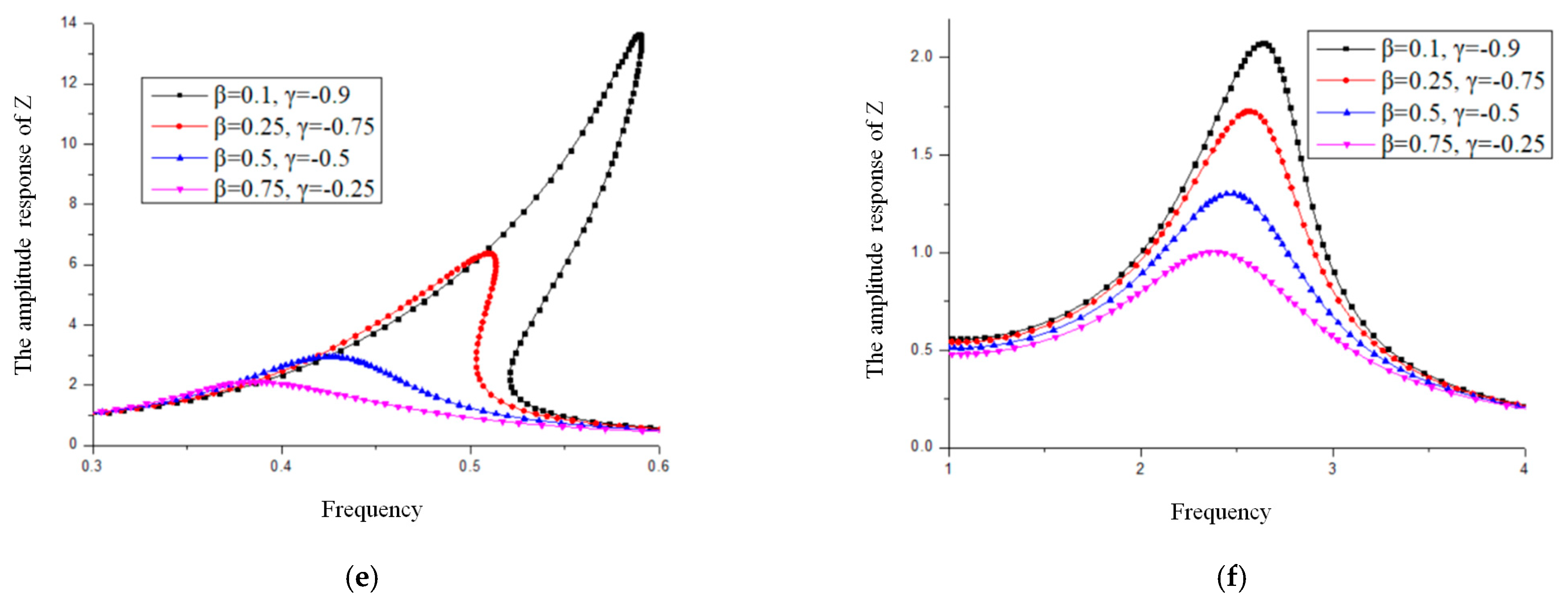
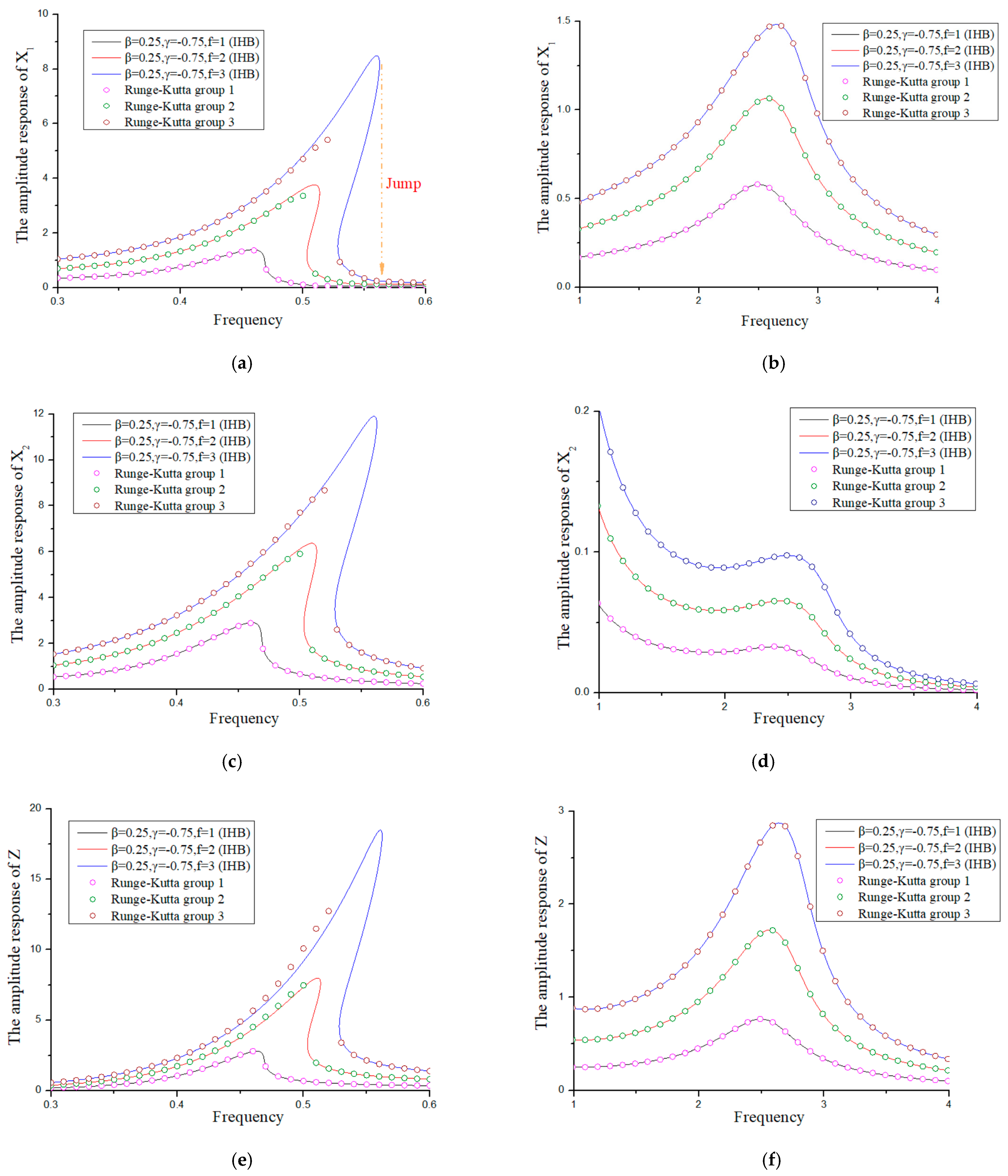
4.1. Influence of the Isolation Control Parameters
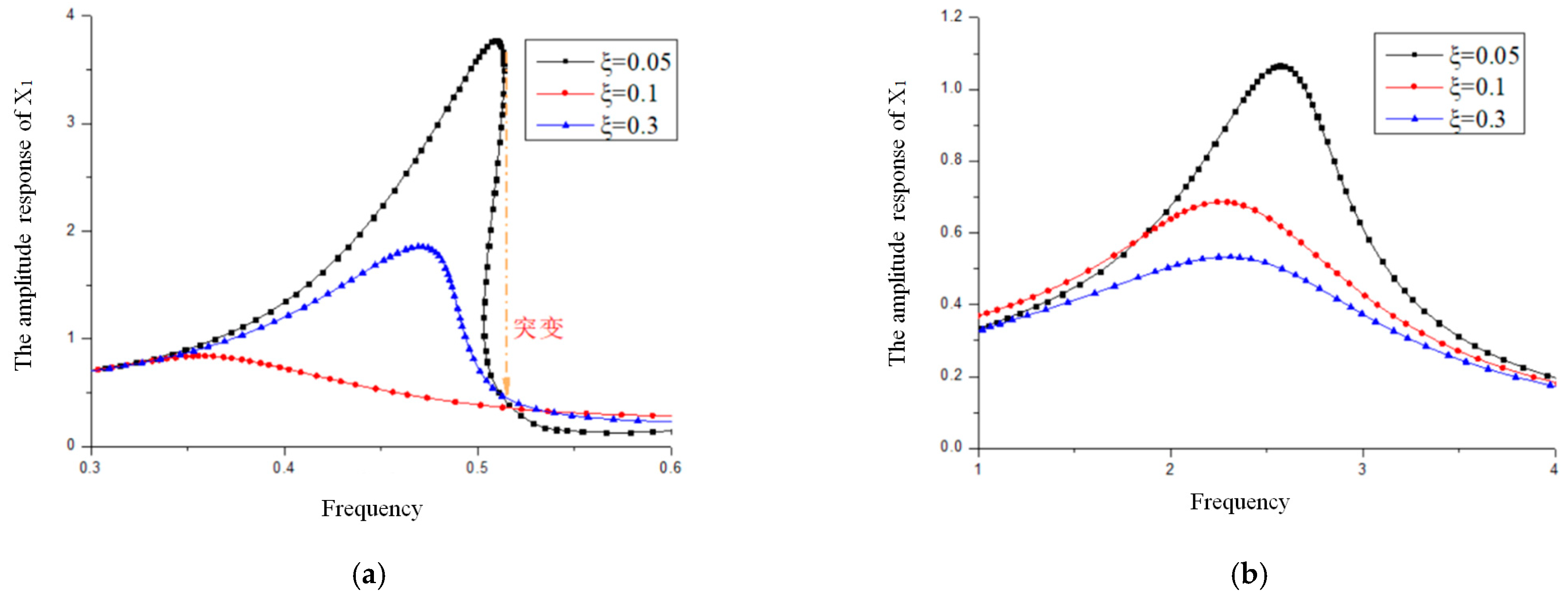
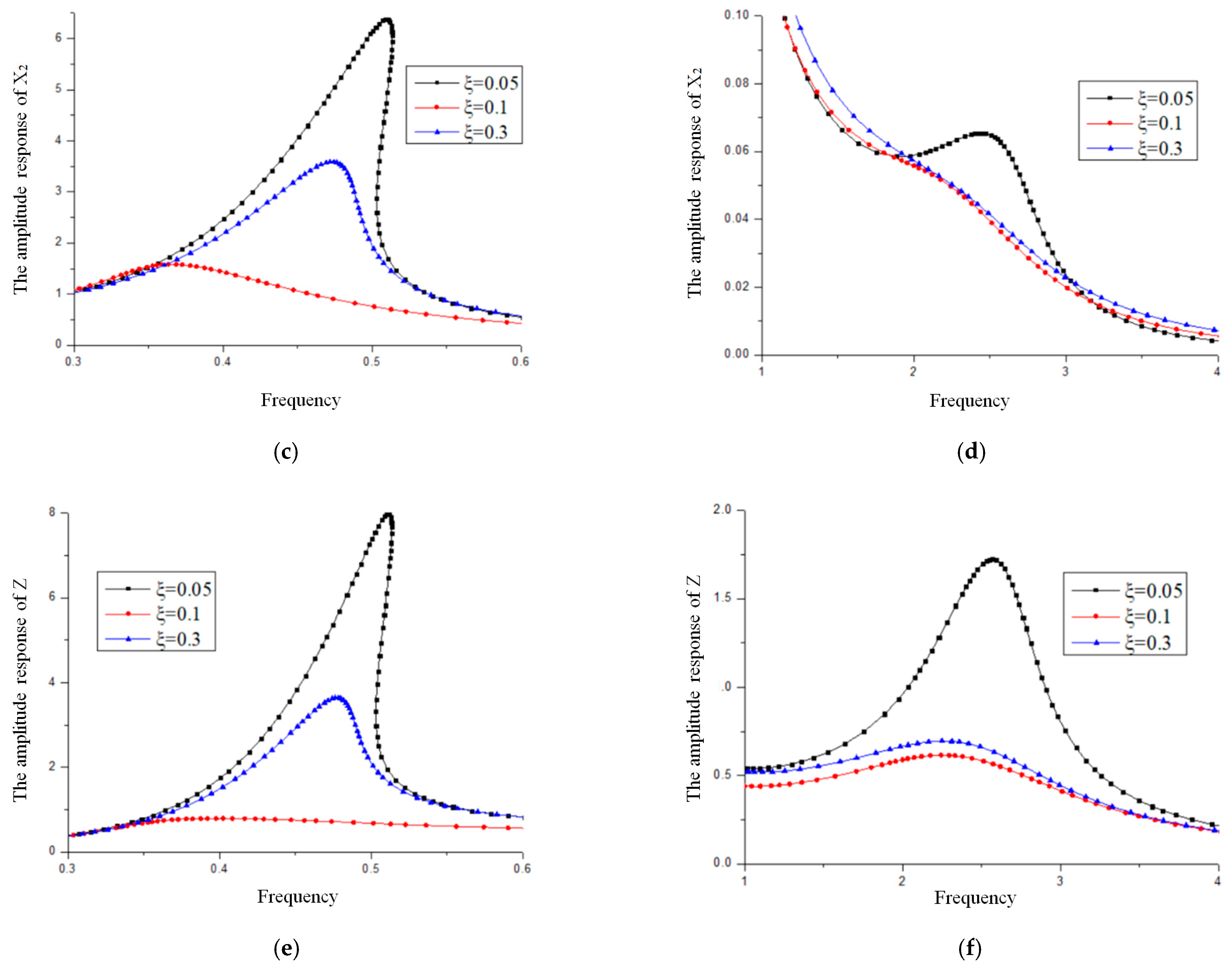
4.2. Influence of the Damping Ratio of the Isolation Layer
4.3. The Influence of External Excitation Amplitude
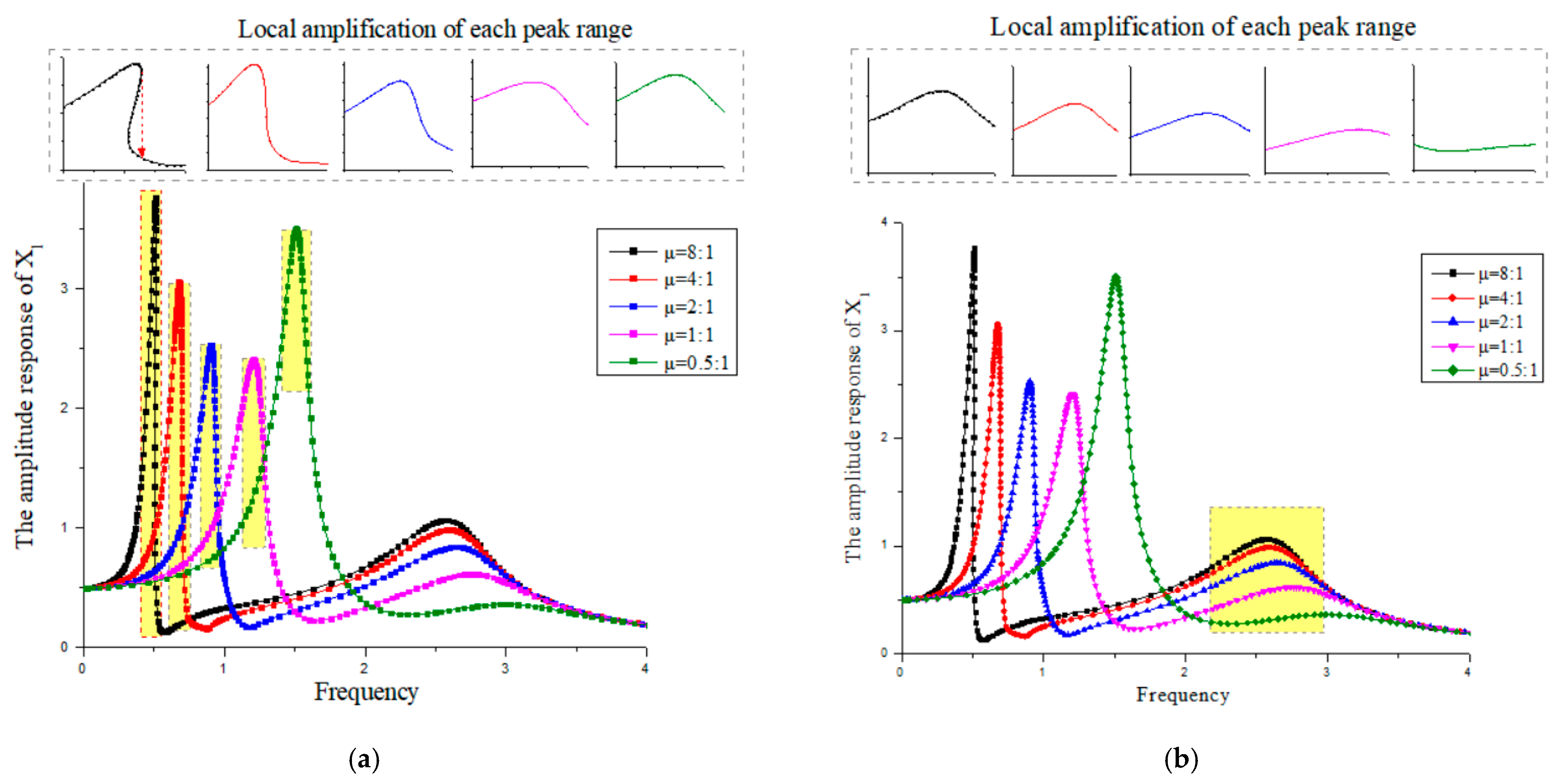
4.4. Influence of Mass Ratio
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jing, M. Research and application progress of energy dissipation and shock absorption technology. J. Earthq. Eng. Eng. Vib. 2017, 107–114. Available online: http://www.ijscience.org/download/IJS-6-9-56-58.pdf (accessed on 29 June 2021).
- Han, M.; Wang, X. Research status of base isolation technology. J. Beijing Inst. Civ. Eng. Archit. 2004, 20, 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Smyth, A.W.; Masri, S.F.; Kosmatopoulos, E.B.; Chassiakos, A.G.; Caughey, T.K. Development of adaptive modeling techniques for non-linear hysteretic systems. Int. J. Non Linear Mech. 2002, 37, 1435–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, A.; Sedaghati, R.; Stiharu, I. Modeling and application of MR dampers in semi-adaptive structures. Comput. Struct. 2008, 86, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foliente, G.C. Hysteresis modeling of wood joints and structural systems. J. Struct. Eng. 1995, 121, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, K.; Wen, Y.; Foutch, D.A. Evaluation of 3D steel moment frames under earthquake excitations. I: Modeling. J. Eng. Mech. 2007, 133, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhou, Q. Dynamic analysis method of a combined energy dissipation system and its experimental verification. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2002, 31, 1251–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxalde, D.; Thouverez, F.; Sinou, J.J. Dynamics of a linear oscillator connected to a small strongly non-linear hysteretic ab-sorber. Int. J. Non Linear Mech. 2006, 41, 969–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liberatore, D.; Addessi, D.; Sangirardi, M. An enriched Bouc-Wen model with damage. Eur. J. Mech. A Solids 2019, 77, 103771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovyov, A.; Semenov, M.; Meleshenko, P.A.; Barsukov, A. Bouc-Wen model of hysteretic damping. Procedia Eng. 2017, 201, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domaneschi, M. Simulation of controlled hysteresis by the semi-active Bouc-Wen model. Comput. Struct. 2012, 106–107, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandelli, E.; Quaglini, V.; Dubini, P.; Limongelli, M.P.; Capolongo, S. Seismic isolation retrofit of hospital buildings with focus on non-structural components. Ing. Sismica Int. J. Earthq. Eng. 2018, 2018, 20–56. [Google Scholar]
- Quaglini, V.; Gandelli, E.; Dubini, P. Numerical investigation of curved surface sliders under bidirectional orbits. Ing. Sismica Int. J. Earthq. Eng. 2019, 2019, 118–136. [Google Scholar]
- Gandelli, E.; Chernyshov, S.; Distl, J. Novel adaptive hysteretic damper for enhanced seismic protection of braced buildings. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2021, 141, 106522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R.C. Particle Swarm Optimization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, WA, Australia, 27 November–1 December 1995; pp. 1942–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Katukura, H.; Izumi, M. Synthesis and extension of one-dimension non-linear hysteretic models. ASCE J. Eng. Mech. 1991, 117, 100–109. [Google Scholar]
- Iwan, W.D.; Lutes, L.D. Response of the Bilinear Hysteretic System to Stationary Random Excitation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1968, 43, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.K. Method for random vibration of hysteretic systems. Proc. ASCE J. Eng. Mech. 1976, 12, 249–263. [Google Scholar]
- Marano, G.C.; Sgobba, S. Stochastic energy analysis of seismic isolated bridges. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2007, 27, 759–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meibodi, A.; Alexander, N.A. Exploring a generalized nonlinear multi-span bridge system subject to multi-support excitation using a Bouc-Wen hysteretic model. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 135, 106160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiatas, G.C.; Charalampakis, A. A new Hysteretic Nonlinear Energy Sink (HNES). Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2018, 60, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.G.; He, X.; Meng, G. Numerical Simulation for Dynamic Characteristics of Bouc-Wen Hysteretic System. J. Syst. Simulation 2004, 9, 2009–2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Rui, X.; Yang, F.; Zhu, W.; Wei, M. An efficient parameters identification method of normalized Bouc-Wen model for MR damper. J. Sound Vib. 2019, 448, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-Y.; Lee, C.-H. Description of asymmetric hysteretic behavior based on the Bouc-Wen model and piece-wise linear strength-degradation functions. Eng. Struct. 2019, 181, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Rui, X.-T. Hysteresis modeling and displacement control of piezoelectric actuators with the frequency dependent behavior using a generalized Bouc–Wen model. Precis. Eng. 2016, 43, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Wang, D.-H. Non-symmetrical Bouc–Wen model for piezoelectric ceramic actuators. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2012, 181, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niola, V.; Palli, G.; Strano, S.; Terzo, M. Nonlinear estimation of the Bouc-Wen model with parameter boundaries: Application to seismic isolators. Comput. Struct. 2019, 222, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casalotti, A.; Lacarbonara, W. Nonlinear Vibration Absorber Optimal Design via Asymptotic Approach. Procedia IUTAM 2016, 19, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, S.; Wang, W.; Xu, B.; Li, X.; Jiang, W. Chaos study of vehicle suspension hysteresis model under road excitation. J. Zhejiang Univ. (Eng. Sci.) 2011, 45, 1259–1264. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, H.; Huang, X. IHB analysis method for bilinear hysteretic vibration system with cubic nonlinear viscous damping. J. Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. 1998, 32, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Ranjbarzadeh, H.; Kakavand, F. Determination of nonlinear vibration of 2DOF system with an asymmetric piecewise-linear compression spring using incremental harmonic balance method. Eur. J. Mech. A Solids 2019, 73, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pun, D.; Liu, Y.B. On the Design of the Piecewise Linear Vibration Absorber. Nonlinear Dyn. 2000, 22, 393–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pun, D.; Lau, S.; Law, S.; Cao, D. Forced vibration analysis of a multi-degree impact vibrator. J. Sound Vib. 1998, 213, 447–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Awrejcewicza, J.; Dzyubak, L.P. Influence of hysteretic dissipation on chaotic responses. J. Sound Vib. 2005, 284, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, D.D.; Gendelman, O.; Kerschen, G.; Sapsis, T.P.; Bergman, L.A.; Vakakis, A.F. Efficiency of targeted energy transfers in coupled nonlinear oscillators associated with 1:1 resonance captures: Part I. J. Sound Vib. 2008, 311, 1228–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeder, C.W.; Stanton, J.F.; Feller, T. Low temperature performance of elastomeric bearings. J. Cold Reg. Eng. 1990, 4, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Zhang, R.; Xu, G. Research Progress on Temperature Correlation of Rubber Isolation Bearing. J. Build. Struct. 2019, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar]



| Parameters | m1 | m2 | c1 | c2 | k1 | k2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Values | 1 | 8 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 4 | 2 |
| γ ≥ 0 | β | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 1.0 | |
| γ | 0.75 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0 | ||
| γ ≤ 0 | β | 0.1 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.75 | |
| γ | −0.9 | −0.75 | −0.5 | −0.25 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Tian, X.; Ge, X. Dynamic Characteristics of the Bouc–Wen Nonlinear Isolation System. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6106. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11136106
Zhang Z, Tian X, Ge X. Dynamic Characteristics of the Bouc–Wen Nonlinear Isolation System. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(13):6106. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11136106
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhiying, Xin Tian, and Xin Ge. 2021. "Dynamic Characteristics of the Bouc–Wen Nonlinear Isolation System" Applied Sciences 11, no. 13: 6106. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11136106
APA StyleZhang, Z., Tian, X., & Ge, X. (2021). Dynamic Characteristics of the Bouc–Wen Nonlinear Isolation System. Applied Sciences, 11(13), 6106. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11136106





